An Effective Prophylactic and Therapeutic Protection Against Botulinum Type A Intoxication in Mice and Rabbits Using a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection of scFv Clone and Full-Length Humanized Antibody
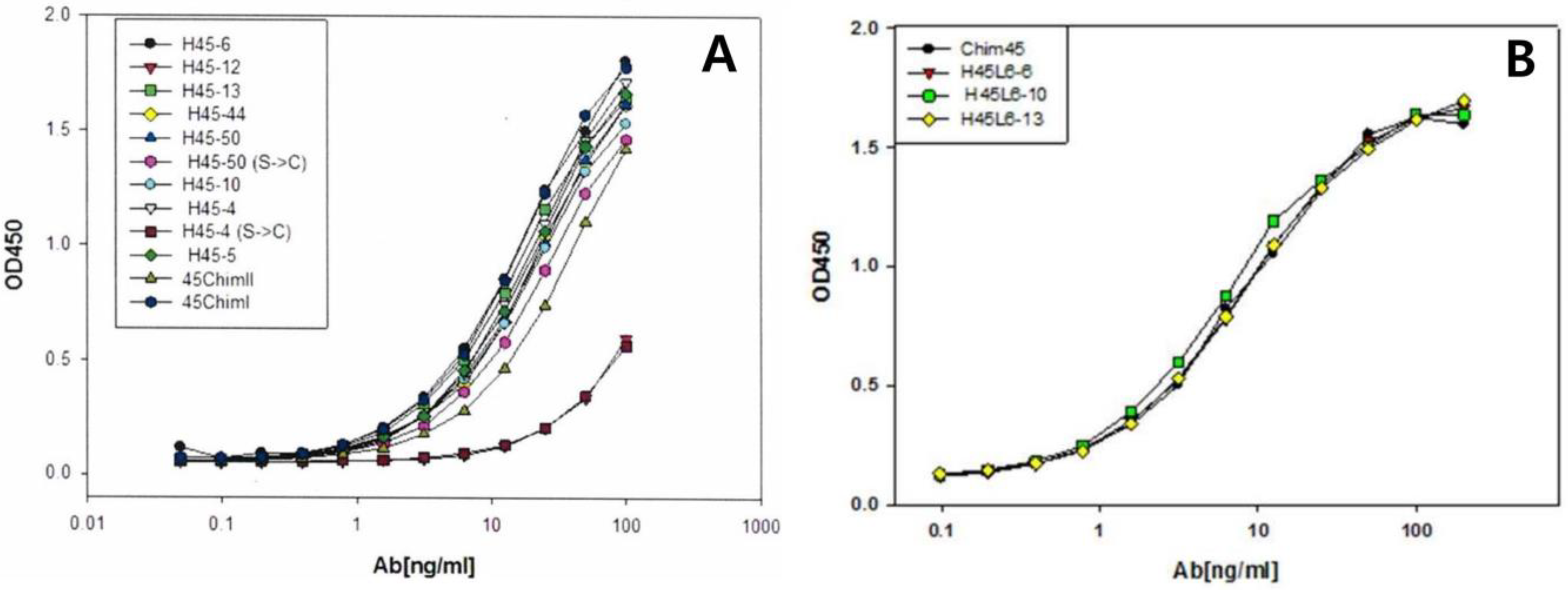
2.2. Binding Affinity
2.3. SNAP-25 Cleavage Assay with HZ45
2.4. In Vivo Neutralizing Assay with HZ45
2.5. Protection of Mice Against BoNT/A Intoxication
2.6. Protection of Rabbits Against BoNT/A Intoxication
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Botulinum Toxin Purification
5.2. Hybridoma Assay
5.2.1. Antigen Preparation
5.2.2. Immunization
5.2.3. Hybridoma Cell Generation and Indirect ELISA
5.3. Sequence Analysis of the Murine BoNT/A Antibody
5.4. scFv Library Construction
5.5. Bio-Panning and Selection of scFv Clone
5.6. Expression of Soluble scFv
5.7. Full-Length Humanized IgG Antibody Conversion of scFv and Sequence Analysis
5.8. Expression and Purification of the Humanized Antibody
5.9. Binding Affinity
5.10. SNAP-25 Cleavage Assay
5.11. Animal Studies
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raffestin, S.; Dupuy, B.; Marvaud, J.C.; Popoff, M.R. BotR/A and TetR are alternative RNA polymerase sigma factors controlling the expression of the neurotoxin and associated protein genes in Clostridium botulinum type A and Clostridium tetani. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dover, N.; Barash, J.R.; Hill, K.K.; Xie, G.; Arnon, S.S. Molecular characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin type H gene. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; et al. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.K.; Smith, T.J.; Helma, C.H.; Ticknor, L.O.; Foley, B.T.; Svensson, R.T.; Brown, J.L.; Johnson, E.A.; Smith, L.A.; Okinaka, R.T.; et al. Genetic diversity among Botulinum Neurotoxin-producing clostridial strains. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, L.L. Identification of the major steps in botulinum toxin action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, R.; Arnon, S.S. Extreme potency of botulinum toxin. Lancet 2000, 355, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St John, R.; Finlay, B.; Blair, C. Bioterrorism in Canada: An economic assessment of prevention and postattack response. Can. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 12, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangene Corp. BAT® [Botulism Antitoxin Heptavalent (A, B, C, D, E, F, G)–(Equine)] Sterile Solution for Injection. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/85514/download (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Maslanka, S.E.; Jewell, N.P.; Hatheway, C.L. Human botulism immune globulin for the treatment of infant botulism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.U.; Griffiss, J.M.; McKenzie, R.; Fuchs, E.J.; Jurao, R.A.; An, A.T.; Ahene, A.; Tomic, M.; Hendrix, C.W.; Zenilman, J.M. Safety and pharmacokinetics of XOMA 3AB, a novel mixture of three monoclonal antibodies against botulinum toxin A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5047–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Du, P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. A human bispecific antibody neutralizes botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, D.M.; Cobb, R.R.; Martinez, J.; Finger-Baker, I.; Collins, L.; Terpening, S.; Syar, E.S.; Niemuth, N.; Kobs, D.; Barnewall, R.; et al. A Monoclonal Antibody Combination against both Serotypes A and B Botulinum Toxin Prevents Inhalational Botulism in a Guinea Pig Model. Toxins 2021, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Yan, S.; Geren, I.N.; Knopp, K.A.; Dong, J.; Sun, Z.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Wen, W.H.; Farr-Jones, S.; et al. A Four-Monoclonal Antibody Combination Potently Neutralizes Multiple Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes C and D. Toxins 2021, 13, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Gunn, R.A. Hypersensitivity reactions associated with botulinal antitoxin. Am. J. Med. 1980, 69, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pless, D.D.; Torres, E.R.; Reinke, E.K.; Bavari, S. High-affinity, protective antibodies to the binding domain of botulinum neurotoxin type A. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razai, A.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Geren, I.N.; Forsyth, C.M.; Robles, Y.; Tsai, R.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Siegel, R.W.; et al. Molecular evolution of antibody affinity for sensitive detection of botulinum neutrotoxin type A. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethe, S.; Rasetti-Escargueil, C.; Liu, Y.; Chahboun, S.; Pelat, T.; Avril, A.; Frenzel, A.; Schirrmann, T.; Thullier, P.; Sesardic, D.; et al. Development of neutralizing scFv-Fc against botulinum neurotoxin A light chain from a macaque immune library. MAbs 2014, 6, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.W.; Stanker, L.H.; Henderson, T.D.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D. Antibody protection against botulinum neurotoxin intoxication in mice. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4305–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L.B.; Borodic, G.E.; First, E.R.; MacCallum, R.D. Measurement of botulinum toxin activity: Evaluation of the lethality assay. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1994, 128, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekar, S.P.; Takahashi, T.; Jones, R.M.; Al-Saleem, F.H.; Ancharski, D.M.; Root, M.J.; Kapadnis, B.P.; Simpson, L.L.; Dessain, S.K. Neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by a human monoclonal antibody specific for the catalytic light chain. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.Z.; Du, W.S.; Yang, F.; Yu, W.Y.; Sun, Z.W. Neutralizing antibodies of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A screened from a fully synthetic human antibody phage display library. J. Biomol. Screen. 2009, 14, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakowski, A.; Wang, C.; Powers, D.B.; Amersdorfer, P.; Smith, T.J.; Montgomery, V.A.; Sheridan, R.; Blake, R.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Potent neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by recombinant oligoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11346–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Zhai, W.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. A three monoclonal antibody combination potently neutralizes multiple botulinum neurotoxin serotype F subtypes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Razai, A.; Geren, I.N.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Wen, W.H.; Farr-Jones, S.; Smith, T.J.; Brown, J.L.; Skerry, J.C.; et al. A Three Monoclonal Antibody Combination Potently Neutralizes Multiple Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype E Subtypes. Toxins 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Song, D.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Joe, H.E.; Jeong, W.H.; Hur, G.H.; Shin, Y.K.; Jeong, S.T. A mutated recombinant subunit vaccine protects mice and guinea pigs against botulinum type A intoxication. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, G.; Milstein, C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur. J. Immunol. 1976, 6, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.J.; Souriau, C. Engineered antibodies. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.Y.; Almagro, J.C.; Buss, T.N.; Tan, P.; Foote, J. Use of human germline genes in a CDR homology-based approach to antibody humanization. Methods 2005, 36, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.T.; Kabat, E.A. Possible use of similar framework region amino acid sequences between human and mouse immunoglobulins for humanizing mouse antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 1992, 29, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthel, G.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.E.; Wanner, L.M.; Tressler, L.E.; Torres-Melendez, E.; Sandwick, S.J.; Retterer, C.J.; Bavari, S. Post-intoxication inhibition of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A within neurons by small-molecule, non-peptidic inhibitors. Toxins 2011, 3, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| HZ45 Dose (μg) | BoNT/A Challenge (LD50) | No. of Surviving Mice/Total No. |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 100 | 5/5 |
| 50 | 100 | 0/5 |
| 50 | 20 | 5/5 |
| 10 | 20 | 5/5 |
| 5 | 20 | 5/5 |
| 1 | 20 | 0/5 |
| BoNT/A Challenge (LD50) | HZ45 | No. of Surviving Mice/Total No. | Survival (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time of Treatment | Dose (µg) | |||
| 20 | 24 h Pre-administration (Mock IgG treatment) | 100 | 0/6 | 0 |
| 20 | 24 h Pre-administration | 100 | 6/6 | 100 |
| 100 | 24 h Pre-administration | 100 | 6/6 | 100 |
| 20 | 24 h Pre-administration | 50 | 6/6 | 100 |
| 20 | 24 h Pre-administration | 10 | 3/6 | 50 |
| 20 | 4 h Post-administration | 100 | 6/6 | 100 |
| 20 | 8 h Post-administration | 100 | 6/6 | 100 |
| 20 | 24 h Post-administration | - | Moribund before treatment | 0 |
| 50 | 8 h Post-administration | - | Moribund before treatment | 0 |
| BoNT/A Challenge (LD50) * | HZ45 | No. of Surviving Rabbits/Total No. | Survival (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time of Treatment | Dose (mg) | |||
| 10 | 24 h Pre-administration (Mock IgG treatment) | 0 | 0/4 | 0 |
| 10 | 24 h Pre-administration | 5 | 4/4 | 100 |
| 10 | Co-administration | 5 | 4/4 | 100 |
| 10 | 4 h Post-administration | 5 | 4/4 | 100 |
| 10 | 8 h Post-administration | 5 | 4/4 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.H.; Song, Y.-J.; Song, D.H.; Joe, H.E.; Kim, C.-H.; Yun, H.; Kim, N.Y.; Sim, E.; Jeong, S.T.; Hur, G.H. An Effective Prophylactic and Therapeutic Protection Against Botulinum Type A Intoxication in Mice and Rabbits Using a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody. Toxins 2025, 17, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030138
Yu CH, Song Y-J, Song DH, Joe HE, Kim C-H, Yun H, Kim NY, Sim E, Jeong ST, Hur GH. An Effective Prophylactic and Therapeutic Protection Against Botulinum Type A Intoxication in Mice and Rabbits Using a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody. Toxins. 2025; 17(3):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030138
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Chi Ho, Young-Jo Song, Dong Hyun Song, Hae Eun Joe, Chang-Hwan Kim, Hyungseok Yun, Na Young Kim, Euni Sim, Seong Tae Jeong, and Gyeung Haeng Hur. 2025. "An Effective Prophylactic and Therapeutic Protection Against Botulinum Type A Intoxication in Mice and Rabbits Using a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody" Toxins 17, no. 3: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030138
APA StyleYu, C. H., Song, Y.-J., Song, D. H., Joe, H. E., Kim, C.-H., Yun, H., Kim, N. Y., Sim, E., Jeong, S. T., & Hur, G. H. (2025). An Effective Prophylactic and Therapeutic Protection Against Botulinum Type A Intoxication in Mice and Rabbits Using a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody. Toxins, 17(3), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030138





