Green-Engineered Montmorillonite Clays for the Adsorption, Detoxification, and Mitigation of Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
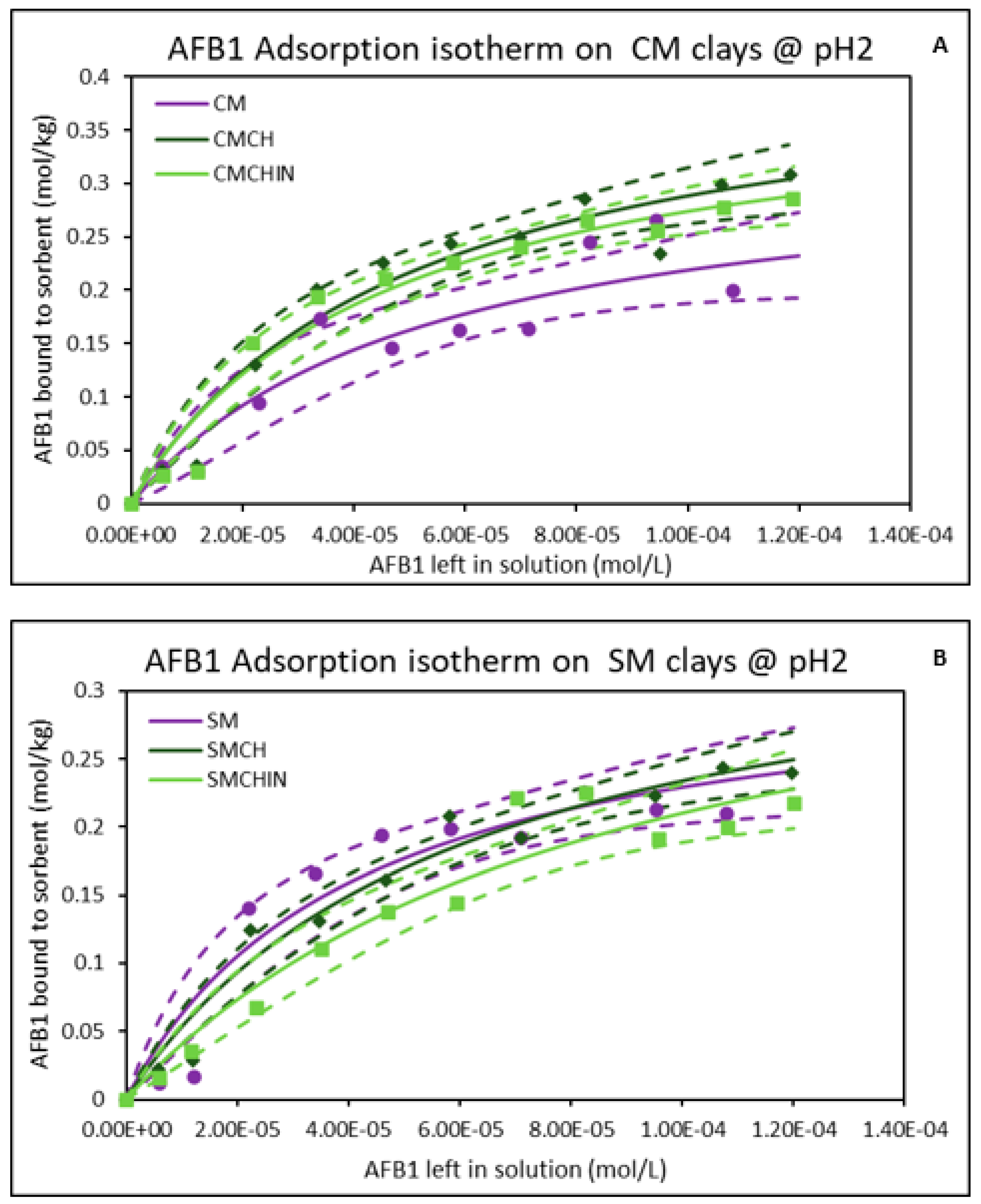
2.1. Isothermal Adsorption of AFB1 on the Clays at pH2 (Gastric Condition)
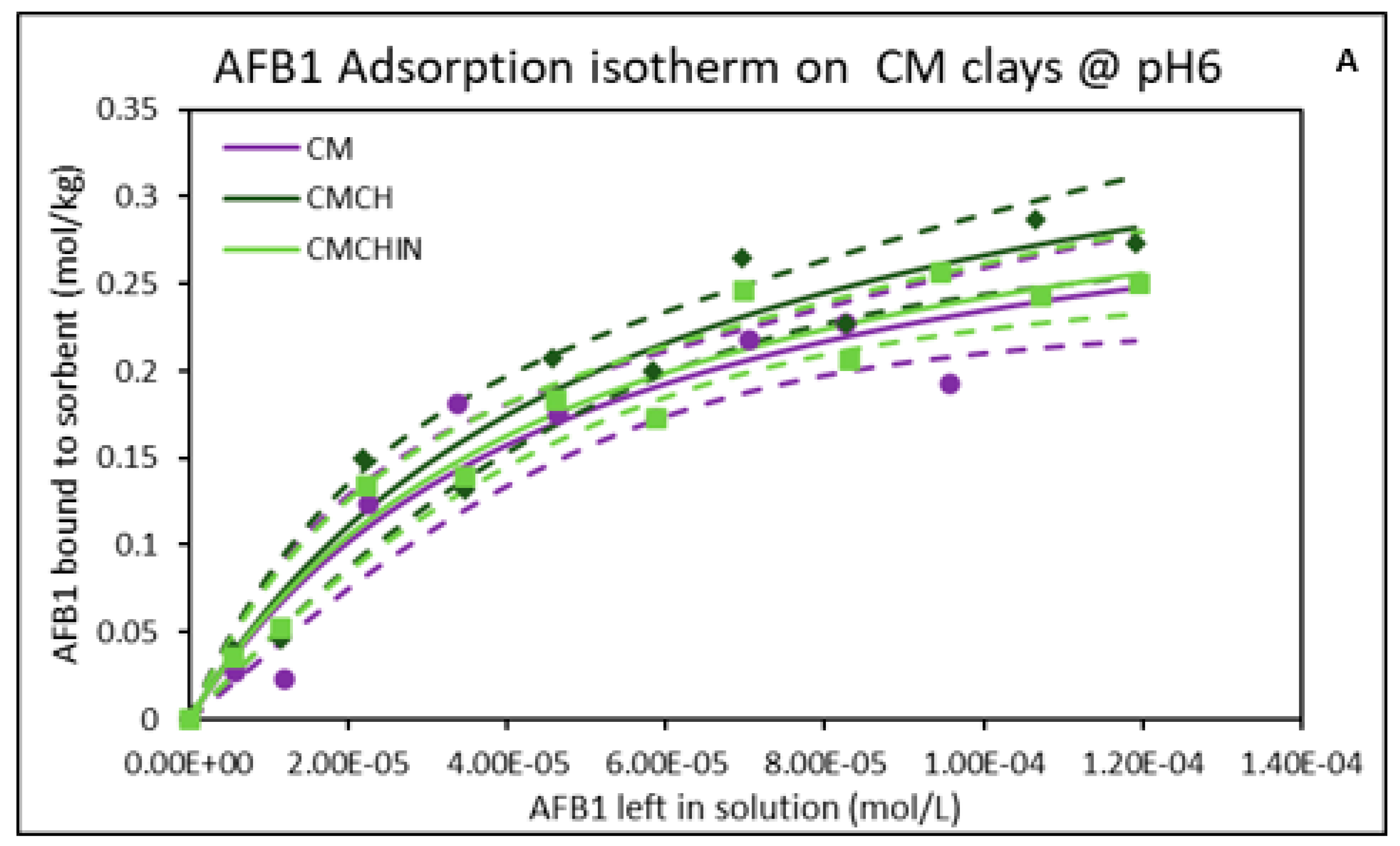
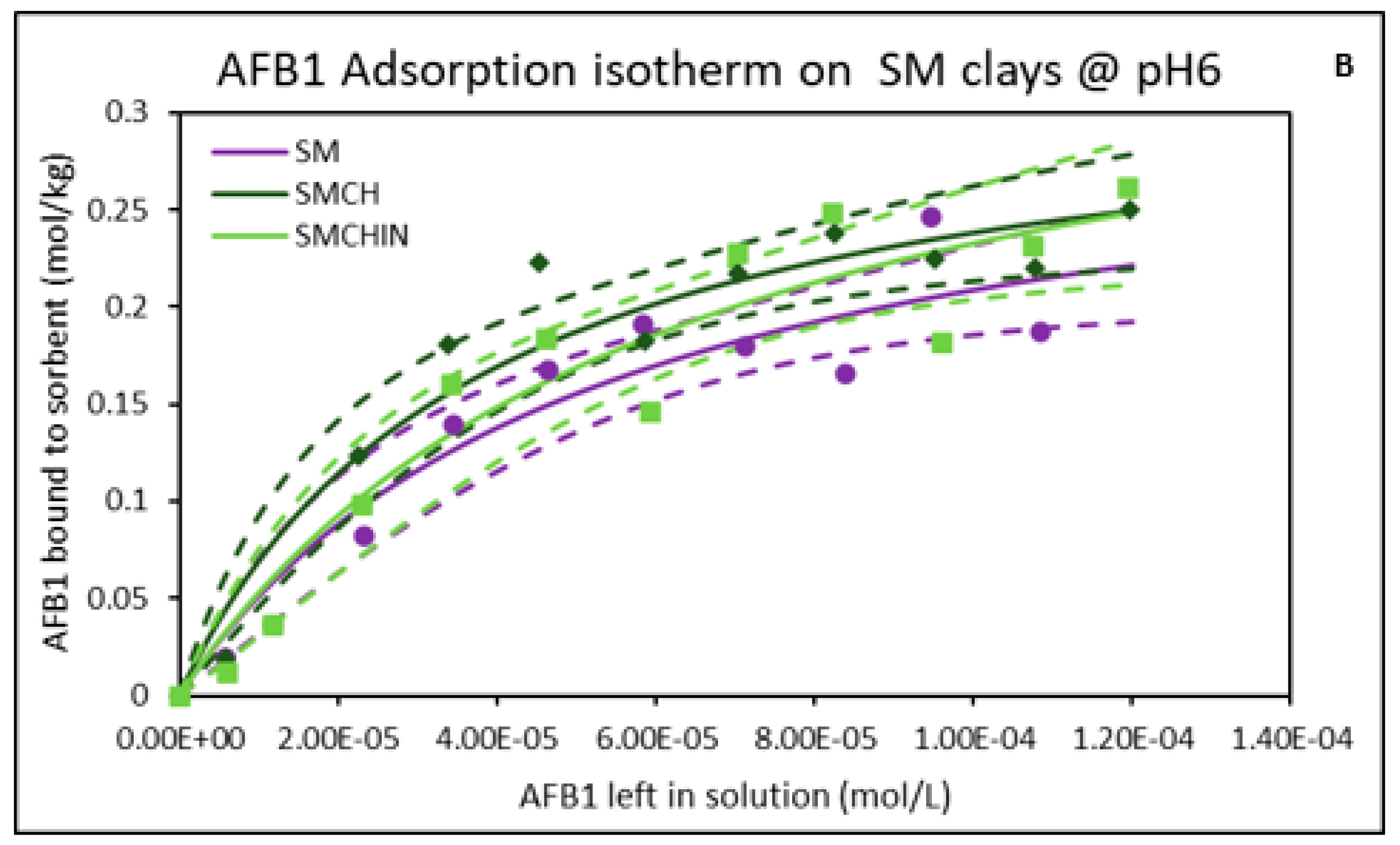
2.2. Isothermal Adsorption of AFB1 on the Clays at pH6 (Intestinal Condition)
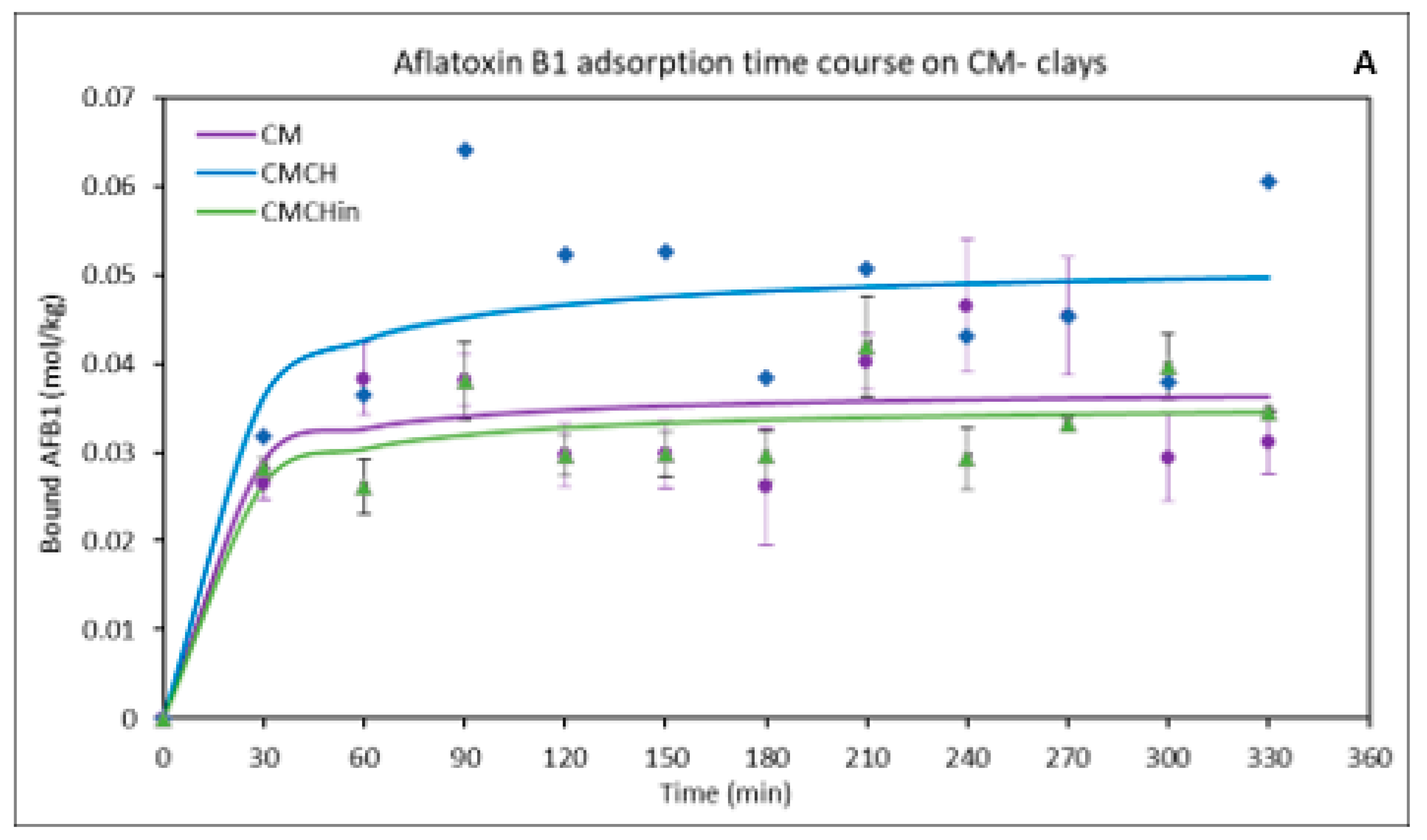
2.3. Kinetics of the Binding of AFB1 on the Clays
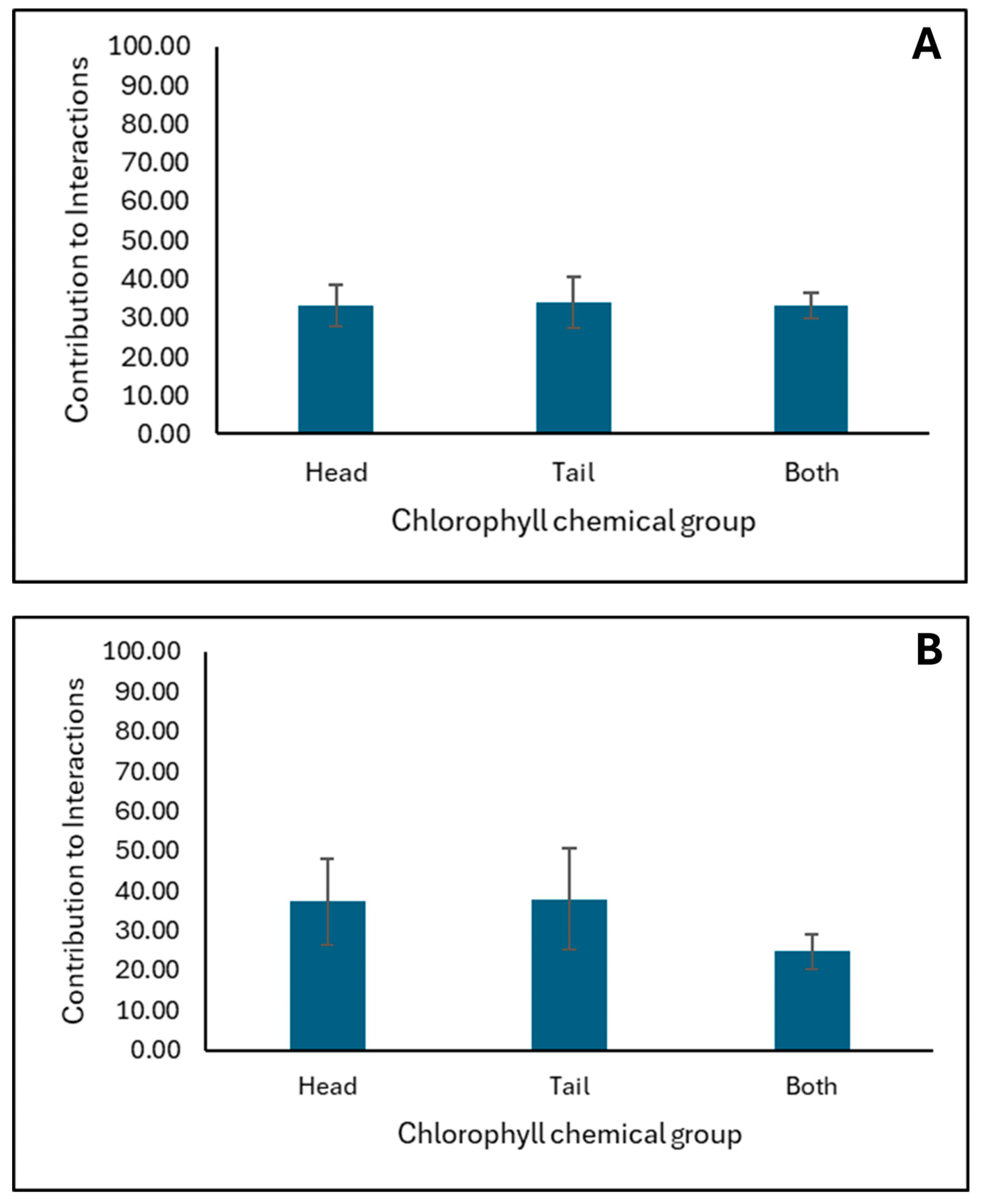
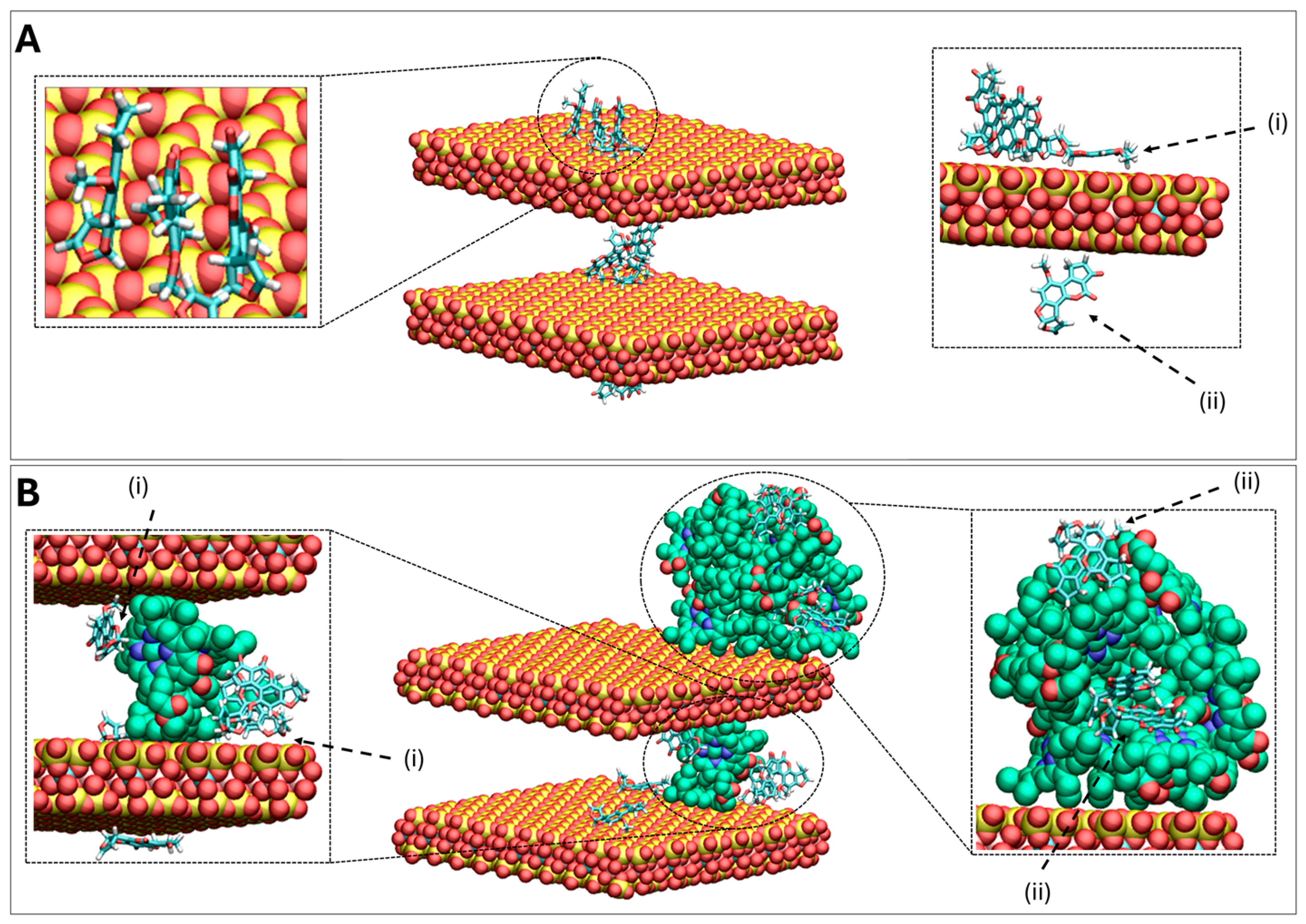
2.4. In Silico Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations Investigating AFB1 Binding to Surfaces of Clay (CM) and Chlorophyll-Engineered Clay (CMCH)
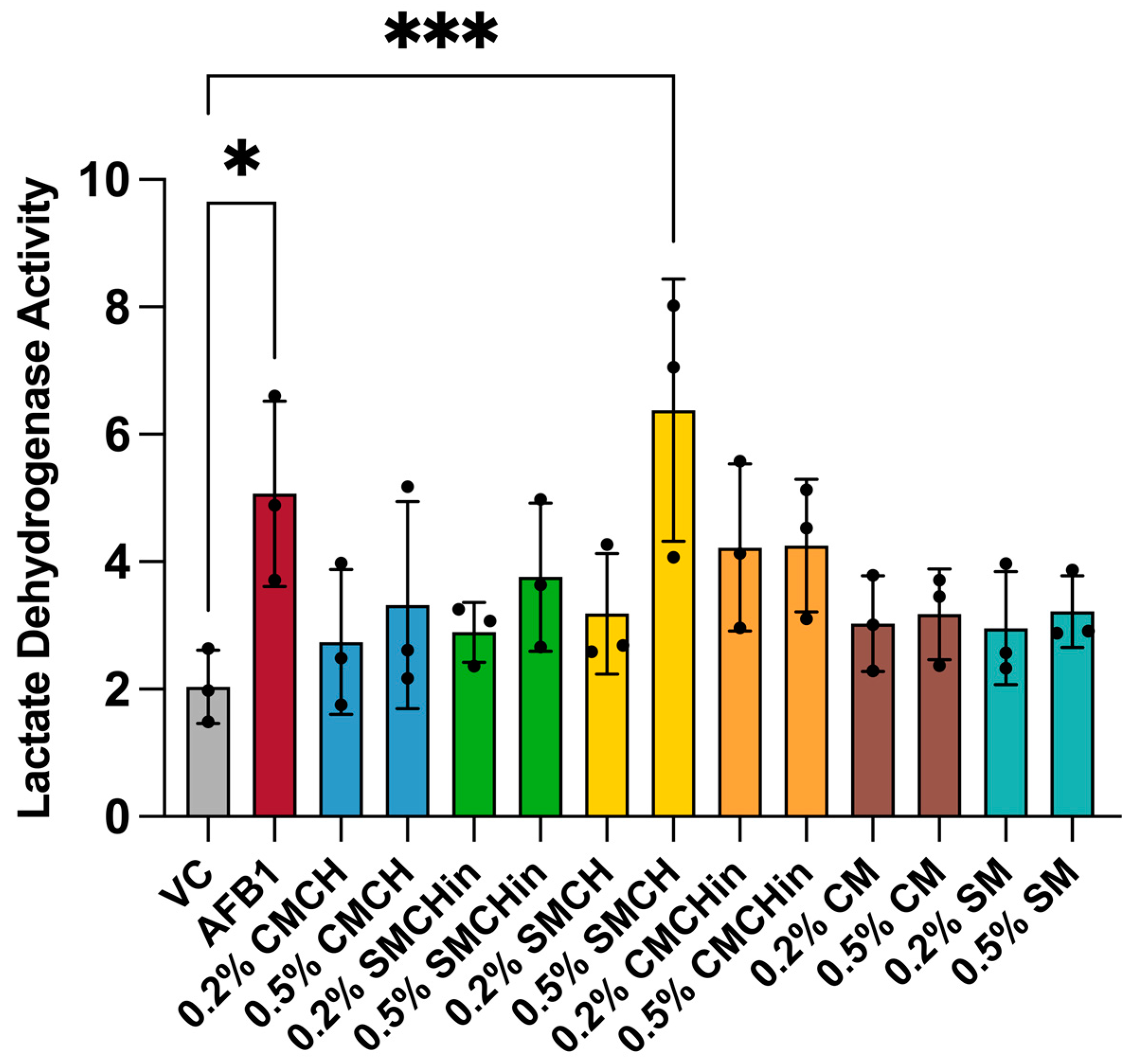
2.5. Cytotoxicity Effect of AFB1 on Hep G2 and Protective Ability of Green-Engineered Clays
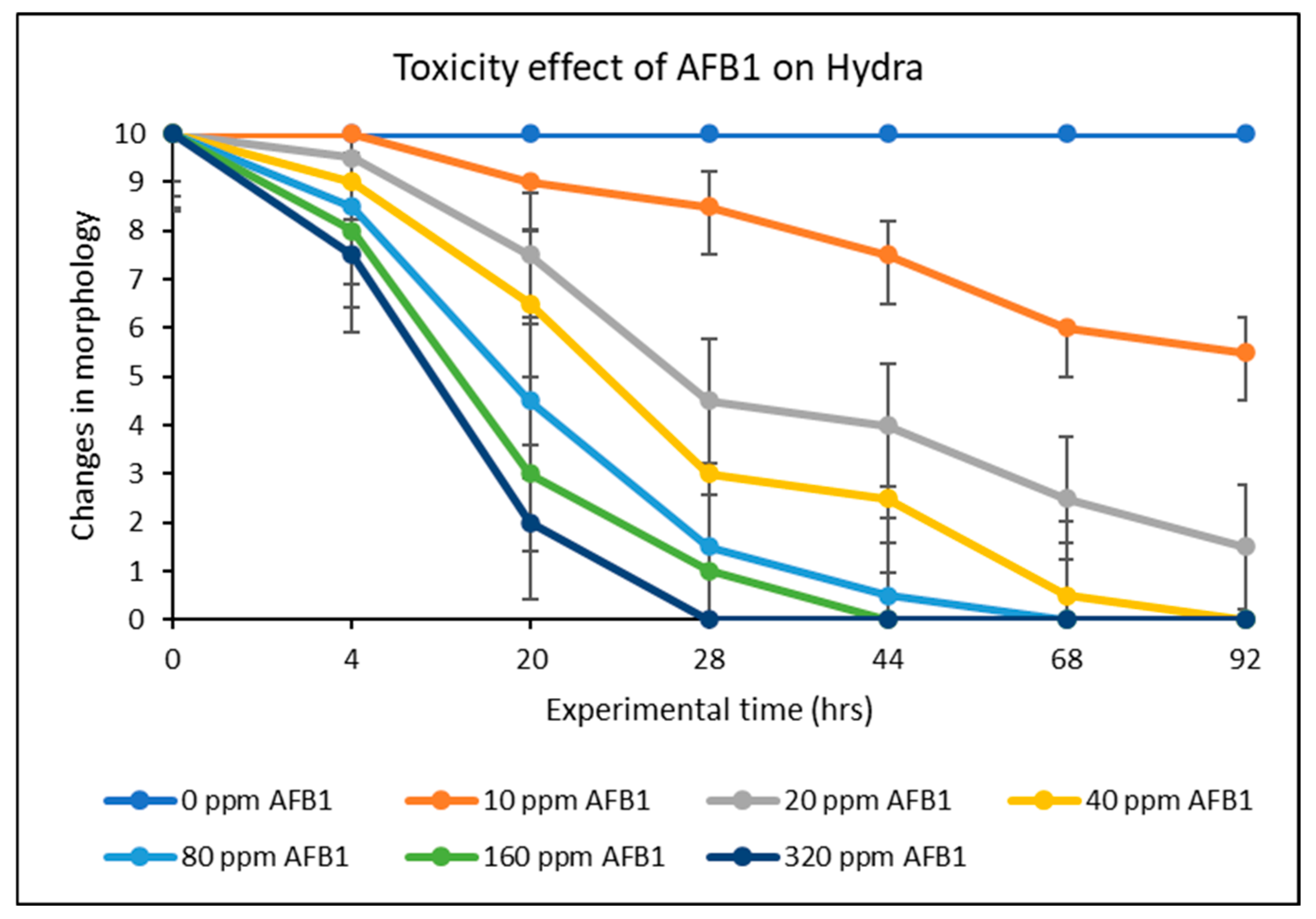
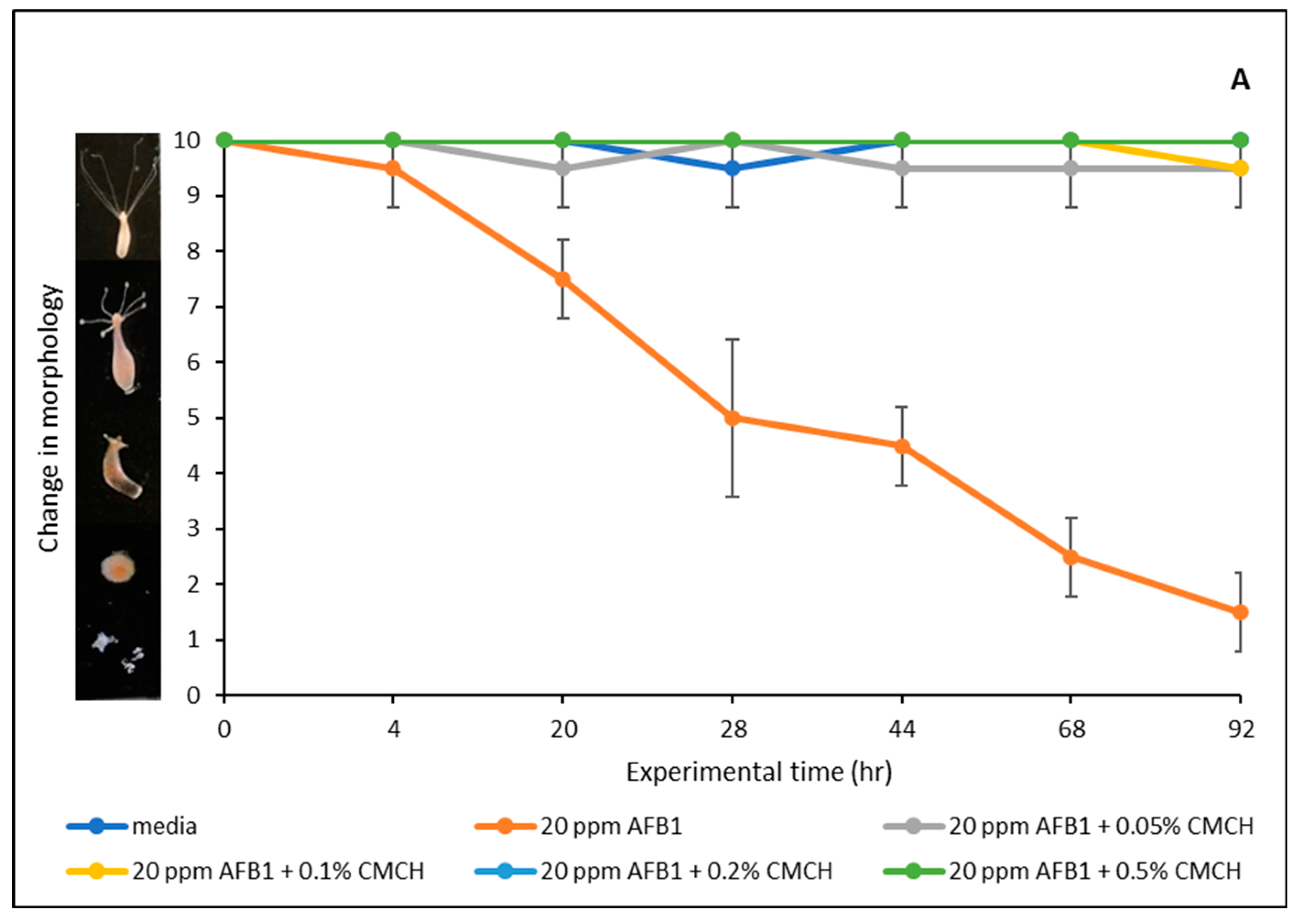
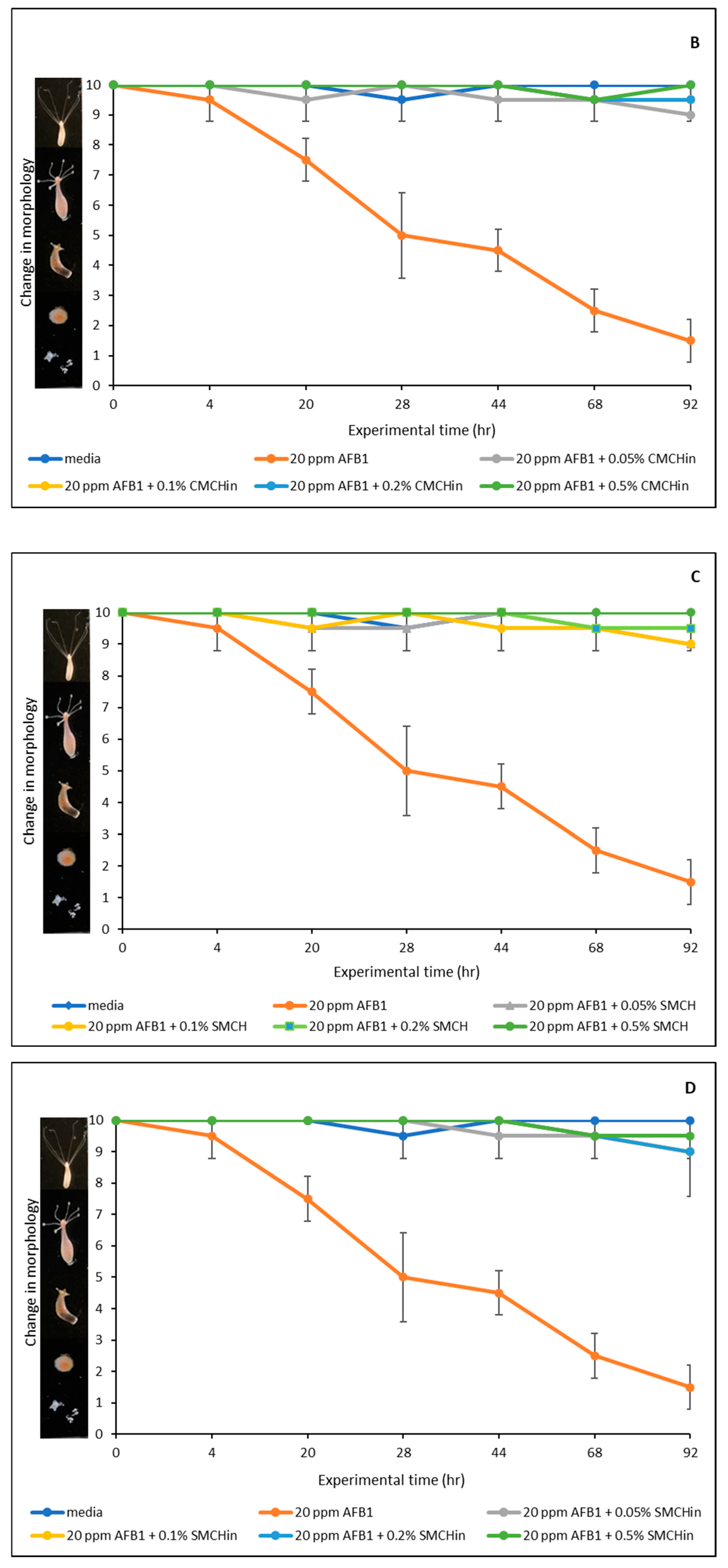
2.6. Effect of AFB1 on Hydra Vulgaris and Detoxification Efficacy of Green-Engineered Clays
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents and Chemicals
5.2. Synthesis and Amendment of GECs
5.3. Sorption Isotherms at Physiological pHs (pH2 and 6)
5.4. Adsorption Kinetics
5.5. Data Calculations and Curve Fitting
5.6. In Silico Studies of AFB1 onto the Binding Surfaces of Chlorophyll-Amended Clay
5.7. Cell Culture and Treatment
5.7.1. Cytotoxicity Assessment
5.7.2. Statistical Analysis
5.8. Hydra Vulgaris In Vivo Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blount, W.P. Turkey “X” Disease. J. Brit. Turkey Fed. 1961, 9, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Asao, T.; Büchi, G.; Abdel-Kader, M.M.; Chang, S.B.; Wick, E.L.; Wogan, G.N. Aflatoxins B and G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 1706–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Aflatoxins. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Scudamore, K.A.; Livesey, C.T. Occurrence and Significance of Mycotoxins in Forage Crops and Silage: A Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klich, M.A. Aspergillus flavus: The Major Producer of Aflatoxin. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Global Burden of Aflatoxin-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Risk Assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, G.S. Aflatoxin and Food Safety: Recent African Perspectives. Toxin Rev. 2003, 22, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Phillips, T.D.; Jolly, P.E.; Stiles, J.K.; Jolly, C.M.; Aggarwal, D. Human Aflatoxicosis in Developing Countries: A Review of Toxicology, Exposure, Potential Health Consequences, and Interventions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robens, J.; Cardwell, K. The Costs of Mycotoxin Management to the USA: Management of Aflatoxins in the United States. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2003, 22, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Bhatnagar, D. Cost-Effectiveness of Aflatoxin Control Methods: Economic Incentives. Toxin Rev. 2008, 27, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, N.J.; Bowers, E.; Hurburgh, C.; Wu, F. Potential Economic Losses to the USA Corn Industry from Aflatoxin Contamination. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubulwa, A.S.; Davis, J. Estimating the Social Costs of the Impacts of Fungi and Aflatoxins in Maize and Peanuts. In Proceedings of the 6th International Working Conference on Stored-Product Protection, Canberra, Australia, 17–23 April 1994; pp. 1017–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki, T.; Wilson, J.S.; Sewadeh, M. Saving Two in a Billion: Quantifying the Trade Effect of European Food Safety Standards on African Exports. Food Policy 2001, 26, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battilani, P.; Toscano, P.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Moretti, A.; Camardo Leggieri, M.; Brera, C.; Rortais, A.; Goumperis, T.; Robinson, T. Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Maize in Europe Increases Due to Climate Change. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Bhatnagar, D.; Bui-Klimke, T.; Carbone, I.; Hellmich, R.; Munkvold, G.; Paul, P.; Payne, G.; Takle, E. Climate Change Impacts on Mycotoxin Risks in US Maize. World Mycotoxin J. 2011, 4, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.D.; Afriyie-Gyawu, E.; Williams, J.; Huebner, H.; Ankrah, N.A.; Ofori-Adjei, D.; Jolly, P.; Johnson, N.; Taylor, J.; Marroquin-Cardona, A.; et al. Reducing Human Exposure to Aflatoxin through the Use of Clay: A Review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, T.D.; Kubena, L.F.; Harvey, R.B.; Taylor, D.R.; Heidelbaugh, N.D. Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate: A High Affinity Sorbent for Aflatoxin. Poult. Sci. 1988, 67, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afriyie-Gyawu, E.; Mackie, J.; Dash, B.; Wiles, M.; Taylor, J.; Huebner, H.; Tang, L.; Guan, H.; Wang, J.S.; Phillips, T.D. Chronic Toxicological Evaluation of Dietary NovaSil Clay in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afriyie-Gyawu, E.; Ankrah, N.; Huebner, H.J.; Ofosuhene, M.; Kumi, J.; Johnson, N.M.; Tang, L.; Xu, L.; Jolly, P.E.; Ellis, W.O.; et al. NovaSil Clay Intervention in Ghanaians at High Risk for Aflatoxicosis. I. Study Design and Clinical Outcomes. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 25, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Afriyie-Gyawu, E.; Tang, Y.; Johnson, N.M.; Xu, L.; Tang, L.; Huebner, H.J.; Ankrah, N.A.; Ofori-Adjei, D.; Ellis, W.; et al. NovaSil Clay Intervention in Ghanaians at High Risk for Aflatoxicosis: II. Reduction in Biomarkers of Aflatoxin Exposure in Blood and Urine. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.D.; Wang, M.; Elmore, S.E.; Hearon, S.; Wang, J. NovaSil Clay for the Protection of Humans and Animals from Aflatoxins and Other Contaminants. Clays Clay Miner. 2019, 67, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivenbark, K.J.; Wang, M.; Lilly, K.; Tamamis, P.; Phillips, T.D. Development and characterization of chlorophyll-amended montmorillonite clays for the adsorption and detoxification of benzene. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladele, J.O.; Wang, M.; Rivenbark, K.J.; Phillips, T.D. Application and efficacy of beidellite clay for the adsorption and detoxification of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladele, J.O.; Wang, M.; Xenophontos, X.; Kendall, L.; Tamamis, P.; Phillips, T.D. Chlorophyll-amended organoclays for the detoxification of ochratoxin A. Toxins 2024, 16, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Phillips, T.D. Green-engineered barrier creams with montmorillonite-chlorophyll clays as adsorbents for benzene, toluene, and xylene. Separations 2023, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaynes, W.F.; Zartman, R.E. Aflatoxin Toxicity Reduction in Feed by Enhanced Binding to Surface-Modified Clay Additives. Toxins 2011, 3, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, G.A.; Khattab, H.M.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A.; Abo El-Nor, S.A.; El-Sayed, H.M.; Kholif, S.M. Clay Minerals as Sorbents for Mycotoxins in Lactating Goat’s Diets: Intake, Digestibility, Blood Chemistry, Ruminal Fermentation, Milk Yield and Composition, and Milk Aflatoxin M1 Content. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 175, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Salma, H.; Hafsa, A.; Elghandour, M.M.M.Y.; Reddy, P.R.K.; Monroy, J.C.; Salem, A.Z.M. Dietary Supplementation with Sodium Bentonite and Coumarin Alleviates the Toxicity of Aflatoxin B1 in Rabbits. Toxicon 2019, 171, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbeye, M.J.; Reddy, P.R.K.; Chilaka, C.A.; Balogun, O.B.; Elghandour, M.M.M.Y.; Rivas-Caceres, R.R.; Salem, A.Z.M. Mycotoxin Toxicity and Residue in Animal Products: Prevalence, Consumer Exposure, and Reduction Strategies—A Review. Toxicon 2020, 177, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marroquin-Cardona, A.; Deng, Y.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.; Johnson, N.M.; Mitchell, N.; Tang, L.; Robinson, A., II; Taylor, J.; Wang, J.-S.; Phillips, T.D. Characterization and Safety of Uniform Particle Size NovaSil Clay as a Potential Aflatoxin Enterosorbent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-S.; Luo, H.; Billam, M.; Wang, Z.; Guan, H.; Tang, L.; Goldston, T.; Afriyie-Gyawu, E.; Lovett, C.; Griswold, J.; et al. Short-Term Safety Evaluation of Processed Calcium Montmorillonite Clay (NovaSil) in Humans. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zychowski, K.E.; Pohlenz, C.; Mays, T.; Romoser, A.; Hume, M.; Buentello, A.; Gatlin, D.M., III; Phillips, T.D. Effects of Dietary NovaSil on Aflatoxin B1-Exposed Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2013, 376–379, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zychowski, K.E.; Rodrigues Hoffmann, A.; Ly, H.J.; Pohlenz, C.; Buentello, A.; Romoser, A.; Gatlin, D.M.; Phillips, T.D. The Effect of Aflatoxin-B1 on Red Drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) and Assessment of Dietary Supplementation of NovaSil for the Prevention of Aflatoxicosis. Toxins 2013, 5, 1555–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinholt, V.; Hendricks, J.; Pereira, C.; Arbogast, D.; Bailey, G. Dietary Chlorophyllin Is a Potent Inhibitor of Aflatoxin B1 Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rainbow Trout. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Simonich, M.T.; Egner, P.A.; Roebuck, B.D.; Orner, G.A.; Jubert, C.; Pereira, C.; Groopman, J.D.; Kensler, T.W.; Dashwood, R.H.; Williams, D.E.; et al. Natural Chlorophyll Inhibits Aflatoxin B1-Induced Multi-Organ Carcinogenesis in the Rat. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egner, P.A.; Wang, J.B.; Zhu, Y.R.; Zhang, B.C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.N.; Qian, G.S.; Kuang, S.Y.; Gange, S.J.; Jacobson, L.P.; et al. Chlorophyllin Intervention Reduces Aflatoxin-DNA Adducts in Individuals at High Risk for Liver Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14601–14606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubert, C.; Mata, J.; Bench, G.; Dashwood, R.; Pereira, C.; Tracewell, W.; Turteltaub, K.; Williams, D.; Bailey, G. Effects of Chlorophyll and Chlorophyllin on Low-Dose Aflatoxin B1 Pharmacokinetics in Human Volunteers. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.G.; Phillips, T.D. Isothermal adsorption of aflatoxin B1 on HSCAS clay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and Inconsistencies Regarding Adsorption of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraja, G.; Prasad, C.; Vijaya, Y.; Subbaiah, M.V. Application of ZnO Nanorods as an Adsorbent Material for the Removal of As(III) from Aqueous Solution: Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Studies. Int. J. Integr. Care 2018, 9, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Chu, Y.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, F.F.; Bhandari, N.; Ruan, G.D.; Dai, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kan, A.T. Determination of adsorption isotherm parameters with correlated errors by measurement error models. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J. Rshiny. 2020. Available online: https://jgong9.shinyapps.io/chemistry_app/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDB. 2022 Chlorophyll A CLA. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/ligand/CLA (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A Web-based Graphical User Interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L., III; MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The biomolecular simulation program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.K.; Kern, N.R.; Kim, S.; Kanhaiya, K.; Afshar, Y.; Jeon, S.H.; Jo, S.; Brooks, B.R.; Lee, J.; Tadmor, E.B.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Nanomaterial Modeler for Modeling and Simulation of Nanomaterial Systems. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2022, 18, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heinz, H.; Lin, T.J.; Mishra, R.K.; Emami, F.S. Thermodynamically consistent force fields for the assembly of inorganic, organic, and biological nanostructures: The INTERFACE force field. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1754–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. Automation of the CHARMM General Force Field (CGenFF) I: Bond perception and atom typing. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.; Adam, S.; Bondar, A.N. Revised force-field parameters for chlorophyll-a, pheophytin-a and plastoquinone-9. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2015, 58, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, P.; Swails, J.; Chodera, J.D.; McGibbon, R.T.; Zhao, Y.; Beauchamp, K.A.; Wang, L.P.; Simmonett, A.C.; Harrigan, M.P.; Stern, C.D.; et al. OpenMM 7: Rapid development of high performance algorithms for molecular dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagles, E.J.; Benstead, R.; MacDonald, S.; Handy, R.D.; Hutchinson, T.H. Environmental Risks to Freshwater Organisms from the Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone Using Species Sensitivity Distributions. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesano, V.; Ambrosone, A.; Bartelmess, J.; Strisciante, F.; Tino, A.; Echegoyen, L.; Tortiglione, C.; Giordani, S. Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1331–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sorbents | Adsorption Parameters @ pH2 | Adsorption Parameters @ pH6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax | Kd | ∆G | r2 | Qmax | Kd | ∆G | r2 | |
| CM | 0.34 | 1.89 × 104 | −19.19 | 0.88 | 0.35 | 2.07 × 104 | −19.83 | 0.93 |
| CMCH | 0.43 | 2.01 × 104 | −20.28 | 0.95 | 0.41 | 1.86 × 104 | −19.95 | 0.96 |
| CMCHin | 0.40 | 2.18 × 104 | −20.07 | 0.96 | 0.36 | 2.09 × 104 | −19.71 | 0.96 |
| SM | 0.32 | 2.40 × 104 | −19.72 | 0.92 | 0.31 | 1.91 × 104 | −19.32 | 0.93 |
| SMCH | 0.38 | 1.66 × 104 | −19.60 | 0.97 | 0.33 | 2.68 × 104 | −19.71 | 0.94 |
| SMCHin | 0.39 | 1.14 × 104 | −19.33 | 0.94 | 0.38 | 1.63 × 104 | −19.83 | 0.92 |
| Pseudo-Second Order Parameters | qe (exp mgkg−1) | qe (cal mgkg−1) | K2 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | 0.05 | 0.04 | 8.32 × 100 | 0.85 |
| CMCH | 0.08 | 0.05 | 3.41 × 100 | 0.87 |
| CMCHin | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.36 × 100 | 0.93 |
| SM | 0.05 | 0.04 | 3.66 × 100 | 0.89 |
| SMCH | 0.07 | 0.05 | 1.36 × 100 | 0.94 |
| SMCHin | 0.07 | 0.06 | 2.75 × 10−1 | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oladele, J.O.; Xenophontos, X.; Elizondo, G.M., III; Daasari, Y.; Wang, M.; Tamamis, P.; Johnson, N.M.; Phillips, T.D. Green-Engineered Montmorillonite Clays for the Adsorption, Detoxification, and Mitigation of Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity. Toxins 2025, 17, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030131
Oladele JO, Xenophontos X, Elizondo GM III, Daasari Y, Wang M, Tamamis P, Johnson NM, Phillips TD. Green-Engineered Montmorillonite Clays for the Adsorption, Detoxification, and Mitigation of Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity. Toxins. 2025; 17(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleOladele, Johnson O., Xenophon Xenophontos, Gustavo M. Elizondo, III, Yash Daasari, Meichen Wang, Phanourios Tamamis, Natalie M. Johnson, and Timothy D. Phillips. 2025. "Green-Engineered Montmorillonite Clays for the Adsorption, Detoxification, and Mitigation of Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity" Toxins 17, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030131
APA StyleOladele, J. O., Xenophontos, X., Elizondo, G. M., III, Daasari, Y., Wang, M., Tamamis, P., Johnson, N. M., & Phillips, T. D. (2025). Green-Engineered Montmorillonite Clays for the Adsorption, Detoxification, and Mitigation of Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity. Toxins, 17(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17030131






