Cytotoxic Effects Induced by Combined Exposure of the Patulin, Ochratoxin A, and Acetamiprid to HK-2 and SK-N-SH Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Individual Effects of PAT, OTA, and ACM Exposure on Cellular IC50 Values
2.2. Cell Viability of Multi-Mixture of Contaminants
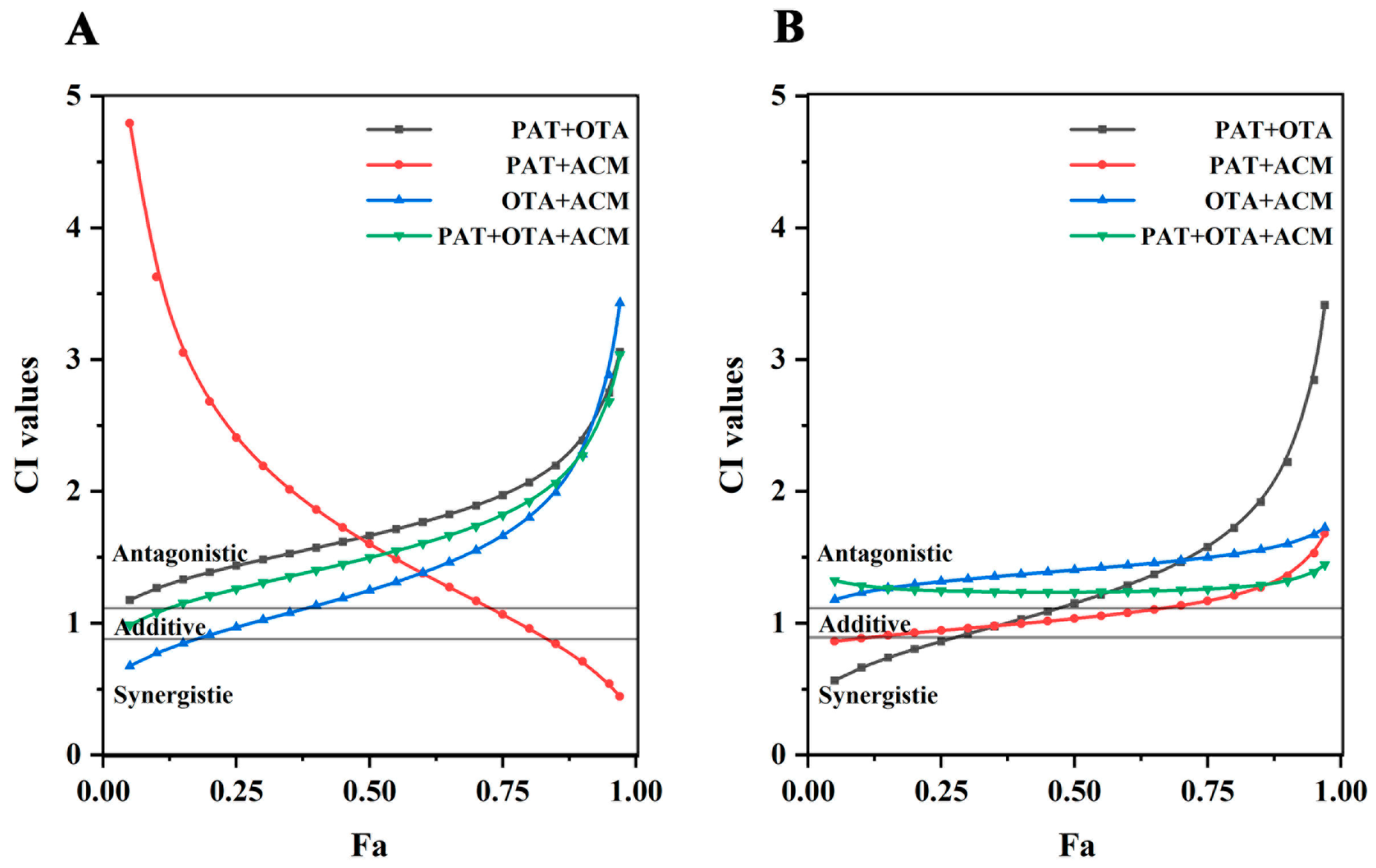
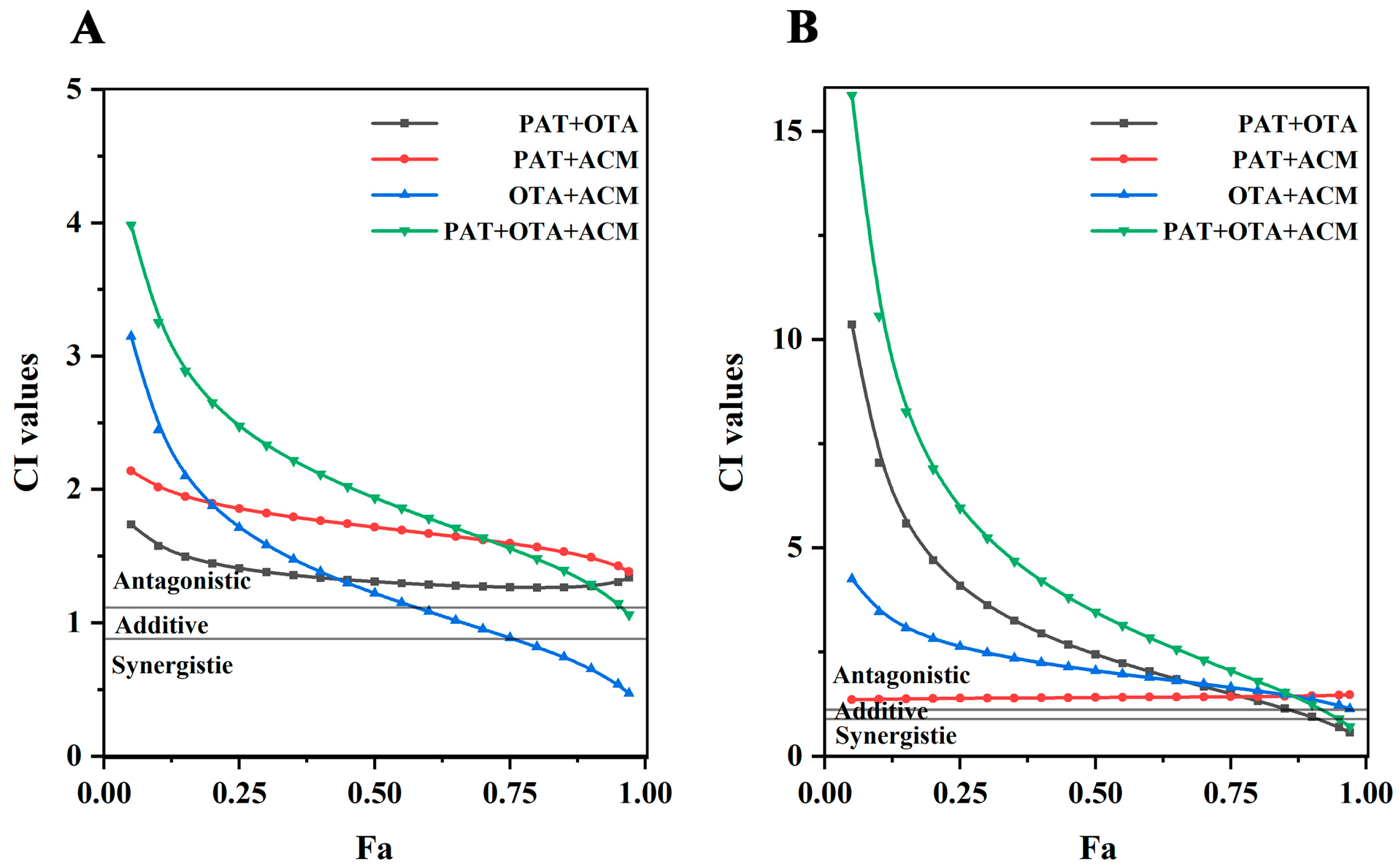
2.3. Combined Toxicity Analysis
2.4. DRI Analyses of Multiple Combined Effects of PAT, OTA, and ACM
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. Individual and Combined Cytotoxicity Assessment
5.4. Cell Viability Assessment
5.5. Combined Index Analysis of Contamination Mixtures
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thakali, A.; MacRae, J.D. A review of chemical and microbial contamination in food: What are the threats to a circular food system? Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Liao, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Shan, Z.; Nüssler, A.K.; Yao, P.; Yan, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates low-dose of deoxynivalenol-induced liver inflammation potentially associating with microbiota. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 374, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Xu, J.; Jiang, K.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, J.; Li, H.; et al. Determination of multiple mycotoxins in paired plasma and urine samples to assess human exposure in Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awuchi, C.G.; Ondari, E.N.; Nwozo, S.; Odongo, G.A.; Eseoghene, I.J.; Twinomuhwezi, H.; Ogbonna, C.U.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Adeleye, A.O.; Okpala, C.O.R. Mycotoxins’ Toxicological Mechanisms Involving Humans, Livestock and Their Associated Health Concerns: A Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ryu, D. Worldwide Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Cereals and Cereal-Derived Food Products: Public Health Perspectives of Their Co-occurrence. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7034–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolakowski, B.; O’ROurke, S.M.; Bietlot, H.P.; Kurz, K.; Aweryn, B. Ochratoxin A Concentrations in a Variety of Grain-Based and Non-Grain-Based Foods on the Canadian Retail Market from 2009 to 2014. J. Food Protect. 2016, 79, 2143–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Waseem, M.; Razis, A.F.A.; Bhatti, I.A.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Mohammed, O.A.; Lakshminarayanan, S.P.; Iqbal, M. Mycotoxin patulin contamination in various fruits and estimating its dietary impact on the consumers: From orchard to table. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, R.; Yang, H.; Qi, P.; Xiao, Y.; Qian, M. Occurrence of patulin in various fruit products and dietary exposure assessment for consumers in China. Food Control 2017, 78, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulson, D. Review: An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seccia, S.; Fidente, P.; Barbini, D.A.; Morrica, P. Multiresidue determination of nicotinoid insecticide residues in drinking water by liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 553, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Han, C.; Qian, Y.; Ding, H.; Chen, X.; Xi, J. Determination of neonicotinoid pesticides residues in agricultural samples by solid-phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4426–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seccia, S.; Fidente, P.; Montesano, D.; Morrica, P. Determination of neonicotinoid insecticides residues in bovine milk samples by solid-phase extraction clean-up and liquid chromatography with diode-array detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1214, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.X. Residues of Neonicotinoid Pesticides in Vegetables and Fruit and Health Risk Assessment of Human Exposure via Food Intake. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2016, 11, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Montiel-León, J.M.; Duy, S.V.; Munoz, G.; Verner, M.-A.; Hendawi, M.Y.; Moya, H.; Amyot, M.; Sauvé, S. Occurrence of pesticides in fruits and vegetables from organic and conventional agriculture by QuEChERS extraction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2019, 104, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção, R.; Martins, C.; Dupont, D.; Alvito, P. Patulin and ochratoxin A co-occurrence and their bioaccessibility in processed cereal-based foods: A contribution for Portuguese children risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Sulyok, M.; Nagl, V.; Faas, J.; Krska, R.; Khiaosa-Ard, R.; Zebeli, Q. Mixtures of mycotoxins, phytoestrogens and pesticides co-occurring in wet spent brewery grains (BSG) intended for dairy cattle feeding in Austria. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2022, 39, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.C.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xue, L.F.; Wang, H.; Ren, H.B.; Jia, X.T.; Yang, X.W. Control measures of pesticide residue and mycotoxin in buckwheat production and storage. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 3370–3374. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, I.; Goktepe, I. The characteristics, occurrence, and toxicological effects of patulin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliege, R.; Metzler, M. Electrophilic properties of patulin. N-acetylcysteine and glutathione adducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Varzakas, T. Advances in Occurrence, Importance, and Mycotoxin Control Strategies: Prevention and Detoxification in Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ráduly, Z.; Szabó, L.; Madar, A.; Pócsi, I.; Csernoch, L. Toxicological and Medical Aspects of Aspergillus-Derived Mycotoxins Entering the Feed and Food Chain. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbert, A.; Haas, M.; Springer, B.; Thielert, W.; Nauen, R. Applied aspects of neonicotinoid uses in crop protection. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, H.-Y.; Li, M.-X.; Li, W.-H.; Ma, K.-G.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhang, J.H. Oxidative Stress: Role in Acetamiprid-Induced Impairment of the Male Mice Reproductive System. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devan, R.S.; Mishra, A.; Prabu, P.; Mandal, T.; Panchapakesan, S. Sub-chronic oral toxicity of acetamiprid in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hoogenboom, R.L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Song, W.; Guan, S.; Song, W.; Rao, Q. Assessing the combined toxicity effects of three neonicotinoid pesticide mixtures on human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH and lepidopteran Sf-9 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, F.; Li, X.; Tan, H.; Zeng, D. Combined toxicity of chlorantraniliprole, lambda-cyhalothrin, and imidacloprid to the silkworm Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera; Bombycidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22598–22605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, S.; Cui, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Yin, S.; Hu, H. Combination of Patulin and Chlorpyrifos Synergistically Induces Hepatotoxicity via Inhibition of Catalase Activity and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11474–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, U.A.; Huntriss, J.; Routledge, M.N.; Gong, Y.Y. Toxicological effects of regulated mycotoxins and persistent organochloride pesticides: In vitro cytotoxic assessment of single and defined mixtures on MA-10 murine Leydig cell line. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 48, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, N.; Ji, J.; Chen, C. An integrated approach for evaluating the interactive effects between azoxystrobin and ochratoxin A: Pathway-based in vivo analyses. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 195, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xing, H.; Shao, W.; Wu, P.; Fan, Y.; He, H.; Barth, S.; Zheng, A.; Liang, X.-J.; Huang, Y. Antitumor synergism between PAK4 silencing and immunogenic phototherapy of engineered extracellular vesicles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 3945–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Hu, H. Combined toxicity of food-borne mycotoxins and heavy metals or pesticides. Toxicon 2022, 217, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, A.; Alvito, P.; Loureiro, S.; Louro, H.; Silva, M. Multi-mycotoxin determination in baby foods and in vitro combined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. World Mycotoxin J. 2013, 6, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzydlewski, P.; Twarużek, M.; Grajewski, J. Cytotoxicity of Mycotoxins and Their Combinations on Different Cell Lines: A Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingales, V.; Piunti, C.; Micheli, S.; Cimetta, E.; Ruiz, M.-J. Development of an Easy-To-Use Microfluidic System to Assess Dynamic Exposure to Mycotoxins in 3D Culture Models: Evaluation of Ochratoxin A and Patulin Cytotoxicity. Foods 2024, 13, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, R.; Pinhão, M.; Loureiro, S.; Alvito, P.; Silva, M.J. A multi-endpoint approach to the combined toxic effects of patulin and ochratoxin a in human intestinal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 313, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liao, G.; Jia, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, T.; Qian, Y. Integrated non-targeted lipidomics and metabolomics analyses for fluctuations of neonicotinoids imidacloprid and acetamiprid on Neuro-2a cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, C.; Zingales, V.; Barat, J.M.; Ruiz, M.-J. Combined Cytotoxic Effects of the Fungicide Azoxystrobin and Common Food-Contaminating Mycotoxins. Foods 2025, 14, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ji, J.; Wang, J.-S.; Sun, X. Co-contamination and interaction of fungal toxins and other environmental toxins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heussner, A.; Dietrich, D.; O’bRien, E. In vitro investigation of individual and combined cytotoxic effects of ochratoxin A and other selected mycotoxins on renal cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2006, 20, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadee, A.; Mahakunakorn, P.; Porasuphatana, S. Oxidative stress and genotoxicity of co-exposure of chlorpyrifos and aflatoxin B1 in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2020, 36, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Castrejón-Godínez, M.L.; Monterrosas-Brisson, N. Pesticide: Environmental Stressors Implicated in the Development of Central Nervous System Disorders and Neurodegeneration. Stresses 2025, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Esparza, M.Á.; Mateo, E.M.; Robles, J.A.; Capoferri, M.; Jiménez, M.; Soria, J.M. Unveiling the Neurotoxic Effects of Ochratoxin A and Its Impact on Neuroinflammation. Toxins 2025, 17, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.T.; Bridgeman, L.; Moyano-López, C.; Penalva-Olcina, R.; Juan, C.S.A.; Juan-García, A. Study of cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma cell line exposed to patulin and citrinin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 186, 114556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ji, J.; Wei, K.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. MAPK/AP-1 and ROS participated in ratio- and time-dependent interaction effects of deoxynivalenol and cadmium on HT-29 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 148, 111921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.S. Interaction of ochratoxin A with bovine serum albumin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 147, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.D.; Ryu, D. Protective Effect of alpha-Tocopherol Against Ochratoxin A in kidney cell line HK-2. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 7034–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, T.H.; Alzubi, M.A.; Harrell, J.C. Identification of synergistic drug combinations using breast cancer patient-derived xenografts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
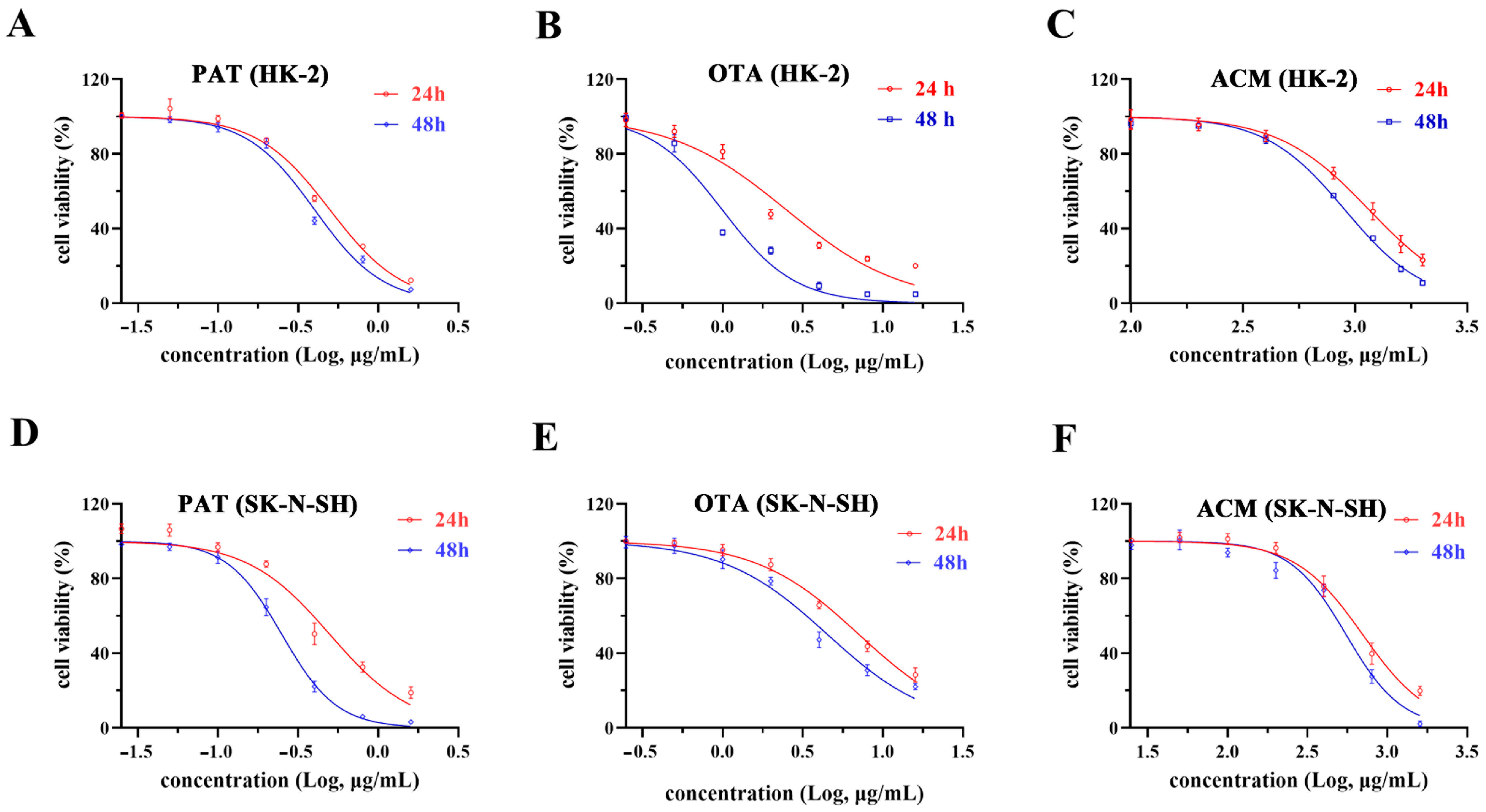

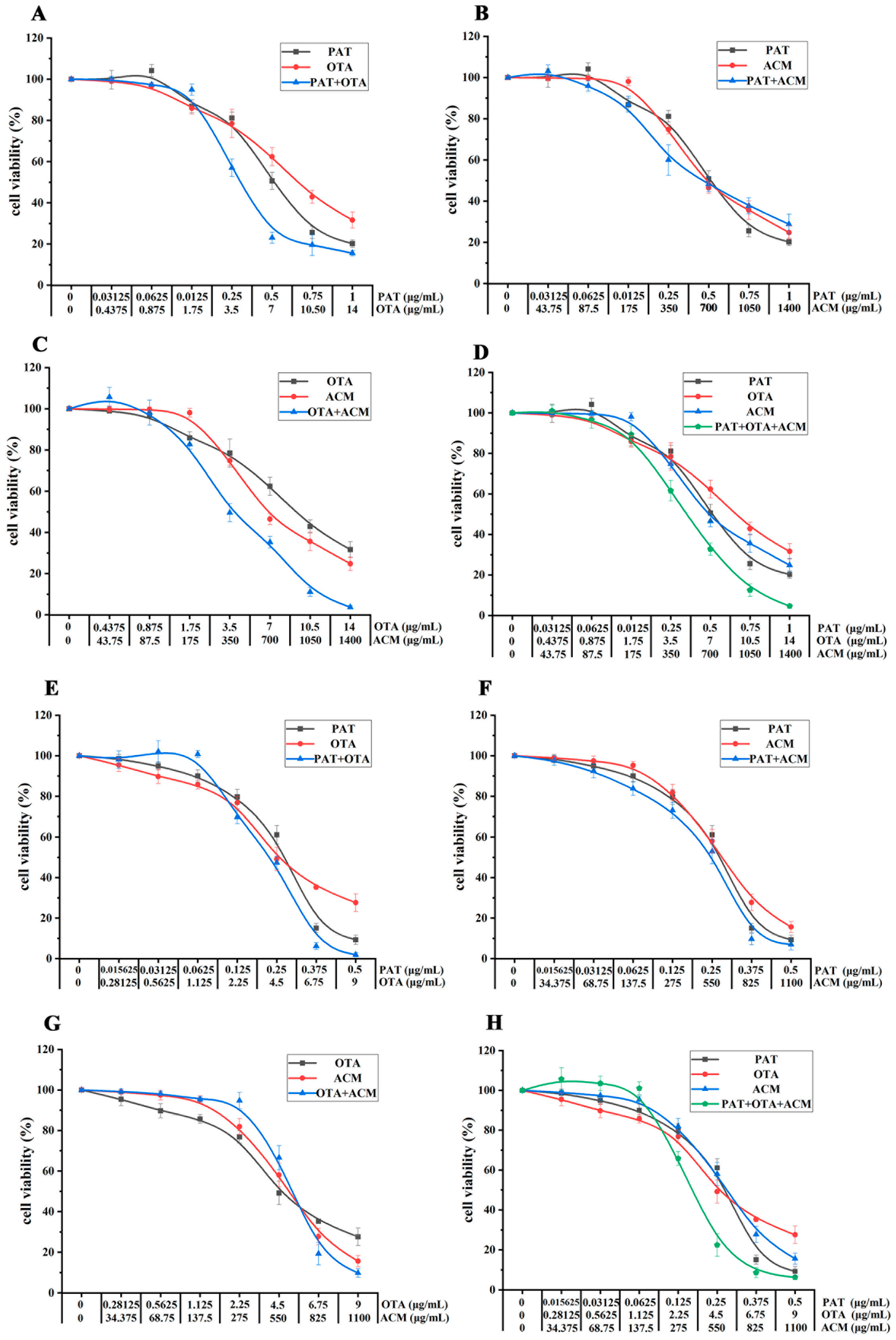


| Cells | Times (h) | PAT (μg/mL) | OTA (μg/mL) | ACM (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HK-2 | 24 | 0.5 ± 0.005 a | 2.5 ± 0.049 c | 1156.3 ± 38.70 a |
| 48 | 0.4 ± 0.006 b | 1.0 ± 0.021 d | 900.2 ± 4.1 b | |
| SK-N-SH | 24 | 0.5 ± 0.024 a | 7.0 ± 0.357 a | 699.8 ± 34.41 c |
| 48 | 0.25 ± 0.001 c | 4.5 ± 0.415 b | 549.5 ± 31.58 d |
| CI Value | Description | Graded Symbols |
|---|---|---|
| <0.10 | Very strong synergism | + + + + + |
| 0.10–0.30 | Strong synergism | + + + + |
| 0.30–0.70 | Common synergism | + + + |
| 0.70–0.85 | Moderate synergism | + + |
| 0.85–0.90 | Slight synergism | + |
| 0.90–1.10 | Nearly additive | ± |
| 1.10–1.20 | Slight antagonism | – |
| 1.20–1.45 | Moderate antagonism | – – |
| 1.45–3.30 | Common antagonism | – – – |
| 3.30–10.0 | Strong antagonism | – – – – |
| >10.0 | Very strong antagonism | – – – – – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yang, X.; Nie, D.; Yang, J.; Han, Z. Cytotoxic Effects Induced by Combined Exposure of the Patulin, Ochratoxin A, and Acetamiprid to HK-2 and SK-N-SH Cell Lines. Toxins 2025, 17, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110563
Zhu Z, Zhao H, Yang X, Nie D, Yang J, Han Z. Cytotoxic Effects Induced by Combined Exposure of the Patulin, Ochratoxin A, and Acetamiprid to HK-2 and SK-N-SH Cell Lines. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110563
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zuoyin, Hanke Zhao, Xianli Yang, Dongxia Nie, Junhua Yang, and Zheng Han. 2025. "Cytotoxic Effects Induced by Combined Exposure of the Patulin, Ochratoxin A, and Acetamiprid to HK-2 and SK-N-SH Cell Lines" Toxins 17, no. 11: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110563
APA StyleZhu, Z., Zhao, H., Yang, X., Nie, D., Yang, J., & Han, Z. (2025). Cytotoxic Effects Induced by Combined Exposure of the Patulin, Ochratoxin A, and Acetamiprid to HK-2 and SK-N-SH Cell Lines. Toxins, 17(11), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110563






