Exposure Type and Duration Determine Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacteria Anatoxins on the Benthic Amphipod Hyalella azteca
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anatoxin Toxicity in Aqueous Exposure, 10d
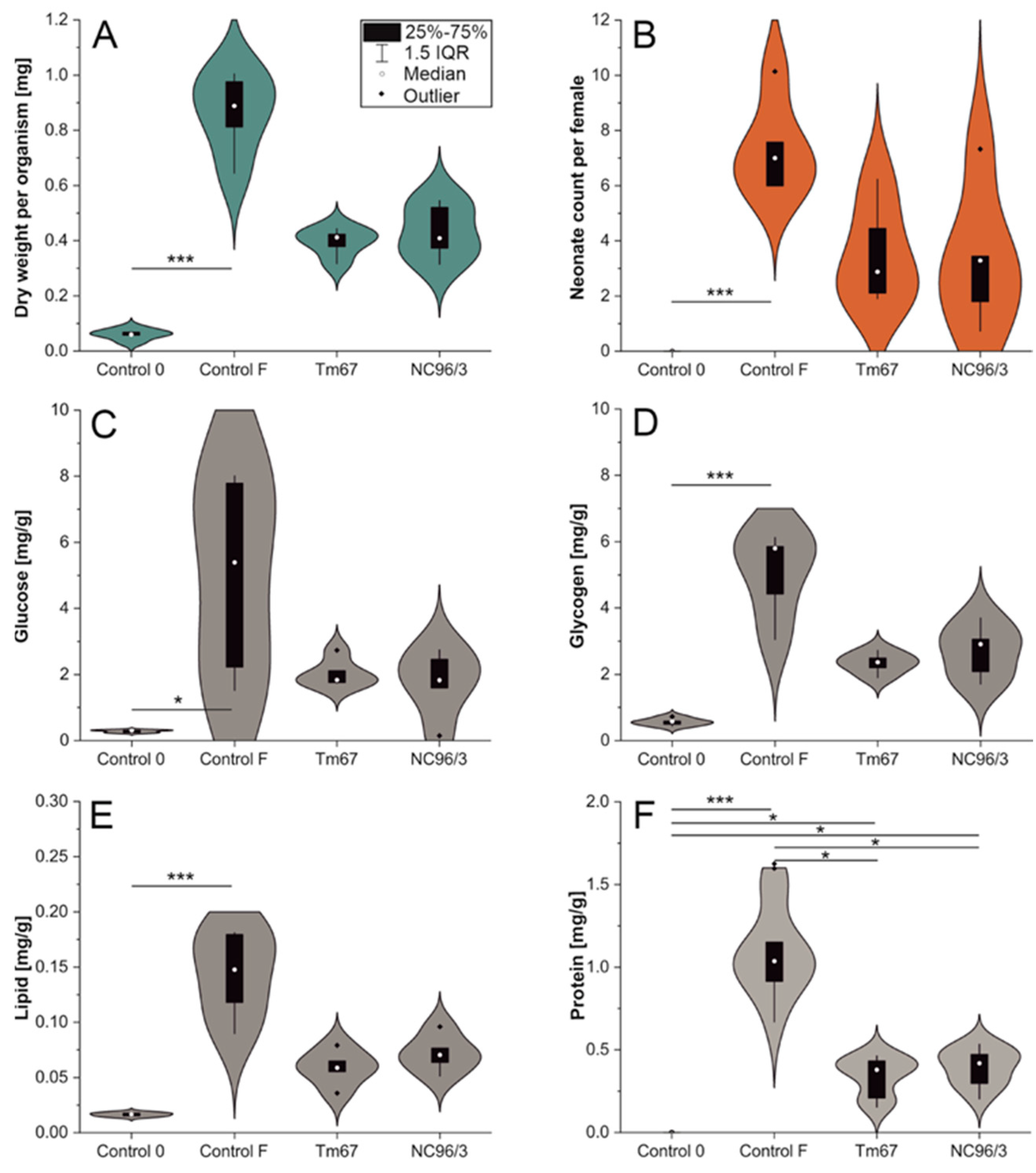
2.2. Anatoxin Toxicity in Dietary Exposure, 42d
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Anatoxins
5.2. Test Organisms
5.3. Toxicity Tests
5.3.1. Toxicity Test with Exposure to Dissolved Synthetic Anatoxins
5.3.2. Toxicity Test with Exposure to Natural Anatoxins via a Tychonema Diet
5.3.3. Assessment of Storage Compounds
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cottingham, K.L.; Weathers, K.C.; Ewing, H.A.; Greer, M.L.; Carey, C.C. Predicting the effects of climate change on freshwater cyanobacterial blooms requires consideration of the complete cyanobacterial life cycle. J. Plankton Res. 2021, 43, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, F.; Wolfschlaeger, I.; Geist, J.; Fastner, J.; Schmalz, C.W.; Raeder, U. Occurrence, distribution and toxins of benthic cyanobacteria in German lakes. Toxics 2023, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, C.E.; Hartmann, H.M. Planktonic bloom-forming Cyanobacteria and the eutrophication of lakes and rivers. Freshw. Biol. 1988, 20, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Cyanobacterial toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water, A Guide to Their Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; E. & F.N. Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ettoumi, A.; El Khalloufi, F.; El Ghazali, I.; Oudra, B.; Amrani, A.; Nasri, H.; Bouaïcha, N. Bioaccumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in aquatic organisms and its consequences for public health. In Zooplankton and Phytoplankton: Types, Characteristics and Ecology; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A. Cyanotoxins. In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 651–675. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I.; Webb, P.M.; Schluter, P.J.; Shaw, G.R. Recreational and occupational field exposure to freshwater cyanobacteria–a review of anecdotal and case reports, epidemiological studies and the challenges for epidemiologic assessment. Environ. Health 2006, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R. Acute animal and human poisonings from cyanotoxin exposure—A review of the literature. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fastner, J.; Beulker, C.; Geiser, B.; Hoffmann, A.; Kröger, R.; Teske, K.; Hoppe, J.; Mundhenk, L.; Neurath, H.; Sagebiel, D.; et al. Fatal neurotoxicosis in dogs associated with tychoplanktic, anatoxin-a producing Tychonema sp. in mesotrophic lake Tegel, Berlin. Toxins 2018, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Edwards, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Barr, W.M.; Gunn, G.J. Fatal attraction to cyanobacteria? Nature 1992, 359, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simola, O.; Wiberg, M.; Jokela, J.; Wahlsten, M.; Sivonen, K.; Syrjä, P. Pathologic findings and toxin identification in cyanobacterial (Nodularia spumigena) intoxication in a dog. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 49, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, F.; Fastner, J.; Bartha-Dima, B.; Breuer, W.; Falkenau, A.; Mayer, C.; Raeder, U. Mass occurrence of anatoxin-a-and dihydroanatoxin-a-producing Tychonema sp. in mesotrophic reservoir Mandichosee (River Lech, Germany) as a cause of neurotoxicosis in dogs. Toxins 2020, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.C.; Gammie, A.J.; Hollinrake, K.; Codd, G.A. Pneumonia associated with contact with cyanobacteria. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1990, 300, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texeira, M.D.G.L.C.; Costa, M.D.C.N.; Carvalho, V.L.P.D.; Pereira, M.D.S.; Hage, E. Gastroenteritis epidemic in the area of the Itaparica Dam, Bahia, Brazil. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. (PAHO) 1993, 27, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Azevedo, S.M.; An, J.S.; Molica, R.J.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Lau, S.; Rinehart, K.L.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: Chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, S.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Lau, S.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru—Brazil. Toxicology 2002, 181, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Bagchi, M.D.; Burch, M.D.; Carmichael, W.W.; Harding, W.R.; Kaya, K.; Utkilen, H.C. Cyanonet: A Global Network for Cyanobacterial Bloom and Toxin Risk Management: Initial Situation Assessment And Recommendations; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Giannuzzi, L.; Sedan, D.; Echenique, R.; Andrinolo, D. An acute case of intoxication with cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in recreational water in Salto Grande Dam, Argentina. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirich, C.A.; Miller, T.R. Freshwater harmful algal blooms: Toxins and children’s health. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2014, 44, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, M.B.; Thakur, J.K.; Singh, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Prasuna, E.G.; Kumar, A. Cyanobacterial toxins: The current status. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 9, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Méjean, A.; Paci, G.; Gautier, V.; Ploux, O. Biosynthesis of anatoxin-a and analogues (anatoxins) in cyanobacteria. Toxicon 2014, 91, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, M.; Ploux, O.; Metcalf, J.S.; Mejean, A.; Pawlik-Skowronska, B.; Furey, A. Anatoxin-a, homoanatoxin-a, and natural analogues. In Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, F.; Stix, M.; Bartha-Dima, B.; Geist, J.; Raeder, U. Spatio-temporal monitoring of benthic anatoxin-a-producing Tychonema sp. in the River Lech, Germany. Toxins 2022, 14, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, H.A.; Rapoport, H. Synthesis of anatoxin a via intramolecular cyclization of iminium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Murakami, T.; Watanabe, M.F.; Oda, T.; Yamada, J.; Tsujimura, S.; Nagai, H.; Oishi, S. Simultaneous production of homoanatoxin-a, anatoxin-a, and a new non-toxic 4-hydroxyhomoanatoxin-a by the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis mediterranea Skuja. Toxicon 2003, 42, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aráoz, R.; Nghiêm, H.O.; Rippka, R.; Palibroda, N.; de Marsac, N.T.; Herdman, M. Neurotoxins in axenic oscillatorian cyanobacteria: Coexistence of anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a determined by ligand-binding assay and GC/MS. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méjean, A.; Mann, S.; Maldiney, T.; Vassiliadis, G.; Lequin, O.; Ploux, O. Evidence that biosynthesis of the neurotoxic alkaloids anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a in the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria PCC 6506 occurs on a modular polyketide synthase initiated by L-proline. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7512–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Smith, F.M.; Heath, M.W.; Palfroy, T.; Gaw, S.; Young, R.G.; Ryan, K.G. Within-mat variability in anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a production among benthic Phormidium (cyanobacteria) strains. Toxins 2012, 4, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastner, J.; Teikari, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Köhler, A.; Hoppe, S.; Dittmann, E.; Welker, M. Cyanotoxins associated with macrophytes in Berlin (Germany) water bodies–Occurrence and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaso, N.; Cerasino, L.; Boscaini, A.; Capelli, C. Planktic Tychonema (Cyanobacteria) in the large lakes south of the Alps: Phylogenetic assessment and toxigenic potential. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoral Uriza, E.A.; Asencio, A.D.; Aboal, M. Are we underestimating benthic cyanotoxins? Extensive sampling results from Spain. Toxins 2017, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Biessy, L.; Puddick, J. Anatoxins are consistently released into the water of streams with Microcoleus autumnalis-dominated (cyanobacteria) proliferations. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Biggs, D.F.; Gorham, P.R. Toxicology and pharmacological action of Anabaena flos-aquae toxin. Science 1975, 187, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, C.; Cerasino, L.; Boscaini, A.; Salmaso, N. Molecular tools for the quantitative evaluation of potentially toxigenic Tychonema bourrellyi (Cyanobacteria, Oscillatoriales) in large lakes. Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulberg, O.M.; Skulberg, R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Andersen, R.A.; Matsunaga, S.; Moore, R.E. Investigations of a neurotoxic oscillatorialean strain (Cyanophyceae) and its toxin. Isolation and characterization of homoanatoxin-a. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1992, 11, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Wonnacott, S.; Swanson, K.L.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Huby, N.J.S.; Thompson, P.; Gallagher, T. Homoanatoxin: A potent analogue of anatoxin-a. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonnacott, S.; Jackman, S.; Swanson, K.L.; Rapoport, H.; Albuquerque, E.X. Nicotinic pharmacology of anatoxin analogs. II. Side chain structure-activity relationships at neuronal nicotinic ligand binding sites. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991, 259, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colas, S.; Marie, B.; Lance, E.; Quiblier, C.; Tricoire-Leignel, H.; Mattei, C. Anatoxin-a: Overview on a harmful cyanobacterial neurotoxin from the environmental scale to the molecular target. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Capelli, C.; Cerasino, L.; Ballot, A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Sivonen, K.; Salmaso, N. Anatoxin-a producing Tychonema (Cyanobacteria) in European waterbodies. Water Res. 2015, 69, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubero-Pascal, N.; Aboal, M. Cyanobacteria and Macroinvertebrate Relationships in Freshwater Benthic Communities beyond Cytotoxicity. Toxins 2024, 16, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Voorhees, J.; Phillips, B.; Fadness, R.; Stancheva, R.; Nichols, J.; Orr, D.; Wood, S.A. Extracts from benthic anatoxin-producing Phormidium are toxic to 3 macroinvertebrate taxa at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Pawlik-Skowrońska, B. Early indicators of behavioral and physiological disturbances in Daphnia magna (Cladocera) induced by cyanobacterial neurotoxin anatoxin-a. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, R.; Geist, J. Climate change affects litter decomposition in the benthic and hyporheic zones of stream mesocosms. Funct. Ecol. 2025, 39, 2817–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenbein, S.; Poynton, H.; Connon, R.E. Contaminant exposure effects in a changing climate: How multiple stressors can multiply exposure effects in the amphipod Hyalella azteca. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollows, J.W.; Townsend, C.R.; Collier, K.J. Diet of the crayfish Paranephrops zealandicus in bush and pasture streams: Insights from stable isotopes and stomach analysis. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covich, A.P.; Palmer, M.A.; Crowl, T.A. The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems: Zoobenthic species influence energy flows and nutrient cycling. BioScience 1999, 49, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate change: A catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Sánchez, M.A.; Nandini, S.; Castellanos-Páez, M.E.; Sarma, S.S.S. Effect of temperature, food quality and quantity on the feeding behavior of Simocephalus mixtus and Hyalella azteca: Implications for biomanipulation. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 27, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.S.; Pascoe, D. Growth, development and reproduction of Hyalella azteca (Saussure, 1858) in laboratory culture. Crustaceana 2001, 74, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, L.L.; Borrely, S.I. Hyalella azteca used for the evaluation of cyanotoxins before and after irradiation with electron beam: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the INAC 2019: International Nuclear Atlantic Conference. Nuclear New Horizons: Fueling Our Future, Santos, Brazil, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 667–671. [Google Scholar]
- Poynton, H.C.; Hasenbein, S.; Benoit, J.B.; Sepulveda, M.S.; Poelchau, M.F.; Hughes, D.S.T.; Murali, S.C.; Chen, S.; Glastad, K.M.; Goodisman, M.A.; et al. The toxicogenome of Hyalella azteca: A model for sediment ecotoxicology and evolutionary toxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6009–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, K.; Ahtiainen, J.; Rapala, J.; Sivonen, K.; Niemelä, S.I. Assessment of rapid bioassays for detecting cyanobacterial toxicity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1995, 21, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasino, L.; Salmaso, N. Diversity and distribution of cyanobacterial toxins in the Italian subalpine lacustrine district. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2012, 41, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, K. Freshwater Algae Control Program: Report to the Washington State Legislature (2008–2009); Water Quality Program, Washington State Department of Ecology: Olympia, WA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.A.; Rasmussen, J.P.; Holland, P.T.; Campbell, R.; Crowe, A.L. First Report of the Cyanotoxin Anatoxin-A From Aphanizomenon issatschenkoi (Cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, N.A.; Tiunov, A.V.; Tsurikov, S.M.; Kurbatova, S.A.; Korneva, L.G.; Makarova, O.S.; Bykova, S.N. Cyanobacteria as a food source for invertebrates: Results of a model experiment. Russ. J. Ecol. 2021, 52, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivosheina, M.G. On insect feeding on cyanobacteria. Paleontol. J. 2008, 42, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briland, R.D.; Stone, J.P.; Manubolu, M.; Lee, J.; Ludsin, S.A. Cyanobacterial blooms modify food web structure and interactions in western Lake Erie. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboal, M.; Belando, M.D.; Ubero, N.; González-Silvera, D.; López-Jiménez, J.A. Photoautotrophs and macroinvertebrate trophic relations in calcareous semiarid streams: The role of Cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Adamovsky, O.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A.; Mijovic, B.; Shi, T.; Tuo, X.; Li, S.-C.; et al. Challenges of using blooms of Microcystis spp. in animal feeds: A comprehensive review of nutritional, toxicological and microbial health evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, J.; Carvalho, A.P.; Guimarães, L.; Guilhermino, L. Toxic effects of pure anatoxin-a on biomarkers of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Toxicon 2013, 70, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.N.; Bartlett, A.J.; Kudla, Y.M.; Prosser, R.S. Optimizing sex ratios of Hyalella azteca to reduce variability in reproduction and improve reproductive toxicity test methods. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 43, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, D.D.S.; Bond-Buckup, G. Reproductive strategies of two sympatric species of Hyalella Smith, 1874 (Amphipoda, Dogielinotidae) in laboratory conditions. J. Nat. Hist. 2007, 41, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyne, R.V. Review of the reproductive biology of amphipods and their endocrine regulation: Identification of mechanistic pathways for reproductive toxicants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.W.; Farrar, J.D. Effect of growth on reproduction in the freshwater amphipod, Hyalella azteca (Saussure). Hydrobiologia 1996, 328, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, I.; Geist, J.; Okihiro, M.; Rosenkranz, P.; Hinton, D.E. Effects of dietary exposure to the pyrethroid pesticide esfenvalerate on medaka (Oryzias latipes). Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 54, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporowska, M.; Pawlik-Skowronska, B.; Kalinowska, R. Accumulation and effects of cyanobacterial microcystins and anatoxin-a on benthic larvae of Chironomus spp.(Diptera: Chironomidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.D.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and effects on aquatic animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.; Kasianchuk, N.; Siemens, E.; Henao, E.; Rzymski, P. A review of common cyanotoxins and their effects on fish. Toxics 2023, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, J.; Rellán, S.; Carvalho, A.P.; Gago, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Acute effects of an anatoxin-a producing cyanobacterium on juvenile fish—Cyprinus carpio L. Toxicon 2007, 49, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, S.; Duval, C.; Marie, B. Toxicity, transfer and depuration of anatoxin-a (cyanobacterial neurotoxin) in medaka fish exposed by single-dose gavage. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 222, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippka, R. [1] Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1988, 167, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novak, L.; Taylor, L. Biological Test Method: Test for Survival, Growth and Reproduction in Sediment and Water Using the Freshwater Amphipod Hyalella azteca/Method Development and Applications Unit, Science and Technology Branch, Environment and Climate Change Canada; Environment and Climate Change Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2018; ISBN 978-0-660-09873-9. [Google Scholar]
- Van Handel, E. Rapid determination of glycogen and sugars in mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc 1985, 1, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Götz, A.; Imhof, H.K.; Geist, J.; Beggel, S. Moving toward standardized toxicity testing procedures with particulates by dietary exposure of gammarids. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Handel, E. Rapid determination of total lipids in mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1985, 1, 302–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.M. The Protein Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]

| 42d Dietary Exposure | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival [%] | Growth [mg ± SD] | Reproduction [Nn ± SD] | Storage Compound Concentration [mg/g ± SD] | ||||
| Glucose | Glycogen | Lipid | Protein | ||||
| Control 0 | 62 a | 0.06 ± 0.02 a | 0 a | 0.28 ± 0.04 a | 0.56 ± 0.11 a | 0.02 ± 0.002 a | 0 (n.d.) a,b |
| Control F | 100 a | 0.87 ± 0.15 a | 7.3 ± 1.7 a | 4.99 ± 3.04 a | 5.05 ± 1.31 a | 0.14 ± 0.04 a | 1.09 ± 0.27 a,b |
| Tm67 | 90 a | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 3.5 ± 1.8 | 2.03 ± 0.42 | 2.34 ± 0.32 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.34 ± 0.11 a |
| NC96/3 | 78 a | 0.43 ± 0.10 | 3.3 ± 2.5 | 1.76 ± 1.02 | 2.69 ± 0.80 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.11 b |
| Tested Toxin | Nominal Concentration [µg/L] | Volume of Test Solution [mL] | Number of Replicates | Number of Organisms Per Test Vessel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATX | 0–23.55 | 275 | 6 | 10 |
| ATX | 235.50 | 275 | 3 | 10 |
| ATX | 587.37 | 125 | 4 | 5 |
| dhATX | 0–235.50 | 275 | 4 | 10 |
| dhATX | 590.31 | 125 | 4 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yogeshwar, I.K.; Kalis, E.J.J.; Geist, J.; Beggel, S. Exposure Type and Duration Determine Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacteria Anatoxins on the Benthic Amphipod Hyalella azteca. Toxins 2025, 17, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110554
Yogeshwar IK, Kalis EJJ, Geist J, Beggel S. Exposure Type and Duration Determine Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacteria Anatoxins on the Benthic Amphipod Hyalella azteca. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110554
Chicago/Turabian StyleYogeshwar, Isabelle Kamalani, Erwin J. J. Kalis, Juergen Geist, and Sebastian Beggel. 2025. "Exposure Type and Duration Determine Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacteria Anatoxins on the Benthic Amphipod Hyalella azteca" Toxins 17, no. 11: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110554
APA StyleYogeshwar, I. K., Kalis, E. J. J., Geist, J., & Beggel, S. (2025). Exposure Type and Duration Determine Ecotoxicological Effects of Cyanobacteria Anatoxins on the Benthic Amphipod Hyalella azteca. Toxins, 17(11), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110554





