Optimisation of a One-Step Reusable Immuno-Affinity Purification Method for the Analysis and Detection of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
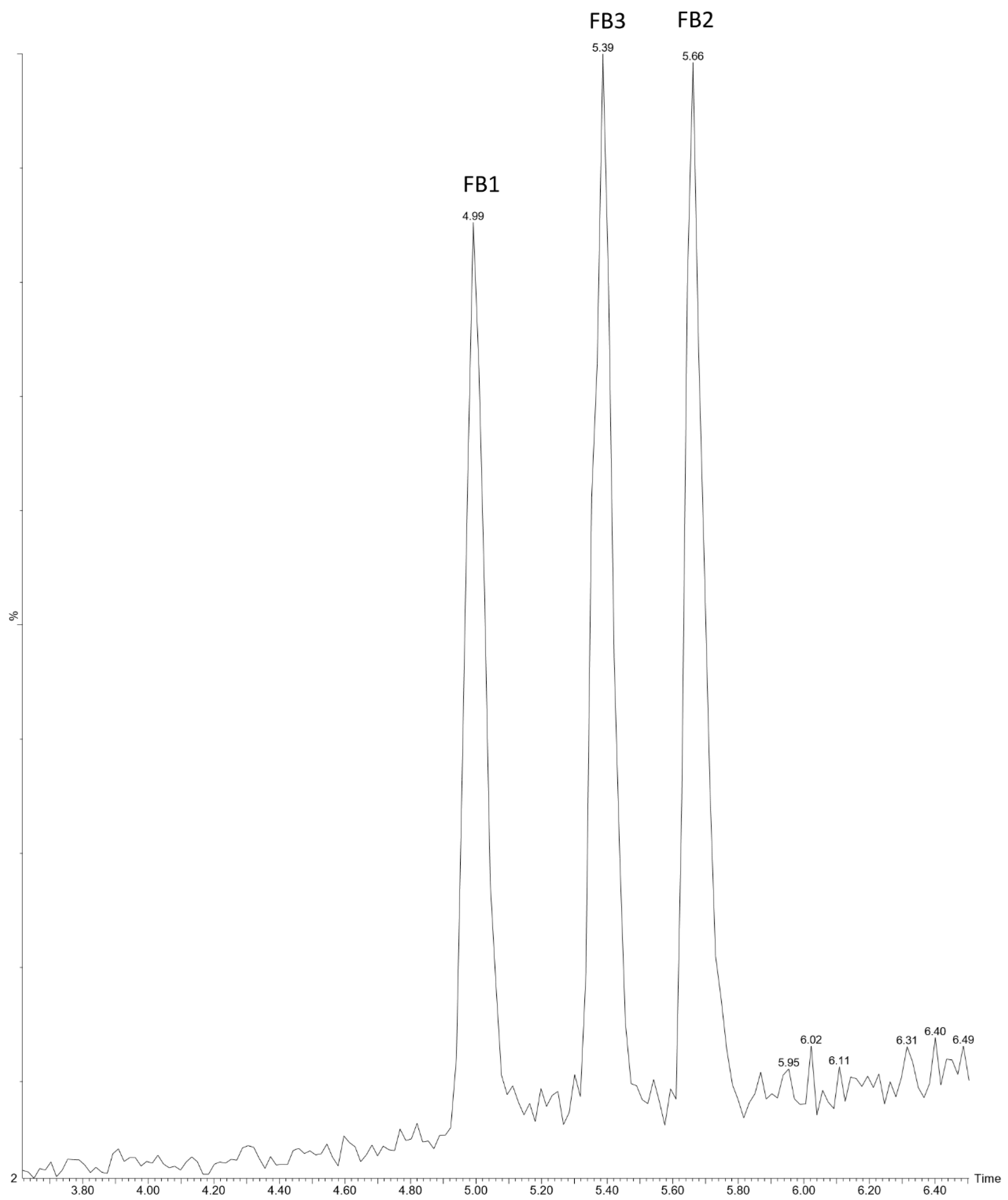
2.1. Extraction and Immuno-Affinity Clean-Up Optimisation
2.2. Performance Characteristics of Developed Method
2.3. Recovery, Repeatability and Inter-Day Reproducibility of Developed Method
2.4. Matrix Effect Studies
2.5. Performance of the Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assay
2.6. Comparing the Developed Immuno-Affinity Purification Method to Commercial Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assay
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Analytical Standards, Samples and Chemicals
4.2. UHPLC-MS/MS Parameters
4.3. Preparation of Immuno-Affinity Purification Column
4.4. Sample Extraction and Immuno-Affinity Clean-Up Procedures
4.5. Recovery and Matrix Effect Study
4.6. Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assay
4.7. Analysis for Masked and Hydrolysed Fumonisins
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elkenany, R.; Awad, A. Types of Mycotoxins and different approaches used for their detection in foodstuffs. Mansoura Vet. Med. J. 2021, 22, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmans, Y.; Schaarschmidt, S.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H. Factors during production of cereal-derived feed that influence mycotoxin contents. Toxins 2022, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anumudu, C.K.; Ekwueme, C.T.; Uhegwu, C.C.; Ejileugha, C.; Augustine, J.; Okolo, C.A.; Onyeaka, H. A review of the mycotoxin family of fumonisins, their biosynthesis, metabolism, methods of detection and effects on humans and animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC, International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. IARC Sci. Publ. 2012, 100, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Pedroso, I.R. Mycotoxins in cereal-based products and their impacts on the health of humans, livestock animals and pets. Toxins 2023, 15, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaković, J.; Šimunić, I.; Jagečić, D.; Hribljan, V.; Mitrečić, D. Overview of neural tube defects: Gene–environment interactions, preventative approaches and future perspectives. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONTAM, European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain; Knutsen, H.-K.; Alexander, J.; Barregard, L.; Bignami, M.; Bruschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; et al. Scientific opinion on the risks for animal health related to the presence of fumonisins, their modified forms and hidden forms in feed. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05242. [Google Scholar]
- Rafael, G.A.B.; Francisco Filho, d.C.C.; Juliana, d.A.C.; Amilton, P.R.C.; Maria, M.G.P.N.; Maria, C.S.M. Fusarium spp. and fumonisin in feed for equine and its importance for occurrence of leukoencephalomalacia. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyprianou, M. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1126/2007 of 28 September 2007—Amending regulation (EC) no 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards Fusarium toxins in maize and maize products. J. Eur. Union 2007, 255, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cheli, F.; Battaglia, D.; Gallo, R.; Dell’Orto, V. EU legislation on cereal safety: An update with a focus on mycotoxins. Food Control 2014, 37, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union, Commission Regulation. COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2023/915 of 25 April 2023 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Guo, X. Advances in biosensors, chemosensors and assays for the determination of fusarium mycotoxins. Toxins 2016, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.A.V.; Borsatto, J.V.B.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Lancas, F.M. Current role of modern chromatography and mass spectrometry in the analysis of mycotoxins in food. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.S.; Wink, M. Exposure, occurrence, and chemistry of fumonisins and their cryptic derivatives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 769–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouakhssase, A.; Ait Addi, E. Mycotoxins in food: A review on liquid chromatographic methods coupled to mass spectrometry and their experimental designs. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2606–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khazrajy, O.S.; Boxall, A.B. Determination of pharmaceuticals in freshwater sediments using ultrasonic-assisted extraction with SPE clean-up and HPLC-DAD or LC-ESI-MS/MS detection. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4190–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariasova, M.; Lacina, O.; Malachova, A.; Kostelanska, M.; Poustka, J.; Godula, M.; Hajslova, J. Novel approaches in analysis of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals employing ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barp, L.; Višnjevec, A.M.; Moret, S. Pressurized liquid extraction: A powerful tool to implement extraction and purification of food contaminants. Foods 2023, 12, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.; Egli, S.; Beattie, M.; Page, F.; Hamoutene, D. Chemical Extraction Techniques for the Determination of Drugs, Pesticides and Antibiotics Used by the Aquaculture Industry; Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat, Secrétariat Canadien de Consultation: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2021.
- Casado, N.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Application of the QuEChERS strategy as a useful sample preparation tool for the multiresidue determination of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in food and feed samples: A critical overview. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ražić, S.; Arsenijević, J.; Mračević, S.Đ.; Mušović, J.; Trtić-Petrović, T. Greener chemistry in analytical sciences: From green solvents to applications in complex matrices. Current challenges and future perspectives: A critical review. Analyst 2023, 148, 3130–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklós, G.; Angeli, C.; Ambrus, Á.; Nagy, A.; Kardos, V.; Zentai, A.; Kerekes, K.; Farkas, Z.; Jóźwiak, Á.; Bartók, T. Detection of aflatoxins in different matrices and food-chain positions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaunay, N.; Combès, A.; Pichon, V. Immunoaffinity extraction and alternative approaches for the analysis of toxins in environmental, food or biological matrices. Toxins 2020, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abi-Ghanem, D.A.; Berghman Luc, R. Immunoaffinity chromatography: A review. Affin. Chromatogr. 2012, 2, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Peltomaa, R.; Barderas, R.; Benito-Peña, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Recombinant antibodies and their use for food immunoanalysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, A.C.; Hage, D.S. Immunoaffinity chromatography: An introduction to applications and recent developments. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 769–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.A.; Sukor, R.; Ismail, M.N.; Selamat, J. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) and LC-MS/MS analysis for multi-mycotoxin in rice bran: Method development, optimization and validation. Toxins 2021, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacina, O.; Zachariasova, M.; Urbanova, J.; Vaclavikova, M.; Cajka, T.; Hajslova, J. Critical assessment of extraction methods for the simultaneous determination of pesticide residues and mycotoxins in fruits, cereals, spices and oil seeds employing ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulyok, M.; Stadler, D.; Steiner, D.; Krska, R. Validation of an LC-MS/MS-based dilute-and-shoot approach for the quantification of >500 mycotoxins and other secondary metabolites in food crops: Challenges and solutions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2607–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Mateus, A.R.; Barros, S.; Pena, A.; Sanches Silva, A. Mycotoxins in pistachios (Pistacia vera L.): Methods for determination, occurrence, decontamination. Toxins 2021, 13, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Takino, M.; Sugita--Konishi, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Leeman, D.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Determination of Fusarium mycotoxins by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry coupled with immunoaffinity extraction. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, V.M.T.; Solfrizzo, M.; Powers, S.; Visconti, A. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins, ochratoxin A and Fusarium toxins in maize by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry after multitoxin immunoaffinity cleanup. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthiller, F.; Cramer, B.; Iha, M.; Krska, R.; Lattanzio, V.; MacDonald, S.; Malone, R.; Maragos, C.; Solfrizzo, M.; Stranska-Zachariasova, M. Developments in mycotoxin analysis: An update for 2016–2017. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 11, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M. Development of a multiple immunoaffinity column for simultaneous determination of multiple mycotoxins in feeds using UPLC–MS/MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6027–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Peng, T.; He, J.-L.; Shao, Y.; Fan, C.-L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.-X.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Pei, X.-Y. Preparation and characterization of an immunoaffinity column for the selective extraction of aflatoxin B1 in 13 kinds of foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 998, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmeen, S.; Suh, K.; Kyei, I.; Jones, J.; Olupathage, H.; Campbell, A.; Hage, D.S. Immunoaffinity chromatography for protein purification and analysis. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Jia, B.; Sun, C.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Reuse of regenerated immunoaffinity column for excellent clean-up and low-cost detection of trace aflatoxins in malt. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M. Chromatographic techniques for estimation of aflatoxins in food commodities. In Aflatoxins-Occurrence, Detoxification, Determination and Health Risks; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marschik, S.; Hepperle, J.; Lauber, U.; Schnaufer, R.; Maier, S.; Kühn, C.; Schwab-Bohnert, G. Extracting fumonisins from maize: Efficiency of different extraction solvents in multi-mycotoxin analytics. Mycotoxin Res. 2013, 29, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocampo-Acuna, Y.D.; Salazar-Rios, E.; Ramírez-Cisneros, M.Á.; Rios, M.Y. Comprehensive review of liquid chromatography methods for fumonisin determination, a 2006–2022 update. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masquelier, J.; Tangni, E.K.; Becker, P.; Sanders, J.; Laporte, J.; Mertens, B. Validation of an LC-MS Method for Quantification of Mycotoxins and Characterization of Fungal Strains Occurring in Food and Feed. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.; Krska, R.; Malachová, A.; Taschl, I.; Sulyok, M. Evaluation of matrix effects and extraction efficiencies of LC–MS/MS methods as the essential part for proper validation of multiclass contaminants in complex feed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3868–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.-H. A quantitative tandem mass spectrometry and scaled-down QuEChERS approach for simultaneous analysis of pesticide multiresidues in human urine. Molecules 2019, 24, 1330. [Google Scholar]
- Maragos, C.M.; Barnett, K.; Morgan, L.; Vaughan, M.M.; Sieve, K.K. Measurement of fumonisins in maize using a portable mass spectrometer. Toxins 2022, 14, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Feng, Y.; Suo, D.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Fan, X. Simultaneous Determination of 11 Mycotoxins in maize via multiple-impurity adsorption combined with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Foods 2022, 11, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiani, T.; Righetti, L.; Suman, M.; Galaverna, G.; Dall’Asta, C. Analytical issue related to fumonisins: A matter of sample comminution? Food Control 2019, 95, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) 2023/2782 of 14 December 2023 Laying Down the Methods of Sampling and Analysis for the Control of the Levels of Mycotoxins in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 401/2006; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, M.; Freitas, A.; Barbosa, J.; Ramos, F. Comprehensive assessment of different extraction methodologies for optimization and validation of an analytical multi-method for determination of emerging and regulated mycotoxins in maize by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandreka, M.K.; Yamini, M.; Abhishek, G.; Gope, E.R.; Raghava, D. Advances in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC). J. Pharma Insights Res. 2024, 2, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Rausch, A.-K.; Brockmeyer, R.; Schwerdtle, T. Development and validation of a QuEChERS-based liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry multi-method for the determination of 38 native and modified mycotoxins in cereals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4657–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, A.A.; Ali, H.; Abd El-Hakim, A.; Gomaa, A.M. Swift and Enhanced-Sensitive Analytical Method for Determination of Fumonisins FB1 And FB2 in Egyptian Oilseeds Using LC-MS/MS. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat-Cabello, N.; Zomer, P.; Sancho, J.V.; Roig-Navarro, A.F.; Mol, H. Comparison of approaches to deal with matrix effects in LC-MS/MS based determinations of mycotoxins in food and feed. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, P.D.; Dantas, R.R.; de Moura, T.L.d.S.; Caldas, E.D. Determination of multi-mycotoxins in cereals and of total fumonisins in maize products using isotope labeled internal standard and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry with positive ionization. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1490, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryła, M.; Roszko, M.; Szymczyk, K.; Jędrzejczak, R.; Obiedziński, M.W. Fumonisins and their masked forms in maize products. Food Control 2016, 59, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Ke, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Wen, K. Development of a new broad-specific monoclonal antibody with uniform affinity for aflatoxins and magnetic beads-based enzymatic immunoassay. Food Control 2017, 79, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, S.; Yu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, A. LC-MS/MS analysis of fumonisin B1, B2, B3, and their hydrolyzed metabolites in broiler chicken feed and excreta. Toxins 2022, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Asta, C.; Falavigna, C.; Galaverna, G.; Dossena, A.; Marchelli, R. In vitro digestion assay for determination of hidden fumonisins in maize. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12042–12047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Generotti, S.; Cirlini, M.; Dall’Asta, C.; Suman, M. Influence of the industrial process from caryopsis to cornmeal semolina on levels of fumonisins and their masked forms. Food Control 2015, 48, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köppen, R.; Koch, M.; Siegel, D.; Merkel, S.; Maul, R.; Nehls, I. Determination of mycotoxins in foods: Current state of analytical methods and limitations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1595–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asam, S.; Rychlik, M. Recent developments in stable isotope dilution assays in mycotoxin analysis with special regard to Alternaria toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7563–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.-D.; Davids, I.; Rheeder, J.; Burger, H.-M.; Shephard, G.; Gelderblom, W. Detoxification of the fumonisin mycotoxins in maize: An enzymatic approach. Toxins 2019, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, G.; Yuan, X.; Gan, J.; Peterson, J.E.; Shen, J.X. Strategy for the quantitation of a protein conjugate via hybrid immunocapture-liquid chromatography with sequential HRMS and SRM-based LC-MS/MS analyses. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5144–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenuwara, G.; Akhtar, P.; Javed, B.; Singh, B.; Byrne, H.J.; Tian, F. Recent Advancements in Lateral Flow Assays for Food Mycotoxin Detection: A Review of Nanoparticle-Based Methods and Innovations. Toxins 2025, 17, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Mehta, A. Rapid and sensitive detection of mycotoxins by advanced and emerging analytical methods: A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2183–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshra, M.H.; El-Housseiny, G.S.; Farag, M.M.; Aboshanab, K.M. Evaluation of ELISA and immunoaffinity fluorometric analytical tools of four mycotoxins in various food categories. AMB Express 2023, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltzov, E.; Guttel, S.; Low Yuen Kei, A.; Sinawang, P.D.; Ionescu, R.E.; Marks, R.S. Lateral flow immunoassays–from paper strip to smartphone technology. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, L.; Calderara, M.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Arletti, E.; Giraudi, G. Development and application of a quantitative lateral flow immunoassay for fumonisins in maize. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 682, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Moon, J.-Y.; An, J.-A.; Kim, Y.-W.; Chung, S.-H.; Lee, C. Distribution analysis of twelve mycotoxins in corn and corn-derived products by LC-MS/MS to evaluate the carry-over ratio during wet-milling. Toxins 2018, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, E.; Mittendorf, K.; Stroka, J.; Senyuva, H. Determination of Fusarium mycotoxins in wheat, maize and animal feed using on-line clean-up with high resolution mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinelli, A.; Grossalber, K.; Krska, R. A rapid lateral flow test for the determination of total type B fumonisins in maize. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Do, B.N.; Nguyen, T.P.T.; Tran, T.T.; Tran, S.C.; Van Nguyen, B.; Van Nguyen, C.; Le, H.Q. Development of an IgY-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of fumonisin B in maize. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.K.; Iftesum, M.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. New technologies and reagents in lateral flow assay (LFA) designs for enhancing accuracy and sensitivity. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 4351–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nji, Q.N.; Babalola, O.O.; Nleya, N.; Mwanza, M. Underreported human exposure to mycotoxins: The case of South Africa. Foods 2022, 11, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.A.; Bae, Y.; Kler, J.S.; Iyer, R.; Zhang, R.; Montgomery, N.D.; Nunes, D.; Pleil, J.D.; Funk, W.E. Advancing global health surveillance of mycotoxin exposures using minimally invasive sampling techniques: A state-of-the-science review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3580–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotayo, O.P.; Omotayo, A.O.; Mwanza, M.; Babalola, O.O. Prevalence of mycotoxins and their consequences on human health. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wu, L.; Zhou, S.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Development of a sensitive and reliable UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of multiple urinary biomarkers of mycotoxin exposure. Toxins 2020, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, F.; Li, P. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins, fumonisin B1, T-2 and cyclopiazonic acid in agri-products by immunomagnetic solid-phase extraction coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.F.; Ngemela, A.F.; Jensen, L.B.; De Medeiros, L.S.; Rasmussen, P.H. UHPLC-MS/MS determination of ochratoxin A and fumonisins in coffee using QuEChERS extraction combined with mixed-mode SPE purification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzo, M.; Gambacorta, L.; Bibi, R.; Ciriaci, M.; Paoloni, A.; Pecorelli, I. Multimycotoxin analysis by LC-MS/MS in cereal food and feed: Comparison of different approaches for extraction, purification, and calibration. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, D.; Allan, A.B.; Cameron, H.; Donelly, C.; Tramaseur, A.; Stratton, J.; MacDonald, S.J. Validation of the 11+ Myco MS-PREP® Method for Determination of Aflatoxins, Fumonisins, Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, Zearalenone, HT-2, and T-2 Toxins in Cereals, Baby Food, Spices, and Animal Feed by Immunoaffinity Column with LC–MS/MS: AOAC Performance Tested Method SM 112401. J. AOAC Int. 2025, 108, 207–252. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lun, L.; Xu, N. Quantifications of saxitoxin concentrations in bivalves by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with the purification of immunoaffinity column. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1147, 122133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, M.; Zhou, J.; Gong, L.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, L. Development and optimization of a multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for the simultaneous determination of three mycotoxins in corn, rice and peanut. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Fotina, H.; Wang, Z. A novel lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for rapid and simultaneous detection of aflatoxin b1 and zearalenone in food and feed samples based on highly sensitive and specific monoclonal antibodies. Toxins 2022, 14, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matos, N.A.V.; de Moraes, M.H.P.; Sartori, A.V.; do Couto Jacob, S. Optimization and validation of an analytical method for the determination of free and hidden fumonisins in corn and corn products by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Elution Solvent | Expected Toxin Concentration | FB1 Recovery ng/g (%) | FB2 Recovery ng/g (%) | FB3 Recovery ng/g (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% MeOH | 50 ng/g | 61.2 (122.4%) | 74.2 (148.4%) | 78.2 (156.4%) |
| 80 ng/g | 79.0 (98.8%) | 103.7 (129.6%) | 107.7 (134.6%) | |
| 0.1M Glycine | 50 ng/g | 7.7 (15.4%) | 4.0 (8%) | 6.5 (13%) |
| 80 ng/g | 6.3 (7.9%) | 4.7 (5.9%) | 5.1 (6.4%) | |
| 50% MeOH | 50 ng/g | 32.0 (64%) | 29.4 (58.8%) | 35.2 (70.4%) |
| 80 ng/g | 43.0 (53.8%) | 51.5 (64.4%) | 52.5 (65.6%) |
| Toxin Source | Spiked Concentration (ng/g) | Recovery (% ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | FB2 | FB3 | ||
| Spiked corn matrix | 50 | 33.8 ± 9% | 36.3 ± 7% | 35.4 ± 7.2% |
| 80 | 27.6 ± 1.8% | 31.3 ± 2.3% | 30.4 ± 1.7% | |
| 150 | 28.4 ± 4.8% | 31 ± 4% | 30.9 ± 3.4% | |
| MEAN | 29.9% | 32.9% | 32.2% | |
| Spiked toxins in PBS | 50 | 61.6 ± 0.4% | 66.3 ± 3.8% | 69.1 ± 4.1% |
| 80 | 65.1 ± 8.15% | 73.1 ± 6.4% | 72.3 ± 6.1% | |
| 150 | 60.2 ± 2.1% | 65.9 ± 2.4% | 63.5 ± 2.8% | |
| MEAN | 62.3% | 68.4% | 68.3% | |
| Toxin Source | Spiked Concentration (ng/g) | Recovery (% ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | FB2 | FB3 | ||
| Spiked corn matrix | 50 | 34.4 ± 1.1% | 36.2 ± 0.3% | 36.7 ± 2.6% |
| 80 | 28.6 ± 1.9% | 31.4 ± 0.1% | 31.6 ± 2.3% | |
| 150 | 29 ± 1.1% | 31.5 ± 1% | 31.5 ± 1.2% | |
| MEAN | 30.7% | 33% | 33.3% | |
| Spiked toxins in PBS | 50 | 64 ± 4.7% | 69.7 ± 9.7% | 70.3 ± 2.4% |
| 80 | 67.3 ± 4.4% | 74.7 ± 3.2% | 74.6 ± 4.5% | |
| 150 | 62.3 ± 4.2% | 66.7 ± 1.6% | 66.4 ± 5.7% | |
| MEAN | 64.5% | 70.4% | 70.4% | |
| Toxin Source | Spiked Concentration (ng/g) | Total Fumonisins (ng/g) | % Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spiked corn matrix | 400 | <300 | |
| 500 | 338 | 67.6% | |
| 750 | 516 | 68.8% | |
| MEAN | 68.2% | ||
| Spiked toxins in PBS | 400 | 317 | 79.3% |
| 500 | 392 | 78.4% | |
| 750 | 578 | 77.1% | |
| MEAN | 78.3% | ||
| Parameter | Developed IAC–UHPLC–MS/MS Method | Typical LC–MS/MS Methods (Literature) |
|---|---|---|
| LOD | 2.5 ng/g | ≤2.4 ng/g [68] |
| LOQ | 5 ng/g | ≤8.2 ng/g [68] |
| Recovery (Maize matrix) | 30–33% | 70–120% [69] |
| Repeatability (RSD, %) | ≤13% (PBS) | ≤13% [69] |
| Analysis Time | <6 min per run | 10–18 min per run [69] |
| Strengths | High sensitivity; reusable IAC column; short run time | Widely validated; good matrix robustness |
| Limitations | Severe matrix suppression; low recovery in maize | Expensive equipment; longer prep time |
| Reference Sample (corn) | Expected Certified Conc. (Total Fumonisin) (ng/g) | Lateral Flow Device | Immuno-Affinity Purification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. (ng/g) | % Recovery | Conc. (ng/g) | % Recovery | ||
| A | 0 | <300 | 189 | 189% | |
| B | 700 | 479 | 68.4% | 403 | 57.6% |
| C | 1000 | 638 | 63.8% | 463 | 46.3% |
| D | 1500 | 997 | 66.5% | 548 | 36.5% |
| E | 2200 | 1433 | 65.1% | 201 | 9.1% |
| F | 2400 | 1831 | 76.3% | 632 | 26.3% |
| G | 3200 | 1891 | 59% | 556 | 17.4% |
| H | 3600 | 2311 | 64.2% | 684 | 19% |
| I | 4000 | 2162 | 54.1% | 590 | 14.8% |
| J | 4700 | 2666 | 56.7% | 674 | 14.3% |
| Analyte | Parent Ion (m/z) | Cone Voltage (V) | Daughter Ions (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Dwell (S) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | 722.25 | 50 | 334.45 | 40 | 0.125 |
| 352.45 | 35 | 0.125 | |||
| FB2 | 706.30 | 55 | 318.45 | 40 | 0.125 |
| 336.50 | 35 | 0.125 | |||
| FB3 | 706.35 | 55 | 336.50 | 35 | 0.125 |
| 354.50 | 30 | 0.125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anumudu, C.K. Optimisation of a One-Step Reusable Immuno-Affinity Purification Method for the Analysis and Detection of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds. Toxins 2025, 17, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110538
Anumudu CK. Optimisation of a One-Step Reusable Immuno-Affinity Purification Method for the Analysis and Detection of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110538
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnumudu, Christian Kosisochukwu. 2025. "Optimisation of a One-Step Reusable Immuno-Affinity Purification Method for the Analysis and Detection of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds" Toxins 17, no. 11: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110538
APA StyleAnumudu, C. K. (2025). Optimisation of a One-Step Reusable Immuno-Affinity Purification Method for the Analysis and Detection of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds. Toxins, 17(11), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110538





