Development of Lab-on-a-Chip LAMP and Real-Time PCR Assays to Detect Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in Hazelnuts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
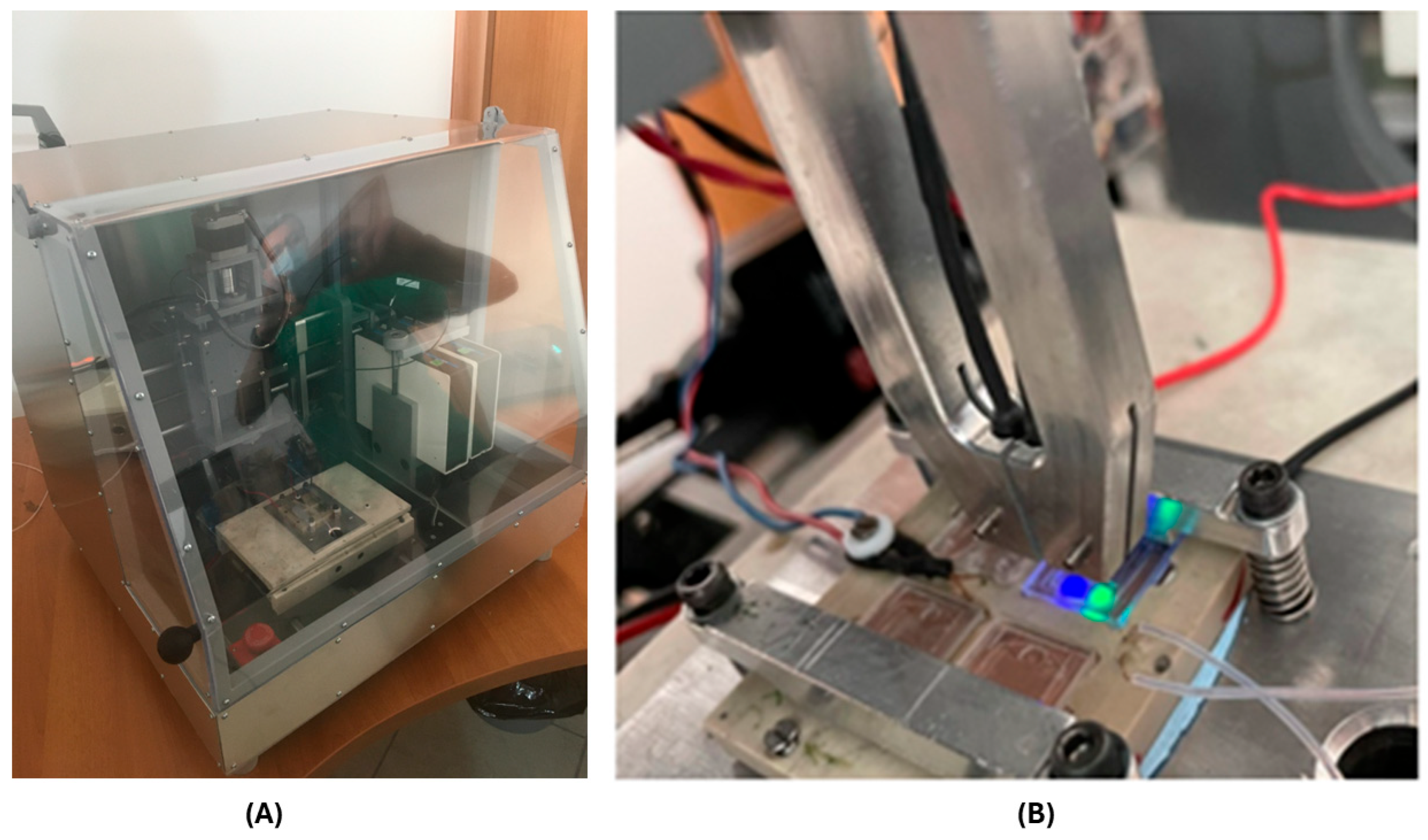
2.1. Development of a Lab-on-a-Chip (LoC) Procedure
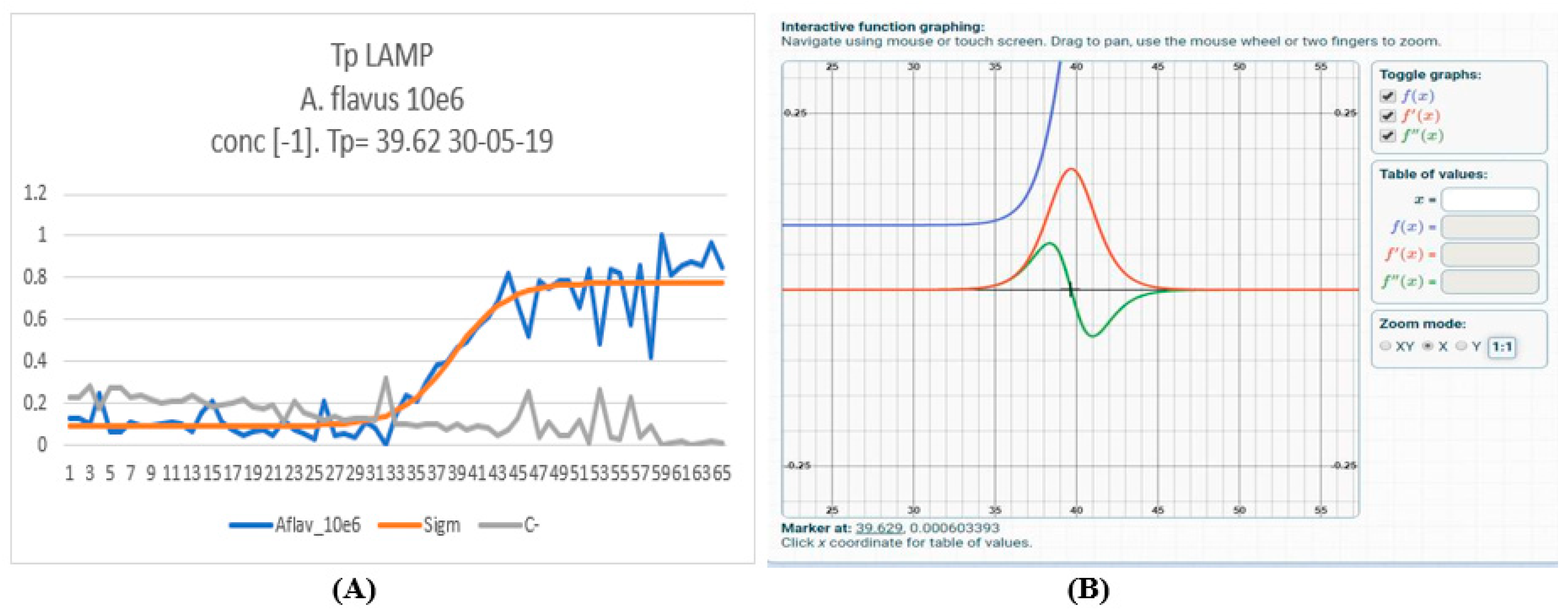
2.2. Development of a Lab-on-a-Chip (LoC)-LAMP and Loc-Real-Time PCR Assays
2.3. Specificity and Sensitivity of LoC-LAMP and LoC-Real-Time PCR
2.4. Repeatability of LoC-LAMP and LoC-Real-Time PCR
2.5. Stability of LoC-LAMP and LoC-Real-Time PCR
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Fungal Isolates
5.2. Inoculation of Hazelnuts
5.3. DNA Extraction
5.4. Real-Time PCR and LAMP
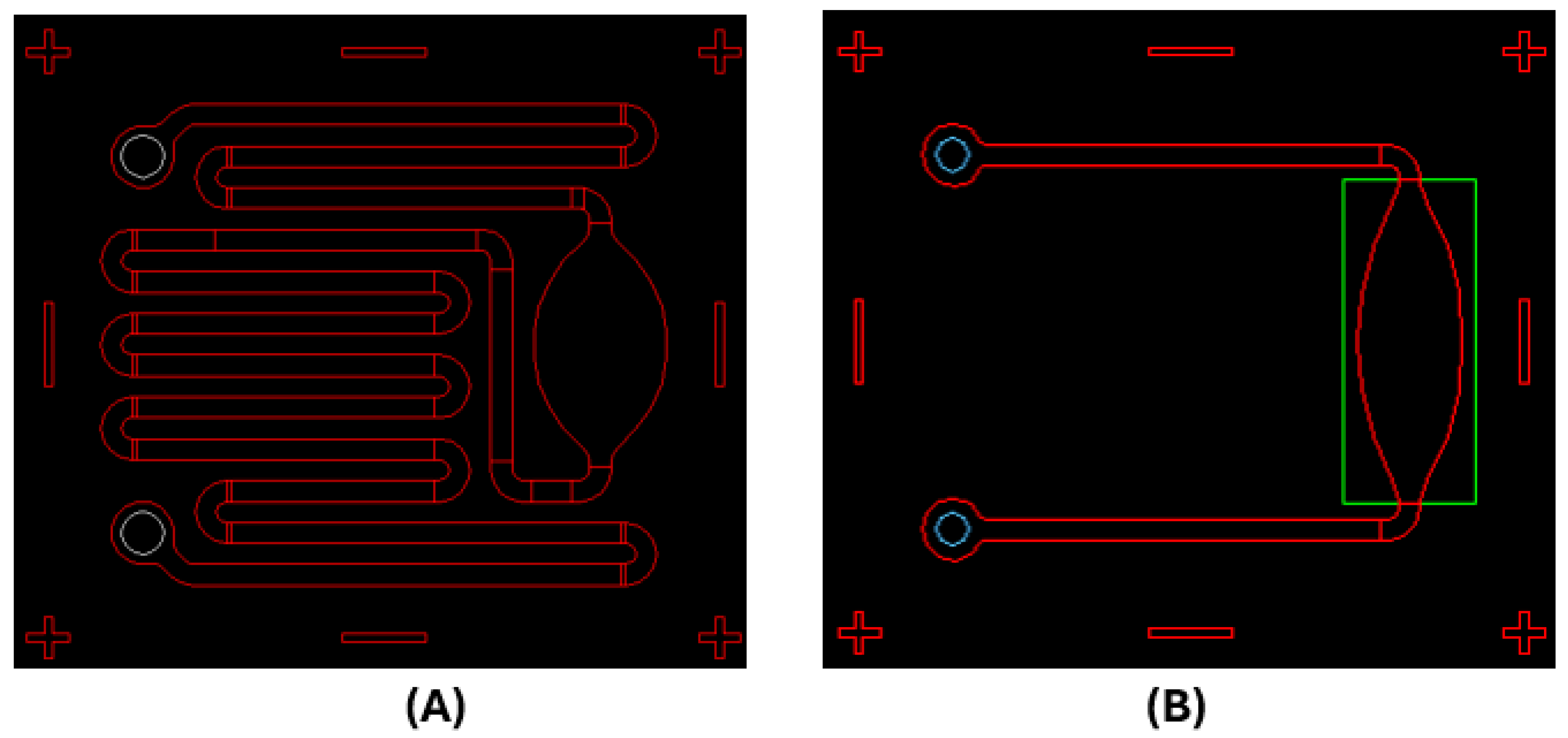
5.5. LoC Fabrication
5.6. LAMP LoC
5.7. Real-Time LoC
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- British Columbia Cook Articulation Committee. Food Safety, Sanitation, and Personal Hygiene; BCcampus: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2014; ISBN 978-1-7753524-6-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.; Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Franco, D. Main Groups of Microorganisms of Relevance for Food Safety and Stability: General Aspects and Overall Description. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation; Barba, F.J., de Souza Sant’Ana, A., Orlien, V., Koubaa, M., Eds.; Academic Press/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 53–107. ISBN 978-0-12-811031-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, S.N.; Jaiswal, P.; Grewal, M.K.; Gupta, M.; Bhardwaj, R. Detection of Adulterants and Contaminants in Liquid Foods—A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1662–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Long, N.N.; Dantigny, P. Fungal Contamination in Packaged Foods. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Barros-Velázquez, J., Ed.; Academic Press/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 45–63. ISBN 978-0-12-800723-5. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, R.R.M.; Lima, N. Filamentous Fungal Human Pathogens from Food Emphasising Aspergillus, Fusarium and Mucor. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannaa, M.; Kim, K.D. Influence of Temperature and Water Activity on Deleterious Fungi and Mycotoxin Production during Grain Storage. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniwaki, M.H.; Pitt, J.I.; Magan, N. Aspergillus Species and Mycotoxins: Occurrence and Importance in Major Food Commodities. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 23, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Hong, S.-B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.J.; Arzanlou, M.; Larsen, T.O.; Sklenář, F.; Mahakarnchanakul, W. Taxonomy of Aspergillus Section Flavi and Their Production of Aflatoxins, Ochratoxins and Other Mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrus, K.; Blank, G.; Abramson, D.; Clear, R.; Holley, R.A. Aflatoxin Production by Aspergillus flavus in Brazil Nuts. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2005, 41, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotty, P.J.; Jaime-Garcia, R. Influences of Climate on Aflatoxin Producing Fungi and Aflatoxin Contamination. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Irisawa, T.; Dicks, L.; Tanasupawat, S. FERMENTED FOODS|Fermentations of East and Southeast Asia. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 846–851. ISBN 978-0-12-384733-1. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia-Quintana, R.; Milić, M.; Jakšić, D.; Šegvić Klarić, M.; Tenorio-Arvide, M.G.; Pérez-Flores, G.A.; Bonassi, S.; Sánchez-Alarcón, J. Environment Changes, Aflatoxins, and Health Issues, a Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, A.; Camardo Leggieri, M.; Toscano, P.; Battilani, P. Changing Climate, Shifting Mycotoxins: A Comprehensive Review of Climate Change Impact on Mycotoxin Contamination. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, T.; Engelsen, S.B. Chemometrics, Mass Spectrometry, and Foodomics. In Foodomics; Cifuentes, A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Luque, M.I.; Martín, A.; Córdoba, J.J. Real-Time PCR Assays for Detection and Quantification of Aflatoxin-Producing Molds in Foods. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, L.; Bechtner, J.; Fodil, S.; Taniwaki, M.H.; Vogel, R.F. LAMP-Based Group Specific Detection of Aflatoxin Producers within Aspergillus Section Flavi in Food Raw Materials, Spices, and Dried Fruit Using Neutral Red for Visible-Light Signal Detection. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, S.F.; Siciliano, I.; Prencipe, S.; Gullino, M.L.; Spadaro, D. Development of PCR, LAMP and qPCR Assays for the Detection of Aflatoxigenic Strains of Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus in Hazelnut. Toxins 2020, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waliyar, F.; Reddy, S.V. Training Manual on “Aspergillus flavus Seed Infection and Aflatoxin Estimation by ELISA” and Aflatoxin Management Options in Groundnut; International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics: Patancheru, Andhra Pradesh, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Menegatti, E.; Berardi, D.; Messina, M.; Ferrante, I.; Giachino, O.; Spagnolo, B.; Restagno, G.; Cognolato, L.; Roccatello, D. Lab-on-a-Chip: Emerging Analytical Platforms for Immune-Mediated Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.M.; Sinton, D. Turning the Page: Advancing Paper-Based Microfluidics for Broad Diagnostic Application. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8447–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, L.; Yang, Y. Microfluidic Technology and Its Application in the Point-of-Care Testing Field. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 10, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ahmed, S.; Kakkar, V. Lab-on-Chip Technology: A Review on Design Trends and Future Scope in Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Bio. Sci. Bio. Technol. 2016, 8, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.Z.; Lu, X. Editorial: Lab-on-a-Chip for Agri-Food Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 149, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkel, J.C.; Van Den Berg, A. Young 4ever—The Use of Capillarity for Passive Flow Handling in Lab on Chip Devices. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Feng, J.; Fang, Z.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Application of Microfluidic “Lab-on-a-Chip” for the Detection of Mycotoxins in Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, Q. Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Based Microfluidic “Lab-on-a-Chip” for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Viruses in Agri-Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 148, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Sundaramurthy, A.; Vaishampayan, V.; Sridhar, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Ponnuchamy, M. Based Lab-on-a-Chip Devices for Detection of Agri-Food Contamination. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yi, W.; Sun, F.; Xu, M.; Zeng, Z.; Bi, X.; Dong, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, M. Application of Lab-on-Chip for Detection of Microbial Nucleic Acid in Food and Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 765375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrogiannopoulou, A.-M.; Tselepi, V.; Ellinas, K. Polymeric and Paper-Based Lab-on-a-Chip Devices in Food Safety: A Review. Micromachines 2023, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolti, O.; Suganthan, B.; Ramasamy, R.P. Lab-on-a-Chip Electrochemical Biosensors for Foodborne Pathogen Detection: A Review of Common Standards and Recent Progress. Biosensors 2023, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Jiang, F.; Xi, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Lab-on-Chip Separation and Biosensing of Pathogens in Agri-Food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 137, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.; Buttner, M.P. Development and Evaluation of a Real-Time Quantitative PCR Assay for Aspergillus flavus. Mycologia 2008, 100, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Soffe, R.; Tang, S.-Y.; Nahavandi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Khoshmanesh, K. Microfluidic Platforms for Biomarker Analysis. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1496–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, W.; Sher, M.; Khan, N.S.; Vyas, J.M.; Demirci, U. Microfluidic Chip for Detection of Fungal Infections. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7474–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Yin, J.; Lv, S.; Wang, B.; Mu, Y. Advanced “Lab-on-a-Chip” to Detect Viruses–Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumpluk, P.; Plubcharoensook, P.; Prasongsuk, S. Rapid Detection of Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus Sp. in Herbal Specimens by a Simple, Bendable, Paper-based Lab-on-a-chip. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.S.; Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Moser, N.; Moniri, A.; Malpartida-Cardenas, K.; Miscourides, N.; Sewell, T.; Kochina, T.; Brackin, A.; Rhodes, J.; et al. Rapid Detection of Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in Clinical and Environmental Isolates by Use of a Lab-on-a-Chip Diagnostic System. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00843-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Long, F. Rapid and Sensitive Point-of-Need Aflatoxin B1 Testing in Feedstuffs Using a Smartphone-Powered Mobile Microfluidic Lab-on-Fiber Device. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, Y.; Esen, E.; Kokturk, G.; Ozer, H.; Muhammad, T.; Olcer, Z.; Basegmez, H.I.O.; Simsek, S.; Barut, S.; Gok, M.Y. Lab-on-a-Chip Based Biosensor for the Real-Time Detection of Aflatoxin. Talanta 2016, 160, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Su, R.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, L.; Chen, J. Colorimetric Detection of Aflatoxin B1 by Using Smartphone-Assisted Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Food Control 2022, 132, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, S.; Matić, S.; Tiberini, A.; Caruso, A.G.; Bella, P.; Torta, L.; Stassi, R.; Davino, S. Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification: Principles and Applications in Plant Virology. Plants 2020, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Ding, T.; Feng, J. Advancing Point-of-Care Microbial Pathogens Detection by Material-Functionalized Microfluidic Systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julich, S.; Riedel, M.; Kielpinski, M.; Urban, M.; Kretschmer, R.; Wagner, S.; Fritzsche, W.; Henkel, T.; Möller, R.; Werres, S. Development of a Lab-on-a-Chip Device for Diagnosis of Plant Pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4070–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jeraldo, P.; Mendes-Soares, H.; Masters, T.; Asangba, A.E.; Nelson, H.; Patel, R.; Chia, N.; Walther-Antonio, M. Amplification of Femtograms of Bacterial DNA Within 3 h Using a Digital Microfluidics Platform for MinION Sequencing. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25642–25651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.M.M.; Dong, T. Microfluidic Biosensor Array with Integrated Poly (2, 7-Carbazole)/Fullerene-Based Photodiodes for Rapid Multiplexed Detection of Pathogens. Sensors 2013, 13, 15898–15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Dong, M.; Santos, S.; Rigatto, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F. Lab-on-a-Chip Platforms for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer Biomarkers. Sensors 2017, 17, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauk, M.; Song, J.; Bau, H.H.; Gross, R.; Bushman, F.D.; Collman, R.G.; Liu, C. Miniaturized Devices for Point of Care Molecular Detection of HIV. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.G.; Jung, D.; Kong, S.H. A Lab-on-a-Chip-Based Non-Invasive Optical Sensor for Measuring Glucose in Saliva. Sensors 2017, 17, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I.; Hocking, A.D. Fungi and Food Spoilage; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Rymaszewski, M. Alkaline Polyethylene Glycol-Based Method for Direct PCR from Bacteria, Eukaryotic Tissue Samples, and Whole Blood. BioTechniques 2006, 40, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. The Condensed Protocols. In Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-87969-772-5. [Google Scholar]

| Species | DNA Concentration | LoC-LAMP | LoC-Real-Time PCR | LAMP | Real-Time PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tp * (min:s) | Ct ** | Tp (min:s) | Ct | ||
| A. flavus AFSP4 | 1 ng | 19:02 | 28.41 ± 1.83 | 23:99 ± 0.04 | 6.92 ± 0.27 |
| A. flavus AFLX8 | 25:75 | 25.00 ± 1.75 | 20:66 ± 1.77 | 7.08 ± 0.23 | |
| A. flavus FS6 | nd *** | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. parasiticus AFLX6 | 25:10 | nd | 20:52 ± 0.62 | 7.04 ± 0.16 | |
| A. parasiticus FV4 | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. flavus AFSP4 | 10 pg | 39:62 | 34.15 ± 0.22 | 26:85 ± 0.01 | 10.68 ± 0.34 |
| A. flavus AFLX8 | 63:08 | 30.27 ± 0.17 | 26:97 ± 0.16 | 10.72 ± 0.50 | |
| A. flavus FS6 | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. parasiticus AFLX6 | nd | nd | 24:95 ± 1.25 | 10.64 ± 0.39 | |
| A. parasiticus FV4 | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. flavus AFSP4 | 10 fg | 106:6 | nd | 29:38 ± 0.00 | 14.74 ± 0.33 |
| A. flavus AFLX8 | nd | nd | 30:85 ± 0.31 | 15.58 ± 0.56 | |
| A. flavus FS6 | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. parasiticus AFLX6 | nd | nd | 31:31 ± 0.96 | 15.07 ± 0.15 | |
| A. parasiticus FV4 | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. flavus AFSP4 | 1 fg | nd | nd | 35:61 ± 0.31 | 26.46 ± 0.30 |
| A. flavus AFLX8 | nd | nd | 35:01 ± 0.29 | 27.63 ± 0.13 | |
| A. flavus FS6 | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| A. parasiticus AFLX6 | nd | nd | 36:94 ± 0.40 | 28.11 ± 0.52 | |
| A. parasiticus FV4 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Species | LoC-LAMP | LoC-Real-Time PCR | LoC-LAMP | LoC-Real-Time PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ng | 10 pg | |||
| A. flavus | 19.071 ± 0.88 | 28.88 ± 1.76 | 40.74 ± 1.07 | 34.20 ± 0.31 |
| A. parasiticus | 24.86 ± 0.56 | nd * | nd | nd |
| Species | LoC-LAMP | LoC-Real-Time PCR | LoC-LAMP | LoC-Real-Time PCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ng | 10 pg | |||||||
| 3 d * | 7 d | 3 d | 7 d | 3 d | 7 d | 3 d | 7 d | |
| A. flavus | 20.01 ± 0.43 | 22.25 ± 0.68 | 28.70 ± 1.12 | 30.39 ± 1.89 | 42.74 ± 1.51 | 44.14 ± 2.04 | 34.50 ± 0.78 | 35.37 ± 0.89 |
| A. parasiticus | 24.53 ± 0.77 | 24.90 ± 1.26 | nd ** | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matić, S.; Cognolato, L.; Sanna, M.; Mezzalama, M.; Laurenti, R.; Spadaro, D. Development of Lab-on-a-Chip LAMP and Real-Time PCR Assays to Detect Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in Hazelnuts. Toxins 2025, 17, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100510
Matić S, Cognolato L, Sanna M, Mezzalama M, Laurenti R, Spadaro D. Development of Lab-on-a-Chip LAMP and Real-Time PCR Assays to Detect Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in Hazelnuts. Toxins. 2025; 17(10):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100510
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatić, Slavica, Livio Cognolato, Martina Sanna, Monica Mezzalama, Riccardo Laurenti, and Davide Spadaro. 2025. "Development of Lab-on-a-Chip LAMP and Real-Time PCR Assays to Detect Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in Hazelnuts" Toxins 17, no. 10: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100510
APA StyleMatić, S., Cognolato, L., Sanna, M., Mezzalama, M., Laurenti, R., & Spadaro, D. (2025). Development of Lab-on-a-Chip LAMP and Real-Time PCR Assays to Detect Aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus in Hazelnuts. Toxins, 17(10), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17100510








