Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Plasma Levels in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
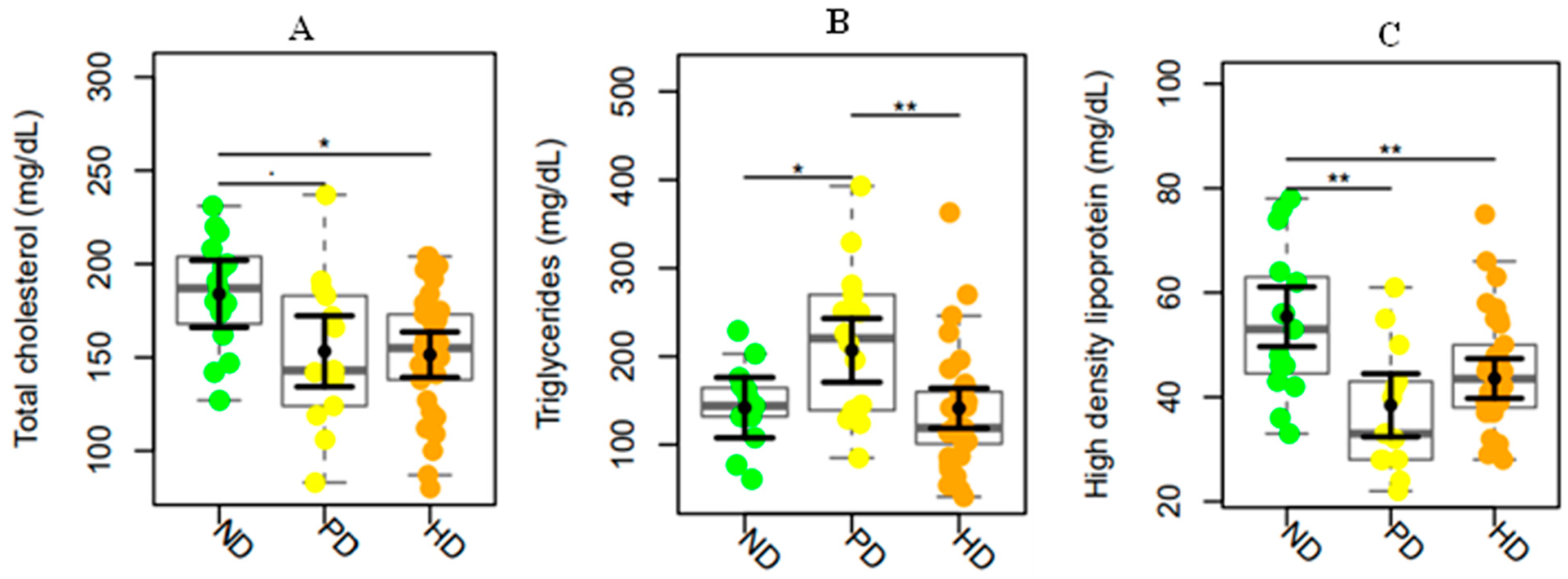
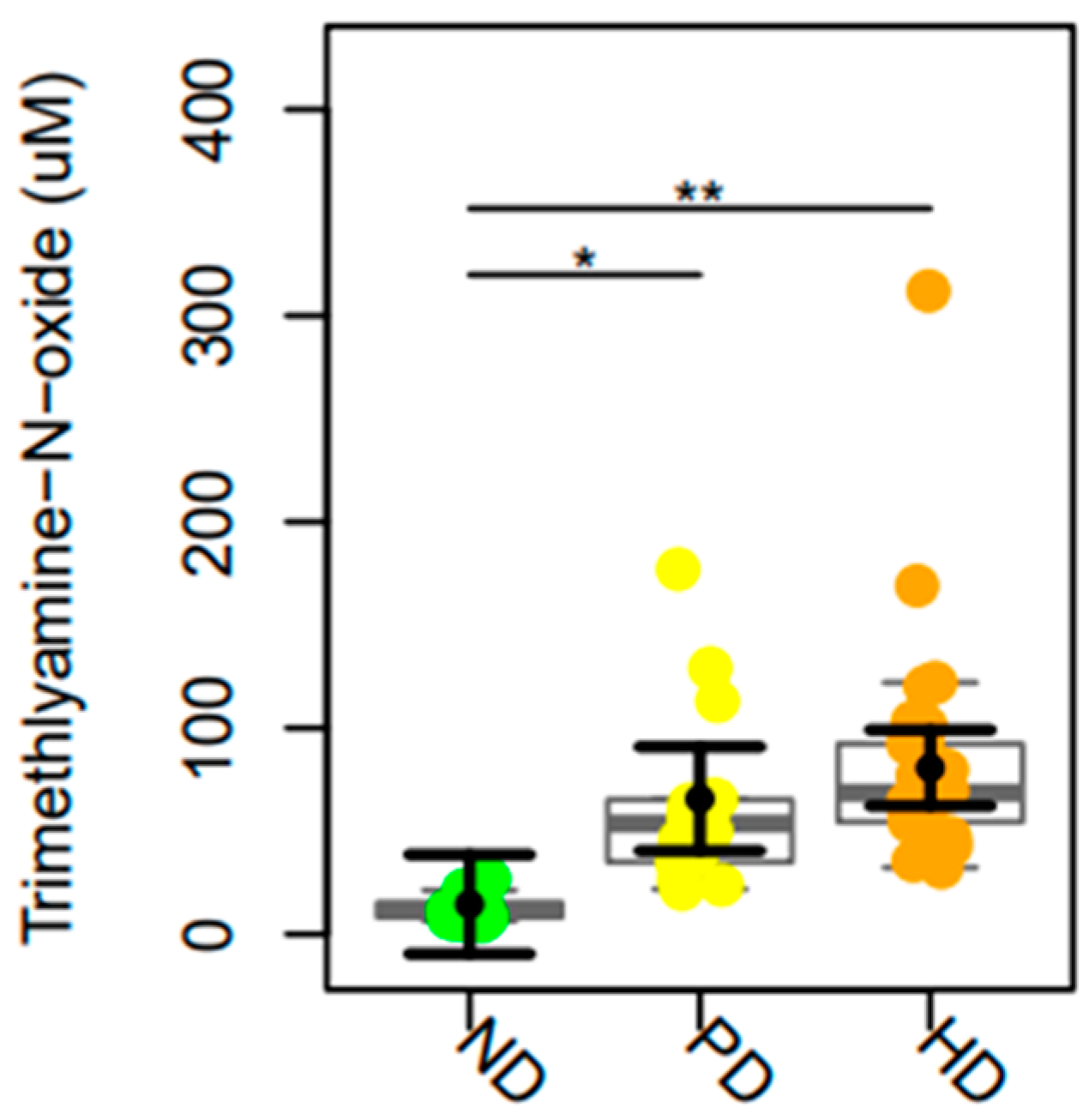
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design and Patients
5.2. Sample Analysis
5.3. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Analysis
5.4. Food Intake and BMI Analysis
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31573641/ (accessed on 31 August 2024).
- KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf. Available online: https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Meyer, T.W.; Hostetter, T.H. Uremia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Sidor, N.A.; Tonial, N.C.; Che, A.; Urquhart, B.L. Uremic Toxins in the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Toxins 2021, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranton, F.; Cohen, G.; De Smet, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Jankowski, J.; Vanholder, R.; Argiles, A.; European Uremic Toxin Work Group. Normal and pathologic concentrations of uremic toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1258–1270, Erratum in: J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 2127–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madero, M.; Cano, K.B.; Campos, I.; Tao, X.; Maheshwari, V.; Brown, J.; Cornejo, B.; Handelman, G.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins during Hemodialysis Using a Binding Competitor. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jameson, E.; Crosatti, M.; Schäfer, H.; Rajakumar, K.; Bugg, T.D.; Chen, Y. Carnitine metabolism to trimethylamine by an unusual Rieske-type oxygenase from human microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4268–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Kennedy, D.J.; Wu, Y.; Buffa, J.A.; Agatisa-Boyle, B.; Li, X.S.; Levison, B.S.; Hazen, S.L. Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Dai, L.; Avesani, C.M.; Kublickiene, K.; Stenvinkel, P. The dietary source of trimethylamine N-oxide and clinical outcomes: An unexpected liaison. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Sheehy, B.T.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schugar, R.C.; Shih, D.M.; Warrier, M.; Helsley, R.N.; Burrows, A.; Ferguson, D.; Brown, A.L.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Heine, M.; Chatterjee, A.; et al. The TMAO-Producing Enzyme Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase 3 Regulates Obesity and the Beiging of White Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2451–2461, Erratum in: Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boini, K.M.; Hussain, T.; Li, P.L.; Koka, S. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Instigates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Endothelial Dysfunction. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Hu, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, J. Trimethylamine N-oxide promove aterosclerose via via MAPK/JNK dependente de CD36. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; Buffa, J.A.; Gupta, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Mehrabian, M.; et al. O metabólito microbiano intestinal TMAO aumenta a hiper-reatividade plaquetária e o risco de trombose. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, A.; Shi, X.; Cheng, S.; Pan, B.; Zheng, L.; et al. Gut flora-dependent metabolite Trimethylamine-N-oxide accelerates endothelial cell senescence and vascular aging through oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 116, 88–100, Erratum in: Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 129, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seldin, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hazen, S.L.; Lusis, A.J.; Shih, D.M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Inflammation Through Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-κB. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; You, T.; Li, J.; Pan, T.; Xiang, L.; Han, Y.; Zhu, L. Circulating trimethylamine N-oxide and the risk of cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 prospective cohort studies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missailidis, C.; Hällqvist, J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Barany, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P.; Bergman, P. Trimetilamina-N-Óxido Sérico Está Fortemente Relacionado à Função Renal e Prediz o Resultado na Doença Renal Crônica. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0141738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.L.; Savoj, J.; Nakata, M.B.; Vaziri, N.D. Altered microbiome in chronic kidney disease: Systemic effects of gut-derived uremic toxins. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Yin, Z.; Liu, N.; Bian, X.; Yu, R.; Su, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y. Gut microbial metabolite TMAO contributes to renal dysfunction in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrikopoulos, P.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Chakaroun, R.; Myridakis, A.; Forslund, S.K.; Nielsen, T.; Adriouch, S.; Holmes, B.; Chilloux, J.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Evidence of a causal and modifiable relationship between kidney function and circulating trimethylamine N-oxide. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Guo, M.; Fang, X.; Teng, F.; Tan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y. Gut Microbiota-Derived Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Kidney Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1286–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.C.; Croyal, M.; Ene, L.; Aguesse, A.; Billon-Crossouard, S.; Krempf, M.; Lemoine, S.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Juillard, L.; Soulage, C.O. Elevation of Trimethylamine-N-Oxide in Chronic Kidney Disease: Contribution of Decreased Glomerular Filtration Rate. Toxins 2019, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaysen, G.A.; Johansen, K.L.; Chertow, G.M.; Dalrymple, L.S.; Kornak, J.; Grimes, B.; Dwyer, T.; Chassy, A.W.; Fiehn, O. Associações de N-óxido de trimetilamina com biomarcadores nutricionais e inflamatórios e resultados cardiovasculares em pacientes novos em diálise. J. Ren. Nutr. 2015, 25, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, J.R.; House, J.A.; Ocque, A.J.; Zhang, S.; Johnson, C.; Kimber, C.; Schmidt, K.; Gupta, A.; Wetmore, J.B.; Nolin, T.D.; et al. Trimetilamina-N-Óxido Sérico é Elevado na DRC e se Correlaciona com a Carga de Aterosclerose Coronária. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, X.; Landeras, V.; Dobre, M.A.; DeOreo, P.; Meyer, T.W.; Hostetter, T.H. Mechanism of prominent trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) accumulation in hemodialysis patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holle, J.; McParland, V.; Anandakumar, H.; Gerritzmann, F.; Behrens, F.; Schumacher, F.; Thumfart, J.; Eckardt, K.U.; Kleuser, B.; Bartolomaeus, H.; et al. Gut dysbiosis contributes to TMAO accumulation in CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 1923–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhong, X.; Gong, N.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tian, J.; et al. Gut microbial metabolite TMAO increases peritoneal inflammation and peritonitis risk in peritoneal dialysis patients. Transl. Res. 2022, 240, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluba, A.; Banach, M.; Hannam, S.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Sakowicz, A.; Rysz, J. The role of Toll-like receptors in renal diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanski, G.; Marin, V.; Montero-Julian, F.; Mantovani, A.; Farnarier, C. IL-6: A regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Shen, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Ye, H.; Huang, N.; Fan, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Elevated Serum Trimethylamine N-Oxide Levels Are Associated with Mortality in Male Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Blood Purif. 2021, 50, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Nie, J.; Dong, J. Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) and clinical outcomes in patients with end-stage kidney disease receiving peritoneal dialysis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2022, 42, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhou, J.; Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wei, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, B. The associations between TMAO-related metabolites and blood lipids and the potential impact of rosuvastatin therapy. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, R.; Awwad, H.M.; Rabagny, Y.; Graeber, S.; Herrmann, W.; Geisel, J. Plasma trimethylamine N-oxide concentration is associated with choline, phospholipids, and methyl metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzababaei, A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Keshtkar, A.; Ashraf, H.; Abaj, F.; Soveid, N.; Hajmir, M.M.; Radmehr, M.; Khalili, P.; Mirzaei, K. Serum levels of trimethylamine N-oxide and kynurenine novel biomarkers are associated with adult metabolic syndrome and its components: A case-control study from the TEC cohort. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1326782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fei’erdun, T.; Zhang, W.; Yilihamujiang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M. Correlation Between Plasma Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Lipid Levels in Hyperlipidemic Patients. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2023, 54, 1030–1034. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Transferrin Predicts Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Levels and Is a Potential Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35538408/ (accessed on 31 August 2024).
- Hsu, C.N.; Lu, P.C.; Lo, M.H.; Lin, I.C.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Trimethylamine N-Oxide Pathway Associated with Cardiovascular Risk in Children with Early-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.A.; Corbin, K.D.; da Costa, K.A.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Galanko, J.A.; Blevins, T.; Bennett, B.J.; O’Connor, A.; Zeisel, S.H. Effect of egg ingestion on trimethylamine-N-oxide production in humans: A randomized, controlled, dose-response study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H.; daCosta, K.A.; Youssef, M.; Hensey, S. Conversion of Dietary Choline to Trimethylamine and Dimethylamine in Rats: Dose-Response Relationship. J. Nutr. 1989, 119, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | ND (N = 15) | PD (N = 14) | HD (N = 34) | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (Male/Female) | 7/8 (46.7/53.3%) | 5/9 (35.7/64.3%) | 15/19 (44.1/55.9%) | 0.818 |
| Age (years) | 64 (12.5) | 57.5 (8.5) | 56 (16.2) | 0.210 |
| Time on dialysis (months) | - | 24.5 (44.7) | 43.5 (45.5) | 0.091 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.72 m2) | 44.0 (11.0) | - | - | - |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 25.2 (4.8) | 27.8 (8.3) | 24.4 (6.1) | 0.371 |
| Parameters | ND (N = 15) | PD (N = 14) | HD (N = 34) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 103.4 (70.0; 136.9) a.b | 128.5 (92.8; 164.1) c | 140.4 (114.2; 166.6) |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 60.6 (46.9; 74.3) a.b | 106.6 (92.1; 121.1) c | 139.9 (129.9; 149.8) |
| Parathormone (pg/mL) | - | 499 (153; 1153) | 825 (497; 1152) |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | - | 11.0 (10.0; 11.9) | 10.0 (10.3; 11.5) |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 10.1 (9.7; 10.4) a.b | 9.3 (8.9; 9.6) | 8.7 (8.5.8.9) |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 4.1 (3.5; 4.7) a.b | 5.4 (4.7; 6.0) | 4.9 (4.5; 5.3) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.6 (4.4; 4.8) a.b | 4.1 (3.9; 4.3) c | 3.8 (3.7; 3.9) |
| Potassium (mg/dL) | 4.7 (4.4; 5.0) b | 4.8 (4.5; 5.2) | 5.1 (4.9; 5.3) |
| hsCRP (mg/dL) | 0.21 (0.11; 0.31) | 0.14 (0.04; 0.25) | 0.16 (0.08.0.23) |
| TMAO (µM) | 11.4 (7.0) a.b | 53.5 (29.3) | 68.6 (37.1) |
| Parameters | ND (N = 15) | PD (N = 14) | HD (N = 34) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal/d) | 1573.4 (1296; 1850) | 1498 (1204; 1792) | 1414 (1235; 1592) |
| Carbohydrates (g/d) | 220 (185; 255) | 192 (153; 231) | 192 (168; 215) |
| Protein (g/d) | 65 (52; 79) | 77 (62; 92) | 65.9 (56; 74) |
| Lipids (g/d) | 50.5 (41.0; 60) | 44.3 (33.8; 54.7) | 41.7 (35.4; 48.1) |
| Fibers (g/d) | 16.1 (13.2; 18.9) | 17.8 (14.7; 20.8) a | 12.3 (9.8; 14.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, M.; Kemp, J.A.; Cardozo, L.; Vargas, D.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Stenvinkel, P.; Mafra, D. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Plasma Levels in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2025, 17, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010015
Ribeiro M, Kemp JA, Cardozo L, Vargas D, Ribeiro-Alves M, Stenvinkel P, Mafra D. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Plasma Levels in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins. 2025; 17(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Marcia, Julie Ann Kemp, Ludmila Cardozo, Drielly Vargas, Marcelo Ribeiro-Alves, Peter Stenvinkel, and Denise Mafra. 2025. "Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Plasma Levels in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease" Toxins 17, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010015
APA StyleRibeiro, M., Kemp, J. A., Cardozo, L., Vargas, D., Ribeiro-Alves, M., Stenvinkel, P., & Mafra, D. (2025). Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) Plasma Levels in Patients with Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins, 17(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17010015






