Human Biomonitoring Guidance Values for Deoxynivalenol Derived under the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of a DON Biomarker of Exposure (Total (Deglucuronidated) DON or DON-15-Glucuronide)
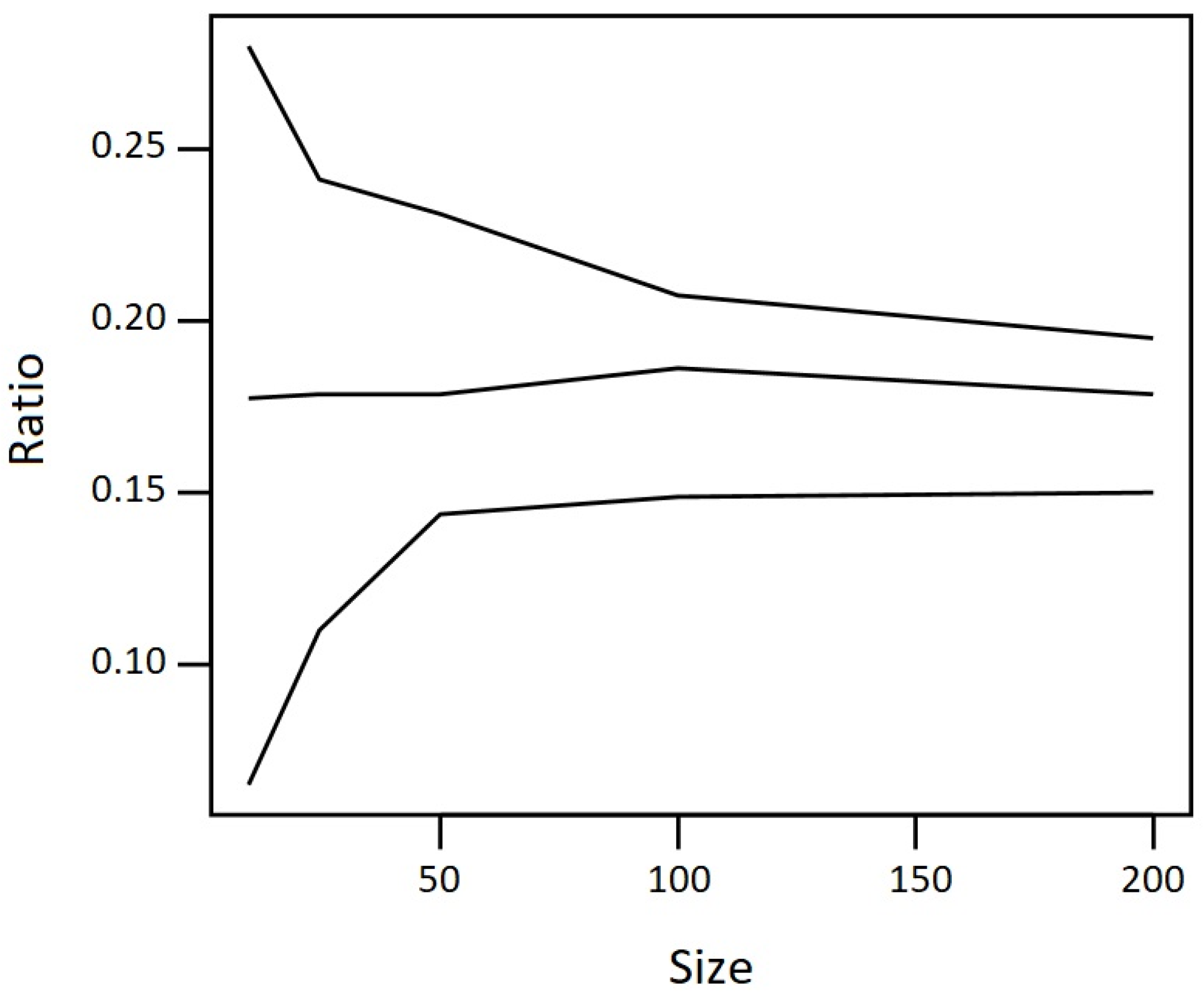
2.2. Derivation of the HBM-GV for DON
2.2.1. Approach for Deriving the HBM-GV
2.2.2. Parameters Used for the Derivation of the HBM-GV
2.2.3. Calculation of the HBM-GV for the General Adult Population
2.3. Level of Confidence Attributed to the HBM-GV
2.3.1. Nature and Quality of the Epidemiological/Toxicological Data and Toxicokinetic Data
2.3.2. The Critical Effect and the Mode of Action
2.3.3. The Selection of the Key Study Regarding the Critical Effect
2.3.4. The Selection of the POD
2.3.5. The Selection of the Other Required Parameters
2.3.6. The Extrapolations across and within Species
2.3.7. Overall LoC
2.4. Limitations and Uncertainties of the Proposed HBM-GV
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Derivation of the HBM-GV for DON
4.1.1. Approach for Deriving the HBM-GV
4.1.2. Parameters Used for the Derivation of the HBM-GV (Three Parameters)
4.1.3. Derivation of the HBM-GV for the General Population (Equation)
4.2. Level of Confidence (Six Factors)
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Deoxynivalenol | Target Population: General Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value/Descriptor | Comments |
| HBM-GV unit | µg/L | |
| HBM-GV year of issue | 2021 | |
| CLP-INDEX-Nr. | - | |
| EC-Nr. | 610-668-0 | |
| CAS-Nr. | 51481-10-8 | |
| Harmonized CLP classification | - | |
| Molar mass | 296.31 g/mol | |
| Identification | Biomarker(s) of exposure | |
| Molar mass of biomarker(s) | DON: 296.31 g/mol DON-15-Glucuronide: 472.4 g/mol | |
| Half-life of selected biomarker(s) * | DON: 2.55 h (CI: 2.2–2.8 h) DON-15-Glucuronide: 2.95 h total DON: 2.95 h | [11] |
| Factor for metabolic conversion (Fue) ** | Fue for DON: 0.14 (0.03–0.42); RDF: 7.20 (CI 2.37–29.1) Fue for DON-15-Glucuronide: 0.37 (0.13–0.71); RDF: 2.67 (CI 1.4–7.96) Fue for total DON: 0.69 (0.14–0.97); RDF: 1.45 (CI 1.03–7.10) | [11] RDF: Reversed dosimetry factor |
| Type of derivation method selected *** | Option 2 as described in [3]: HBM-GV derivation based on a defined external toxicity reference value (TRV) Note: total urinary volume per 24 h used differs from German HBM Commission | Estimation by means of TK extrapolation. |
| Key study, author(s), year | [17] | |
| Species | Animal: mice | |
| Exposure route of study | Oral | |
| Study length | Chronic | |
| Exposure dose and conditions | 0, 0.115, 0.661 and 1.520 mg/kg bw/day in males and 0, 0.098, 0.506 and 1.126 mg/kg bw/day in females for 2 years | |
| Critical endpoint | Reduced body weight gain | |
| Point of departure (POD) value | BMDL05: 0.11 mg DON/kg bw/day | |
| Extrapolations of the starting point | External TRV (group-TDI for DON, 3-acetyl-DON, 15-acetyl-DON and DON-3-Glucoside of 1 µg/kg bw/day) to HBM-GV (linked to urinary total DON by means of TK modelling). | |
| PBTK model for animal-human data extrapolation or intra-species extrapolation | [11] | |
| Assessment factors (AFs) | 100 (from animal POD to external TRV taking into account inter- and intra-species variability into account) | |
| Rounded value of the HBM-GV | Total DON: 0.69 ug DON/kg bw/total 24 h ≡ 23 µg DON/L urine (CI: 5–33 µg/L) # DON-15-glucuronide (DON15GlcA): 0.60 ug DON15GlcA/kg bw/total 24 h ≡ 20 µg DON15GlcA/L urine (CI: 7–39 µg/L) # | # Based on a 24-h urine sample |
| Additional comments | Derivation of the HBM-GV was not based on a steady-state situation due to an elimination half-life that is shorter than the dosing interval | |
References
- HBM4EU, Human Biomonitoring in Europe. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Apel, P.; Lamkarkach, F.; Lange, R.; Sissoko, F.; David, M.; Rousselle, C.; Schoeters, G.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Human biomonitoring guidance values (HBM-GVs) for priority substances under the HBM4EU initiative—New values derivation for deltamethrin and cyfluthrin and overall results. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 248, 114097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.; Rousselle, C.; Lange, R.; Sissoko, F.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Ougier, E. Human biomonitoring initiative (HBM4EU)—Strategy to derive human biomonitoring guidance values (HBM-GVs) for health risk assessment. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 230, 113622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ougier, E.; Ganzleben, C.; Lecoq, P.; Bessems, J.; David, M.; Schoeters, G.; Lange, R.; Meslin, M.; Uhl, M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; et al. Chemical prioritisation strategy in the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU)—Development and results. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 236, 113778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govarts, E.; Gilles, L.; Rodriguez Martin, L.; Santonen, T.; Apel, P.; Alvito, P.; Anastasi, E.; Andersen, H.; Andersson, A.; Andryskova, L.; et al. Harmonized human biomonitoring in European children, teenagers and adults: EU-wide exposure data of 11 chemical substance groups from the HBM4EU Aligned Studies (2014–2021). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 249, 114119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvito, P.; Assuncao, R.M.; Bajard, L.; Martins, C.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; Mol, H.; Namorado, S.; van den Brand, A.D.; Vasco, E.; Viegas, S.; et al. Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU-Lessons Learned and Future Trends. Toxins 2022, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahiout, S.S.T.; Joksić, A.Š.; Gerofke, A.; Scholten, B.; Martins, C.; Louro, H.; Tarazona, J.; Niemann, L.; Woutersen, M. Human Biomonitoring in Risk Assessment: 4th Set of Examples on the Use of HBM in Risk Assessments of HBM4EU Priority Chemicals Deliverable Report D5.11. 2022. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-5-11-human-biomonitoring-in-risk-assessment-4th-set-of-examples-on-the-use-of-hbm-in-risk-assessments-of-hbm4eu-priority-chemicals/ (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Broekaert, N.; Devreese, M.; van Bergen, T.; Schauvliege, S.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Vanhaecke, L.; Berthiller, F.; Michlmayr, H.; Malachová, A.; et al. In vivo contribution of deoxynivalenol-3-β-D-glucoside to deoxynivalenol exposure in broiler chickens and pigs: Oral bioavailability, hydrolysis and toxicokinetics. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Risks to human and animal health related to the presence of deoxynivalenol and its acetylated and modified forms in food and feed. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faeste, C.K.; Ivanova, L.; Sayyari, A.; Hansen, U.; Sivertsen, T.; Uhlig, S. Prediction of deoxynivalenol toxicokinetics in humans by in vitro-to-in vivo extrapolation and allometric scaling of in vivo animal data. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2195–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengelers, M.; Zeilmaker, M.; Vidal, A.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Hoogenveen, R. Biomonitoring of Deoxynivalenol and Deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in Human Volunteers: Renal Excretion Profiles. Toxins 2019, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Sulyok, M.; Fruhmann, P.; Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Hametner, C.; Adam, G.; Fröhlich, J.; Krska, R. Assessment of human deoxynivalenol exposure using an LC–MS/MS based biomarker method. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.S.M.; Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Krska, R. New insights into the human metabolism of the Fusarium mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.; Claeys, L.; Mengelers, M.; Vanhoorne, V.; Vervaet, C.; Huybrechts, B.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M. Humans significantly metabolize and excrete the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol and its modified form deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside within 24 hours. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.C.; White, K.L.; Burley, V.J.; Hopton, R.P.; Rajendram, A.; Fisher, J.; Cade, J.E.; Wild, C.P. A comparison of deoxynivalenol intake and urinary deoxynivalenol in UK adults. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Brand, A.D.; Hoogenveen, R.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; Zeilmaker, M.; Eriksen, G.S.; Uhlig, S.; Brantsaeter, A.L.; Dirven, H.; Husoy, T. Modelling the Renal Excretion of the Mycotoxin Deoxynivalenol in Humans in an Everyday Situation. Toxins 2021, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, F.; Armstrong, C.; Nera, E.; Truelove, J.; Fernie, S.; Scott, P.; Stapley, R.; Hayward, S.; Gunner, S. Chronic feeding study of deoxynivalenol in B6C3F1 male and female mice. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen. 1995, 15, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndaw, S.; Jargot, D.; Antoine, G.; Denis, F.; Melin, S.; Robert, A. Investigating Multi-Mycotoxin Exposure in Occupational Settings: A Biomonitoring and Airborne Measurement Approach. Toxins 2021, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, S.; Assuncao, R.; Nunes, C.; Osteresch, B.; Twaruzek, M.; Kosicki, R.; Grajewski, J.; Martins, C.; Alvito, P.; Almeida, A.; et al. Exposure Assessment to Mycotoxins in a Portuguese Fresh Bread Dough Company by Using a Multi-Biomarker Approach. Toxins 2018, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonen, J.; Malysheva, S.V.; Taevernier, L.; Diana Di Mavungu, J.; De Saeger, S.; De Spiegeleer, B. Human skin penetration of selected model mycotoxins. Toxicology 2012, 301, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, S.; Viegas, C.; Oppliger, A. Occupational Exposure to Mycotoxins: Current Knowledge and Prospects. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2018, 62, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.C.; Hopton, R.P.; White, K.L.; Fisher, J.; Cade, J.E.; Wild, C.P. Assessment of deoxynivalenol metabolite profiles in UK adults. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shephard, G.S.; Burger, H.M.; Gambacorta, L.; Gong, Y.Y.; Krska, R.; Rheeder, J.P.; Solfrizzo, M.; Srey, C.; Sulyok, M.; Visconti, A.; et al. Multiple mycotoxin exposure determined by urinary biomarkers in rural subsistence farmers in the former Transkei, South Africa. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Saez, J.; Hernandez-Mesa, M.; Gallardo-Ramos, J.A.; Gamiz-Gracia, L.; Garcia-Campana, A.M. Assessing human exposure to pesticides and mycotoxins: Optimization and validation of a method for multianalyte determination in urine samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 1935–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyndrickx, E.; Sioen, I.; Huybrechts, B.; Callebaut, A.; De Henauw, S.; De Saeger, S. Human biomonitoring of multiple mycotoxins in the Belgian population: Results of the BIOMYCO study. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; You, L.; Nepovimova, E.; Wang, X.; Musilek, K.; Wu, Q.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Biomarkers of deoxynivalenol (DON) and its modified form DON-3-glucoside (DON-3G) in humans. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brera, C.; de Santis, B.; Debegnach, F.; Miano, B.; Moretti, G.; Lanzone, A.; Del Sordo, G.; Buonsenso, D.; Chiaretti, A.; Hardie, L.; et al. Experimental study of deoxynivalenol biomarkers in urine. EFSA Support. Publ. 2015, 12, 818E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.C.; Hopton, R.P.; Lecluse, Y.; White, K.L.; Fisher, J.; Lebailly, P. Determinants of urinary deoxynivalenol and de-epoxy deoxynivalenol in male farmers from Normandy, France. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5206–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Nepovimova, E.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Deoxynivalenol and its modified forms: Key enzymes, inter-individual and interspecies differences in metabolism. Drug Metab. Rev. 2022, 54, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Li, C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Gong, Y.Y.; Routledge, M.N.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Risk assessment of deoxynivalenol in high-risk area of China by human biomonitoring using an improved high throughput UPLC-MS/MS method. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, B.; Debegnach, F.; Miano, B.; Moretti, G.; Sonego, E.; Chiaretti, A.; Buonsenso, D.; Brera, C. Determination of Deoxynivalenol Biomarkers in Italian Urine Samples. Toxins 2019, 11, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, G.S.; Knutsen, H.K.; Sandvik, M.; Brantsaeter, A.L. Urinary deoxynivalenol as a biomarker of exposure in different age, life stage and dietary practice population groups. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HBM4EU. ICI Report Mycotoxin (DON) in Urine round 3 HBM4EU—Science and Policy for a Healthy Future. 2020. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/mdocs-posts/hbm4eu-ici-report-mycotoxins-don-in-urine-round-3/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Warensjo Lemming, E.; Montano Montes, A.; Schmidt, J.; Cramer, B.; Humpf, H.U.; Moraeus, L.; Olsen, M. Mycotoxins in blood and urine of Swedish adolescents-possible associations to food intake and other background characteristics. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Wells, L.; Williams, C.; White, K.; De Santis, B.; Liu, Y.; Debegnach, F.; Miano, B.; Moretti, G.; Greetham, S.; et al. Assessment of Urinary Deoxynivalenol Biomarkers in UK Children and Adolescents. Toxins 2018, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HBM4EU. Deliverable 5.9 3rd Substance Specific Derivation of EU-Wide Health-Based Guidance Values. 2022. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-5-9-3rd-substance-specific-derivation-of-eu-wide-health-based-guidance-values/ (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Lermen, D.; Bartel-Steinbach, M.; Gwinner, F.; Conrad, A.; Weber, T.; von Briesen, H.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Trends in characteristics of 24-h urine samples and their relevance for human biomonitoring studies—20 years of experience in the German Environmental Specimen Bank. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylward, L.L.; Hays, S.M.; Vezina, A.; Deveau, M.; St-Amand, A.; Nong, A. Biomonitoring Equivalents for interpretation of urinary fluoride. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.L.; Lorber, M.; Koch, H.M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Morgan, M.K. Population variability of phthalate metabolites and bisphenol A concentrations in spot urine samples versus 24- or 48-h collections. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brand, A.D.; Bajard, L.; Steffensen, I.L.; Brantsaeter, A.L.; Dirven, H.; Louisse, J.; Peijnenburg, A.; Ndaw, S.; Mantovani, A.; De Santis, B.; et al. Providing Biological Plausibility for Exposure-Health Relationships for the Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Fumonisin B1 (FB1) in Humans Using the AOP Framework. Toxins 2022, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, H.L.; Markowitz, J.S.; DeVane, C.L. Drug Glucuronidation in Clinical Psychopharmacology. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 21, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mengelers, M.J.B.; van den Brand, A.D.; Zhao, S.; Hoogenveen, R.; Ougier, E. Human Biomonitoring Guidance Values for Deoxynivalenol Derived under the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU). Toxins 2024, 16, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030139
Mengelers MJB, van den Brand AD, Zhao S, Hoogenveen R, Ougier E. Human Biomonitoring Guidance Values for Deoxynivalenol Derived under the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU). Toxins. 2024; 16(3):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030139
Chicago/Turabian StyleMengelers, Marcel J. B., Annick D. van den Brand, Shensheng Zhao, Rudolf Hoogenveen, and Eva Ougier. 2024. "Human Biomonitoring Guidance Values for Deoxynivalenol Derived under the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU)" Toxins 16, no. 3: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030139
APA StyleMengelers, M. J. B., van den Brand, A. D., Zhao, S., Hoogenveen, R., & Ougier, E. (2024). Human Biomonitoring Guidance Values for Deoxynivalenol Derived under the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU). Toxins, 16(3), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16030139





