Pathophysiological and Clinical Significance of Crotalus durissus cascavella Venom-Induced Pulmonary Impairment in a Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
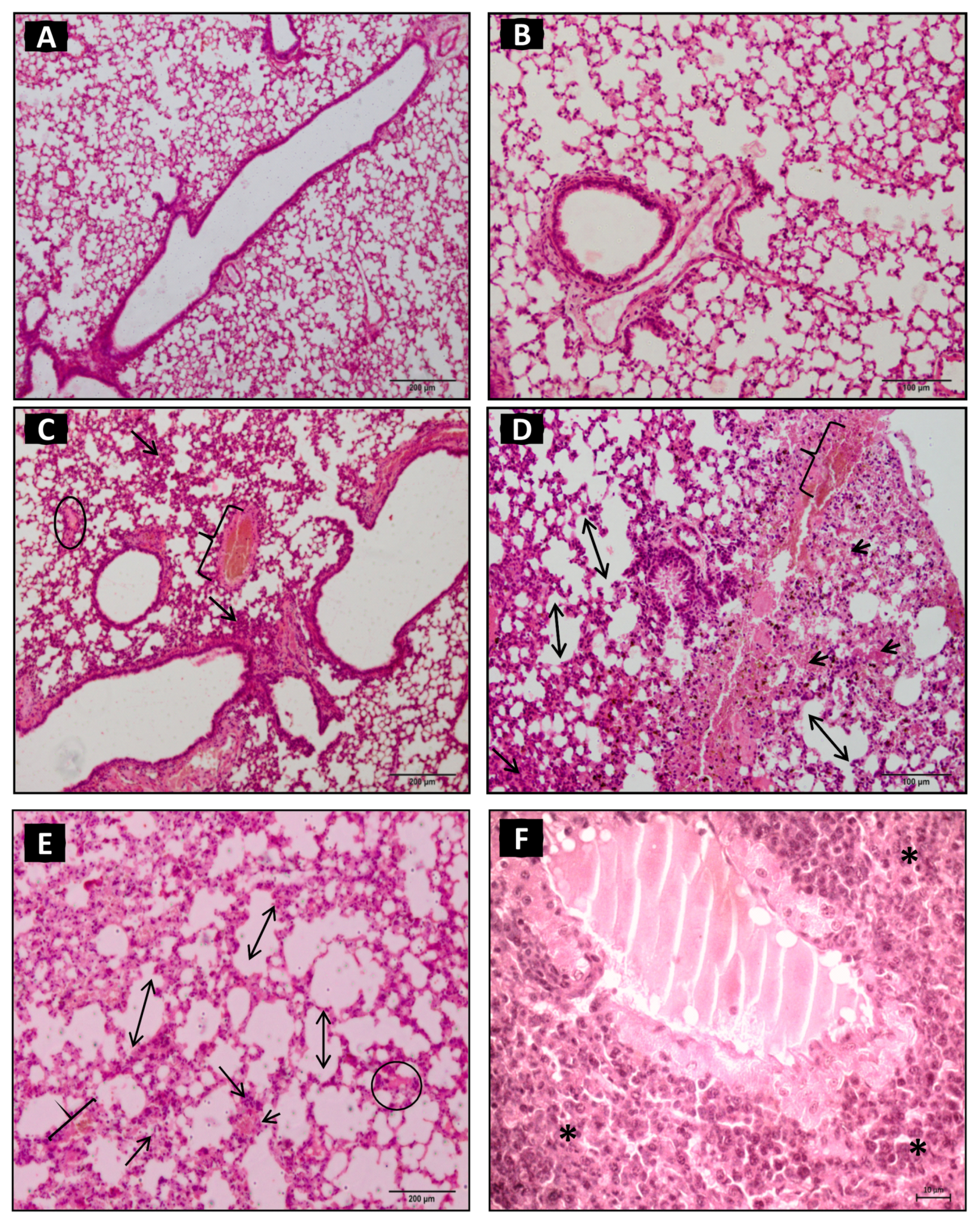
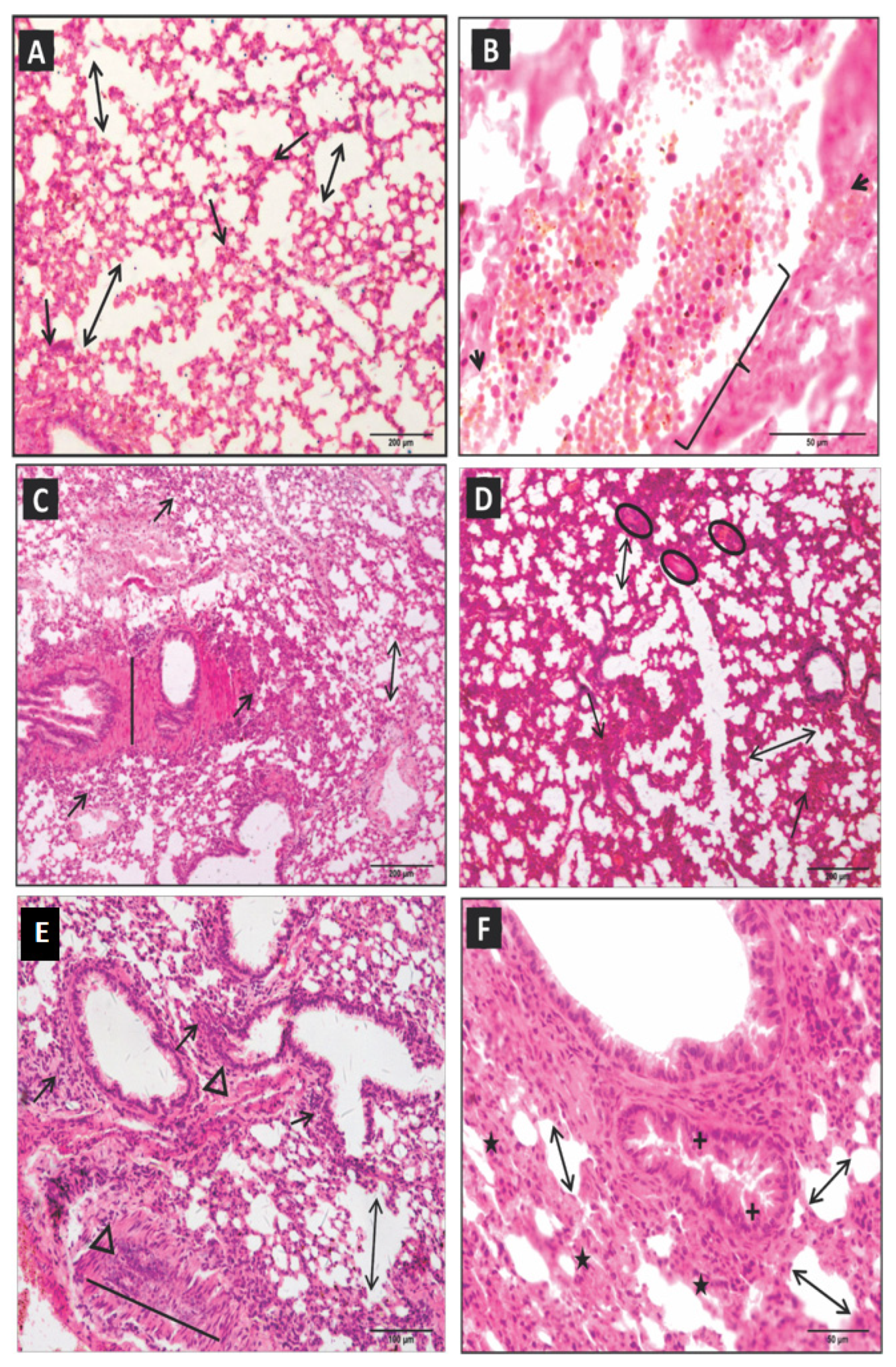
2.1. Lung Histopathological Changes
2.2. Morphometric Analysis of Lung Parenchyma
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
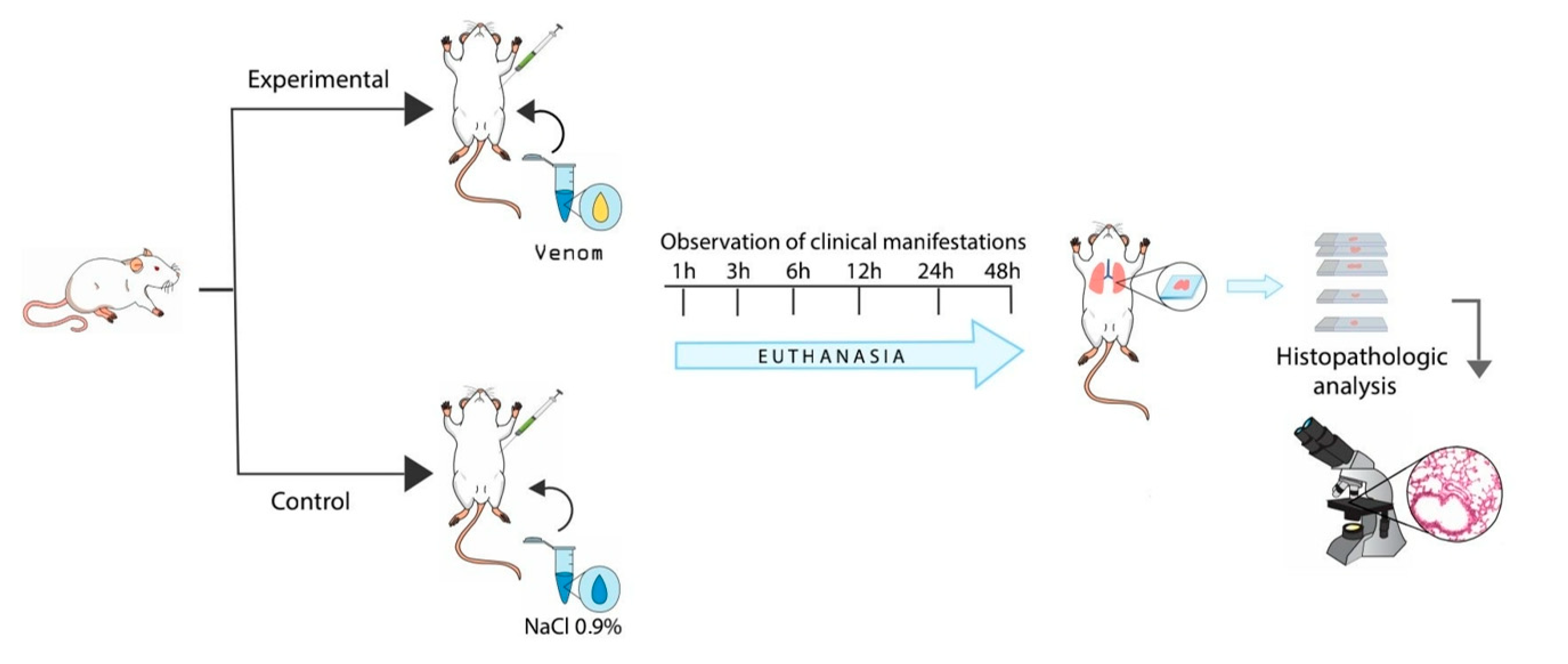
5. Method and Materials
5.1. Biological Material
5.2. Histopathological Analysis of Pulmonary Parenchyma
5.3. Morphometric Analysis of Inflammatory Infiltrates Necrosis Areas, Alveolar Distensions, and Septal Loss
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Williams, D.; Fan, H.W.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming from a global perspective: Towards an integrated approach. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mise, Y.F.; Lira-Da-Silva, R.M.; Carvalho, F. Fatal Snakebite Envenoming and Agricultural Work in Brazil: A Case–Control Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde, Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação-Sinan. Available online: http://tabnet.datasus.gov.br/cgi/deftohtm.exe?sinannet/cnv/animaisbr.def (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Amaral, C.F.S.; Magalhães, R.A.; de Rezende, N.A. Comprometimento respiratório secundário a acidente ofídico crotálico (Crotalus durissus). Rev. Do Inst. Med. Trop. SÃ\Poundso Paulo 1991, 33, 251–255. Available online: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0036-46651991000400002&nrm=iso (accessed on 17 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Sano-Martins, I.; Tomy, S.; Campolina, D.; Dias, M.; de Castro, S.; de Sousa-E.-Silva, M.; Amaral, C.; Rezende, N.; Kamiguti, A.; Warrell, D.; et al. Coagulopathy following lethal and non-lethal envenoming of humans by the South American rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus) in Brazil. Qjm Int. J. Med. 2001, 94, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, P.N.; Amorim, C.F.; Peres, A.C.P.; e Silva, C.A.M.; Zamuner, S.R.; Ribeiro, W.; Cogo, J.C.; Vieira, R.P.; Dolhnikoff, M.; de Oliveira, L.V.F. Pulmonary mechanic and lung histology injury induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanathasan, A.; Rodrigo, C. Pulmonary Effects and Complications of Snakebites. Chest 2014, 146, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palangasinghe, D.R.; Weerakkody, R.; Dalpatadu, C.G.; Gnanathasan, C.A. A fatal outcome due to pulmonary hemorrhage following Russell’s viper bite. Saudi Med. J. 2015, 36, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srirangan, A.; Pushpakumara, J.; Wanigasuriya, K. A life-threatening complication due to pulmonary haemorrhage following hump-nosed viper bite. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshwal, A.; Phan, P.; Datta, J.; Kannan, R.; Thallapuranam, S. A Meta-Analysis of the Protein Components in Rattlesnake Venom. Toxins 2021, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Santos, A.; Dos-Santos, E.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Lima, C.; Cardoso, D.; Mota, I. A comparative study of biological activities of crotoxin and CB fraction of venoms from Crotalus durissus terrificus, Crotalus durissus cascavella and Crotalus durissus collilineatus. Toxicon 2004, 43, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Díaz, C. Hemorrhage induced by snake venom metalloproteinases: Biochemical and biophysical mechanisms involved in microvessel damage. Toxicon 2005, 45, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, L.F.M.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Mendes, M.M.; Costa, T.R.; Grabner, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.M.; da Silva, S.L.; Zanchi, F.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; et al. Snake Venom L-Amino Acid Oxidases: Trends in Pharmacology and Biochemistry. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 196754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratzer, E.; Tian, Y.; Sarich, N.; Wu, T.; Meliton, A.; Leff, A.; Birukova, A.A. Oxidative Stress Contributes to Lung Injury and Barrier Dysfunction via Microtubule Destabilization. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, É.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; de Oliveira, R.H.A. Antivenom therapy: Efficacy and adverse reactions. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 13, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- De Carvalho, A.E.Z.; Giannotti, K.; Junior, E.L.; Matsubara, M.; Santos, M.C.D.; Fortes-Dias, C.L.; Teixeira, C. Crotalus durissus ruruima Snake Venom and a Phospholipase A2 Isolated from This Venom Elicit Macrophages to Form Lipid Droplets and Synthesize Inflammatory Lipid Mediators. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 2745286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Johnson, J.R. The Applicability of Mouse Models to the Study of Human Disease; Methods in Molecular Biology 1940; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, A.L.; França, F.O.; Barbaro, K.C.; Nunes, J.R.; Cardoso, J.L. Pulmonary haemorrhage causing rapid death after Bothrops jararacussu snakebite: A case report. Toxicon 2003, 42, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, D.; Janssens, J.-P. The Pathophysiology of Respiratory Failure: Control of Breathing, Respiratory Load, and Muscle Capacity. Respiration 2018, 97, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, E.; Figueiredo, R.G.; Pinto, R.V.; Ramos, T.; Sampaio, G.P.; Santos, R.P.B.; Guerreiro, M.L.D.S.; Biondi, I.; Trindade, S.C. Evaluation of systemic inflammatory response and lung injury induced by Crotalus durissus cascavella venom. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartim, M.A.; Souza, C.O.S.; Diniz, C.R.A.F.; da Fonseca, V.M.B.; Sousa, L.O.; Peti, A.P.F.; Costa, T.R.; Lourenço, A.G.; Borges, M.C.; Sorgi, C.A.; et al. Crotoxin-Induced Mice Lung Impairment: Role of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and COX-Derived Prostanoids. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Neto, J.; Silveira, J.A.M.; Serra, D.S.; Viana, D.A.; Borges-Nojosa, D.M.; Sampaio, C.M.S.; Monteiro, H.S.A.; Cavalcante FS, Á.; Evangelista, J.S.A.M. Pulmonary mechanic and lung histology induced by Crotalus durissus cascavella snake venom. Toxicon 2017, 137, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.A.; Bronner, J.; Akpunonu, P.D.S.; Plott, J.; Bailey, A.M.; Keyler, D.E. Crotalus durissus terrificus (viperidae; crotalinae) en-venomation: Respiratory failure and treatment with antivipmyn TRI ® antivenom. Toxicon 2019, 163, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polgár, J.; Clemetson, J.M.; Kehrel, B.E.; Wiedemann, M.; Magnenat, E.M.; Wells, T.N.; Clemetson, K.J. Platelet activation and signal transduction by convulxin, a C-type lectin from Crotalus durissus terrificus (Tropical rattlesnake) venom via the p62/GPVI collagen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13576–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rádis-Baptista, G.; Moreno, F.B.M.B.; Nogueira, L.D.L.; Martins, A.M.C.; Toyama, D.D.O.; Toyama, M.H.; Cavada, B.S.; de Azevedo, W.F., Jr.; Yamane, T. Crotacetin, a Novel Snake Venom C-Type Lectin Homolog of Convulxin, Exhibits an Unpredictable Antimicrobial Activity. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 44, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonamine, C.M.; Kondo, M.Y.; Nering, M.B.; Gouvêa, I.E.; Okamoto, D.; Andrade, D.; da Silva, J.A.A.; da Silva, R.P.; Yamane, T.; Juliano, M.A.; et al. Enzyme specificity and effects of gyroxin, a serine protease from the venom of the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus, on protease-activated receptors. Toxicon 2014, 79, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péterfi, O.; Boda, F.; Szabó, Z.; Ferencz, E.; Bába, L. Hypotensive Snake Venom Components—A Mini-Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Bernarde, P.S.; Rocha, A.M.; Viana, P.F.; Farias, R.E.S.; Cerni, F.A.; Oliveira, I.S.; Ferreira, I.G.; Sandri, E.A.; Sachett, J.; et al. Crotalus Durissus Ruruima: Current Knowledge on Natural History, Medical Importance, and Clinical Toxinology. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 659515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, B.T.; Cezarette, G.N.; Bomfim, A.D.S.; Monteiro, W.M.; Russo, E.M.D.S.; Frantz, F.G.; Sampaio, S.V.; Sartim, M.A. Role of crotoxin in coagulation: Novel insights into anticoagulant mechanisms and impairment of inflammation-induced coagulation. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 26, e20200076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Shimizu, S.; Matsuo, J.; Nishibata, Y.; Kusunoki, Y.; Hattanda, F.; Shida, H.; Nakazawa, D.; Tomaru, U.; Atsumi, T.; et al. Measurement of NET formation in vitro and in vivo by flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2017, 91, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, J.M.; Del Fresno, C.; Crainiciuc, G.; Cuartero, M.I.; Casanova-Acebes, M.; Weiss, L.A.; Huerga-Encabo, H.; Silvestre-Roig, C.; Rossaint, J.; Cossio, I.; et al. A Neutrophil Timer Coordinates Immune Defense and Vascular Protection. Immunity 2019, 50, 390–402.e10, Erratum in Immunity 2019, 51, 966–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Petta, A. Pathogenesis of pulmonary emphysema–cellular and molecular events. Einstein (São Paulo) 2010, 8, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraldo, S.; Turato, G.; Saetta, M. Pathophysiology of the Small Airways in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respiration 2012, 84, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, R.; Piscaer, I.; Franssen, F.M.E.; Wouters, E.F.M. Emphysema: Looking beyond alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, L.B.; Pêgo-Fernandes, P.M.; Xavier, A.M.; Pazetti, R.; Rivero, D.H.R.F.; Capelozzi, V.L.; Jatene, F.B. Modelo experimental de enfisema pulmonar em ratos induzido por papaína. J. Pneumol. 2002, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Camelier, A.A.; Winter, D.H.; Jardim, J.R.; Barboza, C.E.G.; Cukier, A.; Miravitlles, M. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: Diagnosis and treatment. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2008, 34, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroni, D.G.; Boner, A.L. Atelectasis: Mechanisms, diagnosis and management. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2000, 1, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, M.; Kavanagh, B.P. Pulmonary atelectasis: A pathogenic perioperative entity. Anesthesiology 2005, 102, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricevich, V.L. Cytokine and Nitric Oxide Production Following Severe Envenomation. Curr. Drug Targets-Inflamm. Allergy 2004, 3, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Sara, G.; Mendonça, R.; Petricevich, V. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Release in Mice Injected with Crotalus durissus terrificus Venom. Mediat. Inflamm. 2008, 2008, 874962. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, D.F.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Macedo, M.S.; Farsky, S.H.P. Role of crotoxin, a phospholipase A2 isolated from Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom, on inflammatory and immune reactions. Mediat. Inflamm. 2001, 10, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Hartsky, M.A.; Warheit, D.B. Time course of quartz and TiO(2) particle-induced pulmonary inflammation and neu-trophil apoptotic responses in rats. Exp. Lung Res. 2002, 28, 641–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova-Acebes, M.; Pitaval, C.; Weiss, L.A.; Nombela-Arrieta, C.; Chèvre, R.; Noelia, A.; Kunisaki, Y.; Zhang, D.; van Rooijen, N.; Silberstein, L.E.; et al. Rhythmic Modulation of the Hematopoietic Niche through Neutrophil Clearance. Cell 2013, 153, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, J.; Vijayan, S.; Drechsler, M.; Hartwig, H.; Mörgelin, M.; Dembinski, R.; Jacobs, M.; Koeppel, T.A.; Binnebösel, M.; Weber, C.; et al. Simvastatin Reduces Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Decreasing Neutrophil Recruitment and Radical Formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydell-Tormanen, K.; Uller, L.; Erjefält, J.S. Direct evidence of secondary necrosis of neutrophils during intense lung inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medan, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Dokka, S.; Castranova, V.; Rojanasakul, Y. Induction of neutrophil apoptosis and secondary necrosis during endotoxin-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice. J. Cell Physiol. 2002, 191, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Brodie, D.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: Advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA 2018, 319, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake bite. Lancet. 2010, 375, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, M.; Liang, Q.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. In Vitro Efficacy of Antivenom and Varespladib in Neutralising Chinese Russell’s Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom Toxicity. Toxins 2023, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.R.; Carter, R.W.; Matteo, I.A.; Samuel, S.P.; Rao, S.; Fry, B.G.; Bickler, P.E. Varespladib in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming: Development History and Preclinical Evidence Supporting Advancement to Clinical Trials in Patients Bitten by Venomous Snakes. Toxins 2022, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Slagboom, J.; Albulescu, L.O.; Somsen, G.W.; Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Kool, J. Neutralising effects of small molecule toxin inhib-itors on nanofractionated coagulopathic Crotalinae snake venoms. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.; Oliveira, I.C.F.; Yoshida, E.H.; Cantuaria, N.M.; Cogo, J.C.; Torres-Bonilla, K.A.; Hyslop, S.; Junior, N.J.S.; Floriano, R.S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Effect of the phospholipase A2 inhibitor Varespladib, and its synergism with crotalic antivenom, on the neuromuscular blockade induced by Crotalus durissus terrificus venom (with and without crotamine) in mouse neuromuscular preparations. Toxicon 2022, 214, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.W.; Gerardo, C.J.; Samuel, S.P.; Kumar, S.; Kotehal, S.D.; Mukherjee, P.P.; Shirazi, F.M.; Akpunonu, P.D.; Bammigatti, C.; Bhalla, A.; et al. The BRAVO Clinical Study Protocol: Oral Varespladib for Inhibition of Secretory Phospholipase A2 in the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming. Toxins 2023, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, S.K.; Clare, R.H.; Xie, C.; Westhorpe, A.; Hall, S.R.; Edge, R.J.; Alsolaiss, J.; Crittenden, E.; Marriott, A.E.; Harrison, R.A.; et al. In vitro and in vivo preclinical venom inhibition assays identify metalloproteinase inhibiting drugs as potential future treatments for snakebite envenoming by Dispholidus typus. Toxicon X 2022, 14, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scatena, R. Prinomastat, a hydroxamate-based matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. A novel pharmacological approach for tissue remodelling-related diseases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahian, S.; Fernandez, I.E.; Eickelberg, O.; Hartl, D. Immune Mechanisms in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016, 55, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randal, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, I. Caracterização Biológica e Bioquímica da Peçonha de Crotalus Durissus Cascavella no Estado da Bahia; State University of Feira de Santana: Novo Horizonte, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]


| Exposure Time in the Lung Parenchyma | Inflammatory Infiltrates | Necrosis Areas | Septal Losses | Alveolar Distension |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | ++ | + | + | + |
| 3 h | +++ | + | ++ | + |
| 6 h | + | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| 12 h | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| 24 h | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| 48 h | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figueiredo, R.G.; Guerreiro, M.L.d.S.; Azevedo, E.; de Moura, M.S.; Trindade, S.C.; de Bessa, J., Jr.; Biondi, I. Pathophysiological and Clinical Significance of Crotalus durissus cascavella Venom-Induced Pulmonary Impairment in a Murine Model. Toxins 2023, 15, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040282
Figueiredo RG, Guerreiro MLdS, Azevedo E, de Moura MS, Trindade SC, de Bessa J Jr., Biondi I. Pathophysiological and Clinical Significance of Crotalus durissus cascavella Venom-Induced Pulmonary Impairment in a Murine Model. Toxins. 2023; 15(4):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040282
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigueiredo, Ricardo G., Marcos Lázaro da Silva Guerreiro, Elen Azevedo, Mateus Souza de Moura, Soraya Castro Trindade, José de Bessa, Jr., and Ilka Biondi. 2023. "Pathophysiological and Clinical Significance of Crotalus durissus cascavella Venom-Induced Pulmonary Impairment in a Murine Model" Toxins 15, no. 4: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040282
APA StyleFigueiredo, R. G., Guerreiro, M. L. d. S., Azevedo, E., de Moura, M. S., Trindade, S. C., de Bessa, J., Jr., & Biondi, I. (2023). Pathophysiological and Clinical Significance of Crotalus durissus cascavella Venom-Induced Pulmonary Impairment in a Murine Model. Toxins, 15(4), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040282





