Aromatic Residues on the Side Surface of Cry4Ba-Domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Function in Binding to Their Counterpart Residues on the Aedes aegypti Alkaline Phosphatase Receptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Possible Binding Residues between the Cry4Ba Toxin and the Aa-mALP Receptor
2.2. Expression and Purification of Cry4Ba and Its Mutants
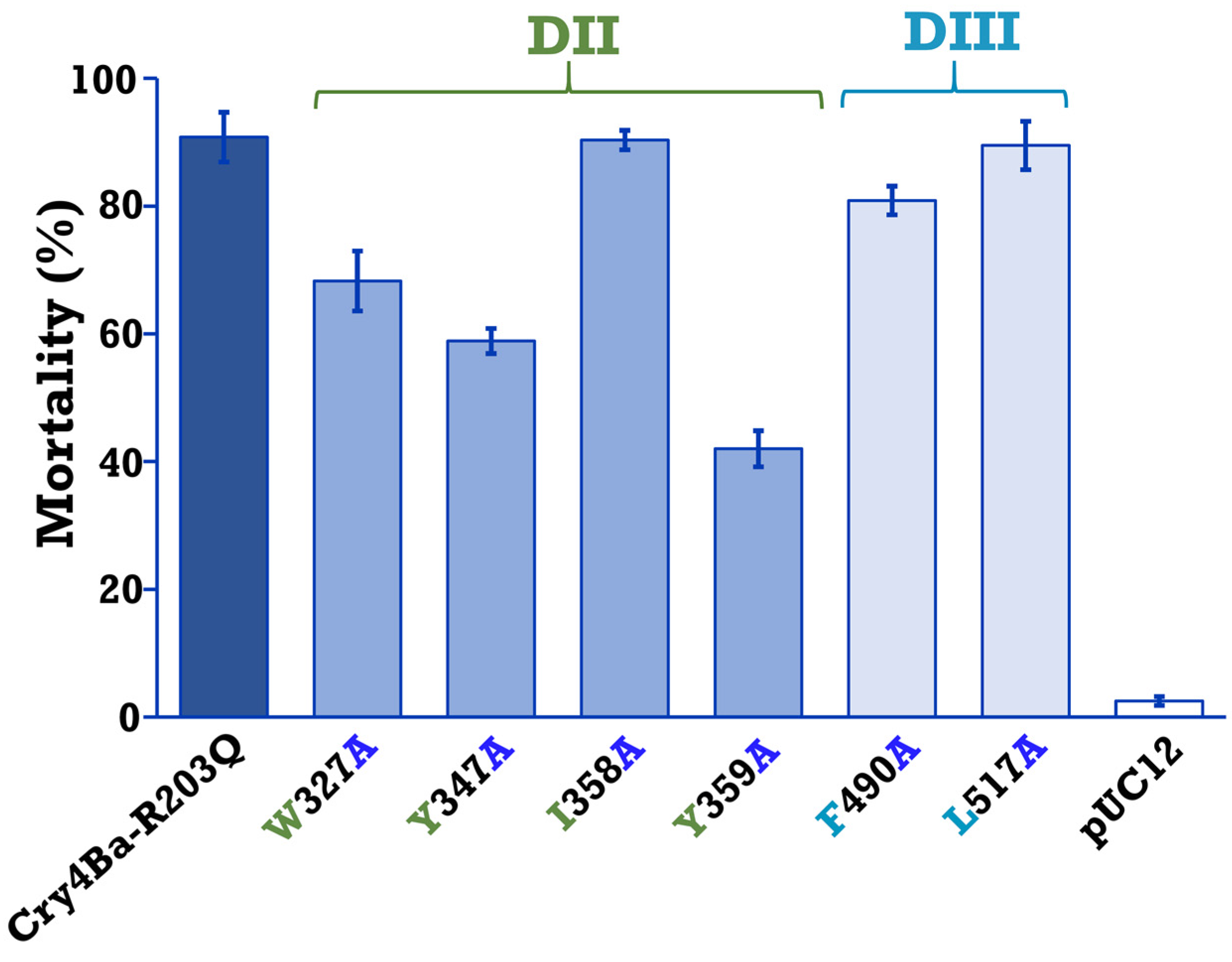
2.3. Larvicidal Activity of Cry4Ba and Its Mutants
2.4. Expression and Purification of Aa-mALP and Its Mutants
2.5. Quantitative Analysis of Cry4Ba Toxin—Aa-mALP Receptor Interactions
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. In Silico Binding Analysis of Cry4Ba Toxin—Aa-mALP Receptor Interaction
5.3. Construction of Cry4Ba Mutant Plasmids
5.4. Construction of Aa-mALP Mutant Plasmids
5.5. Expression and Purification of Cry4Ba and Its Mutants
5.6. Expression and Purification of Aa-mALP and Its Mutants
5.7. Mosquito Larvicidal Activity Assays
5.8. Cry4Ba Toxin-Aa-mALP Binding Assays Using ELISA
5.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Dengue Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control: New Edition; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, P.; Sabeena, S.P.; Varma, M.; Arunkumar, G. Current understanding of the pathogenesis of dengue virus infection. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kularatne, S.A.; Dalugama, C. Dengue infection: Global importance, immunopathology and management. Clin. Med. 2022, 22, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Brady, O.J.; Golding, N.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Wint, G.R.W.; Ray, S.E.; Pigott, D.M.; Shearer, F.M.; Johnson, K.; Earl, L.; et al. The current and future global distribution and population at risk of dengue. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Dengue vaccine: WHO position paper, September 2018-Recommendations. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4848–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Jang, Y.-S. Current status and perspectives on vaccine development against dengue virus infection. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, A.L. Bacillus thuringiensis serovariety israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus for mosquito control. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2007, 23, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Filha, M.; Romão, T.; Rezende, T.; Carvalho, K.; de Menezes, H.G.; Nascimento, N.A.D.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacterial toxins active against mosquitoes: Mode of action and resistance. Toxins 2021, 13, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreau, G.; Stalinski, R.; David, J.-P.; Després, L. Monitoring resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis in the field by performing bioassays with each Cry toxin separately. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brühl, C.A.; Després, L.; Frör, O.; Patil, C.D.; Poulin, B.; Tetreau, G.; Allgeier, S. Environmental and socioeconomic effects of mosquito control in Europe using the biocide Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis (Bti). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 137800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, K.D.S.; Crespo, M.M.; Araújo, A.P.; Da Silva, R.S.; De Melo-Santos, M.A.V.; De Oliveira, C.M.F.; Silva-Filha, M.H.N.L. Long-term exposure of Aedes aegypti to Bacillus thuringiensis svar. israelensis did not involve altered susceptibility to this microbial larvicide or to other control agents. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Dov, E. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and its dipteran-specific toxins. Toxins 2014, 6, 1222–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonserm, P.; Davis, P.; Ellar, D.J.; Li, J. Crystal structure of the mosquito-larvicidal toxin Cry4Ba and its biological implications. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayyareddy, K.; Andacht, T.M.; Abdullah, M.A.; Adang, M.J. Proteomic identification of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis toxin Cry4Ba binding proteins in midgut membranes from Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti Linnaeus (Diptera, Culicidae) larvae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, A.I.; Reyes, E.Z.; Cancino-Rodezno, A.; Bedoya-Pérez, L.P.; Caballero-Flores, G.G.; Muriel-Millan, L.F.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Gill, S.S.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M. Aedes aegypti alkaline phosphatase ALP1 is a functional receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa toxins. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengwiman, S.; Aroonkesorn, A.; Dedvisitsakul, P.; Sakdee, S.; Leetachewa, S.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Pootanakit, K. In vivo identification of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin receptors by RNA interference knockdown of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked aminopeptidase N transcripts in Aedes aegypti larvae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechklar, M.; Tiewsiri, K.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Pootanakit, K. Functional expression in insect cells of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked alkaline phosphatase from Aedes aegypti larval midgut: A Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin receptor. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroonkesorn, A.; Pootanakit, K.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Two specific membrane-bound aminopeptidase N isoforms from Aedes aegypti larvae serve as functional receptors for the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin implicating counterpart specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammasittirong, A.; Dechklar, M.; Leetachewa, S.; Pootanakit, K.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Aedes aegypti membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase expressed in Escherichia coli retains high-affinity binding for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6836–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thammasittirong, A.; Thammasittirong, S.N.-R.; Imtong, C.; Charoenjotivadhanakul, S.; Sakdee, S.; Li, H.-C.; Okonogi, S.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba insecticidal toxin exploits Leu615 in its C-terminal domain to interact with a target receptor—Aedes aegypti membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase. Toxins 2021, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaokhiew, T.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Promptmas, C. Correlative effect on the toxicity of three surface-exposed loops in the receptor-binding domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 300, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehouck, Y.; Kwasigroch, J.M.; Rooman, M.; Gilis, D. BeAtMuSiC: Prediction of changes in protein–protein binding affinity on mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W333–W339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, A.L.D.A.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. Bacillus thuringiensis: Mechanism of action, resistance, and new applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vílchez, S. Making 3D-Cry toxin mutants: Much more than a tool of understanding toxins mechanism of action. Toxins 2020, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.K.; Zhang, S. Computational prediction of protein hot spot residues. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhivker, G.M.; Bouzida, D.; Gehlhaar, D.K.; Rejto, P.A.; Freer, S.T.; Rose, P.W. Monte Carlo simulations of the peptide recognition at the consensus binding site of the constant fragment of human immunoglobulin G: The energy landscape analysis of a hot spot at the intermolecular interface. Proteins 2002, 48, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattapally, S.; Singh, M.; Murthy, K.S.; Asthana, S.; Banerjee, S.K. Computational modeling suggests impaired interactions between NKX2.5 and GATA4 in individuals carrying a novel pathogenic D16N NKX2.5 mutation. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13713–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almond, B.D.; Dean, D.H. Structural stability of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin homolog-scanning mutants determined by susceptibility to proteases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Elkayam, T.; Wolfson, H.; Nussinov, R. Protein-protein interactions: Structurally conserved residues distinguish between binding sites and exposed protein surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5772–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, J.; Nussinov, R.; Ma, B. Local and global anatomy of antibody-protein antigen recognition. J. Mol. Recognit. 2018, 31, e2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.-P.; Lee, K.H.; Jian, J.-W.; Yang, A.-S. Origins of specificity and affinity in antibody–protein interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2656–E2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Bandelac, G.; Volgina, A.; Korostoff, J.; DiRienzo, J.M. Role of aromatic amino acids in receptor binding activity and subunit assembly of the cytolethal distending toxin of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 2812–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton-Witt, J.A.; Bentsen, L.M.; Tweten, R.K. Identification of functional domains of Clostridium septicum alpha toxin. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 14347–14354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singkhamanan, K.; Promdonkoy, B.; Chaisri, U.; Boonserm, P. Identification of amino acids required for receptor binding and toxicity of the Bacillus sphaericus toxin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 303, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhivker, G.M.; Agajanian, S.; Oztas, D.Y.; Gupta, G. Comparative perturbation-based modeling of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binding with host receptor and neutralizing antibodies: Structurally adaptable allosteric communication hotspots define spike sites targeted by global circulating mutations. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1459–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamwiriyasati, N.; Sakdee, S.; Chuankhayan, P.; Katzenmeier, G.; Chen, C.-J.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of a full-length active form of the Cry4Ba toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2010, 66, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwimol, W.; Aroonkesorn, A.; Sakdee, S.; Kanchanawarin, C.; Uchihashi, T.; Ando, T.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Potential prepore trimer formation by the Bacillus thuringiensis mosquito-specific toxin: Molecular insights into a critical prerequisite of membrane-bound monomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20793–20803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thammasittirong, A.; Thammasittirong, S.N.-R. Aromatic Residues on the Side Surface of Cry4Ba-Domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Function in Binding to Their Counterpart Residues on the Aedes aegypti Alkaline Phosphatase Receptor. Toxins 2023, 15, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020114
Thammasittirong A, Thammasittirong SN-R. Aromatic Residues on the Side Surface of Cry4Ba-Domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Function in Binding to Their Counterpart Residues on the Aedes aegypti Alkaline Phosphatase Receptor. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020114
Chicago/Turabian StyleThammasittirong, Anon, and Sutticha Na-Ranong Thammasittirong. 2023. "Aromatic Residues on the Side Surface of Cry4Ba-Domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Function in Binding to Their Counterpart Residues on the Aedes aegypti Alkaline Phosphatase Receptor" Toxins 15, no. 2: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020114
APA StyleThammasittirong, A., & Thammasittirong, S. N.-R. (2023). Aromatic Residues on the Side Surface of Cry4Ba-Domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Function in Binding to Their Counterpart Residues on the Aedes aegypti Alkaline Phosphatase Receptor. Toxins, 15(2), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020114




