Discovery of the Nicotinic Receptor Toxin Anabaseine in a Polystiliferan Nemertean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
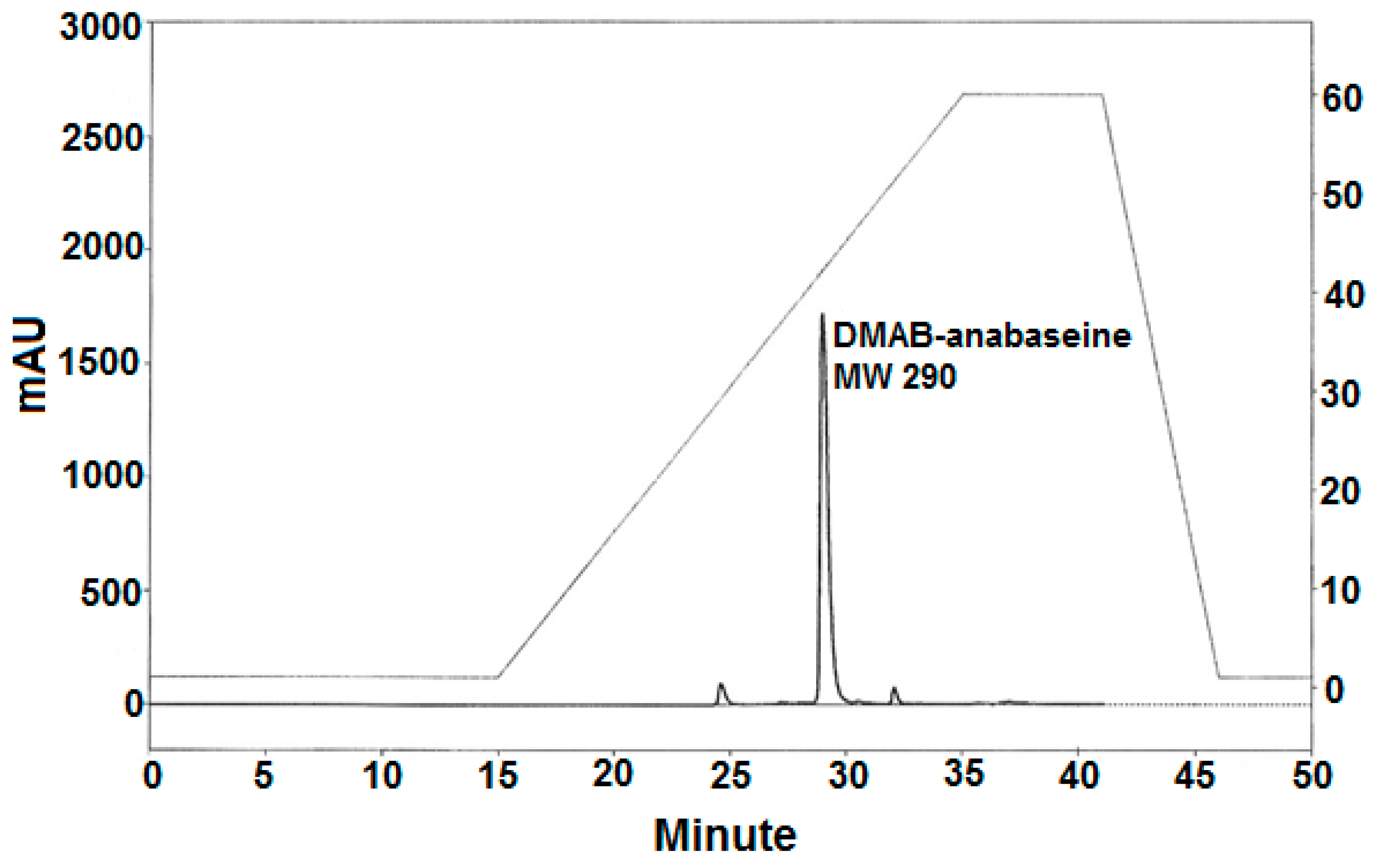
2.1. Anabaseine Identification
2.2. Anabaseine Concentrations in Pc Tissues
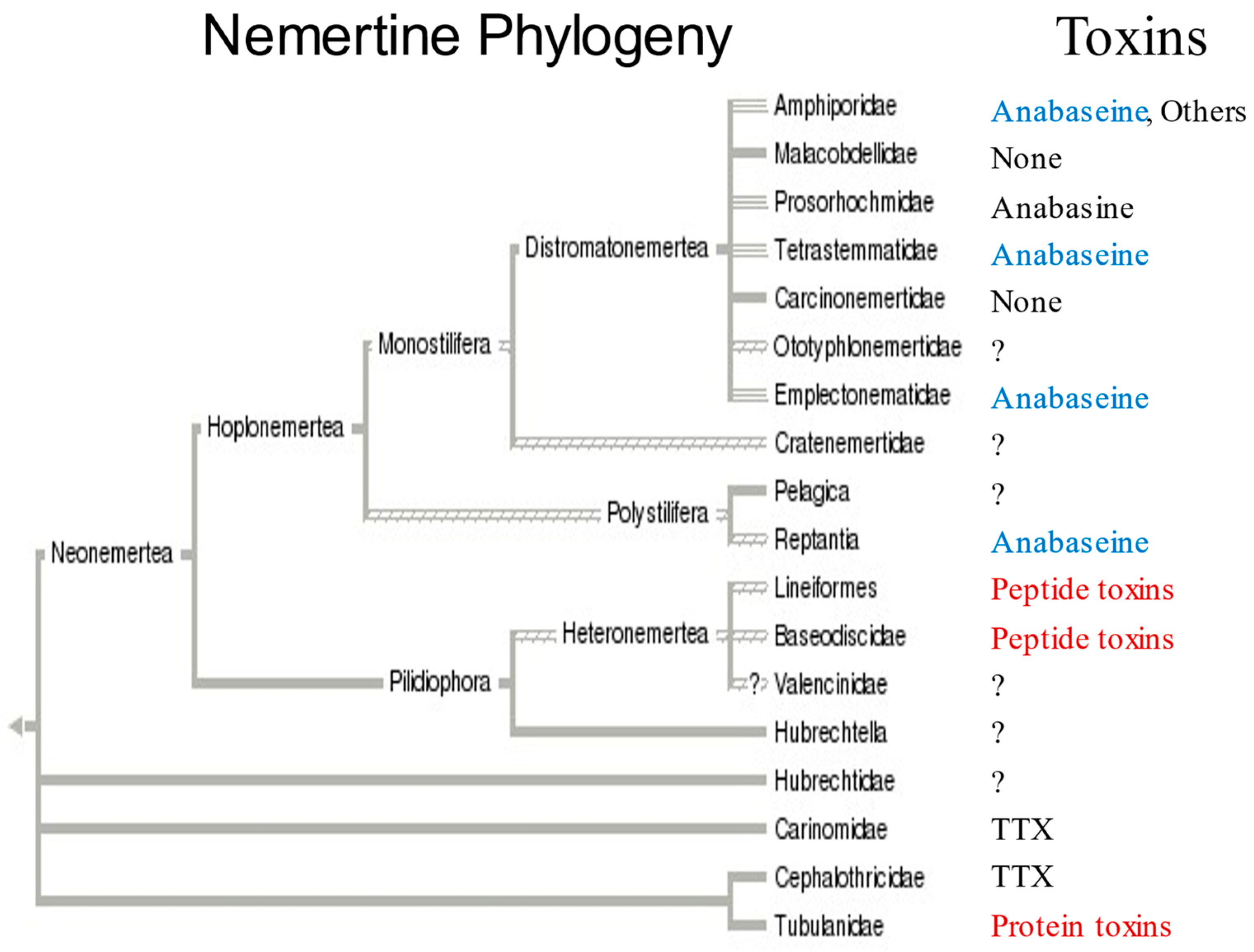
3. Discussion
4. Concluding Remarks
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animal Collection
5.2. Alkaloid Extraction
5.3. Purification of Pc Alkaloids
5.4. Tissue Anabaseine Determinations
5.5. MS and NMR Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pawlowsky, E.N. Giftiere und Ihre Giftigkeit; Verlag von Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1927; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Reisinger, E. Nemertini. Schnurwurmer. Biol. Tiere Dtl. 1926, 17, 7.1–7.24. [Google Scholar]
- Bacq, Z.M. Les poisons des nemertiens. Bull. Cl. Sci. Acad. Roy. Belg. S 1936, 22, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Bacq, Z.M. L”amphiporine” et la “nemertine,” poisons des vers nemertiens. Arch. Int. Physiol. 1937, 44, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H. Amphiporine, an active base from the marine worm Amphiporus lactifloreus. J. Chem. Soc. 1939, 1365, (Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kem, W.R.; Abbott, B.C.; Coates, R.M. Isolation and structure of a hoplonemertine toxin. Toxicon 1971, 9, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kem, W.R. A study of the occurrence of anabaseine in Paranemertes and other nemertines. Toxicon 1971, 9, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kem, W.R. Pyridine alkaloid distribution in the hoplonemertines. Hydrobiologia 1988, 156, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spath, E.; Mamoli, L. Eine neue synthese des D,L-anabasins. Chem. Ber. 1936, 69, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kem, W.R.; Scott, K.N.; Duncan, J.H. Hoplonemertine worms—A new source of pyridine neurotoxins. Experientia 1976, 32, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kem, W.R.; Rocca, J.; Garraffo, H.M.; Spande, T.F.; Daly, J.W.; Soti, F. Synthesis and spectroscopic comparison of the eight methyl-2,3′-bipyridyls and identification of a hoplonemertine alkaloid as 3-methyl-2,3′-bipyridyl. Heterocycles 2009, 79, 1025–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Keshwah, S.; Rouchaud, A.; Kem, W.R. A pharmacological comparison of two isomeric nicotinic receptor agonists: The marine toxin isoanatabine and the tobacco alkaloid anatabine. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kem, W.R.; Soti, F. Amphiporus alkaloid multiplicity implies functional diversity: Initial studies on crustacean pyridyl receptors. Hydrobiologia 2001, 456, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslakova, S.A.; Norenburg, J.L. Phylogenetic study of pelagic nemerteans (Pelagica, Polystilifera.). Hydrobiologia 2001, 456, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, S.; Laumer, C.E.; Junoy, J.; Giribet, G. New insights into the phylogeny, systematics and DNA barcoding of Nemertea. Invertebr. Syst. 2014, 28, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thollesson, M.; Norenburg, J.L. Ribbon worm relationships: A phylogeny of the phylum Nemertea. J. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlin, M. Tree-thinking and nemertean systematics, with a systematization of the Eureptantia. Hydrobiologia 1998, 365, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, E.M. On Paradrepanophorus crassus (Quatr.), a nemertean worm new to the British fauna. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1935, 15, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, C.D.; Little, C.; Stirling, P.; Pilling, G.; Dlouhy-Massengale, B. Lusitanian nemertean species in Lough Hyne Marine Reserve: Paradrepanophorus crassus and Punnettia splendida. Mar. Biodiv. Rec. 2013, 6, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrra-Bachiller, A.; Fernandez-Alvarez, F.A.; Junoy, J. A Taxonomic catalogue of the nemerteans (Phylum Nemertea) of Spain and Portugal. Zool. Sci. 2015, 32, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoltewicz, J.A.; Bloom, L.B.; Kem, W.R. Quantitative determination of the ring-chain hydrolysis equilibrium constant for anabaseine and related tobacco alkaloids. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 4462–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrud, K.; Xing, H.; Gabrielsen, B.; Bloom, L.; Mahnir, V.; Lee, S.; Green, B.T.; Lindstrom, J.; Kem, W.R. Investigation of the possible pharmacologically active forms of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist anabaseine. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kem, W.R. A Chemical Investigation of Nemertine Toxins. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 1969; pp. 1–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kem, W.R. Purification and characterization of a new family of polypeptide neurotoxins from the heteronemertine Cerebratulus lacteus (Leidy). J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 4184–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kem, W.R.; Blumenthal, K.M. Purification and characterization of the cytolytic Cerebratulus A toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 5752–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsson, E.; Andersson, H.S.; Strand, M.; Peigneur, S.; Eriksson, C.; Loden, H.; Shariatgorji, M.; Andren, P.E.; Lebbe, E.K.M.; Rosengren, K.J.; et al. Peptide ion channel toxins from the bootlace worm, the longest animal on earth. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göransson, U.; Jacobsson, E.; Strand, M.; Andersson, H.S. The toxins of nemertean worms. Toxins 2019, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, K.; Higashiyama, M.; Ito, K.; Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin in two species of ribbon worm (Nemertini), Lineus fuscoviridis and Tubulanus punctatus. Toxicon 1988, 26, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.E.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin and related substances in a ribbon worm Cephalothrix linearis (Nemertean). Toxicon 1990, 28, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, S.A.; Cloney, R.A. The stylet apparatus of the nemertean Paranemertes peregrina; Its ultrastructure and role in prey capture. Zoomorphology 1981, 87, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, S.A.; Cloney, R.A. Stylet formation in nemerteans. Biol. Bull. 1982, 162, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, S.A.; Weiner, S. Amorphous calcium phosphate in the stylets produced by a marine worm (Nemertea). Experientia 1985, 41, 1557–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.J. Status of the nemertea as prey in marine ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2001, 456, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, R.J.; Roe, P.; Norenburg, J.L. Dietary immunoassay of pelagic nemerteans by use of cross-reacting polyclonal antibodies: Preliminary findings. Hydrobiologia 1998, 365, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| H Position | Number | Chemical Shift 1 | Multiplicity 2 | Coupling, SYN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | SYN | NP = SYN | J, Herz | ||
| 2’ | 1 | 8.74 | 8.73 | dd | 2.3, 0.8 |
| 4’ | 1 | 7.81 | 7.81 | dt | 7.8, 1.9 |
| 5’ | 1 | 7.32 | 7.32 | ddd | 7.8, 4.9, 0.8 |
| 6’ | 1 | 8.62 | 8.62 | dd | 4.9, 1.7 |
| 4 | 2 | 2.87 | 2.87 | td | 6.7, 1.8 |
| 5 | 2 | 1.83 | 1.83 | qnt | 6.0 |
| 6 | 2 | 3.82 | 3.83 | t | 5.5 |
| 7 | 1 | 6.55 | 6.54 | br t | 1.7 |
| 9&12 | 2 | 7.23 | 7.24 | m~brd | 8.9 |
| 10&14 | 2 | 6.68 | 6.67 | m~brd | 8.9 |
| 11-N(CH3)2 | 6 | 2.99 | 2.99 | s | _ |
| Tissue | Paradrepanophoros crassus (Polystiliferan) | Paranemertes peregrina (Monostiliferan) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Part | [Ae] 1 µg/g | Fr Wt 2 g | Total Ae % | [Ae] µg/g | Fr Wt g | Total Ae % |
| Body (-Prob.) | 888 | 2.656 | 97.7 | 2420 | 0.214 | 69 |
| Anterior Prob | 245 | 0.196 | 2.00 | 10,800 | 0.0182 | 27 |
| Median Prob | 44.4 | 0.027 | 0.05 | 7.2 | 0.003 | 0.76 |
| Posterior Prob | 288 | 0.025 | 0.30 | 3.2 | 0.0063 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kem, W.R.; Rocca, J.R.; Johnson, J.V.; Junoy, J. Discovery of the Nicotinic Receptor Toxin Anabaseine in a Polystiliferan Nemertean. Toxins 2023, 15, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010046
Kem WR, Rocca JR, Johnson JV, Junoy J. Discovery of the Nicotinic Receptor Toxin Anabaseine in a Polystiliferan Nemertean. Toxins. 2023; 15(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleKem, William R., James R. Rocca, Jodie V. Johnson, and Juan Junoy. 2023. "Discovery of the Nicotinic Receptor Toxin Anabaseine in a Polystiliferan Nemertean" Toxins 15, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010046
APA StyleKem, W. R., Rocca, J. R., Johnson, J. V., & Junoy, J. (2023). Discovery of the Nicotinic Receptor Toxin Anabaseine in a Polystiliferan Nemertean. Toxins, 15(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15010046





