Clinical Implications of Difference in Antigenicity of Different Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Preparations: Clinical Take-Home Messages from Our Research Pool and Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
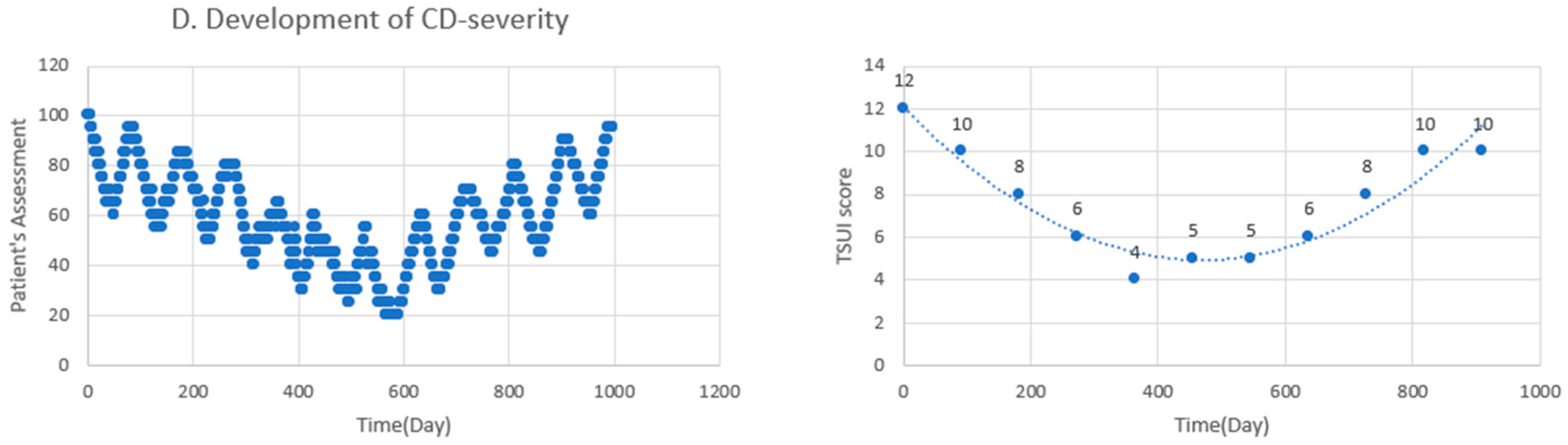
2.1. Clinical Hints for the Presence of NABs in an Individual Patient
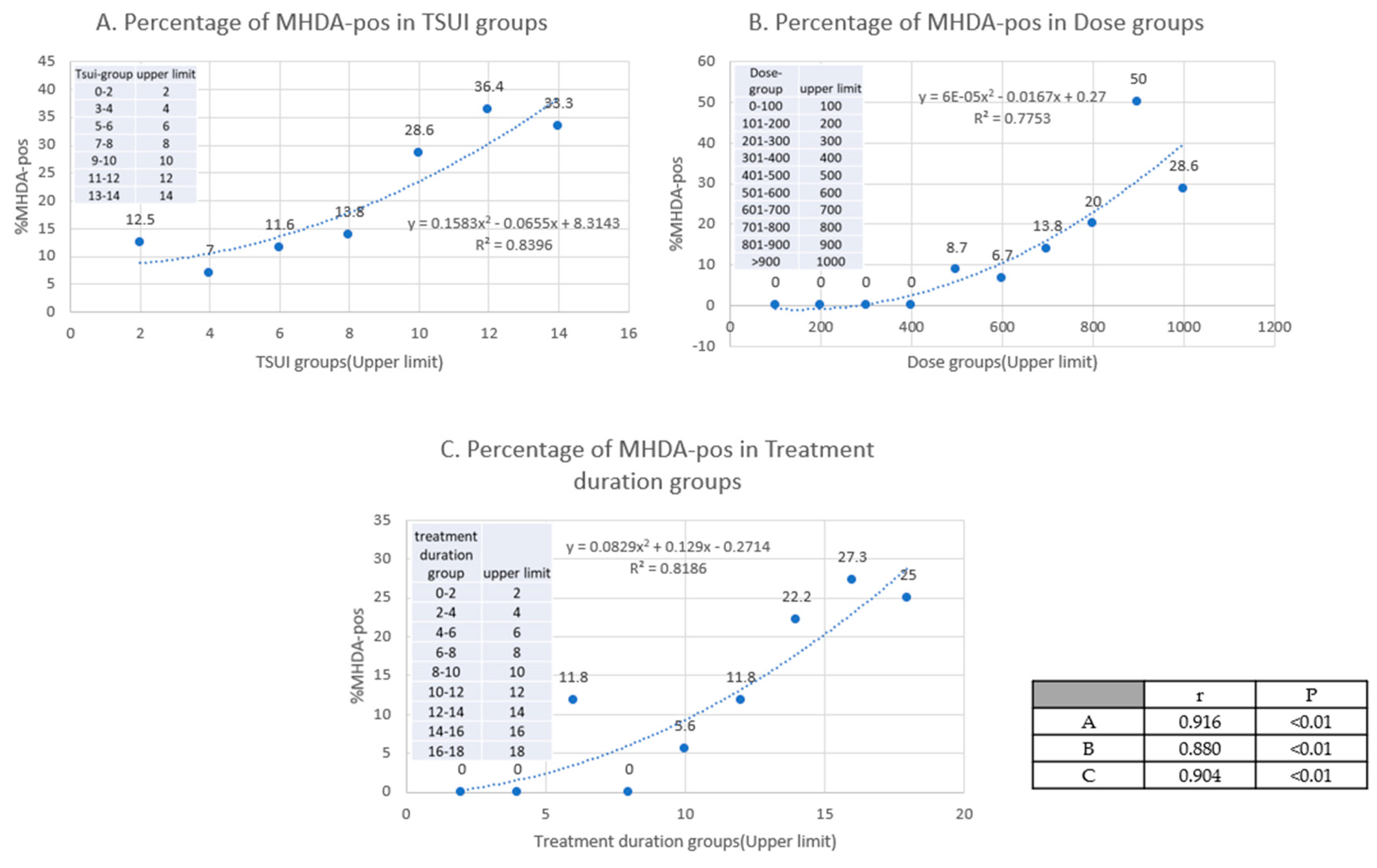
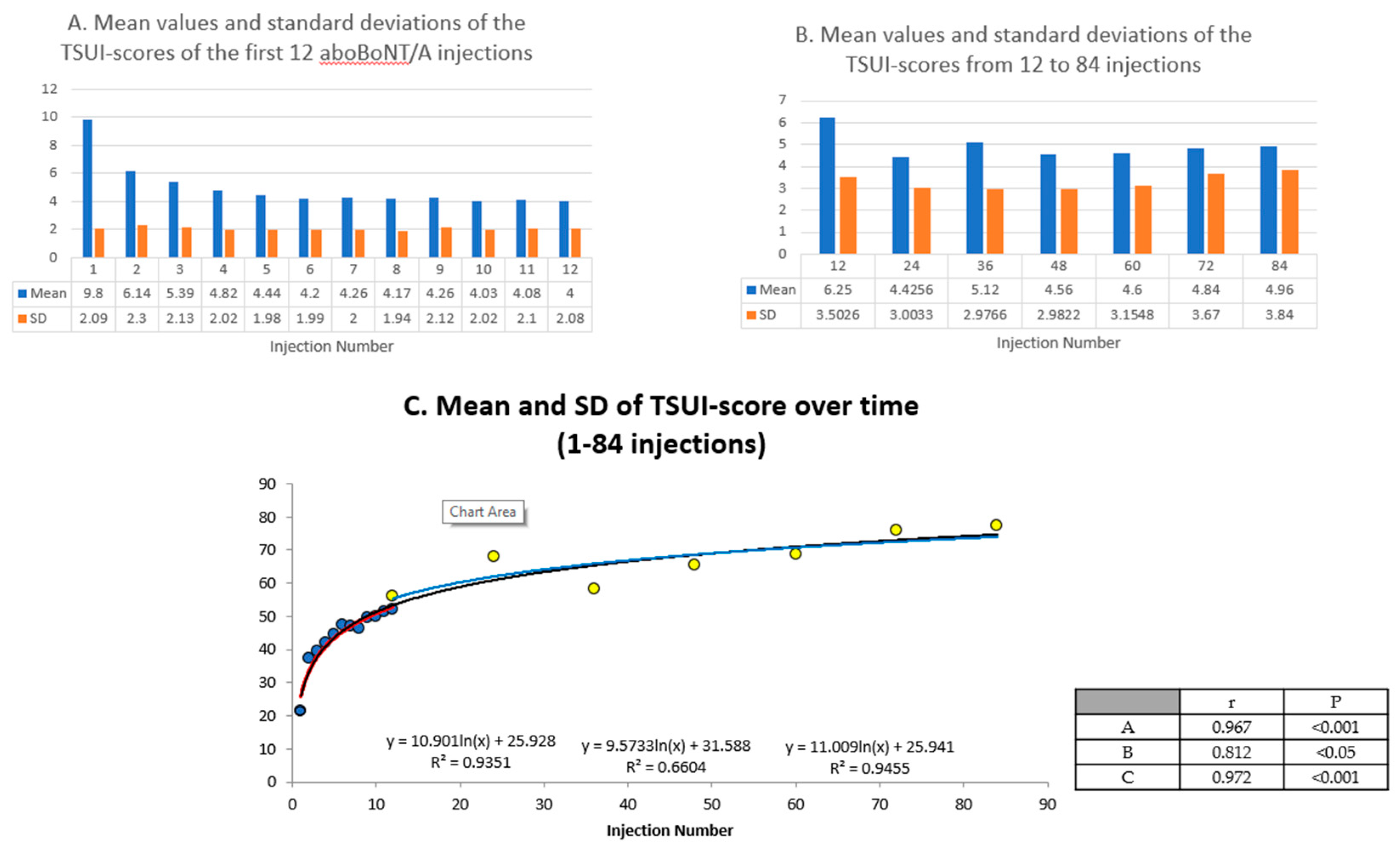
2.2. Clinical Hints for the Presence of NAB Positive Patients in a Cohort of Patients
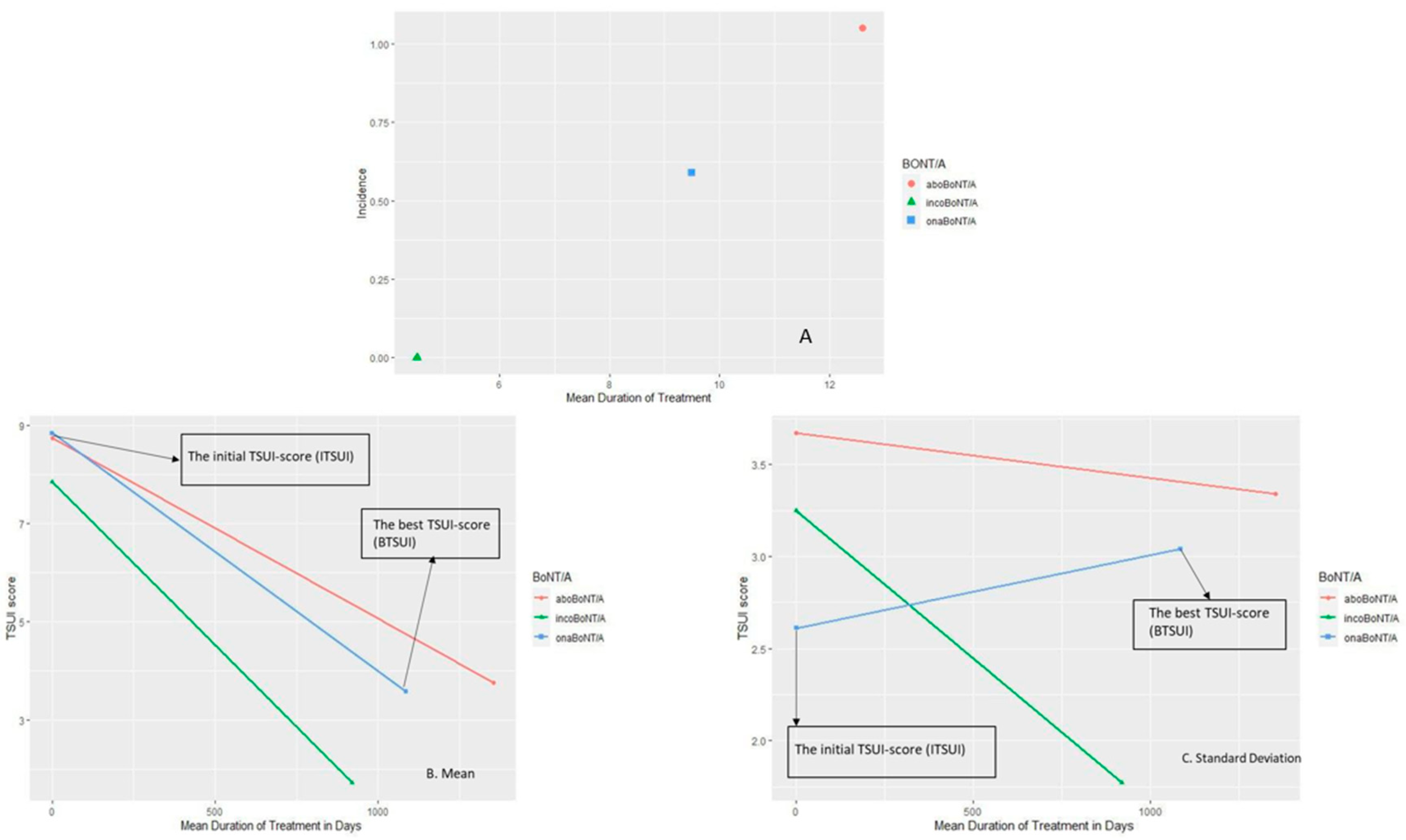
2.3. Incidence and Prevalence of NAB-Induction Is Different for the Three BoNT/A Preparations
2.4. Best Outcome Is Different for the Three BoNT/A Preparations
3. Discussion
3.1. Clinical Hints for the Presence of NABs in an Individual Patient
3.2. Clinical Hints for the Presence of NABs in a Cohort
3.3. The Influence of Protein Load of a BoNT/A Preparation on NAB Induction
3.4. Best Outcome Is Different between the Three BoNT/A Preparations
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. The Cross-Sectional Study of 212 CD Patients
5.2. The Cross-Sectional Study of STF-CD Patients in Comparison to Patients under Monotherapy with IncoBoNT/A
5.3. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BoNT/A | botulinum neurotoxin type A |
| CD | cervical dystonia |
| NAB | neutralizing antibody |
| aboBoNT/A | abobotulinum |
| onaBoNT/A | onabotulinumtoxin |
| incoBoNT/A | incobotulinumtoxin |
| TSUI score | clinical score for evaluating cervical dystonia |
| MU | mouse unit |
| uDU | unified dose unit |
| AB | antibody |
| PSTF | partial secondary treatment failure |
| CSTF | complete secondary treatment failure |
| MHDA | the mouse hemidiaphragm test |
| MV | mean value |
| SD | standard deviation |
| BTSUI | best outcome or best TSUI score |
| ITSUI | initial TSUI score |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| VAS | visual analogue scale |
| SWI | switchers |
| CC group | patients treated with a preparation containing complex proteins (ona- + abo group) |
| CF group | patients treated with preparation without complex proteins (inco group) |
| Special Abbreviations | |
| First study: | |
| ABO group | patients on aboBoNT/A monotherapy |
| INCO group | patients on incoBoNT/A monotherapy |
| ONA group | patients on onaBoNT/A monotherapy |
| Second study: | |
| abo group | patients with switch from aboBoNT/A to incoBoNT/A |
| ona group | patients with switch from onaBoNT/A to incoBoNT/A |
| inco group | patients on incoBoNT/A monotherapy |
References
- Simpson, D.M.; Hallett, M.; Ashman, E.J.; Comella, C.L.; Green, M.W.; Gronseth, G.S.; Armstrong, M.J.; Gloss, D.; Potrebic, S.; Jankovic, J.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 86, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefter, H.; Brauns, R.; Ürer, B.; Rosenthal, D.; Albrecht, P. Effective long-term treatment with incobotulinumtoxin (Xeomin®) without neutralizing antibody induction: A monocentric, cross-sectional study. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D. Clinical presentation and management of antibody-induced failure of botulinum toxin therapy. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19 (Suppl. 8), S92–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefter, H.; Spiess, C.; Rosenthal, D. Very early reduction in efficacy of botulinum toxin therapy for cervical dystonia in patients with subsequent secondary treatment failure: A retrospective analysis. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Mühlenhoff, C.; Benecke, R.; Dressler, D.; Mix, E.; Alt, J.; Matthias, W.; Dudesek, A.; Storch, A.; Kamm, C. Frequency and risk factors of antibody-induced secondary failure of botulinum neurotoxin therapy. Neurology 2020, 94, e2109–e2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, P.; Fahn, S.; Diamond, B. Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Mov. Disord. 1994, 9, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Schwartz, K. Response and immunoresistance to botulinum toxin injections. Neurology 1995, 45, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefter, H.; Rosenthal, D.; Moll, M. High Botulinum Toxin-Neutralizing Antibody Prevalence under Long-Term Cervical Dystonia Treatment. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2016, 3, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, N.I.; Vuong, K.D.; Jankovic, J. Long-term botulinum toxin efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Buhr, N.; Bigalke, H.; Krampfl, K.; Dengler, R.; Kollewe, K. A long-term follow-up of botulinum toxin A in cervical dystonia. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göschel, H.; Wohlfarth, K.; Frevert, J.; Dengler, R.; Bigalke, H. Botulinum A toxin therapy: Neutralizing and nonneutralizing antibodies—therapeutic consequences. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 147, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefter, H.; Rosenthal, D.; Bigalke, H.; Moll, M. Clinical relevance of neutralizing antibodies in botulinum toxin long-term treated still-responding patients with cervical dystonia. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419892078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Bigalke, H.; Kopp, B.; Jim, L.; Dressler, D. Comparing lanbotulinumtoxinA (Hengli®) with onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®) and incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) in the mouse hemidiaphragm assay. Neurol. Preclin. Neurol. Studie. 2019, 126, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.R. Preclinical update on BOTOX® (botulinum toxin type A)-purified neurotoxin complex relative to other botulinurn neurotoxin preparations. Eur. J. Neurol. 1999, 6 (Suppl. 4), s3–s10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Vuong, K.D.; Ahsan, J. Comparison of efficacy and immunogenicity of original versus current botulinum toxin in cervical dystonia. Neurology 2003, 60, 1186–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F.; Comella, C.L.; Jankovic, J.; Lai, F.; Naumann, M. Long-term treatment with botulinum toxin type A in cervical dystonia has low immunogenicity by mouse protection assay. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.R.; Guyer, B. Botulinum toxin type A and other botulinum toxin serotypes: A comparative review of biochemical and pharmacological actions. Eur. J. Neurol. 2001, 8 (Suppl. 5), 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frevert, J. Content of botulinum neurotoxin in Botox®/Vistabel®, Dysport®/Azzalure®, and Xeomin®/Bocouture®. Drugs R D 2010, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frevert, J. Pharmaceutical, biological, and clinical properties of botulinum neurotoxin type A products. Drugs R D 2015, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, C.; Schümann, F.; Mix, E.; Benecke, R. Secondary antibody-induced treatment failure under therapy with incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®) in a patient with segmental dystonia pretreated with abobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®). J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 350, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefter, H.; Hartmann, C.; Kahlen, U.; Moll, M.; Bigalke, H. Prospective analysis of neutralising antibody titres in secondary non-responders under continuous treatment with a botulinumtoxin type A preparation free of complexing proteins—A single cohort 4-year follow-up study. BMJ Open 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, P.; Jansen, A.; Lee, J.I.; Mollm, M.; Ringelstein, M.; Rosenthal, D.; Bigalke, H.; Aktas, O.; Hartung, H.-S.; Hefter, H. High prevalence of neutralizing antibodies after long-term botulinum neurotoxin therapy. Neurology 2019, 92, e48–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, J.K.; Eisen, A.; Stoessl, A.J.; Calne, S.; Calne, D.B. Double-blind study of botulinum toxin in spasmodic torticollis. Lancet 1986, 2, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, J.; Kanovsky, P.; Ruzicka, E.; Bares, M.; Hortova, H.; Streitova, H.; Jech, R.; Roth, J.; Brenneis, C.; Müller, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a standardised 500 unit dose of Dysport (clostridium botulinum toxin type A haemaglutinin complex) in a heterogeneous cervical dystonia population: Results of a prospective, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kessler, K.R.; Skutta, M.; Benecke, R. Long-term treatment of cervical dystonia with botulinum toxin A: Efficacy, safety, and antibody frequency. German Dystonia Study Group. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, M.; Deitiker, P.R.; Jankovic, J.; Duane, D.D.; Aoki, K.R.; Atassi, M.Z. Human T-cell responses to botulinum neurotoxin. Responses in vitro of lymphocytes from patients with cervical dystonia and/or other movement disorders treated with BoNT/A or BoNT/B. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 240–241, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolimbek, B.Z.; Aoki, K.R.; Steward, L.E.; Jankovic, J.; Atassi, M.Z. Mapping of the regions on the heavy chain of botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A) recognized by antibodies of cervical dystonia patients with immunoresistance to BoNT/A. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atassi, M.Z.; Dolimbek, B.Z.; Jankovic, J.; Steward, L.E.; Aoki, K.R. Regions of botulinum neurotoxin A light chain recognized by human anti-toxin antibodies from cervical dystonia patients immunoresistant to toxin treatment. The antigenic structure of the active toxin recognized by human antibodies. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, O.; Bigalke, H.; Dengler, R.; Wegner, F.; DeGroot, M.; Wohlfarth, K. Neutralizing antibodies and secondary therapy failure after treatment with botulinum toxin type A: Much ado about nothing? Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2009, 32, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.; Leodori, G.; Fernandes, R.M.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Marti, M.J.; Colosimo, C.; Ferreira, J.J. Neutralizing Antibody and Botulinum Toxin Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 29, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blümel, J.; Frevert, J.; Schwaier, A. Comparative antigenicity of three preparations of botulinum neurotoxin type A in the rabbit. Neurotox. Res. 2006, 9, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Contarino, M.F.; Van Den Dool, J.; Balash, Y.; Bhatia, K.; Giladi, N.; Koelman, J.H.; Lokkegaard, A.; Marti, M.J.; Postma, M.; Relja, M.; et al. Clinical Practice: Evidence-Based Recommendations for the Treatment of Cervical Dystonia with Botulinum Toxin. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ürer, B.; Brauns, R.; Samadzadeh, S.; Hefter, H. Effective Long-Term Treatment with Incobotulinum Toxin after Immunoresistance to Abo- or Ona- Botulinum Toxin in Patients with Cervical Dystonia. Eur. Med. J. Neurol. 2020, 8, 52–54, Abstract Review: No:AR9. [Google Scholar]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samadzadeh, S.; Ürer, B.; Brauns, R.; Rosenthal, D.; Lee, J.-I.; Albrecht, P.; Hefter, H. Clinical Implications of Difference in Antigenicity of Different Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Preparations: Clinical Take-Home Messages from Our Research Pool and Literature. Toxins 2020, 12, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080499
Samadzadeh S, Ürer B, Brauns R, Rosenthal D, Lee J-I, Albrecht P, Hefter H. Clinical Implications of Difference in Antigenicity of Different Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Preparations: Clinical Take-Home Messages from Our Research Pool and Literature. Toxins. 2020; 12(8):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080499
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamadzadeh, Sara, Beyza Ürer, Raphaela Brauns, Dietmar Rosenthal, John-Ih Lee, Philipp Albrecht, and Harald Hefter. 2020. "Clinical Implications of Difference in Antigenicity of Different Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Preparations: Clinical Take-Home Messages from Our Research Pool and Literature" Toxins 12, no. 8: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080499
APA StyleSamadzadeh, S., Ürer, B., Brauns, R., Rosenthal, D., Lee, J.-I., Albrecht, P., & Hefter, H. (2020). Clinical Implications of Difference in Antigenicity of Different Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Preparations: Clinical Take-Home Messages from Our Research Pool and Literature. Toxins, 12(8), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080499




