Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
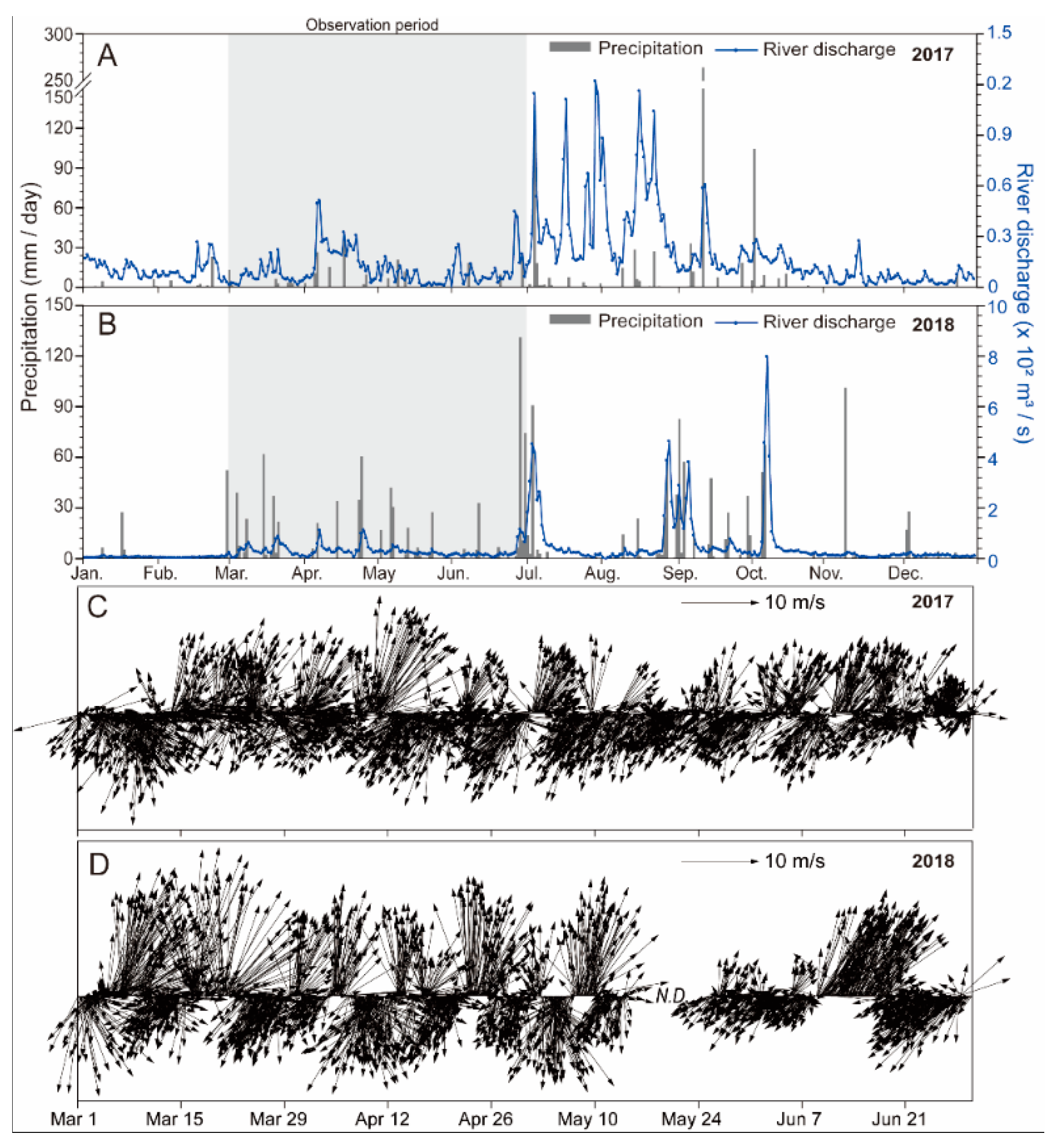
2.1. Wind and Nakdong River Discharges Affecting the Geoje Coast
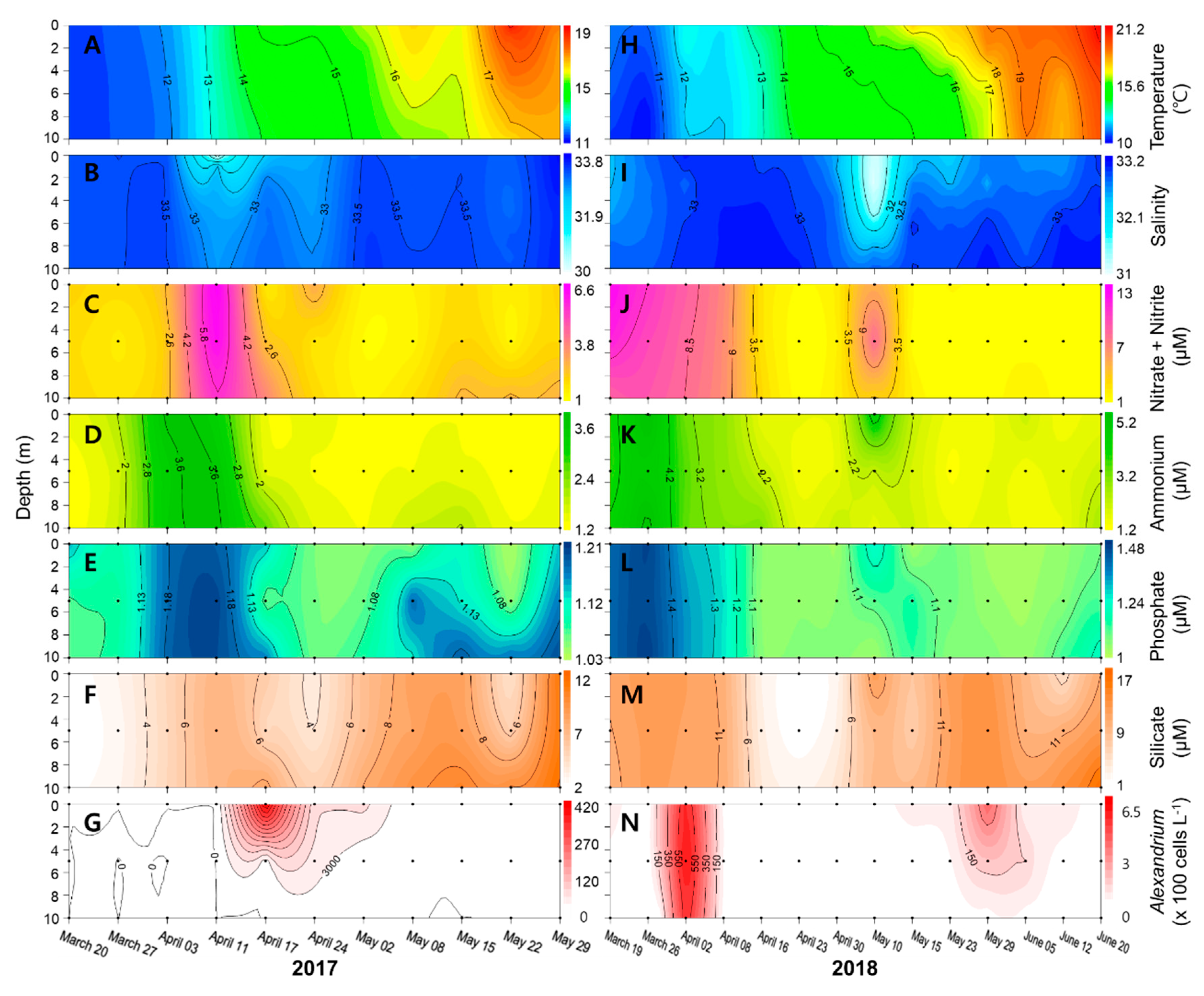
2.2. Physicochemical Factors along the Geoje Coast
2.3. Dynamics of Alexandrium Species
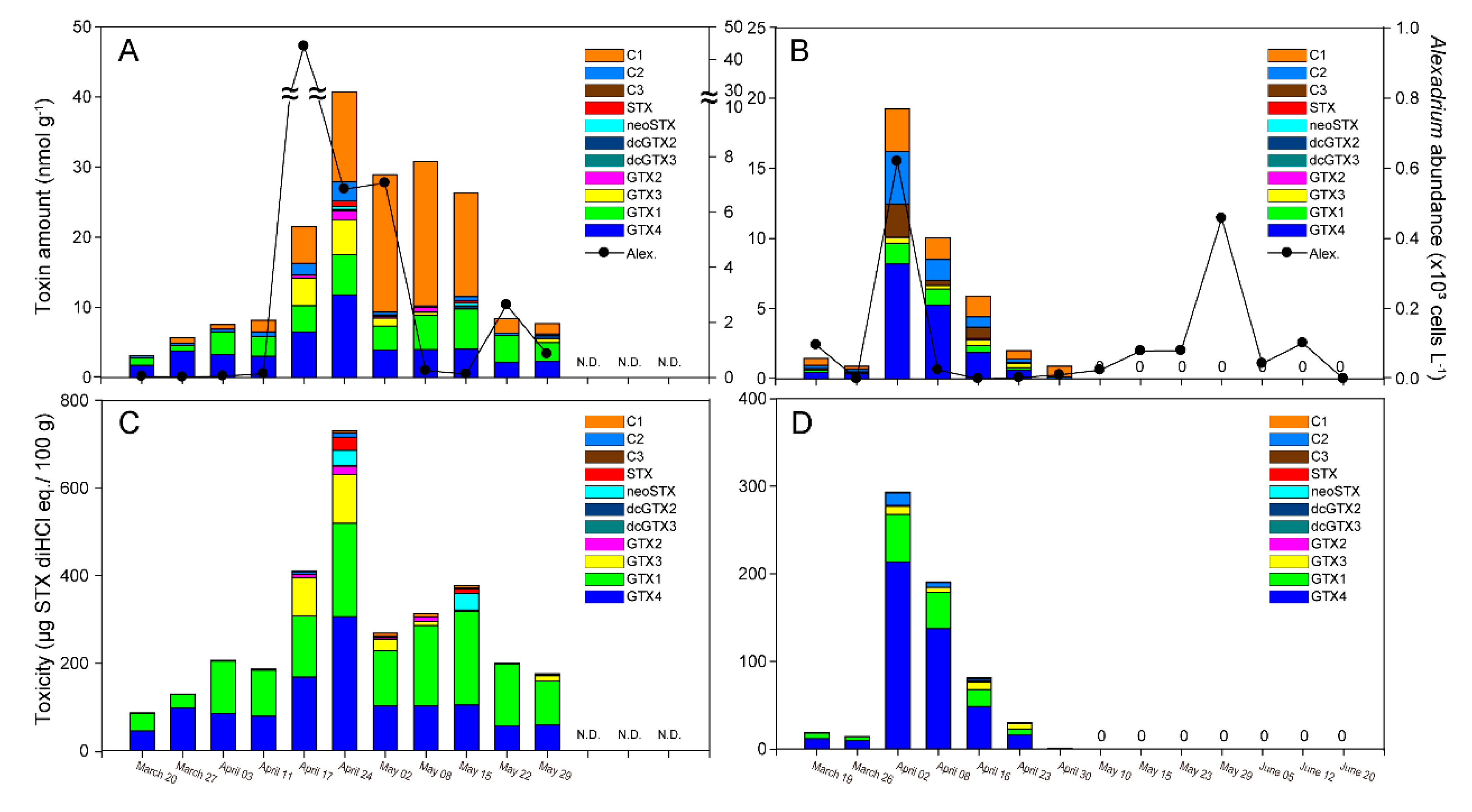
2.4. PSTs in Mussels
3. Discussion
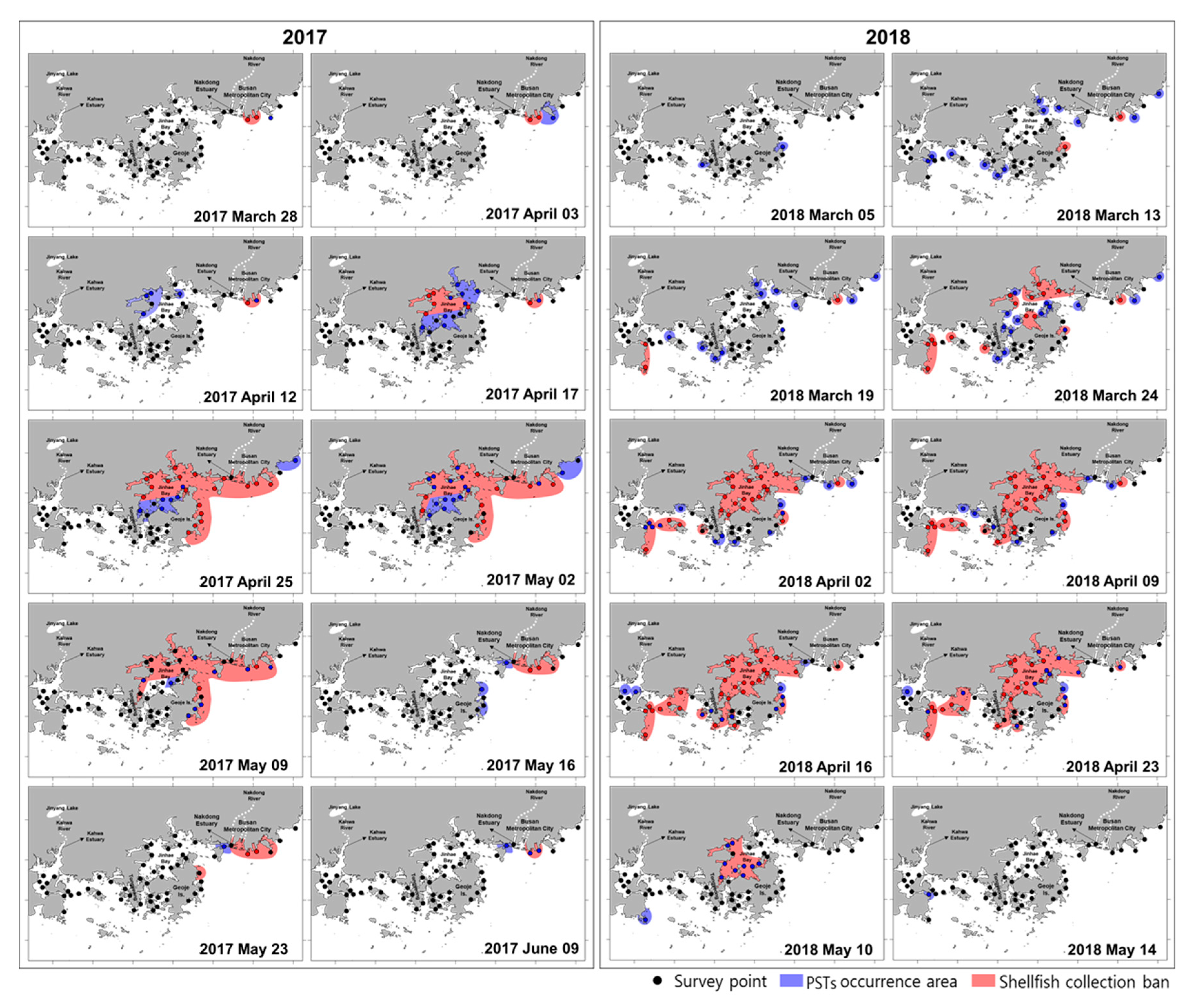
3.1. PSTs Outbreaks and Management in Southern Korean Coastal Waters
3.2. Dynamics of A. Catenella in the Geoje Coast
3.3. PSTs in M. galloprovincialis and A. catenella
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
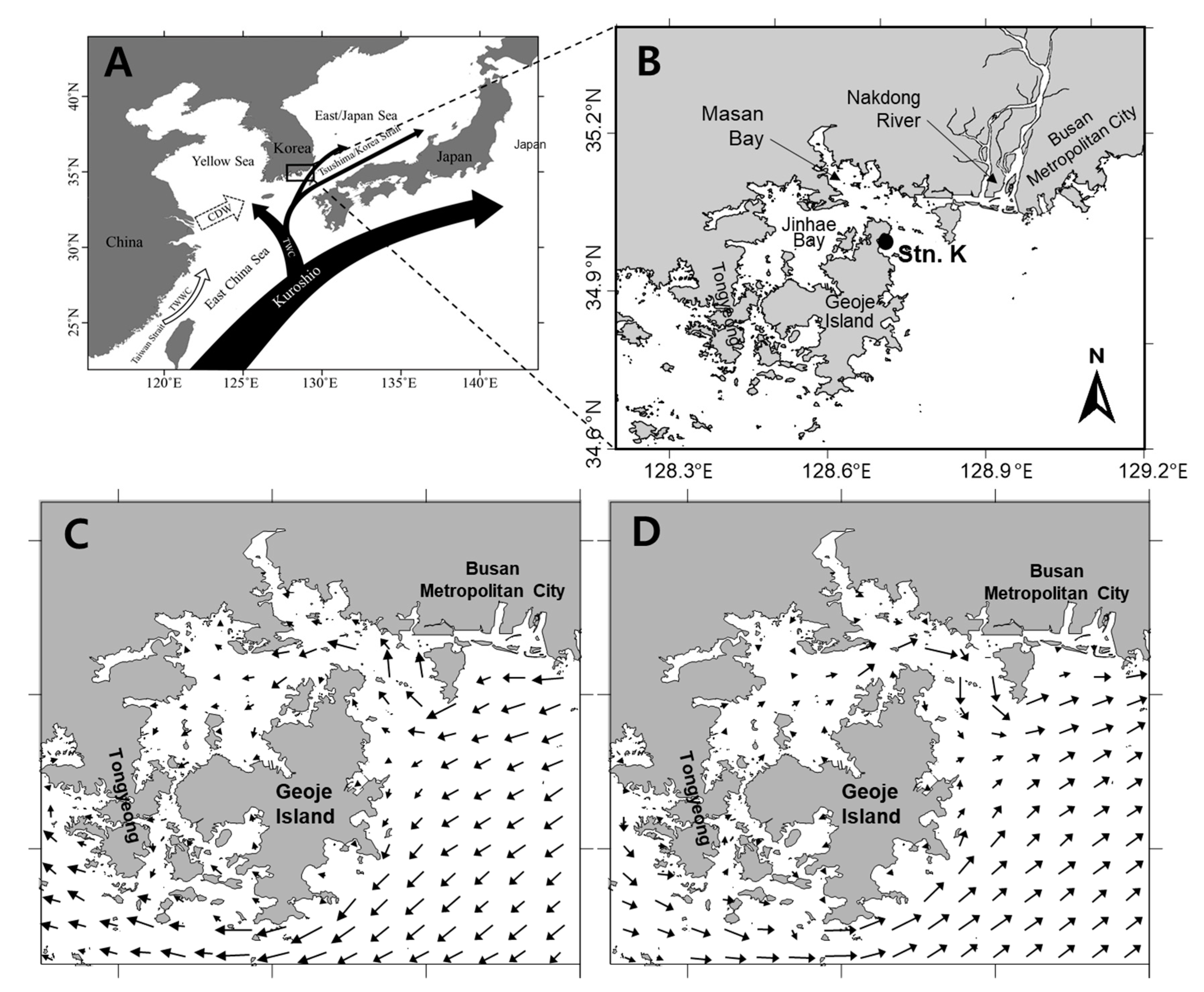
5.1. Study Area
5.2. Field Water Sampling and Analyses
5.3. Mussel and Plankton Sampling for Toxin Analysis
5.4. PSTs Analysis
5.5. Hydrological and Meteorological Environment Data
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Kulis, D.M.; Binder, B.J. Sexuality and cyst formation in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax tamarensis: Cyst yield in batch cultures. J. Phycol. 1984, 20, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, F.J.R.; Fukuyo, Y.; Larsen, J. Taxonomy of harmful dinoflagellates. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; IOC Manuals and Guides No. 33. IOC of UNESCO; Hallegraeff, G.M., Abderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Eds.; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO): Paris, France, 2003; pp. 281–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 1993, 32, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M. Turning back the harmful red tide. Nature 1997, 388, 513–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway, S.E. A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1990, 21, 65–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smayda, T.J. Harmful algal blooms: Their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.S.; Shin, I.S.; Pyeun, J.H.; Park, Y.H. A study on paralytic shellfish poison of sea messel Mytilus edulis. Bull. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 1987, 20, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Chang, D.S. Parlytic shellfish toxins in the mussel, Mytilus edulis, caused the shellfish poisoning accident at Geoje, Korea, in 1996. J. Korean Fish. Soc. 1997, 30, 158–160. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.S.; Jeon, J.K.; Kim, Y.O. Occurrence of dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense, a causative organism of paralytic shellfish posisoning in Chinhae Bay, Korea. J. Plankton. Res. 1992, 14, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Yamasaki, M. Non-selective retention of PSP toxins by the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, I.D.; Shumway, S.E. The effect of a toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on the oxygen uptake of juvenile filter feeding bivalve moolluscs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1993, 106, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Lee, J.H.; Cembella, A.D.; Anderson, D.M. Uptake kinetics of paralytic shellfish toxins from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 63, 117–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Wang, W.X.; Hsieh, D.P.F. Feeding and absorption of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense by two marine bivalves from the South China Sea. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, K.S.; Lim, P.T.; Kon, N.F.; Takata, Y.; Usup, G.; Leaw, C.P. Physiological and transcriptional responses to inorganic nutrition in a tropical Pacific strain of Alexandrium minutum: Implications for the saxitoxin genes and toxin production. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.O.; Choi, K.H.; Han, M.S. Spring bloom of Alexandrium tamarense in Chinhae Bay, Korea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 33, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, Y.O.; Park, M.H.; Han, M.S. Role of cyst germination in the bloom initiation of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae) in Masan Bay, Korea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 29, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.O.; Son, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S. Seasonal changes in abiotic environmental conditions in the Busan coastal region (South Korea) due to the Nakdong River in 2013 and effect of these changes on phytoplankton communities. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, R.; Levasseur, M.; Weise, A.M.; Fauchot, J.; Campbell, P.G.; Weissenboeck, B.J.; Merzouk, A.; Gosselin, M.; Vigneault, B. Growth stimulation of Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae) by humic sustances from the Manicouagan River (Eastern Canada). J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaguchi, H.; Fujiki, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Toda, T. Relationship between the bloom of Noctiluca scintillans and environmental factors in the coastal waters of Sagami Bay, Japan. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Kim, Y.B. Spring phytoplankton community response to an episodic windstorm event in oligotrophic waters offshore from the Ulleungdo and Dokdo islands, Korea. J. Sea Res. 2018, 132, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S.; Lim, Y.K. Variation in phytoplankton community due to an autumn typhoon and wind water turbulence in southern Korean coastal waters. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, L.H.; Pozdnyakov, D. Monitoring of Harmful Algal Blooms; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.J.; Matsuyama, Y.; Nagai, S.; Itakura, S.; Yoon, Y.H.; Yang, H.S. Comparative study on the PSP component and toxicity produced by Alexandrium tamiyavanchii (Dinophyceae) strains occurring in Japanese coastal water. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, K.; Siu, Y.; Maria, L.C.; Chan, D.K.O. Environmental and nutritional factors which regulate population dynamics and toxin production in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Hydrobiologia 1997, 353, 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- MacLean, J.L. Observation on Pyrodinium bahamense, a toxic dinoflagellate in Papua New Guinea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacutan, R.O.; Tabbu, M.Y.; Aujero, E.J.; Icatlo, J.F. Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to Pyrodinium bahamense var. compressa in Mati, Davao Oriental, Phillippines. Mar. Biol. 1985, 87, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamber, J.S.; Magnusson, H.W. Seasonal variation in toxicity of butter clams from selected Alaska beaches. U.S. Fish Wildlife Serv. Spec. Sci. Rep. Fish. 1950, 53, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.S.; Lee, H.O.; Anderson, D.M.; Kim, B.H. Paralytic shellfish toxin production by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum (Chinhae Bay, Korea) in axenic, nutrient-limited chemostat cultures and nutrient-enriched batch cultures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Sullivan, J.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Taylor, F.J.R.; Andersen, R.J.V. Ariation in paralytic shellfish toxin composition within the Protogonyaulax tamaronsis/catenella species complex; red tide dinoflagellates. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1987, 15, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Kanahara, Y.; Yamada, M.; Tatsuno, R.; Yoshikawa, H.; Doi, H.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Contrasting toxin selectivity between the marine pufferfish Takifugu pardalis and the freshwater pufferfish Pao suvattii. Toxins 2019, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, V.; Botana, A.M.; Alvarez, M.; Antelo, A.; Botana, L.M. Liquid Chromatography with a fluorimetric detection method for analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxin based on a porous graphitic carbon column. Toxins 2016, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Shida, Y.; Onoue, Y. Occurrence of carbamoyl-N-hydroxy derivatives of saxitoxin and neosaxitoxin in a xanthid crab Zosimus aeneus. Toxicon 1994, 32, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO); World Health Organization (WHO). Technical Paper on Toxicity Equivalency Factors for Marine Biotoxins Associated with Bivalve Molluscs; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016; p. 108.

| Total Survey | 2017 | 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| Temperature | −0.494 | 0.076 | −0.802 | −0.202 | −0.862 | 0.409 |
| Salinity | −0.133 | −0.816 | −0.197 | −0.941 | 0.091 | −0.179 |
| NOx | 0.882 | 0.210 | 0.421 | 0.801 | 0.982 | 0.029 |
| NH4 | 0.811 | 0.370 | 0.779 | 0.362 | 0.825 | 0.094 |
| PO4 | 0.938 | 0.096 | 0.655 | 0.305 | 0.961 | 0.073 |
| SiO2 | 0.682 | 0.155 | −0.204 | −0.078 | 0.460 | 0.761 |
| Wind speed | 0.220 | 0.240 | 0.285 | 0.125 | 0.475 | −0.666 |
| R. discharge | 0.149 | 0.766 | −0.045 | 0.864 | 0.368 | −0.571 |
| Precipitation | 0.329 | 0.660 | 0.647 | 0.328 | 0.337 | −0.255 |
| Alexandrium | 0.005 | −0.459 | −0.883 | 0.230 | 0.034 | 0.685 |
| Eigenvalue | 4.42 | 1.46 | 4.26 | 2.02 | 4.36 | 2.06 |
| Variability (%) | 44.24 | 14.60 | 42.63 | 20.19 | 43.65 | 20.58 |
| Cumulative (%) | 44.24 | 58.84 | 42.63 | 62.82 | 43.65 | 64.23 |
| Toxin Content | Toxicity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fmol cell−1 | Ratio (%) | μg STX diHCl equivalents cell−1 | Ratio (%) | |
| C2 | 0.33 | 1.54 | 0.0012 | 1.17 |
| GTX2 | 2.90 | 13.37 | 0.0432 | 41.09 |
| GTX1 | 1.46 | 6.71 | 0.0543 | 51.71 |
| C1 | 17.01 | 78.37 | 0.0063 | 6.03 |
| Total | 21.70 | 100 | 0.11 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, S.H.; Choi, J.M.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Jeon, J.-K.; Kim, Y.O. Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season. Toxins 2020, 12, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070442
Baek SH, Choi JM, Lee M, Park BS, Zhang Y, Arakawa O, Takatani T, Jeon J-K, Kim YO. Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season. Toxins. 2020; 12(7):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070442
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Seung Ho, Jung Min Choi, Minji Lee, Bum Soo Park, Yuchengmin Zhang, Osamu Arakawa, Tomohiro Takatani, Joong-Kyun Jeon, and Young Ok Kim. 2020. "Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season" Toxins 12, no. 7: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070442
APA StyleBaek, S. H., Choi, J. M., Lee, M., Park, B. S., Zhang, Y., Arakawa, O., Takatani, T., Jeon, J.-K., & Kim, Y. O. (2020). Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season. Toxins, 12(7), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070442





