Selenium Yeast Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathways in Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
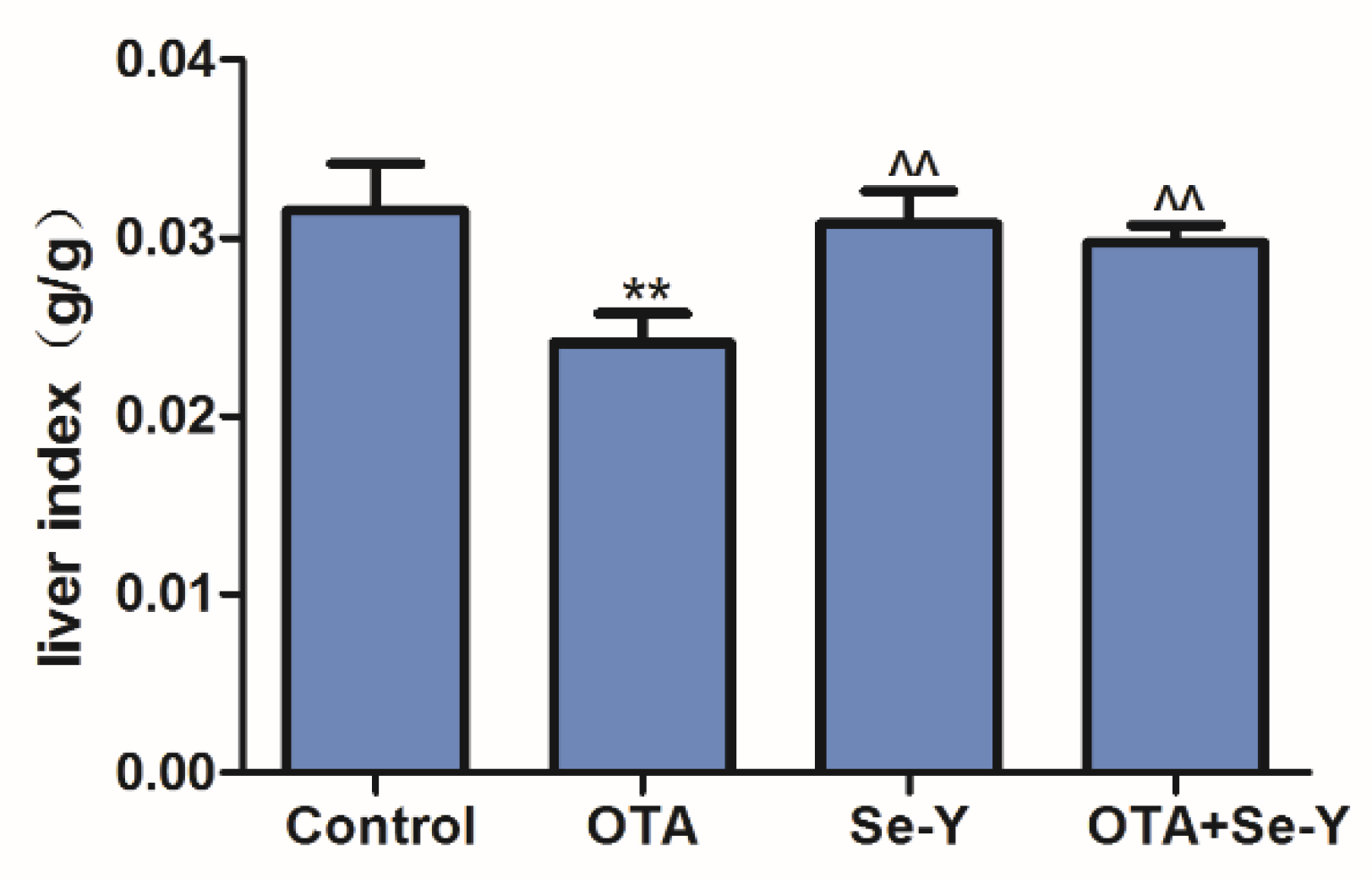
2.1. Effects of Se-Y on OTA-Induced Changes in the Liver Index
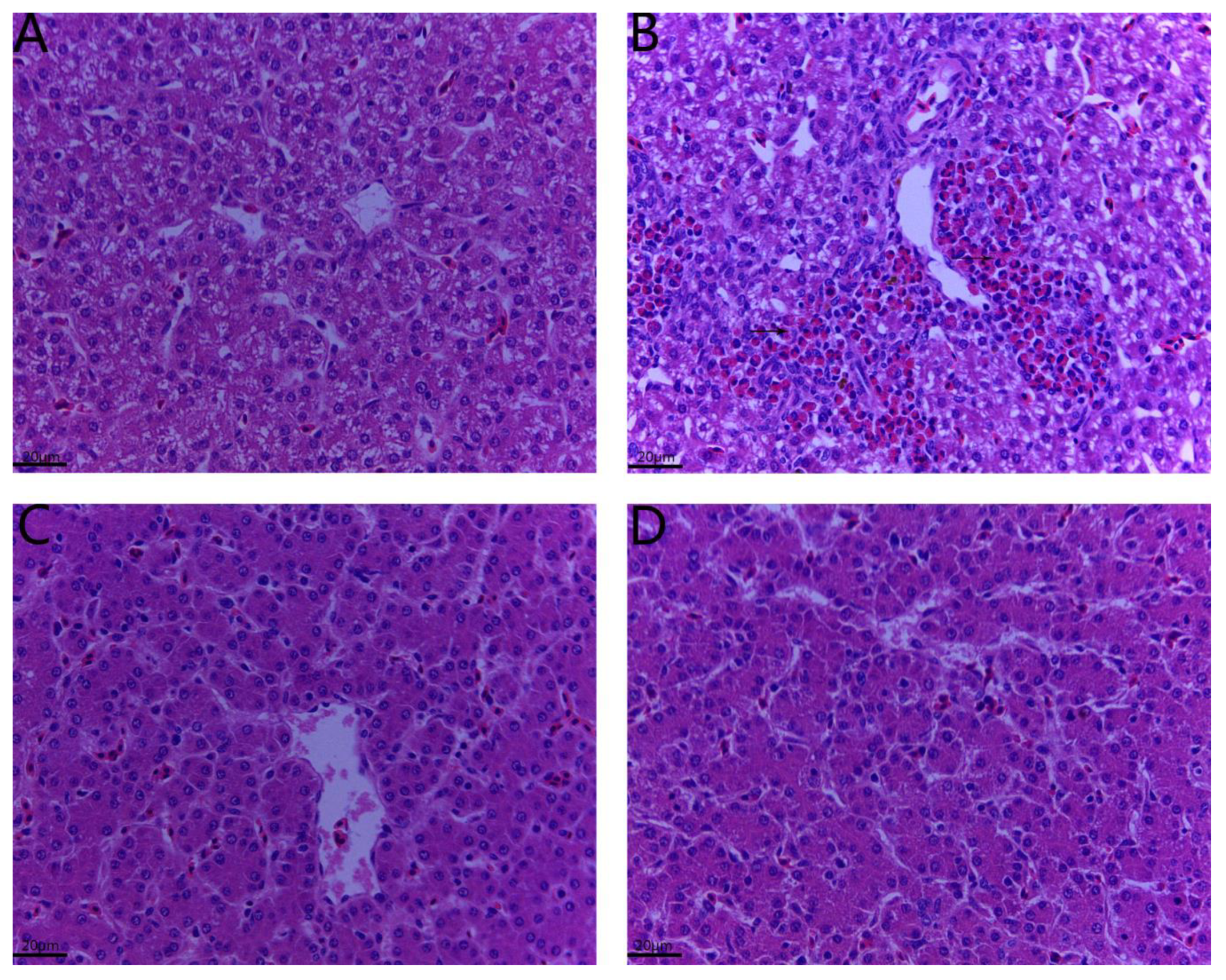
2.2. Histopathological Changes in the Liver
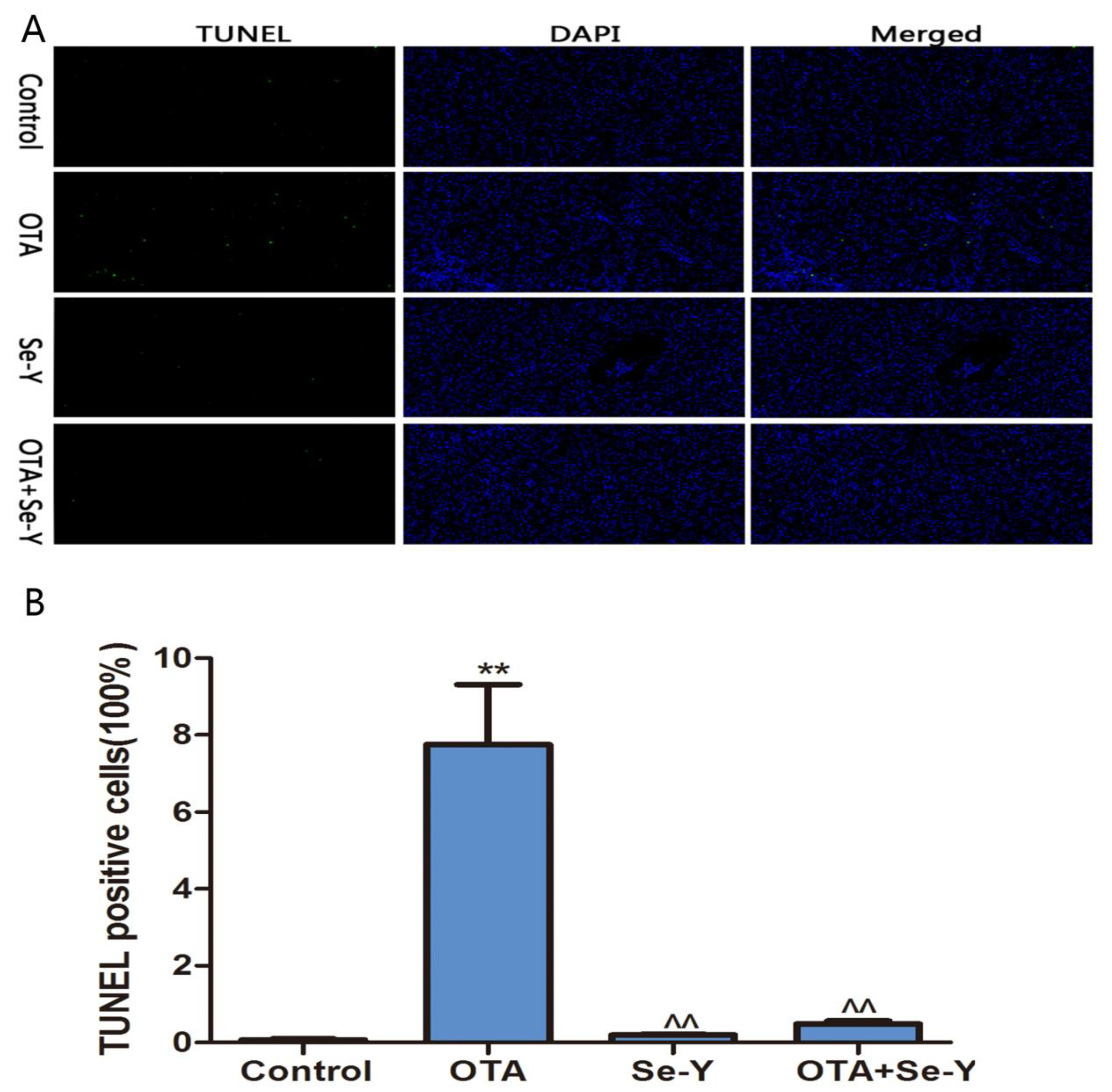
2.3. Analysis of Apoptosis by TUNEL
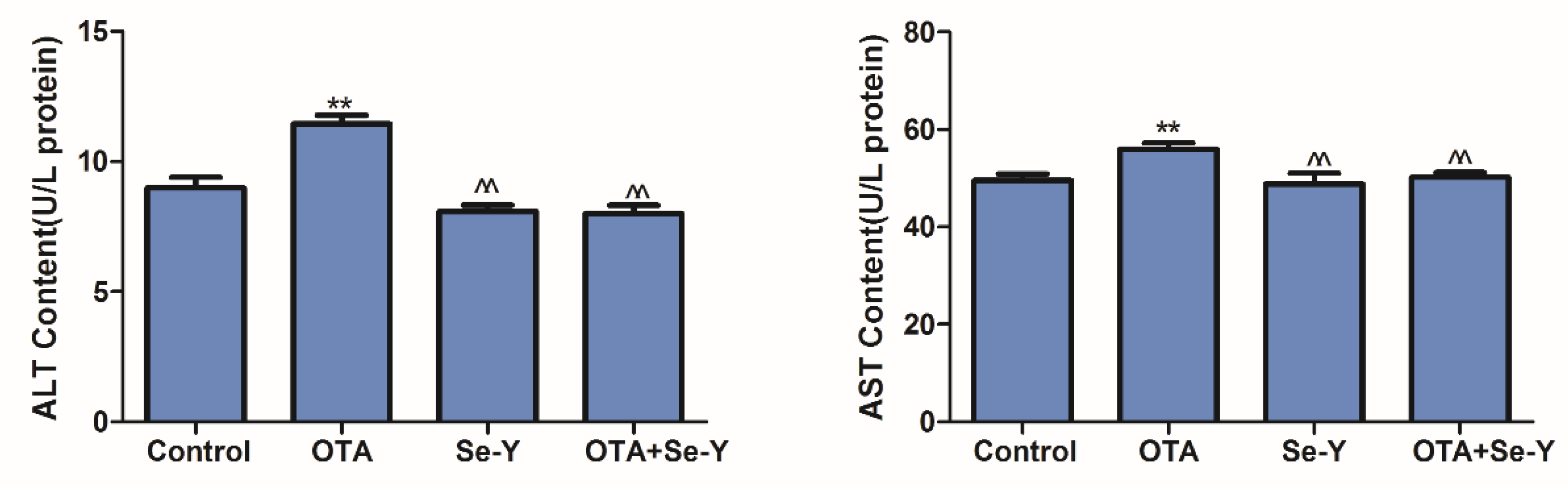
2.4. Effects of Se-Y on OTA-Induced Serum Biochemical Parameters
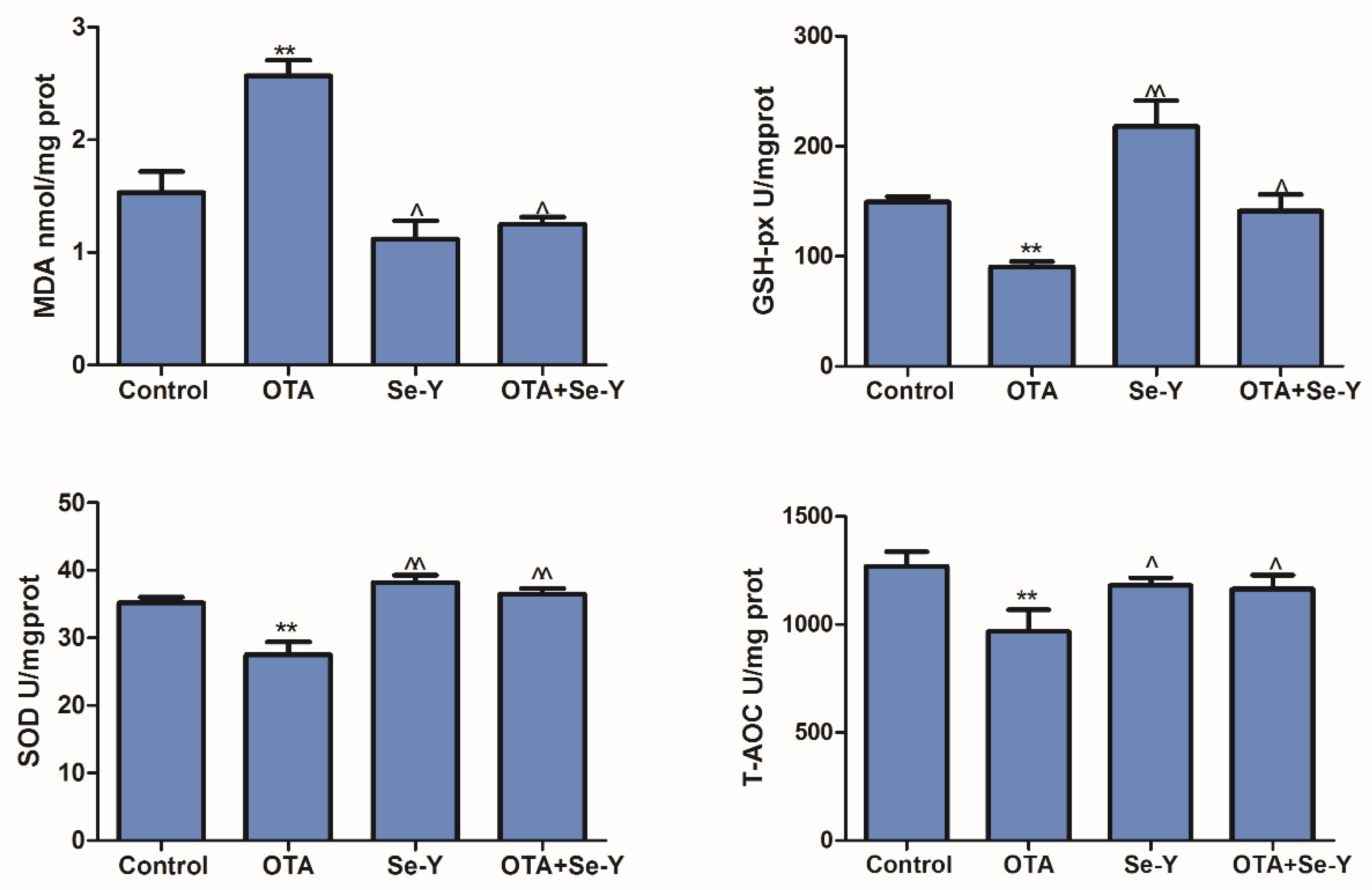
2.5. Effect of Se-Y on OTA-Induced Changes in the Oxidative Parameters
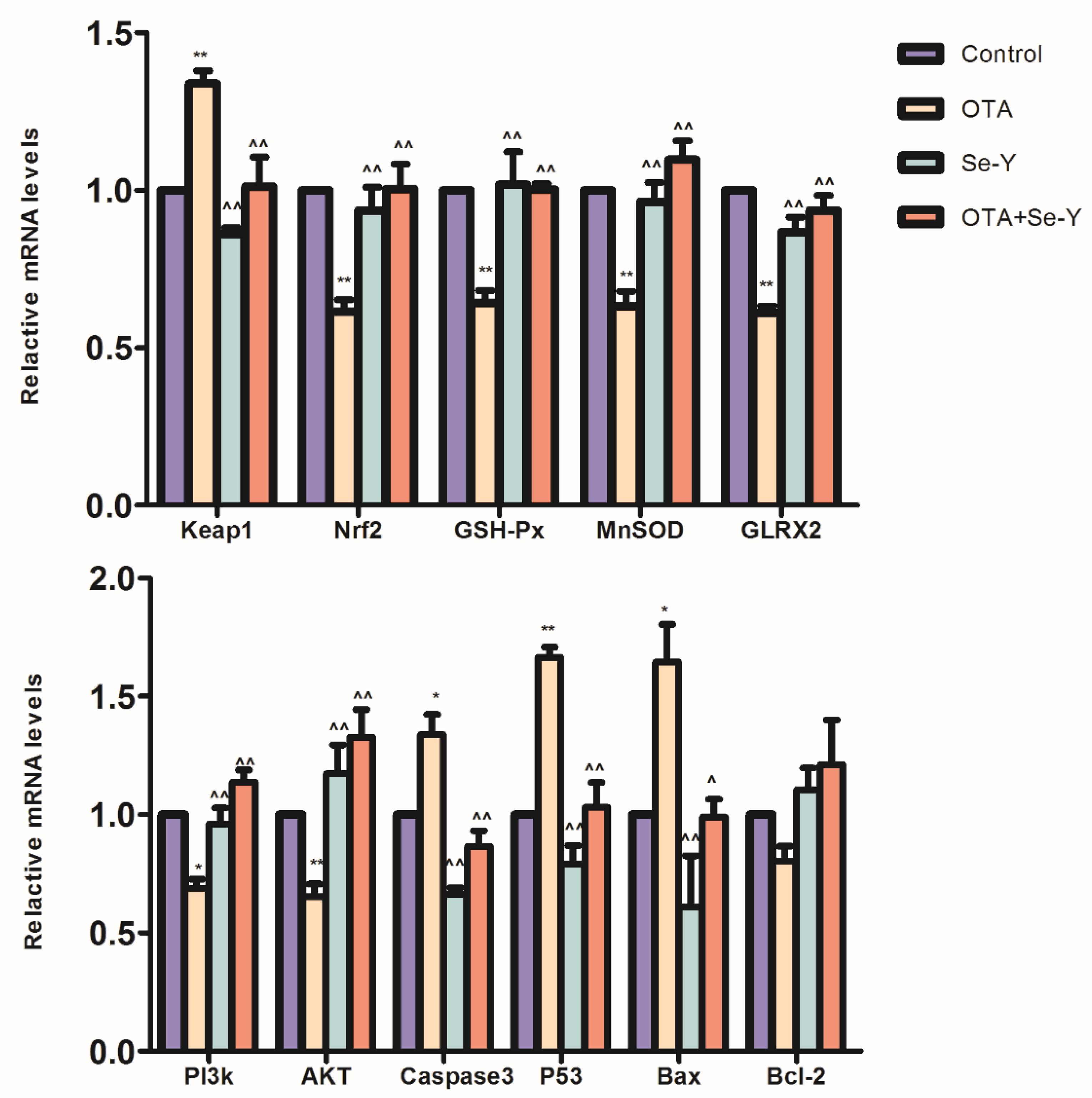
2.6. Nrf2-Keap1 Signaling and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway Gene Expression
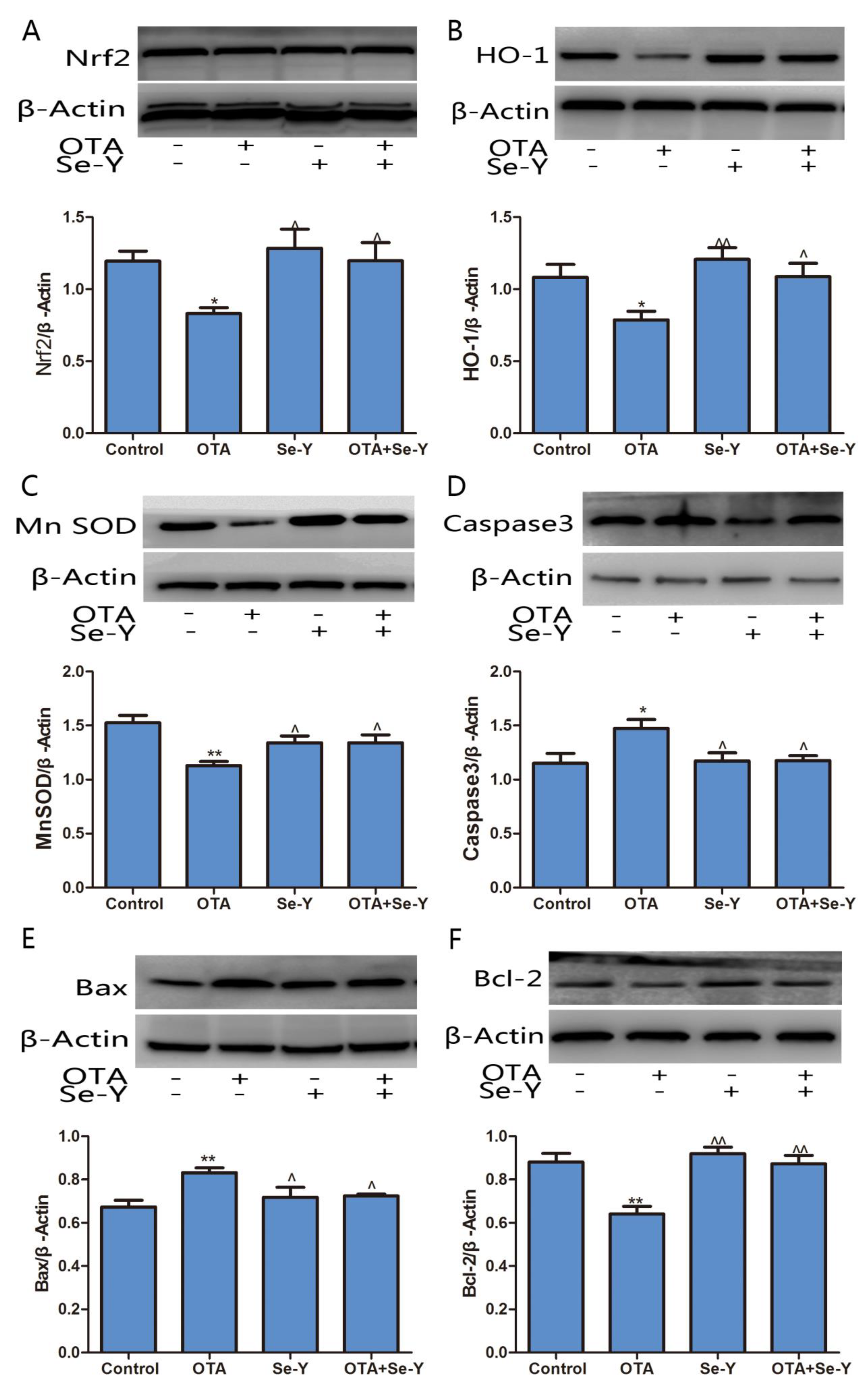
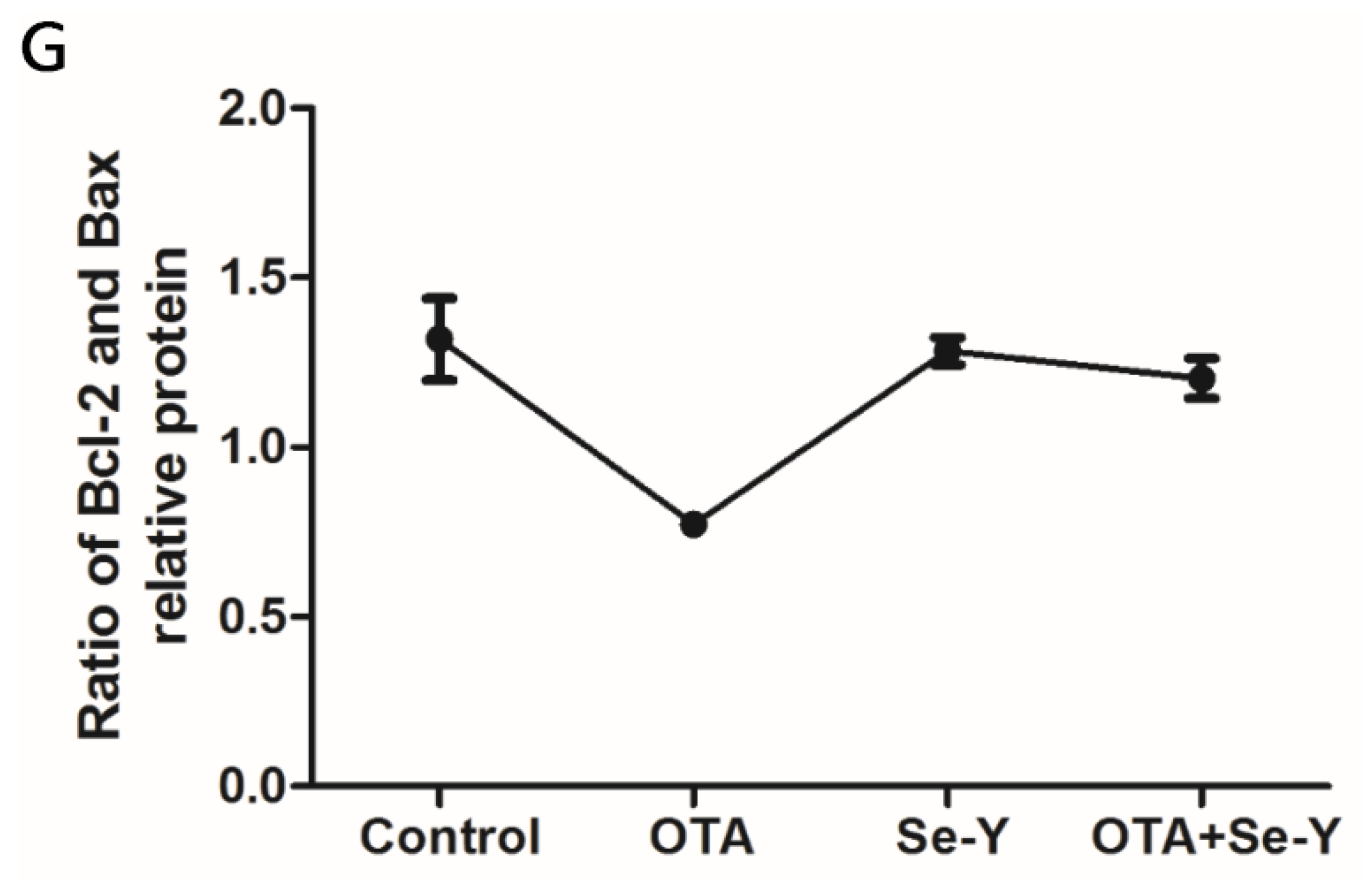
2.7. Effect of Se-Y on OTA-Induced Changes in Protein Expression
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Animals and Treatments
5.3. Collection of Samples
5.4. Histopathological Evaluation
5.5. TUNEL Apoptosis Analysis
5.6. Detection of AST and ALT
5.7. Analysis of the Oxidative Parameters of Liver
5.8. Gene Expression Analyses
5.9. Western Blot Analysis
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altafini, A.; Fedrizzi, G.; Roncada, P. Occurrence of ochratoxin a in typical salami produced in different regions of italy. Mycotoxin Res. 2018, 35, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballo, D.; Tolosa, J.; Ferrer, E.; Berrada, H. Dietary exposure assessment to mycotoxins through total diet studies. A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Advances in biodetoxification of ochratoxin a-a review of the past five decades. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.L. Biodegradation of ochratoxin a by alcaligenes faecalis isolated from soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljkovic-Trailovic, J.; Trailovic, S.; Resanovic, R.; Milicevic, D.; Jovanovic, M.; Vasiljevic, M. Comparative investigation of the efficacy of three different adsorbents against ota-induced toxicity in broiler chickens. Toxins 2015, 7, 1174–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razafimanjato, H.; Garmy, N.; Guo, X.J.; Varini, K.; Di Scala, C.; Di Pasquale, E.; Taieb, N.; Maresca, M. The food-associated fungal neurotoxin ochratoxin a inhibits the absorption of glutamate by astrocytes through a decrease in cell surface expression of the excitatory amino-acid transporters glast and glt-1. Neurotoxicology 2010, 31, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lim, W.; You, S.; Song, G. Ochratoxin a exerts neurotoxicity in human astrocytes through mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and intracellular calcium overload. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 313, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavin, C.; Delatour, T.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Fenaille, F.; Holzhäuser, D.; Guignard, G.; Bezençon, C.; Piguet, D.; Parisod, V.; Richoz-Payot, J.; et al. Ochratoxin A–Mediated DNA and Protein Damage: Roles of Nitrosative and Oxidative Stresses. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-Y.; Sun, X.-F.; Li, L.; Ma, J.-M.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Li, N.; Liu, X.-L.; Dyce, P.W.; Shen, W. Ochratoxin a exposure impairs porcine granulosa cell growth via the pi3k/akt signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, F.; Tian, J.; Guo, X.; An, R. Protective effects of compound ammonium glycyrrhizin, l-arginine, silymarin and glucurolactone against liver damage induced by ochratoxin a in primary chicken hepatocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, V.; Darroudi, F.; Uhl, M.; Steinkellner, H.; Gann, M.; Majer, B.J.; Eisenbauer, M.; Knasmüller, S. Genotoxic effects of ochratoxin A in human-derived hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundhausen, C.; Bösch-Saadatmandi, C.; Augustin, K.; Blank, R.; Wolffram, S.; Rimbach, G. Effect of vitamin e and polyphenols on ochratoxin a-induced cytotoxicity in liver (hepg2) cells. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramyaa, P.; Padma, V.V. Ochratoxin-induced toxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis ameliorated by quercetin—Modulation by nrf2. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.; Utan, A.; Cervellati, R.; Speroni, E.; Guerra, M.C. Catechins: Natural free-radical scavengers against ochratoxin a-induced cell damage in a pig kidney cell line (llc-pk1). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzulli, C.; Galvano, F.; Pierdomenico, L.; Speroni, E.; Guerra, M.C. Effects of rosmarinic acid against aflatoxin b1 and ochratoxin-a-induced cell damage in a human hepatoma cell line (hep g2). J. Appl. Toxicol. 2004, 24, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrenner, H.; Sies, H. Selenium homeostasis and antioxidant selenoproteins in brain: Implications for disorders in the central nervous system. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 536, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, H.; Shen, Y.; Luo, M.; Xin, X.; Xu, Z. Selenium bio-absorption and antioxidant capacity in mice treated by selenium modified rice germ polysaccharide. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhrle, J.; Jakob, F.; Contempré, B.; Dumont, J.E. Selenium, the Thyroid, and the Endocrine System. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 944–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.P.; Fu, J.; Xu, F.P.; Wang, X.S.; Li, S. The role of heat shock proteins in oxidative stress damage induced by Se deficiency in chicken livers. BioMetals 2014, 28, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.Y.; Mahan, D.C. Comparative effects of high dietary levels of organic and inorganic selenium on selenium toxicity of growing-finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Lu, P.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H.; Song, B.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, R. Selenium-yeast alleviated inflammatory damage caused by lead via inhibiting ras/erk pathway and inflammatory factors in chicken skeletal muscles. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global mycotoxin occurrence in feed: A ten-year survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golli Bennour, E.E.; Rodriguez-Enfedaque, A.; Bouaziz, C.; Ladjimi, M.; Renaud, F.; Bacha, H. Toxicities induced in cultured human hepatocarcinoma cells exposed to ochratoxin a: Oxidative stress and apoptosis status. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2009, 23, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujahid, H. Protective effect of yeast sludge and whey powder against ochratoxicosis in broiler chicks. Pak. Vet. J. 2019, 39, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Xu, F.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N.; Pan, Y.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Ochratoxin A: Toxicity, oxidative stress and metabolism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, J.-C.; Holzhaeuser, D.; Markovic, J.; Gremaud, E.; Schilter, B.; Turesky, R.J. Oxidative damage and stress response from ochratoxin a exposure in rats. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 2001, 30, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D. Mechanistic studies of the nrf2-keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metab. Rev. 2006, 38, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Xing, L.; Shen, H.; Wu, S.; Lian, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Ochratoxin a induces oxidative DNA damage and g1 phase arrest in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, Y.X.; Dong, X.Y.; Zou, X. Effect of mercury chloride on oxidative stress and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signalling molecule in liver and kidney of laying hens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.-H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Long, M.; He, J.-B.; Yang, S.-H. Protective effects of proanthocyanidins against cadmium-induced testicular injury through the modification of nrf2-keap1 signal path in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Long, M.; He, J. Proanthocyanidins protect against β-hydroxybutyrate-induced oxidative damage in bovine endometrial cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnett, L.J. Lipid peroxidation—DNA damage by malondialdehyde. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1999, 424, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S. Effect of selenium on the levels of cytokines and trace elements in toxin-mediated oxidative stress in male rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 169, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.S.; Yu, T.; Fan, X.M.; Chen, P.; Zeng, H.; Huang, M.; Bi, H.C. Schisandrol b protects against acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity in mice via activation of the nrf2/are signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Motohashi, H. Roles of nrf2 in cell proliferation and differentiation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenilmez, A. Antioxidant effects of melatonin and coenzyme q10 on oxidative damage caused by single-dose ochratoxin a in rat kidney. Chin. J. Physiol. 2010, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.-L.; Shen, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chiang, C.-K. Ochratoxin A induces ER stress and apoptosis in mesangial cells via a NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species-mediated calpain activation pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 19376–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Hou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Effects of ochratoxin a on er stress, mapk signaling pathway and autophagy of kidney and spleen in pigs. Env. Toxicol 2017, 32, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Deng, L.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; et al. MiR-122 partly mediates the ochratoxin A-induced GC-2 cell apoptosis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 30, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Piva, A.; Sorrenti, V.; Vanella, L.; Piva, G.; Casadei, G.; La Fauci, L.; Ritieni, A.; Bognanno, M.; et al. Protective effect of cyanidin 3-o-beta-d-glucoside on ochratoxin a-mediated damage in the rat. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, V.; Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Barbagallo, I.; Bognanno, M.; Galvano, F. Toxicity of Ochratoxin A and Its Modulation by Antioxidants: A Review. Toxins 2013, 5, 1742–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Stachurska, A.; Sobczak, M.; Podkalicka, P.; Mucha, O.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Nrf2 deficiency exacerbates ochratoxin a-induced toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Toxicology 2017, 389, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; Li, P. Analysis of the mirna expression profiles in the zearalenone-exposed tm3 leydig cell line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Lou, Y.; Wolffram, S.; Huebbe, P.; Rimbach, G. Ochratoxin a induces apoptosis in neuronal cells. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmadani, A.; Steyn, P.S.; Tramu, G.; Betbeder, A.M.; Baudrimont, I.; Creppy, E.E. Selective toxicity of ochratoxin a in primary cultures from different brain regions. Arch. Toxicol. 1999, 73, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, C.; Zhong, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fu, J. Pi3k/akt pathway mediates nrf2/are activation in human l02 hepatocytes exposed to low-concentration hbcds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12434–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.J.; Lee, J.T.; Joe, E.H.; Kwon, T.K. An ikappabalpha phosphorylation inhibitor induces heme oxygenase-1(ho-1) expression through the activation of reactive oxygen species (ros)-nrf2-are signaling and ros-pi3k/akt signaling in an nf-kappab-independent mechanism. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solcan, C.; Pavel, G.; Floristean, V.C.; Chiriac, I.S.; Slencu, B.G.; Solcan, G. Effect of ochratoxin a on the intestinal mucosa and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues in broiler chickens. Acta Vet. Hung. 2015, 63, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshalinejad, R.; Kakhki, R.A.M.; Zoidis, E. Effects of different dietary sources and levels of selenium supplements on growth performance, antioxidant status and immune parameters in Ross 308 broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2018, 59, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Sequence | Amplicon size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| R-Nrf2-F: R-Nrf2-R: R-Keap1-F: R-Keap1-R: R-GSH-Px-F: R-GSH-Px-R: R-MnSOD-F: R-MnSOD-R: R-GLRX2-F: R-GLRX2-R: R-Bax-F: R-Bax-R: R-Bcl-2-F: R-Bcl-2-R: R-PI3K-F: R-PI3K-R: R-AKT-F: R-AKT-R: R-Caspase3-F: R-Caspase3-R R-P53-F: R-P53-R: R-β-actin-F: R-β-actin-R: | 5’ CATAGAGCAAGTTTGGGAAGAG 3’ 5’ GTTTCAGGGCTCGTGATTGT 3’ 5’ ACTTCGCTGAGGTCTCCAAG 3’ 5’ CAGTCGTACTGCACCCAGTT 3’ 5’ CCAATTCGGGCACCAGGAGAA 3’ 5’ CTCTCTCAGGAAGGCGAACAG 3’ 5’ AAGGAGCAGGGACGTCTACA 3’ 5’ CCAGCAATGGAATGAGACCTGT 3’ 5’ ACGGAAGCCAGATCCAAGAC 3’ 5’ GTAGCACCTCCAACAAAAGACC 3’ 5’ GTGATGGCATGGGACATAGCTC 3’ 5’ TGGCGTAGACCTTGCGGATAA 3’ 5’ ATCGTCGCCTTCTTCGAGTT 3’ 5’ GTAGCACCTCCAACAAAAGA 3’ 5’ TACATTCTTGGGCTCCTT 3’ 5’ AGTGCGTGGAAATCTAAT 3’ 5’ AGTGCGTGGAAATCTAAT 3’ 5’ ATAATGACTATGGTCGTGC 3’ 5’ AAGCGAAGCAGTTTTGTTTGTG 3’ 5’ GCTAGACTTCTGCACTTGTCACCTC 3’ 5’ AAGCGAAGCAGTTTTGTTTGTG 3’ 5’ GCTAGACTTCTGCACTTGTCACCTC 3’ 5’ AGGAGAAGCTGTGCTACGTC 3’ 5’ TACCACAGGACTCCATACCCAA 3’ | 105 bp 142 bp 157 bp 82 bp 151 bp 91 bp 151 bp 170 bp 146 bp 128 bp 157 bp 183 bp |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Li, K.; Zou, C.; Tong, C.; Sun, L.; Cao, Z.; Yang, S.; Lyu, Q. Selenium Yeast Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathways in Chickens. Toxins 2020, 12, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12030143
Li P, Li K, Zou C, Tong C, Sun L, Cao Z, Yang S, Lyu Q. Selenium Yeast Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathways in Chickens. Toxins. 2020; 12(3):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12030143
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peng, Kang Li, Chao Zou, Cui Tong, Lin Sun, Zhongjun Cao, Shuhua Yang, and Qiufeng Lyu. 2020. "Selenium Yeast Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathways in Chickens" Toxins 12, no. 3: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12030143
APA StyleLi, P., Li, K., Zou, C., Tong, C., Sun, L., Cao, Z., Yang, S., & Lyu, Q. (2020). Selenium Yeast Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Modulation of the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathways in Chickens. Toxins, 12(3), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12030143





