Ssu72 Regulates Fungal Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
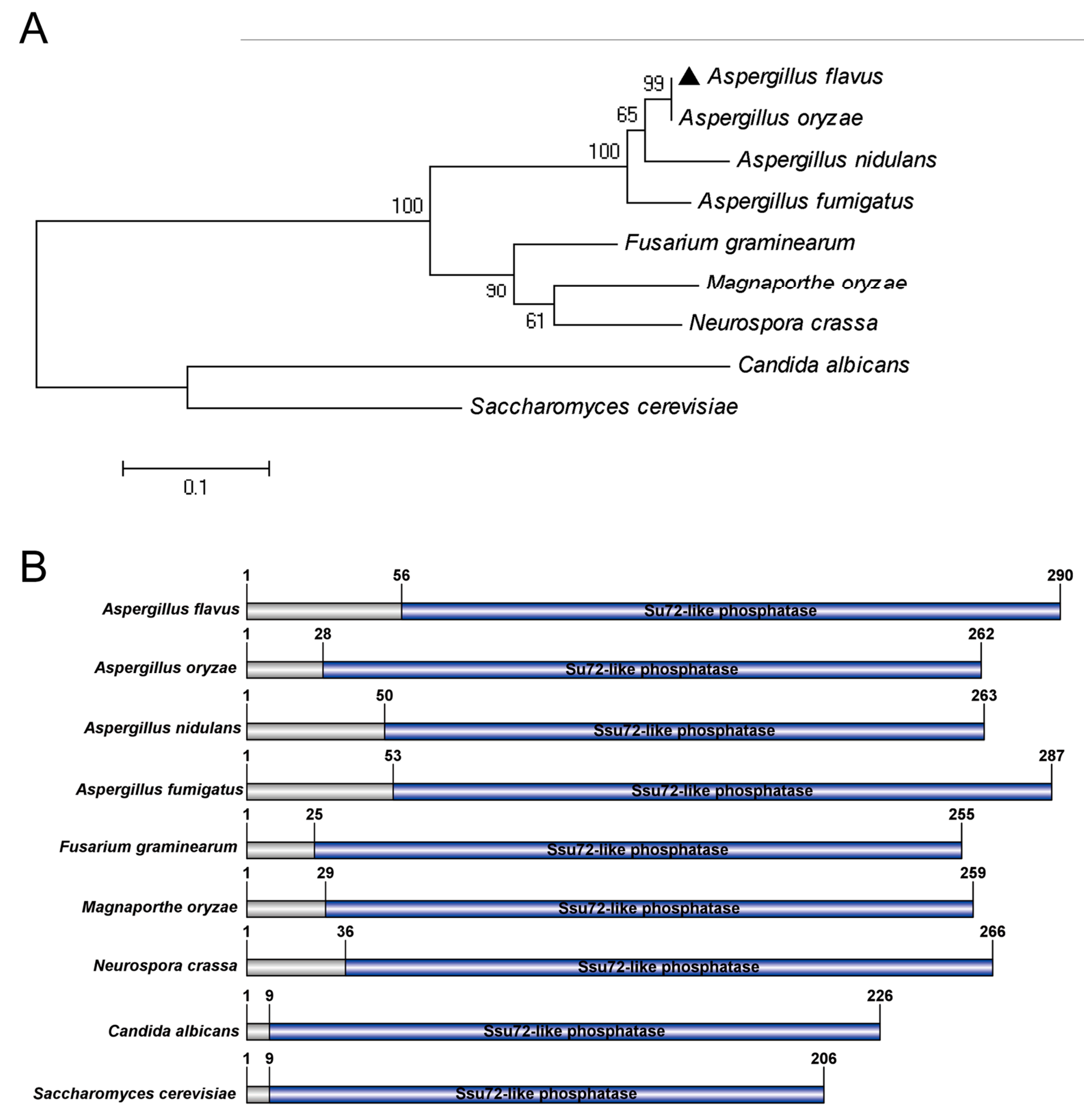
2.1. Identification of Putative Phosphatase Ssu72 in A. flavus
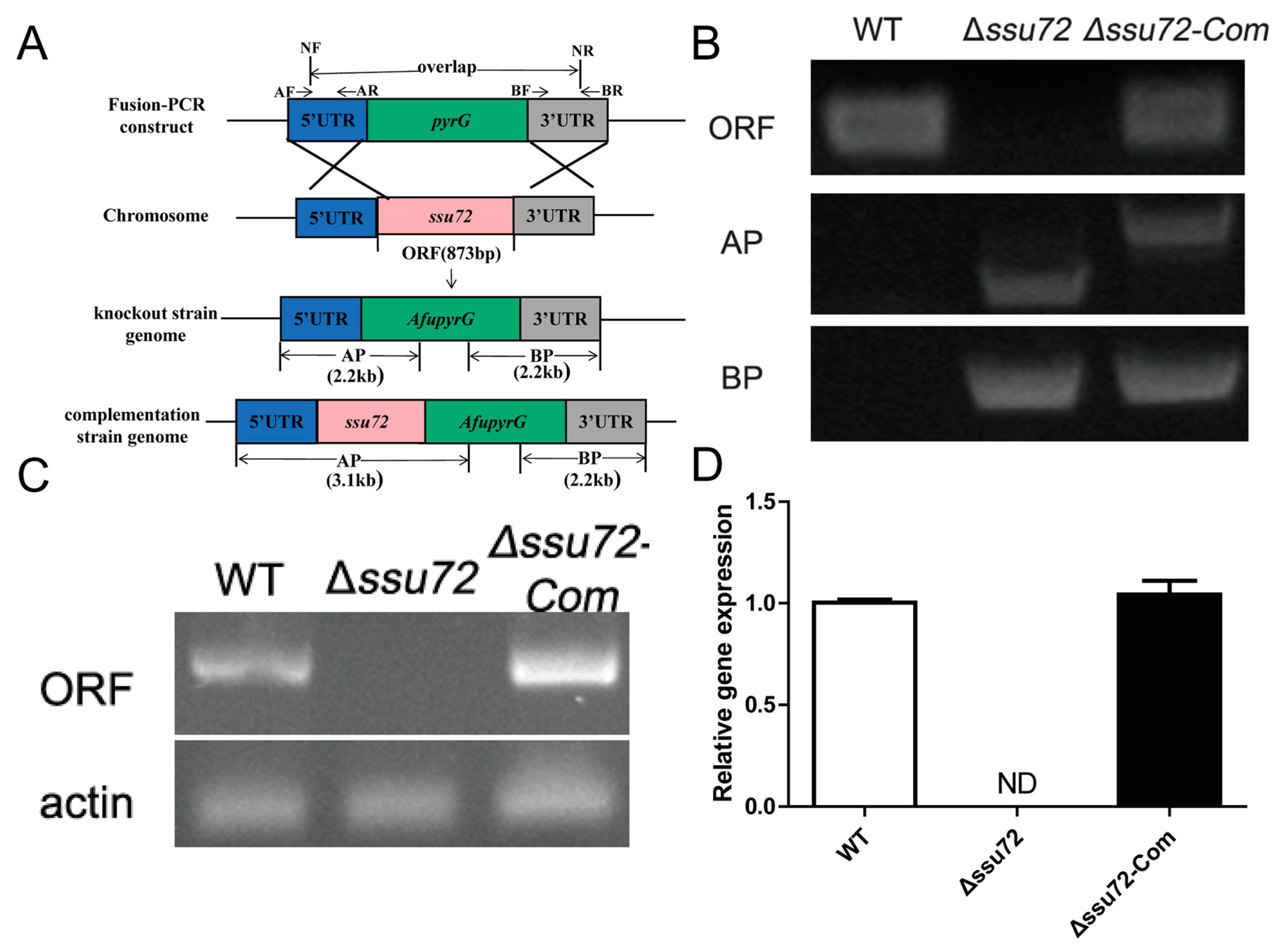
2.2. Construction of the ssu72 Mutant Strains
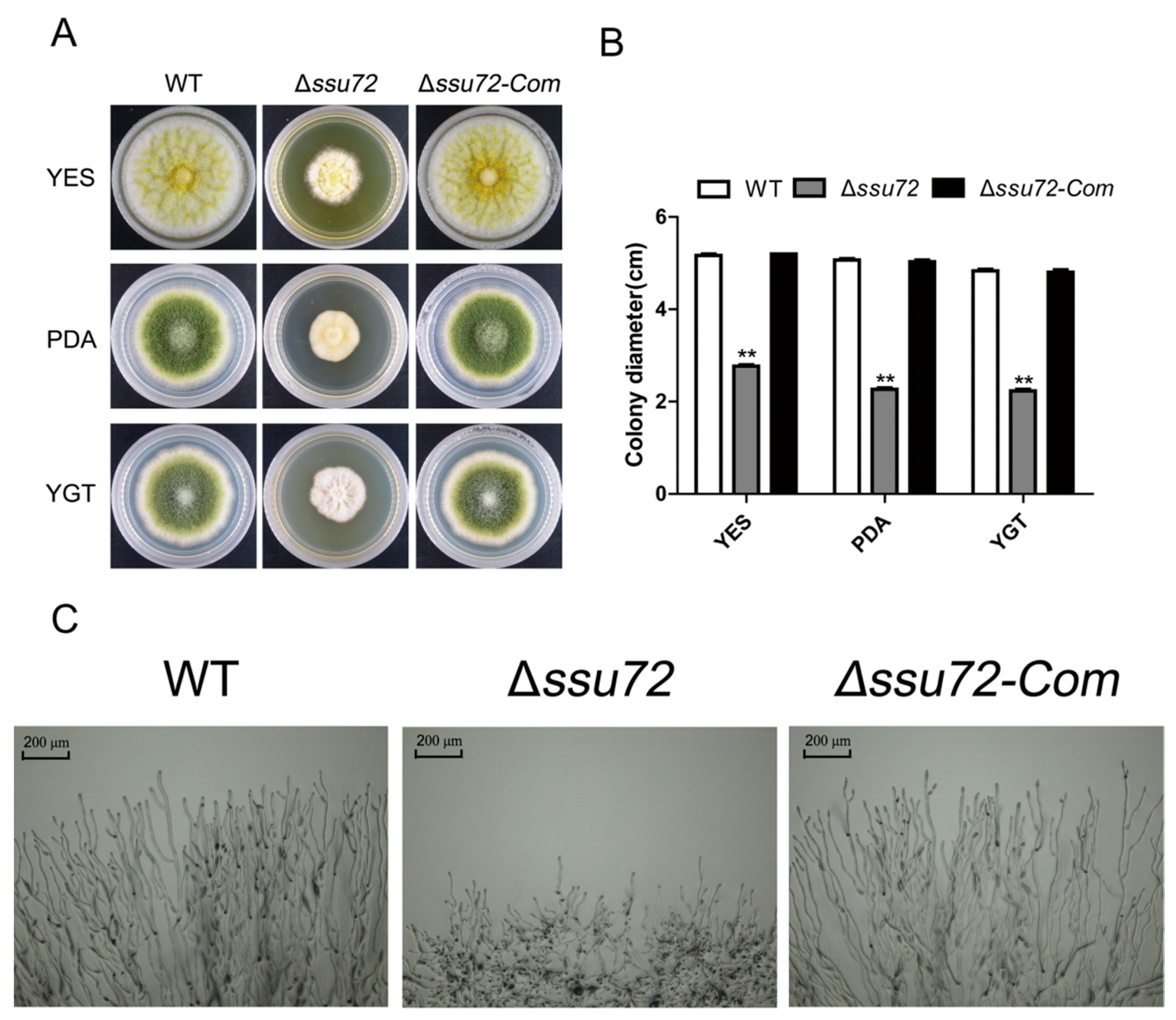
2.3. Ssu72 Is Involved in Vegetative Growth in A. flavus
2.4. Ssu72 Is Critical for Conidiation in A. flavus
2.5. Ssu72 Is Required for Sclerotia Formation in A. flavus
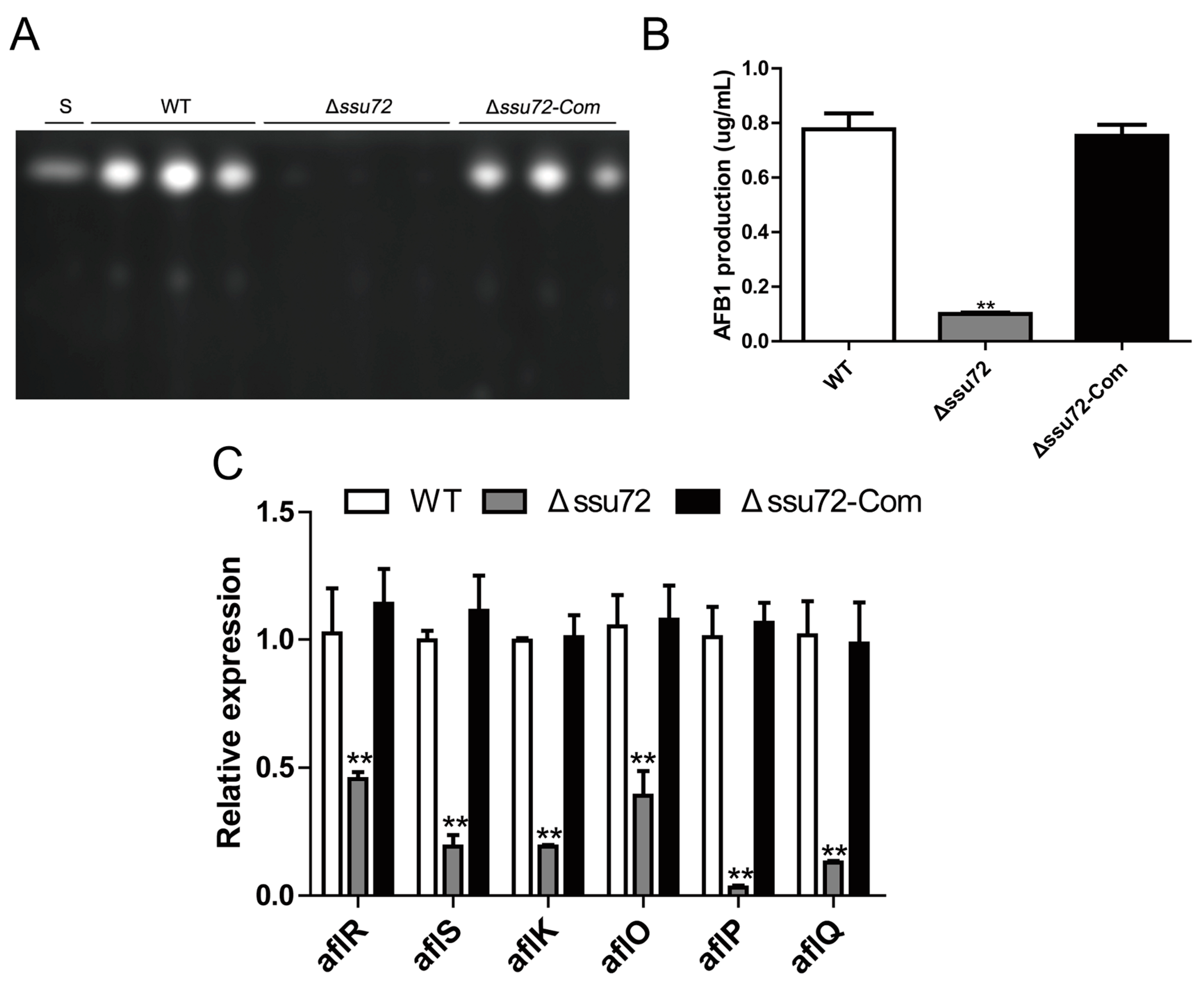
2.6. Ssu72 Plays a Positive Role in Regulation of Aflatoxin Biosynthesis
2.7. Ssu72 Contributes to Pathogenicity in Crop Seeds in A. flavus
2.8. Ssu72 Response to Multiple Stresses in A. flavus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Mutant Strains Construction
4.3. Phenotpic Assays
4.4. Aflatoxin Production Assays
4.5. Pathogenicity Assays
4.6. Stress Assay
4.7. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Huang, L.; Deng, J.; Tan, C.; Geng, L.; Liao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S. A Cell Wall Integrity-Related MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase AflBck1 Is Required for Growth and Virulence in Fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zha, W.; Liang, L.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Wu, L.; Wang, S. The bZIP Transcription Factor AflRsmA Regulates Aflatoxin B(1) Biosynthesis, Oxidative Stress Response and Sclerotium Formation in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2020, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasoyin, O.E.; Yang, K.; Qiu, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Regulation of Morphology, Aflatoxin Production, and Virulence of Aspergillus flavus by the Major Nitrogen Regulatory Gene areA. Toxins 2019, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, L.; Xie, R.; Lan, H.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Cyclase-Associated Protein Cap with Multiple Domains Contributes to Mycotoxin Biosynthesis and Fungal Virulence in Aspergillus flavus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4200–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.K.; Zhang, Q.; Scharfenstein, L.; Mack, B.; Yoshimi, A.; Miyazawa, K.; Abe, K. Aspergillus flavus GPI-anchored protein-encoding ecm33 has a role in growth, development, aflatoxin biosynthesis, and maize infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5209–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drott, M.T.; Satterlee, T.R.; Skerker, J.M.; Pfannenstiel, B.T.; Glass, N.L. The Frequency of Sex: Population Genomics Reveals Differences in Recombination and Population Structure of the Aflatoxin-Producing Fungus Aspergillus flavus. mBio 2020, 11, e00963-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, B.A.; Lohmar, J.M.; Satterlee, T.; McDonald, T.; Cary, J.W.; Calvo, A.M. The 14-3-3 Protein Homolog ArtA Regulates Development and Secondary Metabolism in the Opportunistic Plant Pathogen Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02241-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Wu, L.; Sun, R.; Keller, N.P.; Yang, K.; Ye, L.; He, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. The HosA Histone Deacetylase Regulates Aflatoxin Biosynthesis Through Direct Regulation of Aflatoxin Cluster Genes. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Nie, X.; Wang, S. Integrative analyses reveal transcriptome-proteome correlation in biological pathways and secondary metabolism clusters in A. flavus in response to temperature. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.; Zhong, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. RNA-Seq-based transcriptome analysis of aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus in response to water activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3187–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Yue, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S. Global Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals the Involvement of Phosphorylation in Aflatoxins Biosynthesis in the Pathogenic Fungus Aspergillus flavus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yue, Y.; Ren, S.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ge, F.; Wang, S. Lysine acetylation contributes to development, aflatoxin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 4792–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Yang, M.; Yue, Y.; Ge, F.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Nie, X.; Wang, S. Lysine Succinylation Contributes to Aflatoxin Production and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Lin, G.; Xu, Z.; Lan, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. The Putative Histone Methyltransferase DOT1 Regulates Aflatoxin and Pathogenicity Attributes in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2017, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Yu, S.; Qiu, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Aspergillus flavus SUMO Contributes to Fungal Virulence and Toxin Attributes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, R.; Lang, R. Dual Specificity Phosphatases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Biological Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, H.; Flández, M.; Nombela, C.; Molina, M. Protein phosphatases in MAPK signalling: We keep learning from yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 58, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelströter, L.K.; Bom, V.L.; de Castro, P.A.; Ramalho, L.N.; Goldman, M.H.; Brown, N.A.; Rajendran, R.; Ramage, G.; Bovier, E.; Dos Reis, T.F.; et al. High osmolarity glycerol response PtcB phosphatase is important for Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 96, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariño, J.; Casamayor, A.; González, A. Type 2C protein phosphatases in fungi. Eukaryot. Cell 2011, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wulf, P.; Montani, F.; Visintin, R. Protein phosphatases take the mitotic stage. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offley, S.R.; Schmidt, M.C. Protein phosphatases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 2019, 65, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, S.; Heck, L.; Gruber, C.; Neumann, H.; Distler, U.; Tenzer, S.; Yemelin, A.; Thines, E.; Jacob, S. Fungicide resistance toward fludioxonil conferred by overexpression of the phosphatase gene MoPTP2 in Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 662–677. [Google Scholar]
- Sacristán-Reviriego, A.; Martín, H.; Molina, M. Identification of putative negative regulators of yeast signaling through a screening for protein phosphatases acting on cell wall integrity and mating MAPK pathways. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yu, F.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Z. Involvement of protein tyrosine phosphatases BcPtpA and BcPtpB in regulation of vegetative development, virulence and multi-stress tolerance in Botrytis cinerea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M.; Garg, A.; Shuman, S.; Schwer, B. Genetic interactions and transcriptomics implicate fission yeast CTD prolyl isomerase Pin1 as an agent of RNA 3′ processing and transcription termination that functions via its effects on CTD phosphatase Ssu72. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4811–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwer, B.; Sanchez, A.M.; Shuman, S. Inactivation of fission yeast Erh1 de-represses pho1 expression: Evidence that Erh1 is a negative regulator of prt lncRNA termination. RNA 2020, 10, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M.; Garg, A.; Shuman, S.; Schwer, B. Inositol pyrophosphates impact phosphate homeostasis via modulation of RNA 3′ processing and transcription termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 16, 8452–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwer, B.; Sanchez, A.M.; Shuman, S. RNA polymerase II CTD phospho-sites Ser5 and Ser7 govern phosphate homeostasis in fission yeast. RNA 2015, 21, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allepuz-Fuster, P.; O’Brien, M.J.; González-Polo, N.; Pereira, B.; Dhoondia, Z.; Ansari, A.; Calvo, O. RNA polymerase II plays an active role in the formation of gene loops through the Rpb4 subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 8975–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado-Lugo, J.D.; Hampsey, M. The Ssu72 phosphatase mediates the RNA polymerase II initiation-elongation transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33916–33926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwer, B.; Ghosh, A.; Sanchez, A.M.; Lima, C.D.; Shuman, S. Genetic and structural analysis of the essential fission yeast RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase Fcp1. RNA 2015, 21, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escandell, J.M.; Carvalho, E.S.; Gallo-Fernandez, M.; Reis, C.C.; Matmati, S.; Luís, I.M.; Abreu, I.A.; Coulon, S. Ssu72 phosphatase is a conserved telomere replication terminator. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M.; Shuman, S. RNA polymerase II CTD interactome with 3′ processing and termination factors in fission yeast and its impact on phosphate homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10652–E10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.R.; Ma, Z. Functional analysis of the Fusarium graminearum phosphatome. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hadi, A.; Schmidt-Heydt, M.; Parra, R.; Geisen, R.; Magan, N. A systems approach to model the relationship between aflatoxin gene cluster expression, environmental factors, growth and toxin production by Aspergillus flavus. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Wu, L.; Sun, R.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Geng, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, S. Investigation of Aspergillus flavus in animal virulence. Toxicon 2018, 145, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.K. Genome-wide nucleotide variation distinguishes Aspergillus flavus from Aspergillus oryzae and helps to reveal origins of atoxigenic A. flavus biocontrol strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Hu, Y.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Yue, Y.; Chen, L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, S. The Aspergillus flavus Phosphatase CDC14 Regulates Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cao, X.; Ma, G.; Qin, L.; Wu, Y.; Lin, J.; Ye, P.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S. MAPK pathway-related tyrosine phosphatases regulate development, secondary metabolism and pathogenicity in fungus Aspergillus flavus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 1462–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; He, X.; Reyes-Reyes, M.; Moore, C.; Hampsey, M. Ssu72 Is an RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Servin, J.A.; Park, G.; Borkovich, K.A. Global analysis of serine/threonine and tyrosine protein phosphatase catalytic subunit genes in Neurospora crassa reveals interplay between phosphatases and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. G3 2014, 4, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.K.; Scharfenstein, L.L.; Mack, B.; Ehrlich, K.C. Deletion of the Aspergillus flavus orthologue of A. nidulans fluG reduces conidiation and promotes production of sclerotia but does not abolish aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7557–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, J.W.; Harris-Coward, P.Y.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Mack, B.M.; Kale, S.P.; Larey, C.; Calvo, A.M. NsdC and NsdD affect Aspergillus flavus morphogenesis and aflatoxin production. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mupunga, I.; Izaaks, C.D.; Shai, L.J.; Katerere, D.R. Aflatoxin biomarkers in hair may facilitate long-term exposure studies. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Geng, L.; Deng, J.; Huang, L.; Zhong, H.; Xin, S.; Fasoyin, O.E.; Wang, S. The MAP kinase AflSlt2 modulates aflatoxin biosynthesis and peanut infection in the fungus Aspergillus flavus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 322, 108576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumukunde, E.; Li, D.; Qin, L.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Yuan, J. Osmotic-Adaptation Response of sakA/hogA Gene to Aflatoxin Biosynthesis, Morphology Development and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2019, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, M.G.; Keller, N.P. Molecular mechanisms of Aspergillus flavus secondary metabolism and development. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 66, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Wu, L.; Fan, K.; Sun, R.; Yang, G.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, J.; et al. Set3 Is Required for Asexual Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis, and Fungal Virulence in Aspergillus flavus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, G.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, Z. The PHD Transcription Factor Rum1 Regulates Morphogenesis and Aflatoxin Biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2018, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoyin, O.E.; Wang, B.; Qiu, M.; Han, X.; Chung, K.R.; Wang, S. Carbon catabolite repression gene creA regulates morphology, aflatoxin biosynthesis and virulence in Aspergillus flavus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2018, 115, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Nie, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, S. Molecular and structural basis of nucleoside diphosphate kinase-mediated regulation of spore and sclerotia development in the fungus Aspergillus flavus. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 12415–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, F.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, Z. PbsB Regulates Morphogenesis, Aflatoxin B1 Biosynthesis, and Pathogenicity of Aspergillus flavus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 2–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Strains | Genotype Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| A. flavus CA14 PTS | ∆ku70, ∆pyrG | Our lab |
| wild-type (WT) | ∆ku70, ∆pyrG::AfpyrG | This study |
| ∆ssu72 | ∆ku70, ∆pyrG::AfpyrG, ∆ssu72 | This study |
| ∆ssu72-Com | ∆ku70, ∆ssu72::Aflssu72, ∆pyrG::AfpyrG | This study |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| ssu72-AF | AAACCGACCACGAAGACA | 5 ‘UTR of ssu72 |
| ssu72-AR | GGGTGAAGAGCATTGTTTGAGGCTCAAGGAGGCTGGAAGAT | |
| ssu72-BF | GCATCAGTGCCTCCTCTCAGACGGCTAGGGTCAACGAACA | 3′UTR of ssu72 |
| ssu72-BR | CCCTTCCCTCCTTCAGCA | |
| pyrG-F | GCCTCAAACAATGCTCTTCACCC | fumigatus pyrG |
| pyrG-R | GTCTGAGAGGAGGCACTGATGC | |
| ssu72-NF | GGTCCACTGGGTGGTAAT | Fusion PCR |
| ssu72-NR | GCACGATACAAGGCGATGG | |
| ssu72-OF | ACCCAGGAGCAACAGTCA | ssu72 ORF verification |
| ssu72-OR | CCAGCCTTCAGAGTTATTCG | |
| P801-R | CAGGAGTTCTCGGGTTGTCG | Verification of AP and BP |
| P1020-F | CAGAGTATGCGGCAAGTCA | |
| ssu72-Com-AF | AACTAGTGAACACATCTTC | 5′UTR of ∆ssu72-Com |
| ssu72-Com-AR | GGGTGAAGAGCATTGTTTGAGGCCCAATGTTCGTTGACCCTA | |
| ssu72-Com-BF | GCATCAGTGCCTCCTCTCAGACCTGTATGCAGATCCAAAT | 3′UTR of ∆ssu72-Com |
| ssu72-Com-BR | CTTCTAAAGCTCCTATCC | |
| ssu72-Com-NF | TTCTGTTGGCCTGCGTAT | Fusion PCR |
| ssu72-Com-NR | GTATGCCTCTTGACTCCC |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| ssu72-F | GAGTCTTCAGACGGGACTGC | ssu72 detection |
| ssu72-R | CACATTAGGTTGCGTGATGG | |
| brlA-F | GCCTCCAGCGTCAACCTTC | brlA qRT-PCR |
| brlA-R | TCTCTTCAAATGCTCTTGCCTC | |
| abaA-F | TCTTCGGTTGATGGATGATTTC | abaA qRT-PCR |
| abaA-R | CCGTTGGGAGGCTGGGT | |
| nsdC-F | GCCAGACTTGCCAATCAC | nsdC qRT-PCR |
| nsdC-R | CATCCACCTTGCCCTTTA | |
| nsdD-F | GGACTTGCGGGTCGTGCTA | nsdD qRT-PCR |
| nsdD-R | AGAACGCTGGGTCTGGTGC | |
| aflR-F | AAAGCACCCTGTCTTCCCTAAC | aflR qRT-PCR |
| aflR-R | GAAGAGGTGGGTCAGTGTTTGTAG | |
| aflS-F | CGAGTCGCTCAGGCGCTCAA | aflS qRT-PCR |
| aflS-R | GCTCAGACTGACCGCCGCTC | |
| aflK-F | GAGCGACAGGAGTAACCGTAAG | aflK qRT-PCR |
| aflK-R | CCGATTCCAGACACCATTAGCA | |
| aflQ-F | GTCGCATATGCCCCGGTCGG | aflQ qRT-PCR |
| aflQ-R | GGCAACCAGTCGGGTTCCGG | |
| aflO-F | GATTGGGATGTGGTCATGCGATT | aflO qRT-PCR |
| aflO-R | GCCTGGGTCCGAAGAATGC | |
| aflP-F | ACGAAGCCACTGGTAGAGGAGATG | aflP qRT-PCR |
| aflP-R | GTGAATGACGGCAGGCAGGT | |
| actin-F | ACGGTGTCGTCACAAACTGG | The endogenos gene |
| actin-R | CGGTTGGACTTAGGGTTGATAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; Cao, X.; Qin, L.; Yan, L.; Hong, R.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S. Ssu72 Regulates Fungal Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins 2020, 12, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110717
Yang G, Cao X, Qin L, Yan L, Hong R, Yuan J, Wang S. Ssu72 Regulates Fungal Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins. 2020; 12(11):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110717
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Guang, Xiaohong Cao, Ling Qin, Lijuan Yan, Rongsheng Hong, Jun Yuan, and Shihua Wang. 2020. "Ssu72 Regulates Fungal Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus" Toxins 12, no. 11: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110717
APA StyleYang, G., Cao, X., Qin, L., Yan, L., Hong, R., Yuan, J., & Wang, S. (2020). Ssu72 Regulates Fungal Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity in Aspergillus flavus. Toxins, 12(11), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110717





