Antidotal Potency of the Novel, Structurally Different Adsorbents in Rats Acutely Intoxicated with the T-2 Toxin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Experimental Animals’ General Condition
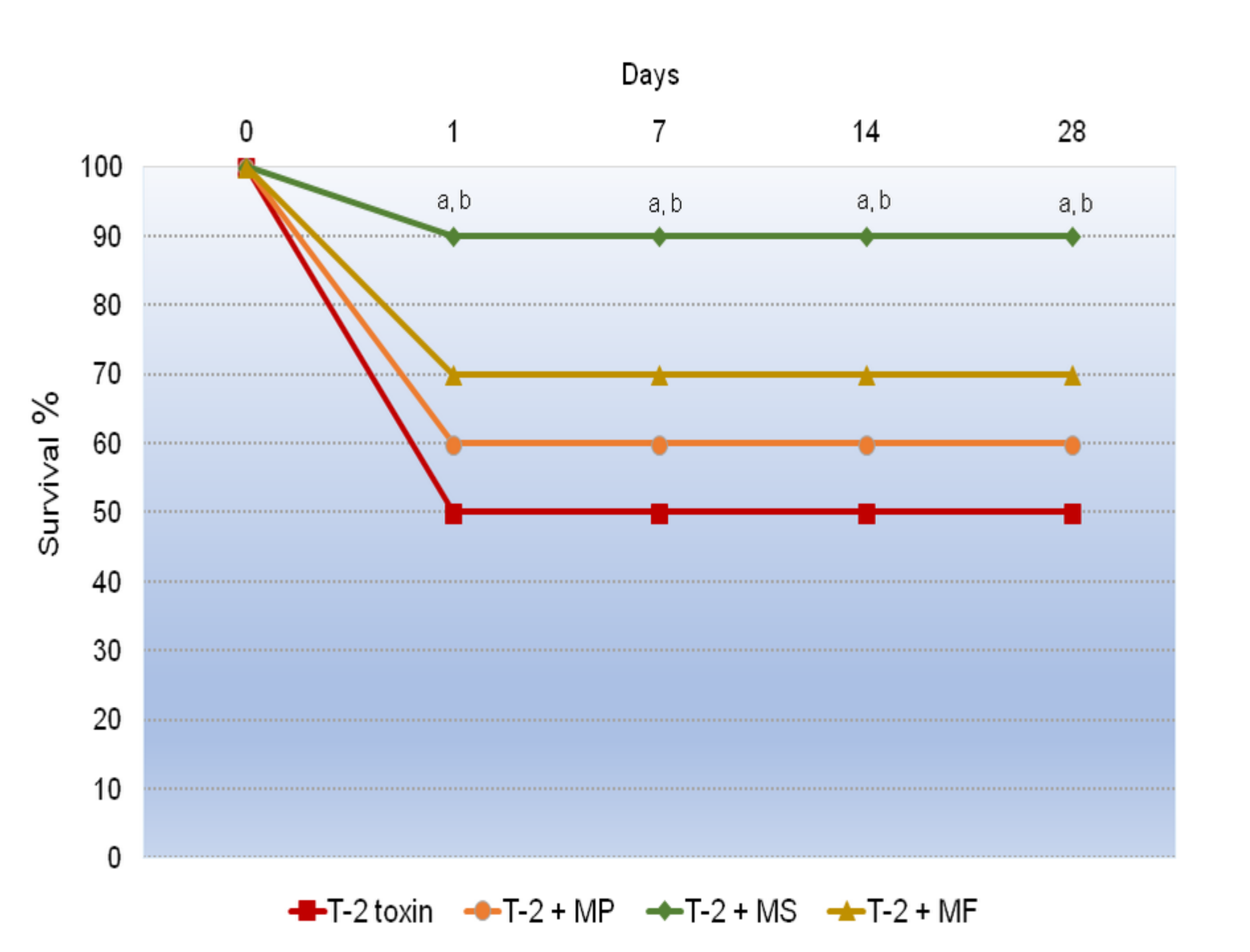
2.2. The Influence of Various Adsorbents on the Survival Rate in the T-2 Toxin-Treated Animals
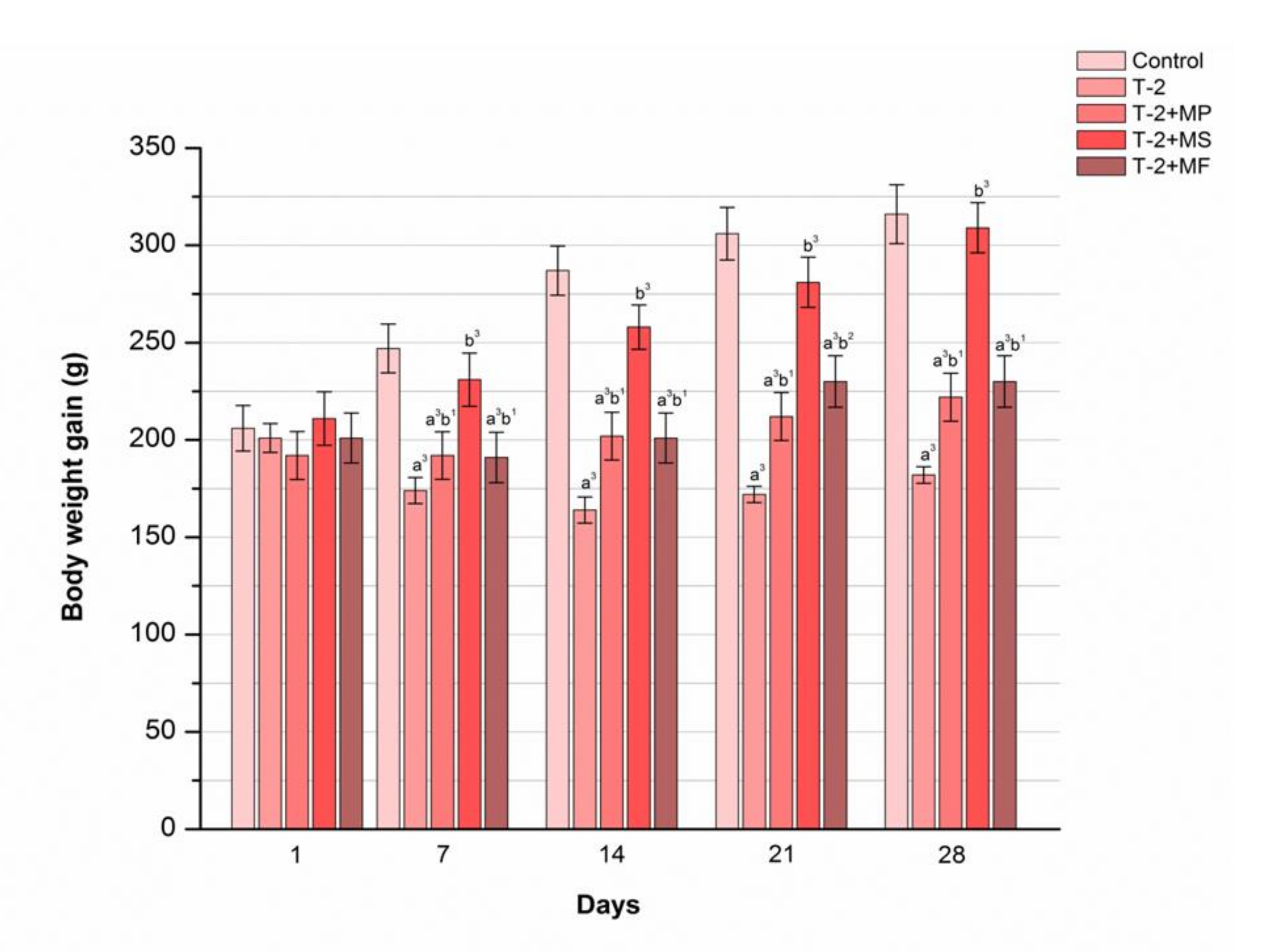
2.3. The Influence of Various Adsorbents on Body Weight Gain in T-2 Toxin-Treated Animals
2.4. The Influence of Various Adsorbents on Food Consumption in T-2 Toxin-Treated Animals
2.5. The Influence of Various Adsorbents on Water Consumption in T-2 Toxin-Treated Animals
2.6. The Influence of Various Adsorbents on Gastric Damage of T-2 Toxin-Treated Animals
2.7. A Semiquantitative Evaluation of the Influence of Various Asorbents on the Gastric Damage of T-2 Toxin-Treated Animals
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Animals
5.2. T-2 Toxin
5.3. Various Commercial Adsorbents
5.4. Protective Effects of Commercial Adsorbents
5.5. Experimental Design
5.6. Histopathological Examination
5.7. Semiquantitative Analysis
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, B.; Applegate, T.J. Modulation of intestinal function following mycotoxin ingestion: Meta-analysis of published experiments in animals. Toxins 2013, 5, 396–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, P. State of art of trichothecenes analysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.; de Smet, D.; de Saeger, S.; Zhang, S. T-2 Toxin, a trichothecene mycotoxin: Review of toxicity, metabolism, and analytical methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3441–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudakin, D.L. Trichothecenes in the environment: Relevance to human health. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 143, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.K.; Yoshizawa, T.; Shier, W.T. Cytotoxicity and phytotoxicity of trichothecene mycotoxins produced by Fusarium spp. Toxicon 2013, 74, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V. Therapy of Acute Poisoning by T-2 Toxin, 1st ed.; Andrejevic Foundation: Belgrade, Serbia, 2006; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Jaćević, V.; Kuca, K.; Milovanovic, Z.; Bocarov-Stancic, A.; Rancic, I.; Bokonjic, D.; Dragojevic-Simic, V.; Segrt, Z. Gastroprotective effects of amifostine in rats treated by T-2 toxin. Tox. Rev. 2018, 3, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speijers, G.; Speijers, M. Combined toxic effects of mycotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Kuča, K.; Yuanet, Z. Trichothecenes: Structure-toxic activity relationships. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013, 14, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resanović, R.M.; Nešić, K.D.; Nešić, V.D.; Palić, T.D.; Jaćević, V.M. Mycotoxins in poultry production. Proc. Nat. Sci. 2009, 116, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borison, L.H.; Goodheart, L.M.; Thut, C.D. Hypovolemic shock in acute lethal T-2 mycotoxicosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1991, 108, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Nussler, A.K.; Xiong, L.; Kuča, K.; Dohnal, V.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z. Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity and metabolism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in animals and humans: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Nepovimova, E.; Miron, A.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Su, D.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Kuča, K. Trichothecenes: Immunomodulatory effects, mechanisms, and anti-cancer potential. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3737–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V.; Wu, Q.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K. Efficacy of methylprednisolone on T-2 toxin-induced cardiotoxicity in vivo: A pathohistological study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 103221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaćević, V.; Wu, Q.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K. Cardiomyopathy induced by T-2 toxin in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaćević, V. Absorbents Efficacy in the Therapy of Acute T-2 Toxin Poisoning, 1st ed.; Andrejevic Foundation: Belgrade, Serbia, 2006; pp. 1–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jaćević, V.; Resanović, R.; Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Đorđević, S.; Dragojević-Simić, V.; Vukajlović, A.; Bokonjić, D. Gastroprotective effects of novel antidotal combination in rats acutely poisoned by T-2 toxin. Acta Vet. 2010, 60, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Engemann, A.; Cramer, B.; Welsch, T.; Yuan, Z.; Humpf, H.-U. Intestinal metabolism of T-2 toxin in the pig cecum model. Mycotoxin Res. 2012, 28, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, G.; Pestka, J. Immunomodulation by fungal toxins. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2000, 3, 109–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Uetsuka, K. Mechanisms of mycotoxin-induced neurotoxicity through oxidative stress-associated pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5213–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, K.R.; Batchu, S.N.; Seubert, J.M. Cytochrome P450 enzymes and the heart. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matés, J.M. Erratum to ‘Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology’. Toxicology 2000, 153, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadinejad, F.; Geir Møller, S.; Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori, M.; Bidkhori, G.; Jami, M.S. Molecular mechanisms behind free radical scavengers’ function against oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagiri, A.; Murakami, M. Roles of NADPH oxidase in the occurrence of gastric damage and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 during ischemia/reperfusion in rat stomachs. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 111, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.S. A possible new approach to the problem of refractory peptic ulceration. A role for free radical scavengers? Scott. Med. J. 1990, 36, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.P. Effects of T-2 mycotoxin on gastrointestinal tissues: A review of in vivo and in vitro models. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1989, 18, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackei, M.; Orbán, K.; Molnár, A.; Pál, L.; Dublecz, K.; Husvéth, F.; Neogrády, Z.; Mátis, G. Cellular effects of T-2 toxin on primary hepatic cell culture models of chickens. Toxins 2020, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S. Metabolic pathways of T-2 toxin in vivo and in vitro systems of Wistar rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9734–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, H.; Moosavi, M. Review on T-2 toxin. Jundish. J. Nat. Pharmaceut. Prod. 2010, 5, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, M.; Sun, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Bi, S.; Gooneratne, R.; Zhao, J. Effects of T-2 toxin on digestive enzyme activity, intestinal histopathology and growth in shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayakwadi, S.; Ramu, R.; Kumar Sharma, A.K.; Gupta, V.; Rajukumar, K.; Kumar, V.; Shirahatti, P.S.; Rashmi, L.; Basalingappa, K.M. Toxicopathological studies on the effects of T-2 mycotoxin and their interaction in juvenile goats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.R.; Avila, E.; Rosiles, R.; Petrone, V.M. Evaluation of two mycotoxin binders to reduce the toxicity of broiler diets containing ochratoxin A and T-2 toxin contaminated grain. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daković, A.; Kragović, M.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Ledoux, D.R.; Butkeraitis, P.; Vojislavljević, D.Z.; Zarić, S.D.; Stamenić, L. Preparation and characterization of zinc-exchanged montmorillonite and its effectiveness as aflatoxin B1 adsorbent. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković-Trailović, J.; Stefanović, S.; Trailovic, S. In vitro investigation three different adsorbents against ochratoxin A in broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2013, 54, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković-Trailović, J.; Trailović, S.; Resanović, R.; Milićević, D.; Jovanovic, M.; Vasiljevic, M. Comparative investigation of the efficacy of three different adsorbents against OTA-induced toxicity in broiler chickens. Toxins 2015, 7, 1174–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisanaba, S.; Pichardo, S.; Puerto, M.; Gutiérrez-Praena, D.; Cameán, A.M.; Jos, A. Toxicological evaluation of clay minerals and derived nanocomposites. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, M.; Daković, A.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Petković, A.; Kragović, M.; Krajišnik, D.; Milić, J. Ochratoxin A and zearalenone adsorption by the natural zeolite treated with benzalkonium chloride. Colloids Surfaces A 2017, 529, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V.M.; Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Resanović, R.D.; Đorđević, S.; Bokonjić, D.; Stojiljković, M.P. Basic mechanisms of the cellular alterations in T-2 toxin poisoning: Influence on the choice and result of the therapy. Proc. Nat. Sci. 2007, 113, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nešić, K.; Resanović, R.; Jakić-Dimić, D.; Nešić, V. Efficiency of various feed additives on the performance of broilers treated with T-2 toxin. Biotech. Anim. Husban. 2011, 27, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Lu, C.; Gu, C.; Kuča, K.; Wu, W. Effects of montmorillonite on growth performance, serum biochemistry and oxidative stress of red-crowned crane (Grus japonensis) fed mycotoxin-contaminated feed. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, G.J.; Cortes, A.; Roldan, L. Evaluation of the efficacy of four feed additives against the adverse effects of T-2 toxin in growing broiler chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2005, 14, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V.; Lazarević, M.; Vukajlović, A.; Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Resanović, R.; Điorđević, S. Antidotal efficacy of various adsorbents in rats acutely poisoned with T-2 toxin: A comparative evaluation. In Proceedings of the Alltech’s 25rd International Symposium—Science and Technology in the Feed Industry, Lexington, KY, USA, 17–20 May 2009; p. 708. [Google Scholar]
- Yazar, S.; Omurtag, G.Z. Fumonisins, trichothecenes and zearalenone in cereals. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2062–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Dohnal, V.; Huang, L.; Kuca, K.; Yuan, Z. Metabolic pathways of trichothecenes. Drug Metab. Rev. 2010, 42, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Giuberti, G.; Frisvad, J.C.; Bertuzzi, T.; Nielsen, K.F. Review on mycotoxin issues in ruminants: Occurrence in forages, effects of mycotoxin ingestion on health status and animal performance and practical strategies to counteract their negative effects. Toxins 2015, 7, 3057–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannikouris, A.; Jouany, J.P. Mycotoxins in feeds and their fate in animals: A review. Anim. Res. 2002, 51, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, S.C.; Hancock, D.S.; Schiefer, H.B.; Babiuk, L.A. Experimental T-2 toxicosis in sheep. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1983, 47, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, M.A.; Miguel, A.R.; Carlos, J.P. T-2 mycotoxin intoxication in piglets: A systematic pathological approach and apoptotic immune-histochemical studies. Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 2, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Fitzpatrick, D.W.; Wilson, J.R. Effect of dietary T-2 toxin on biogenic monoamines in discrete areas of the rat brain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszenicza, G.; Fekete, S.; Szigeti, G.; Kulcsár, M.; Kellems, R.O.; Nagy, P.; Cseh, S.; Veresegyházy, T.; Huilár, I. Ovarian consequences of low dose peroral fusarium (T-2) toxin in a ewe and heifer model. Theriogenology 2000, 53, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreras, M.C.; Benavides, J.; Garcia-Pariente, C.; Delgado, L.; Fuertes, M.; Munoz, M.; García-Marín, J.F.; Pérez, V. Acute and chronic disease associated with naturally occurring T-2 mycotoxicosis in sheep. J. Comp. Pathol. 2013, 148, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemboi, D.C.; Antonissen, G.; Ochieng, P.E.; Croubels, S.; Okoth, S.; Kangethe, E.K.; Faas, J.; Lindahl, J.F.; Gathumbi, J.K. A review of the impact of mycotoxins on dairy cattle health: Challenges for food safety and dairy production in sub-Saharan Africa. Toxins 2020, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannikouris, A.; Jouany, J.P.; Bertin, G. Counteracting mycotoxin contamination: The effectiveness of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall glucans in Mycosorb® for sequestering mycotoxins. In Proceedings of the Alltech’s 23rd Annual Symposium, Stamford, UK, 28–29 June 2007; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Kubena, L.F.; Harvey, R.B.; Huff, W.E.; Corrier, D.E.; Phillips, T.D.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Efficacy of a hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate to reduce the toxicity of aflatoxin and T-2 toxin. Poult. Sci. 1990, 69, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubena, L.F.; Harvey, R.B.; Huff, W.E.; Elissalde, M.H.; Yersin, A.G.; Phillips, D.E.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Efficacy of a hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate to reduce the toxicity of aflatoxin and diacetoxyscirpenol. Poult. Sci. 1993, 72, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T.D. Dietary clay in the chemoprevention of aflatoxin-induced disease. Toxicol. Sci. 1999, 52, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Binder, E.M.; Heidler, D.; Krska, R. Structural characterization of metabolites after the microbial degradation of type A trichothecenes by the bacterial strain BBSH 797. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorska, J.E.; Surai, P.F. Effects of T-2 Toxin, zeolite and Mycosorb on antioxidant systems of growing quail. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorska, J.E.; Surai, P.F.; Speake, B.K.; Sparks, N.H. Protective effect of modified glucomannans against aurofusarin-induced changes in quail egg and embryo. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 135C, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, H.V.L.N.; Smith, T.K.; Cotter, P.F.; Boermans, H.J.; Sefton, A.E. Effects of feeding blends of grains naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins on production and metabolism in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2002, 81, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, H.V.L.N.; Smith, T.K.; MacDonald, E.J.; Boermans, H.J.; Squires, E.J. Effects of feeding a blend of grains naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins on swine performance, brain regional neurochemistry, and serum chemistry and the efficacy of a polymeric glucomannan mycotoxin adsorbent. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalludin, M.; Wang, S.; Boldogh, I.; Tian, B.; Brasier, A.R. (2007). TNF-alpha-induced NFkappaB/RelA Ser (276) phosphorylation and enhanceosome formation is mediated by a ROS-dependent PKAc pathway. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babbar, N.; Casero, R.A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases reactive oxygen species by inducing spermine oxidase in human lung epithelial cells: A potential mechanism for inflammation-induced carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11125–11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Jaćević, V.; Resanović, R.; Bjelić, M. Optimization of laboratory conditions for the biosynthesis of type trichothecenes proc. Proc. Nat. Sci. 2007, 113, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Lević, J.T.; Dimić, G.R.; Stanković, S.Ž.; Salma, N.M. Investigation of the toxigenic potential of fungal species by the use of a simple screening method. Proc. Nat. Sci. Matica Srpska Novi Sad 2009, 116, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Salma, N.M.; Pantić, V.R.; Adamović, M.J.; Miljković, A.D.; Suzić, S.V. Microbiological and mycotoxicological correctness of protein feed ingredients in Vojvodina. Proc. Nat. Sci. Matica Srpska Novi Sad 2011, 120, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, J.; Wilcoxon, F. A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1949, 96, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Jaćević, V.; Jovic, D.; Kuča, K.; Dragojevic-Simic, V.; Dobric, S.; Trajkovic, S.; Borisev, I.; Segrt, Z.; Milovanovic, Z.; Bokonjic, D.; et al. Effects of Fullerenol nanoparticles and Amifostine on radiation-induced tissue damages: Histopathological analysis. J. Appl. Biomed. 2016, 14, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V.; Djordjevic, A.; Srdjenovic, B.; Milic-Tores, V.; Segrt, Z.; Dragojevic-Simic, V.; Kuca, K. Fullerenol nanoparticles prevent doxorubicin-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 102, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V.; Dragojević-Simić, V.; Tatomirović, Ž.; Dobrić, S.; Bokonjić, D.; Kovačević, A.; Nepovimova, E.; Vališ, M.; Kuča, K. The efficacy of amifostine against multiple-dose doxorubicin-induced toxicity in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćević, V.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K. Toxic injury to the muscle tissue of rats following acute oximes exposure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nežić, L.; Škrbić, R.; Amidžić, L.; Gajanin, R.; Kuča, K.; Jaćević, V. Simvastatin protects cardiomyocytes against endotoxin-induced apoptosis and up-regulates survivin/NF-κB/p65 expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nežić, L.; Amidžić, L.; Škrbić, R.; Gajanin, R.; Nepovimova, E.; Vališ, M.; Kuča, K.; Jaćević, V. Simvastatin inhibits endotoxin-induced apoptosis in liver and spleen through up-regulation of survivin/NF-kB/p65 expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaćević, V.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K. Acute toxic injuries of rat’s visceral tissues induced by different oximes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Treatment | LD50 | 95% Confidence Limit | f(LD50) | Protective Index (PI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-2 | 1.67 | 1.27–2.19 | 1.31 | - |
| T-2 + MP | 2.18 | 1.77–2.88 | 1.36 | 1.31 |
| T-2 + MS | 3.75 | 3.08–4.42 | 1.35 | 2.25 |
| T-2 + MF | 2.98 | 2.28–3.52 | 1.51 | 1.79 |
| Treatments | GDS (Mean Number (X ± SD) (4 Stomachs/Group × 8 Slices/Stomach)) | |
|---|---|---|
| 7th day | 28th day | |
| Control | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.4 |
| T-2 | 3.5 ± 0.5 a | 4.2 ± 0.4 a |
| T-2 + MP | 2.8 ± 0.4 a | 3.5 ± 0.5 a |
| T-2 + MS | 1.5 ± 0.5 a,b | 2.1 ± 0.3 a,b |
| T-2 + MF | 2.7 ± 0.3 a | 3.2 ± 0.4 a |
| Grade | Definition |
|---|---|
| 0 | Normal histological structure of the stomach |
| 1 | Mild alteration: segmental loss of the superficial epithelium, discrete vasodilatation of the blood vessels, and single inflammatory cells |
| 2 | Moderate damage: exfoliation of the surface epithelium, strong vasodilatation of the blood vessels, and inflammatory cell infiltration |
| 3 | Severe, focal damage: erosion of the epithelium, hemorrhages, and inflammatory cell infiltration |
| 4 | Severe, diffuse damage: pronounced ulcerations, hemorrhages, and inflammatory cell infiltration |
| 5 | Tissue necrosis |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaćević, V.; Dumanović, J.; Lazarević, M.; Nepovimova, E.; Resanović, R.; Milovanović, Z.; Wu, Q.; Kuča, K. Antidotal Potency of the Novel, Structurally Different Adsorbents in Rats Acutely Intoxicated with the T-2 Toxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100643
Jaćević V, Dumanović J, Lazarević M, Nepovimova E, Resanović R, Milovanović Z, Wu Q, Kuča K. Antidotal Potency of the Novel, Structurally Different Adsorbents in Rats Acutely Intoxicated with the T-2 Toxin. Toxins. 2020; 12(10):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100643
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaćević, Vesna, Jelena Dumanović, Miodrag Lazarević, Eugenie Nepovimova, Radmila Resanović, Zoran Milovanović, Qinghua Wu, and Kamil Kuča. 2020. "Antidotal Potency of the Novel, Structurally Different Adsorbents in Rats Acutely Intoxicated with the T-2 Toxin" Toxins 12, no. 10: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100643
APA StyleJaćević, V., Dumanović, J., Lazarević, M., Nepovimova, E., Resanović, R., Milovanović, Z., Wu, Q., & Kuča, K. (2020). Antidotal Potency of the Novel, Structurally Different Adsorbents in Rats Acutely Intoxicated with the T-2 Toxin. Toxins, 12(10), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100643







