Two-Dimensional Layered Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Microbial Toxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detection of Bacterial Toxins
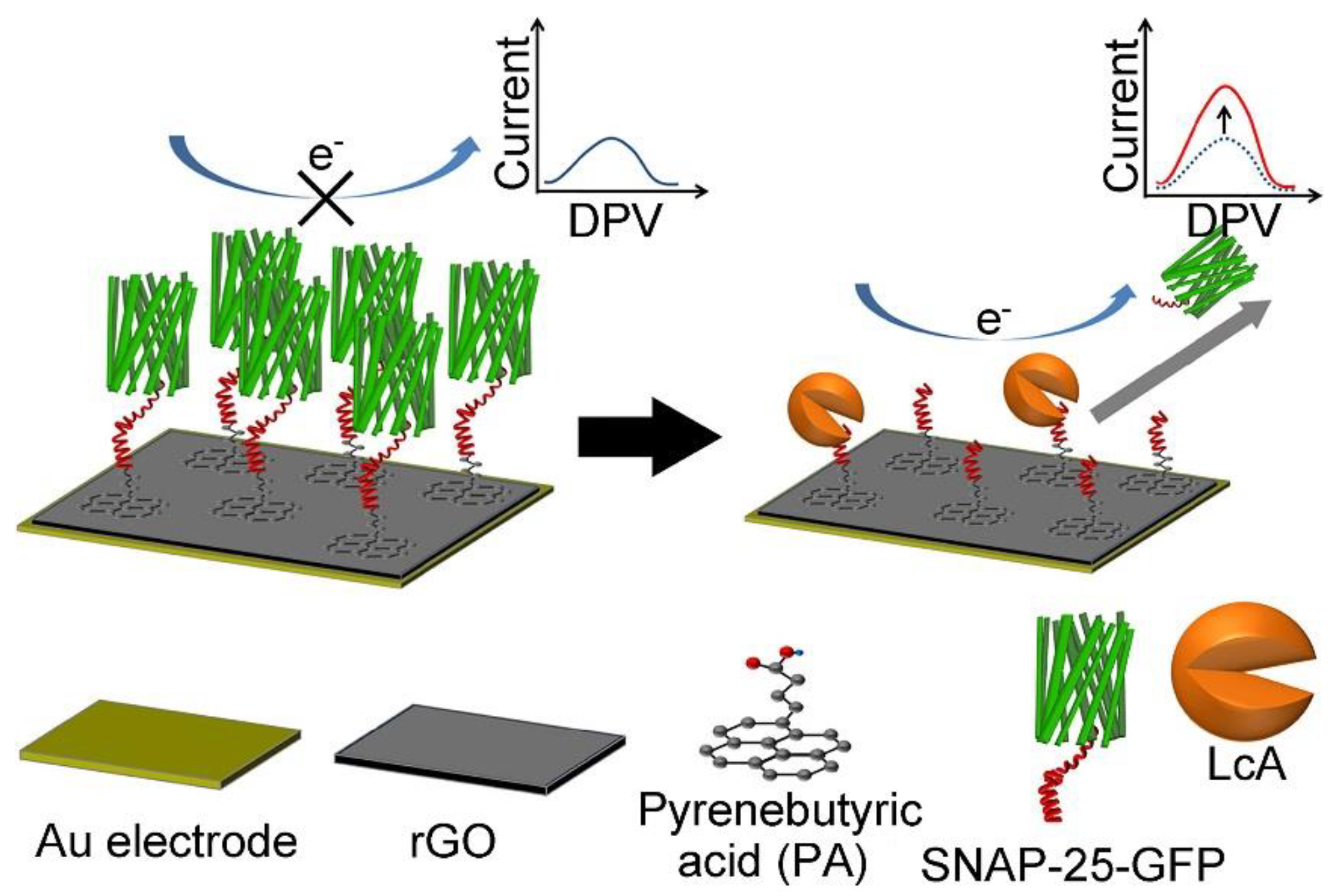
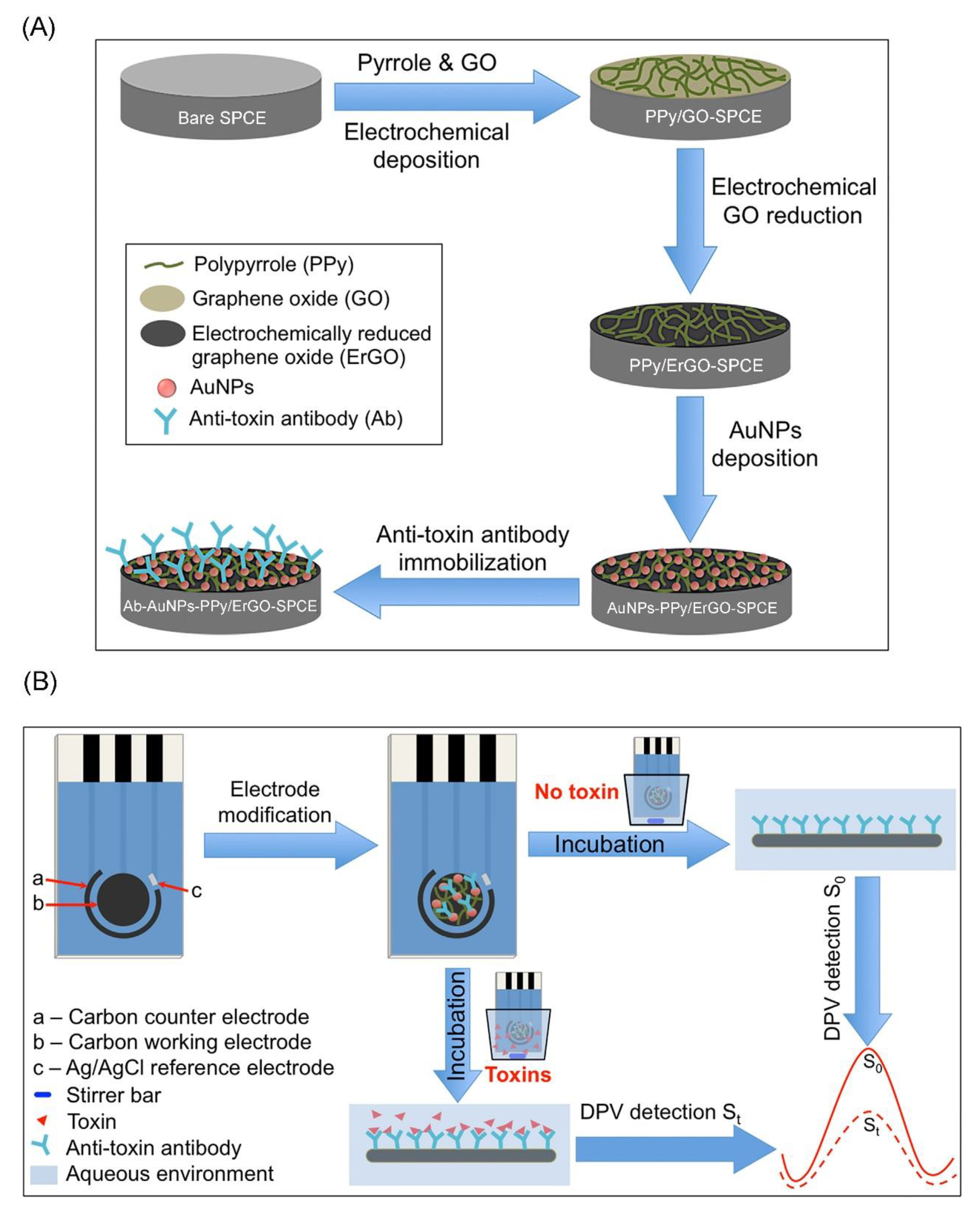
2.1. Botulinum Neurotoxins
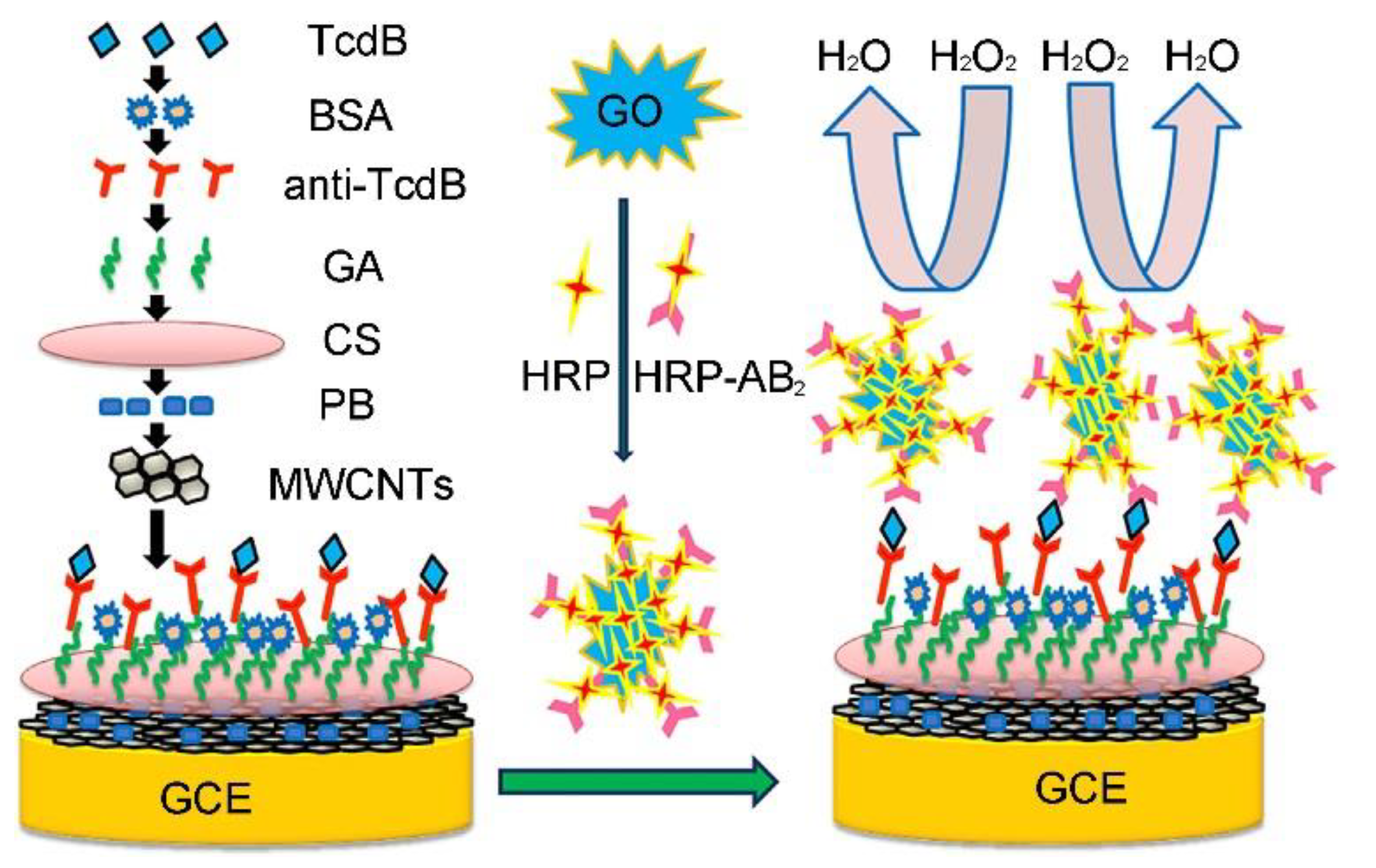
2.2. Clostridium difficile Toxin B
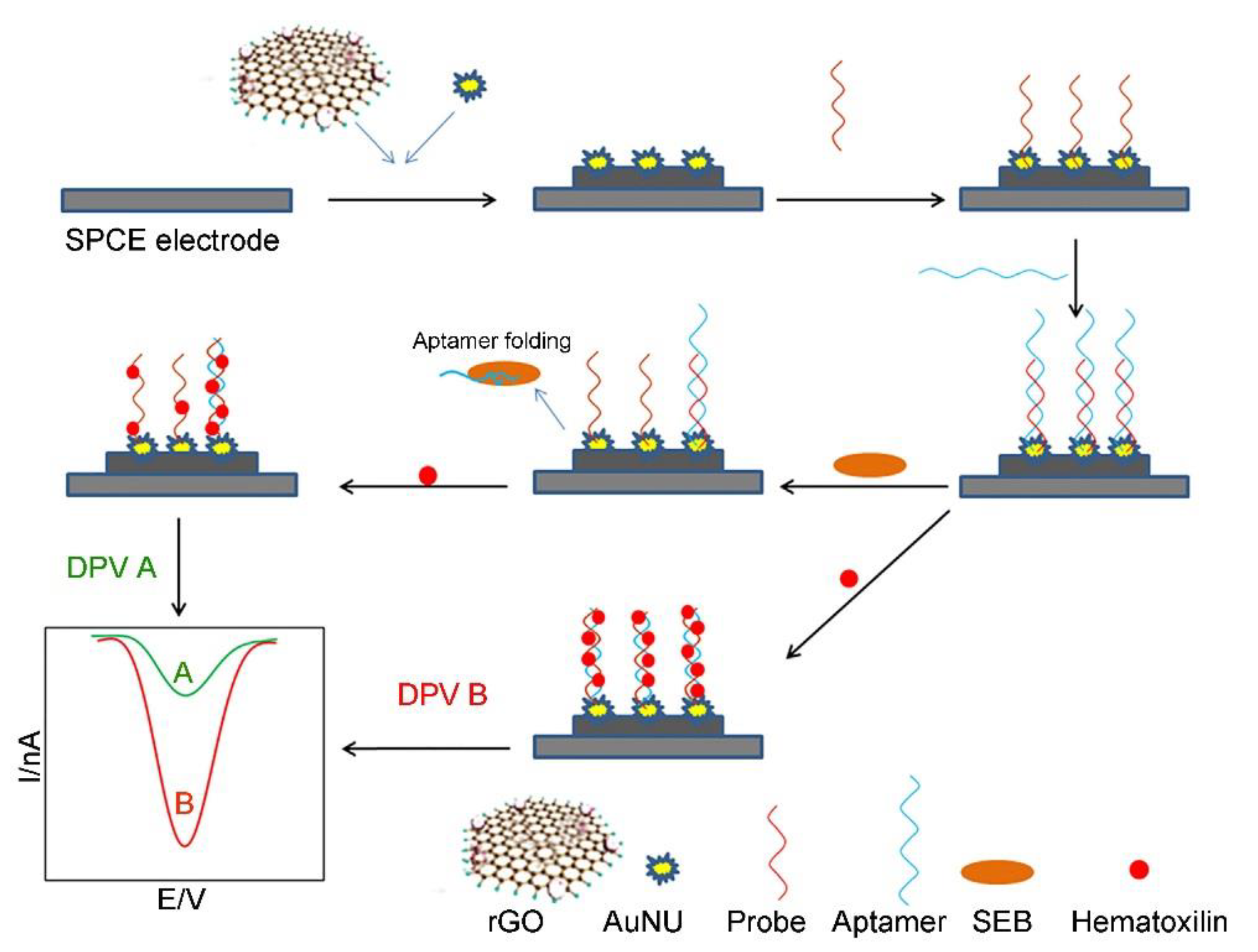
2.3. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B
3. Detection of Fungal Toxins
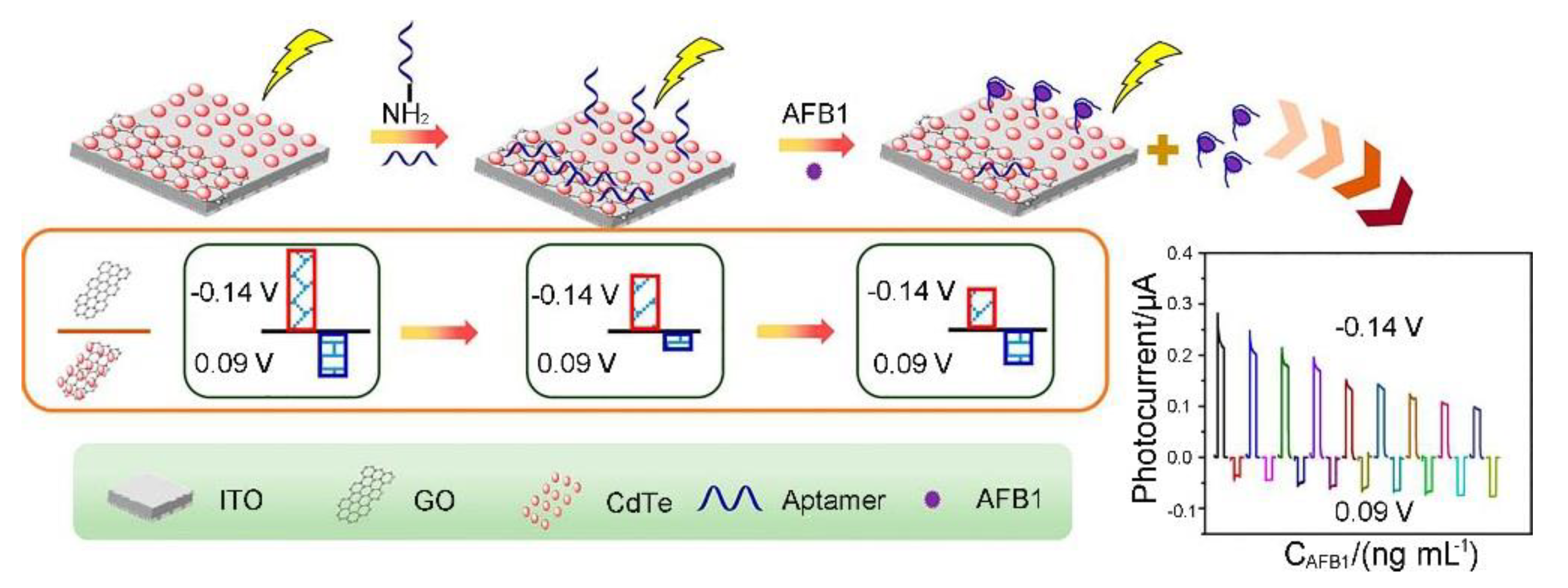
3.1. Aflatoxins
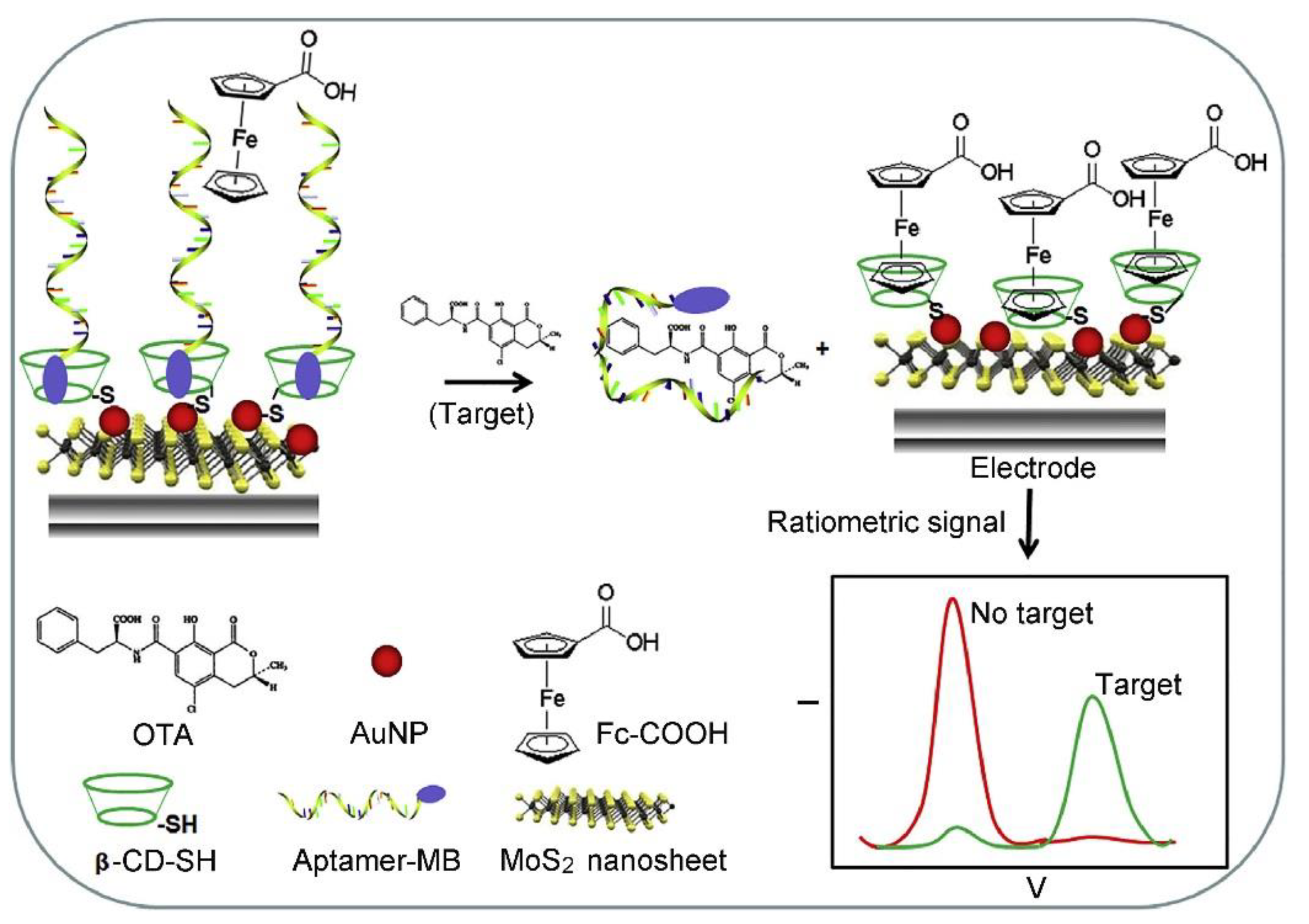
3.2. Ochratoxin
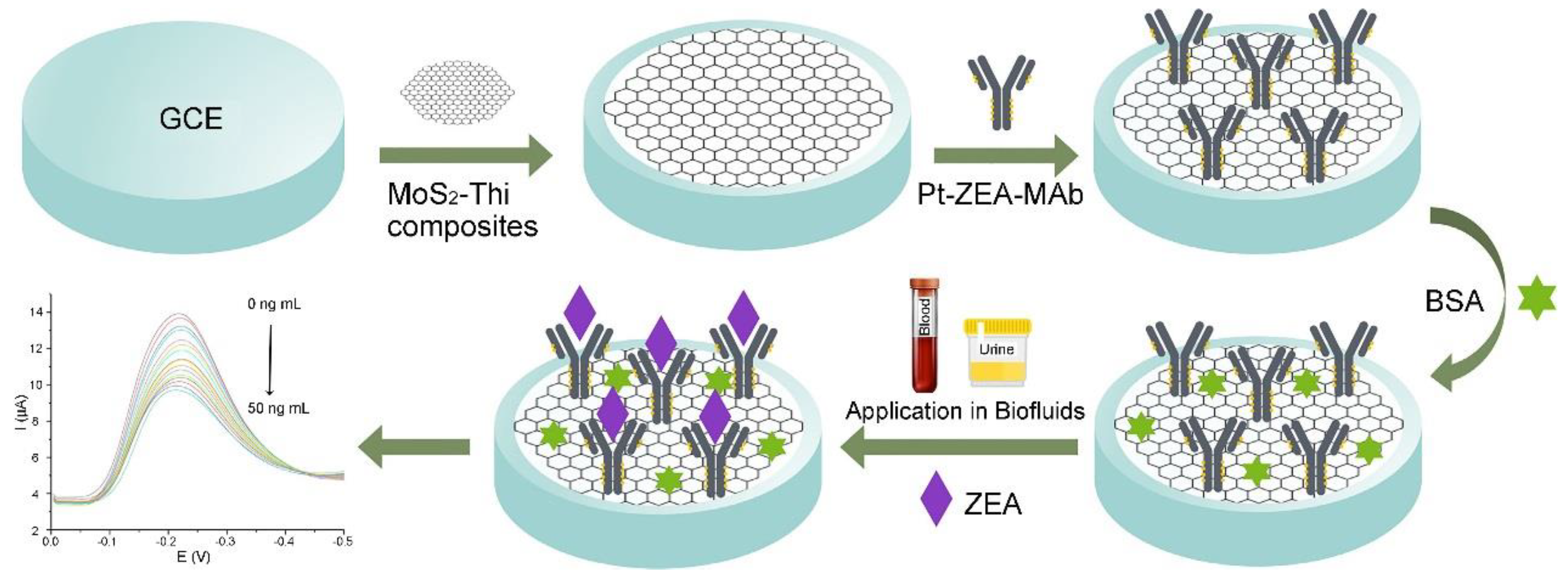
3.3. Mycotoxins Produced by Fusarium
4. Detection of Algal Toxins
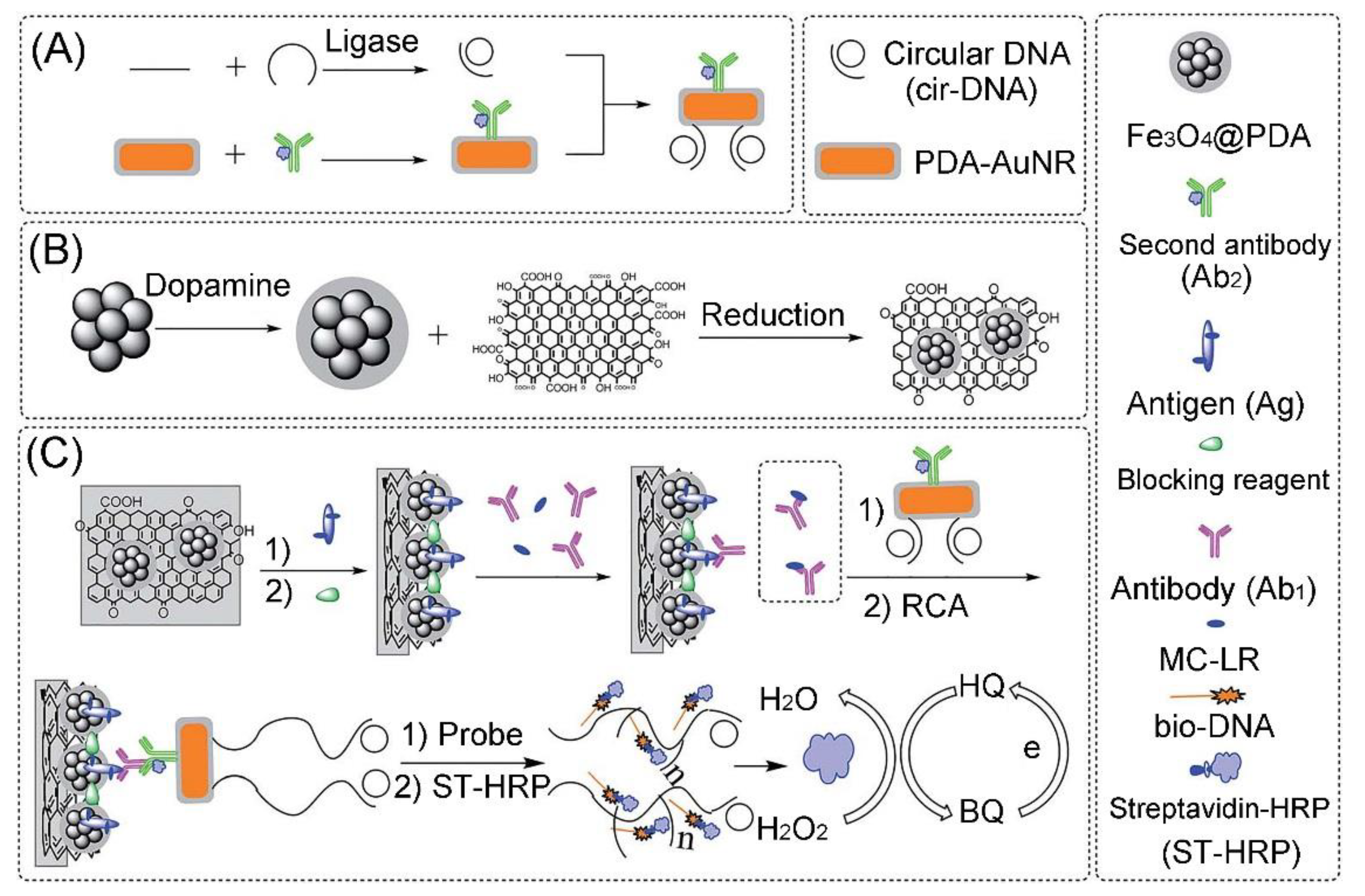
4.1. Microcystins
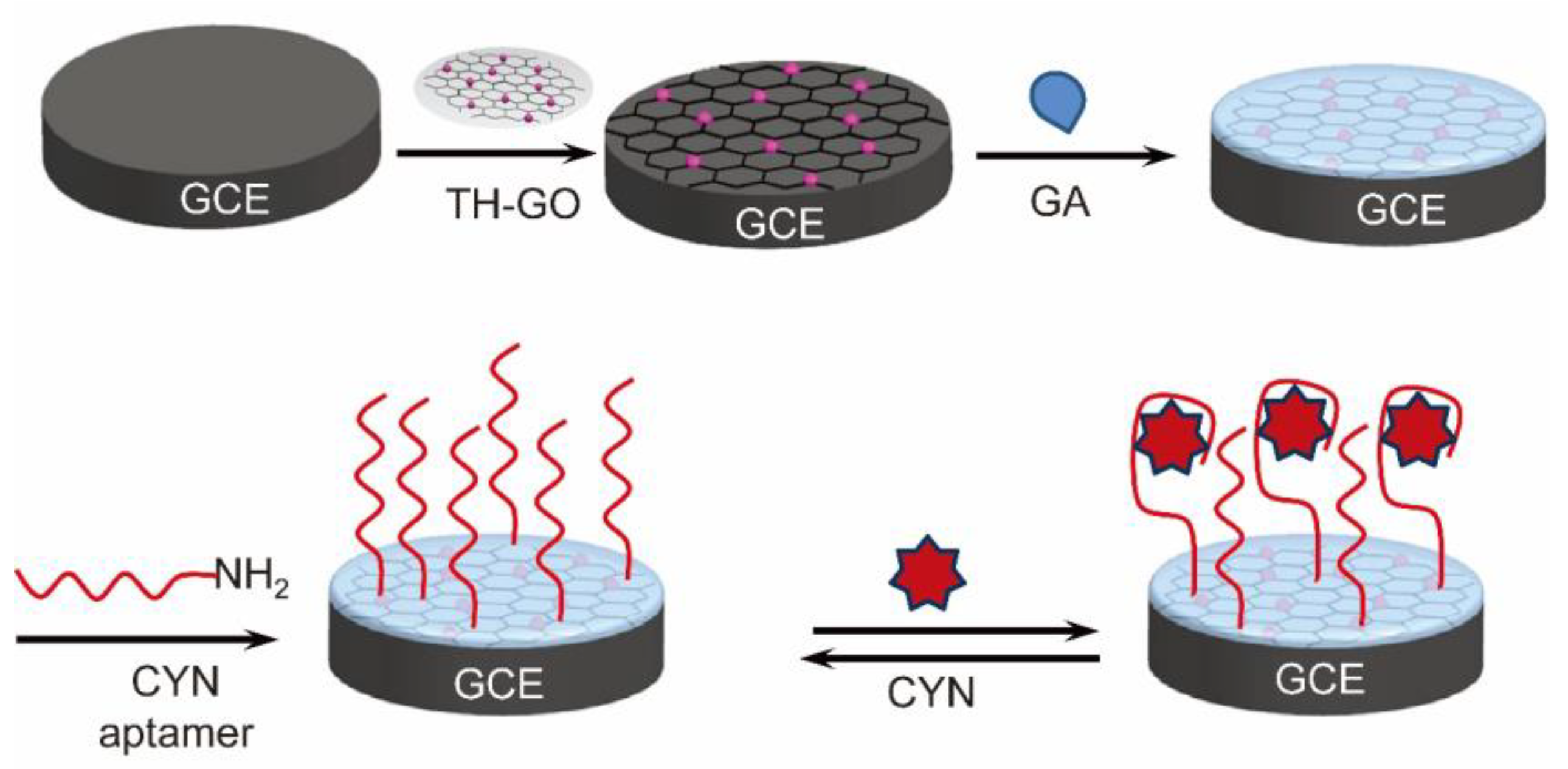
4.2. Cylindrospermopsin
4.3. Saxitoxins
4.4. Brevetoxin B
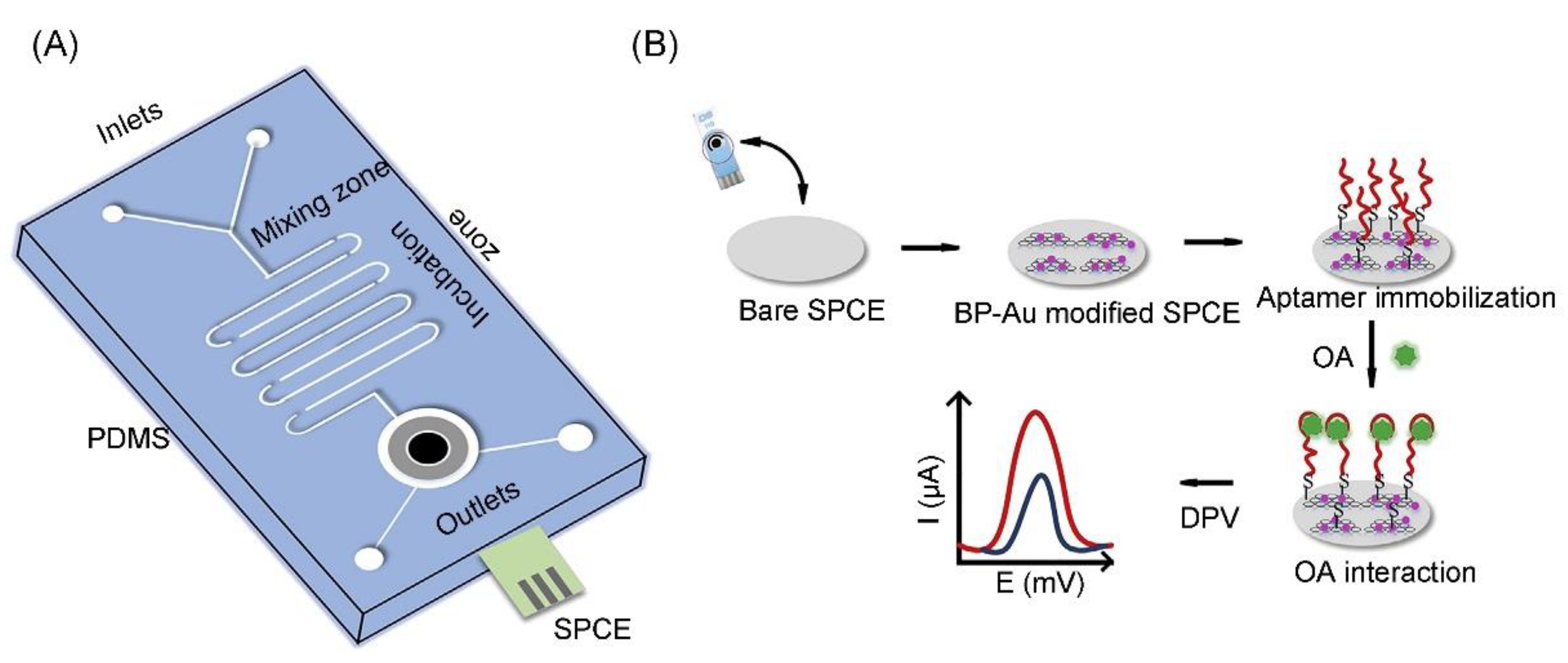
4.5. Okadaic Acid
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Graphene electrochemistry: An overview of potential applications. Analyst 2010, 135, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ratinac, K.R.; Ringer, S.P.; Thordarson, P.; Gooding, J.J.; Braet, F. Carbon nanomaterials in biosensors: Should you use nanotubes or graphene? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2114–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, P. Biological and chemical sensors based on graphene materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2283–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Yang, R.; Chen, H.; Nan, F.; Ge, T.; Jiao, K. Electrocatalytic activity of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets enhanced by self-doped polyaniline for highly sensitive and synergistic determination of adenine and guanine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.K.; Late, D.J.; Morgan, H.; Rout, C.S. Recent developments in 2D layered inorganic nanomaterials for sensing. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13293–13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverte, L.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Campas, M. New advances in electrochemical biosensors for the detection of toxins: Nanomaterials, magnetic beads and microfluidics systems. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 908, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkar, M.; Tuteja, S.K.; Sharma, A.L.; Kumar, V.; Paul, A.K.; Kim, K.H.; Sabherwal, P.; Deep, A. A new electrolytic synthesis method for few-layered MoS2 nanosheets and their robust biointerfacing with reduced antibodies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16555–16563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.A.; Ahmed, M.U. Electrochemical immunosensors and their recent nanomaterial-based signal amplification strategies: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 24995–25014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tan, C.; Xiao, Z.; Lu, Q. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide nanomaterials for biosensing applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2016, 1, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Comes, A.R.; Freitas, A.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Graphene based sensors and biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Huang, K.J.; Wu, X. Recent advances in transition-metal dichalcogenides based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X. Two-dimensional MoS2: A promising building block for biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goud, K.Y.; Kalisa, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Tsang, Y.F.; Lee, S.E.; Gobi, K.V.; Kim, K.H. Progress on nanostructured electrochemical sensors and their recognition elements for detection of mycotoxins: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Ping, J. Recent progress in application of nanomaterial-enabled biosensors for ochratoxin A detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Liu, Y.; Geng, J.; Kou, X.; Xin, Z.; Yang, D. Engineering nanomaterials-based biosensors for food safety detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Maduraiveeran, G. Nanomaterial-based environmental sensing platforms using state-of-the-art electroanalytical strategies. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, T.; Ye, H.; Ji, H.; Tsang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, T.; Chen, H. Recent progress in nanomaterial-based assay for the detection of phytotoxins in foods. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Singh, E.; Singh, P.; Meyyappan, M.; Nalwa, H.S. A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8778–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalila, N.R.; Arshad, M.K.M.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Norhaimi, W.M.W.; Fathil, M.F.M. Current and future envision on developing biosensors aided by 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) productions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Pokatilov, E.P.; Nika, D.L.; Balandin, A.A.; Bao, W.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Extremely high thermal conductivity of graphene: Prospects for thermal management applications in nanoelectronic circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 151911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and prospects. Science 2009, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, L.A.; Yang, R.; Mohiuddin, T.M.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Novoselov, K.S.; Morozov, S.V.; Zhukov, A.A.; Schedin, F.; Hill, E.W.; Geim, A.K. Effect of a high-kappa environment on charge carrier mobility in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 206603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Y. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using high-performance screen-printed graphene electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Nikoleli, G.P.; Pingarron, J.M.; Nikolelis, D.P. Hybrid 2D-nanomaterials-based electrochemical immunosensing strategies for clinical biomarkers determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, A.; Jia, X.; Ho, J.; Nezich, D.; Son, H.; Bulovic, V.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Kong, J. Large area, few-layer graphene films on arbitrary substrates by chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhowalla, M.; Shin, H.S.; Eda, G.; Li, L.J.; Loh, K.P.; Zhang, H. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakilas, V.; Otyepka, M.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Chandra, V.; Kim, N.; Kemp, K.C.; Hobza, P.; Zboril, R.; Kim, K.S. Functionalization of graphene: Covalent and non-covalent approaches, derivatives and applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6156–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.F.; Billups, E. Synthesis of soluble graphite and graphene. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liang, T.; Shi, M.; Chen, H. Graphene-like two-dimensional materials. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3766–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, A.; Samori, P. Graphene via sonication assisted liquid-phase exfoliation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randviir, E.P.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. A decade of graphene research: Production, applications and outlook. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, D.L.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, Y.H. van der Waals layered materials: Opportunities and challenges. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11803–11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzeli, S.; Ovchinnikov, D.; Pasquier, D.; Yazyev, O.V.; Kis, A. 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L.; Shi, G. Graphene-based smart materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 0014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Aljarb, A.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.J. Epitaxial growth of two-dimensional layered transition-metal dichalcogenides: Growth mechanism, controllability, and scalability. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6134–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosi, A.; Chua, C.K.; Bonanni, A.; Pumera, M. Electrochemistry of graphene and related materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7150–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Q.; Xiao, F.; Duan, H. 2D nanomaterials based electrochemical biosensors for cancer diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimene, D.; Alge, D.L.; Gaharwar, A.K. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Emerging trends and future prospects. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7261–7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawn, J.E.; Cousens, S.; Zupan, J. 4 million neonatal deaths: When? where? why? Lancet 2005, 365, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.C.; Chang, S.J.; Gao, X.; Geiger, T.; Stack, G.; Galan, J.E. Emerging insights into the biology of typhoid toxin. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 35, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J. Accumulation of dinophysis toxins in bivalve molluscs. Toxins 2018, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitois, F.; Fastner, J.; Pagotto, C.; Dechesne, M. Multi-toxin occurrences in ten french water resource reservoirs. Toxins 2018, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, E.; Ceremuga, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Biological toxins as the potential tools for bioterrorism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological properties and their involvement in cancer development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partida-Martinez, L.P.; Hertweck, C. Pathogenic fungus harbours endosymbiotic bacteria for toxin production. Nature 2005, 437, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koropatnick, T.A.; Engle, J.T.; Apicella, M.A.; Stabb, E.V.; Goldman, W.E.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. Microbial factor-mediated development in a host-bacterial mutualism. Science 2004, 306, 1186–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D. Water analysis: Emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4295–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Adam, G.; Krska, R. Formation, determination and significance of masked and other conjugated mycotoxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Galan, M.J.; Diaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barcelo, D. Combining chemical analysis and ecotoxicity to determine environmental exposure and to assess risk from sulfonamides. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 804–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Liang, G.; Li, A.; Pan, L. Analytical methods for the determination of alternaria mycotoxins. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steil, D.; Pohlentz, G.; Legros, N.; Mormann, M.; Mellmann, A.; Karch, H.; Muething, J. Combining mass spectrometry, surface acoustic wave interaction analysis, and cell viability assays for characterization of shiga toxin subtypes of pathogenic Escherichia coil bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8989–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.D. (Bio)sensors for measurement of analytes implicated in food safety: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dorst, B.; Mehta, J.; Bekaert, K.; Rouah-Martin, E.; De Coen, W.; Dubruel, P.; Blust, R.; Robbens, J. Recent advances in recognition elements of food and environmental biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1178–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, T.F.; Elliott, C.T.; Fodey, T.L. Biosensors for the analysis of microbiological and chemical contaminants in food. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Feng, X. Biotoxin sensing in food and environment via microchip. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duracova, M.; Klimentova, J.; Fucikova, A.; Dresler, J. Proteomic methods of detection and quantification of protein toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltomaa, R.; Benito-Pena, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Bioinspired recognition elements for mycotoxin sensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 747–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.; Andreescu, S. Chemical and biological sensors for food-quality monitoring and smart packaging. Foods 2018, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabullini, F.; Lucarelli, F.; Palchetti, I.; Marrazza, G.; Mascini, M. Disposable electrochemical genosensor for the simultaneous analysis of different bacterial food contaminants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonel, L.; Vidal, J.C.; Duato, P.; Castillo, J.R. An electrochemical competitive biosensor for ochratoxin A based on a DNA biotinylated aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3254–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, X. Recent progress on cell-based biosensors for analysis of food safety and quality control. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; East, A.K. Phylogeny and taxonomy of the food-borne pathogen Clostridium botulinum and its neurotoxins. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, H.; Rummel, A. Medical aspects of toxin weapons. Toxicology 2005, 214, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, A.; Haefner, K.; Mahrhold, S.; Darashchonak, N.; Holt, M.; Jahn, R.; Beermann, S.; Karnath, T.; Bigalke, H.; Binz, T. Botulinum neurotoxins C, E and F bind gangliosides via a conserved binding site prior to stimulation-dependent uptake with botulinum neurotoxin F utilising the three isoforms of SV2 as second receptor. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh-Panahi, P.; Baradaran, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Hejazi, M.; Sohrabi, H.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Maleki, A. Recent progress in optical and electrochemical biosensors for sensing of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 103, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.; Sharma, M.K.; Ponmariappan, S.; Sarita; Shaik, M.; Upadhyay, S. Electrochemical immunosensor for botulinum neurotoxin type-E using covalently ordered graphene nanosheets modified electrodes and gold nanoparticles-enzyme conjugate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, C.; Tsang, M.K.; Tian, F.; Hao, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, M. A reduced graphene oxide-Au based electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of enzymatic activity of botulinum neurotoxin A. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 220, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Hashemi, P.; Bagheri, H.; Salimian, J.; Ahmadi, A.; Madrakian, T. Impedimetic immunosensor for the label-free and direct detection of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A using Au nanoparticles/graphene-chitosan composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ueno, K.; Nozawa, Y. 2 Toxins (D-1 and D-2) of Clostridium-Difficile causing antibiotic-associated colitis-purification and some characterization. Biochem. Int. 1981, 2, 629–635. [Google Scholar]
- Depitre, C.; Delmee, M.; Avesani, V.; L’Haridon, R.; Roels, A.; Popoff, M.; Corthier, G. Serogroup F strains of Clostridium difficile produce toxin B but not toxin A. J. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 38, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambol, S.P.; Merrigan, M.M.; Lyerly, D.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S. Toxin gene analysis of a variant strain of Clostridium difficile that causes human clinical disease. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, S.M.; Simor, A.E. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2004, 171, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehne, S.A.; Cartman, S.T.; Heap, J.T.; Kelly, M.L.; Cockayne, A.; Minton, N.P. The role of toxin A and toxin B in Clostridium difficile infection. Nature 2010, 467, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Novak, W.S.; Woods, C.W.; Peterson, L.R.; Davis, T.; Schreckenberger, P.; Fang, F.C.; Dascal, A.; Gerding, D.N.; Nomura, J.H.; et al. Impact of strain type on detection of toxigenic clostridium difficile: Comparison of molecular diagnostic and enzyme immunoassay approaches. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, L.T.; Mali, B.L.; Geddes, C.D.; Baillie, L. Extraction and sensitive detection of toxins A and B from the human pathogen Clostridium difficile in 40 s using microwave-accelerated metal-enhanced fluorescence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Wang, L.S.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, J.F. Simple approach for ultrasensitive electrochemical immunoassay of Clostridium difficile toxin B detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chang, D.; Li, Y. Discovery and biosensing applications of diverse RNA-cleaving DNAzymes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2273–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrack, P.; Kappler, J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science 1990, 248, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfora, V.; Caprioli, A.; Marri, N.; Sagrafoli, D.; Boselli, C.; Giacinti, G.; Giangolini, G.; Sorbara, L.; Dottarelli, S.; Battisti, A.; et al. Enterotoxin genes, enterotoxin production, and methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and dairy products in Central Italy. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 42, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rao, V.K.; Kamboj, D.V.; Gaur, R.; Shaik, M.; Shrivastava, A.R. Enzyme free detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) using ferrocene carboxylic acid labeled monoclonal antibodies: An electrochemical approach. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8334–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapini, R.; Marrazza, G. Electrochemical aptasensors for contaminants detection in food and environment: Recent advances. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 118, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Jurik, T.; Kovar, D.; Trnkova, L.; Skladal, P. Nanoparticle-based immunochemical biosensors and assays: Recent advances and challenges. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9973–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodoushan, S.M.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Amani, J.; Halabian, R.; Fooladi, A.A.I. An electrochemical aptasensor for staphylococcal enterotoxin B detection based on reduced graphene oxide and gold nano-urchins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourama, H.; Bullerman, L.B. Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus: Aflatoxigenic fungi of concern in foods and feeds: A review. J. Food Prot. 1995, 58, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.P.; Turner, G.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal secondary metabolism-From biochemistry to genomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, D.M.; Pitt, J.I.; Taylor, J.W. Cryptic speciation and recombination in the aflatoxin-producing fungus Aspergillus flavus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kumar, V.; Ali, M.A.; Solanki, P.R.; Srivastava, A.; Sumana, G.; Saxena, P.S.; Joshi, A.G.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrophoretically deposited reduced graphene oxide platform for food toxin detection. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Ali, M.A.; Umrao, S.; Parashar, U.K.; Srivastava, A.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B.D.; Pandey, S.S.; Hayase, S. Graphene oxide-based biosensor for food toxin detection. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Abraham, S.; Singh, C.; Ali, M.A.; Srivastava, A.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B.D. Protein conjugated carboxylated gold@reduced graphene oxide for aflatoxin B-1 detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 5, 5406–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kumar, V.; Arora, K.; Singh, C.; Ali, M.A.; Puri, N.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Antibody conjugated metal nanoparticle decorated graphene sheets for a mycotoxin sensor. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56518–56526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Xia, Q.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J. An immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B-1 with an enhanced electrochemical performance based on graphene/conducting polymer/gold nanoparticles/the ionic liquid composite film on modified gold electrode with electrodeposition. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 174, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Tang, D. Cobalt-porphyrin-platinum-functionalized reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanostructures: A novel peroxidase mimetic system for improved electrochemical immunoassay. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.M. Multifunctionalized reduced graphene oxide-doped polypyrrole/pyrrolepropylic acid nanocomposite impedimetric immunosensor to ultra-sensitively detect small molecular aflatoxin B-1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, J.; Datta, S.; RoyChaudhuri, C. A graphene field effect capacitive Immunosensor for sub-femtomolar food toxin detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhou, Z.; Hua, R.; Qian, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, K. Design of a dual channel self-reference photoelectrochemical biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10133–10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goud, K.Y.; Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Satyanarayana, M.; Gobi, K.V.; Marty, J.L. An electrochemical aptasensor based on functionalized graphene oxide assisted electrocatalytic signal amplification of methylene blue for aflatoxin B1 detection. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 244, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; He, L.; Yan, X.; Su, T.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Li, C. A novel aflatoxin B-1 biosensor based on a porous anodized alumina membrane modified with graphene oxide and an aflatoxin B-1 aptamer. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 95, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Li, X.; Cui, F.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, H. Aflatoxin B1 electrochemical aptasensor based on tetrahedral DNA nanostructures functionalized three dimensionally ordered macroporous MoS2-AuNPs film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17551–17559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, G.S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z. A novel reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide/polyaniline nanocomposite-based electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B-1. Analyst 2018, 143, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, H.; Pandey, M.K.; Rajesh; Sumana, G. Electrochemical Aflatoxin B1 immunosensor based on the use of graphene quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti-Marnani, A.; Hatefi-Mehrjardi, A.; Es’haghi, Z. A sensitive biosensing method for detecting of ultra-trace amounts of AFB1 based on “Aptamer/reduced graphene oxide” nano-bio interaction. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 175, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Alwarappan, S. A photoelectrochemical aptasensor for aflatoxin B1 detection based on an energy transfer strategy between Ce-TiO2@MoSe2 and Au nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9115–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althagafi, I.I.; Ahmed, S.A.; El-Saidid, W.A. Fabrication of gold/graphene nanostructures modified ITO electrode as highly sensitive electrochemical detection of Aflatoxin B1. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Yang, C.; Guo, Q.; Nie, G. Simple “signal-on” photoelectrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detecting AFB1 based on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide/poly(5-formylindole)/Au nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 134, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, E.; Dietrich, D.R. Ochratoxin A: The continuing enigma. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2005, 35, 33–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses-An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. An update on direct genotoxicity as a molecular mechanism of ochratoxin A carcinogenicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Qian, J.; Yang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, K. Amplified impedimetric aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles covalently bound graphene sheet for the picomolar detection of ochratoxin A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 806, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Yan, Y.; Mao, H.; Wang, K. Highly sensitive impedimetric aptasensor based on covalent binding of gold nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide with good dispersity and high density. Analyst 2014, 139, 5587–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Jiang, L.; Qian, J.; Wang, K. Ultrasensitive electrochemical Ochratoxin A aptasensor based on CdTe quantum dots functionalized graphene/Au nanocomposites and magnetic separation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 781, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, G.; Hayat, A.; Andreescu, S. A generic amplification strategy for electrochemical aptasensors using a non-enzymatic nanoceria tag. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13230–13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, A.H.; Bonanni, A.; Pumera, M. Mycotoxin aptasensing amplification by using inherently electroactive graphene-oxide nanoplatelet labels. Chemelectrochem 2015, 2, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, D. Amplified impedimetric immunosensor based on instant catalyst for sensitive determination of ochratoxin A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.J.; Shuai, H.L.; Chen, Y.X. Layered molybdenum selenide stacking flower-like nanostructure coupled with guanine-rich DNA sequence for ultrasensitive ochratoxin A aptasensor application. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 225, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, G.P.; Wang, X.N.; Tang, D. Homogeneous electrochemical detection of ochratoxin A in foodstuff using aptamer-graphene oxide nanosheets and DNase I-based target recycling reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, V.; Ang, W.L.; Bonanni, A. The Role of Surface Chemistry in Impedimetric Aptasensing. Chemelectrochem 2018, 5, 3654–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Kou, F.; Xu, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, W.; Chi, Y.; Lin, Z. Label-free ochratoxin A electrochemical aptasensor based on target-induced noncovalent assembly of peroxidase-like graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 270, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ning, G.; Bi, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y. A novel ratiometric electrochemical assay for ochratoxin A coupling Au nanoparticles decorated MoS2 nanosheets with aptamer. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 285, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xiong, P.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, S.; Zhu, Z.Q. Enzymatic oxydate-triggered AgNPs etching: A novel signal-on photoelectrochemical immunosensing platform based on Ag@AgCl nanocubes loaded RGO plasmonic heterostructure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Bharti, A.; Batra, S.; Rana, S.; Rana, S.; Bhalla, A.; Prabhakar, N. An electrochemical aptasensor based on graphene doped chitosan nanocomposites for determination of Ochratoxin A. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifuzzaman, M.; Barman, S.C.; Zahed, M.A.; San, N.J.; Park, J.Y. Green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide decorated with few-layered MoS2-nanoroses and Au/Pd/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles for ultrasensitive label-free immunosensing platforms. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B249–B257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.T.; Zhang, H.B.; He, C.H.; Wu, W.D.; Zhang, H.B. DNA Electrochemical aptasensor for detecting fumonisins B1 based on graphene and thionine nanocomposite. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Jia, F.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z. Impedimetric aptamer-based determination of the mold toxin fumonisin B1. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Seenivasan, R.; Wang, Y.C.; Yu, J.H.; Gunasekaran, S. An electrochemical immunosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of mycotoxins fumonisin B1 and deoxynivalenol. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wu, D.; Fan, H.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Ultrasensitive non-enzymatic and non-mediator electrochemical biosensor using nitrogen-doped graphene sheets for signal amplification and nanoporous alloy as carrier. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Nie, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, K.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Han, Z. Thin-layer MoS2 and thionin composite-based electrochemical sensing platform for rapid and sensitive detection of zearalenone in human biofluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yan, X. An amperometric zearalenone aptasensor based on signal amplification by using a composite prepared from porous platinum nanotubes, gold nanoparticles and thionine-labelled graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, R.M. The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon 1998, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, J.H. The effects of harmful algal blooms on aquatic organisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2002, 10, 113–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, P. A review of reproductive toxicity of microcystins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preece, E.P.; Hardy, F.J.; Moore, B.C.; Bryan, M. A review of microcystin detections in estuarine and marine waters: Environmental implications and human health risk. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dixon, M.B.; Saint, C.; Teng, K.S.; Furumai, H. Electrochemical biosensing of Algal toxins in water: The current state-of-the-art. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogiazi, V.; de la Cruz, A.; Mishra, S.; Shanov, V.; Heineman, W.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. A comprehensive review: Development of electrochemical biosensors for detection of cyanotoxins in freshwater. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1151–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, B.; Wu, D.; Cai, Y.; Mao, K.; Li, H.; Xu, C. Nanoporous PtRu alloy enhanced nonenzymatic immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of microcystin-LR. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4193–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tian, J.; Quan, X. A graphene and multienzyme functionalized carbon nanosphere-based electrochemical immunosensor for microcystin-LR detection. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 103, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, J. Electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of microcystin-LR based on graphene-gold nanocomposite/functional conducting polymer/gold nanoparticle/ionic liquid composite film with electrodeposition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.L.; Fu, X.W.; Wen, Y.P.; Qiu, Z.J.; Xiong, L.M.; Hong, N.Z.; Yang, Y.H. A label-free immunosensor for microcystins-LR based on graphene and gold Nanocage. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 42, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhao, H.; Quan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, S. Fabrication of graphene quantum dots/silicon nanowires nanohybrids for photoelectrochemical detection of microcystin-LR. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 196, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Ng, A.; Siaj, M.; Zourob, M. Label-free voltammetric aptasensor for the sensitive detection of microcystin-LR using graphene-modified electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7551–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Jiang, D.; Dai, L.; Zhou, L.; Hao, N.; Qian, J.; Qiu, B.; Wang, K. Fabricating photoelectrochemical aptasensor for selectively monitoring microcystin-LR residues in fish based on visible light-responsive BiOBr nanoflakes/N-doped graphene photoelectrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Han, C.; Jia, B.; Saint, C.; Nadagouda, M.; Falaras, P.; Sygellou, L.; Vogiazi, V.; Dionysiou, D.D. A 3D graphene-based biosensor as an early microcystin-LR screening tool in sources of drinking water supply. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 236, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wei, J.; Gan, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y. A rolling circle amplification signal-enhanced immunosensor for ultrasensitive microcystin-LR detection based on a magnetic graphene-functionalized electrode. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39906–39913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Yan, F.; Pang, P.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, W. A molybdenum disulfide/gold nanorod composite-based electrochemical immunosensor for sensitive and quantitative detection of microcystin-LR in environmental samples. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 244, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.; Teng, X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, W.; Barrow, C.J. Ultrasensitive enzyme-free electrochemical immunosensor for microcystin-LR using molybdenum disulfide/gold nanoclusters nanocomposites as platform and Au@Pt core-shell nanoparticles as signal enhancer. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 266, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.X.; Shang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.F.; Guo, Z.Y. A label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on multi-functionalized graphene oxide for ultrasensitive detection of microcystin-LR. Chem. Pap. 2017, 72, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Hao, N.; You, T.; Wang, K. An intriguing signal-off responsive photoelectrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of microcystin-LR and its mechanism study. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 259, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jia, B.; Furumai, H. Fabrication of graphene film composite electrochemical biosensor as a pre-screening algal toxin detection tool in the event of water contamination. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Khan, M.Z.H. A highly sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for detection of microcystin-LR based on a dual signal amplification strategy. Analyst 2019, 144, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W. Toxins of Cyanobacteria. Sci. Am. 1994, 270, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Apeldoorn, M.E.; van Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.A.; Bakker, G.J.I. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westrick, J.A.; Szlag, D.C.; Southwell, B.J.; Sinclair, J. A review of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal/inactivation in drinking water treatment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, C.; Azevedo, J.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Cylindrospermopsin: Occurrence, methods of detection and toxicology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiblier, C.; Wood, S.; Echenique-Subiabre, I.; Heath, M.; Villeneuve, A.; Humbert, J.F. A review of current knowledge on toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacteria-Ecology, toxin production and risk management. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5464–5479. [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa, M.G.; Gutierrez-Praena, D.; Prieto, A.I.; Guzman-Guillen, R.; Jos, A.; Camean, A.M. Neurotoxicity induced by microcystins and cylindrospermopsin: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z. A label-free electrochemical impedance aptasensor for cylindrospermopsin detection based on thionine-graphene nanocomposites. Analyst 2015, 140, 5570–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratakou, S.; Nikoleli, G.P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Karapetis, S.; Tzamtzis, N. Development of an electrochemical biosensor for the rapid detection of saxitoxin based on air stable lipid films with incorporated anti-STX using graphene electrodes. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hou, L.; Tang, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, G. Magneto-controlled electrochemical immunoassay of brevetoxin B in seafood based on guanine-functionalized graphene nanoribbons. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, S.; Silvestro, S.; Faggio, C. How the marine biotoxins affect human health. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. A graphene-based electrochemical competitive immunosensor for the sensitive detection of okadaic acid in shellfish. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7593–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Chand, R.; Singh, C.B.; Singh, A. Phosphorene-gold nanocomposite based microfluidic aptasensor for the detection of okadaic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, X.; Jian, M.; Geleta, G.S.; Wang, Z. Two-Dimensional Layered Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Microbial Toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010020
Li Z, Li X, Jian M, Geleta GS, Wang Z. Two-Dimensional Layered Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Microbial Toxins. Toxins. 2020; 12(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhuheng, Xiaotong Li, Minghong Jian, Girma Selale Geleta, and Zhenxin Wang. 2020. "Two-Dimensional Layered Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Microbial Toxins" Toxins 12, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010020
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, X., Jian, M., Geleta, G. S., & Wang, Z. (2020). Two-Dimensional Layered Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Microbial Toxins. Toxins, 12(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010020





