Botulinum Toxin Type A and Physiotherapy in Spasticity of the Lower Limbs Due to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Population and Inclusion Criteria
5.2. Methods
5.3. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morfini, G.A.; Bosco, D.A.; Brown, H.; Gatto, R.; Kaminska, A.; Song, Y.; Molla, L.; Baker, L.; Marangoni, M.N.; Berth, S.; et al. Inhibition of Fast Axonal Transport by Pathogenic SOD1 Involves Activation of p38 MAP Kinase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.R.; Al-Chalabi, A. Clinical phenotypes. In The Motor Neurone Disease Handbook; Kiernan, M., Ed.; Australasian Medical Publishing Company Limited: Pyrmont, Australia, 2007; pp. 56–73. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, J.D.; Engel, L.S.; Richardson, D.B.; Gammon, M.D.; Baird, C.; Umbach, D.M.; Allen, K.D.; Stanwyck, C.L.; Keller, J.; Sandler, D.P.; et al. Military service, deployments, and exposures in relation to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis etiology. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeJesus-Hernandez, M.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Boxer, A.L.; Baker, M.; Rutherford, N.J.; Nicholson, A.M.; Finch, N.A.; Flynn, H.; Adamson, J.; et al. Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in non-coding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron 2011, 72, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renton, A.E.; Majounie, E.; Waite, A.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Rollinson, S.; Gibbs, J.R.; Schymick, J.C.; Laaksovirta, H.; Van Swieten, J.C.; Myllykangas, L.; et al. A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 Is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 2011, 72, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, R.; Pisa, D.; Marina, A.I.; Morato, E.; Rábano, A.; Rodal, I.; Carrasco, L. Evidence for Fungal Infection in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Brain Tissue from Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.D.; Wokke, J.H.; Borasio, G.D. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I (rhIGF-I) for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren, L.; Almay, B.G.; Holmgren, G.; Wall, S. Epidemiology of motor neuron disease in northern Sweden. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1983, 68, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cookson, M.R.; Shaw, P.J. Oxidative stress and motor neurone disease. Brain Pathol. 1999, 9, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, N.C.; Wang, Y.D.; Scarborough, E.A.; Moore, J.; Diaz, Z.; MacLea, K.S.; Freibaum, B.; Li, S.; Molliex, A.; et al. Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multi system proteinopathy and ALS. Nature 2013, 495, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Tandan, R. RNA quality control and protein aggregates in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A review. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.H.; Neumann, M.; Bloch, K.E. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis–diagnosis and treatment. Praxis 2012, 101, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, S.; Schreiber, S.; Heinze, H.; Dengler, R.; Petri, S.; Vielhaber, S. The Dyspnea-ALS-Scale (DALS-15) optimizes individual treatment in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) suffering from dyspnea. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2019, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzos, M.; Evangelopoulos, E.; Sereti, E.; Zouvelou, V.; Marmara, S.; Alexakis, T.; Evdokimidis, I. Alterations of T cell subsets in ALS: A systemic immune activation? Acta Neurol. Scand. 2011, 125, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulla, S.; Vielhaber, S.; Kollewe, K.; Machts, J.; Heinze, H.J.; Dengler, R. The impact of physical impairment on emotional well-being in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 2014, 15, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Biology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 200–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.J.; Hill, K.K.; Raphael, B.H. Historical and current perspectives on Clostridium botulinum diversity. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, O.; Pirazzini, M.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxins: Genetic, structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, A. The long journey of botulinum neurotoxins into the synapse. Toxicon 2015, 107, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Rasotto, M.B. On botulinum neurotoxin variability. MBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L. The life history of a botulinum toxin molecule. Toxicon 2013, 68, 40–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D. Clinical applications of botulinum toxin. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressler, D.; Saberi, F.A.; Kollewe, K.; Schrader, C. Safety aspects of incobotulinumtoxinA high-dose therapy. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.M.; Hallett, M.; Ashman, E.J.; Comella, C.L.; Green, M.W.; Gronseth, G.S.; Armstrong, M.J.; Gloss, D.; Potrebic, S.; Jankovic, J.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of blepharospasm, cervical dystonia, adult spasticity, and headache: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 86, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.G.; Mitchell, J.D.; Moore, D.H. Riluzole for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)/motor neuron disease (MND). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourke, S.C.; Tomlinson, M.; Williams, T.L.; Bullock, R.E.; Shaw, P.J.; Gibson, G.J. Effects of non-invasive ventilation on survival and quality of life in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, J.; Kurent, J.; Ludolph, A. Drug therapy for pain in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.; Khan, F.; Young, C.A.; Galea, M. Symptomatic treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, N.L.; Satkunam, L.E.; Deforge, D. Treatment for spasticity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, M.; Zhu, C.; He, L. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Costa, J.; Máñez, I.; Alabajos, A.; Guevara Salazar, M.; Roda, C.; Sevilla, T. Safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin A for the treatment of spasticity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Results of a pilot study. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, P.M.; Abrahams, S.; Borasio, G.D.; de Carvalho, M.; Chio, A.; Van Damme, P.; Hardiman, O.; Kollewe, K.; Morrison, K.E.; Petri, S. EFNS guidelines on the clinical management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (MALS)–revised report of an EFNS task force. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, N.; Humberstone, M.; Wills, A.; Arthur, A. The use of botulinum toxin injections to manage drooling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neurone disease: A systematic review. Dysphagia 2014, 29, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, A.J.; Byl, N.N. A systematic review of the effect of moderate intensity exercise on function and disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2009, 33, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvulli, R.; Megna, M.; Romanelli, E.; Mastromauro, L.; Conte, E.; Lancioni, G.; Dargenio, M.; De Venuto, G.; Gallo, G.A.; Lerario, R.; et al. Effectiveness of the Treatment with Botulinum Toxin type A (BTX-A) in the Management of the Spasticity in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Clin. Immunol. Endocr Metab. Drugs 2016, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Coco, D.; La Bella, V. Fatigue, sleep, and nocturnal complaints in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smania, N.; Picelli, A.; Munari, D.; Geroin, C.; Ianes, P.; Waldner, A.; Gandolfi, M. Rehabilitation procedures in the management of spasticity. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 423–438. [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes Barros Fucs, P.M.; Svartman, C.; de Assumpção, R.M.; Yamada, H.H.; Simis, S.D. Surgical technique: Medial column arthrodesis in rigid spastic planovalgus feet. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ianieri, G.; Marvulli, R.; Gallo, G.A.; Fiore, P.; Megna, M. “Appropriate Treatment” and Therapeutic Window in Spasticity Treatment with IncobotulinumtoxinA: From 100 to 1000 Units. Toxins 2018, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, L.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, K.C.; Lur, S.Y. Quantitative mechanical properties of the relaxed biceps and triceps brachii muscles in patients with subacute stroke: A reliability study of the myoton-3 myometer. Stroke Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 617694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianieri, G.; Saggini, R.; Marvulli, R.; Tondi, G.; Aprile, A.; Ranieri, M.; Benedetto, G.; Altini, S.; Lancioni, G.E.; Goffredo, L.; et al. New approach in the assessment of the tone, elasticity and the muscular resistance: Nominal scales vs MYOTON. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhiney, M.C.; Rabkin, J.G.; Gordon, P.H.; Goetz, R.; Mitsumoto, H. Prevalence of fatigue and depression in ALS patients and change over time. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
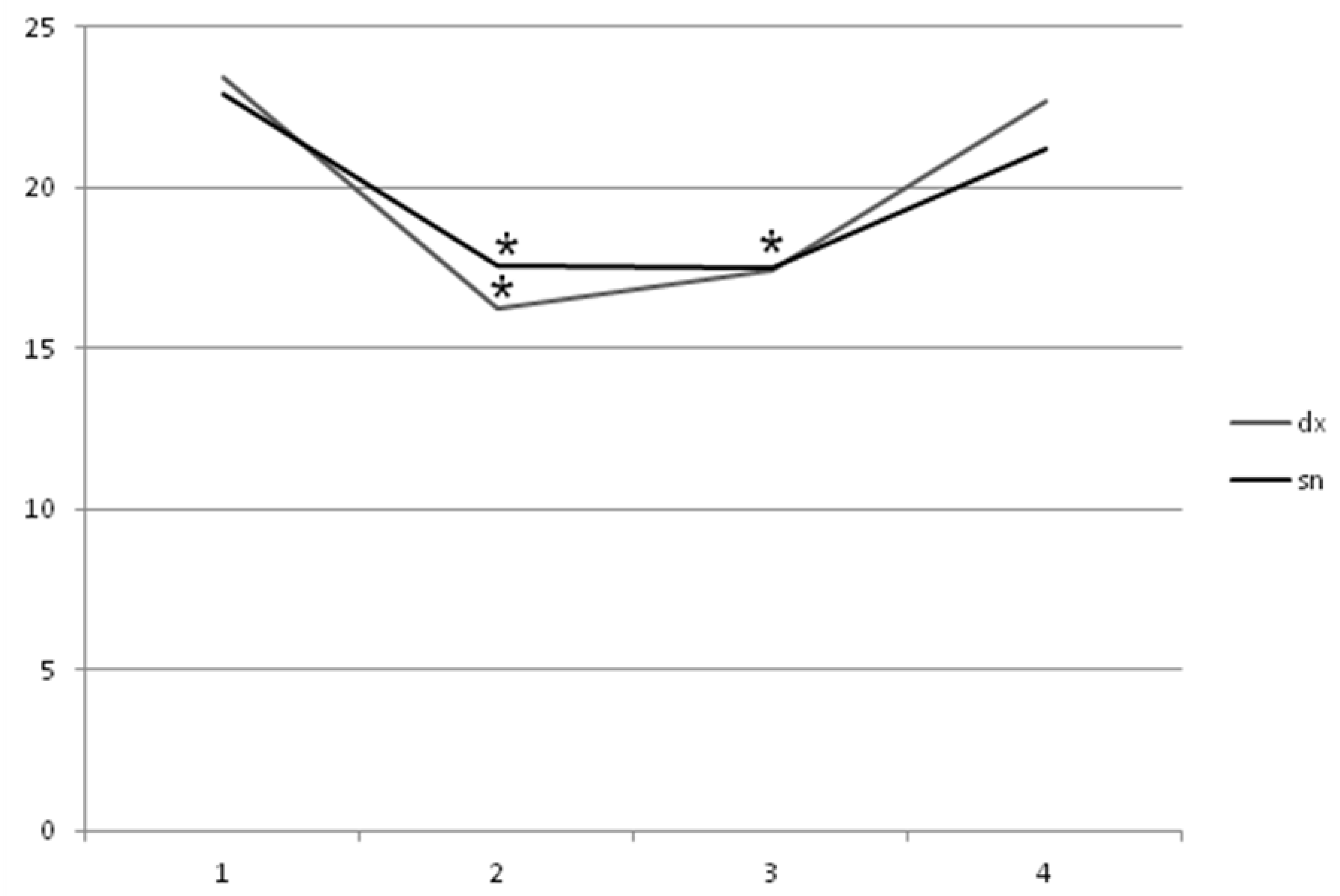


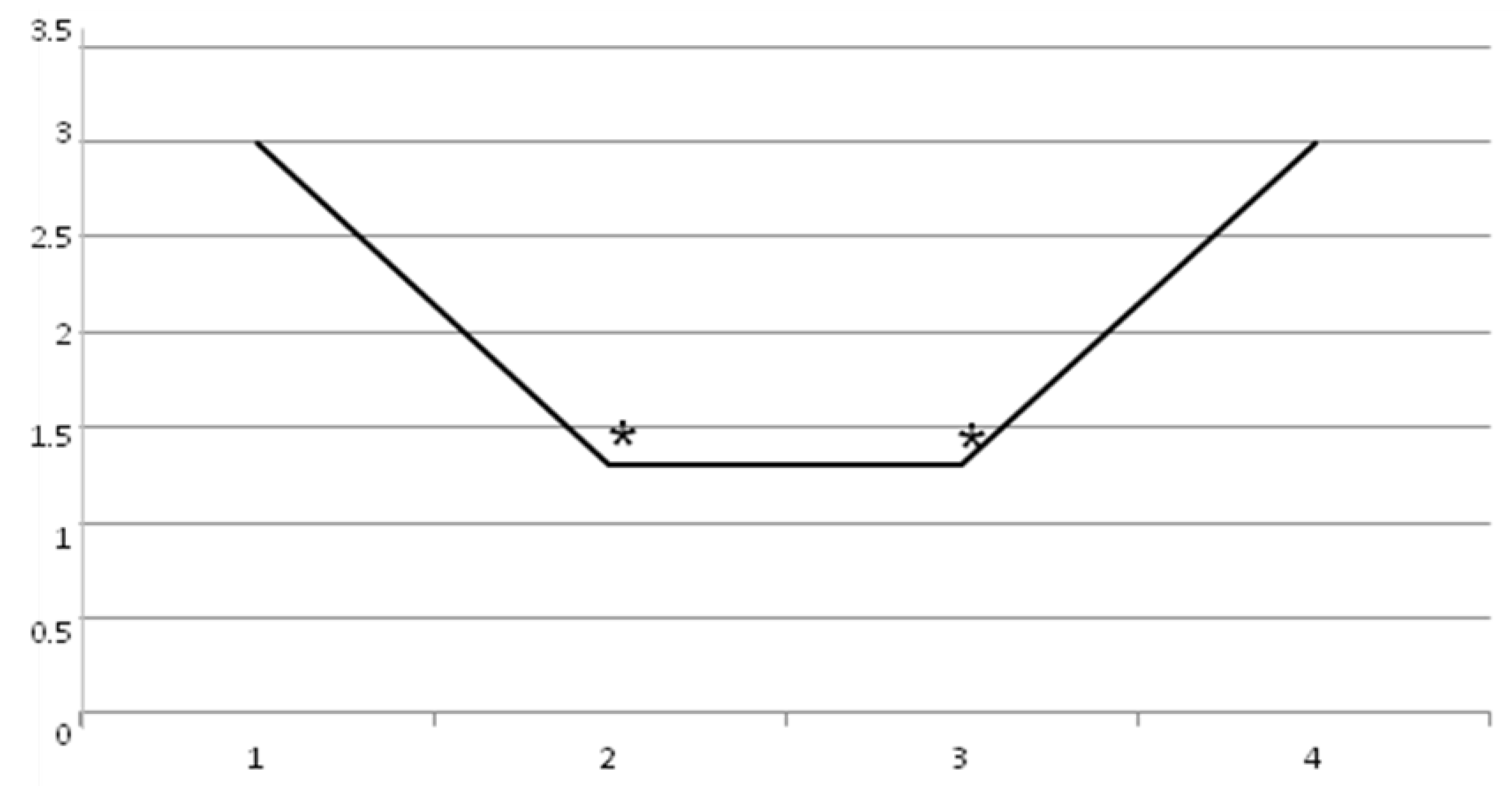
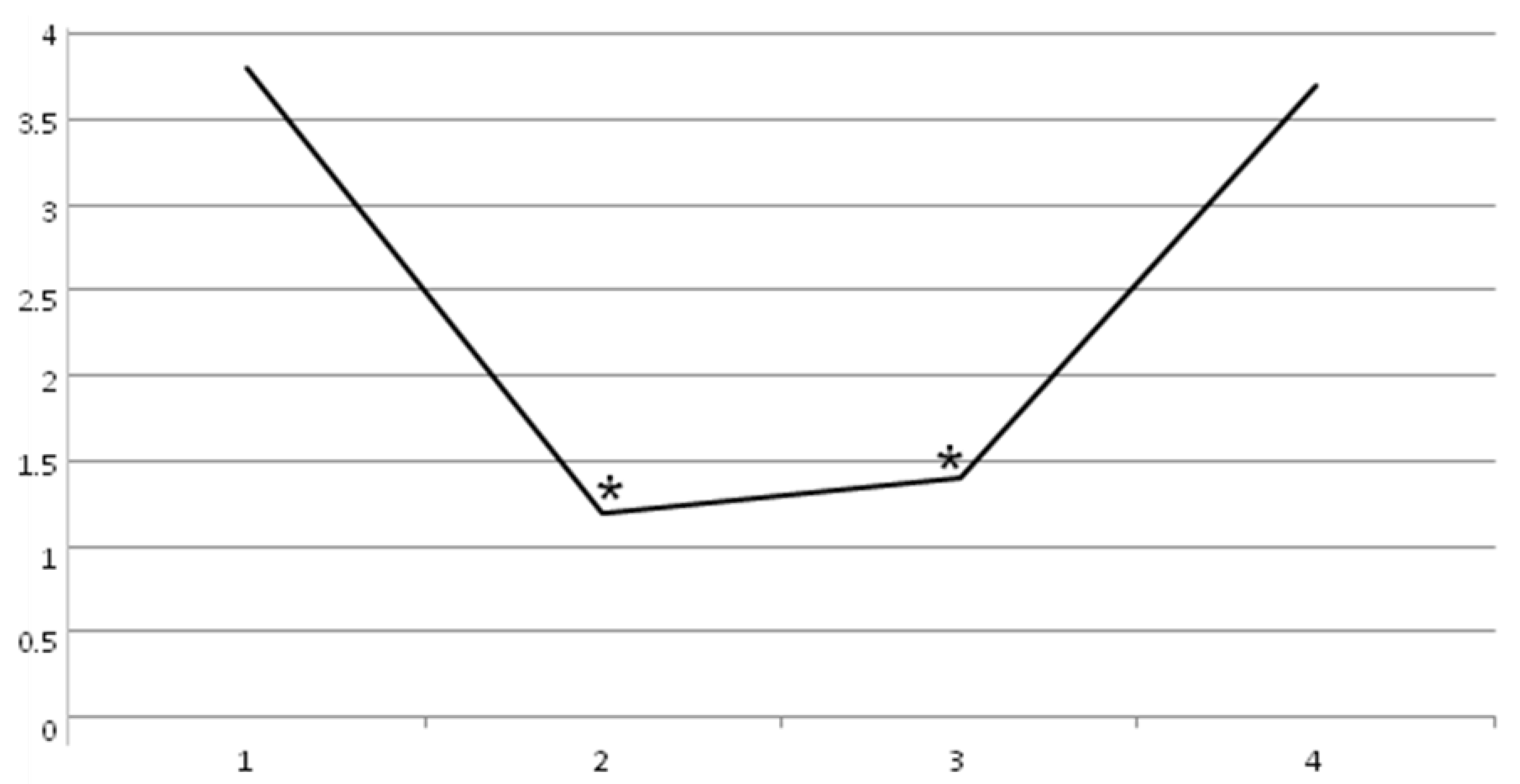
| Pt 1 | Pt 2 | Pt 3 | Pt 4 | Pt 5 | Pt 6 | Pt 7 | Pt 8 | Pt 9 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 | Pt 12 | Pt 13 | Pt 14 | Pt 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 55 | 45 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 45 | 46 | 58 | 45 | 45 | 47 | 47 | 55 | 43 | 40 |
| Sex | M | M | M | M | F | M | F | F | M | F | F | M | M | M | M |
| Dg | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2017 | 2015 | 2018 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2016 |
| BS | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Pt 1 | Pt 2 | Pt 3 | Pt 4 | Pt 5 | Pt 6 | Pt 7 | Pt 8 | Pt 9 | Pt 10 | Pt 11 | Pt 12 | Pt 13 | Pt 14 | Pt 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R AM | 110 | 120 | 100 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| L AM | 110 | 120 | 120 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 80 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 110 | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marvulli, R.; Megna, M.; Citraro, A.; Vacca, E.; Napolitano, M.; Gallo, G.; Fiore, P.; Ianieri, G. Botulinum Toxin Type A and Physiotherapy in Spasticity of the Lower Limbs Due to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Toxins 2019, 11, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11070381
Marvulli R, Megna M, Citraro A, Vacca E, Napolitano M, Gallo G, Fiore P, Ianieri G. Botulinum Toxin Type A and Physiotherapy in Spasticity of the Lower Limbs Due to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Toxins. 2019; 11(7):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11070381
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarvulli, Riccardo, Marisa Megna, Aurora Citraro, Ester Vacca, Marina Napolitano, Giulia Gallo, Pietro Fiore, and Giancarlo Ianieri. 2019. "Botulinum Toxin Type A and Physiotherapy in Spasticity of the Lower Limbs Due to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" Toxins 11, no. 7: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11070381
APA StyleMarvulli, R., Megna, M., Citraro, A., Vacca, E., Napolitano, M., Gallo, G., Fiore, P., & Ianieri, G. (2019). Botulinum Toxin Type A and Physiotherapy in Spasticity of the Lower Limbs Due to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Toxins, 11(7), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11070381





