ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II, Two Novel Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Trans-Pecos Copperhead Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster Venom: Biochemical and Functional Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
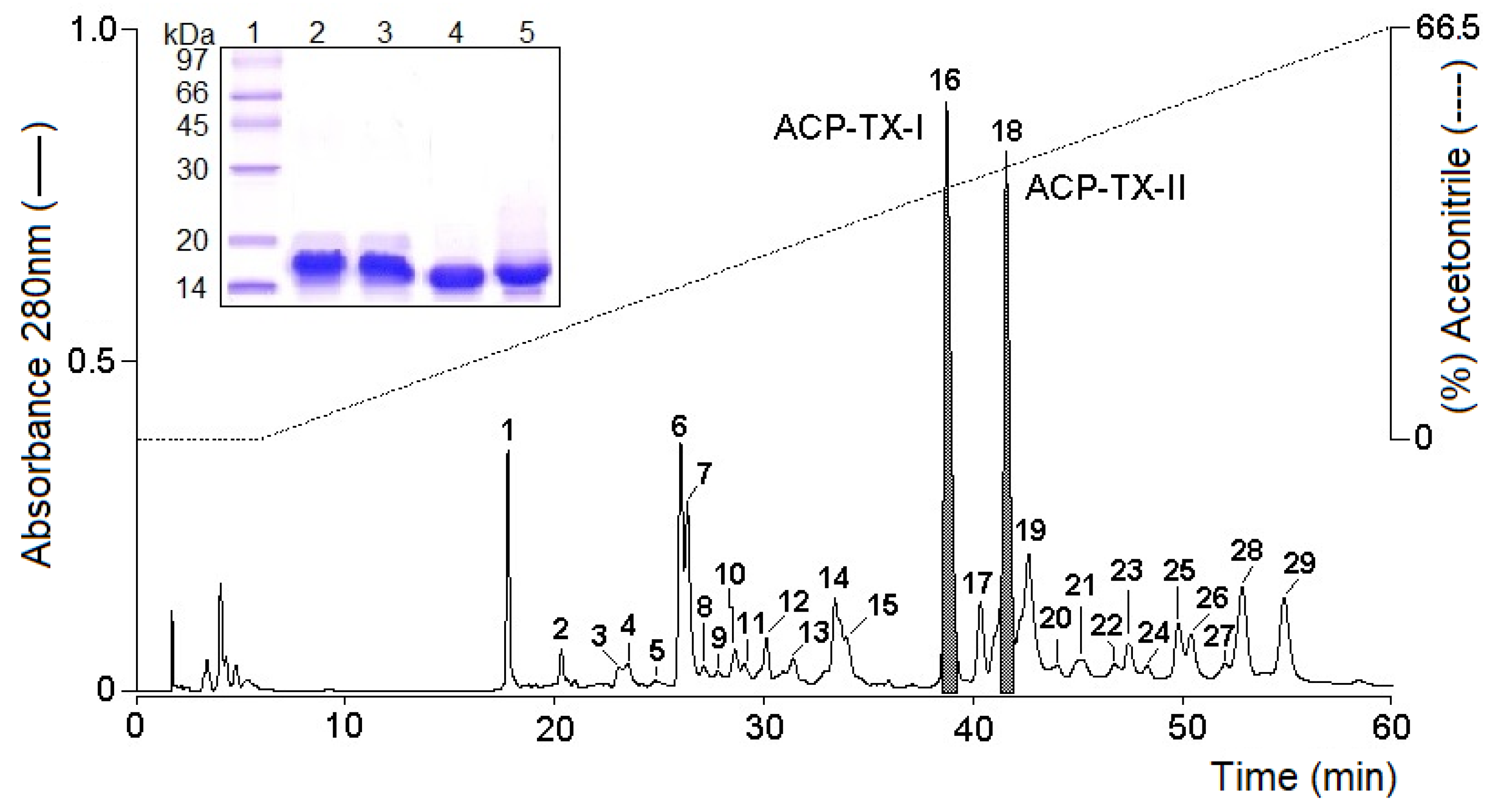
2.1. Purification and Biochemical Characterization of ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II
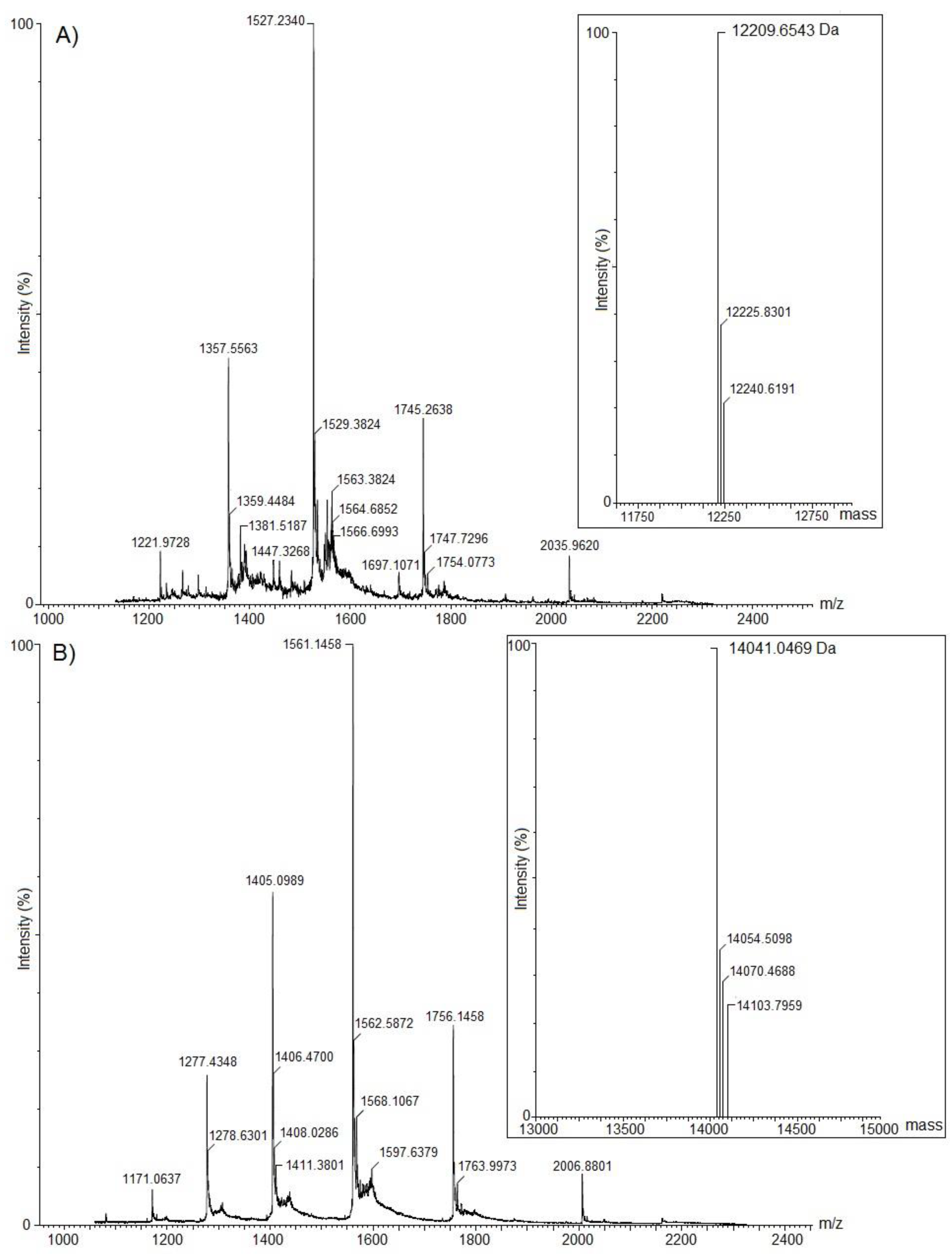
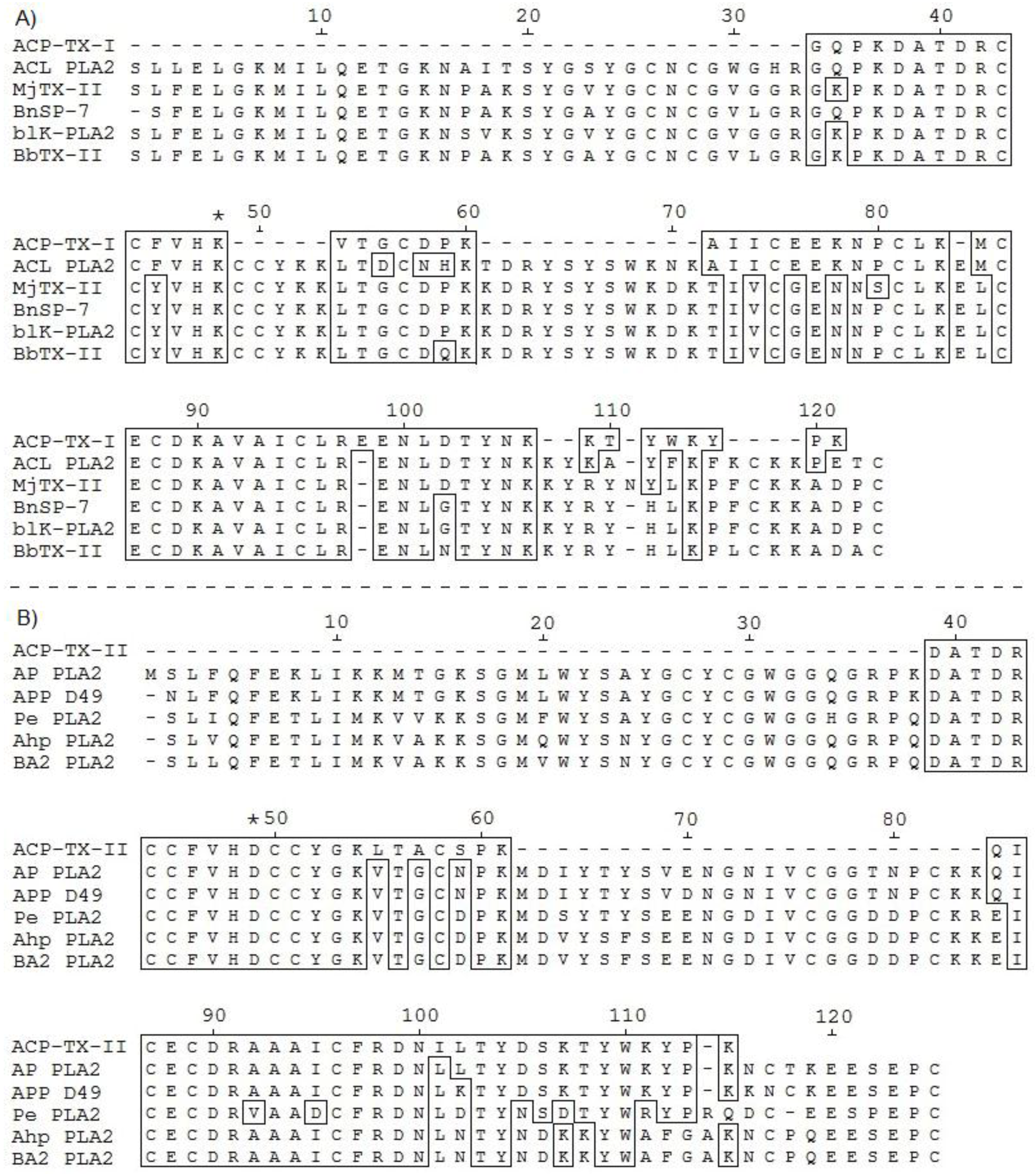
2.2. Determination of the Amino Acid Sequences of ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II
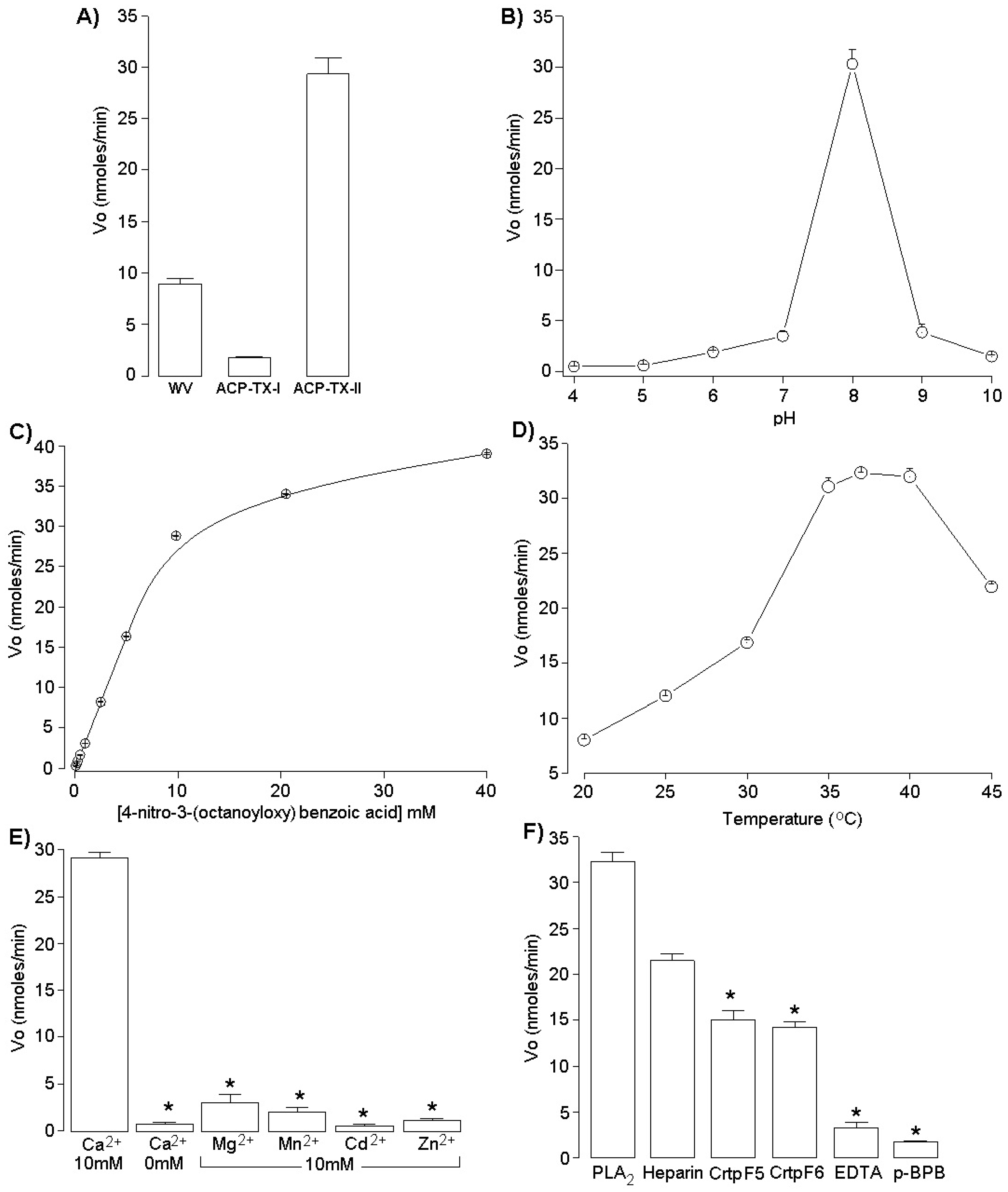
2.3. Activity Measurements of ACP-TX-II
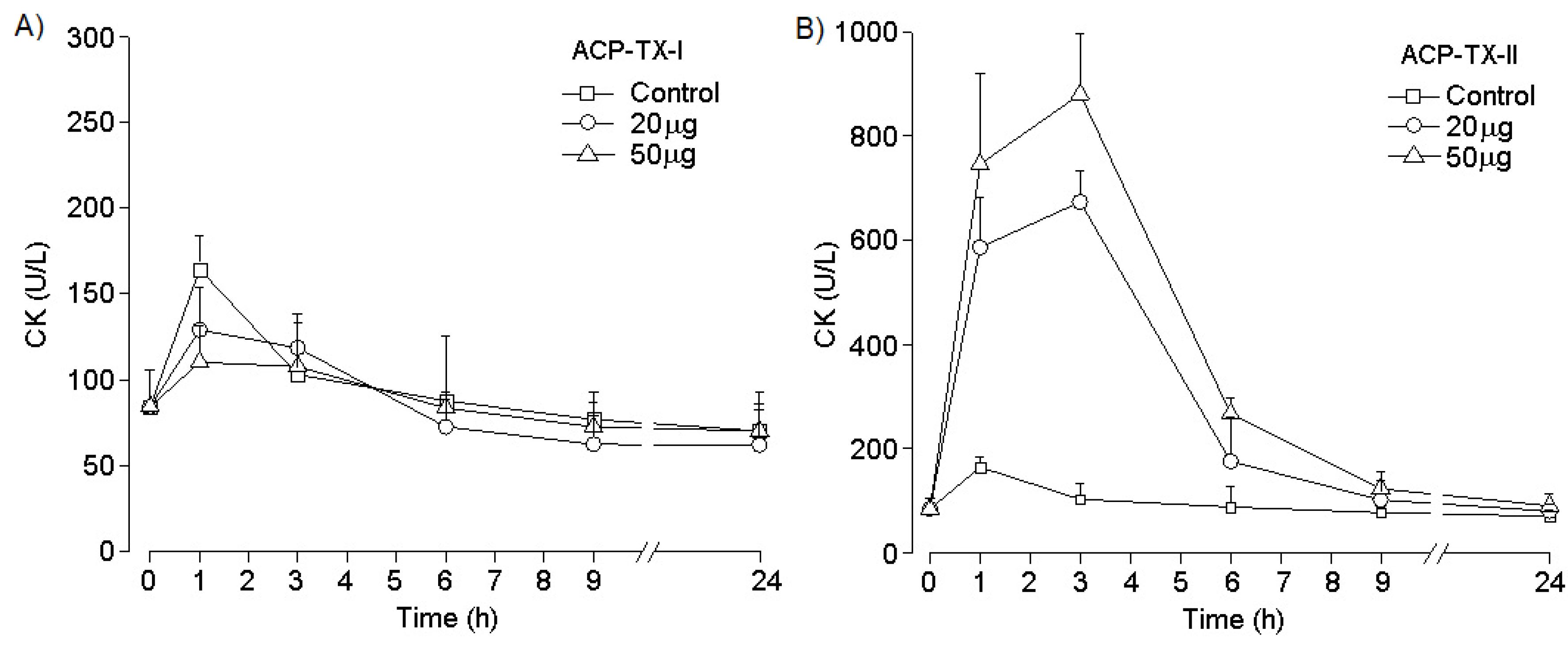
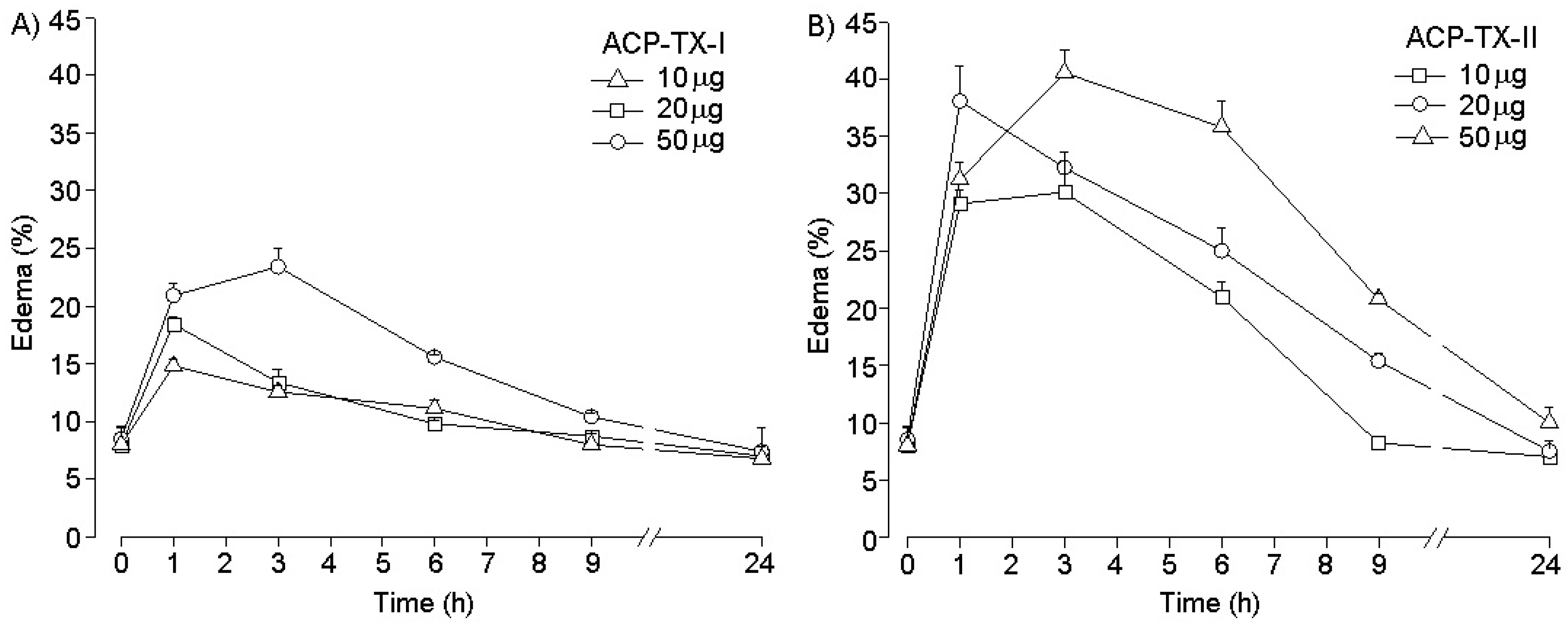
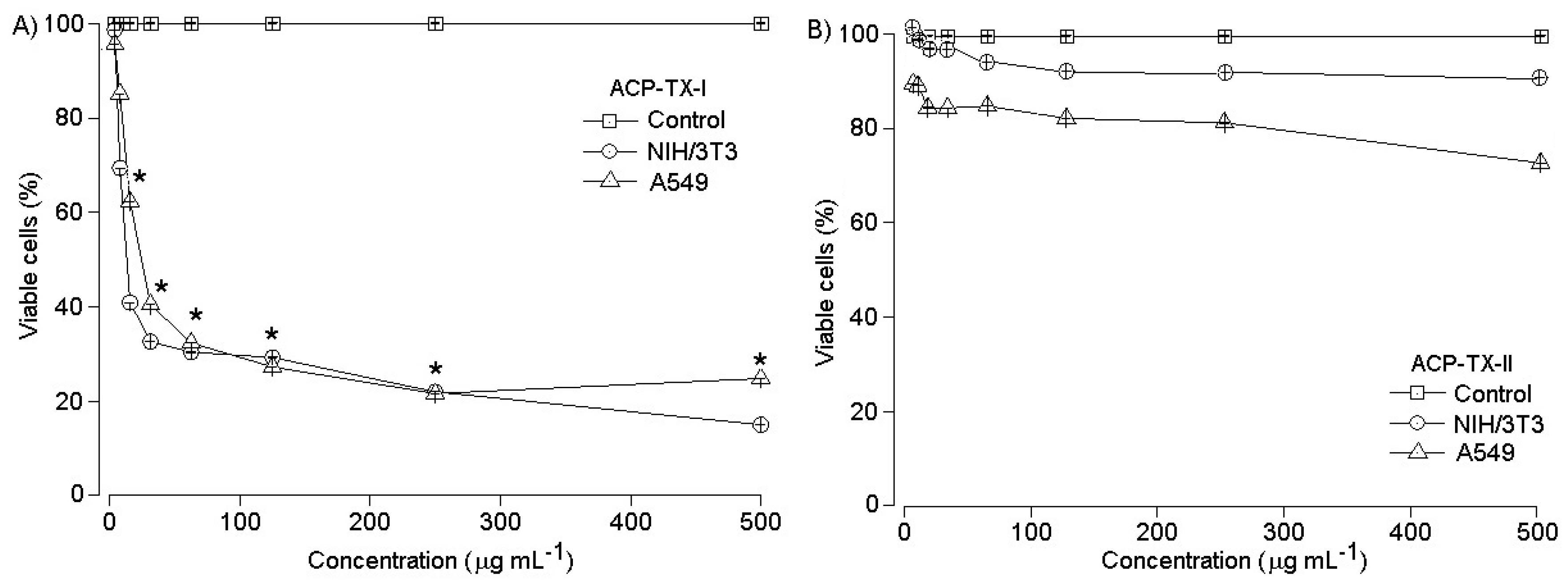
2.4. Pharmacological Activities of ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venom and Reagents
4.2. Purification of ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II
4.3. Electrophoresis
4.4. Determination of Molecular Masses of the Purified Proteins by Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Analysis of Tryptic Digests
4.6. PLA2 Activity
4.7. Inhibition and Chemical Modifications
4.8. Myotoxic Activity
4.9. Edema-Forming Activity
4.10. Cytotoxic Activity
4.11. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical statement
References
- Kini, R.M. Excitement ahead: Structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon 2003, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipases A2: Unveiling the secrets of a functionally versatile group of snake venom toxins. Toxicon 2013, 62, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaloske, R.H.; Dennis, E.A. The phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, D.A.; Dennis, E.A. The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A2 enzymes: Classification and characterization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2000, 1488, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Bleicher, L.; Schrago, C.G.; Silva Junior, F.P. Conservation analysis and decomposition of residue correlation networks in the phospholipase A2 superfamily (PLA2s): Insights into the structure-function relationships of snake venom toxins. Toxicon 2018, 146, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Martins-de-Souza, D.; Marangoni, S. Structural and functional characterization of brazilitoxins II and III (BbTX-II and -III), two myotoxins from the venom of Bothrops brazili snake. Toxicon 2009, 54, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Martins-De-Souza, D.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of PhTX-I a new myotoxic phospholipase A 2 isolated from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2011, 154, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. PhTX-II a basic myotoxic phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora snake venom, pharmacological characterization and amino acid sequence by mass spectrometry. Toxins 2014, 6, 3077–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roodt, A.; Fernández, J.; Solano, D.; Lomonte, B. A myotoxic Lys49 phospholipase A2-homologue is the major component of the venom of Bothrops cotiara from Misiones, Argentina. Toxicon 2018, 148, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, A.N.; Alfonso, J.; Kayano, A.M.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Dos Santos, A.P.A.; Caldeira, C.A.S.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Gome, A.; Grabner, F.P.; Cardoso, F.F.; et al. BmajPLA2-II, a basic Lys49-phospholipase A2 homologue from Bothrops marajoensis snake venom with parasiticidal potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.A.H.; Comparetti, E.J.; Borges, R.J.; Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Ponce, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Soares, A.M.; Fontes, M.R.M. Structural bases for a complete myotoxic mechanism: Crystal structures of two non-catalytic phospholipases A2-like from Bothrops brazili venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, L.F.G.; Borges, R.J.; Viviescas, M.A.; Fernandes, C.A.H.; Fontes, M.R.M. Structural studies with BnSP-7 reveal an atypical oligomeric conformation compared to phospholipases A2-like toxins. Biochimie 2017, 142, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; dos Santos, J.I.; Lomonte, B.; Fontes, M.R.M. Crystal structure of a phospholipase A2 from Bothrops asper venom: Insights into a new putative myotoxic cluster. Biochimie 2017, 133, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Villarreal, J. Phospholipases A2 purified from cottonmouth snake venoms display no antibacterial effect against four representative bacterial species. Toxicon 2018, 151, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B. Biochemistry and toxicology of toxins purified from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper. Toxicon 2009, 54, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Cornell University: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Guiher, T.J.; Burbrink, F.T. Demographic and phylogeographic histories of two venomous North American snakes of the genus Agkistrodon. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.A. Molecular Systematics of the Agkistrodon Complex; Texas Tech University: Lubbock, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Domanski, K.; Kleinschmidt, K.C.; Greene, S.; Ruha, A.M.; Berbata, V.; Onisko, N.; Campleman, S.; Brent, J.; Wax, P. Cottonmouth snake bites reported to the ToxIC North American snakebite registry 2013–2017. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, F.G.; Stolz, U.; Shirazi, F.; Walter, C.M.; McNally, J. Epidemiology of the reported severity of copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix) snakebite. South. Med. J. 2012, 105, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.K.; Ownby, C.L. Isolation of a myotoxin from the venom of Agkistrodon contortrix laticinctus (broad-banded copperhead) and pathogenesis of myonecrosis induced by it in mice. Toxicon 1993, 31, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian, A.; Urbanik, M.; Hus, K.; Łyskowski, A.; Petriaal, V.; Andrejčáková, Z.; Petrillová, M.; Legáth, J. Proteomic analyses of Agkistrodon contortrix contortrix venom using 2D electrophoresis and MS techniques. Toxins 2016, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fořtová, H.; Suttnar, J.; Dyr, J.E.; Pristach, J. Simultaneous isolation of protein C activator, fibrin clot promoting enzyme (fiprozyme) and phospholipase A2 from the venom of the southern copperhead snake. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1997, 694, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, S.; Rodríguez-Acosta, A.; Grilli, E.; Alfonso, A.; Goins, A.; Ogbata, I.; Walls, R.; Suntravat, M.; Uzcátegui, N.L.; Guerrero, B.; et al. The characterization of trans-pecos copperhead (Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster) venom and isolation of two new dimeric disintegrins. Biologicals 2016, 44, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomontea, B.; Tsai, W.-C.; Ureña-Diaz, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Mora-Obando, D.; Sánchez, E.E.; Fry, B.G.; Gutiérreza, J.M.; Gibbs, H.L.; Sovic, G.M.; et al. Venomics of New World pit vipers: Genus-wide comparisons of venom proteomes across Agkistrodon. J. Proteom. 2014, 96, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araujo, H.S.S.; White, S.P.; Ownby, C.L. cDNA cloning and sequence analysis of a lysine-49 phospholipase A 2 myotoxin from Agkistrodon contortrix laticinctus snake venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 326, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Homsi-Brandeburgo, M.I.; Toyama, M.H.; Lombardi, F.R.; Armo, R.K.; Giglio, J.R. A rapid procedure for the isolation of the LYS-49 myotoxin II from bothrops moojeni (caissaca) venom: Biochemical characterization, crystallization, myotoxic and edematogenic activity. Toxicon 1998, 36, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.M.; Guerra-Sá, R.; Borja-Oliveira, C.R.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Rodrigues, V.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Giglio, J.R. Structural and functional characterization of BnSP-7, a Lys49 myotoxic phospholipase A2 homologue from Bothrops neuwiedi pauloensis venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 378, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, D.A.; Barbosa, C.M.V.; Bincoletto, C.; Chagas, J.R.; Magalhaes, A.; Richardson, M.; Sanchez, E.F.; Pesquero, J.B.; Araujo, R.C.; Pesquero, J.L. Purification and partial characterization of two phospholipases A2 from Bothrops leucurus (white-tailed-jararaca) snake venom. Biochimie 2007, 89, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, B.K.; Burack, W.R.; Biltonen, R.L.; Rule, G.S. Expression of a group II phospholipase A2 from the venom of Agkistrodon piscivorus piscivorus in Escherichia coli: Recovery and renaturation from bacterial inclusion bodies. Protein Expr. Purif. 1992, 3, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welches, W.; Reardon, I.; Heinrikson, R.L. An examination of structural interactions presumed to be of importance in the stabilization of phospholipase A2 dimers based upon comparative protein sequence analysis of a monomeric and dimeric enzyme from the venom of Agkistrodon p. piscivorus. J. Protein Chem. 1993, 12, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijiwa, T.; Tokunaga, E.; Ikeda, R.; Terada, K.; Ogawa, T.; Oda-Ueda, N.; Hattori, S.; Nozaki, M.; Ohno, M. Discovery of novel [Arg49] phospholipase A2 isozymes from Protobothrops elegans venom and regional evolution of Crotalinae snake venom phospholipase A2 isozymes in the southwestern islands of Japan and Taiwan. Toxicon 2006, 48, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, G.; Zhao, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Giese, R.; Peng, S. Bioassay-directed purification of an acidic phospholipase A 2 from Agkistrodon halys pallas venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Liu, X.; Ou-Yang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, X. Diversity of cDNAs encoding phospholipase A 2 from Agkistrodon halys Pallas venom, and its expression in E. coli. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.P.; Esteves, A.; Lancellotti, M.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. Novel acidic phospholipase A2 from Porthidium hyoprora causes inflammation with mast cell rich infiltrate. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 1, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marangoni, F.A.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S.; Landucci, E.C.T. Unmasking snake venom of bothrops leucurus: Purification and pharmacological and structural characterization of new PL A2 Bleu TX-III. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Victor, C.C.; Floriano, R.S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Winck, F.V.; Baldasso, P.A.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; Marangoni, S. Biochemical, pharmacological, and structural characterization of new basic PLA2 Bbil-TX from bothriopsis bilineata snake venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sucasaca-Monzón, G.; Randazzo-Moura, P.; Rocha, T.; Torres-Huaco, F.D.; Vilca-Quispe, A.; Alberto Ponce-Soto, L.; Marangoni, S.; da Cruz-Höfling, M.A.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. Bp-13 PLA2: Purification and neuromuscular activity of a new Asp49 toxin isolated from bothrops pauloensis snake venom. Biochem. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Kamata, S.; Ishii, K.; Maruno, T.; Ghanem, N.; Uchiyama, S.; Kato, K.; Suzuki, A.; Oda-Ueda, N.; Ogawa, T.; et al. SDS-induced oligomerization of Lys49-phospholipase A2 from snake venom. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gourinath, S.; Sharma, S.; Paramasivam, M.; Srinivasan, A.; Singh, T.P. Sequence and crystal structure determination of a basic phospholipase A2 from common krait (Bungarus caeruleus) at 2.4 A resolution: Identification and characterization of its pharmacological sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz Filho, E.B.S.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, D.O.; Fagundes, F.H.R.; Oliveira, S.C.B.; Fonseca, F.V.; Calgarotto, A.K.; Joazeiro, P.P.; Toyama, M.H. Enzymatic and structural characterization of new PLA2 isoform isolated from white venom of Crotalus durissus ruruima. Toxicon 2009, 53, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.Z.; Jain, M.K.; Berg, O.G. The Divalent Cation Is Obligatory for the Binding of Ligands to the Catalytic Site of Secreted Phospholipase A2. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 6485–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Correa, D.H.A.; Hollanda, L.M.; Lancellotti, M.; Ramos, C.H.I.; Ponce-Soto, L.A. Chemical modifications of PhTX-I myotoxin from porthidium hyoprora snake venom: Effects on structural, enzymatic, and pharmacological properties. Biomed. Res. Int 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, S.D.; Kaiser, I.I.; Lewis, R.V.; Kruggel, W.G. Rattlesnake presynaptic neurotoxins: Primary structure and evolutionary origin of the acidic subunit. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 7054–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Cellular pathology induced by snake venom phospholipase A2 myotoxins and neurotoxins: Common aspects of their mechanisms of action. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ownby, C.L. Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: Insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon 2003, 42, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Alberto Ponce-Soto, L.; Marangoni, S.; Lomonte, B. Systemic and local myotoxicity induced by snake venom group II phospholipases A2: Comparison between crotoxin, crotoxin B and a Lys49 PLA2 homologue. Toxicon 2008, 51, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Chaves, F.; Moreno, E.; Cerdas, L. Activities of a Toxic a Isolated From the Venom of the Snake Bothrops. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C: Comp. Pharmacol. 1986, 84, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Calderón, L. An overview of lysine-49 phospholipase A2 myotoxins from crotalid snake venoms and their structural determinants of myotoxic action. Toxicon 2003, 42, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonte, B.; Rangel, J. Snake venom Lys49 myotoxins: From phospholipases A2 to non-enzymatic membrane disruptors. Toxicon 2012, 60, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.H.M.; Fernandes, G.A.H.; Magro, A.J.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P.; Cavalcante, W.L.G.; Fernandez, R.M.; Gallacci, M.; Soares, A.M.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Fontes, M.R.M. Structural and Phylogenetic Studies with MjTX-I Reveal a Multi-Oligomeric Toxin—a Novel Feature in Lys49-PLA2s Protein Class. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, F.; León, G.; Alvarado, V.H.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Pharmacological modulation of edema induced by Lys-49 and Asp-49 myotoxic phospholipases A2 isolated from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper (terciopelo). Toxicon 1998, 36, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.M.; Zamuner, S.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Teixeira, C.F.P. Inflammatory events induced by Lys-49 and Asp-49 phospholipases A2 isolated from Bothrops asper snake venom: Role of catalytic activity. Toxicon 2005, 45, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.C.; Kao, P.H.; Lin, S.R.; Sen Chang, L. p38 MAPK activation and mitochondrial depolarization mediate the cytotoxicity of Taiwan cobra phospholipase A2 on human neuroblastoma SK-N.-SH cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 180, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panini, S.R.; Yang, L.; Rusinol, A.E.; Sinensky, M.S.; Bonventre, J.V.; Leslie, C.C. Arachidonate metabolism and the signaling pathway of induction of apoptosis by oxidized LDL/oxysterol. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1678–1686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zouari-Kessentini, R.; Luis, J.; Karray, A.; Kallech-Ziri, O.; Srairi, N.; Bazaa, A.; Loret, E.; Sofiane, B.; Mohamed, E.; Marrakchi, N. Two purified and characterized phospholipases A2 from Cerastes cerastes venom, that inhibit cancerous cell adhesion and migration. Toxicon 2009, 53, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, N.J.; Martin, C.A.; Perez, M.; Newman, R.A.; Vidal, J.C.; Etcheverry, M. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activity by crotoxin, a snake venom phospholipase A2 toxin: A novel growth inhibitory mechanism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrim, L.C.; Marcussi, S.; Menaldo, D.; de Menezes, C.S.R.; Nomizo, A.; Hamaguchi, A.; Silveira-Lacerda, E.P.; Homsi-Brandeburgo, A.I.; Sampaio, S.V.; Soares, A.M.; et al. Antitumor effects of snake venom chemically modified Lys49 phospholipase A2-like BthTX-I and a synthetic peptide derived from its C-terminal region. Biologicals 2009, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.R.; Menaldo, D.L.; Oliveira, C.Z.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Teixeira, S.S.; Nomizo, A.; Fuly, A.L.; Monteiro, M.C.; Souza, B.M.; Palma, M.S.; et al. Myotoxic phospholipases A2 isolated from Bothrops brazili snake venom and synthetic peptides derived from their C-terminal region: Cytotoxic effect on microorganism and tumor cells. Peptides 2008, 29, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H.; von Jagow, G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 166, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Mackessy, S.P. An aqueous endpoint assay of snake venom phospholipase A2. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Camargo, E.A.; Ribela, M.T.C.P.; Damico, D.C.; Marangoni, S.; Antunes, E.; Nucci, G.D.; Landucci, E.C.T. Inflammatory oedema induced by Lachesis muta muta (Surucucu) venom and LmTX-I in the rat paw and dorsal skin. Toxicon 2009, 53, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, G.; Rogiers, T.V.; Rodrigues, R.M. Assaying Cellular Viability Using the Neutral Red Uptake Assay. Cell Viability Assays 2017, 1601, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
| Peptides | Mass (Da) Expected | Amino Acid Sequence | Mass (Da) Calculated |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACP-TX-I | |||
| 1 | 9.864.857 | GQ/KPK/QDATDR | 9.864.781 |
| 2 | 14.075.661 | DATDRCCFVHQ/K | 14.076.024 |
| 3 | 7.753.587 | VTGCDPK | 7.753.535 |
| 4 | 14.737.322 | AI/LI/LCEEK/QNPCL/IQ/K | 14.737.319 |
| 5 | 17.537.551 | MCECDK/QAVAI/LCL/IRE | 17.537.619 |
| 6 | 11.235.574 | ENL/IDTYNQ/KQ/K | 11.235.509 |
| 7 | 9.844.505 | TYWK/QYPQ/K | 9.845.069 |
| ACP-TX-II | |||
| 1 | 20.627.936 | DATDRCCFVHDCCYGQ/K | 20.627.754 |
| 2 | 15.045.434 | CCFVHDCCYGQ/K | 15.045.356 |
| 3 | 22.618.772 | CCFVHDCCYGK/QI/LTACSPQ/K | 22.619.149 |
| 4 | 17.687.631 | Q/KI/LCECDRAAAI/LCFR | 17.687.807 |
| 5 | 10.494.556 | DNI/L/I/LTYDSQ/K | 10.494.666 |
| 6 | 9.845.087 | TYWKYPQ/K | 9.845.069 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huancahuire-Vega, S.; Hollanda, L.M.; Gomes-Heleno, M.; Newball-Noriega, E.E.; Marangoni, S. ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II, Two Novel Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Trans-Pecos Copperhead Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster Venom: Biochemical and Functional Characterization. Toxins 2019, 11, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110661
Huancahuire-Vega S, Hollanda LM, Gomes-Heleno M, Newball-Noriega EE, Marangoni S. ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II, Two Novel Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Trans-Pecos Copperhead Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster Venom: Biochemical and Functional Characterization. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110661
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuancahuire-Vega, Salomón, Luciana M. Hollanda, Mauricio Gomes-Heleno, Edda E. Newball-Noriega, and Sergio Marangoni. 2019. "ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II, Two Novel Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Trans-Pecos Copperhead Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster Venom: Biochemical and Functional Characterization" Toxins 11, no. 11: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110661
APA StyleHuancahuire-Vega, S., Hollanda, L. M., Gomes-Heleno, M., Newball-Noriega, E. E., & Marangoni, S. (2019). ACP-TX-I and ACP-TX-II, Two Novel Phospholipases A2 Isolated from Trans-Pecos Copperhead Agkistrodon contortrix pictigaster Venom: Biochemical and Functional Characterization. Toxins, 11(11), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110661





