Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Vegetable Oils Using Fe3O4/rGO Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fluorescence with Post-Column Photochemical Derivatization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
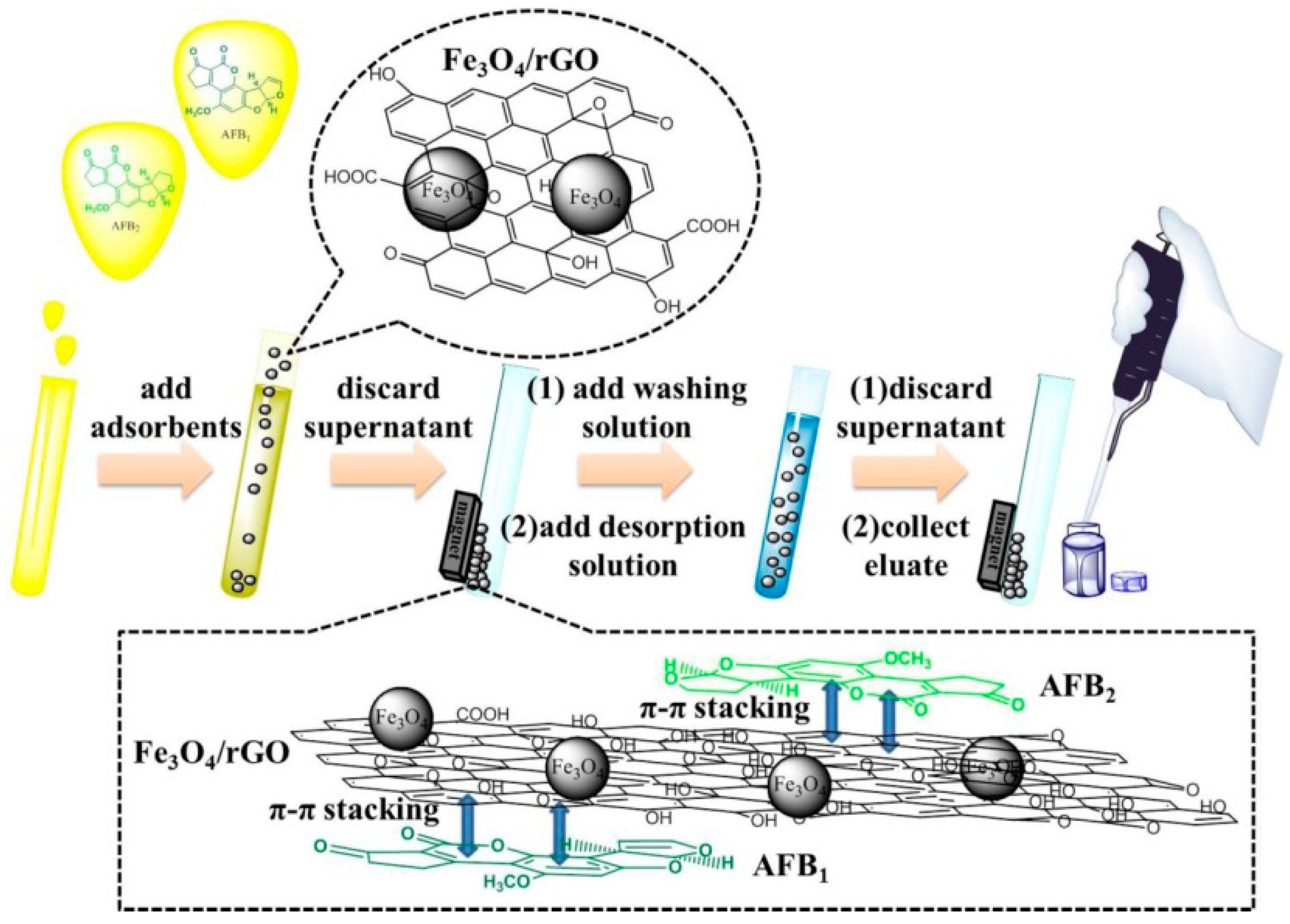
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4/rGO Adsorbents
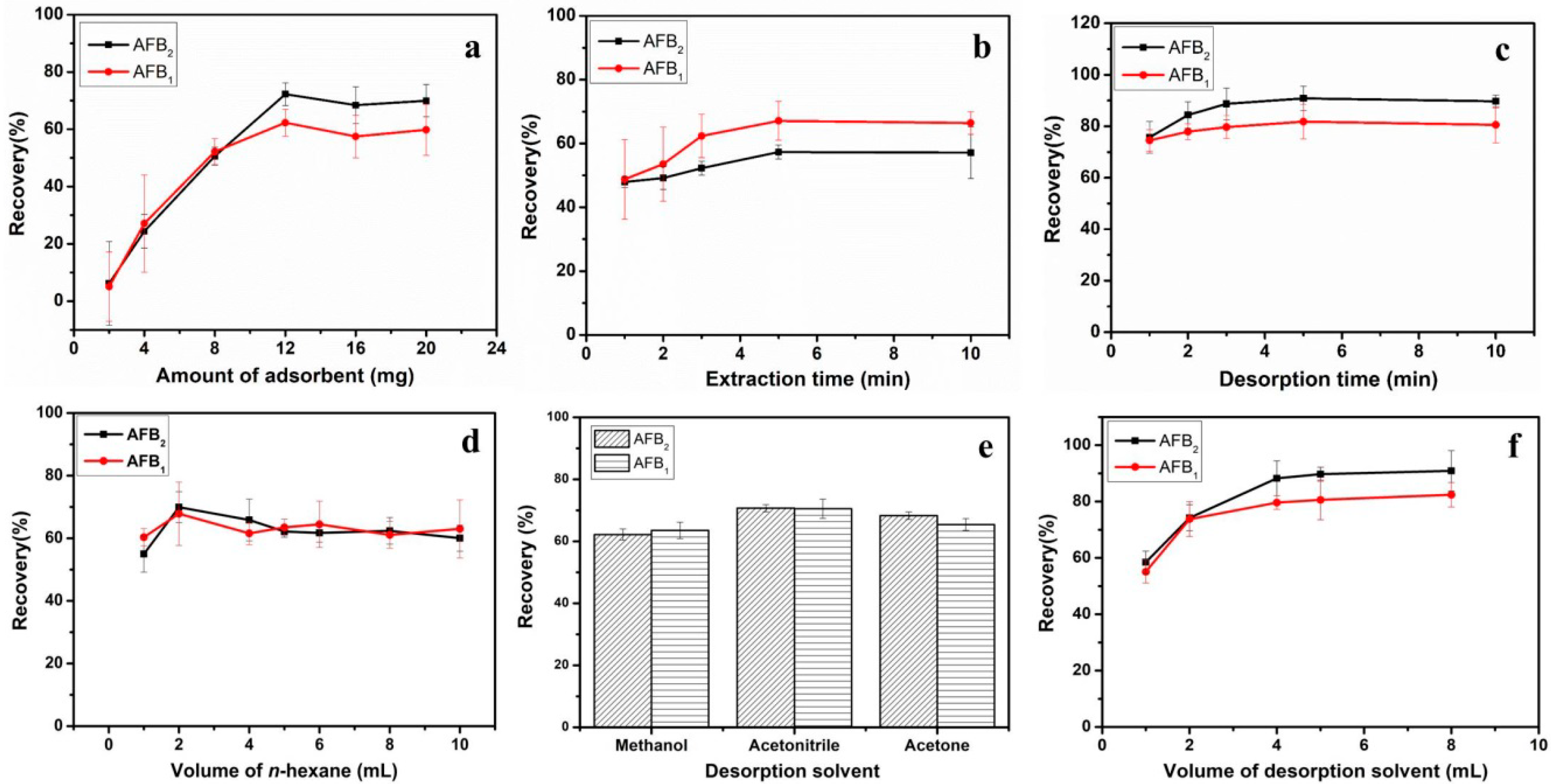
2.2. Optimization of MSPE Conditions
2.2.1. Amount of Fe3O4/rGO Adsorbents
2.2.2. Extraction and Desorption Time
2.2.3. Washing Conditions
2.2.4. Desorption Conditions
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Matrix Effect
2.3.2. Linearity, Accuracy and Precision of the Method
2.3.3. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Apparatus
4.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4/rGO Adsorbents
4.4. Sample Preparation
4.5. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Procedure
4.6. HPLC-PCD-FLD Analytical Conditions
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. A review of chemical composition and nutritional properties of minor vegetable oils in China. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 74, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Reddy, K.R.N. Challenges and issues concerning mycotoxins contamination in oil seeds and their edible oils: Updates from last decade. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Immunoassays for aflatoxins. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer. Aflatoxins. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 1993; Volume 56, pp. 245–395. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. (EC) Commission Regulation (EC) 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L364, 5–24. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1566893371128&uri=CELEX:32006R1881 (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- European Commission. (EC) Commission Regulation (EC) 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L50, 8–12. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1566894448529&uri=CELEX:32010R0165 (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Wu, L.X.; Ding, X.X.; Li, P.W.; Du, X.H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Bai, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.X. Aflatoxin contamination of peanuts at harvest in China from 2010 to 2013 and its relationship with climatic conditions. Food Control 2016, 60, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Criterion of China. Maximum Levels of Mycotoxins in Foods; GB 2761-2017; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Scott, P.M.; Lawrence, J.W.; Van Walbeek, W. Detection of mycotoxins by thin-layer chromatography: Application to screening of fungal extracts. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 20, 839–842. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.A.; Wang, S.; Allan, R.D.; Kennedy, I.R. A rapid aflatoxin B1 ELISA: Development and validation with reduced matrix effects for peanuts, corn, pistachio, and soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, C.; Foglia, P.; Guarino, C.; Nazzari, M.; Samperi, R.; Laganà, A. Determination of aflatoxins in olive oil by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 596, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-Pérez, J.F.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Hitzler, D.; Castro-Guerrero, F.G.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; García-Campaña, A.M. Simple determination of aflatoxins in rice by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to chemical post-column derivatization and fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheijooni-Fumani, N.; Hassan, J.; Yousefi, S.R. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in cereals by homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.Z.; Liu, P.; Su, X.C.; Liao, Y.H.; Lei, N.S.; Liang, Y.H.; Zhou, S.H.; Lin, W.S.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.Q.; et al. Low-cost humic acid-bonded silica as an effective solid-phase extraction sorbent for convenient determination of aflatoxins in edible oils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 970, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, C.; Qu, B. Determination of 16 mycotoxins in vegetable oils using a QuEChERS method combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, N.; Molyneux, R.J. Rapid analytical method for the determination of aflatoxins in plant-derived dietary supplement and cosmetic oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4065–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blesa, J.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Marín, R.; Mañes, J. Determination of aflatoxins in peanuts by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1011, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Yang, Y. Determination of aflatoxin B1 and B2 in peanut and peanut oil using cloud point extraction followed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2013, 36, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, Á.; Zougagh, M. Recent advances in magnetic nanomaterials for improving analytical processes. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2016, 84, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Duan, H.; Lü, J.; Lü, C. Fabrication of thermo-responsive polymer functionalized reduced graphene oxide@Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanocomposites for enhanced catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5088–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.P.; Liang, R.P.; Qiu, J.D. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@Al2O3 core-shell nanoparticles and their application to the highly specific capture of heme proteins for direct electrochemistry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3005–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Pi, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Photocatalytic degradation of acephate, omethoate, and methyl parathion by Fe3O4@SiO2@mTiO2 nanomicrospheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 315, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, B.; Lou, D. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from water samples using titanium-based metal-organic framework functionalized magnetic microspheres. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1579, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condina, M.R.; Guthridge, M.A.; McColl, S.R.; Hoffmann, P. A sensitive magnetic bead method for the detection and identification of tyrosine phosphorylation in proteins by MALDI-TOF/TOF MS. Proteomics 2009, 9, 3047–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.T.; Ha, W.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.P. Highly dispersed magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with well-defined thin film for the selective extraction of glycoprotein. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneva, G.; Ye, H.; Gogotsi, Y.; Halverson, D.; Friedman, G.; Bradley, J.C.; Kornev, K.G. Carbon nanotubes loaded with magnetic particles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, T.V.; Sandhu, A. Chemical synthesis of Fe3O4-graphene oxide nanohybrids as building blocks for magnetic and conductive membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. B-Adv. Funct. Solid-State Mater. 2014, 189, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, H.L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R.S.; Lin, J.M. Recent advances in graphene-based magnetic composites for magnetic solid-phase extraction. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Wang, X. Graphene oxide: an adsorbent for the extraction and quantification of aflatoxins in peanuts by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1318, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L. Rapid determination of trans-resveratrol in vegetable oils using magnetic hydrophilic multi-walled carbon nanotubes as adsorbents followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, D.; Ghanbarian, M.; Mostafavi, A.; Shamspur, T.; Ghaseminezhad, S. A novel method for high preconcentration of ultra trace amounts of B1, B2, G1 and G2 aflatoxins in edible oils by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction after immunoaffinity column clean-up. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1247, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Peng, T.; He, J.L.; Shao, Y.; Fan, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.X.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Pei, X.Y.; et al. Preparation and characterization of an immunoaffinity column for the selective extraction of aflatoxin B1 in 13 kinds of foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 998–999, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Li, C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Hyphenation of supercritical fluid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry for fast determination of four aflatoxins in edible oil. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Duan, C.; Geng, X.; Li, S.; Ding, K.; Guan, Y. One step rapid dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction with in-situ derivatization for determination of aflatoxins in vegetable oils based on high performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Feng, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. A facile one-pot solvothermal method to produce superparamagnetic graphene-Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its application in the removal of dye from aqueous solution. Colloid Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2013, 101, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Analyte | Liner Range (μg/kg) | Linear Equation | R2 | LOD (µg/kg) | LOQ (µg/kg) | Intra-Day Precision (RSD %, n = 6) | Inter-Day Precision (RSD %, n = 4) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 20 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 20 | ||||||
| AFB1 | 0.10–25 | y = 130.686x (±11.029) − 2.31921 (±1.14467) | 0.9967 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 8.7 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 3.7 | 2.3 | 10.5 | 9.8 | 6.2 | 3.9 | 3.2 |
| AFB2 | 0.10–20 | y = 480.364x (±10.605) + 1.55194 (±0.43423) | 0.9978 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 4.9 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 9.8 | 9.0 | 5.1 | 5.8 | 3.9 |
| Analyte | Recovery (%, n = 3) b | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn Oil | Soybean Oil | Rapeseed Oil | Rice Oil | Almond Oil | Peanut Oil I | Peanut Oil II | Peanut Oil III | |
| AFB1 | 86.3 (5.3) | 88.7 (5.0) | 80.4 (4.6) | 82.1 (5.6) | 96.6 (7.7) | 88.7 (6.7) | 94.1 (6.4) | 93.2 (8.1) |
| AFB2 | 105.8 (6.3) | 102.6 (6.7) | 98.1 (2.8) | 100.6 (3.2) | 103.5 (4.2) | 106.0 (4.4) | 103.2 (3.5) | 95.3 (6.1) |
| Adsorbents | Pretreatment | Pretreatment Time (min) | Derivatization Condition | Determination | Recovery (%) | LOQs (μg/kg) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction after IAC clean up | <120 | - | LC-FLD | 96–109.9 | 2.8 × 103 (AFB1) 0.4 × 103 (AFB2) | [31] |
| IAC clean up | <30 | - | UPLC-MS/MS | 90–105 | 0.12–0.15 (AFB1) | [32] | |
| - | Supercritical fluid chromatography | 15 | - | UPC2-MS/MS | 98, 104 | 0.05 (AFB1) 0.08 (AFB2) | [33] |
| Humic acid-bonded silica | SPE | 8–10 | - | HPLC-MS/MS | 82–106 | 0.044 (AFB1) 0.057 (AFB2) | [14] |
| C18, PSA & neutral Al2O3 | QuEChERS | 38 | - | HPLC-MS/MS | 83–100.3 | 0.18 (AFB1) 0.13 (AFB2) | [15] |
| - | Dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction | <20 | In situ chemical derivatization | HPLC-FLD | 91.8–121.5 | 0.10 (AFB1) 0.017 (AFB2) | [34] |
| rGO-Fe3O4 | MSPE | 15 | photochemical derivatization | HPLC-FLD | 80.38–109.03 | 0.10 (AFB1) 0.10 (AFB2) | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Vegetable Oils Using Fe3O4/rGO Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fluorescence with Post-Column Photochemical Derivatization. Toxins 2019, 11, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110621
Yu L, Ma F, Zhang L, Li P. Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Vegetable Oils Using Fe3O4/rGO Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fluorescence with Post-Column Photochemical Derivatization. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110621
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Li, Fei Ma, Liangxiao Zhang, and Peiwu Li. 2019. "Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Vegetable Oils Using Fe3O4/rGO Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fluorescence with Post-Column Photochemical Derivatization" Toxins 11, no. 11: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110621
APA StyleYu, L., Ma, F., Zhang, L., & Li, P. (2019). Determination of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Vegetable Oils Using Fe3O4/rGO Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fluorescence with Post-Column Photochemical Derivatization. Toxins, 11(11), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110621








