Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize by Modified Montmorillonite Clay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
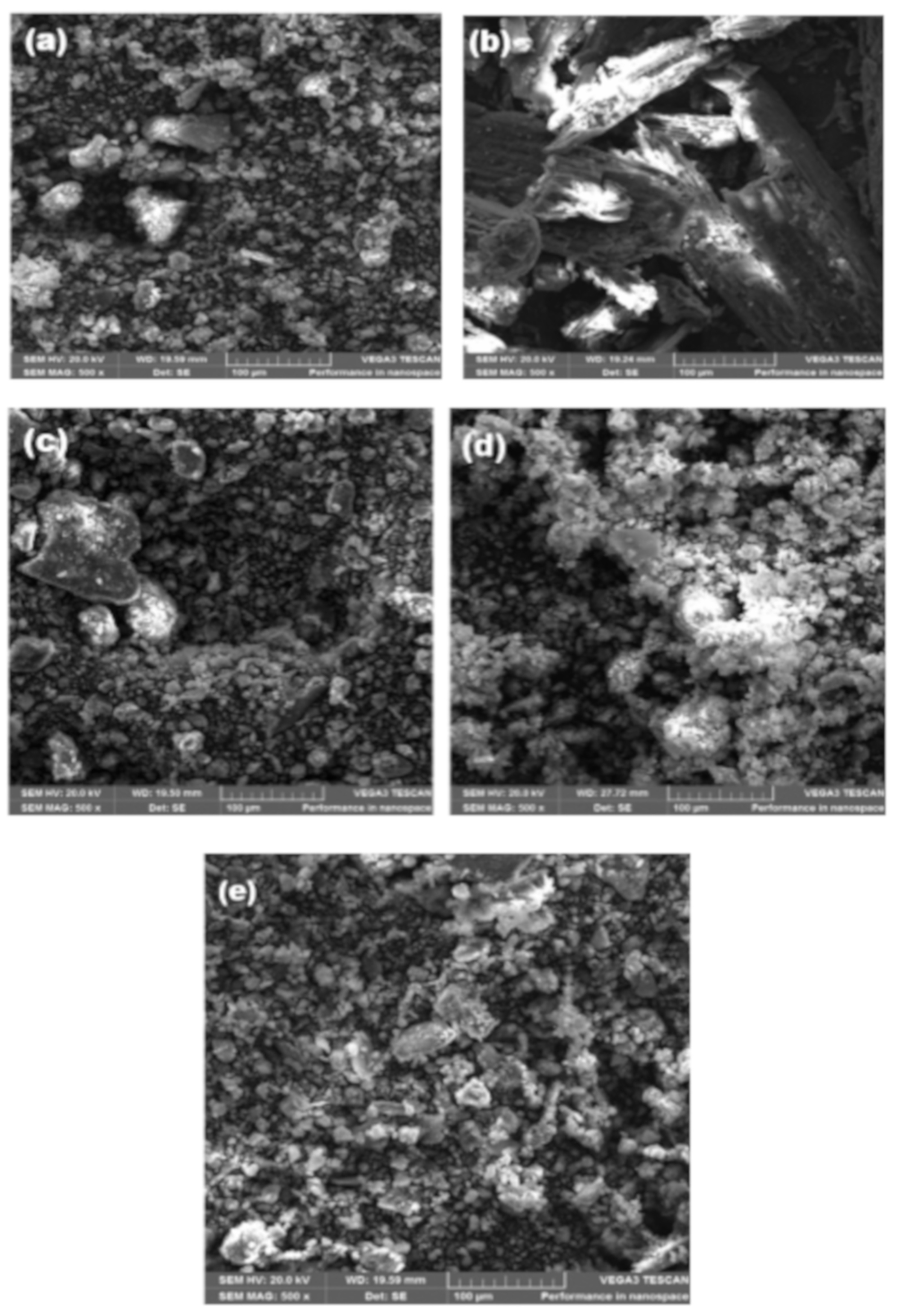
2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
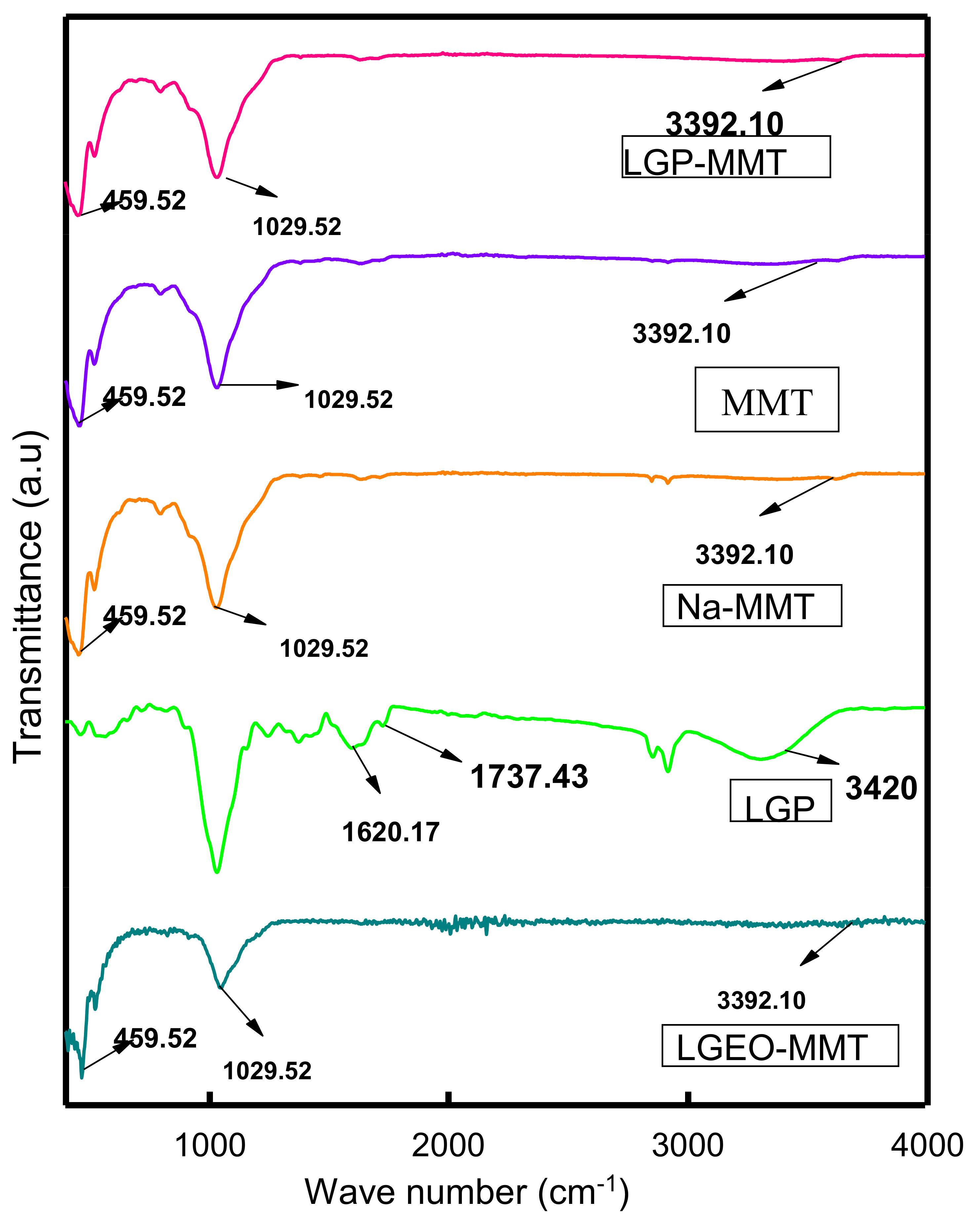
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
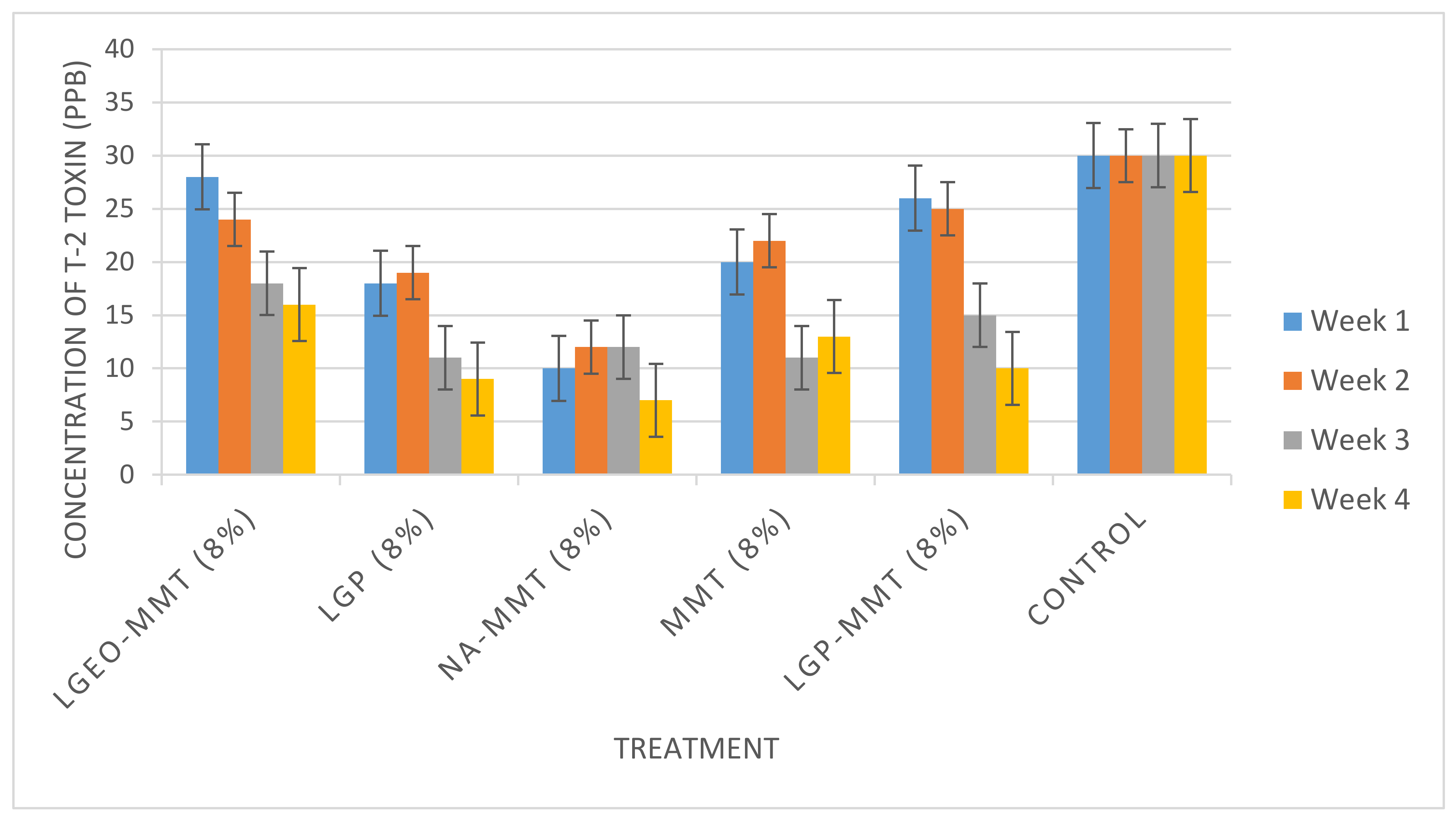
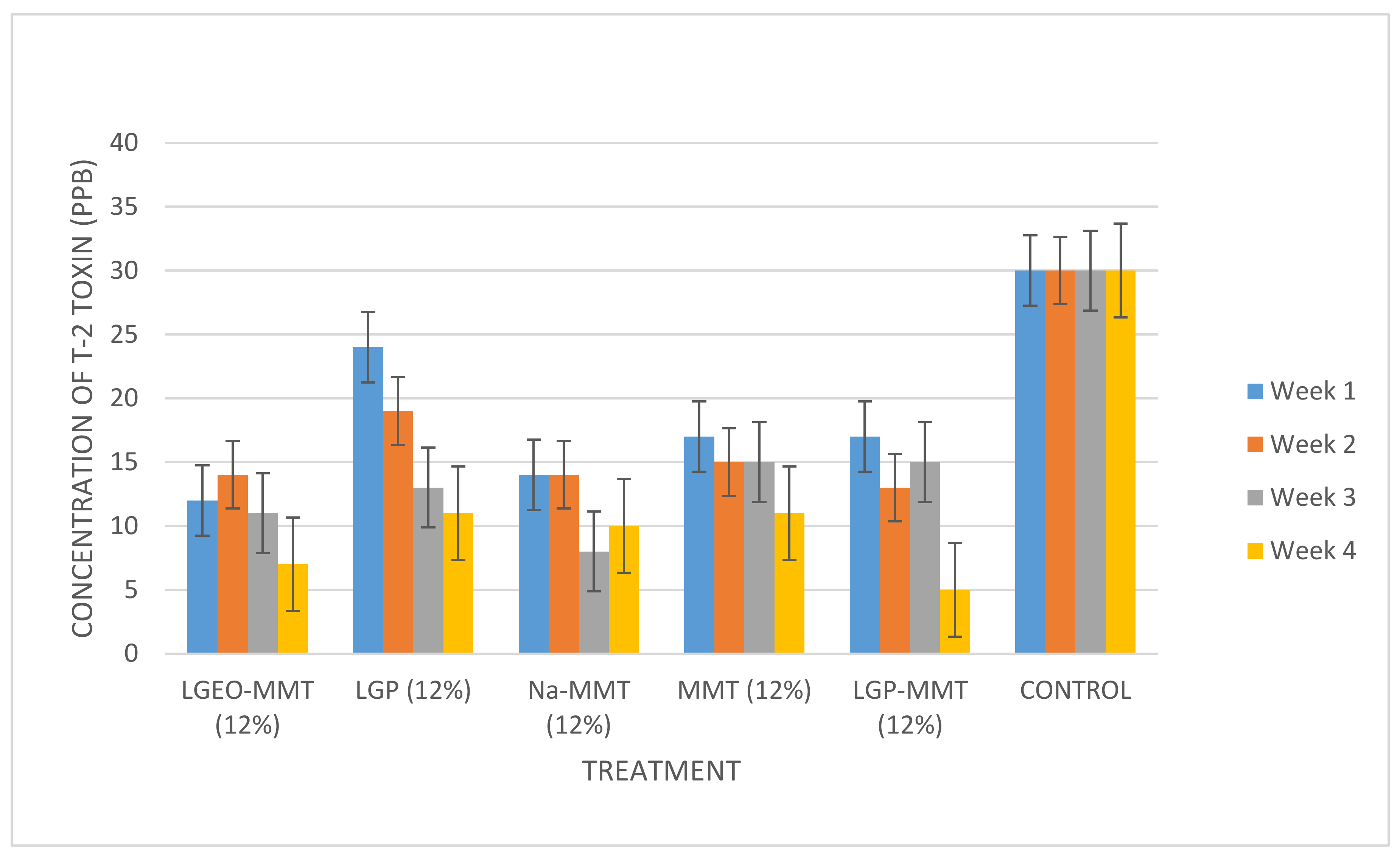
2.3. The Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.5. Evaluation of T-2 Toxin before Treatment
4.6. Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bw | body weight |
| LGEO-MMT | lemongrass essential oil-modified montmorillonite clay |
| LGP | lemongrass powder |
| Na-MMT | montmorillonite clay washed with 1 mM NaCl |
| MMT | montmorillonite clay |
| LGP-MMT | lemongrass powder mixed with montmorillonite clay |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| LSD | Least Significant Difference |
| AF | Aflatoxin |
| NEO | neosolaniol |
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| FB1 | fumonisin B1 |
| NIV | nivalenol |
| ZEA | zearalenone |
References
- Ranum, P.; Pena-Rosas, J.P.; García-Casal, M.N. Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1312, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krska, R.; Malachova, A.; Berthiller, F.; Van Egmond, H. Determination of T-2 and HT-2 toxins in food and feed: An update. World Mycotoxin J. 2014, 7, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, A.; Moretti, A.; Spicer, L.J.; Caloni, F. Fusarium Molds and Mycotoxins: Potential Species-Specific Effects. Toxins 2018, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonissen, G.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Verbrugghe, E.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Li, S.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F.; Croubels, S. The Impact of Fusarium Mycotoxins on Human and Animal Host Susceptibility to Infectious Diseases. Toxins 2014, 6, 430–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, M.; Mochizuki, N.; Nagatomi, Y.; Harayama, K.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. A Method for Simultaneous Determination of 20 Fusarium Toxins in Cereals by High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry with a Pentafluorophenyl Column. Toxins 2015, 7, 1664–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oranusi, S.U.; Olarewaju, S.A. Mycoflora and aflatoxin contamination of some foodstuffs. Int. J. Biotechnol. Allied Fields 2013, 1, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nathanail, A.V.; Varga, E.; Meng-Reiterer, J.; Bueschl, C.; Michlmayr, H.; Malachova, A.; Fruhmann, P.; Jestoi, M.; Peltonen, K.; Adam, G.; et al. Metabolism of the Fusarium Mycotoxins T-2 Toxin and HT-2 Toxin in Wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7862–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-H.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Nussler, A.K.; Xiong, L.-Y.; Kuca, K.; Dohnal, V.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yuan, Z.-H. Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity and metabolism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in animals and humans: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1309–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, J. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by mixed mycotoxins (T-2 and HT-2 toxin) on primary hepatocytes of broilers in vitro. Toxicon 2017, 129, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoev, S.D.; Diakov, L.; Koynarski, V.; Angelov, A. Special Pathology and Diagnostics of Mycoses, Mycotoxicoses, Parasitoses, Intoxications and Avitaminoses; Publishing House CD Contrast: Stara Zagora, Bulgaria, 2010; pp. 1–239. [Google Scholar]
- Agag, B.I. Mycotoxins in foods and feeds. Ass. Univ. Bull. Environ Res. 2005, 8, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, M.; Negi, B.; Kaushik, N.; Adhikari, A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. T-2 mycotoxin: Toxicological effects and decontamination strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33933–33952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Gonkowski, S. The Impact of T-2 Toxin on Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide-Like Immunoreactive (VIP-LI) Nerve Structures in the Wall of the Porcine Stomach and Duodenum. Toxins 2018, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Zielonka, L.; Gonkowski, S. The Influence of Low Doses of Zearalenone and T-2 Toxin on Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide-Like Immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) Neurons in the ENS of the Porcine Descending Colon. Toxins 2017, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovo, F.; Corassin, C.H.; Rosim, R.E.; De Oliveira, C.A.F. Efficiency of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains for Decontamination of Aflatoxin M1 in Phosphate Buffer Saline Solution and in Skimmed Milk. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 6, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avantaggiato, A.; Solfrizzo, M.; Visconti, A. Recent advances on the use of adsorbent materials for detoxification of Fusarium mycotoxins. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council for Agricultural Science and Technology. Mycotoxins: Risks in Plant, Animal, and Human Systems, 1st ed.; CAST: Ames, IA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Calado, T.; Venâncio, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Irradiation for Mold and Mycotoxin Control: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, M.C.; De Neeff, D.V.; Jager, A.V.; Corassin, C.H.; Carão, C.D.P.A.; De Albuquerque, R.; De Azevedo, A.C.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Mineral adsorbents for prevention of mycotoxins in animal feeds. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyagin, I.; Efremenko, E. Enzymes for Detoxification of Various Mycotoxins: Origins and Mechanisms of Catalytic Action. Molecules 2019, 24, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.L.; Junior, A.M.; Vieira, B.A.; Dias, L.R.S.; De Sousa, V.P.; Castro, H.C.; Rodrigues, C.R.; Cabral, L.M. Sodium Montmorillonite/Amine-Containing Drugs Complexes: New Insights on Intercalated Drugs Arrangement into Layered Carrier Material. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Lazzara, G.; Riela, S. The Use of Some Clay Minerals as Natural Resources for Drug Carrier Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-T.; Wu, K.-T.; Sun, H.; Khalil, M.M.; Dai, J.-F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Qi, D.-S.; Sun, L.-H. A Novel Modified Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate (HSCAS) Adsorbent Can Effectively Reduce T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestinal Morphology in Chicks. Toxins 2019, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, M.S.; Mohamad Kassim, M.H.; Mohapatra, L.; Gilani, M.A.; Raza, M.R.; Majeed, K. Nanoclay Reinforced Polymer Composites; Engineering Materials 2016; Springer Science: Singapore, 2016; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.-C.; Lee, J.-F.; Lee, C.-K.; Chao, H.-P. Effects of cation exchange on the pore and surface structure and adsorption characteristics of montmorillonite. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 239, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Boutahala, M. Preparation and characterization of organo-montmorillonites. Application in adsorption of the 2,4,5-trichlorophenol from aqueous solution. Adv. Powder Technol. 2011, 22, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambolena, S.J.; Zunino, P.M.; López, G.A.; Rubinstein, R.H.; Zygadlo, A.J.; Mwangi, W.J.; Thoithi, N.G.; Kibwage, O.I.; Mwalukumbi, M.J.; Kariuki, T.S. Essential oils composition of Ocimum basilicum L. and Ocimum gratissimum L. from Kenya and their inhibitory effect on growth and fumonisin production by verticillioides. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 239–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanda, O.O.; Olopade, T.A. Effect of lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus (DC) Stapf.) treatments on Aspergillus flavus (SGS-421) infestation and aflatoxin B1 content of maize grains. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Olorunnisola, S.K.; Asiyanbi, H.T.; Hammed, A.M.; Simsek, S. Biological properties of lemongrass: An overview. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Fandohan, P.; Gnonlonfin, B.; Laleye, A.; Gbenou, J.; Darboux, R.; Moudachirou, M. Toxicity and gastric tolerance of essential oils from Cymbopogon citratus, Ocimum gratissimum and Ocimum basilicum in Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-F.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.; Fowler, P.; Baird, M. Characteristics of degraded cellulose obtained from steam-exploded wheat straw. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.B.; Mazzola, E.P. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: An Introduction to Principles, Applications, and Experimental Methods; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, I.A.; Moodley, B. Synthesis, characterization and application of imidazolium-based ionic liquid modified montmorillonite sorbents for the removal of amaranth dye. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61913–61924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, R. Potential for Using Aluminosilicates for Removal of Heavy Metals and Mycotoxins from Feed and Water. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Norway, May 2018. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/ (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Erminawati, R.N.; Sitoresmi, I.; Sidik, W.; Bachtiar, A. Antioxidant activity of microencapsulated lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) extract. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 250, p. 012054. [Google Scholar]
- Prins, C.L.; Freitas, S.D.P.; Gomes, M.D.; Vieira, I.J.C.; Gravina, G.D.A. Citral accumulation in Cymbopogon citratus plant as influenced by N6- benzyl amino purine and light intensity. Theo. Exp. Plant Phys. 2013, 25, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirhan, A.Y.; Tan, G.H.; Wong, R.C.S. Simultaneous detection of type A and type A trichothecenes in cereals by liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS). J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 1945–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Hahn, J.; Toth, S.; Nagy, I.; Kukolya, J. Mycotoxin-degradation profile of Rhodococcus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachowska, U.; Packa, D.; Wiwart, M. Microbial Inhibition of Fusarium Pathogens and Biological Modification of Trichothecenes in Cereal Grains. Toxins 2017, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Yi, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, N.; Tian, Y. Autophagy and Apoptosis Interact to Modulate T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Liver Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oranusi, S.; Braide, W.; Nwodo, C.F.; Nwosu, U.P. Assay for Aflatoxins in some local food condiments. Int. J. Biol. Pharm. Allied Sci. 2013, 2, 529–537. [Google Scholar]
- Ojewumi, M.E.; Banjo, M.G.; Oresegun, M.O.; Ogunbiyi, T.A.; Ayoola, A.A.; Awolu, O.O.; Ojewumi, E.O. Analytical investigation of the extract of lemongrass leaves in repelling mosquito. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Olopade, B.K.; Oranusi, S.U.; Nwinyi, O.C.; Njobeh, P.B.; Lawal, I.A. Modification of montmorillonite clay with Cymbopogon citratus for the decontamination of zearalenone in millet. AIMS Agric. Food 2019, 4, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noudem, J.A.; Nguemtchouin Mbouga, M.G.; Kaptso, K.G.; Khalfaoui, M.; Noumi, G.B. Saponins-clay modified materials: A new approach against Callosobruchus subinnotatus in stored products. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 6, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sulyok, M.; Berthiller, F.; Krska, R.; Schuhmacher, R. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of 39 mycotoxins in wheat and maize. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2649–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olopade, B.K.; Oranusi, S.U.; Nwinyi, O.C.; Lawal, I.A.; Gbashi, S.; Njobeh, P.B. Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize by Modified Montmorillonite Clay. Toxins 2019, 11, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110616
Olopade BK, Oranusi SU, Nwinyi OC, Lawal IA, Gbashi S, Njobeh PB. Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize by Modified Montmorillonite Clay. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110616
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlopade, Bunmi K., Solomon U. Oranusi, Obinna C. Nwinyi, Isiaka A. Lawal, Sefater Gbashi, and Patrick B. Njobeh. 2019. "Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize by Modified Montmorillonite Clay" Toxins 11, no. 11: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110616
APA StyleOlopade, B. K., Oranusi, S. U., Nwinyi, O. C., Lawal, I. A., Gbashi, S., & Njobeh, P. B. (2019). Decontamination of T-2 Toxin in Maize by Modified Montmorillonite Clay. Toxins, 11(11), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110616