Development of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Post-Column Fluorescent Derivatization for the Rapid Detection of Saxitoxin Analogues and Analysis of Bivalve Monitoring Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
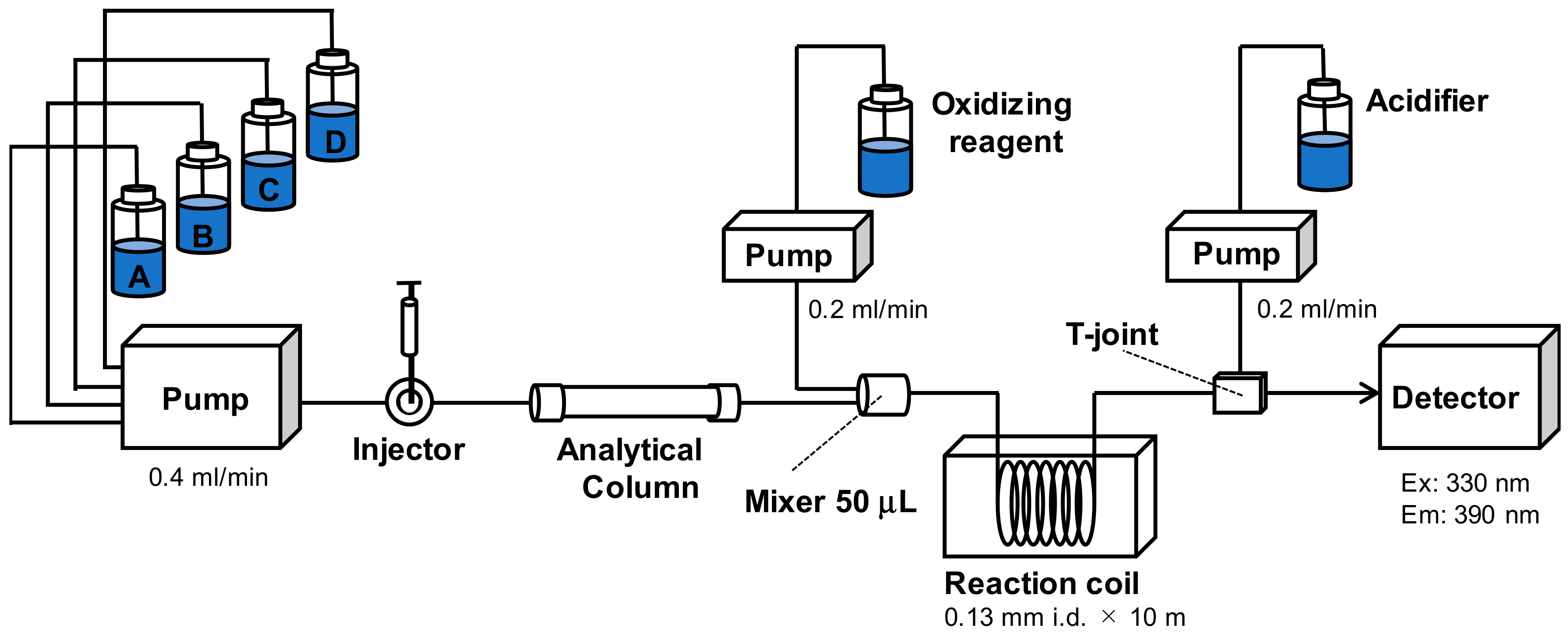
2.1. Development of UPLC/OX/FD
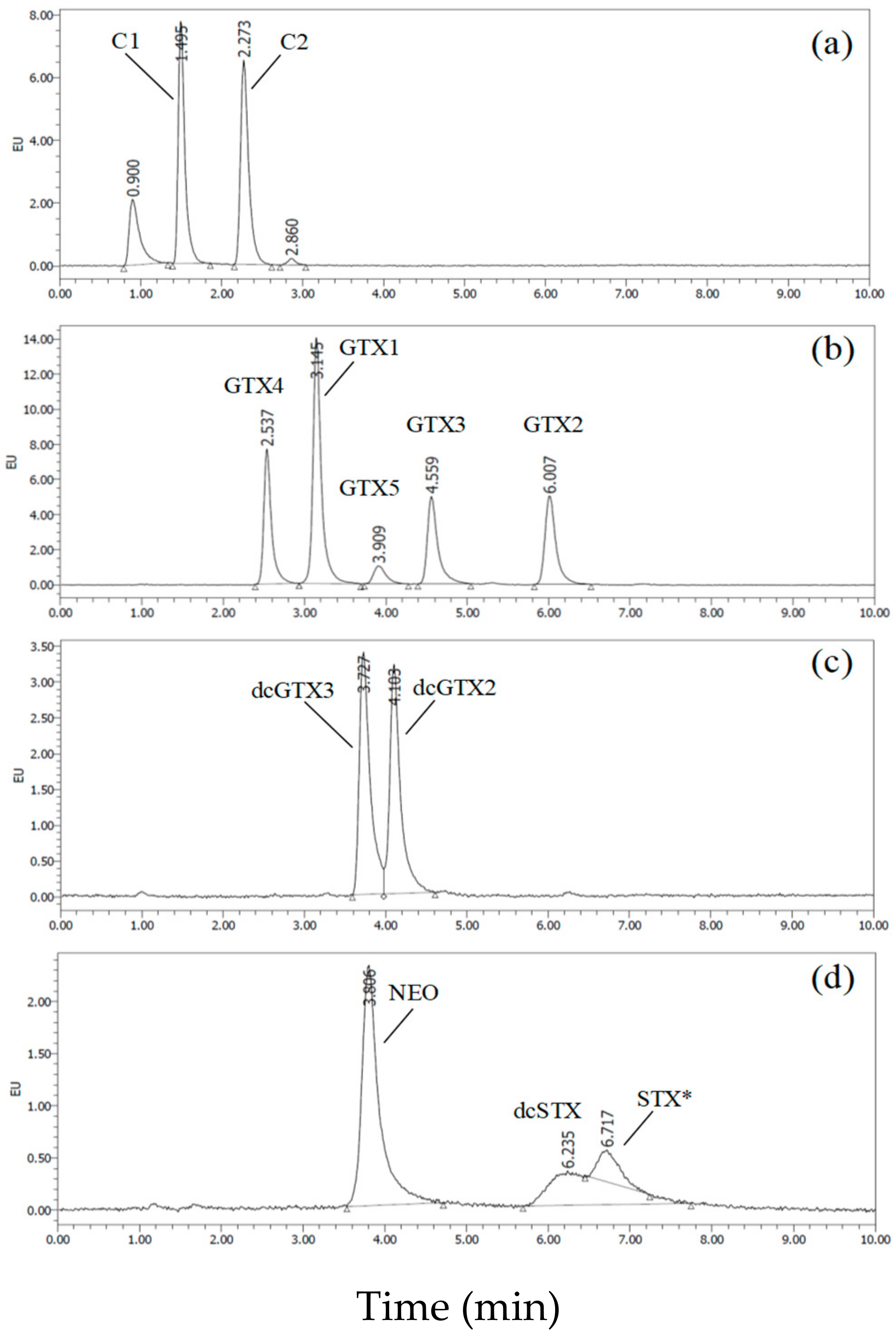
2.1.1. Method Development
2.1.2. Characteristics of the Rapid UPLC/OX/FD Method
2.2. The Toxin Concentration of the STXs in Scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis Collected from Different Water Depths
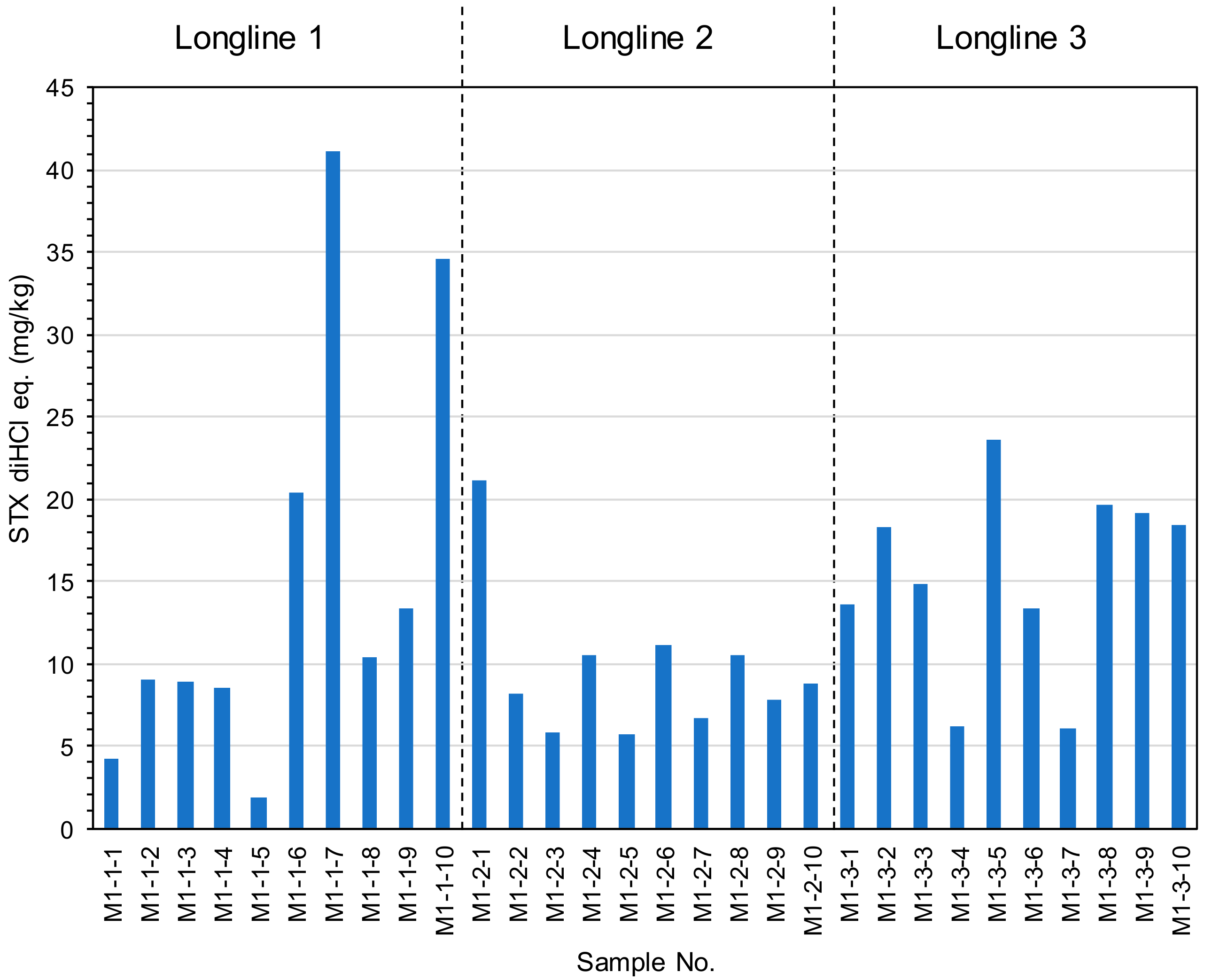
2.3. The Toxin Concentration of the STXs in Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Collected from Different Water Depths and Geographical Distances.
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Apparatus
5.2. Specimens and Sample Preparation
5.3. Toxin Detection
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaga, S.; Sekiguchi, R.; Yoshida, M.; Ogata, T. Occurrence and toxin production of Alexandrium spp. (Dinophyceae) in coastal waters of Iwate Prefecture, Japan. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish. 2006, 72, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T.; Kodama, M.; Ogata, T.; Fukuyo, Y.; Matsuura, F. Features of paralytic shellfish poison occurring in Tohoku district. Bull. Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, H.; Fujita, T.; Satomi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kotani, Y.; Yano, Y. Accumulation of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in the edible shore crab Telmessus acutidens. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, H.; Fujita, T.; Saito, K.; Watabe, S.; Satomi, M.; Yano, Y. Comparison of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin between carnivorous crabs (Telmessus acutidens and Charybdis japonica) and their prey mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) in an inshore food chain. Toxicon 2004, 43, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, H.; Satomi, M.; Watabe, S.; Yano, Y. Accumulation and depuration rates of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in the shore crab Telmessus acutidens by feeding toxic mussels under laboratory controlled conditions. Toxicon 2005, 45, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, H.; Fujita, T.; Saito, K.; Satomi, M.; Yano, Y. Difference in the level of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin accumulation between the crabs Telmessus acutidens and Charybdis japonica collected in Onahama, Fukushima Prefecture. Fish. Sci. 2007, 73, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, J.R.; Landsberg, J.H.; Etheridge, S.M.; Pitcher, G.C.; Longan, S.W. Non-traditional vectors for paralytic shellfish poisoning. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 308–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic Alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Cestéle, S.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Yu, F.H.; Konoki, K.; Scheuer, T. Voltage-gated ion channels and gating modifier toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGrasse, S.; Rivera, V.; Roach, J.; White, K.; Callahan, J.; Coouture, D.; Simone, K.; Peredy, T.; Poli, M. Paralytic shellfish toxins in clinical matrices: Extension of AOAC official method 2005.06 to human urine and serum and application to a 2007 case study in Maine. Deep-Sea Res. Ii. 2014, 103, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.M.; Ojeda-Torres, G.; Bragg, W.; Fearey, D.; McKinney, P.; Castrodale, L.; Verbrugge, D.; Stryker, K.; DeHart, E.; Cooper, M.; et al. Saxitoxin exposure confirmed by human urine and food analysis. J. Anal.Toxicol. 2018, 42, e61–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, R.W.A.; Zhang, V.Y.; Azcue, N.; Hartigan, C.E.; Shkreta, A.; Prabhakara, J.; Berde, C.B.; Lellogg, M.D. Measurement of neosaxitoxin in human plasma using liquid-chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: Proof of concept for a pharmacokinetic application. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1036–1037, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; McNabb, P.S.; Harwood, D.T.; Selwood, A.I.; Boundy, M.J. Single-laboratory validation of a multitoxin ultra-performance LC-hydrophilic interaction LC-MS/MS method for quantitation of paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve shellfish. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T.; McNabb, P.S.; Turner, A.D. Development of a sensitive and selective liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for high throughput analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins using graphitized carbon solid phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1387, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon, A. Official Method 2005.06 Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Shellfish. Prechromatographic Oxidation and Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescent Detection; Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, First action 2005; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Anon, A. Official Method 2011.02 Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Mussels, Clams, Oysters, and Scallops; Postcolumn oxidation method (PCOX). First Action 2011; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lawerence, J.F.; Niedzwiadek, B.; Menard, C. Quantitative determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish using prechromatographic oxidation and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.D.; Hatfield, R.G. Refinement of AOAC official method 2005.06 liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection method to improve performance characteristics for the determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in king and queen scallops. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, Y. Postcolumn derivatization liquid chromatographic method for paralytic shellfish toxins. J. Aoac Int. 1995, 78, 528–532. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, V.; Botana, A.M.; Alvarez, M.; Antelo, A.; Botana, L.M. Liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection method for analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxin based on a porus graphitic carbon column. Toxins 2016, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Loreal, H.; Toyofuku, H.; Hess, P.; Karunasagar, I.; Ababouch, L. Assessment and management of biotoxin risks in bivalve molluscs. FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Pap. 2011, 551, 274–276. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.hro.or.jp/list/fisheries/research/hakodate/section/zoushoku/tpc05300000004y7.html (accessed on 5 October 2018).
- Anon, A. Official Method 959.08 Paralytic shellfish poison. Biological method; Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Final action. AOAC Off. Methods Anal. 2005, 49, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
| Toxins | LOD 1 (nM) | LOQ 2 (nM) | Toxins | LOD 1 (nM) | LOQ 2 (nM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 10.6 | 35.2 | dcGTX3 | 1.6 | 5.4 | |
| C2 | 3.3 | 11.1 | dcGTX2 | 6.1 | 20.5 | |
| GTX4 | 4.2 | 13.9 | NEO | 84.0 | 279.9 | |
| GTX1 | 6.9 | 23.1 | dcSTX | 135.6 | 451.9 | |
| GTX5 | 43.4 | 144.7 | ||||
| GTX3 | 1.8 | 6.0 | ||||
| GTX2 | 5.3 | 17.5 |
| Water Qualities | 8 April | 18 May | 15 June | 21 July | 1 September | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water temperature (°C) 2 | 3.9 | 6.6 | 9.8 | 12.9 | 19.9 | |
| Salinity (psu) 2 | 31.77 | 31.99 | 31.88 | 32.04 | 32.36 | |
| Clearance (m) | 4.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 13.0 | 8.0 | |
| Depth (m) | 0 | 0 | 340 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 360 | 40 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10 | 0 | 600 | 640 | 0 | 0 | |
| 15 | 0 | 70 | 80 | 0 | 0 | |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| 30 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Steps | Ratio of Mobile Phases (%) | Time (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||
| Equilibrate | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| GTXs analyses | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 10 × n |
| Equilibrate | 93 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 15 |
| STXs analyses | 93 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 10 × n |
| Column wash | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 0 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 15 | |
| 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 10 | |
| Equilibrate | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 10 |
| Cs analyses | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 10 × n |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, R.; Kanamori, M.; Yoshida, H.; Okumura, Y.; Uchida, H.; Matsushima, R.; Oikawa, H.; Suzuki, T. Development of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Post-Column Fluorescent Derivatization for the Rapid Detection of Saxitoxin Analogues and Analysis of Bivalve Monitoring Samples. Toxins 2019, 11, 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100573
Watanabe R, Kanamori M, Yoshida H, Okumura Y, Uchida H, Matsushima R, Oikawa H, Suzuki T. Development of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Post-Column Fluorescent Derivatization for the Rapid Detection of Saxitoxin Analogues and Analysis of Bivalve Monitoring Samples. Toxins. 2019; 11(10):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100573
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Ryuichi, Makoto Kanamori, Hidetsugu Yoshida, Yutaka Okumura, Hajime Uchida, Ryoji Matsushima, Hiroshi Oikawa, and Toshiyuki Suzuki. 2019. "Development of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Post-Column Fluorescent Derivatization for the Rapid Detection of Saxitoxin Analogues and Analysis of Bivalve Monitoring Samples" Toxins 11, no. 10: 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100573
APA StyleWatanabe, R., Kanamori, M., Yoshida, H., Okumura, Y., Uchida, H., Matsushima, R., Oikawa, H., & Suzuki, T. (2019). Development of Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Post-Column Fluorescent Derivatization for the Rapid Detection of Saxitoxin Analogues and Analysis of Bivalve Monitoring Samples. Toxins, 11(10), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100573





