Effects of Aged Garlic Extract on Cholinergic, Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems with Regard to Cognitive Impairment in Aβ-Induced Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Aged Garlic Extract
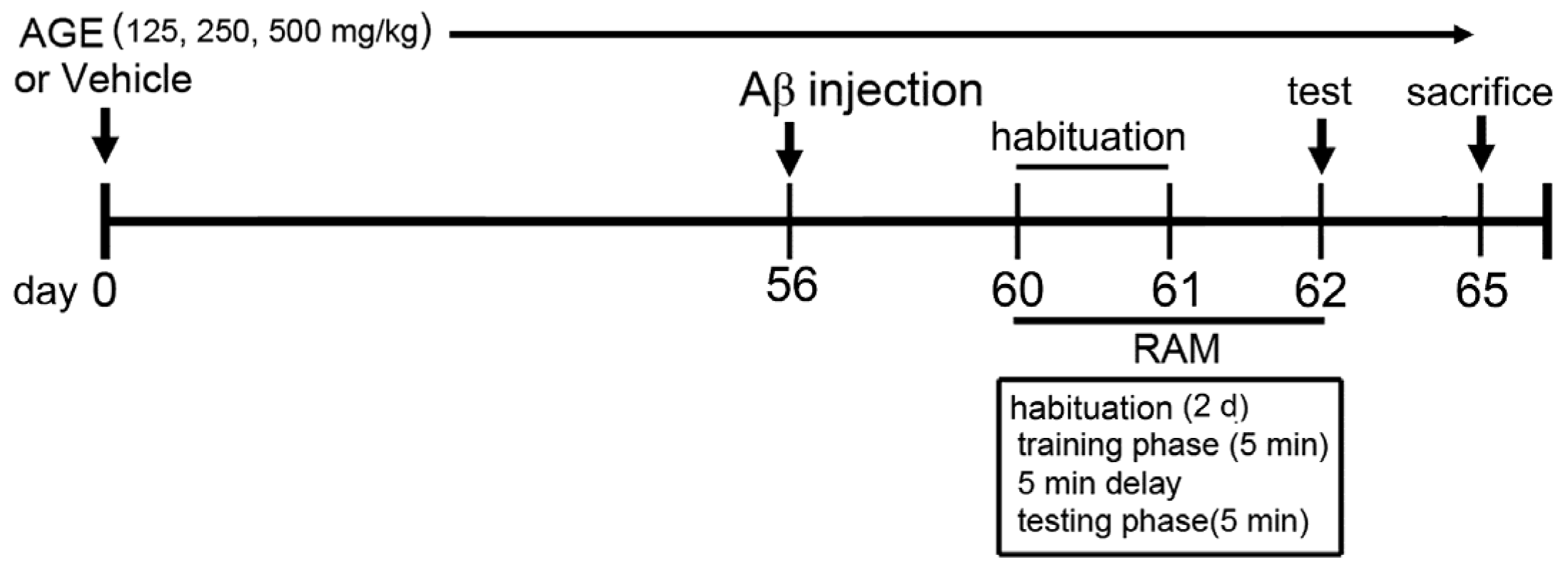
2.2. Animals and Treatment Protocol
2.3. Aβ (1–42) Treatment
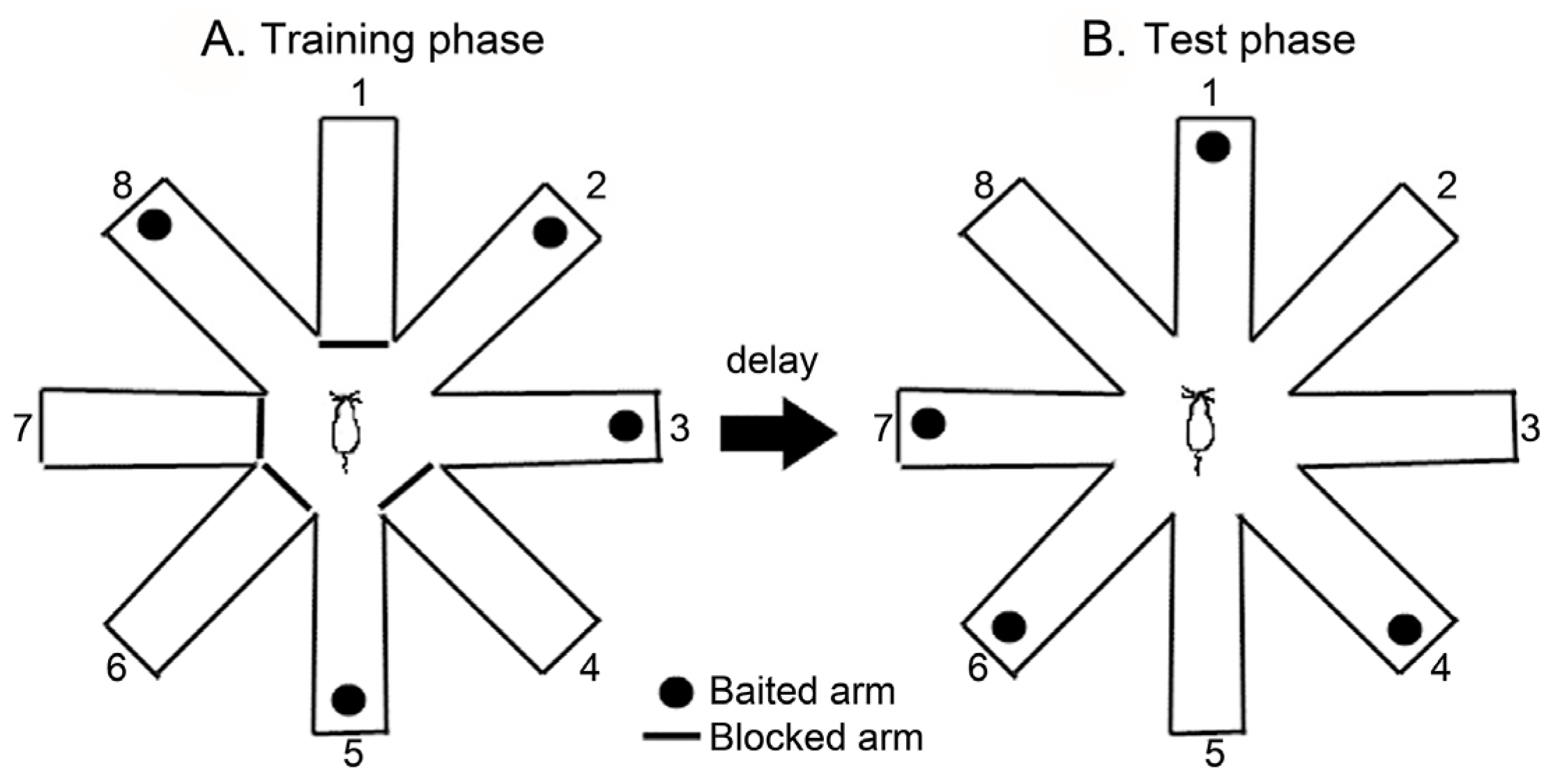
2.4. Radial Arm Maze Test (RAM)
2.5. Tissue Preparation
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
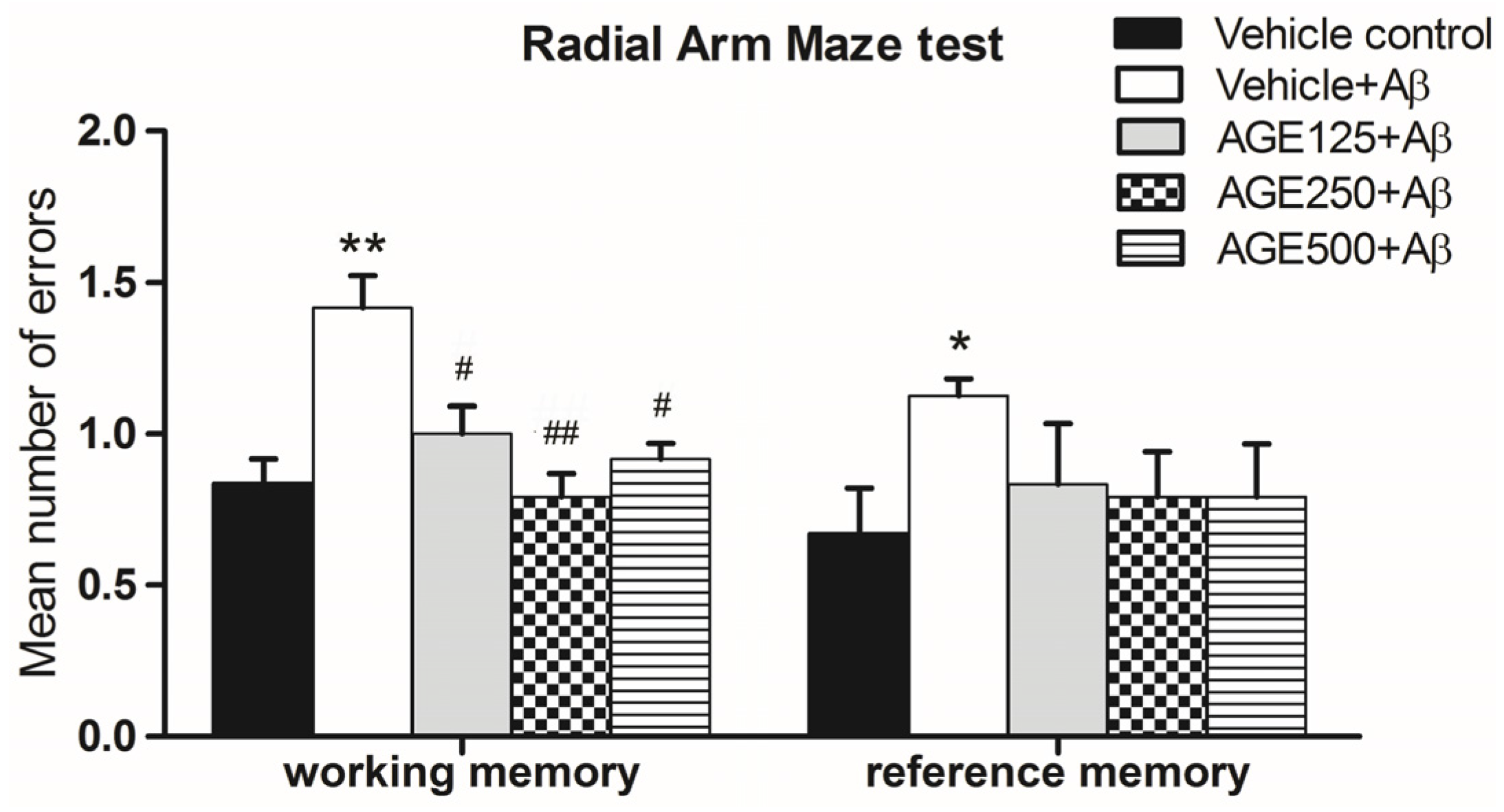
3.1. Effect of AGE on Working and Reference Memory in Radial Arm Maze Test
3.2. Effect of AGE on Cholinergic Neurons in the Hippocampal Region
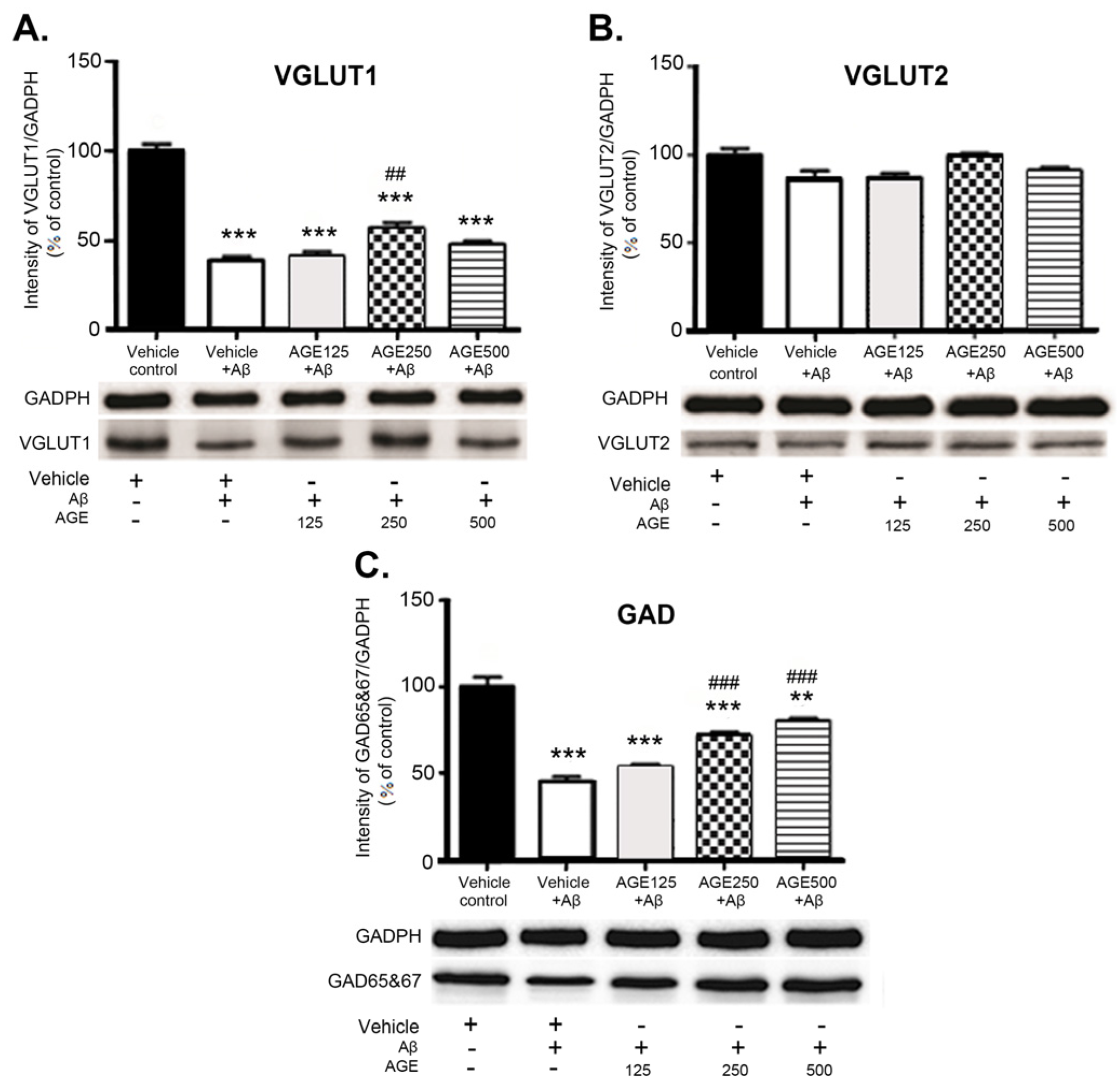
3.3. Effect of AGE on VGLUT1, VGLUT2, and GAD 65 and 67 in the Hippocampal Region
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AGE | Aged garlic extract |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AP | Anterior-posterior |
| Aβ | β-amyloid |
| BW | Body weight |
| Ca2+ | Calcium |
| ChAT | Choline acetyltransferase |
| CRD-HHP | Center for Research and Development of Herbal Health Products |
| DPX | Depex mounting medium |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GAD | Glutamate decarboxylase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| HCL | Hydrochloric |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| MWM | Morri water maze |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen ion |
| RAM | Radial arm maze |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| S.E.M. | Standard error of mean |
| SAC | S-allyl cysteine |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SI | Superior-inferior |
| TBS-T | Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1% tween 20 |
| VGLUT1 | Vesicular glutamate transporter1 |
| VGLUT2 | Vesicular glutamate transporter2 |
References
- Khakpai, F.; Nasehi, M.; Haeri-Rohani, A.; Eidi, A.; Zarrindast, M.R. Septo-hippocampo-septal loop and memory formation. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centonze, D.; Picconi, B.; Gubellini, P.; Bernardi, G.; Calabresi, P. Dopaminergic control of synaptic plasticity in the dorsal striatum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.T.; Palmer, A.M.; Snape, M.; Wilcock, G.K. The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: A review of progress. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtha, S.J.; Pappas, B.A. Neurochemical histopathological and mnemonic effects of combined lesions of the medial septal and serotonin afferents to the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1994, 651, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, P.T.; Lisman, J.E. Low-frequency stimulation at the troughs of theta-oscillation induces long-term depression of previously potentiated ca1 synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 75, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fremeau, R.T., Jr.; Troyer, M.D.; Pahner, I.; Nygaard, G.O.; Tran, C.H.; Reimer, R.J.; Bellocchio, E.E.; Fortin, D.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Edwards, R.H. The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters defines two classes of excitatory synapse. Neuron 2001, 31, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Hioki, H.; Fujiyama, F.; Kaneko, T. Postnatal changes of vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT)1 and VGLUT2 immunoreactivities and their colocalization in the mouse forebrain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 492, 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Nannapaneni, N.; Shore, S. Vessicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2 are differentially associated with auditory nerve and spinal trigeminal inputs to the cochlear nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 500, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.J.; Hughes, D.I.; Polgar, E.; Nagy, G.G.; Mackie, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Maxwell, D.J. The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 in neurochemically defined axonal populations in the rat spinal cord with emphasis on the dorsal horn. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.O.; Paulsen, O. Role of gabaergic inhibition in hippocampal network oscillations. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, S.N.; Martin, S.B.; Martin, D.L. Regional distribution and relative amounts of glutamate decarboxylase isoforms in rat and mouse brain. Neurochem. Int. 1999, 35, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, C.B.; Gilbert, P.E.; Kesner, R.P. The role of the hippocampus in the retrieval of a spatial location. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2005, 83, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueredo, L.Z.P.; Moreira, K.M.; Ferreira, T.L.; Fornari, R.V.; Oliveira, M.G.M. Interaction between glutamatergic-NMDA and cholinergic-muscarinic systems in classical fear conditioning. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 77, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujan, R.; Shigemoto, R.; Lopez-Bendito, G. Glutamate and GABA receptor signalling in the developing brain. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Wu, M.Q.; She, X.J. Effects of chronic noise exposure on spatial learning and memory of rats in relation to neurotransmitters and NMDAR2B alteration in the hippocampus. J. Occup. Health 2009, 51, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.T. Glutamatergic systems in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2003, 18, S15–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, S.L.; Francis, P.T.; Procter, A.W.; Palmer, A.M.; Davison, A.N.; Bowen, D.M. Gamma-aminobutyric acid concentration in brain tissue at two stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 1988, 111, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solas, M.; Puerta, E.; Ramirez, M.J. Treatment options in alzheimer s disease: The GABA story. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 4960–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, M.; Joghataei, M.T.; Mohseni, S.; Roghani, M. Genistein ameliorates learning and memory deficits in amyloid beta(1–40) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2011, 95, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall'Igna, O.P.; Fett, P.; Gomes, M.W.; Souza, D.O.; Cunha, R.A.; Lara, D.R. Caffeine and adenosine a(2a) receptor antagonists prevent beta-amyloid (25-35)-induced cognitive deficits in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 203, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, K.S.; Knox, J.; Inglis, J.; Bernard, A.; Martin, S.J.; Justice, A.; McConlogue, L.; Games, D.; Freedman, S.B.; et al. A learning deficit related to age and beta-amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2000, 408, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Lue, L.; Yang, L.; Roher, A.; Kuo, Y.; Strohmeyer, R.; Goux, W.J.; Lee, V.; Johnson, G.V.; Webster, S.D.; et al. Complement activation by neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 305, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Guo, H.; Cha, Y.; Ban, Y.H.; Seo, D.W.; Choi, Y.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, J.C.; Choi, E.K.; et al. CereboostTM, an american ginseng extract, improves cognitive function via up-regulation of choline acetyltransferase expression and neuroprotection. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2016, 78, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.P.; Chu, T.; Yang, F.S.; Beech, W.; Frautschy, S.A.; Cole, G.M. The curry spice curcumin reduces oxidative damage and amyloid pathology in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 8370–8377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canas, P.M.; Simoes, A.P.; Rodrigues, R.J.; Cunha, R.A. Predominant loss of glutamatergic terminal markers in a beta-amyloid peptide model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, B.; Chauhan, N.B.; Lahiri, D.K. Oxidative insults to neurons and synapse are prevented by aged garlic extract and S-allyl-l-cysteine treatment in the neuronal culture and APP-Tg mouse model. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, T.; Saito, H.; Nishiyama, N. Aged garlic extract prolongs longevity and improves spatial memory deficit in senescence-accelerated mouse. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nillert, N.; Pannangrong, W.; Welbat, J.U.; Chaijaroonkhanarak, W.; Sripanidkulchai, K.; Sripanidkulchai, B. Neuroprotective effects of aged garlic extract on cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation induced by beta-amyloid in rats. Nutrients 2017, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, T.; Saito, H.; Nishiyama, N. Anti-ageing effect of aged garlic extract in the inbred brain atrophy mouse model. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1997, 24, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espina-Marchant, P.; Pinto-Hamuy, T.; Bustamante, D.; Morales, P.; Robles, L.; Herrera-Marschitz, M. Spatial cognition and memory: A reversible lesion with lidocaine into the anteromedial/posterior parietal cortex (AM/PPC) affects differently working and long-term memory on two foraging tasks. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.J.; Herbert, J. Stimulation of neurogenesis in the hippocampus of the adult rat by fluoxetine requires rhythmic change in corticosterone. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, S.; Walker, A.; Bennett, G.; Wigmore, P.M. 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy affects spatial working memory and newborn neurons in the adult rat hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeKosky, S.T.; Scheff, S.W.; Styren, S.D. Structural correlates of cognition in dementia: Quantification and assessment of synapse change. Neurodegeneration 1996, 5, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, D.S.; Kornecook, T.J.; Bastianetto, S.; Quirion, R. Alzheimer’s disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic system: Relations to beta-amyloid peptides, cognition, and treatment strategies. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 68, 209–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczynski, T.J. Gabaergic deafferentation hypothesis of brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Brain Res. Bull. 1998, 45, 341–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, R.; Prediger, R.D.S.; Passos, G.F.; Pandolfo, P.; Duarte, F.S.; Franco, J.L.; Dafre, A.L.; Di Giunta, G.; Figueiredo, C.P.; Takahashi, R.N.; et al. Connecting TNF-alpha signaling pathways to iNOS expression in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: Relevance for the behavioral and synaptic deficits induced by amyloid beta protein. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5394–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canas, P.M.; Porciuncula, L.O.; Cunha, G.M.A.; Silva, C.G.; Machado, N.J.; Oliveira, J.M.A.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine A2A receptor blockade prevents synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction caused by beta-amyloid peptides via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14741–14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, A.; Fukuta, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Nabeshima, T. Continuous infusion of beta-amyloid protein into the rat cerebral ventricle induces learning impairment and neuronal and morphological degeneration. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 73, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes-Tavares, N.; Santos, L.E.; Stutz, B.; Brito-Moreira, J.; Klein, W.L.; Ferreira, S.T.; de Mello, F.G. Inhibition of choline acetyltransferase as a mechanism for cholinergic dysfunction induced by amyloid-beta peptide oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19377–19385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blusztajn, J.K.; Rinnofner, J. Intrinsic cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus: Fact or artifact? Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2016, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frotscher, M.; Schlander, M.; Léránth, C. Cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus. A combined light- and electron-microscopic immunocytochemical study in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1986, 246, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaker, S.N.; Armstrong, D.M.; Gage, F.H. Cholinergic neurons within the rat hippocampus: Response to fimbria-fornix transection. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 272, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.A.; Salvaterra, P.M.; Crawford, G.D.; Houser, C.R.; Vaughn, J.E. An immunocytochemical study of choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons and axon terminals in normal and partially deafferented hippocampal formation. Brain Res. 1987, 402, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Catudio-Garrett, E.; Gabriel, R.; Wilhelm, M.; Erdelyi, F.; Szabo, G.; Deisseroth, K.; Lawrence, J. Hippocampal “cholinergic interneurons” visualized with the choline acetyltransferase promoter: Anatomical distribution, intrinsic membrane properties, neurochemical characteristics, and capacity for cholinergic modulation. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2015, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frotscher, M.; Vida, I.; Bender, R. Evidence for the existence of non-gabaergic, cholinergic interneurons in the rodent hippocampus. Neuroscience 2000, 96, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefft, S.; Hulo, S.; Bertrand, D.; Muller, D. Synaptic transmission at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal organotypic cultures and slices. J. Physiol. 1999, 515, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, K.F.S.; de Kort, G.J.L.; Steggerda, S.; Shigemoto, R.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A.; Cuello, A.C. Structural involvement of the glutamatergic presynaptic boutons in a transgenic mouse model expressing early onset amyloid pathology. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 353, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremeau, R.T.; Kam, K.; Qureshi, T.; Johnson, J.; Copenhagen, D.R.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Edwards, R.H. Vesicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2 target to functionally distinct synaptic release sites. Science 2004, 304, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Moriguchi, T.; Saito, H.; Nishiyama, N. Functional relationship between age-related immunodeficiency and learning deterioration. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 3869–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.B.; Indi, S.S.; Rao, K.S. Garlic extract exhibits antiamyloidogenic activity on amyloid-beta fibrillogenesis: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belle, L.P.; de Bona, K.S.; Abdalla, F.H.; Pimentel, V.C.; Pigatto, A.S.; Moretto, M.B. Comparative evaluation of adenosine deaminase activity in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of young and adult rats: Effect of garlic extract (Allium sativum L.) on their susceptibility to heavy metal exposure. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 104, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Munajjam, A.; Vaishnav, B.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, A.; Kishore, K.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, D.; Kumari, R.; Tiwari, A.; et al. Involvement of adenosine and standardization of aqueous extract of garlic (Allium sativum Linn.) on cardioprotective and cardiodepressant properties in ischemic preconditioning and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiac injury. J. Biomed. Res 2012, 26, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliah, E.; Terry, R.D.; DeTeresa, R.M.; Hansen, L.A. Immunohistochemical quantification of the synapse-related protein synaptophysin in Alzheimer disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1989, 103, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, C.I.; Bi, H.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Filley, C.M.; Martin, L.J. Selective regional loss of exocytotic presynaptic vesicle proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brains. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000, 175, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limon, I.D.; Mendieta, L.; Diaz, A.; Chamorro, G.; Espinosa, B.; Zenteno, E.; Guevara, J. Neuroprotective effect of alpha-asarone on spatial memory and nitric oxide levels in rats injected with amyloid-beta (25–35). Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 453, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, A.; Horne, P.; Yager, D.; Eckman, C.; Eckman, E.; Janus, C. Amyloid beta and impairment in multiple memory systems in older transgenic APP TgCRND8 mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucke, L.; Selkoe, D.J. Neurotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein: Synaptic and network dysfunction. Csh Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichai, T.; Pannangrong, W.; Welbat, J.U.; Chaichun, A.; Sripanidkulchai, K.; Sripanidkulchai, B. Effects of aged garlic extract on spatial memory and oxidative damage in the brain of β-amyloid induced rats. (submitted).
- Penley, S.C.; Gaudet, C.M.; Threlkeld, S.W. Use of an eight-arm radial water maze to assess working and reference memory following neonatal brain injury. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thorajak, P.; Pannangrong, W.; Welbat, J.U.; Chaijaroonkhanarak, W.; Sripanidkulchai, K.; Sripanidkulchai, B. Effects of Aged Garlic Extract on Cholinergic, Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems with Regard to Cognitive Impairment in Aβ-Induced Rats. Nutrients 2017, 9, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070686
Thorajak P, Pannangrong W, Welbat JU, Chaijaroonkhanarak W, Sripanidkulchai K, Sripanidkulchai B. Effects of Aged Garlic Extract on Cholinergic, Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems with Regard to Cognitive Impairment in Aβ-Induced Rats. Nutrients. 2017; 9(7):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070686
Chicago/Turabian StyleThorajak, Piyaporn, Wanassanun Pannangrong, Jariya Umka Welbat, Wunnee Chaijaroonkhanarak, Kittisak Sripanidkulchai, and Bungorn Sripanidkulchai. 2017. "Effects of Aged Garlic Extract on Cholinergic, Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems with Regard to Cognitive Impairment in Aβ-Induced Rats" Nutrients 9, no. 7: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070686
APA StyleThorajak, P., Pannangrong, W., Welbat, J. U., Chaijaroonkhanarak, W., Sripanidkulchai, K., & Sripanidkulchai, B. (2017). Effects of Aged Garlic Extract on Cholinergic, Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems with Regard to Cognitive Impairment in Aβ-Induced Rats. Nutrients, 9(7), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070686




