Vitamin B12-Containing Plant Food Sources for Vegetarians
Abstract
:1. Introduction
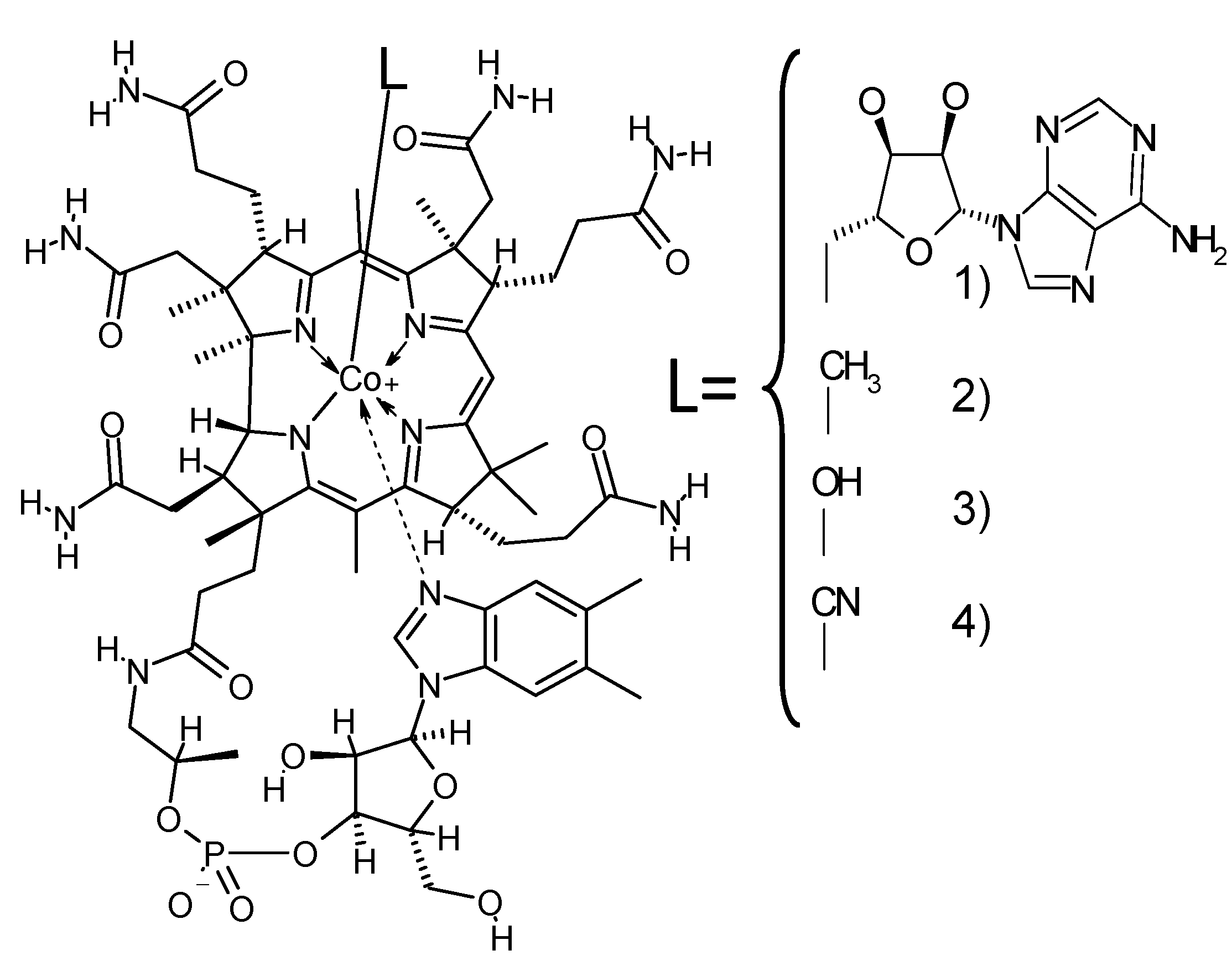
2. Main Types of Vegetarian Diets
3. Nutritional Characterization of Vegetarian Diets
| Rich | Low |
|---|---|
| Fiber | Vitamin A |
| Vitamin C | Vitamin D3 |
| Vitamin E | Vitamin B12 |
| Folate | Iron |
| Magnesium | Cholesterol |
| n-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids | n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| Carbohydrates | Saturated fatty acids |
4. Vitamin B12-Containing Plant-Derived Food Sources
4.1. Vitamin B12-Enriched Beans and Vegetables Produced Using Organic Fertilizers or Hydroponics
4.2. Fermented Beans and Vegetables
4.3. Edible Mushrooms
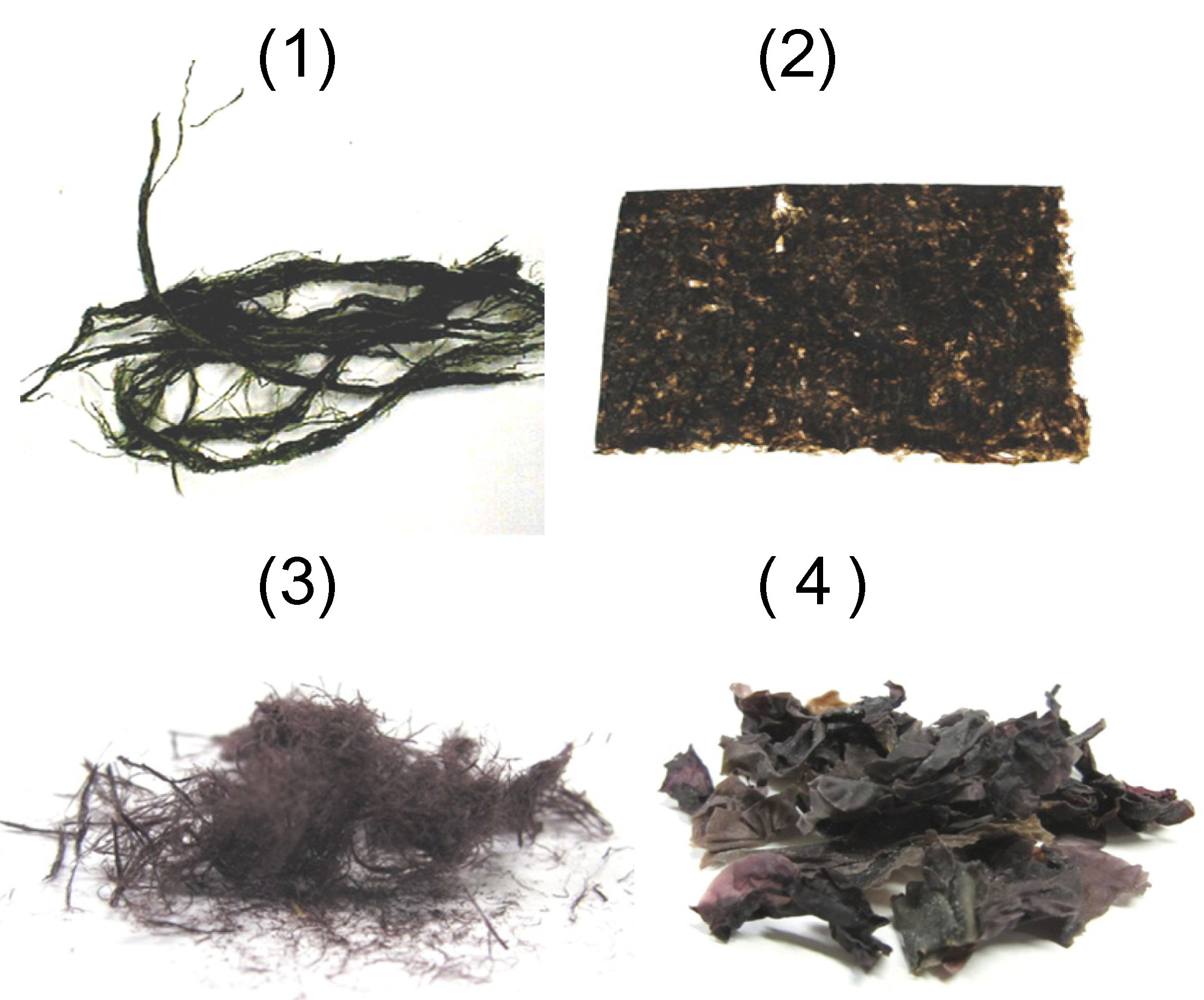
4.4. Edible Algae

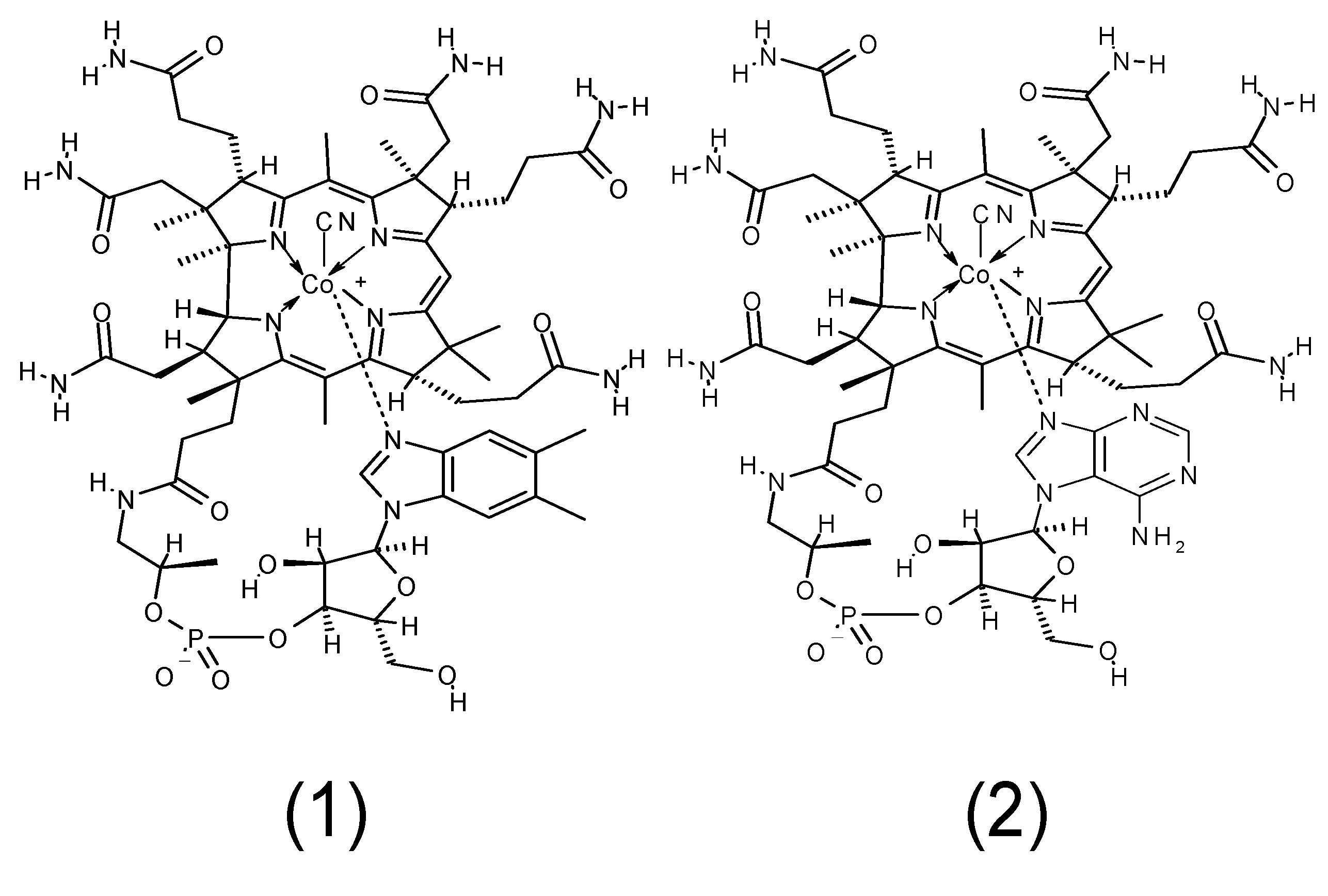
5. Conclusions
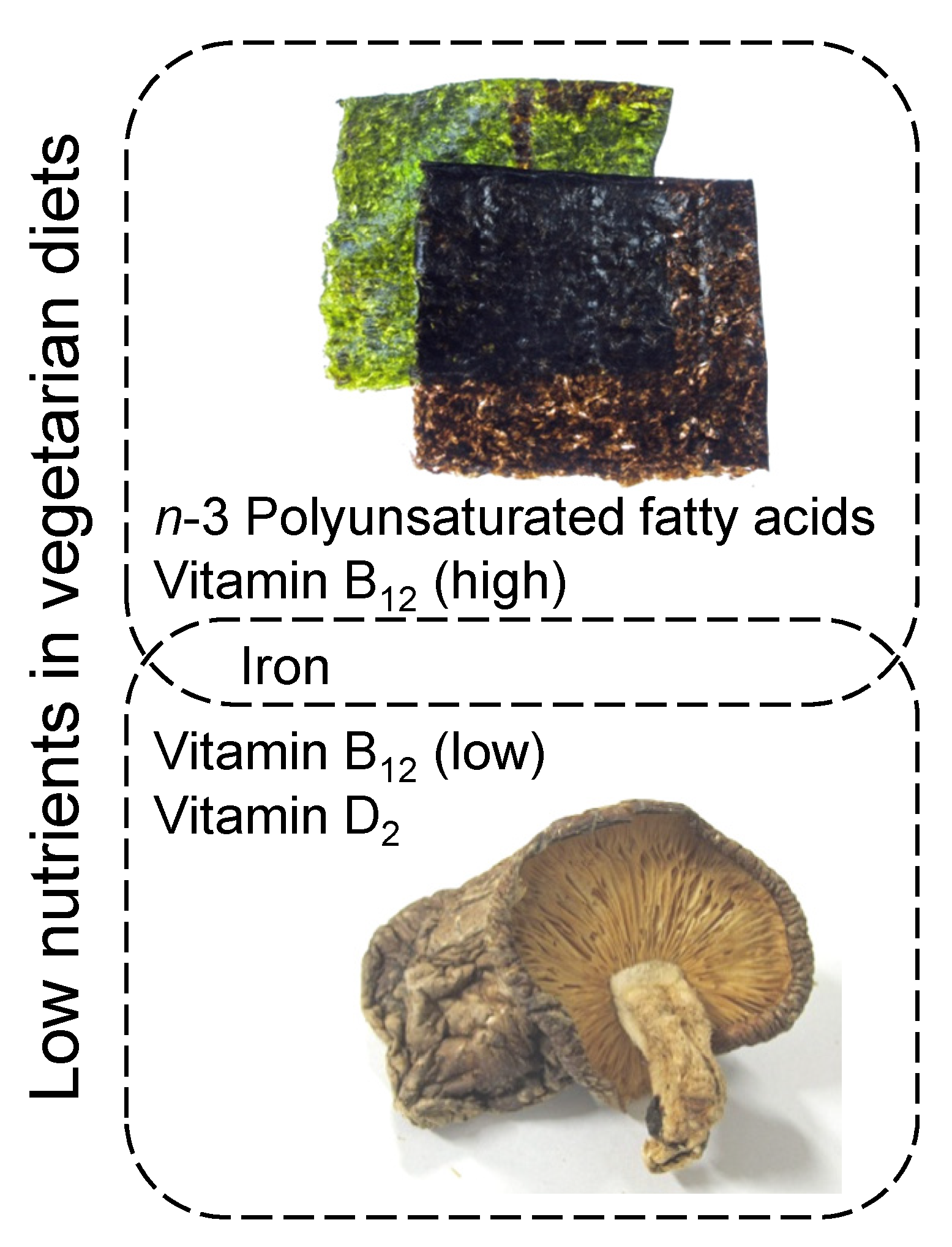
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watanabe, F.; Miyamoto, E. Hydrophilic Vitamins. In Handbook of Thin-Layer Chromatography, 3rd ed.; Sherma, J., Fried, B., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 589–605. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Crippen, K.; Gulati, S.; Banerjee, R. Purification and kinetic mechanism of a mammalian methionine synthase from pig liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27193–27197. [Google Scholar]
- Fenton, W.A.; Hack, A.M.; Willard, H.F.; Gertler, A.; Rosenberg, L.E. Purification and properties of methylmalonyl coenzyme A mutase from human liver. Arch. Biochem. 1982, 228, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, F. Vitamin B12 sources and bioavailability. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Yabuta, Y.; Tanioka, Y.; Bito, T. Biologically active vitamin B12 compounds in foods for preventing deficiency among vegetarians and elderly subjects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6769–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Vitamin B12. In Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic, Acid, Biotin, and Choline; Institute of Medicine, National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 306–356. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, K.; Fukuwatari, T.; Imai, E.; Hayakawa, H.; Watanabe, F.; Takimoto, H.; Watanabe, T.; Umegaki, K. Dietary reference intakes for Japanese 2010: Water-soluble vitamins. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, S67–S82. [Google Scholar]
- Millet, P.; Guilland, J.C.; Fuchs, F.; Klepping, J. Nutrient intake and vitamin status of healthy French vegetarians and nonvegetarians. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 718–727. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, R.; Parrott, S.J.; Raj, S.; Cullum-Dugan, D.; Lucus, D. How prevalent is vitamin B12 deficiency among vegetarians? Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.E.; Yen, C.H.; Cheng, C.H.; Huang, Y.C. Vitamin B12 status is not associated with plasma homocysteine in parents and their preschool children: Lacto-ovo, lacto, and ovo-vegetarians and omnivores. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, M.S. Metabolic vitamin B12 status on a mostly raw vegan diet with follow-up using tablets, nutritional yeast, or probiotic supplements. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2000, 44, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J. Convergence of plant-rich and plant-only diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 70, 620S–622S. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Krawinkel, M. The nutritional status of iron, folate, and vitamin B12 of Buddhist vegetarians. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dusseldorp, M.; Schneede, J.; Refsum, H.; Ueland, P.M.; Thomas, C.M.; de Boer, E.; van Staveren, W.A. Risk of persistent cobalamin deficiency in adolescents fed a macrobiotic diet in early life. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, A.S.; Mahida, V.I.; Gupte, S.C. Iron status of Hindu brahmin, Jain and Muslim communities in Surat, Gujarat. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2007, 23, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.J.; Appleby, P.N.; Rosell, M.S. Health effects of vegetarian and vegan diets. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2006, 65, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.J. Nutrition concerns and health effects of vegetarian diets. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2010, 25, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Chemistry behind vegetarianism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo-Bouwman, C.A.; Naber, T.H.; Schaafsma, G. A review of vitamin A equivalency of β-carotene in various food matrices for human consumption. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, R.J.; Lu, Z.; Bogusz, J.M.; Williams, J.E.; Holick, M.F. Photobiology of vitamin D in mushrooms and its bioavailability in humans. Dermatoendocrinology 2013, 1, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, B.; Querings, K.; Reichrath, J. Vitamin D and skin: New aspects for dermatology. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, M.W.; Naber, E.C. Vitamin profiles of eggs as indicators of nutritional status in the laying hen: Vitamin B12 study. Poult. Sci. 1992, 71, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Doscherholmen, A.; McMahon, J.; Ripley, D. Vitamin B12 absorption from eggs. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1975, 149, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doscherholmen, A.; McMahon, J.; Ripley, D. Inhibitory effect of eggs on vitamin B12 absorption: Description of a simple ovalbumin 57Co vitamin B12 absorption test. Br. J. Haematol. 1976, 33, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, G.F.M. Vitamin B12. In Bioavailability and Analysis of Vitamins in Foods; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1998; pp. 497–515. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, F.; Abe, K.; Fujita, T.; Goto, M.; Hiemori, M.; Nakano, Y. Effects of microwave heating on the loss of vitamin B12 in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkbage, K.; Witthoft, C.; Fonden, R.; Jagerstad, M. Retention of vitamin B12 during manufacture of six fermented dairy products using a validated radio protein-binding assay. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Wang, X.; Mizoguchi, K. A modified form of a vitamin B12 compound extracted from whey fermented by Lactobacillus helveticus. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, H.W.; Russell, R.M. Vitamin B12 deficiency in the elderly. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1999, 19, 357–377. [Google Scholar]
- Cuskelly, G.J.; Mooney, K.M.; Young, I.S. Folate and vitamin B12: Friendly or enemy nutrients for the elderly. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalle, N.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Garg, M.K.; Naik, S.S. Vitamin B12 deficiency and hyperhomocysteinemia as correlates of cardiovascular risk factors in Indian subjects with coronary artery disease. J. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Lachner, C.; Steinle, N.I.; Regenold, W.T. The neuropsychiatry of vitamin B12 deficiency in elderly patients. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 24, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.H.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Oakley, G.P.; Omenn, G.S. Considering the case for vitamin B12 fortification of flour. Food Nutr. Bull. 2010, 31, S36–S46. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, K.L.; Olson, B.; Bakun, P.; Dallal, G.E.; Selhub, J.; Rosenberg, I.H. Breakfast cereal fortified with folic acid, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 increases vitamin concentrations and reduces homocysteine concentrations: A randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 805–811. [Google Scholar]
- Mozafar, A. Enrichment of some B-vitamins in plants with application of organic fertilizers. Plant Soil 1994, 167, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bito, T.; Ohishi, N.; Takenaka, S.; Yabuta, Y.; Miyamoto, E.; Nishihara, E.; Watanabe, F. Characterization of vitamin B12 compounds in biofertilizers containing purple photosynthetic bacteria. Trends Chromatogr. 2012, 7, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.H.; Stabler, S.P. Identification and quantitation of cobalamin and cobalamin analogues in human feces. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Kudo, Y.; Muramatsu, K. Incorporation of a high level of vitamin B12 into a vegetable, kaiware daikon (Japanese radish sprout), by the absorption from its seeds. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1672, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bito, T.; Ohishi, N.; Hatanaka, Y.; Takenaka, S.; Nishihara, E.; Yabuta, Y.; Watanabe, F. Production and characterization of cyanocobalamin-enriched lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) grown using hydroponics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3852–3858. [Google Scholar]
- Nout, M.J.R.; Rombouts, F.M. Recent developments in tempe research. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 69, 609–633. [Google Scholar]
- Denter, J.; Bisping, B. Formation of B-vitamins by bacteria during the soaking process of soybeans for tempe fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1994, 22, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, N.; Hadioetomo, P.S.; Nikkuni, S.; Katoh, K.; Ohta, T. Vitamin B12 content of fermented foods in the tropics. Rept. Nalt. Food Res. Inst. 1983, 43, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, C.S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Watanabe, F.; Park, S.C. Vitamin B12 contents in some Korean fermented foods and edible seaweeds. Korean J. Nutr. 2008, 41, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, E.; Kittaka-Katsura, H.; Adachi, S.; Watanabe, F. Assay of vitamin B12 in edible bamboo shoots. Vitamins 2005, 79, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, U.; Rudramma, Rati E.R.; Joseph, R. Nutritional quality of lactic fermented bitter gourd and fenugreek leaves. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 49, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Babuchowski, A.; Laniewska-Moroz, L.; Warminska-Radyko, I. Propionibacteria in fermented vegetables. Lait 1999, 79, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kittaka-Katsura, H.; Watanabe, F.; Nakano, Y. Occurrence of vitamin B12 in green, blue, red, and black tea leaves. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2004, 50, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittaka-Katsura, H.; Ebara, S.; Watanabe, F.; Nakano, Y. Characterization of corrinoid compounds from a Japanese black tea (Batabata-cha) fermented by bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 909–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Schwarz, J.; Takenaka, S.; Miyamoto, E.; Ohishi, N.; Nelle, E.; Hochstrasser, R.; Yabuta, Y. Characterization of vitamin B12 compounds in the wild edible mushrooms black trumpet (Craterellus cornucopioides) and golden chanterelle (Cantharellus cibarius). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2012, 58, 438–441. [Google Scholar]
- Bito, T.; Teng, F.; Ohishi, N.; Takenaka, S.; Miyamoto, E.; Sakuno, E.; Terashima, K.; Yabuta, Y.; Watanabe, F. Characterization of vitamin B12 compounds in the fruiting bodies of shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) and bed logs after fruiting of the mushroom. Mycoscience 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, F.; Bito, T.; Takenaka, S.; Yabuta, Y.; Watanabe, F. Vitamin B12[c-lactone], a biologically inactive corrinoid compound, occurs in cultured and dried lion’s mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) fruiting bodies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Stabler, S.P.; Brass, E.P.; Marcell, P.D.; Allen, R.H. Inhibition of cobalamin-dependent enzymes by cobalamin analogues in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, F.; Takenaka, S.; Katsura, H.; Masumder, S.A.; Abe, K.; Tamura, Y.; Nakano, Y. Dried green and purple lavers (nori) contain substantial amounts of biologically active vitamin B12 but less of dietary iodine relative to other edible seaweeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2341–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, F.; Takenak, S.; Kittaka-Katsura, H.; Ebara, S.; Miyamoto, E. Characterization and bioavailability of vitamin B12-compounds from edible algae. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2002, 48, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, F.; Takenaka, S.; Katsura, H.; Miyamoto, E.; Abe, K.; Tamura, Y.; Nakatsuka, T.; Nakano, Y. Characterization of a vitamin B12 compound in the edible purple laver, Porphyra yezoensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2712–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Katsura, H.; Miyamoto, E.; Takenaka, S.; Abe, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Nakano, Y. Characterization of vitamin B12 in an edible green laver (Entromopha prolifera). Appl. Biol. Sci. 1999, 5, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, E.; Yabuta, Y.; Kwak, C.S.; Enomoto, T.; Watanabe, F. Characterization of vitamin B12 compounds from Korean purple laver (Porphyra sp.) products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2793–2796. [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka, S.; Sugiyama, S.; Ebara, S.; Miyamoto, E.; Abe, K.; Tamura, Y.; Watanabe, F.; Tsuyama, S.; Nakano, Y. Feeding dried purple laver (nori) to vitamin B12-deficient rats significantly improves vitamin B12 status. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 85, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Shibata, Y.; Takayama, M.; Narita, Y.; Sugiwara, K.; Fukuda, M. Content and characteristics of vitamin B12 in some seaweeds. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1997, 42, 497–505. [Google Scholar]
- Suziki, H. Serum vitamin B12 levels in young vegans who eat brown rice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1995, 41, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Helliwell, K.E.; Wheeler, G.L.; Leptos, K.C.; Goldstein, R.E.; Smith, A.G. Insights into the evolution of vitamin B12 auxotrophy from sequenced algal genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2921–2933. [Google Scholar]
- Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan-2010; The Council for Science and Technology Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, JAPAN (Ed.) Official Gazette Co-operation of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2010.
- Yabuta, Y.; Fujimura, H.; Kwak, C.S.; Enomoto, T.; Watanabe, F. Antioxidant activity of the phycoerythrobilin compound formed from a dried Korean purple laver (Porphyra sp.) during in vitro digestion. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2010, 16, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kittaka-Katsura, H.; Fujita, T.; Watanabe, F.; Nakano, Y. Purification and characterization of a corrinoid-compound from chlorella tablets as an algal health food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4994–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Katsura, H.; Takenaka, S.; Fujita, T.; Abe, K.; Tamura, Y.; Nakatsuka, T.; Nakano, Y. Pseudovitamin B12 is the predominate cobamide of an algal health food, spirulina tablets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4736–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, E.; Tanioka, Y.; Nakao, T.; Barla, F.; Inui, H.; Fujita, T.; Watanabe, F.; Nakano, Y. Purification and characterization of a corrinoidcompound in an edible cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae as a nutritional supplementary food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9604–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Miyamoto, E.; Fujita, T.; Tanioka, Y.; Nakano, Y. Characterization of a corrinod compound in the edible (blue-green) algae, suizenji-nori. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 3066–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Tanioka, Y.; Miyamoto, E.; Fujita, T.; Takenaka, H.; Nakano, Y. Purification and characterization of corrinoid-compounds from the dried powder of an edible cyanobacterium, Nostoc commune (Ishikurage). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2007, 53, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, E.; Yabuta, Y.; Takenaka, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Takenaka, H.; Watanabe, F. Characterization of corrinoid compounds from edible cyanobacterium Nostochopsis sp. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2012, 58, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, F.; Bito, T.; Takenaka, S.; Takenaka, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yabuta, Y.; Watanabe, F. Characterization of corrinoid compounds in the edible cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme the hair vegetable. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, F.; Yabuta, Y.; Bito, T.; Teng, F. Vitamin B12-Containing Plant Food Sources for Vegetarians. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1861-1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6051861
Watanabe F, Yabuta Y, Bito T, Teng F. Vitamin B12-Containing Plant Food Sources for Vegetarians. Nutrients. 2014; 6(5):1861-1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6051861
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Fumio, Yukinori Yabuta, Tomohiro Bito, and Fei Teng. 2014. "Vitamin B12-Containing Plant Food Sources for Vegetarians" Nutrients 6, no. 5: 1861-1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6051861
APA StyleWatanabe, F., Yabuta, Y., Bito, T., & Teng, F. (2014). Vitamin B12-Containing Plant Food Sources for Vegetarians. Nutrients, 6(5), 1861-1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6051861





