Effects of Fish Oil with Heat Treatment on Obesity, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Metabolic Assessments
2.3. RT-qPCR
2.4. 16S rRNA Sequencing and Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
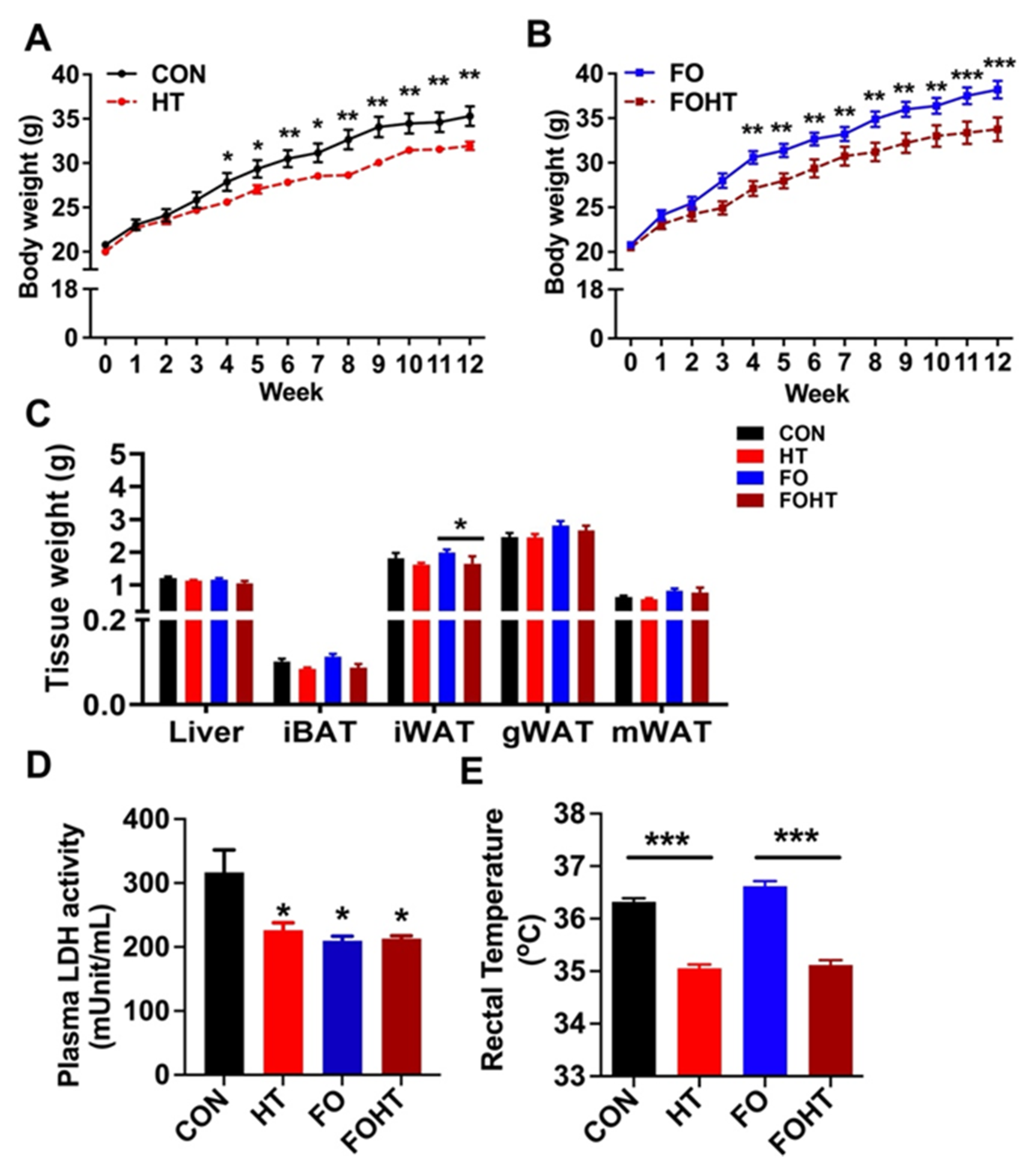
3.1. HT Attenuated Body Weight Gain and Induced Metabolic Adaptation Without Causing Cell Damage Independent of FO Supplementation
3.2. HT Significantly Improved Insulin Sensitivity in OVX Mice, Comparable to FO Supplementation
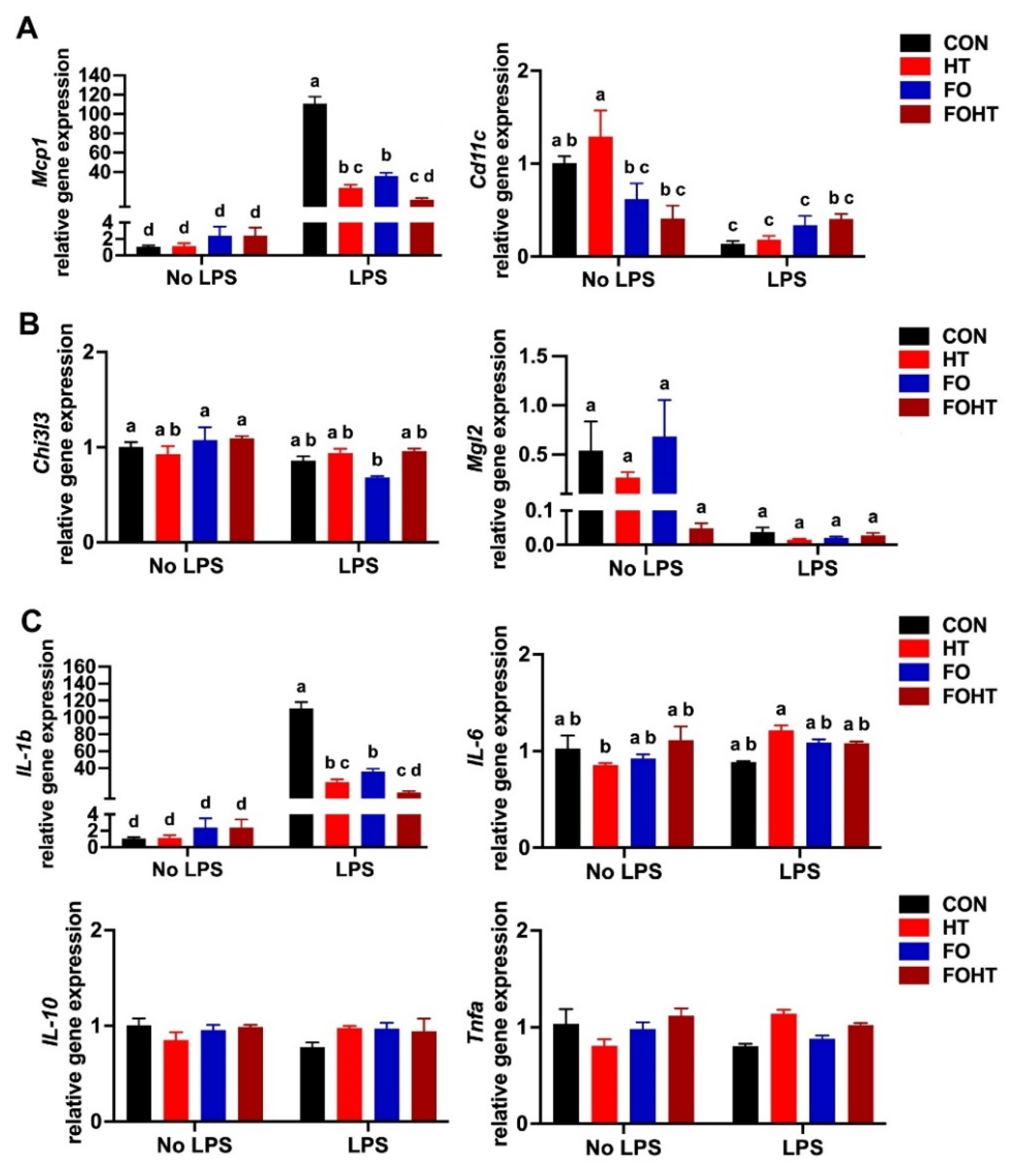
3.3. FO and HT Synergistically Reduced Inflammation in the Liver of the OVX Mice
3.4. FO and HT Altered Microbiota Diversity and Composition in OVX Mice
3.5. FO and HT Significantly Protected Against LPS-Induced Acute Inflammation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, H.G.; Park, H. Metabolic disorders in menopause. Metabolites 2022, 12, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, M.C. The emergence of the metabolic syndrome with menopause. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2404–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.-M.; Lei, F.; Qin, J.-J.; Zhao, Y.-C. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 suggests that metabolic risk factors are the leading drivers of the burden of ischemic heart disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1943–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auro, K.; Joensuu, A.; Fischer, K.; Kettunen, J.; Salo, P.; Mattsson, H.; Niironen, M.; Kaprio, J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Lehtimäki, T. A metabolic view on menopause and ageing. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, G.B.; Carreau, A.-M.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Bergeron, J.; Labrie, F.; Lemieux, S.; Tchernof, A. Increased body fat mass explains the positive association between circulating estradiol and insulin resistance in postmenopausal women. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E448–E456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, D.; Winters, S.J.; Hornung, C.A. Bilateral oophorectomy and the risk of incident diabetes in postmenopausal women. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Clegg, D.J.; Hevener, A.L. The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 309–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, J.; Nielsen, C.; St, B.P.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Richelsen, B. Estrogen reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines in rodent adipose tissue: Studies in vivo and in vitro. Horm. Metab. Res. 2003, 35, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Kumar, S.P.S.; Shi, H. Estradiol regulates insulin signaling and inflammation in adipose tissue. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2014, 17, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Weiss, N.S.; Newcomb, P.; Barlow, W.; White, E. Hormone replacement therapy in relation to breast cancer. JAMA 2002, 287, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, L.; Collins, P.; Herrington, D.M.; Mendelsohn, M.E.; Pasternak, R.C.; Robertson, R.M.; Schenck-Gustafsson, K.; Smith, J.; Sidney, C.; Taubert, K.A.; et al. Hormone replacement therapy and cardiovascular disease: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2001, 104, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Monroe, J.C.; Gavin, T.P.; Roseguini, B.T. Skeletal muscle adaptations to heat therapy. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henstridge, D.C.; Whitham, M.; Febbraio, M.A. Chaperoning to the metabolic party: The emerging therapeutic role of heat-shock proteins in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, V.E.; Howard, M.J.; Francisco, M.A.; Ely, B.R.; Minson, C.T. Passive heat therapy improves endothelial function, arterial stiffness and blood pressure in sedentary humans. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5329–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, S.; Jackson, S.; Fatania, G.; Leicht, C. The effect of passive heating on heat shock protein 70 and interleukin-6: A possible treatment tool for metabolic diseases? Temperature 2017, 4, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Cohen, M. Clinical effects of regular dry sauna bathing: A systematic review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1857413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilch, W.; Szygula, Z.; Palka, T.; Pilch, P.; Cison, T.; Wiecha, S. Comparison of physiological reactions and physiological strain in healthy men under heat stress in dry and steam heat saunas. Biol. Sport 2014, 31, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sminia, P.; Zee, J.V.D.; Wondergem, J.; Haveman, J. Effect of hyperthermia on the central nervous system: A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 1994, 10, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiya, H.; Katsumata, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Tsutsumi, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Fukushima, T. Photothermal stress triggered by near-infrared-irradiated carbon nanotubes up-regulates osteogenesis and mineral deposition in tooth-extracted sockets. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.-M. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolin, R.C.; Vargas, A.; Gasparotto, J.; Chaves, P.; Schnorr, C.E.; Martinello, K.B.; Silveira, A.; Rabelo, T.K.; Gelain, D.; Moreira, J. A new animal diet based on human Western diet is a robust diet-induced obesity model: Comparison to high-fat and cafeteria diets in term of metabolic and gut microbiota disruption. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylander, B.L.; Qiao, G.; Gomez, E.C.; Singh, P.; Repasky, E.A. Housing temperature plays a critical role in determining gut microbiome composition in research mice: Implications for experimental reproducibility. Biochimie 2023, 210, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huus, K.E.; Ley, R.E. Blowing hot and cold: Body temperature and the microbiome. Msystems 2021, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, J.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Bulló, M.; Lopez, J.V.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Vidal, J.; Atzeni, A.; Fernandez-García, J.C.; Torres-Collado, L.; et al. Effect on gut microbiota of a 1-y lifestyle intervention with Mediterranean diet compared with energy-reduced Mediterranean diet and physical activity promotion: PREDIMED-Plus Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Cheung, C.K.Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Ye, D.; Guo, J.; Tse, M.A.; et al. Gut microbiome fermentation determines the efficacy of exercise for diabetes prevention. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 77–91.e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhan, V.; Joshi, N.; Nagarajan, P.; Upadhyay, P. Protocol for long duration whole body hyperthermia in mice. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2012, 66, e3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, A.A.; Bomhoff, G.L.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Geiger, P.C. Heat treatment improves glucose tolerance and prevents skeletal muscle insulin resistance in rats fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes 2009, 58, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, B.; Bröde, P.; Schütte, M.; Griefahn, B. Lowering of resting core temperature during acclimation is influenced by exercise stimulus. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Ping, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Zhao, W.; Guo, M.; Shen, F. Local hyperthermia therapy induces browning of white fat and treats obesity. Cell 2022, 185, 949–966.e919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, P.; Stanford, K.I. Exercise-induced adaptations to adipose tissue thermogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-R.; Directo, D. Fish Oil Supplementation with Resistance Exercise Training Enhances Physical Function and Cardiometabolic Health in Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-R.; Directo, D.; Khamoui, A.V. Fish oil administration combined with resistance exercise training improves strength, resting metabolic rate, and inflammation in older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 3073–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CON | HT | FO | FOHT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 217.8 ± 9.2 a | 230.8 ±9.4 a | 158.3 ± 18.2 b | 174.0 ± 17.7 ab |
| Triglycerides (mM) | 0.72 ± 0.10 | 0.62 ± 0.06 | 0.66 ±0.08 | 0.58 ± 0.05 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 206.5 ± 5.5 a | 163.3± 3.5 c | 188.1 ± 4.3 b | 157.4 ± 3.0 c |
| FSH (ng/mL) | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.6 ±1.3 | 3.9 ± 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, R.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-C.; Chung, S. Effects of Fish Oil with Heat Treatment on Obesity, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030549
Fan R, Kim J, Kim Y-C, Chung S. Effects of Fish Oil with Heat Treatment on Obesity, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030549
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Rong, Judy Kim, Young-Cheul Kim, and Soonkyu Chung. 2025. "Effects of Fish Oil with Heat Treatment on Obesity, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030549
APA StyleFan, R., Kim, J., Kim, Y.-C., & Chung, S. (2025). Effects of Fish Oil with Heat Treatment on Obesity, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice. Nutrients, 17(3), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030549






