Sleep Duration, Dietary Inflammatory Potential, and Obesity in Relation to Colorectal Cancer Incidence in the Multiethnic Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
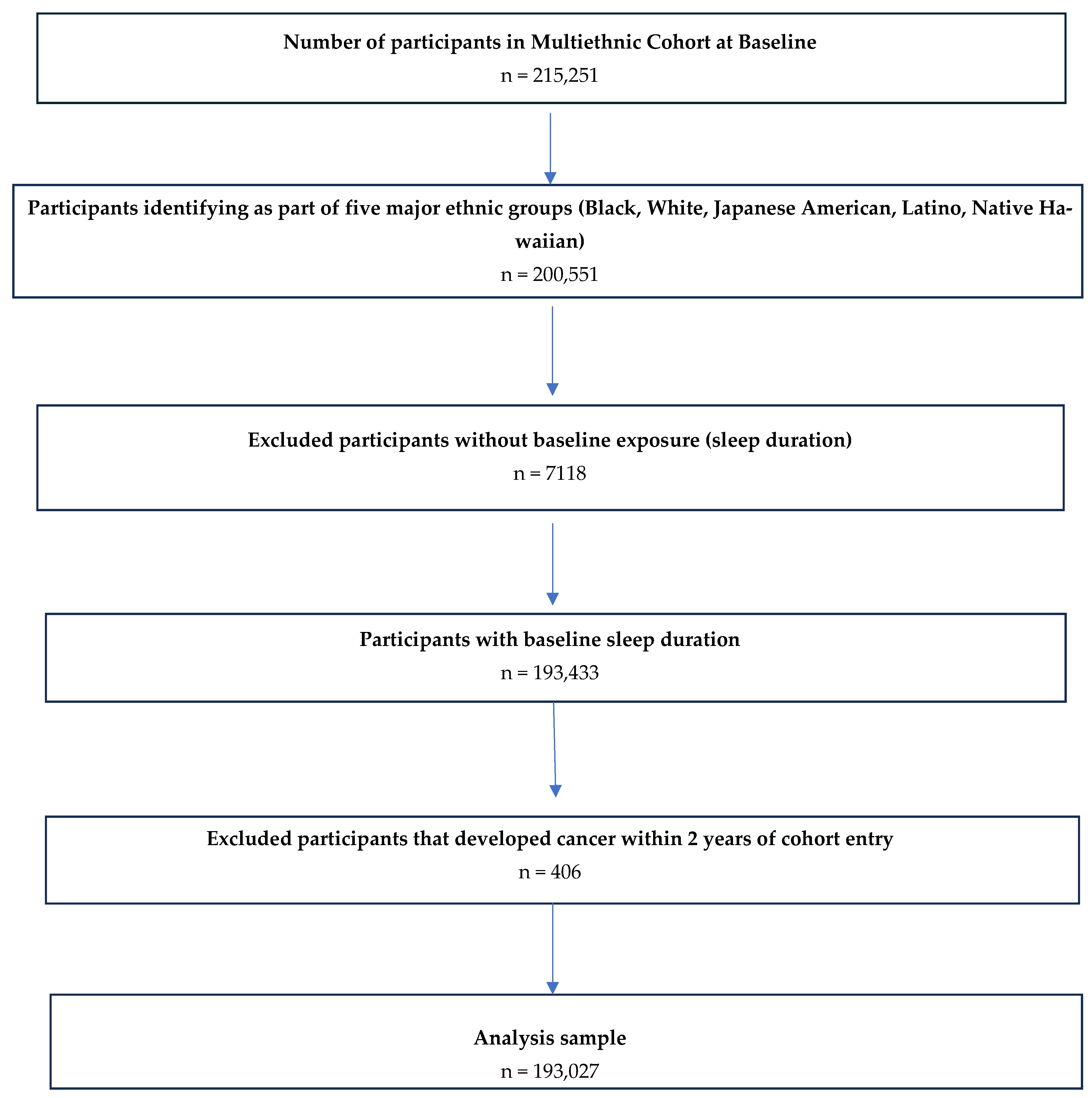
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Exposures
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aHR | Adjusted hazard ratio |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| E-DII | Energy-adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index |
| MEC | Multiethnic cohort |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Colorectal Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- Ollberding, N.J.; Nomura, A.M.; Wilkens, L.R.; Henderson, B.E.; Kolonel, L.N. Racial/ethnic differences in colorectal cancer risk: The multiethnic cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashktorab, H.; Kupfer, S.S.; Brim, H.; Carethers, J.M. Racial Disparity in Gastrointestinal Cancer Risk. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustus, G.J.; Ellis, N.A. Colorectal Cancer Disparity in African Americans: Risk Factors and Carcinogenic Mechanisms. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.C.; Sandler, R.S.; Sanoff, H.K.; Yang, Y.C.; Lund, J.L.; Baron, J.A. Decrease in Incidence of Colorectal Cancer Among Individuals 50 Years or Older After Recommendations for Population-based Screening. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2017, 15, 903–909.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzić, J.; Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Karin, M. Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2101–2114.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed Soffian, S.S.; Mohammed Nawi, A.; Hod, R.; Ja’afar, M.H.; Isa, Z.M.; Chan, H.K.; Hassan, M.R.A. Meta-Analysis of the Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsimalis, F.; Basta, M.; Varouchakis, G.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Vgontzas, A.; Kryger, M. Cytokines and pathological sleep. Sleep Med. 2008, 9, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R. Sleep and inflammation: Partners in sickness and in health. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.P., Jr.; Drake, A.L.; Frey, D.J.; Fleshner, M.; Desouza, C.A.; Gronfier, C.; Czeisler, C.A. Influence of sleep deprivation and circadian misalignment on cortisol, inflammatory markers, and cytokine balance. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 47, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.P.; Dutil, C.; Featherstone, R.; Ross, R.; Giangregorio, L.; Saunders, T.J.; Janssen, I.; Poitras, V.J.; Kho, M.E.; Ross-White, A.; et al. Sleep duration and health in adults: An overview of systematic reviews. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45 (Suppl. 2), S218–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, C.; Mahajan, S.; Valero-Elizondo, J.; Massey, D.; Lu, Y.; Roy, B.; Riley, C.; Annapureddy, A.R.; Murugiah, K.; Elumn, J.; et al. Evaluation of Temporal Trends in Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Sleep Duration Among US Adults, 2004–2018. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e226385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, F.; Wei, L.; Li, X.; Lyu, Z.; Feng, X.; Wen, Y.; Guo, L.; He, J.; Dai, M.; et al. Sleep duration and the risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis including dose-response relationship. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, N.; Yin, J.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Z. Association between sleep duration and cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, A.; Sun, H. Exploring the association between sleep duration and cancer risk in middle-aged and older Chinese adults: Observations from a representative cohort study (2011–2020). BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Xiao, Q.; Chu, L.W.; Yu, K.; Matthews, C.E.; Hsing, A.W.; Caporaso, N.E. Sleep Duration and Cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study Cohort. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.A.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.H.; Chang, H.J.; Sohn, D.K.; Shin, A.; Kim, J. Genetic Risk Score, Combined Lifestyle Factors and Risk of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.E.; Wirth, M.D.; Boushey, C.J.; Wilkens, L.R.; Draluck, E.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hofseth, L.; Haiman, C.A.; Le Marchand, L.; et al. The Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated with Colorectal Cancer Risk in the Multiethnic Cohort. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, R.; Odjidja, E.N.; Scott, D.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Hodge, A.; de Courten, B. The dietary inflammatory index, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors and diseases. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2022, 23, e13349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. International Agency for Research on Cancer Handbook Working Group. Body Fatness and Cancer--Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.; O’Hara, C.; Bardon, L.A.; Gibney, E.R. Comparison of Meal Patterns Across Common Racial Groups in the UK and the USA, Examining Associations with Weight Status and Diet Quality: A Secondary Analysis of NDNS and NHANES Datasets. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2023, 12, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.; Pan, L.; Blanck, H.M. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Adult Obesity in the United States: CDC’s Tracking to Inform State and Local Action. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2019, 16, E46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolonel, L.N.; Henderson, B.E.; Hankin, J.H.; Nomura, A.M.; Wilkens, L.R.; Pike, M.C.; Stram, D.O.; Monroe, K.R.; Earle, M.E.; Nagamine, F.S. A multiethnic cohort in Hawaii and Los Angeles: Baseline characteristics. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, N.F.; Badr, M.S.; Belenky, G.; Bliwise, D.L.; Buxton, O.M.; Buysse, D.; Dinges, D.F.; Gangwisch, J.; Grandner, M.A.; Kushida, C.; et al. Recommended Amount of Sleep for a Healthy Adult: A Joint Consensus Statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep 2015, 38, 843–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stram, D.O.; Hankin, J.H.; Wilkens, L.R.; Pike, M.C.; Monroe, K.R.; Park, S.; Henderson, B.E.; Nomura, A.M.; Earle, M.E.; Nagamine, F.S.; et al. Calibration of the dietary questionnaire for a multiethnic cohort in Hawaii and Los Angeles. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Murphy, S.P.; Wilkens, L.R.; Au, D.; Shen, L.; Kolonel, L.N. Extending a multiethnic food composition table to include standardized food group servings. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hussey, J.R.; Hurley, T.G. Perspective: The Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII)-Lessons Learned, Improvements Made, and Future Directions. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Duan, Z.; Sangi-Haghpeykar, H.; Hale, L.; White, D.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Sleep duration and incidence of colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Wu, K.; Gao, X.; Hu, F.; Ogino, S.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Fuchs, C.S.; Redline, S.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Associations of self-reported sleep duration and snoring with colorectal cancer risk in men and women. Sleep 2013, 36, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, J.J.; Lin, C.H.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.L.; Qin, T.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.J. Association of sleep duration, sleep apnea, and shift work with risk of colorectal neoplasms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Nice, E.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y. Circadian rhythms and cancers: The intrinsic links and therapeutic potentials. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R.; Zhu, X.; Storfer-Isser, A.; Mehra, R.; Jenny, N.S.; Tracy, R.; Redline, S. Sleep duration and biomarkers of inflammation. Sleep 2009, 32, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneri, P.G.; Tirrò, E.; Pennisi, M.S.; Massimino, M.; Stella, S.; Romano, C.; Manzella, L. The Insulin/IGF System in Colorectal Cancer Development and Resistance to Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Xie, Y.; Zou, X. Association between sleep duration and depression in US adults: A cross-sectional study. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Lin, L.; Austin, D.; Young, T.; Mignot, E. Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin, elevated ghrelin, and increased body mass index. PLoS Med. 2004, 1, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Egmond, L.T.; Meth, E.M.S.; Engström, J.; Ilemosoglou, M.; Keller, J.A.; Vogel, H.; Benedict, C. Effects of acute sleep loss on leptin, ghrelin, and adiponectin in adults with healthy weight and obesity: A laboratory study. Obesity 2023, 31, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychter, A.M.; Łykowska-Szuber, L.; Zawada, A.; Szymczak-Tomczak, A.; Ratajczak, A.E.; Skoracka, K.; Kolan, M.; Dobrowolska, A.; Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. Why Does Obesity as an Inflammatory Condition Predispose to Colorectal Cancer? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, J.C.; Manasson, J.; Scher, J.U. The role of the gut microbiome in systemic inflammatory disease. BMJ 2018, 360, j5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, C.; Fava, F.; Gobbetti, M.; Tuohy, K. Healthy dietary patterns to reduce obesity-related metabolic disease: Polyphenol-microbiome interactions unifying health effects across geography. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.J.; Santos, A.; Prada, P.O. Linking Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Physiology 2016, 31, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusnic, O.; Onisor, D.; Boicean, A.; Hasegan, A.; Ichim, C.; Guzun, A.; Chicea, R.; Todor, S.B.; Vintila, B.I.; Anderco, P.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: Insights into Colon Carcinogenesis and Immune Regulation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Intestinal Microbiota and Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, W. Role of the Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Tumorigenesis or Development of Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2205563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Green, S.J.; Mutlu, E.; Engen, P.; Vitaterna, M.H.; Turek, F.W.; Keshavarzian, A. Circadian disorganization alters intestinal microbiota. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Tait, C.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Catalano, C.; Rustgi, V.K. Circadian Rhythms, the Gut Microbiome, and Metabolic Disorders. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Forsyth, C.B.; Bishehsari, F.; Voigt, R.M.; Keshavarzian, A.; Swanson, G.R. Disease Implications of the Circadian Clocks and Microbiota Interface. In Circadian Rhythms in Bacteria and Microbiomes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.L.; Patel, S.R.; Jackson, W.B., 2nd; Lutsey, P.L.; Redline, S. Agreement between self-reported and objectively measured sleep duration among white, black, Hispanic, and Chinese adults in the United States: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofseth, L.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Chanda, A.; Chen, H.; Love, B.L.; Pena, M.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Sajish, M.; Sheth, A.; Buckhaults, P.J.; et al. Early-onset colorectal cancer: Initial clues and current views. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.K.; Daschner, P.; Ishibe, N.; Wali, A.; Hall, K.; Czajkowski, S.; Mahabir, S.; Watson, J.M.; Nebeling, L.; Ross, S.; et al. Metabolic Dysregulation and Cancer Risk Program (MeDOC): A transdisciplinary approach to obesity-associated cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2024, 116, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, C.; Liu, J. Global burden of sleep disturbances among older adults and the disparities by geographical regions and pandemic periods. SSM-Popul. Health 2023, 25, 101588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Sleep Duration | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤6 h 66,194 (34.3%) | 7–8 h 108,986 (56.5%) | ≥9 h 17,847 (9.2%) | n = 193,027 | |
| Number of CRC Cases | 2038 | 3215 | 572 | 5825 |
| Geographic Location, n (%) | ||||
| Hawaii | 30,961 (46.8) | 54,122 (49.7) | 7482 (41.9) | 92,565 (47.9) |
| California | 35,233 (53.2) | 54,864 (50.3) | 10,365 (58.1) | 100,462 (52.1) |
| Age at Cohort Entry (y), n (%) | ||||
| 45–54 | 21,960 (33.2) | 34,884 (32.0) | 4759 (26.7) | 61,603 (31.9) |
| 55–64 | 21,970 (33.2) | 36,627 (33.6) | 5694 (31.9) | 64,219 (33.3) |
| ≥65 | 22,264 (33.6) | 37,475 (34.4) | 7394 (41.4) | 67,133 (34.8) |
| Sex of Participant, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 28,885 (43.6) | 50,117 (46.0) | 8511 (47.7) | 87,513 (45.3) |
| Female | 37,309 (56.4) | 58,869 (54.0) | 9336 (52.3) | 105,514 (54.7) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | ||||
| Black/African American | 13,290 (20.1) | 15,074 (13.8) | 3343 (19.2) | 31,798 (16.5) |
| Native Hawaiian | 5773 (8.7) | 6835 (6.3) | 1264 (7.1) | 13,872 (7.2) |
| Japanese American | 20,847 (31.5) | 30,771 (28.2) | 3222 (18.1) | 54,840 (28.4) |
| Latino | 14,528 (22.0) | 25,096 (23.0) | 4915 (27.5) | 44,539 (23.1) |
| White/European American | 11,756 (17.7) | 31,210 (28.7) | 5012 (28.1) | 47,978 (24.8) |
| Education Level, n (%) | ||||
| Less than high school | 11,797 (17.8) | 17,819 (16.4) | 4186 (23.5) | 33,802 (17.5) |
| High school/vocational school | 23,225 (35.1) | 35,918 (33.0) | 6311 (35.4) | 65,454 (33.9) |
| College level | 22,776 (34.4) | 39,181 (36.0) | 5421 (30.4) | 67,378 (34.9) |
| Graduate/professional | 7624 (11.5) | 14,998 (13.8) | 1686 (9.5) | 24,308 (12.6) |
| Missing data | 772 (1.2) | 1070 (0.8) | 243 (1.2) | 2085 (1.1) |
| Marital Status, n (%) | ||||
| Never married | 4666 (7.1) | 7044 (6.5) | 1203 (6.7) | 12,913 (6.7) |
| Married | 41,089 (62.1) | 74,768 (68.6) | 11,777 (66.0 | 127,634 (66.1) |
| Divorced/separated/widowed | 19,876 (30.0) | 26,340 (24.2) | 4703 (26.4) | 50,919 (26.4) |
| Missing data | 563 (0.8) | 834 (0.7) | 164 (0.9) | 1561 (0.8) |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2), n (%) | ||||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 1207 (1.8) | 1765 (1.6) | 312 (1.8) | 3284 (1.7) |
| Normal weight (18.5 to 24.9) | 24,392 (36.8) | 45,073 (41.4) | 6216 (34.8) | 75,681 (39.2) |
| Overweight (25 to 29.9) | 25,460 (38.5) | 41,533 (38.1) | 6779 (38.0) | 73,772 (38.2) |
| Obese (≥30) | 14,389 (21.7) | 19,739 (18.1) | 4320 (24.2) | 38,448 (19.9) |
| Missing data | 746 (1.2) | 876 (0.8) | 220 (1.2) | 1842 (1.0) |
| E-DII Quartiles, n (%) | ||||
| Quartile 1 (−6.4 to −2.9) | 16,443 (24.8) | 29,223 (26.8) | 3954 (22.1) | 49,620 (25.7) |
| Quartile 2 (−2.8 to −1.5) | 15,404 (23.3) | 26,645 (24.5) | 4026 (22.6) | 46,075 (23.9) |
| Quartile 3 (−1.4 to 0.1) | 15,354 (23.2) | 25,355 (23.3) | 4335 (24.3) | 45,044 (23.3) |
| Quartile 4 (0.2 to 5) | 16,059 (24.3) | 24,202 (22.2) | 4722 (26.5) | 44,983 (23.3) |
| Missing data | 2934 (4.4) | 3561 (3.2) | 810 (4.5) | 7305 (3.8) |
| Smoking Status, n (%) | ||||
| Never | 29,358 (44.4) | 47,640 (43.7) | 6801 (38.1) | 83,799 (43.4) |
| Previous smoker | 24,872 (37.6) | 43,307 (39.7) | 7462 (41.8) | 75,641 (39.2) |
| Current smoker | 10,887 (16.5) | 16,619 (15.3) | 3292 (18.5) | 30,798 (16.0) |
| Missing data | 1077 (1.5) | 1420 (1.3) | 292 (1.6) | 2789 (1.4) |
| Estrogen use, n (%) | ||||
| Never | 19,685 (25.7) | 30,173 (27.7) | 4914 (27.5) | 54,772 (28.4) |
| Previous user | 6882 (10.4) | 9913 (9.1) | 1695 (9.5) | 18,490 (9.6) |
| Current user | 9625 (14.5) | 17,346 (15.9) | 2451 (13.7) | 29,442 (15.2) |
| Missing/not applicable (male) | 30,002 (45.4) | 51,554 (47.3) | 8787 (49.3) | 90,343 (46.8) |
| Progesterone use, n (%) | ||||
| Never | 15,716 (23.7) | 23,664 (21.7) | 3953 (22.2) | 43,333 (22.5) |
| Previous user | 3368 (5.1) | 5495 (5.0) | 847 (4.8) | 9710 (5.0) |
| Current user | 3956 (6.0) | 7770 (7.1) | 1075 (6.0) | 12,801 (6.6) |
| Missing/not applicable (male) | 43,154 (65.2) | 72,057 (66.2) | 11,972 (67.0) | 127,183 (65.9) |
| Dietary Supplement use, n (%) | ||||
| No | 23,869 (36.1) | 38,573 (35.4) | 6990 (39.2) | 69,432 (36.0) |
| Yes | 42,325 (63.9) | 70,413 (64.6) | 10,857 (60.8) | 123,595 (64.0) |
| Family History of Colon Cancer, n (%) | ||||
| No | 51,887 (78.4) | 87,493 (80.3) | 14,010 (78.5) | 153,390 (79.5) |
| Yes | 5344 (8.1) | 8543 (7.8) | 1301 (7.3) | 15,188 (7.9) |
| Missing | 8963 (13.5) | 12,950 (11.9) | 2536 (14.2) | 24,449 (12.6) |
| * Previous Chronic Condition, n (%) | ||||
| No | 52,749 (76.7) | 89,969 (82.6) | 13,207 (74.0) | 155,925 (80.8) |
| Yes | 13,445 (20.3) | 19,017 (17.4) | 4640 (26.0) | 37,102 (19.2) |
| Continuous Variables | ||||
| Age at Cohort Entry (years) (Mean ± SD) | 59.6 ± 8.8 | 59.7 ± 8.8 | 61.2 ± 8.8 | 59.8 ± 8.8 |
| Age at CRC Diagnosis (years) (Mean ± SD) | 74.1 ± 9.1 | 74.6 ± 8.9 | 74.8 ± 8.8 | 74.5 ± 9.0 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) (Mean ± SD) | 26.9 ± 5.3 | 26.3 ± 4.9 | 27.2 ± 5.5 | 26.6 ± 5.1 |
| ** Physical Activity (METs) (Mean ± SD) | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 |
| E-DII Score (Mean ± SD) | −1.3 ± 2.0 | −1.4 ± 1.9 | −1.2 ± 2.0 | −1.4 ± 2.0 |
| Pack Years of Smoking, (Mean ± SD) | 9.7 ± 14.6 | 10.1 ± 14.9 | 12.4 ± 16.6 | 10.4 ± 16.6 |
| Alcohol Consumption (g/day), (Mean ± SD) | 8.1 ± 25.1 | 9.2 ± 24.3 | 11.5 ± 30.2 | 9.0 ± 25.2 |
| Sleep Duration | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤6 h | 7–8 h | ≥9 h | |
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |
| All Participants | |||
| Model 1 (Crude) | 1.08 (1.02,1.14) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.15 (1.05,1.25) |
| Model 2 (Adjusted) | 1.04 (0.98,1.10) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.10 (1.01,1.22) |
| Black/African American | |||
| Model 1 (Crude) | 1.06 (0.94,1.20) | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.96 (0.78,1.19) |
| Model 2 (Adjusted) | 1.02 (0.89,1.18) | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.87 (0.69,1.10) |
| Native Hawaiian | |||
| Model 1 (Crude) | 1.06 (0.96,1.16) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.21 (1.01,1.45) |
| Model 2 (Adjusted) | 1.15 (0.91,1.44) | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.99 (0.66,1.48) |
| Japanese American | |||
| Model 1 (Crude) | 0.96 (0.85,1.09) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.25 (1.05,1.48) |
| Model 2 (Adjusted) | 1.04 (0.94,1.15) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.19 (0.99,1.44) |
| Latino | |||
| Model 1 (Crude) | 0.96 (0.85,1.09) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.25 (1.05,1.49) |
| Model 2 (Adjusted) | 1.02 (0.88,1.18) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.22 (1.01,1.48) |
| White/European American | |||
| Model 1 (Crude) | 1.05 (0.91,1.20) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.19 (0.99,1.42) |
| Model 2 (Adjusted) | 0.99 (0.86,1.15) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.13 (0.93,1.37) |
| Sleep Duration, aHR (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short (≤6 h) | Normal/Adequate (7–8 h) | Long (≥9 h) | p Interaction | |
| Obesity | 0.08 | |||
| BMI < 30 kg/m2 | 0.99 (0.93,1.06) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.09 (0.97,1.22) | |
| BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 | 1.35 (1.21,1.51) | 1.16 (1.06,1.29) | 1.36 (1.14,1.64) | |
| E-DII Score | 0.69 | |||
| <−1.5 (median) | 1.04 (0.96,1.13) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.08 (0.94,1.25) | |
| ≥−1.5 (median) | 1.05 (0.97,1.14) | 1.04 (0.97,1.12) | 1.19 (1.05,1.34) | |
| E-DII Score | 0.82 | |||
| <0 | 1.01 (0.95,1.08) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.10 (0.99,1.24) | |
| ≥0 | 1.12 (1.02,1.24) | 1.07 (0.99,1.17) | 1.22 (1.05,1.43) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tembo, P.; Zhao, L.; Le Marchand, L.; Wilkens, L.R.; Park, S.-Y.; Haiman, C.A.; Wirth, M.D.; Hébert, J.R. Sleep Duration, Dietary Inflammatory Potential, and Obesity in Relation to Colorectal Cancer Incidence in the Multiethnic Cohort. Nutrients 2025, 17, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030370
Tembo P, Zhao L, Le Marchand L, Wilkens LR, Park S-Y, Haiman CA, Wirth MD, Hébert JR. Sleep Duration, Dietary Inflammatory Potential, and Obesity in Relation to Colorectal Cancer Incidence in the Multiethnic Cohort. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030370
Chicago/Turabian StyleTembo, Penias, Longgang Zhao, Loïc Le Marchand, Lynne R. Wilkens, Song-Yi Park, Christopher A. Haiman, Michael D. Wirth, and James R. Hébert. 2025. "Sleep Duration, Dietary Inflammatory Potential, and Obesity in Relation to Colorectal Cancer Incidence in the Multiethnic Cohort" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030370
APA StyleTembo, P., Zhao, L., Le Marchand, L., Wilkens, L. R., Park, S.-Y., Haiman, C. A., Wirth, M. D., & Hébert, J. R. (2025). Sleep Duration, Dietary Inflammatory Potential, and Obesity in Relation to Colorectal Cancer Incidence in the Multiethnic Cohort. Nutrients, 17(3), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030370







