Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Inherited Metabolic Disorders at Risk of Hypoglycemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Hypoglycemia and Safety
4. Case 1
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saudubray, J.-M.; Sedel, F.; Walter, J.H. Clinical Approach to Treatable Inborn Metabolic Diseases: An Introduction. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, A.; Iannucci, D.; Guarino, M.; Blasetti, A.; Chiarelli, F. Hypoglycemia in Children: Major Endocrine-Metabolic Causes and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, C.; Mention, K.; Dobbelaere, D.; Wemeau, J.-L.; Saudubray, J.-M.; Vantyghem, M.-C. Hypoglycaemia Related to Inherited Metabolic Diseases in Adults. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, C.; Jannin, A.; Vantyghem, M.-C. Rare Causes of Hypoglycemia in Adults. Ann. Endocrinol. 2020, 81, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, D.A.; Steuerwald, U.; De Souza, C.F.M.; Derks, T.G.J. Inborn Errors of Metabolism with Hypoglycemia: Glycogen Storage Diseases and Inherited Disorders of Gluconeogenesis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 65, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczyk, A.; Romanowska, H.; Majkowska, L. Rare causes of hypoglycemia in adults—Disorders of gluconeogenesis and fatty acid oxidation disorders. Pol. Merkur. Lek. Organ Pol. Tow. Lek. 2011, 30, 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, E.; Hindmarch, C.C.T.; Dunham-Snary, K.J. Medium-chain Acyl-COA Dehydrogenase Deficiency: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 6, e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, D.; Rossi, A.; Pivonello, R.; Salerno, M.; Balivo, F.; Spadarella, S.; Muscogiuri, G.; Casa, R.D.; Formisano, P.; Andria, G.; et al. Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia (GSDIa) but Not Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ib (GSDIb) Is Associated to an Increased Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: Possible Role of Microsomal Glucose 6-Phosphate Accumulation. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dios-Fuentes, E.; Gonzalo Marin, M.; Remón-Ruiz, P.; Benitez Avila, R.; Bueno Delgado, M.A.; Blasco Alonso, J.; Doulatram Gamgaram, V.K.; Olveira, G.; Soto-Moreno, A.; Venegas-Moreno, E. Cardiometabolic and Nutritional Morbidities of a Large, Adult, PKU Cohort from Andalusia. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, Y.; Okubo, M.; Tanaka, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Murase, T. Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Glycogen Storage Disease Type III. Diabet. Med. 2000, 17, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, R.; Rakover-Tenenbaum, Y.; Mandel, H.; Lumelski, D.; Admoni, O.; Horovitz, Y. Secondary Diabetes Mellitus: Late Complication of Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1b. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 2005, 18, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengos, K.; Michelakakis, H.; Vontzalidis, A.; Zouvelou, V.; Manta, P. Diabetes Mellitus Associated with Glycogen Storage Disease Type III. Muscle Nerve 2009, 39, 876–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, A.; Ohri, A. Diabetes Mellitus in a Patient with Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2017, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, A.; Patel, D.; Kulshreshtha, B. Secondary Diabetes as a Rare Complication of Glycogen Storage Disease 1a: Case Report and Review of Literature. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 27, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemaru, Y.; Harada, N.; Wada, N.; Yasuda, T.; Okamura, E.; Fujii, T.; Ogura, M.; Inagaki, N. A Case Report of Diabetes in a Patient with Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1a. Intern. Med. Tokyo Jpn. 2024, 63, 2153–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, N.; Gautschi, M.; Bosanska, L.; Meienberg, F.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Spinas, G.A.; Hochuli, M. Glycemic Control and Complications in Glycogen Storage Disease Type I: Results from the Swiss Registry. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 126, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochuli, M.; Christ, E.; Meienberg, F.; Lehmann, R.; Krützfeldt, J.; Baumgartner, M.R. Alternative Nighttime Nutrition Regimens in Glycogen Storage Disease Type I: A Controlled Crossover Study. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolinder, J.; Antuna, R.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.; Kröger, J.; Weitgasser, R. Novel Glucose-Sensing Technology and Hypoglycaemia in Type 1 Diabetes: A Multicentre, Non-Masked, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Welsh, Z.; Ells, S.; Seibold, A. The Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring on Glycaemic Control as Measured by HbA1c: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials and Real-World Observational Studies. Diabetes Ther. Res. Treat. Educ. Diabetes Relat. Disord. 2020, 11, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, T.; Hanaire, H.; Ajjan, R.; Hermanns, N.; Riveline, J.-P.; Rayman, G. Flash Glucose-Sensing Technology as a Replacement for Blood Glucose Monitoring for the Management of Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicenter, Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershkovitz, E.; Rachmel, A.; Ben-Zaken, H.; Phillip, M. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Children with Glycogen Storage Disease Type I. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2001, 24, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maran, A.; Crepaldi, C.; Avogaro, A.; Catuogno, S.; Burlina, A.; Poscia, A.; Tiengo, A. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Conditions Other than Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2004, 20 (Suppl. S2), S50–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, F.J.; Jones, S.A. The Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Practical Management of Glycogen Storage Disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapkara, Ç.S.; Cinasal Demir, G.; Hasanoğlu, A.; Tümer, L. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Children with Glycogen Storage Disease Type I. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, M.; Pendyal, S.; Rairikar, M.; Halaby, C.; Benjamin, R.W.; Kishnani, P.S. Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Management of Glycogen Storage Disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeks, F.; Hoogeveen, I.J.; Feldbrugge, R.L.; Burghard, R.; de Boer, F.; Fokkert-Wilts, M.J.; van der Klauw, M.M.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Derks, T.G.J. A Retrospective In-Depth Analysis of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Datasets for Patients with Hepatic Glycogen Storage Disease: Recommended Outcome Parameters for Glucose Management. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.Q.; Wei, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Hu, M.H.; Hou, L.; Wu, W.; Liang, Y.; Luo, X.P. The application of continuous glucose monitoring in the management of hepatic glycogen storage disease. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi Chin. J. Pediatr. 2021, 59, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Venema, A.; Haarsma, P.; Feldbrugge, L.; Burghard, R.; Rodriguez-Buritica, D.; Parenti, G.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Derks, T.G.J. A Prospective Study on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia: Toward Glycemic Targets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3612–e3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overduin, R.J.; Venema, A.; Lubout, C.M.A.; Fokkert-Wilts, M.J.; De Boer, F.; Schreuder, A.B.; Rossi, A.; Derks, T.G.J. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in People with Liver Glycogen Storage Disease and Idiopathic Ketotic Hypoglycemia: A Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2024, 143, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugelmo, G.; Maines, E.; Boscari, F.; Lenzini, L.; Fadini, G.P.; Burlina, A.; Avogaro, A.; Vitturi, N. Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Inherited Metabolic Disorders at Risk for Hypoglycemia and Nutritional Implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Geddes, J.; Freeman, J.V.; Emery, C.J.; Heller, S.R.; Frier, B.M. Frequency of Biochemical Hypoglycaemia in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes with and without Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycaemia: No Identifiable Differences Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiel, S.A.; Aschner, P.; Childs, B.; Cryer, P.E.; Galan, B.E.d.; Frier, B.M.; Gonder-Frederick, L.; Heller, S.R.; Jones, T.; Khunti, K.; et al. Hypoglycaemia, Cardiovascular Disease, and Mortality in Diabetes: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beers, C.A.J.; DeVries, J.H.; Kleijer, S.J.; Smits, M.M.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.H.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Diamant, M.; Snoek, F.J.; Serné, E.H. Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycaemia (IN CONTROL): A Randomised, Open-Label, Crossover Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddlesworth, T.D.; Beck, R.W.; Gal, R.L.; Connor, C.G.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Lee, S.; Willi, S.M. Optimal Sampling Duration for Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Determine Long-Term Glycemic Control. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of Patients | n = 18 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 30.5 ± 12.5 | ||
| Gender (male)—n (%) | 11 (61.1) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.1 ± 5.3 | ||
| HbA1c (%) | 5.5 ± 0.6 | ||
| IMDs type—n (%) | |||
| FAODs | 9 (50) | MCAD deficiency (n = 4) | |
| LCAD deficiency (n = 1) | |||
| CACT deficiency (n = 1) | |||
| CPT II deficiency (n = 2) | |||
| MADD deficiency (n = 1) | |||
| GSD | 5 (27.8) | Hepatic: 4 (80) | Type Ib (n = 1) |
| Type IIIa (n = 1) | |||
| Type IX (n = 2) | |||
| Muscle: 1 (20) | Type V (n = 1) | ||
| GLUD-1 deficiency | 2 (11.2) | ||
| MMA | 1 (5.5) | ||
| HFI | 1 (5.5) | ||
| History of hypoglycemia—n (%) | Symptomatic 9 (50) | ||
| Nocturnal 6 (33.3) | |||
| Severe 2 (11.1) | |||
| IMD Subgroups (n) | FAODs (9) | GSD (5) | GLUD-1 | MMA | HFI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCAD | LCAD | CACT | CPTII | MADD | Ib | IIIa | IX | V | ||||
| N | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Type of nighttime nutrition | ||||||||||||
| UCCS | 2 (22.2) | 1 (11.1) | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | 2 (40) | 0 | 1 (50) | 0 | 0 |
| UCCS intake (g/day/person) | 40 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| History of hypoglycemia | ||||||||||||
| Childhood | 2 (22.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 1 (50) | 0 | 1 |
| Adults | 1 (11.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 1 (20) | 0 | 2 (40) | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 1 |
| Symptomatic | 2 (22.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (11.1) | 1 (20) | 0 | 2 (20) | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 1 |
| Nocturnal | 2 (22.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | 2 (100) | 0 | 0 |
| Severe | 1 (11.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IMDs (n = 18) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | p | |
| N | 18 | 18 | 18 | |
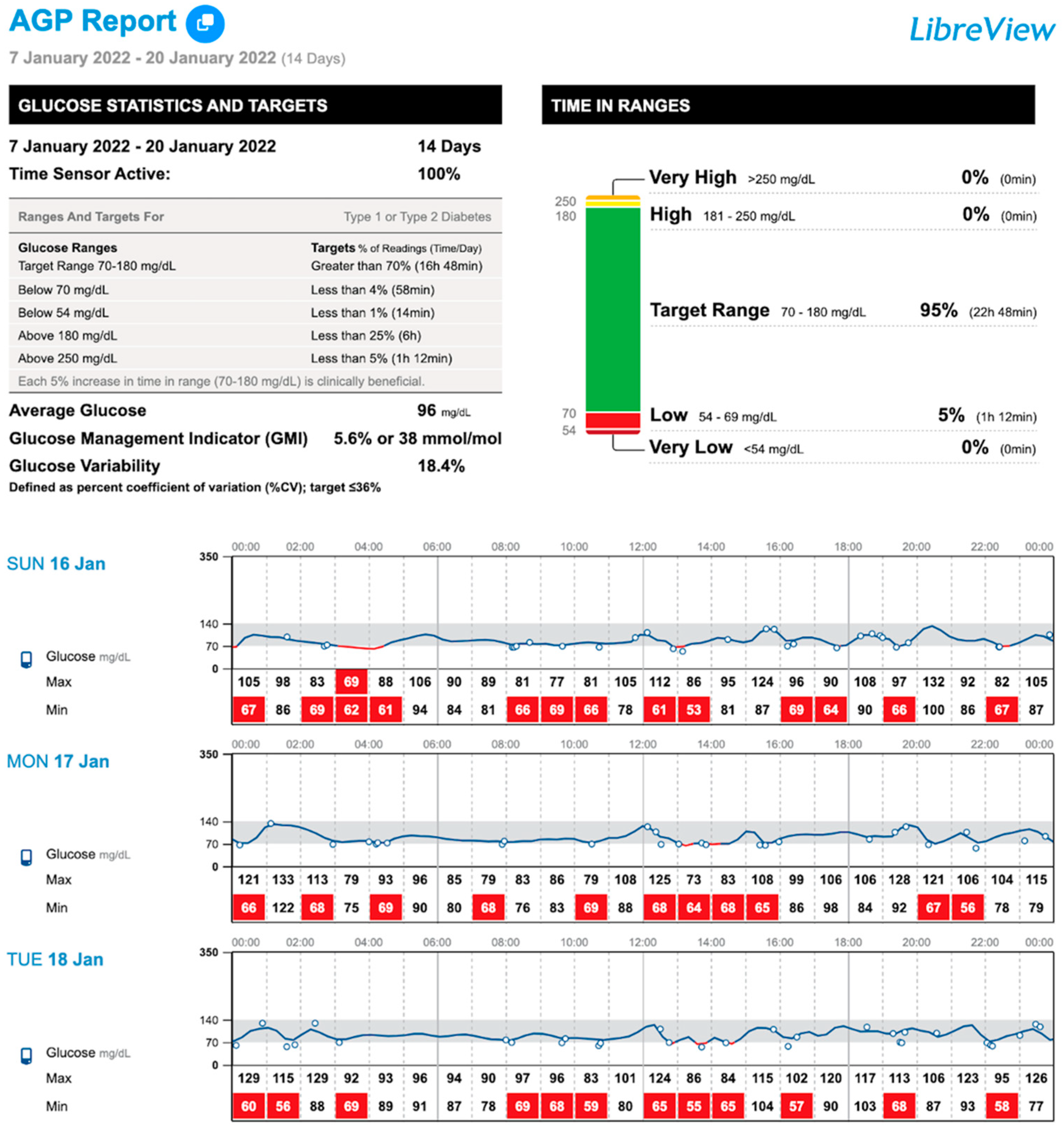
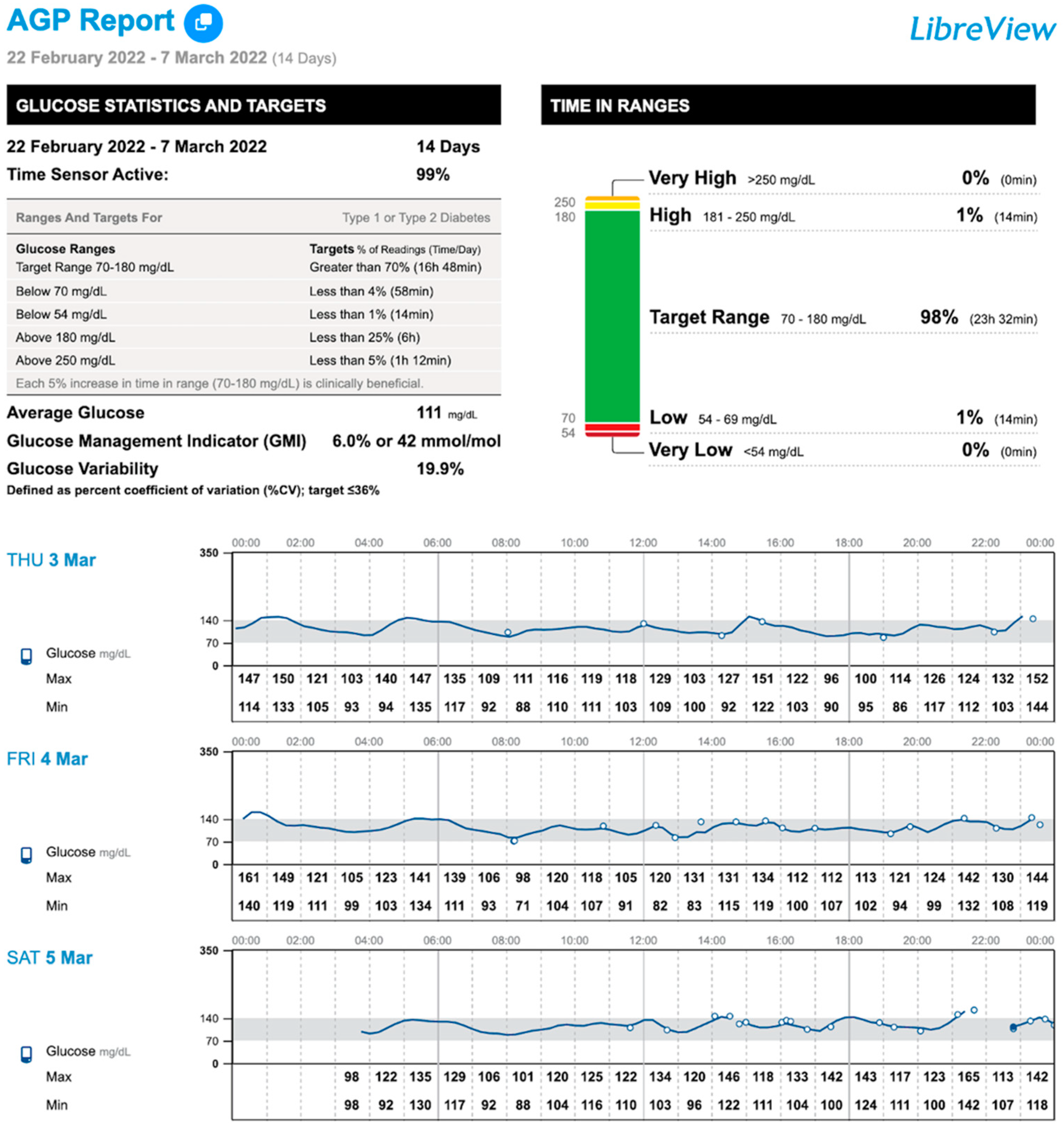
| TIR (%, 70–140 mg/dL) 1 | 94 (88–97) | 95 (88–97) | 94.5 (87–98) | 0.214 |
| TIR (%, 70–180 mg/dL) 1 | 98 (94–100) a | 98.5 (95–100) | 99 (98–100) b | 0.020 |
| TAR (%, >140 mg/dL) 1 | 2 (1–7) | 2.5 (1–8) | 2 (2–11.5) | 0.167 |
| TAR (%, >180 mg/dL) 1 | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0.2) | 0.751 |
| TAR (%, >250 mg/dL) 1 | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.368 |
| TBR (%, <70 mg/dL) 1 | 1.5 (0–3) a | 1 (0–2) | 0 (0–1) b | 0.005 |
| TBR (%, <54 mg/dL) 1 | 0 (0–2) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.035 |
| TBR total (%) 1 | 1.5 (0–4) a | 1 (0–3) | 0 (0–1) b | 0.021 |
| Low glucose events (n) 1 | 1 (0–7) a | 1 (0–6) | 0 (0–3) b | 0.040 |
| Average duration (min) 2 | 61.4 ± 62.5 | 57 ± 54.4 | 33.8 ± 41.5 | 0.223 |
| CV (%) 1 | 17.4 (14–19) a | 16.6 (14–19) | 16.6 (14–19) b | 0.476 |
| Mean glucose (mg/dL) 2 | 103 ± 10.3 a | 105.8 ± 11.8 | 105.3 ± 9.7 b | 0.034 |
| GMI (%) 2 | 5.8 ± 0.2 | 5.8 ± 0.2 | 5.8 ± 0.2 | 0.697 |
| Sensor use (%) 1 | 93 (72–99) | 93 (86–99) | 93 (78–98) | 0.129 |
| Scans/day (n) 1 | 6 (5–13) a | 7 (4–15) | 5 (4–12) b | 0.021 |
| IMDs (n) | TBR, % | Low Glucose Events (n) | Average Duration (Min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <70 mg/dL | <54 mg/dL | Total | |||
| FAODs (9) | |||||
| 1 Week | 1.6 ± 3.6 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | 2 ± 4.3 | 2.2 ± 4.1 | 47.4 ± 81.2 |
| 2 Weeks | 1.2 ± 2.2 | 0 ± 0 | 1.2 ± 2.2 | 1.9 ± 2.9 | 42.1 ± 69.4 |
| 2 Months | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 0 ± 0 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 3.6 | 27.5 ± 33.7 |
| GSD (5) | |||||
| 1 Week | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | 2.6 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 4.2 | 72 ± 25.4 |
| 2 Weeks | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.8 | 2.8 ± 1.8 | 61.6 ± 28 |
| 2 Months | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0 ± 0 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 2.6 ± 2.8 | 60.8 ± 35 |
| GLUD-1 (2) | |||||
| 1 Week | 6.5 ± 5 | 0.5 ± 0.7 | 7 ± 5.6 | 6 ± 4.2 | 80 ± 28.3 |
| 2 Weeks | 5.5 ± 5 | 2 ± 2.8 | 7.5 ± 7.7 | 5.5 ± 5 | 83.5 ± 0.7 |
| 2 Months | 2.5 ± 3.5 | 0 ± 0 | 2.5 ± 3.5 | 3 ± 2.8 | 57 ± 38.2 |
| MMA (1) | |||||
| 1 Week | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 45 |
| 2 Weeks | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 45 |
| 2 Months | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 45 |
| HFI (1) | |||||
| 1 Week | 7 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 151 |
| 2 Weeks | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 128 |
| 2 Months | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 136 |
| FAODs (9) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCAD (4) | LCAD (1) | CACT (1) | CPT II (2) | MADD (1) | |||||||||||
| 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | |
| TBR (%, <70 mg/dL) | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 11 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0.5 ± 0.7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| TBR (%, <54 mg/dL) | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TBR total (%) | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 13 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0.5 ± 0.7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Low glucose events (n) | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 11 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 4.5 ± 4.9 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Average duration (min) | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 151 | 156 | 65 | 216 | 163 | 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 59 ± 22.6 | 60 | 60 | 65 |
| GSD (5) | |||||||||||||||
| Type Ib (1) | Type IIIa (1) | Type IX (2) | Type V (1) | ||||||||||||
| 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | 1 Week | 2 Weeks | 2 Months | ||||
| TBR (%, <70 mg/dL) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0 ± 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| TBR (%, <54 mg/dL) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| TBR total (%) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0 ± 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Low glucose events (n) | 11 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 2 ± 1.4 | 2.5 ± 2.1 | 0 ± 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||
| Average duration (min) | 93 | 46 | 40 | 55 | 95 | 50 | 76 ± 41 | 78.5 ± 44 | 0 ± 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amuedo, S.; Dios-Fuentes, E.; Benítez-Ávila, R.; Remón-Ruiz, P.; Soto-Moreno, A.; Venegas-Moreno, E. Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Inherited Metabolic Disorders at Risk of Hypoglycemia. Nutrients 2025, 17, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020222
Amuedo S, Dios-Fuentes E, Benítez-Ávila R, Remón-Ruiz P, Soto-Moreno A, Venegas-Moreno E. Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Inherited Metabolic Disorders at Risk of Hypoglycemia. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020222
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmuedo, Sandra, Elena Dios-Fuentes, Rosa Benítez-Ávila, Pablo Remón-Ruiz, Alfonso Soto-Moreno, and Eva Venegas-Moreno. 2025. "Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Inherited Metabolic Disorders at Risk of Hypoglycemia" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020222
APA StyleAmuedo, S., Dios-Fuentes, E., Benítez-Ávila, R., Remón-Ruiz, P., Soto-Moreno, A., & Venegas-Moreno, E. (2025). Impact of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Adults with Inherited Metabolic Disorders at Risk of Hypoglycemia. Nutrients, 17(2), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020222







