Adulteration of Sports Supplements with Anabolic Steroids—From Innocent Athlete to Vicious Cheater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
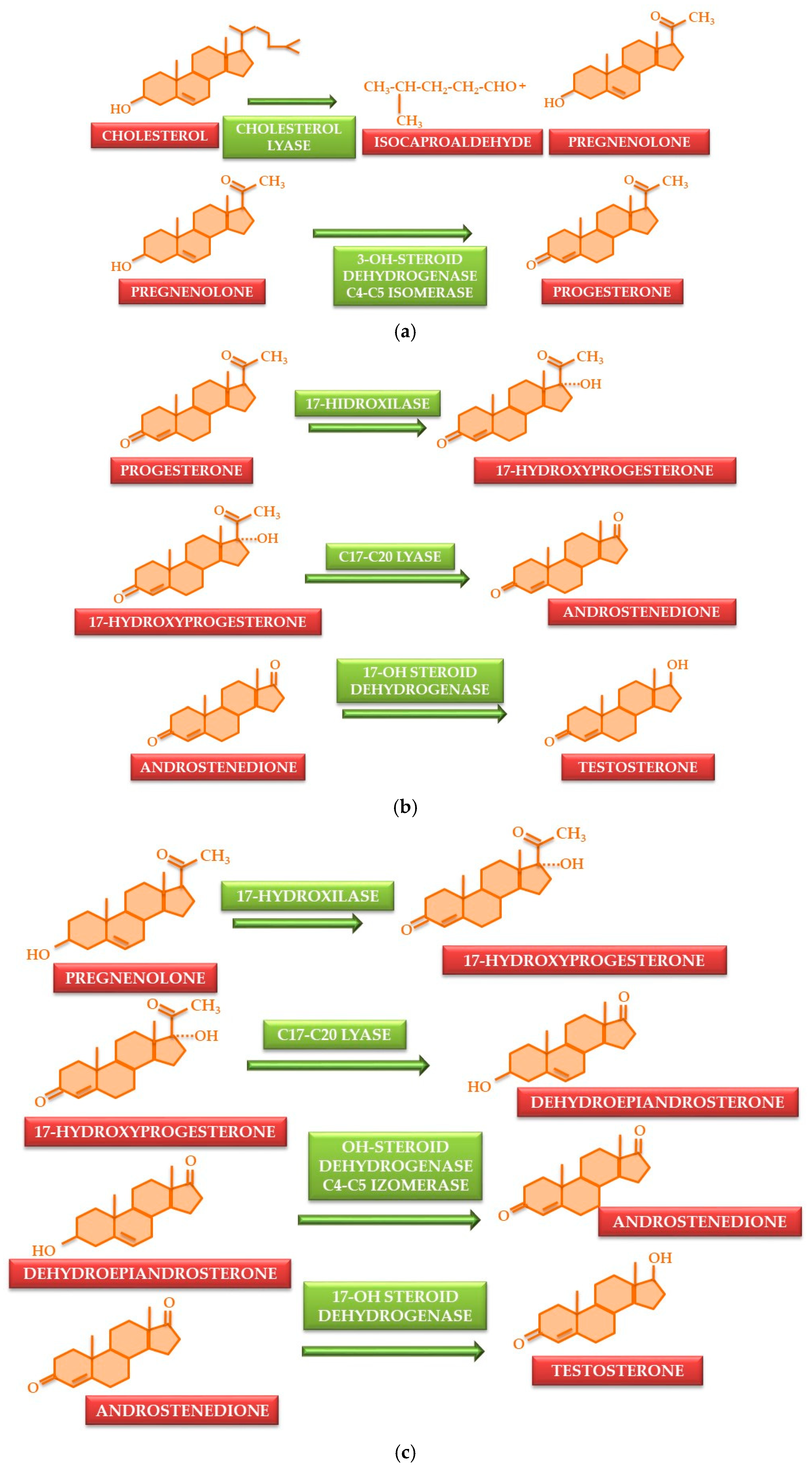
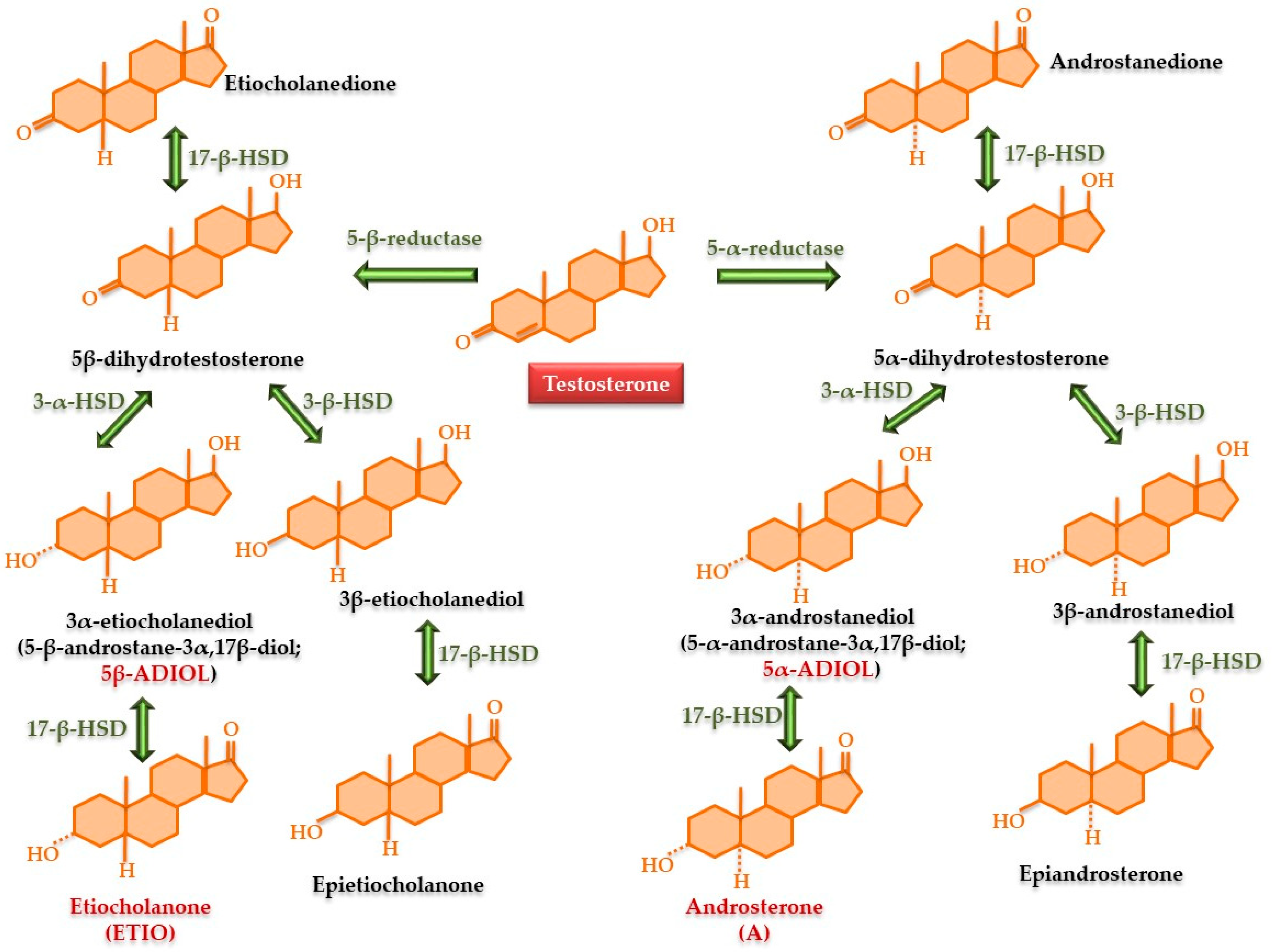
3. Synthesis and Metabolic Transformations of Testosterone and Major Synthetic Anabolic Steroids
- -
- Esterification at the 17-OH group causes a reduction in release speed, yielding formulations with sustained release. Esterified testosterone forms, such as undecanoate, propionate, phenylpropionate, enanthate, cypionate, and undecylate, used in form of an oily solution, exhibit slower absorption and prolonged action due to the gradual enzymatic hydrolysis of the ester bond at the site of administration [49,50].
- -
- C10 demethylation increases the relative potency of substances. These compounds can also be C17 esters; e.g., nandrolone [51].
- -
- -
- -
- Androgens that cannot be reduced to dihydrotestosterone exhibit a ratio of anabolic to androgenic actions that favors anabolic effects, e.g., oxandrolone and oxymetholone [55].

4. Innocent Athlete: Adulteration of Dietary Supplements with Testosterone, Testosterone Derivatives, and Other Synthetic Anabolic Steroids
5. Non-Therapeutic Patterns of Steroid Administration in Sport
6. Detection of Abuse in Laboratory
7. Vicious Cheater Athletes: Pharmacological Agents Used to Mask Identification
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DHEA | Dehydroepiandrosterone |
| DHT | Dihydrotestosterone |
| T | Testosterone |
| E | Epitestosterone |
| A | Androsterone |
| ETIO | Etiocholanolone |
| 5-α-ADIOL | 5-α-androstane-3α,17β-diol |
| 5-β-ADIOL | 5-β-androstane-3α,17β-diol |
| WADA | World Anti-Doping Agency |
| ABP | Athlete Biological Passport |
| HDS | Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| IR | Isotope ratio |
| HCG | Human chorionic gonadotropin |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| DS | Dietary supplement |
| OTC | Over-the-counter |
| CE | Capillary electrophoresis |
| HPLC | High-performance LC |
| UHPLC-QTOF-MS | Ultra HPLC-quadrupole time-of-flight MS |
| SERS | Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy |
| ERC | Endogenous reference compounds |
| VPDB | Vienna Pee Dee Belemnite |
| miRNA | microRNA |
References
- Malsagova, K.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Sinitsyna, A.A.; Stepanov, A.A.; Izotov, A.A.; Butkova, T.V.; Chingin, K.; Klyuchnikov, M.S.; Kaysheva, A.L. Sports Nutrition: Diets, Selection Factors, Recommendations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, J.A.; Kilding, A.E.; Plews, D.J. What Should I Eat before Exercise? Pre-Exercise Nutrition and the Response to Endurance Exercise: Current Prospective and Future Directions. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnagöl, H.H.; Koşar, Ş.N.; Güzel, Y.; Aktitiz, S.; Atakan, M.M. Nutritional Considerations for Injury Prevention and Recovery in Combat Sports. Nutrients 2022, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motti, M.L.; Tafuri, D.; Donini, L.; Masucci, M.T.; De Falco, V.; Mazzeo, F. The Role of Nutrients in Prevention, Treatment and Post-Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). Nutrients 2022, 14, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, C.; Mooney, E.; Mc Cloat, A. Nutritional Intake and Dietary Knowledge of Athletes: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Ortega, Á.; Rodríguez-Rodrigo, M.-A.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Calleja-González, J. Triathlon: Ergo Nutrition for Training, Competing, and Recovering. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Ortega, Á.; Barrenetxea-Garcia, J.; Rodríguez-Rodrigo, M.-A.; García-Ordóñez, E.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Calleja-González, J. Ergonutrition Supplementation and Recovery in Water Polo: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrejko, M.; Kała, K.; Muszyńska, B. Anserine, Balenine, and Ergothioneine: Impact of Histidine-Containing Compounds on Exercise Performance—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzejska, R.E. Dietary Supplements—For Whom? The Current State of Knowledge about the Health Effects of Selected Supplement Use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, R.; Correia, M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Amaral, J.S. Adulteration of Brain Health (Cognitive, Mood, and Sleep Enhancement) Food Supplements by the Addition of Pharmaceutical Drugs: A Comprehensive Review of Analytical Approaches and Trends. Foods 2024, 13, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidžić, M.; Banović Fuentes, J.; Banović, J.; Torović, L. Notifications and Health Consequences of Unauthorized Pharmaceuticals in Food Supplements. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagim, A.R.; Harty, P.S.; Erickson, J.L.; Tinsley, G.M.; Garner, D.; Galpin, A.J. Prevalence of adulteration in dietary supplements and recommendations for safe supplement practices in sport. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1239121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozhuharov, V.R.; Ivanov, K.; Ivanova, S. Dietary Supplements as Source of Unintentional Doping. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8387271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbonetti, A.; D’Andrea, S.; Francavilla, S. Testosterone replacement therapy. Andrology 2020, 8, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Goulis, D.G.; Huhtaniemi, I.; Zitzmann, M.; Toppari, J.; Forti, G.; Vanderschueren, D.; Wu, F.C. European Academy of Andrology (EAA) guidelines on investigation, treatment and monitoring of functional hypogonadism in males: Endorsing organization: European Society of Endocrinology. Andrology 2020, 8, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, V.; Vanderschueren, D.; Antonio, L. Treatment of Men with Central Hypogonadism: Alternatives for Testosterone Replacement Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Swerdloff, R.S. Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Hypogonadal Men. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 51, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, B.; Napolitano, L.; Abate, M.; Cirillo, L.; Reccia, P.; Passaro, F.; Turco, C.; Morra, S.; Mastrangelo, F.; Scarpato, A.; et al. The Role of Testosterone in the Elderly: What Do We Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.R.; Baber, R.; Panay, N.; Bitzer, J.; Cerdas Perez, S.; Islam, R.M.; Kaunitz, A.M.; Kingsberg, S.A.; Lambrinoudaki, I.; Liu, J.; et al. Global Consensus Position Statement on the Use of Testosterone Therapy for Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4660–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzmann, M. Testosterone deficiency and chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2024, 37, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchen, J.; Jurášek, M.; Huml, L.; Rimpelová, S. Medicinal Use of Testosterone and Related Steroids Revisited. Molecules 2021, 26, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romejko, K.; Rymarz, A.; Sadownik, H.; Niemczyk, S. Testosterone Deficiency as One of the Major Endocrine Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Pan, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, X. Anemia and testosterone deficiency risk: Insights from NHANES data analysis and a Mendelian randomization analysis. Aging Male 2024, 27, 2346312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, R.; York, A.E.; Dimitrakakis, C. Incidence of invasive breast cancer in women treated with testosterone implants: A prospective 10-year cohort study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranto, P.; de Brito Sales, D.; Maluf, F.C.; Guendelmann, R.A.K.; de Melo Pompei, L.; Leal, A.; Buzaid, A.C.; Schvartsman, G. Safety and efficacy of topical testosterone in breast cancer patients receiving ovarian suppression and aromatase inhibitor therapy. Breast Cancer Res. 2024, 26, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovitz, G.; Cotton, M. Breast Cancer Incidence Reduction in Women Treated with Subcutaneous Testosterone: Testosterone Therapy and Breast Cancer Incidence Study. Eur. J. Breast Health 2021, 17, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Singh, S.M.; Hsueh, J.; Grutman, A.; An, C.; Able, C.; Choi, U.; Kohn, J.; Clifton, M.; Kohn, T.P. Testosterone therapy in females is not associated with increased cardiovascular or breast cancer risk: A claims database analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2024, 21, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, M.; Holer, L.; Rothgiesser, K.; Schönfeld, W.; Riniker, S.; von Moos, R.; Trojan, A.; Kralidis, E.; Rabaglio, M.; Fehr, M.K.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis of the Phase II SAKK 21/12 Trial of Transdermal CR1447 in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2025, 25, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, D.J. Androgen Misuse and Abuse. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 457–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieschlag, E.; Nieschlag, S. Endocrine history: The history of discovery, synthesis and development of testosterone for clinical use. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, R201–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arnés, J.A.; García-Casares, N. Endocrinología del dopaje y losdeportes: Andrógenosanabolizantes. Rev. Clínica Española 2022, 222, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicman, A.T. Pharmacology of anabolic steroids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Anti-Doping Code International Standard Prohibited List 2025. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/world-anti-doping-code-and-international-standards/prohibited-list (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Flangea, C.; Vlad, D.; Popescu, R.; Dumitrascu, V.; Rata, A.L.; Tryfon, M.E.; Balasoiu, B.; Vlad, C.S. Cannabis: Zone Aspects of Raw Plant Components in Sport—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhouse, S.H. A Behaviourally Informed Approach to Reducing the Risk of Inadvertent Anti-doping Rule Violations from Supplement Use. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, M.; Camacho, C.B.; Daher, J.; El Khoury, D. Dietary Supplements: A Gateway to Doping? Nutrients 2023, 15, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duiven, E.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Spruijt, L.; Koert, W.; de Hon, O.M. Undeclared Doping Substances are Highly Prevalent in Commercial Sports Nutrition Supplements. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2021, 20, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voravuth, N.; Chua, E.W.; Tuan Mahmood, T.M.; Lim, M.C.; Wan Puteh, S.E.; Safii, N.S.; Wong, J.E.; Jamil, A.T.; Jamal, J.A.; Shamsuddin, A.F.; et al. Engaging community pharmacists to eliminate inadvertent doping in sports: A study of their knowledge on doping. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, M.; Ferrante, L.; Tafuri, D.; Meccariello, R.; Mazzeo, F. Trends in Antidepressant, Anxiolytic, and Cannabinoid Use Among Italian Elite Athletes (2011–2023): A Longitudinal Anti-Doping Analysis. Sports 2025, 13, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntoumanis, N.; Dølven, S.; Barkoukis, V.; Boardley, I.D.; Hvidemose, J.S.; Juhl, C.B.; Gucciardi, D.F. Psychosocial predictors of doping intentions and use in sport and exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2024, 58, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Walker, W.H. The regulation of spermatogenesis by androgens. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naamneh Elzenaty, R.; du Toit, T.; Flück, C.E. Basics of androgen synthesis and action. BestPract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 36, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornatovská, Z.; Hill, M.; Jandová, D.; Krejčí, M.; Zwierzchowska, A. Steroids Static Postural Balance Changes After Exercise Intervention Correlate with Steroidome in Elderly Female. Metabolites 2025, 15, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, B.M.; O’Donnell, L.; Smith, L.B.; Rebourcet, D. New Insights into Testosterone Biosynthesis: Novel Observations from HSD17B3 Deficient Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ronde, W.; Smit, D.L. Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in young males. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R102–R111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudan, C.; Baume, N.; Robinson, N.; Avois, L.; Mangin, P.; Saugy, M. Testosterone and doping control. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, i21–i24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.I.; Stanton, S.J. Testosterone and sport: Current perspectives. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Vallejo, L. Current use and abuse of anabolic steroids. Actas Urológicas Españolas 2020, 44, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wit, J.M.; Oostdijk, W. Novel approaches to short stature therapy. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Basaria, S. Diagnosis and treatment of hypogonadism in men. BestPract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, F.G.; Liberto, A.; Maria Maglitto, A.N.; Malandrino, P.; Esposito, M.; Amico, F.; Cocimano, G.; Rosi, G.L.; Condorelli, D.; Nunno, N.D.; et al. Nandrolone Decanoate: Use, Abuse and Side Effects. Medicina 2020, 56, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, B.; Das, B.; Chakraborty, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Alam, M.M.M.; Mian, S.; Iqbal, M.M. Optimization of 17alpha-methyltestosterone dose to produce quality mono-sex Nile tilapia Oreochromisniloticus. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temerdashev, A.; Dmitrieva, E.; Azaryan, A.; Gashimova, E. Determination of oxprenolol, methandienone and testosterone in meat samples by UHPLC-Q-ToF. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodi, G.; Turza, A.; Bende, A. Exploring the Polymorphism of Drostanolone Propionate. Molecules 2020, 25, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holubová, B.; Kubešová, P.; Huml, L.; Vlach, M.; Lapčík, O.; Jurášek, M.; Fukal, L. Tailor-Made Immunochromatographic Test for the Detection of Multiple 17α-Methylated Anabolics in Dietary Supplements. Foods 2021, 10, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Pereira, F.; Curtis, J.; Rojas, J.; Evans, C. The Top 5 Can’t-Miss Sport Supplements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.L.K.; Lambert, M.N.T.; Haubek, D.; Bastani, N.E.; Skålhegg, B.S.; Overgaard, K.; Jensen, J.; Jeppesen, P.B. The Effect of Alginate Encapsulated Plant-Based Carbohydrate and Protein Supplementation on Recovery and Subsequent Performance in Athletes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo-Vallejo, J.E.; Cardona-Guzmán, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Alcivar, E.J.; Kočí, J.; Petro, J.L.; Kreider, R.B.; Cannataro, R.; Bonilla, D.A. Nutritional Strategies in the Rehabilitation of Musculoskeletal Injuries in Athletes: A Systematic Integrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, M.D.; Martínez-Sanz, J.M.; García, C.J.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Ferreres, F.; Escribano, M.; Giménez-Monzó, D.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á. Health Claims for Protein Food Supplements for Athletes—The Analysis Is in Accordance with the EFSA’s Scientific Opinion. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, M.D.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; García, C.J.; Gabaldón, J.A.; Ferreres, F.; Giménez-Monzó, D.; Martínez-Sanz, J.M. Health Claims for Sports Drinks—Analytical Assessment according to European Food Safety Authority’s Scientific Opinion. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaedini, S.; Amirahmadi, M.; Kobarfard, F.; Rastegar, H.; Nasirahmadi, S.; Shoeibi, S. Survey of protein-based sport supplements for illegally added anabolic steroids methyltestosterone and 4-androstenedione by UPLC-MS/MS. Steroids 2021, 165, 108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Huo, J.; Luo, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J. Simultaneous detection of 93 anabolic androgenic steroids in dietary supplements using gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 211, 114619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, E.J.; Ham, H.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Kim, N.S.; Kim, H.I.; Baek, S.Y. Application of LC–MS/MS and UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap methods for determining 54 steroids in illegal dietary supplements and other sample types. Rapid Commun. MassSpectrom 2022, 36, 9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micalizzi, G.; Huszti, K.; Pálinkás, Z.; Mandolfino, F.; Martos, É.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Utczás, M. Reliable identification and quantification of anabolic androgenic steroids in dietary supplements by using gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, R.; Berger, I.; Copeland, J. “No pain, no gainz”? Performance and image enhancing drugs, health effects and information seeking. Drugs Educ. Prev. Pol. 2017, 24, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova-Gueorguieva, E.; Gueorguiev, S.; Lebanova, H.; Mihaylova, A.; Madzharov, V. Investigation of the content of anabolic steroids in food supplements used in sports practice. All Life 2023, 16, 2270722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpurgis, K.; Thomas, A.; Geyer, H.; Mareck, U.; Thevis, M. Dietary Supplement and Food Contaminations and Their Implications for Doping Controls. Foods 2020, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.L.; de Oliveira, F.A.G.; Jooris, L.F.; Padilha, M.C.; Pereira, H.M.G. The presence of doping agents in dietary supplements: A glimpse into the Brazilian situation. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 16, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabresse, N.; Gheddar, L.; Kintz, P.; Knapp, A.; Larabi, I.A.; Alvarez, J.C. Analysis of pharmaceutical products and dietary supplements seized from the black market among bodybuilders. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 322, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yun, Y.H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Authentication and quality assessment of whey protein-based sports supplements using portable near-infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging. Food Res. Int. 2025, 203, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Du, W.; Song, W.; Gu, W.; Kong, X. Smartphone Video Imaging Combined with Machine Learning: A Cost-Effective Method for Authenticating Whey Protein Supplements. Foods 2025, 14, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari Moghaddam, H.; Tamiji, Z.; Amini, M.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Kobarfrad, F.; Sadeghi, N.; Hajimahmoodi, M. Development of non-destructive methods for the assessment of authenticity of sports whey protein supplements. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2024, 41, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancu, G.; Székely-Szentmiklósi, B.; Stroia, D.G.; Kelemen, H. Applications of Capillary Electrophoresis for the Detection of Adulterants in Dietary Supplements. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wen, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y. Fast Screening and Identification of Illegal Adulterated Glucocorticoids in Dietary Supplements and Herbal Products Using UHPLC-QTOF-MS with All-Ion Fragmentation Acquisition Combined with Characteristic Fragment Ion List Classification. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 785475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, S.; Weesepoel, Y.; Erasmus, S.; Sinkeldam, J.; Piccinelli, A.L.; van Ruth, S. A multi-analyte screening method for the rapid detection of illicit adulterants in dietary supplements using a portable SERS analyzer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zeeuw, T.; Brunt, T.M.; van Amsterdam, J.; van de Ven, K.; van den Brink, W. Anabolic Androgenic Steroid Use Patterns and Steroid Use Disorders in a Sample of Male Gym Visitors. Eur. Addict. Res. 2023, 29, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarth, M.; Westlye, L.T.; Havnes, I.A.; Bjørnebekk, A. Investigating anabolic-androgenic steroid dependence and muscle dysmorphia with network analysis among male weightlifters. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Putukian, M.; Aerni, G.; Diamond, A.B.; Hong, E.S.; Ingram, Y.M.; Reardon, C.L.; Wolanin, A.T. Mental Health Issues and Psychological Factors in Athletes: Detection, Management, Effect on Performance, and Prevention: American Medical Society for Sports Medicine Position Statement. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 30, e61–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatkowski, T.; Whiteside, B.; Robertson, J.; Henning, A.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Dunn, M. What is the prevalence of anabolic-androgenic steroid use among women? A systematic review. Addiction 2024, 119, 2088–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.; Kean, J.; Vali, N.; Campbell, J.; Maden, L.; Bijral, P.; Dhillo, W.S.; McVeigh, J.; Quinton, R.; Jayasena, C.N. The use of post-cycle therapy is associated with reduced withdrawal symptoms from anabolic-androgenic steroid use: A survey of 470 men. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prevent. Policy 2023, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, M.G.; Esposito, M.; Alloca, S.; Franco, S.; Francaviglia, M.; Volonnino, G.; Rinaldi, R.; Di Fazio, N.; Di Mauro, L. Anabolic–Androgenic Steroids and Brain Damage: A Review of Evidence and Medico-Legal Implications. Forensic Sci. 2025, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, R.; Almont, T.; Diligent, C.; Hubert, N.; Eschwège, P.; Hubert, J. Anabolic steroids abuse and male infertility. Basic Clin. Androl. 2016, 26, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ronde, W.; Smit, D.L. Anabolic–androgenic steroid abuse and testicular function in men; recent insights. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 67, 102318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.B.; Ng, M.Z.; Huang, S.S.; Ding, M.; Hu, K. Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Misuse: Mechanisms, Patterns of Misuse, User Typology, and Adverse Effects. J. Sports Med. 2021, 2021, 7497346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, P.C.A.; Yarrow, M. Anabolic steroid abuse: Physiological and anaesthetic considerations. Anaesthesia 2005, 60, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenbo, Z.; Yan, Z. The Uses of Anabolic Androgenic Steroids Among Athletes; Its Positive and Negative Aspects—A Literature Review. J. Multidisciplin. Healthc. 2023, 16, 4293–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, B.S.; Hildebrandt, T.; Wallisch, P. Anabolic–androgenic steroid use is associated with psychopathy, risk-taking, anger, and physical problems. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, P.; Smit, D.L.; deRonde, W. Anabolic–androgenic steroids: How do they work and what are the risks? Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1059473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.D.; Amico, F.; Cocimano, G.; Liberto, A.; Maglietta, F.; Esposito, M.; Rosi, G.L.; Di Nunno, N.; Salerno, M.; Montana, A. Adverse Effects of Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids: A Literature Review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yang, X.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Zhong, H.; Jiang, J.; Yang, C. Glucocorticoid guides mobilization of bone marrow stem/progenitor cells via FPR and CXCR4 coupling. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.Y.; Zhang, J.J. Effects of glucocorticoids on leukocytes: Genomic and non-genomic mechanisms. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 7187–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, A.; Vukadin, S.; Sikora, R.; Bojanic, K.; Smolic, R.; Plavec, D.; Wu, G.Y.; Smolic, M. Anabolic androgenic steroid-induced liver injury: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, E.; Nicoll, A.; Batt, N.; George, J.; Perananthan, V.; Prince, D.; Wallace, M.; Gow, P.; Vaz, K.; Chitturi, S.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury from selective androgen receptor modulators, anabolic-androgenic steroids and bodybuilding supplements in Australia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Girolamo, F.G.; Biasinutto, C.; Mangogna, A.; Fiotti, N.; Vinci, P.; Pisot, R.; Mearelli, F.; Simunic, B.; Roni, C.; Biolo, G. Metabolic Consequences of Anabolic Steroids, Insulin, and Growth Hormone Abuse in Recreational Bodybuilders: Implications for the World Anti-Doping Agency Passport. Sports Med. 2024, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.R.; Davies, B.; Grace, F.M.; Evans, P.J.; Baker, J.S. Exercise, Science and Designer Doping: Traditional and Emerging Trends. J. Steroids Horm. 2012, 3, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Krumm, B.; Botrè, F.; Saugy, J.J.; Faiss, R. Future opportunities for the Athlete Biological Passport. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 4, 986875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, S.; Rzeppa, S.; Thieme, D.; Keiler, A.M. Agreement of steroid profiles in Athlete Biological Passport residues and corresponding serum samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 16, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragčević, D.; Pandžić, J.V.; Jakšić, O. Athlete biological passport: Longitudinal biomarkers and statistics in the fight against doping. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2024, 75, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WADA Athlete Biological Passport Operating Guidelines—Version 9.0—July 2023. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/2023-07/guidelines_abp_v9_2023_final_eng_1.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Athlete Passport Management Unit Requirements and Procedures, WADA Technical Document—TD2023APMU. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/2022-11/td2023apmu_eng_final.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- WADA Technical Document—TD2024 INDEX. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/lab-documents/technical-documents-index#resource-download (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- WADA Technical Document—TD2016 EAAS. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/sites/default/files/resources/files/wada-td2016eaas-eaas-measurement-and-reporting-en.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Dikunets, M.A.; Dudko, G.A.; Virus, E.D. Development and Validation of Sensitive, Fast and Simple LC-MS/MS Method to Investigate the Association between Adrenocortical Steroidogenesis and the High Intensity Exercise in Elite Athletes. Metabolites 2023, 13, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csöndör, É.; Karvaly, G.; Ligetvári, R.; Kovács, K.; Komka, Z.; Móra, Á.; Stromájer-Rácz, T.; Oláh, A.; Tóth, M.; Ács, P. Adrenal, Gonadal and Peripherally Steroid Changes in Response to Extreme Physical Stress for Characterizing Load Capacity in Athletes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, T.M. New frontiers in androgen biosynthesis and metabolism. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2010, 17, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N. The 5α-androstanedione pathway to dihydrotestosterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer. J. Investig. Med. 2012, 60, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareck, U.; Geyer, H.; Opfermann, G.; Thevis, M.; Schanzer, W. Factors influencing the steroid profile in doping control analysis. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2008, 43, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Renterghem, P.; Viaene, W.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Barrabin, J.; Iannone, M.; Polet, M.; Sjoen, G.T.; Deventer, K.; VanEenoo, P. Validation of an ultra-sensitive detection method for steroid esters in plasma for doping analysis using positive chemical ionization GC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1141, 122026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, T.; Fußhöller, G.; Thevis, M. Employing 11-Ketotestosterone as a Target Analyte for Adrenosterone (11OXO) Administration in Doping Controls. Metabolites 2024, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walpurgis, K.; Piper, T.; Thevis, M. Androgens, sports, and detection strategies for anabolic drug use. BestPractRes. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 36, 101609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, R.L.; De Paoli, G.; Hall, S.; Nisbet, L.A. A review of the analytical techniques for the detection of anabolic–androgenic steroids within biological matrices. WIREs Forensic Sci. 2024, 6, e1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temerdashev, A.; Nesterenko, P.; Dmitrieva, E.; Zhurkina, K.; Feng, Y.Q. GC-MS/MS Determination of Steroid Hormones in Urine Using Solid-Phase Derivatization as an Alternative to Conventional Methods. Molecules 2022, 27, 5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.L.; Lee, Y.C.; Chung, B.C.; Hong, J. Profiling of Steroid Metabolic Pathways in Human Plasma by GC-MS/MS Combined with Microwave-Assisted Derivatization for Diagnosis of Gastric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.T.; Osswald, A.; Zopp, S.; Rubinstein, G.; Vogel, F.; Riester, A.; Honegger, J.; Eisenhofer, G.; Constantinescu, G.; Deutschbein, T.; et al. Delineating endogenous Cushing’s syndrome by GC-MS urinary steroid metabotyping. eBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.F.; Le, J.; Wang, S.T.; Li, Y. An LC/MS/MS method for analyzing the steroid metabolome with high accuracy and from small serum samples. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enver, E.O.; Vatansever, P.; Guran, O.; Bilgin, L.; Boran, P.; Turan, S.; Haklar, G.; Bereket, A.; Guran, T. Adrenal steroids reference ranges in infancy determined by LC-MS/MS. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.H.; Yun, W.S.; Cho, S.H. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for profiling 39 urinary steroids (estrogens, androgens, corticoids, and progestins). Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Qin, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Pan, B.; et al. A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)-based assay to profile 20 plasma steroids in endocrine disorders. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Lin, G.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Y. Development of an automated immunologic mass spectrometry (iMS) method to overcome matrix effect for quantification: Steroid hormones as the example. Talanta 2025, 282, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putz, M.; Piper, T.; Dubois, M.; Delahaut, P.; Thevis, M. Analysis of endogenous steroids in urine by means of multi-immunoaffinity chromatography and isotope ratio mass spectrometry for sports drug testing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7563–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schött, H.F.; Konings, M.C.J.M.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; Mensink, R.P.; Plat, J. A Validated Method for Quantification of Fatty Acids Incorporatedin Human Plasma Phospholipids by Gas Chromatography−TripleQuadrupole Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, E.; Wiebel, M.; Hopmann, C.; Kampschulte, N.; Schebb, N.H. Rapid quantification of fatty acids in plant oils and biological samples by LC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5439–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skubic, C.; Vovk, I.; Rozman, D.; Križman, M. Simplified LC-MS Method for Analysis of Sterols in Biological Samples. Molecules 2020, 25, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuma, C.; Thomas, A.; Braun, H.; Thevis, M. Development of an LC-HRMS/MS Method for Quantifying Steroids and Thyroid Hormones in Capillary Blood: A Potential Tool for Assessing Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S). Metabolites 2024, 14, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimpel, O.; Altieri, B.; Dischinger, U.; Fuss, C.T.; Kurlbaum, M.; Fassnacht, M. Early Detection of Recurrence and Progress Using Serum Steroid Profiling by LC–MS/MS in Patients with Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Metabolites 2024, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, S.; Denham, S.G.; Lee, P.; Simpson, J.P.; Homer, N.Z.M. Using LC-MS/MS to Determine Salivary Steroid Reference Intervals in a European Older Adult Population. Metabolites 2023, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ye, H. Overview of Lipidomic Analysis of Triglyceride Molecular Species in Biological Lipid Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8895–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabruja, M.; Priotti, J.; Domizi, P.; Papsdorf, K.; Kroetz, D.L.; Brunet, A.; Contrepois, K.; Snyder, M.P. In-depth triacylglycerol profiling using MS3 Q-Trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandu, R.; Mok, H.J.; Kim, K.P. Phospholipids as cancer biomarkers: Mass spectrometry-based analysis. Mass. Spec. Rev. 2018, 37, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flangea, C.; Fabris, D.; Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D. Mass Spectrometry of Gangliosides from Human Sensory and Motor Cortex. Austral. J. Chem. 2013, 66, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, A.D.; Fabris, D.; Capitan, F.; Munteanu, C.; Vukelić, Ž.; Flangea, C. Profiling and sequence analysis of gangliosides in human astrocytoma by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7321–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranbileg, B.; Sakai, E.; Kubota, M.; Isago, H.; Sumitani, M.; Yatomi, Y.; Kurano, M. Development of an advanced liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry measurement system for simultaneous sphingolipid analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardines, D.; Botrè, F.; Colamonici, C.; Curcio, D.; Procida, G.; de la Torre, X. Longitudinal evaluation of the isotope ratio mass spectrometric data: Towards the ‘isotopic module’ of the athlete biological passport? Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Geyer, H.; Nieschlag, E.; Bally, L.; Thevis, M. Carbon isotope ratios of endogenous steroids found in human serum—Method development, validation, and reference population-derived thresholds. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5655–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieloch, T.; Sharkey, T.D.; Werner, R.A.; Schleucher, J. Intramolecular carbon isotope signals reflect metabolite allocation in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 2558–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronin, E.; Banaś, K.; Chmara, R.; Ronowski, R.; Merdalski, M.; Santoni, A.-L.; Mathieu, O. Lobelia Lakes’ Vegetation and Its Photosynthesis Pathways Concerning Water Parameters and the Stable Carbon Isotopic Composition of Plants’ Organic Matter. Plants 2024, 13, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, G.; Courtheyn, D.; Mangelinckx, S.; Prévost, S.; Bichon, E.; Monteau, F.; De Poorter, G.; De Kimpe, N.; Le Bizec, B. Use of isotope ratio mass spectrometry to differentiate between endogenous steroids and synthetic homologues in cattle: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 772, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkels, F.M.S.A.; de Boer, H.J.; Hernández, P.C.; Martes, C.R.T.; van der Meer, M.T.J.; Basu, S.; Usman, M.O.; Peterse, F. Carbon isotopic ratios of modern C3 and C4 vegetation on the Indian peninsula and changes along the plant–soil–river continuum—Implications for vegetation reconstructions. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 4107–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann-Ene, V.; Vetter, W. Stable Carbon Isotope Ratios (δ13C Values [‰]) of Individual Sterols in the Oils of C3, C4, and CAM Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kong, K.; Yan, X. Characterization and Biological Activities of Four Biotransformation Products of Diosgenin from Rhodococcus erythropolis. Molecules 2023, 28, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B. Guidelines and recommended terms of expression of stable-isotope-ratio and gas-ratio measurement results. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2011, 25, 2538–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Q.; Liu, B.; Chen, P. Advances in steroid purification for novel techniques in carbon isotope ratio mass spectrometry of doping control. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 17548–17561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Thevis, M. Improving the Determination of Carbon Isotope Ratios of Endogenous Steroids Found in Human Serum. Drug Test. Anal. 2025, 17, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, G.; Rizk, T.; Akoka, S.; Bejjani, J. Cholesterol, a powerful (13)C isotopic biomarker. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1089, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Thevis, M. Addressing recent challenges in isotope ratio mass spectrometry: Development of a method applicable to 1-androstene-steroids, 6alpha-hydroxy-androstenedione, and androstatrienedione. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honesova, L.; Viaene, W.; Van Eenoo, P.; Polet, M. High-temperature liquid chromatography-isotope ratio massspectrometry methodology forcarbon isotope ratio determination of anabolic steroids in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1324, 343092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honesova, L.; Van Eenoo, P.; Polet, M. Evaluation of analytical columns suitable for high-temperature liquid-chromatography-isotope-ratio-mass-spectrometry analysis of anabolic steroids. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1731, 465191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, A.T.; Trout, G.J.; Kazlauskas, R.; Howe, C.J.; George, A.V. Carbon isotope ratio (delta13C) values of urinary steroids for doping control in sport. Steroids 2009, 74, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybowski, M.P.; Siwek, K. Application of the transient matrix effect for determination of anabolic-androgenic steroids in biological samples by GC-MS/MS. Forensic Toxicol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Giacomello, G.; Girreser, U.; Steff, J.; Bureik, M.; de la Torre, X.; Botrè, F.; Parr, M.K. Characterization and quantitation of a sulfoconjugated metabolite for detection of methyltestosterone misuse and direct identification by LC-MS. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 242, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoussi, O.; Bambagiotti, G.; Gameli, P.S.; Daziani, G.; Tavoletta, F.; Tini, A.; Basile, G.; Lo Faro, A.F.; Carlier, J. In Vitro and In Vivo Human Metabolism of Ostarine, a Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator and Doping Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E., Jr.; Leaptrot, K.L.; Koomen, D.C.; May, J.C.; Cavalcanti, G.A.; Padilha, M.C.; Pereira, H.M.G.; McLean, J.A. Multidimensional Separations of Intact Phase II Steroid Metabolites Utilizing LC-Ion Mobility-HRMS. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 10990–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Licciardello, G.; Privitera, F.; Iannuzzi, S.; Liberto, A.; Sessa, F.; Salerno, M. Forensic Post-Mortem Investigation in AAS Abusers: Investigative Diagnostic Protocol. A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göschl, L.; Gmeiner, G.; Gärtner, P.; Stadler, G.; Enev, V.; Thevis, M.; Schänzer, W.; Guddat, S.; Forsdahl, G. Stanozolol-N-glucuronide metabolites in human urine samples as suitable targets in terms of routine anti-doping analysis. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhö, P.; Scholz, K.; Kärkkäinen, N.; Haapala, M.; Räikkönen, H.; Kostiainen, R.; Vaikkinen, A. Analysis of steroids in urine by gas chromatography-capillary photoionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1598, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzetto, F.; Mehl, F.; Boccard, J.; Baume, N.; Rudaz, S.; Saugy, M.; Nicoli, R. Longitudinal monitoring of endogenous steroids in human serum by UHPLC-MS/MS as a tool to detect testosterone abuse in sports. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, L.; Van Renterghem, P.; Van Eenoo, P.; Polet, M. Development and validation of a fast gas chromatography combustion isotope ratio mass spectrometry method for the detection of epiandrosterone sulfate in urine. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; Nicoli, R.; Schweizer-Grundisch, C.; Grabherr, S.; Kuuranne, T.; Musenga, A. Comparison of analytical approaches for the detection of oral testosterone undecanoate administration in men. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 16, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, S.; Shiomura, S.; Alechaga, É.; Bressan, C.; Monfort, N.; Ventura, R.; Okano, M. Detection of Oral Testosterone Undecanoate Administration in UGT2B117 del/del and del/ins Individuals. Part I: Urinary Steroid Profile and IRMS Markers. Drug Test. Anal. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojanperä, S.; Leinonen, A.; Apajalahti, J.; Lauraeus, M.; Alaja, S.; Moisander, T.; Kettunen, A. Characterization of microbial contaminants in urine. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 2, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albeiroti, S.; Ahrens, B.D.; Sobolevskii, T.; Butch, A.W. The influence of small doses of ethanol on the urinary testosterone to epitestosterone ratio in men and women. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P. Testing for anabolic steroids in hair: A review. Leg. Med. 2003, 5, S29–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.Y.; Choi, T.L.S.; Kwok, W.H.; Wong, J.K.Y.; Wan, T.S.M. Detection of anabolic and androgenic steroids and/or their esters in horse hair using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1493, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P. A new series of hair test results involving anabolic steroids. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2017, 29, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, N.; Hussain, I.; Barker, J.; Petroczi, A.; Naughton, D.P. Analysis of anabolic steroids in human hair using LC–MS/MS. Steroids 2010, 75, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintz, P.; Gheddar, L.; Raul, J.S. Simultaneous testing for anabolic steroids in human hair specimens collected from various anatomic locations has several advantages when compared with the standard head hair analysis. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdloff, R.S.; Dudley, R.E.; Page, S.T.; Wang, C.; Salameh, W.A. Dihydrotestosterone: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Clinical Implications of Elevated Blood Levels. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 220–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarrow, J.F.; Wronski, T.J.; Borst, S.E. Testosterone and Adult Male Bone: Actions Independent of 5α-Reductase and Aromatase. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2015, 43, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Pozo, O.J.; Van Renterghem, P.; Van Eenoo, P.; Marcos, J.; Segura, J.; Ventura, R. Detection of dihydrotestosterone gel, oraldehydroepiandrosterone, and testosterone gelmisuse through the quantification oftestosterone metabolites released after alkaline treatment. Drug Test. Analysis 2011, 3, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Renterghem, P.; Van Eenoo, P.; Sottas, P.E.; Saugy, M.; Delbeke, F. Subject-based steroid profiling and the determination of novel biomarkers for DHT and DHEA misuse in sports. Drug Test. Analysis 2010, 2, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.F.; Seco-Calvo, J.; Arribalzaga, S.; Díez, R.; Lopez, C.; Fernandez, M.N.; Garcia, J.J.; Diez, M.J.; de la Puente, R.; Sierra, M.; et al. Online information and availability of three doping substances (anabolic agents) in sports: Role of pharmacies. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1305080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzato, E.C.; Filonzi, M.; Rosa, H.S.; de Bairros, A.V. Pretreatment of different biological matrices for exogenous testosterone analysis: A review. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2017, 27, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, P.; Jardines, D.; Martinez-Brito, D.; Domenici, E.; de la Torre, X.; Parr, M.K.; Botrè, F. Metabolomics workflow as a driven tool for rapid detection of metabolites in doping analysis. Development and validation. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Fusshöller, G.; Geyer, H.; Toboc, A.; Dănilă, M.G.; Thevis, M. Detecting the misuse of 7-oxo-DHEA by means of carbon isotope ratio mass spectrometry in doping control analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzetto, F.; Parasiliti-Caprino, M.; Gesmundo, I.; Marinelli, L.; Nonnato, A.; Nicoli, R.; Kuuranne, T.; Mengozzi, G.; Ghigo, E.; Settanni, F. Single-run UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of endogenous steroids and their phase II metabolites in serum for anti-doping purposes. Talanta 2023, 255, 124218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collomp, K.; Buisson, C.; Lasne, F.; Collomp, R. DHEA, physical exercise and doping. J. Steroid Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2015, 145, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravisse, N.; Vibarel-Rebot, N.; Labsy, Z.; Do, M.C.; Gagey, O.; Dubourg, C.; Audran, M.; Collomp, K. Short-term Dehydroepiandrosterone Intake and Supramaximal Exercise in Young Recreationally-trained Women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2018, 39, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczyk, F.Z.; Mandelbaum, R.; Baker, M.; Ma, L.; Sriprasert, I.; Dancz, C.E.; Legro, R.S. Quantitation of 5α-androstanedione in normal women and women with PCOS. J. Steroid Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2023, 231, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczna, L.; Plenis, A.; Olędzka, I.; Kowalski, P.; Bączek, T. Optimization of LC method for the determination of testosterone and epitestosterone in urine samples in view of biomedical studies and anti-doping research studies. Talanta 2011, 83, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuuranne, T.; Ahola, L.; Pussinen, C.; Leinonen, A. Analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG): Application of routine immunological methods for initial testing and confirmation analysis in doping control. Drug Test. Anal. 2013, 5, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrum, J.M.; Moore, C.; Crouch, A.K.; Eichner, D.; Miller, G.D. Influence of multiple human chorionic gonadotropin administrations on serum and urinary steroid Athlete Biological Passport profiles in males. Drug Test. Anal. 2023, 15, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahm, E.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Pralong, F.; Dvorak, J.; Saugy, M.; Baume, N. Influence of multiple injections of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) on urine and serum endogenous steroids concentrations. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 213, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Escudero, P.; Muñoz-Guerra, J.A.; García-Tenorio, S.V.; Garde, E.S.; Soldevilla-Navarro, A.B.; Galindo-Canales, M.; Prado, N.; Fuentes-Ferrer, M.E.; Fernández-Pérez, C. Impact of the UGT2B17 polymorphism on the steroid profile. Results of a crossover clinical trial in athletes submitted to testosterone administration. Steroids 2019, 141, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WADA: Detection of Recombinant Human LH as Doping Agent. Available online: https://www.wada-ama.org/en/resources/scientific-research/detection-recombinant-human-lh-doping-agent (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Santana, F.F.V.; Lozi, A.A.; Gonçalves, R.V.; Da Silva, J.; Da Matta, S.L.P. Comparative effects of finasteride and minoxidil on the male reproductive organs: A systematic review of in vitro and in vivo evidence. Toxicol. App. Pharmacol. 2023, 478, 116710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traish, A.M. Health Risks Associated with Long-Term Finasteride and Dutasteride Use: It’s Time to Sound the Alarm. World J. Men. Health 2020, 38, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Seo, W.W.; Park, R.W.; Rhee, S.Y.; Cha, J.M.; Hah, Y.S.; Jeong, C.W.; Kim, K.J.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Comparison of Finasteride and Dutasteride on Risk of Prostate Cancer in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Pooled Analysis of 15 Real-world Databases. World J. Men. Health 2025, 43, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquraini, H.; Auchus, R.J. Strategies that athletes use to avoid detection of androgenic-anabolic steroid doping and sanctions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 464, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, T.; Geyer, H.; Haenelt, N.; Huelsemann, F.; Schaenzer, W.; Thevis, M. Current Insights into the Steroidal Module of the Athlete Biological Passport. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzel, D.M.; Nichols, L.; Conover, C.F.; Marangi, S.A.; Kura, J.R.; Iannaccone, D.K.; Clark, D.J.; Gregory, C.M.; Sonntag, C.F.; Wokhlu, A.; et al. Musculoskeletal and body composition response to high-dose testosterone with finasteride after chronic incomplete spinal cord injury—A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled pilot study. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1479264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.J.; Stone, G.L.; Overbeek, D.L.; Chiba, T.; Burns, M.M. Performance-enhancing drugs and the Olympics. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevis, M.; Geyer, H.; Mareck, U.; Flenker, U.; Schänzer, W. Doping-control analysis of the 5alpha-reductase inhibitor finasteride: Determination of its influence on urinary steroid profiles and detection of its major urinary metabolite. Ther. Drug Monit. 2007, 29, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannella, L.; Colamonici, C.; Curcio, D.; Botrè, F.; de la Torre, X. 5α-reductase inhibitors: Evaluation of their potential confounding effect on GC-C-IRMS doping analysis. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1852–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarino, M.; Martellone, L.; Comunità, F.; de la Torre, X.; Molaioni, F.; Botrè, F. Detection of 5α-reductase inhibitors by UPLC–MS/MS: Application to the definition of the excretion profile of dutasteride in urine. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksak, P.; Nepovimova, E.; Valko, M.; Alwasel, S.; Alomar, S.; Kuca, K. Comprehensive analysis of prohibited substances and methods in sports: Unveiling trends, pharmacokinetics, and WADA evolution. Envirom. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 108, 104447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, H.C.; Green, E.; Sleven, M.; Stanton, A.L. Aromatase inhibitors: The unexpected breast cancer treatment. J. Ger. Oncol. 2020, 11, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althuwaibi, M.F.; Fernandez-Garcia, C.; Hayes, L.; McNally, R.; Coughlan, D. Systematic review of economic evaluations of aromatase inhibitors in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Quality evaluation. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, T.; Marino, C.C.; Ahmad, S.; Nasrazadani, A.; Brufsky, A.M. Aromatase Inhibitor-Associated Musculoskeletal Syndrome: Understanding Mechanisms and Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 713700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochoy, M.; Danel, A.; Chazard, E.; Gautier, S.; Berkhout, C. Doping with aromatase inhibitors and oestrogen receptor modulators in steroid users: Analysis of a forum to identify dosages, durations and adverse drug reactions. Therapies 2022, 77, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favretto, D.; Snenghi, R.; Pertile, R.; El Mazloum, R.; Tucci, M.; Visentin, S.; Vogliardi, S. Hair analysis to discriminate voluntary doping vs inadvertent ingestion of the aromatase inhibitor letrozole. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Sung, W.W. Clomiphene Citrate Treatment as an Alternative Therapeutic Approach for Male Hypogonadism: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; He, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Crosstalk of methylation and tamoxifen in breast cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 30, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fohlin, H.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Rosell, J.; Fernö, M.; Fornander, T.; Rydén, L.; Skoog, L.; Nordenskjöld, B.; Stål, O. Breast cancer hormone receptor levels and benefit from adjuvant tamoxifen in a randomized trial with long-term follow-up. Acta Oncol. 2024, 63, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, D.; Dandekar, A.; Bhattaccharjee, S.; Singh, O.N.; Agrahari, V.; Peet, M.M.; Doncel, G.F.; Banga, A.K. Formulation Development for Transdermal Delivery of Raloxifene, a Chemoprophylactic Agent against Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwashmi, A.S.S.; Khan, N.U.; Chen, T. Risk-benefits assessment of tamoxifen or raloxifene as chemoprevention for risk reduction of breast cancer among BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lukong, K.E. Treating ER-positive breast cancer: A review of the current FDA-approved SERMs and SERDs and their mechanisms of action. Oncol. Rev. 2025, 19, 1564642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.D.; Moore, C.; Nair, V.; Hill, B.; Willick, S.E.; Rogol, A.D.; Eichner, D. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis Effects and Urinary Detection Following Clomiphene Administration in Males. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havnes, I.A.; BordadoHenriksen, H.C.; Johansen, P.W.; Bjørnebekk, A.; Neupane, S.P.; Hisdal, J.; Seljeflot, I.; Wisløff, C.; Jørstad, M.L.; McVeigh, J.; et al. Off-label use of clomiphene citrate to treat anabolic androgenic steroid induced hypogonadism upon cessation among men (CloTASH)—A pilot study protocol. MethodsX 2024, 13, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, C.; Mujica, P.; Illanes-González, J.; López, A.; Vargas, C.; Sáez, J.C.; González-Jamett, A.; Ardiles, Á.O. Probenecid, an Old Drug with Potential New Uses for Central Nervous System Disorders and Neuroinflammation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Ma, A.; Mao, J.; Song, D.; Zhao, X. Overview of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of URAT1 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, M.M.; Abo-El Fetoh, M.E.; Afify, H.; Ramadan, L.A.A.; Mohamed, W.R. Probenecid ameliorates testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia: Implications of PGE-2 on ADAM-17/EGFR/ERK1/2 signaling cascade. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.C.; Arkell, P.; Riezk, A.; Gilchrist, M.; Wheeler, G.; Hope, W.; Holmes, A.H.; Rawson, T.M. Addition of probenecid to oral β-lactam antibiotics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, R.J.; Gardiner, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Begg, R.; Chambers, S.T.; Turnidge, J.; Begg, E.J. Probenecid effects on cephalexin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huriez, P.; Ourghanlian, C.; Razazi, K.; Vindrios, W.; Hulin, A.; Lepeule, R.; Habibi, A.; Gallien, S. Probenecid, an old β-lactams pharmacokinetic enhancer for a renewed use: A retrospective study. Infect. Dis. Now. 2022, 52, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R.; Segura, J. Masking and manipulation. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 195, 327–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, S.R.; Goebel, C.; Burke, L.M.; Greaves, R.F. Doping in sport and exercise: Anabolic, ergogenic, health and clinical issues. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 53, 196–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmersbach, P. The Probenecid-story—A success in the fight against doping through out-of-competition testing. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaque-Fernandez, F.; Allard, B.; Monteiro, L.; Lafoux, A.; Huchet, C.; Jaimovich, E.; Berthier, C.; Jacquemond, V. Probenecid affects muscle Ca2+ homeostasis and contraction independently from pannexin channel block. J. Gen. Physiol. 2023, 155, e202213203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadwallader, A.B.; De La Torre, X.; Tieri, A.; Botrè, F. The abuse of diuretics as performance-enhancing drugs and masking agents in sport doping: Pharmacology, toxicology and analysis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, L.; Roels, K.; Polet, M.; Van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K. Identification and confirmation of diuretics and masking agents in urine by turbulent flow online solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry for doping control. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1579, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscovici, H.F.; Lara, P.H.S.; Solera, F.A.G.; Cohen, M.; Pagura, J.R.; Arliani, G.G. Doping control in male soccer players in brazil: 10 years of follow-up. ActaOrtop. Bras. 2024, 32, e273282. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.W.; Bae, E.; Hwang, K.; Jang, H.N.; Park, H.J.; Jeon, D.H.; Cho, H.S.; Chang, S.H.; Park, D.J. Severe hypokalemic paralysis and rhabdomyolysis occurring after binge eating in a young bodybuilder: Case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondaryk, M.; Kurzątkowski, W.; Staniszewska, M. Antifungal agents commonly used in the superficial and mucosal candidiasis treatment: Mode of action and resistance development. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2013, 30, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivonello, R.; Ferrigno, R.; De Martino, M.C.; Simeoli, C.; Di Paola, N.; Pivonello, C.; Barba, L.; Negri, M.; De Angelis, C.; Colao, A. Medical Treatment of Cushing’s Disease: An Overview of the Current and Recent Clinical Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; Botrè, F.; de la Torre, X.; Fiacco, I.; Iannone, M.; Mazzarino, M. Drug-drug interactions and masking effects in sport doping: Influence of miconazole administration on the urinary concentrations of endogenous anabolic steroids. Forensic Toxicol. 2016, 34, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarino, M.; Comunità, F.; de la Torre, X.; Molaioni, F.; Botrè, F. Effects of the administration of miconazole by different routes on the biomarkers of the “steroidal module” of the Athlete Biological Passport. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Di Mizio, G.; Bertozzi, G.; Messina, G.; Tomaiuolo, B.; Pisanelli, D.; Maglietta, F.; Ricci, P.; Pomara, C. Anabolic Androgenic Steroids: Searching New Molecular Biomarkers. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Maglietta, F.; Bertozzi, G.; Salerno, M.; Di Mizio, G.; Messina, G.; Montana, A.; Ricci, P.; Pomara, C. Human Brain Injury and miRNAs: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Cipolloni, L.; Bertozzi, G.; Messina, G.; Mizio, G.D.; Asmundo, A.; Pomara, C. Anabolic-androgenic steroids and brain injury: miRNA evaluation in users compared to cocaine abusers and elderly people. Aging 2020, 12, 15314–15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Salerno, M.; Bertozzi, G.; Cipolloni, L.; Messina, G.; Aromatario, M.; Polo, L.; Turillazzi, E.; Pomara, C. miRNAs as Novel Biomarkers of Chronic Kidney Injury in Anabolic-Androgenic Steroid Users: An Experimental Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirpoor, A.; Naderi, R. Nandrolone decanoate induced kidney injury through miRNA-146a targeting IRAK1 and TRAF6 via activation of the NF-κB pathway: The effect of moderate exercise. Steroids 2024, 211, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Escudero, P.; Muñoz-Guerra, J.A.; García-Tenorio, S.V.; Serrano-Garde, E.; Soldevilla-Navarro, A.B.; Cortes-Carrillo, N.; Galindo-Canales, M.; del Prado, N.; Fuentes-Ferrer, M.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; et al. Bioanalytical Detection of Steroid Abuse in Sports Based on the Androgenic Activity Measurement. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, S.; Shiomura, S.; Alechaga, É.; Bressan, C.; Monfort, N.; Okano, M.; Ventura, R. Detection of Oral Testosterone Undecanoate Administration in UGT2B17 del/del and del/ins Individuals. Part II: Urinary Endogenous Steroid Sulfate Markers. Drug Test. Anal. 2025, 17, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, M.; Shiomura, S. Effectiveness of blood steroidal passport markers for detecting testosterone abuse in Asians. Drug Test. Anal. 2024, 16, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Maximum Concentration Above Which Doping Is Suspected | Ratios |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone (T) | >200 ng/mL male >50 ng/mL female | T/E >4 A/T <20 5αADIOL/5βADIOL >2.4 5αADIOL/E >10 |
| Epitestosterone (E) | >200 ng/mL male >50 ng/mL female | |
| Androsterone (A) | >10,000 ng/mL | |
| Etiocholanolone (ETIO) | >10,000 ng/mL | |
| 5-α-androstane-3α,17β-diol (5αADIOL) | >250 ng/mL male >150 ng/mL female | |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) | >200 ng/mL |
| Masking Agent(s) | Class | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| DHT | Androgen | It is a metabolite of T; does not influence the T/E ratio [107,167]. |
| DHEA | Androgen | It is a metabolite of T; does not influence the T/E ratio. DHEA is endogenously transformed into T [174,175]. |
| Androstanedione | Androgen | It is converted endogenously into DHT; does not influence the T/E ratio [107,178]. |
| E | Androgen | It reduces the T/E ratio in the sense of masking the administration of exogenous T [179]. |
| HCG | Hormone | Stimulates endogenous T production; does not influence the T/E ratio [180,181]. |
| LH | Hormone | Similar to HCG [181,182,183]. |
| α-reductase inhibitors | Enzyme inhibitor | It inhibits T metabolism, maintaining it at high concentrations for longer; it does not alter the T/E ratio [188]. |
| Aromatase inhibitors | Enzyme inhibitor | They are not masking agents; prevent the appearance of gynecomastia by inhibiting the conversion of T to estradiol [199,200]. |
| Antiestrogens | Estrogen-receptor blocker | They are not masking agents; prevent the appearance of gynecomastia by blocking estrogen binding to the receptor [199]. |
| Probenecid | Uricosuric | It reduces the urinary excretion of anabolic steroids, reducing their urinary concentration and detection capacity [107,216]. |
| Diuretics | Increases elimination of water and electrolytes | Dilution of urine reduces the detection of anabolic steroids and their metabolites [218]. |
| Azole-derivatives | Antifungal agents | It inhibits endogenous T synthesis by inhibiting 17-hydroxylase, 11-hydroxylase, and C17–20 lyase, contributing to the reduction of the T/E ratio [224,225]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puscasiu, D.; Flangea, C.; Vlad, D.; Popescu, R.; Vlad, C.S.; Barac, S.; Rata, A.L.; Marina, C.; Cobec, I.M.; Laitin, S.M.D. Adulteration of Sports Supplements with Anabolic Steroids—From Innocent Athlete to Vicious Cheater. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193146
Puscasiu D, Flangea C, Vlad D, Popescu R, Vlad CS, Barac S, Rata AL, Marina C, Cobec IM, Laitin SMD. Adulteration of Sports Supplements with Anabolic Steroids—From Innocent Athlete to Vicious Cheater. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193146
Chicago/Turabian StylePuscasiu, Daniela, Corina Flangea, Daliborca Vlad, Roxana Popescu, Cristian Sebastian Vlad, Sorin Barac, Andreea Luciana Rata, Cristina Marina, Ionut Marcel Cobec, and Sorina Maria Denisa Laitin. 2025. "Adulteration of Sports Supplements with Anabolic Steroids—From Innocent Athlete to Vicious Cheater" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193146
APA StylePuscasiu, D., Flangea, C., Vlad, D., Popescu, R., Vlad, C. S., Barac, S., Rata, A. L., Marina, C., Cobec, I. M., & Laitin, S. M. D. (2025). Adulteration of Sports Supplements with Anabolic Steroids—From Innocent Athlete to Vicious Cheater. Nutrients, 17(19), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193146






