The Sweet Side of Constipation: Colonic Motor Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
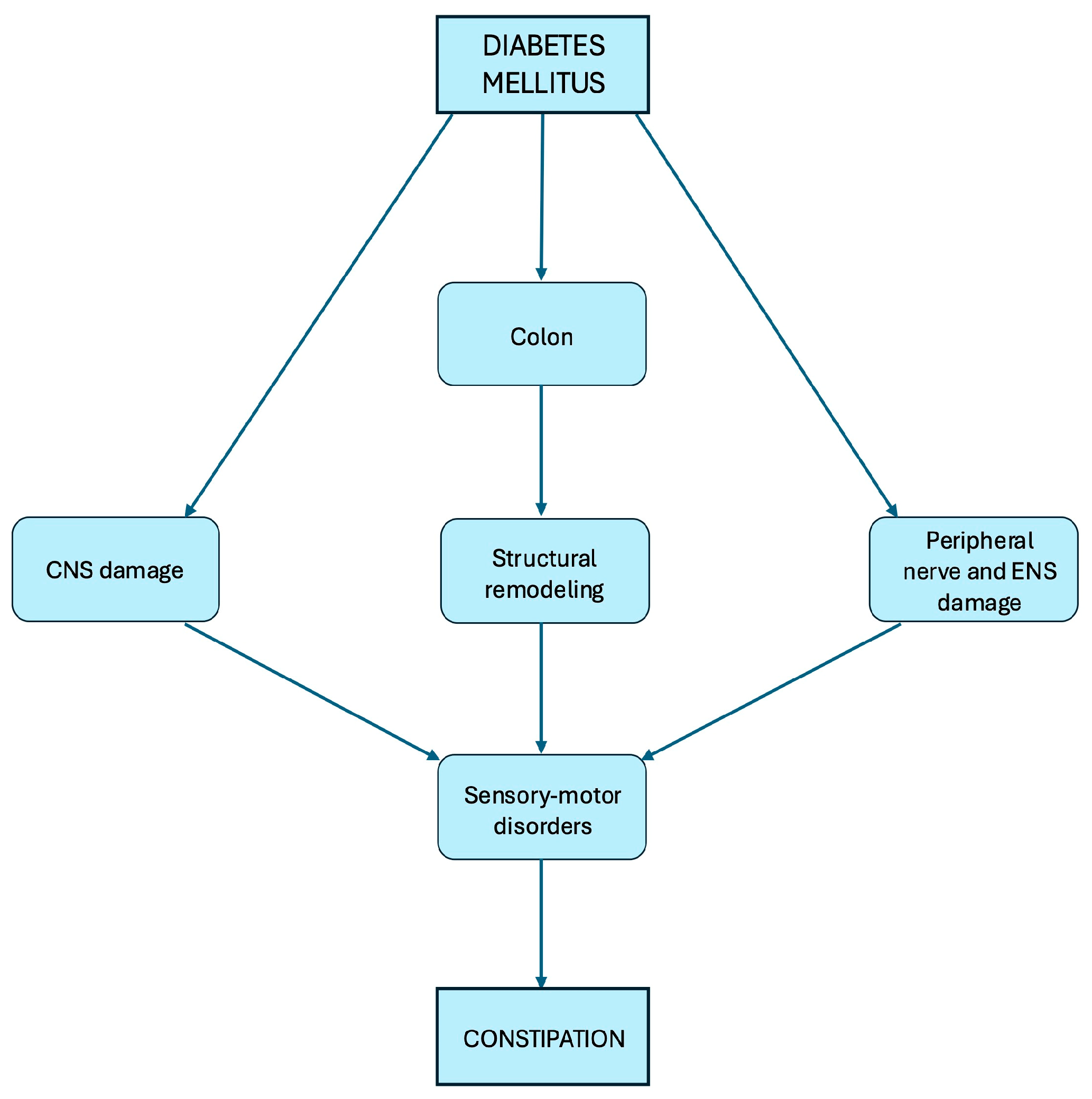
2. Pathophysiology of Constipation in Diabetes Mellitus
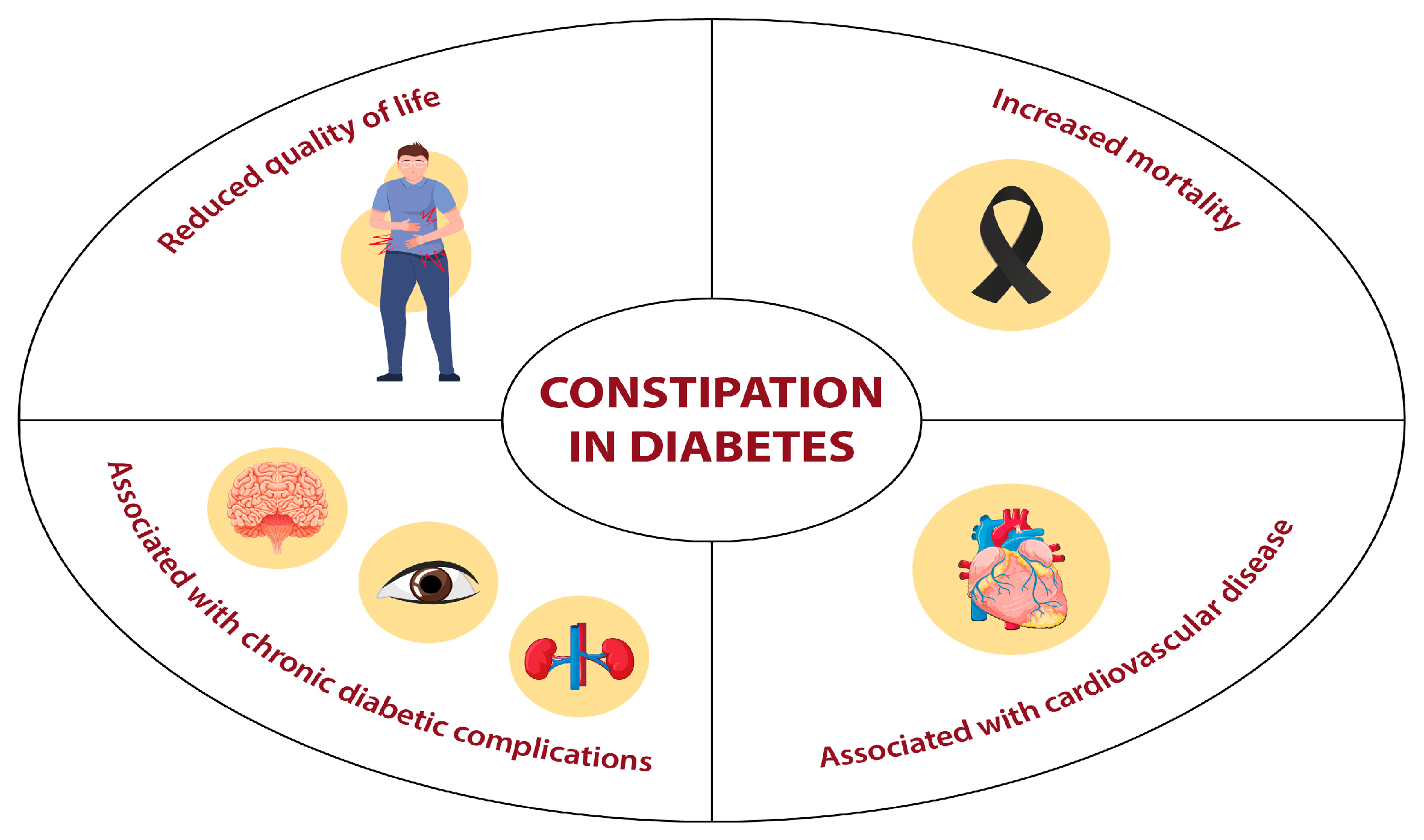
3. Clinical Implications of Constipation in Diabetes Mellitus
4. Constipation as an Adverse Event of Treatment with GLP-1 RAs
5. Diagnosis of Chronic Constipation
6. Treatment of Chronic Constipation
6.1. Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
6.2. Pharmacological Management
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolli, G.B.; Porcellati, F.; Lucidi, P.; Fanelli, C.G. The physiological basis of insulin therapy in people with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 175, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournel, A.; Marlin, A.; Abot, A.; Pasquio, C.; Cirillo, C.; Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C. Glucosensing in the gastrointestinal tract: Impact on glucose metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G645–G658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, G. Diabetes and gastrointestinal motor activity. Recent. Prog. Med. 1991, 82, 334–337. [Google Scholar]
- Meldgaard, T.; Keller, J.; Olesen, A.E.; Olesen, S.S.; Krogh, K.; Borre, M.; Farmer, A.; Brock, B.; Brock, C.; Drewes, A.M. Pathophysiology and management of diabetic gastroenteropathy. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819852047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Frühbeck, G.; Garruti, G.; Di Ciaula, A. Novel insights into the pathogenic impact of diabetes on the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annese, V.; Lombardi, G.; Frusciante, V.; Germani, U.; Andriulli, A.; Bassotti, G. Cisapride and erythromycin prokinetic effects in gastroparesis due to type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai-Satta, P.; Bellini, M.; Morelli, O.; Geri, F.; Lai, M.; Bassotti, G. Gastroparesis: New insights into an old disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, M.S.; Saad, R.J. Diabetes mellitus and the colon. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2017, 15, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, B.E.; Mearin, F.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J.; Simren, M.; Spiller, R. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugie, S.M.; Benninga, M.A.; Di Lorenzo, C. Epidemiology of constipation in children and adults: A systematic review. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, A.D.; Palsson, O.; Goode, P.S.; Burgio, K.L.; Busby-Whitehead, J.; Whitehead, W.E. Association of low dietary intake of fiber and liquids with constipation: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Pemberton, J.H.; Locke, G.R., 3rd. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on constipation. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.; Schiller, L.R. Disorders of gastrointestinal motility associated with diabetes mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 1983, 98, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enck, P.; Rathmann, W.; Spiekermann, M.; Czerner, D.; Tschöpe, D.; Ziegler, D.; Strohmeyer, G.; Gries, F.A. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetic patients and non-diabetic subjects. Z. Gastroenterol. 1994, 32, 637–641. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, D.; Locke, G.R.; Camilleri, M.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Yawn, B.P.; Leibson, C.; Melton, L.J. Gastrointestinal tract symptoms among persons with diabetes mellitus in the community. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2808–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, L.; Basilisco, G.; Corazziari, E.; Stanghellini, V.; Bassotti, G.; Bellini, M.; Perelli, I.; Cuomo, R.; LIRS Study Group. Constipation severity is associated with productivity losses and healthcare utilization in patients with chronic constipation. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2014, 2, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsey, J.; Greenfield, S.; Candy, D.; Geraint, M. Systematic review: Impact of constipation on quality of life in adults and children. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, K.; Molnar, M.Z.; Potukuchi, P.K.; Thomas, F.; Lu, J.L.; Yamagata, K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kovesdy, C.P. Constipation and risk of death and cardiovascular events. Atherosclerosis 2018, 281, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, D.; Camilleri, M.; Burton, D.D.; Rath-Harvey, D.M.; Oenning, L.; Pemberton, J.H.; Low, P.A. Pilot study of pathophysiology of constipation among community diabetics. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liao, D.; Zhao, J. Diabetes-induced mechanophysiological changes in the small intestine and colon. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Frøkjaer, J.B.; Drewes, A.M.; Ejskjaer, N. Upper gastrointestinal sensory-motor dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2846–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, A.M.; Søfteland, E.; Dimcevski, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Brock, C.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Krogh, K.; Drewes, A.M. Brain changes in diabetes mellitus patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarandi, S.S.; Srinivasan, S. Diabetic gastrointestinal motility disorders and the role of enteric nervous system: Current status and future directions. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azpiroz, F.; Malagelada, C. Diabetic neuropathy in the gut: Pathogenesis and diagnosis. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frøkjaer, J.B.; Andersen, S.D.; Ejskaer, N.; Funch-Jensen, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Gregersen, H.; Drewes, A.M. Gut sensations in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Pain 2007, 131, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.M.; Sanders, K.M. Involvement of intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal in neuroeffector transmission in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Physiol. 2006, 576, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babizhayev, M.A.; Strokov, I.A.; Nosikov, V.V.; Savel’yEva, E.L.; Sitnikov, V.F.; Yegorov, Y.E.; Lankin, V.Z. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Neuropathy: Generation of Free Radical Species in the Glycation Reaction and Gene Polymorphisms Encoding Antioxidant Enzymes to Genetic Susceptibility to Diabetic Neuropathy in Population of Type I Diabetic Patients. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 1425–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vague, P.; Coste, T.C.; Jannot, M.F.; Raccah, D.; Tsimaratos, M. C-peptide, Na+, K(+)-ATPase, and diabetes. Exp. Diabesity Res. 2004, 5, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, L.; Finnerup, N.B.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Olesen, R.A.; Drasbek, K.R.; Knudsen, L.; Jespersen, S.N.; Frystyk, J.; Charles, M.; Thomsen, R.W.; et al. The effects of capillary dysfunction on oxygen and glucose extraction in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagishi, T.; Nishizawa, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Sekiya, K.; Morii, H. Segmental gut transit in diabetes mellitus: Effect of cisapride. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1992, 17, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, B.; Anitha, M.; Blatt, R.; Shahnavaz, N.; Kooby, D.; Staley, C.; Mwagi, S.; Jones, D.P.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Srinivasan, S. Colonic motor dysfunction in human diabetes is associated with enteric neuronal loss and increased oxidative stress. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 131–138, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, F.L.; Parveen, S.; Vandrunen, M.; Sood, K.B.; Reza, F.; Serlovsky, R.; Reddy, S. Relation of symptoms to impaired stomach, small bowel, and colon motility in long-standing diabetes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narducci, F.; Bassotti, G.; Gaburri, M.; Morelli, A. Twenty-four-hour manometric recording of colonic motor activity in a healthy man. Gut 1987, 28, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Wegeberg, A.M.L.; Jensen, S.L.; Sørensen, P.S.; Wigh, I.M.N.; Zaugg, V.S.; Færch, K.; Quist, J.S.; Brock, C. The day-night pattern of colonic contractility is not impaired in type 1 diabetes and distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegeberg, A.M.; Liao, D.; Jensen, S.L.; Sørensen, P.S.; Wigh, I.M.N.; Zaugg, S.V.; Brock, C. Gastrocolic reflex is delayed and diminished in adults with type 1 diabetes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.X.; Matos, H.C.; Machado, J.P.; Almeida, C.C. Transit of radiopaque particles through the gastrointestinal tract: Comparison between type 2 diabetes patients and healthy individuals. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2012, 104, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Low, P.; Camilleri, M.; Veil, E.; Burton, D.; Kudva, Y.; Shah, P.; Gehrking, T.; Zinsmeister, A.R. A randomised controlled study of the effect of cholinesterase inhibition on colon function in patients with diabetes mellitus and constipation. Gut 2013, 62, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Watabe, K.; Nakahara, M.; Ogiyama, H.; Kiyohara, T.; Tsutsui, S.; Tamura, S.; Shinomura, Y.; Hayashi, N. Disturbed gastrointestinal motility and decreased interstitial cells of Cajal in diabetic db/db mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Chen, W.; Liang, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, J. Downregulation of BDNF-TrkB signaling may contribute to the colonic motility disorders in mice with streptozocin-induced diabetes. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 7, e14647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, F.; Feng, P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits colonic smooth muscle cell apoptosis in diabetic rats with colonic dysmotility. Regul. Pept. 2014, 194–195, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Ha, S.E.; Wei, L.; Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Clemmensen, B.; Heredia, D.J.; Gould, T.W.; Sanders, K.M.; Ro, S. Colonic Motility Is Improved by the Activation of 5-HT2B Receptors on Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Diabetic Mice. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 608–622.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, A.; Huizinga, J.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, L.W.; Parsons, M. Increase in stretch-induced rhythmic motor activity in the diabetic rat colon is associated with loss of ICC of the submuscular plexus. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G315–G326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvarcz, E.; Palmér, W.L.; Aman, J.; Horowitz, M.; Stridsberg, M.; Berne, C. Physiological hyperglycemia slows gastric emptying in normal subjects and patients with Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, D.; Camilleri, M.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Rizza, R.R. Effect of acute hyperglycemia on colorectal motor and sensory function in humans. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, G859–G864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Iwase, M.; Fujii, H.; Ide, H.; Komorita, Y.; Yoshinari, M.; Oku, Y.; Higashi, T.; Nakamura, U.; Kitazono, T. Defecation frequency and glycemic control in patients with diabetes: The Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 35, 107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Leemon, M.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Prevalence of gastro-intestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: A population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihana-Sugiyama, N.; Nagata, N.; Yamamoto-Honda, R.; Izawa, E.; Kajio, H.; Shimbo, T.; Kakei, M.; Uemura, N.; Akiyama, J.; Noda, M. Constipation, hard stools, fecal urgency, and incomplete evacuation, but not diarrhea is associated with diabetes and its related factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3252–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, C.K.; Samsom, M.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. Relationships of upper gastrointestinal motor and sensory function with glycemic control. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, R.B.N.; Peltier, A.; Figaro, M.K. Constipation and glycemic control. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, S.T.T.; Nezami, B.G.; Shetty, A.; Chetty, V.K.; Srinivasan, S. Association of high dietary saturated fat intake and uncontrolled diabetes with constipation: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Neurogastroentereol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushref, M.A.; Srinivasan, S. Effect of high fat-diet and obesity on gastrointestinal motility. Ann. Transl. Med. 2013, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fano, M.; Porcellati, F.; Fanelli, C.G.; Corio, S.; Mazzieri, A.; Lucidi, P.; Bolli, G.B.; Bassotti, G. The role of gastric emptying in glucose homeostasis and defense against hypoglycemia: Innocent bystander or partner in crime? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 203, 110828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, R.L.; Senadheera, S.; Tanoto, A.; Tan, K.L.; Howitt, L.; Chen, H.; Murphy, T.V.; Sandow, S.L.; Liu, L.; Bertand, P.P. Serotonin availability in rat colon is reduced during a Western diet model of obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G424–G434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezami, B.G.; Mwangi, S.M.; Lee, J.E.; Jeppsson, S.; Anitha, M.; Yarandi, S.S.; Farris, A.B.; Srinivisan, S. MicroRNA 375 mediates palmitate-induced enteric neuronal damage and high-fat diet-induced delayed intestinal transit in mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 473 e3–483 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, G.T.C.; Chan, W.-B.; Chan, J.C.N.; Tsang, L.W.W.; Cockram, C.S. Gastrointestinal symptoms in Chinese patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 1999, 16, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battle, W.M.; Cohen, J.D.; Snape, W.J. Disorders of colonic motility in patients with diabetes mellitus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1983, 56, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Ko, S.Y.; Hong, S.N.; Sung, I.K.; Shim, C.S.; Song, K.H.; Kim, D.L.; Kim, S.K.; Oh, J. Diabetic factors associated with gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Choi, M.G.; Kang, M.I.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, S.S.; Choi, H.; Han, S.K.; et al. The prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2009, 24, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.X.; Borges, C.I.C.; Panão, E.A.; Delgado, F.J.; Simões, M.A.; Coelho, Á.C.; Silva, A.L.; Almeida, C.C. Recto-anal manometric characteristic of type 2 diabetes patients who have sensation of incomplete defecation. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2013, 27, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharucha, A.E. Pelvic floor anatomy and function. Neurogastroenetrol. Motil. 2006, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reszczyńska, M.; Kempiński, R. The Prevalence of Enteropathy Symptoms from the Lower Gastrointestinal Tract and the Evaluation of Anorectal Function in Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeds, J.S.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Tesfaye, S.; Sanders, D.S. Lower gastrointestinal symptoms are associated with worse glycemic control and quality of life in type 1 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2018, 6, e000514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, E.; Namiki, Y.; Takano, Y.; Takamine, H.; Inazumi, K.; Sasaki, H.; Yamada, M.; Ito, S.; Iwasaki, T.; Mantani, N.; et al. Clinical factors associated with the symptoms of constipation in patients with diabetes mellitus: A multicenter study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Ito, K.; Tanaka, M.; Hokamura, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kusano, E.; Kondo, J.; Izutsu, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Inoue, H.; et al. Constipation is a frequent problem associated with vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Iwase, M.; Fujii, H.; Ide, H.; Komorita, Y.; Yoshinari, M.; Oku, Y.; Higashi, T.; Oshiro, A.; Nakamura, U.; et al. Constipation and diabetic kidney disease: The Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021, 25, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes-state-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, D.K.; Marx, N.; Mulvagh, S.L.; Deanfield, J.E.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Pop-Busui, R.; Mann, J.F.E.; Emerson, S.S.; Poulter, N.R.; Engelmann, M.D.M.; et al. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, L.L.; et al. Effects of semaglutide on chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabery, S.; Salinas, C.G.; Paulsen, S.J.; Ahnfelt-Ronne, J.; Alanentalo, T.; Baquero, A.F.; Buckley, S.T.; Farkas, E.; Fekete, C.; Frederiksen, K.S.; et al. Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e133429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, L. Association between different GLP-1 receptor agonists and gastrointestinal adverse reactions: A real-world disproportionality study based on FDA adverse event reporting system database. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1043789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldhaleei, W.A.; Abegaz, T.M.; Bhagavathula, A.S. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Associated Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the National Institutes of Health All of Us Cohort. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, I.; Di Gioia, L.; Di Molfetta, S.; Cignarelli, A.; Palmer, S.C.; Natale, P.; Strippoli, G.F.M.; Perrini, S.; Natalicchio, A.; Laviola, L.; et al. Glucometabolic outcomes of GLP-1 receptor agonist-based therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 64, 102181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. The evolving story of incretins (GIP and GLP-1) in metabolic and cardiovascular disease: A pathophysiological update. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23 (Suppl. 3), 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, I.; Di Gioia, L.; Di Molfetta, S.; Caporusso, M.; Cignarelli, A.; Sorice, G.P.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. The real-world safety profile of tirzepatide: Pharmacovigilance analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borner, T.; Geisler, C.E.; Fortin, S.M.; Cosgrove, R.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Dogra, M.; Doebley, S.; Sanchez-Navarro, M.J.; Leon, R.M.; Gaisinsky, J.; et al. GIP receptor agonism attenuates GLP-1 receptor agonist-induced nausea and emesis in preclinical models. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Gastroenterology Chronic Constipation Task Force. An evidence-based approach to the management of chronic constipation in North America. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100 (Suppl. 1), S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, M.; Usai-Satta, P.; Bassotti, G. Digital Rectal Examination: The Whole World is a Country! Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, G.; Usai, G.; Satta, P.U.; Bellini, M. Chronic Idiopathic Constipation in Adults: A Review on Current Guidelines and Emerging Treatment Options. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Wald, A.M. Anorectal disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Lissner, S. The pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of constipation. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2009, 106, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Bassotti, G.; Clarke, J.; Dinning, P.; Fox, M.; Grover, M.; Hellström, P.M.; Ke, M.; Layer, P.; Malagelada, C.; et al. International Working Group for Disorders of Gastrointestinal Motility and Function. Expert consensus document: Advances in the diagnosis and classification of gastric and intestinal motility disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiase, C.; D’Alba, L.; Galeazzi, F.; Bassotti, G.; Consalvo, D.; Battaglia, E.; Cataudella, G.; Neri, M.C.; Londoni, C.; Rossitti, P.; et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Constipation in Italy: Results from a Survey Conducted among Italian Gastroenterologists. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconi, G.; Bassotti, G. Editorial: Sonographic assessment of colonic content-A new tool for constipation? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.G.M.; Abraham, P. Management of chronic constipation in patients with diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 36, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassotti, G.; Villanacci, V. A practical approach to diagnosis and management of functional constipation in adults. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Cummings, J.H. Mechanism of action of dietary fibre in the human colon. Nature 1980, 284, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwee, K.A.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Gonlachanvit, S.; Chua, A.S.B.; Myung, S.J.; Rajindrajith, S.; Patcharatrakul, T.; Choi, M.G.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chen, M.H.; et al. Primary care management of chronic constipation in Asia: The ANMA chronic constipation tool. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiali, D.; Corazziari, E.; Habib, F.I.; Tomei, E.; Bausano, G.; Magrini, P.; Anzini, F.; Torsoli, A. Effect of wheat bran in treatment of chronic nonorganic constipation. A double-blind controlled trial. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1995, 40, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.Y.; Whorwell, P.J. Bran and irritable bowel syndrome: Time for reappraisal. Lancet 1994, 344, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: Standards of Care in diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S86–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Muller-Lissner, S.; Stanghellini, V.; Boeckxstaens, G.; Kamm, M.A.; Simren, M.; Galmiche, J.P.; Fried, M. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic constipation-a European perspective. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRorie, J.W.; Daggy, B.P.; Morel, J.G.; Diersing, P.S.; Miner, P.B.; Robinson, M. Psyllium is superior to docusate sodium for treatment of chronic constipation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 12, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheskin, L.J.; Kamal, N.; Crowell, M.D.; Schuster, M.M.; Whitehead, W.E. Mechanisms of constipation in older persons and effects of fiber compared with placebo. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1995, 43, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanian, N.; Janghorbani, M.; Adibi, P. Effects of psyllium vs. placebo on constipation, weight, glycemia, and lipids: A randomized trial in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic constipation. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanian, N.; Janghorbani, M. Effect of flaxseed or psyllium vs. placebo on management of constipation, weight, glycemia, and lipids: A randomized trial in constipated patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 29, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, M.; Garcia, J.J.; Fernandez, N.; Diez, M.J.; Calle, A.P. Therapeutic effects of psyllium in type 2 diabetic patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, A. Current management of strategies and therapeutic targets in chronic constipation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2011, 4, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, M.D.; Schwartz, H.J.; Roby, R.; Fleisher, S. Tolerance and efficacy of polyethylene glycol 3350/electrolyte solution versus lactulose in relieving opiate induced constipa-tion: A double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 37, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhnik, Y.; Neut, C.; Raskine, L.; Michel, C.; Riottot, M.; Andrieux, C.; Guillemot, F.; Dyard, F.; Flouriè, B. Prospective, randomized, parallel-group trial to evaluate the effects of lactulose and polyethylene glycol-4000 on colonic flora in chronic idiopathic constipation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.H.; Englyst, H.N. Fermentation in the human large intestine and the available substrates. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1987, 45, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnunen, O.; Salokannel, J. Constipation in elderly long-stay patients: Its treatment by magnesium hydroxide and bulk-laxative. Ann. Clin. Res. 1987, 19, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larsen, N.; Vogensen, F.K.; van den Berg, F.W.; Nielsen, D.S.; Andreasen, A.S.; Pedersen, B.K.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, L.H.; Jakobsen, M. Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.; Vandeplassche, L.; Kerstens, R.; Ausma, J. Clinical trial: The efficacy, impact on quality of life, and safety and tolerability of prucalopride in severe chronic constipation—A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Kerstens, R.; Rykx, A.; Vandeplassche, L. A placebo-controlled trial of prucalopride for severe chronic constipation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2344–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, G.; Usai, G.; Satta, P.U.; Bellini, M. Prucalopride for the treatment of constipation: A view from 2015 and beyond. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.F.; Morton, D.; Geenen, J.; Ueno, R. Multicenter, 4-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of lubiprostone, a locally-acting type-2 chloride channel activator, in patients with chronic constipation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.F.; Ueno, R. Lubiprostone, a locally acting chloride channel activator, in adult patients with chronic constipation: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study to evaluate efficacy and safety. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barish, C.F.; Drossman, D.; Johanson, J.F.; Ueno, R. Efficacy and safety of lubiprostone in patients with chronic constipation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, G.; Usai-Satta, P.; Bellini, M. Linaclotide for the treatment of chronic constipation. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, A.; Camilleri, M. Elobixibat and its potential role in chronic idiopathic constipation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishida, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Tsukiyama, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishizaki, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Sone, M. Effects of elobixibat in patients with diabetes and concomitant chronic constipation: An 8-week, prospective, single-center, single-arm study. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 4205–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinobu, S.; Hasuzawa, N.; Nagayama, A.; Iwata, S.; Yasuda, J.; Tokubuchi, R.; Kabashima, M.; Gobaru, M.; Hara, K.; Murotani, K.; et al. Effects of elobixibat, an inhibitor of ileal bile acid transporter, on glucose and lipid metabolism: A single-arm pilot study in patients with T2DM. Clin. Ther. 2022, 44, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chedid, V.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Camilleri, M. Elobixibat for the treatment of constipation. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudling, M.; Camilleri, M.; Graffner, H.; Holst, J.J.; Rikner, L. Specific inhibition of bile acid transport alters plasma lipids and GLP-1. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2015, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassotti, G. Relief from behind: Enemas, the back door enforcement to help treating chronic constipation in adults. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 17, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassotti, G.; Battaglia, E. Considerations for laxatives in terms of their interactions with other drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment of Constipation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-pharmacological | ||||
| Lifestyle | Diet: More consumption of non-fermentable fibers (consume 20–30 g of dietary fiber per day) | Physical activity: 150 min or more of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week | ||
| Pharmacological | ||||
| Laxatives | Category | Drugs | Mechanism | Evidence |
| Bulk-forming | Methylcellulose, bran, ispaghula/psyllium husk | Enhance stool bulk with soluble fiber | First line recommended. better glycemic control. | |
| Osmotics | Inorganic salts (magnesium compounds) and Organic sugars (lactitol, lactulose) | Generate osmotic gradient with greater water retention in the bowel | Employed for both chronic and occasional constipation | |
| Stimulant | Bisacodyl, senna, sodium picosulfate | Directly stimulate peristalsis and sensory nerve endings | Only in acute for resistant constipation | |
| Others | Drugs | Pharmacokinetics | Mechanism | Evidence |
| Prucalopride | 5-HT4 receptor agonist | Enhances colonic prokinetic activity with activity on 5-HT3 and hERG receptors. | Improvement of constipation in 80% of patients refractory to laxatives | |
| Lubiprostone | Derivative of prostaglandin E1 | Chloride-channel activator: more intestinal fluid secretion, accelerating colonic transit, and softening stool consistency | Improvement of self-reported symptoms of chronic constipation | |
| Linaclotide | Guanylate cyclase-C agonist | Enhances intestinal fluid secretion and transit | Improvement in abdominal symptoms, global measures of constipation, and QoL in 20% of patients | |
| Elobixibat | Selective inhibitor of IBAT | enhanced delivery of BAs to the colon, with colonic contractility, water accumulation, and electrolyte secretion | Only in Japan. Improving frequency of spontaneous bowel movements per week | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Fano, M.; Baluganti, S.; Manco, M.; Porcellati, F.; Fanelli, C.G.; Bassotti, G. The Sweet Side of Constipation: Colonic Motor Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193038
De Fano M, Baluganti S, Manco M, Porcellati F, Fanelli CG, Bassotti G. The Sweet Side of Constipation: Colonic Motor Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193038
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Fano, Michelantonio, Sara Baluganti, Marcello Manco, Francesca Porcellati, Carmine G. Fanelli, and Gabrio Bassotti. 2025. "The Sweet Side of Constipation: Colonic Motor Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193038
APA StyleDe Fano, M., Baluganti, S., Manco, M., Porcellati, F., Fanelli, C. G., & Bassotti, G. (2025). The Sweet Side of Constipation: Colonic Motor Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients, 17(19), 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193038






