The Home as a Modulator of Milk Immunity: Association Between Domestic Factors and Immune Cell Populations in Human Breast Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Milk Sample Collection
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.5.1. Gating Strategy—Phenotype
2.5.2. Gating Strategy—Lactocytes and Stem Cells
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
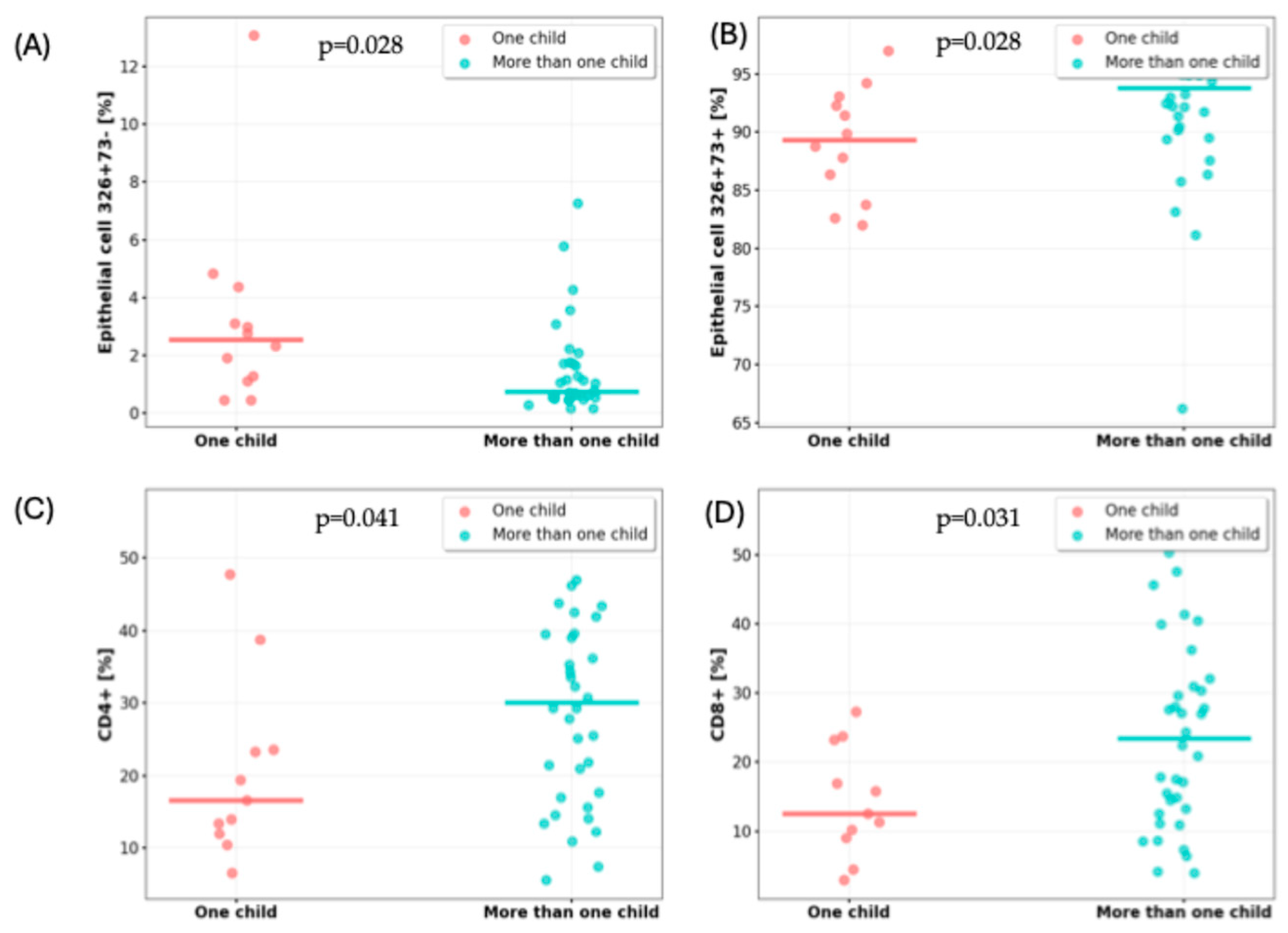
3.2. Impact of Number of Children on Milk Cell Composition
3.3. Impact of Co-Sleeping on Milk Composition
3.4. Impact of Pet Ownership on Milk Cell Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
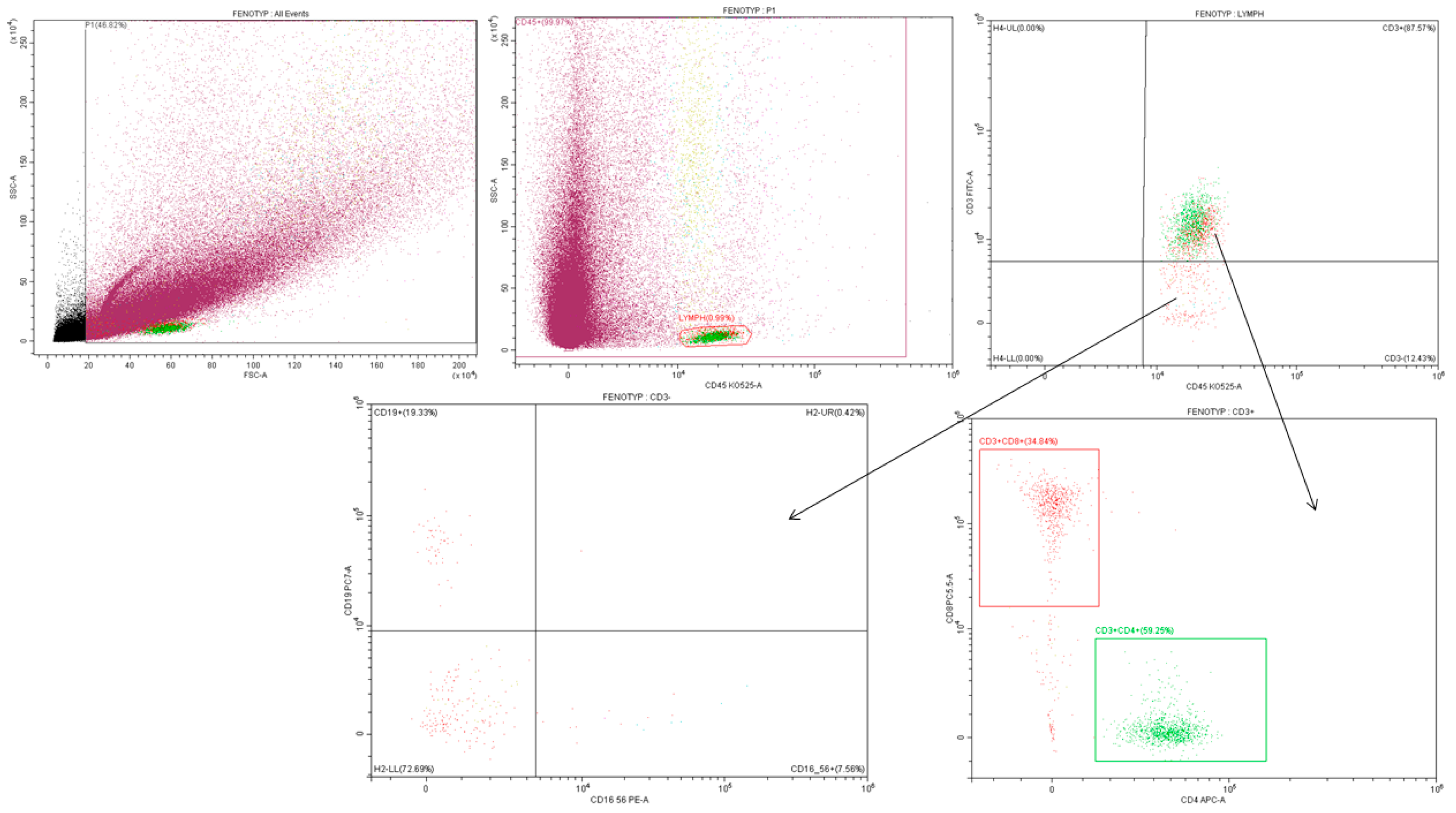
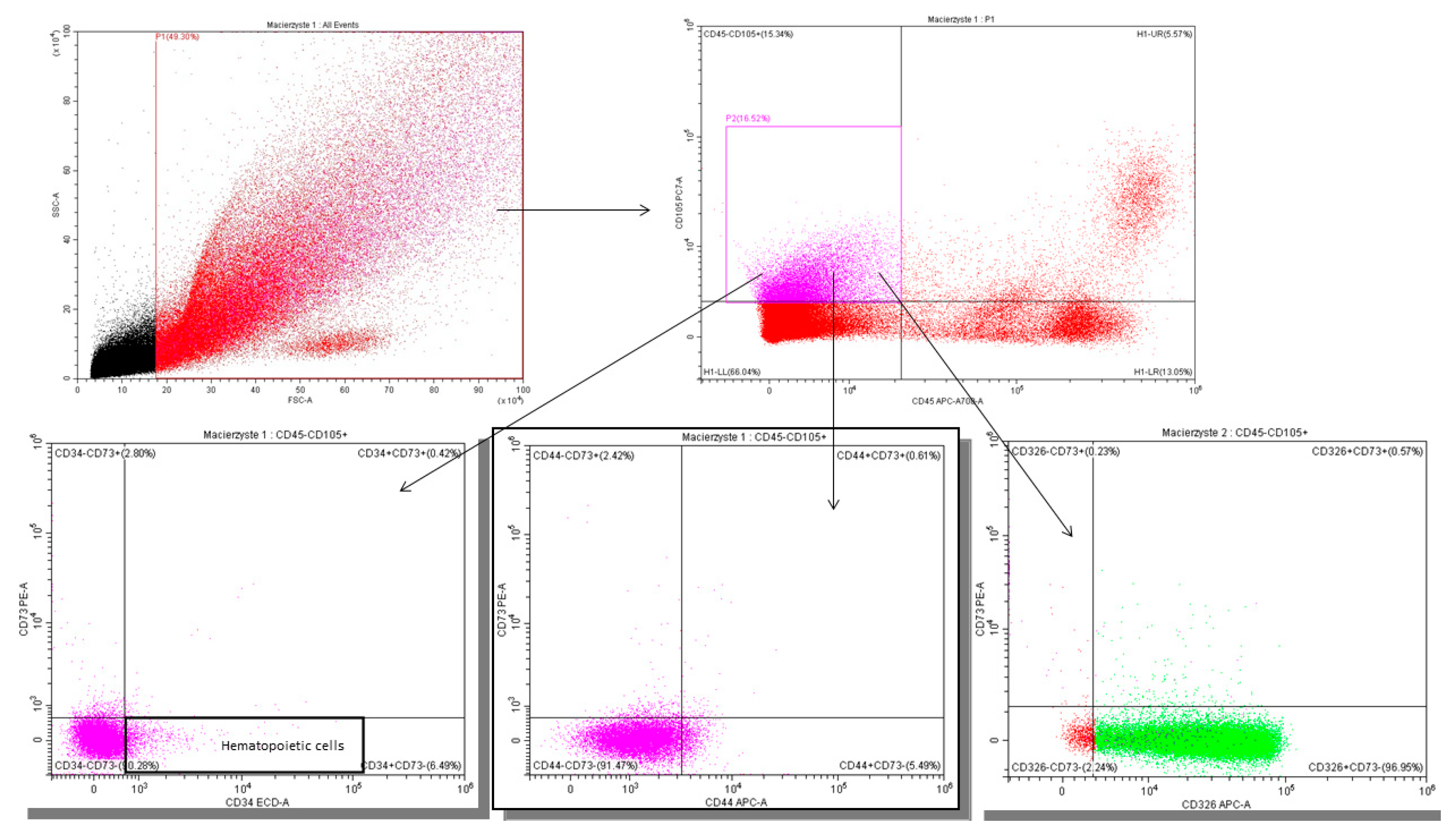
Appendix B
| Variable | One Child (n = 12) | More Than One Child (n = 37) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Age [years]; mean (±SD) | 30.92 (2.81) | 32.65 (3.01) | pSt = 0.085 |
| Gestational age [week]; median (IQR) | 40.0 (39.0–40.0) | 39.0 (39.0–40.0) | pUMW = 0.415 |
| Mode of delivery; n (%) | |||
| Vaginal | 5 (41.7) | 25 (67.6) | Pchi2 = 0.110 |
| Cesarean section | 7 (58.3) | 12 (32.4) | |
| Infant characteristics | |||
| Age [months]; mean (±SD) | 3.83 (1.46) | 3.03 (1.70) | pUMW = 0.149 |
| Birth weight [g]; median (IQR) | 3765 (3340–3995) | 3600 (3340–3800) | pUMW = 0.396 |
| Birth length [cm]; median (IQR) | 55.0 (53.25–58.75) | 55.0 (54.0–56.50) | pUMW = 0.589 |
| Additional feeding with formula milk; n (%) | 8 (66.7) | 11 (29.7) | Pchi2 = 0.022 |
| Breastfeeding initiated <2 h postpartum; n (%) | 7 (58.3) | 33 (89.2) | Pchi2 = 0.016 |
| Variable | Extra Feeding with Formula Milk (n = 19) | No Extra Feeding with Formula Milk (n = 30) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD45-CD105+CD34+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.62 (0.18–0.97) | 0.39 (0.21–1.19) | pUMW = 0.901 |
| CD45-CD105+73+44+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.73 (0.56–1.91) | 1.68 (0.83–2.91) | pUMW = 0.605 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.83 (0.97–3.21) | 0.70 (0.49–1.70) | pUMW = 0.051 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73− [%], median (IQR) | 91.35 (86.15–95.69) | 93.02 (89.56–95.92) | pUMW = 0.333 |
| CD45+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.16 (4.10–6.49) | 5.18 (2.82–14.03) | pUMW = 0.562 |
| CD3+ [%], median (IQR) | 83.09 (75.24–92.03) | 80.58 (62.52–88.79) | pUMW = 0.431 |
| CD4+ [%], mean (±SD) | 27.80 (12.15) | 27.72 (15.36) | pst = 0.493 |
| CD8+ [%], mean (±SD) | 22.39 (12.58) | 21.45 (14.13) | pSt = 0.410 |
| CD16/56+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.82 (3.18–9.82) | 7.64 (4.88–12.73) | pUMW = 0.237 |
| CD19+ [%], median (IQR) | 3.81 (1.71–8.21) | 4.82 (2.52–7.09) | pUMW = 0.406 |
| Variable | Breastfeeding Initiated > 2 h (n = 9) | Breastfeeding Initiated < 2 h (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD45-CD105+CD34+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.63 (0.15–1.42) | 0.45 (0.21–0.99) | pUMW = 0.805 |
| CD45-CD105+73+44+ [%], median (IQR) | 2.11 (0.67–4.92) | 1.68 (0.81–2.01) | pUMW = 0.505 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.25 (0.47–4.01) | 1.10 (0.55–2.24) | pUMW = 0.919 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73− [%], median (IQR) | 90.75 (86.66–95.10) | 93.02 (89.21–95.73) | pUMW = 0.354 |
| CD45+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.34 (4.04–18.14) | 4.80 (3.29–7.95) | pUMW = 0.317 |
| CD3+ [%], median (IQR) | 83.75 (63.44–93.66) | 81.50 (69.55–88.64) | pUMW = 0.449 |
| CD4+ [%], mean (±SD) | 28.00 (16.50) | 27.69 (13.69) | pst = 0.954 |
| CD8+ [%], mean (±SD) | 20.72 (13.56) | 22.08 (13.56) | pSt = 0.788 |
| CD16/56+ [%], median (IQR) | 6.33 (2.93–8.76) | 7.20 (4.39–13.16) | pUMW = 0.344 |
| CD19+ [%], median (IQR) | 4.82 (1.49–22.51) | 4.51 (2.55–6.87) | pUMW = 0.871 |
References
- Carr, L.E.; Virmani, M.D.; Rosa, F.; Munblit, D.; Matazel, K.S.; Elolimy, A.A.; Yeruva, L. Role of Human Milk Bioactives on Infants’ Gut and Immune Health. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 604080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyller, H.; Antosz, K.; Batko, J.; Mytych, A.; Dziedziak, M.; Wrześniewska, M.; Braksator, J.; Pytrus, T. Bioactive Components of Human Milk and Their Impact on Child’s Health and Development, Literature Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisha, S.; Joarder, I.; Wijenayake, S.; McGowan, P.O. Non-nutritive bioactive components in maternal milk and offspring development: A scoping review. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2022, 13, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, B.; Ellsworth, L.; Pavela, G.; Shah, K.; Berger, P.K.; Isganaitis, E.; VanOmen, S.; Demerath, E.W.; Fields, D.A. Bioactive compounds in mothers milk affecting offspring outcomes: A narrative review. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.S.; Hickey, R.M.; Davey, G.P. Interactions of human milk oligosaccharides with the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2025, 15, 1523829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peroni, D.G.; Chirumbolo, S.; Veneri, D.; Piacentini, G.L.; Tenero, L.; Vella, A.; Ortolani, R.; Raffaelli, R.; Boner, A.L. Colostrum derived B and T cells as an extra lymphoid compartment of effector cell populations in humans. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patki, S.; Kadam, S.; Chandra, V.; Bhonde, R. Human breast milk is a rich source of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Hum. Cell 2010, 23, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaingade, P.M.; Somasundaram, I.; Nikam, A.B.; Sarang, S.A.; Patel, J.S. Assessment of growth factors secreted by human breastmilk mesenchymal stem cells. Breastfeed. Med. 2016, 11, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassiotou, F.; Geddes, D.T. Immune cell mediated protection of the mammary gland and the infant during breastfeeding. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Chong, Y.S.; Choolani, M.A.; Cregan, M.D.; Chan, J.K.Y. Unravelling the mystery of stem/progenitor cells in human breast milk. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowska Zimny, M.; Kaminska El Hassan, E. Cells of human breast milk. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twigger, A.J.; Hepworth, A.R.; Tat Lai, C.; Chetwynd, E.; Stuebe, A.M.; Blancafort, P.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Kakulas, F. Gene expression in breastmilk cells is associated with maternal and infant characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.J. The immunological components of human milk and their effect on immune development in infants. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninkina, N.; Kukharsky, M.S.; Hewitt, M.V.; Lysikova, E.A.; Skuratovska, L.N.; Deykin, A.V.; Buchman, V.L. Stem cells in human breast milk. Hum. Cell 2019, 32, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briere, C.E.; Jensen, T.; McGrath, J.M.; Young, E.E.; Finck, C. Stem like cell characteristics from breast milk of mothers with preterm infants as compared to mothers with term infants. Breastfeed. Med. 2017, 12, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enstad, S.; Cheema, S.; Thomas, R.; Fichorova, R.N.; Martin, C.R.; O’Tierney Ginn, P.; Wagner, C.L.; Sen, S. The impact of maternal obesity and breast milk inflammation on developmental programming of infant growth. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Yang, M.; Lee, S.; Behrendt, C.L.; Hooper, L.V.; Saghatelian, A.; Wan, Y. Maternal Western diet causes inflammatory milk and TLR2/4 dependent neonatal toxicity. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, K.M.; Marino, R.C.; Haapala, J.L.; Foster, L.; Smith, K.D.; Teague, A.M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Fontaine, P.L.; McGovern, P.M.; Schoenfuss, T.C.; et al. Associations of maternal weight status before, during, and after pregnancy with inflammatory markers in breast milk. Obesity 2017, 25, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagos, P.G.; Vishwanathan, R.; Penfield Cyr, A.; Matthan, N.R.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Sen, S. Breastmilk from obese mothers has pro inflammatory properties and decreased neuroprotective factors. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.A.; Lefèvre, C.; Watt, A.; Nicholas, K.R. Analysis of human breast milk cells: Gene expression profiles during pregnancy, lactation, involution, and mastitic infection. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio Aige, K.; Azagra Boronat, I.; Castell, M.; Selma Royo, M.; Collado, M.C.; Rodríguez Lagunas, M.J.; Pérez Cano, F.J. The breast milk immunoglobulinome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, G.; Barrera, M.J.; Contreras Duarte, S. The impact of maternal chronic inflammatory conditions on breast milk composition: Possible influence on offspring metabolic programming. Nutrients 2025, 17, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarik, A.R.; Havstad, S.; Levin, A.M.; Lynch, S.V.; Fujimura, K.E.; Ownby, D.R.; Johnson, C.C.; Wegienka, G. Dog introduction alters the home dust microbiota. Indoor Air 2018, 28, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddock, S.A.; Purnell, M.T.; Blair, P.S.; Pease, A.; Elder, D.; Galland, B.C. The influence of bed sharing on infant physiology, breastfeeding and behaviour: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2019, 43, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.D.; Hjelmsø, M.H.; Thorsen, J.; Shah, S.; Redgwell, T.; Poulsen, C.E.; Trivedi, U.; Russel, J.; Gupta, S.; Chawes, B.L.; et al. The developing airway and gut microbiota in early life is influenced by age of older siblings. Microbiome 2022, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, I.; Ferrara, C.; Romano, F.; Loperfido, F.; Sottotetti, F.; El Masri, D.; Vincenti, A.; Cena, H.; De Giuseppe, R. The influence of maternal lifestyle factors on human breast milk microbial composition: A narrative review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Human breast milk composition and function in human health: From nutritional components to microbiome and microRNAs. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Esch, B.C.A.M.; Porbahaie, M.; Abbring, S.; Garssen, J.; Potaczek, D.P.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; van Neerven, R.J.J. The Impact of Milk and Its Components on Epigenetic Programming of Immune Function in Early Life and Beyond: Implications for Allergy and Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, N.; Alashkar Alhamwe, B.; Caraballo, L.; Ding, M.; Ferrante, A.; Garn, H.; Garssen, J.; Hii, C.S.; Irvine, J.; Llinás-Caballero, K.; et al. Perinatal and Early-Life Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Allergy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaweed, M.; Hepworth, A.R.; Lefèvre, C.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Hassiotou, F. Human milk microRNA and total RNA differ depending on milk fractionation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, S.P.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T.; Thompson, L.F. Physiological roles for ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73). Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.; Rivera, R.; Russo, I.H. Influence of age and parity on the development of the human breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1992, 23, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdacka, L.M.; Jakubas, A.; Jagiełło, J.; Daniłowska, K.; Picheta, N.; Gil Kulik, P. Epigenetic and immune mechanisms linking breastfeeding to lower breast cancer rates. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e945451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepicka, P.F.; Somasundara, A.V.H.; dos Santos, C.O. The molecular basis of mammary gland development and epithelial differentiation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 114, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Corrêa Silva, S.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Corrêa de Souza, E.; Macaferri da Fonseca, F.A.; Gilio, A.E.; Carneiro Sampaio, M.; Palmeira, P. Infant respiratory infections modulate lymphocyte homing to breast milk. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1481410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskin, A.; Almog, M.; Peri, R.; Halasz, K.; Srugo, I.; Kessel, A. Changes in immunomodulatory constituents of human milk in response to active infection in the nursing infant. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 71, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, A.; Jeleniewska, A.; Porębska, K.; Królikowska, K.; Rustecka, A.; Lipińska Opałka, A.; Będzichowska, A.; Zdanowski, R.; Aleksandrowicz, K.; Kloc, M.; et al. Immunomodulatory effect of infectious disease of a breastfed child on the cellular composition of breast milk. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, R.L.; Skobic, I.; Pope, B.T.; Zhu, A.; Chamas, H.; Sharma, N.; Larsen, K.M.; Bright, H.S.; Haynes, P.L. Mother infant bed sharing is associated with increased breastfeeding: A systematic review. Breastfeed. Med. 2025, 20, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beghetti, I.; Biagi, E.; Martini, S.; Brigidi, P.; Corvaglia, L.; Aceti, A. Human milk’s hidden gift: Implications of the milk microbiome for preterm infants’ health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shehri, S.S.; Knox, C.L.; Liley, H.G.; Cowley, D.M.; Wright, J.R.; Henman, M.G.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Charles, B.G.; Shaw, P.N.; Sweeney, E.L.; et al. Breastmilk saliva interactions boost innate immunity by regulating the oral microbiome in early infancy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyas, M.; Apanasewicz, A.; Krzystek Korpacka, M.; Jamrozik, N.; Cierniak, A.; Babiszewska Aksamit, M.; Ziomkiewicz, A. The association between maternal stress and human milk concentrations of cortisol and prolactin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 75307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.D.; Adam, E.K.; McKinney, C.O.; Krohn, J.B.; Shalowitz, M.U. Breastfeeding, bed sharing, and maternal cortisol. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 55, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanackovic, D.; Nowottne, U.; Freier, E.; Weber, C.S.; Meyer, S.; Bartels, K.; Hildebrandt, Y.; Cao, Y.; Kröger, N.; Brunner Weinzierl, M.C.; et al. Acute psychological stress increases peripheral blood CD3+CD56+ natural killer T cells in healthy men: Possible implications for the development and treatment of allergic and autoimmune disorders. Stress 2013, 16, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolghanizadeh, S.; Salmeh, E.; Mirzakhani, F.; Soroush, E.; Siadat, S.D.; Tarashi, S. Microbiota insights into pet ownership and human health. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 171, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.C.; Gascon, M.; Osornio Vargas, A.R.; Shier, C.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Azad, M.B.; Sears, M.R.; Lefebvre, D.L.; Moraes, T.J.; et al. Natural environments in the urban context and gut microbiota in infants. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Sarwar, K. The farm like effect: Rural exposures in early life, the microbiome, and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjavainen, P.V.; Karvonen, A.M.; Adams, R.I.; Täubel, M.; Roponen, M.; Tuoresmäki, P.; Loss, G.; Jayaprakash, B.; Depner, M.; Ege, M.J.; et al. Farm like indoor microbiota in non farm homes protects children from asthma development. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langgartner, D.; Weimer, K.; Brunner Weisser, J.; Winkler, R.; Mannes, M.; Huber Lang, M.; Sterrett, J.D.; Lowry, C.A.; Rohleder, N.; Bajrami, B.; et al. Pawsitive impact: How pet contact ameliorates adult inflammatory stress responses in individuals raised in an urban environment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 127, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenot, J.D.; Gavin, M.A.; Rudensky, A.Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Exclusive or predominant breastfeeding | Introduction of solid foods |
| Infant age between 1 and 6 months | Active respiratory infection (mother or child) |
| Gestational age ≥ 38 weeks | Chronic illness in mother or infant |
| Birth weight between the 10th and 90th percentiles | Preterm birth |
| Written informed consent | History of mastitis |
| Lack of informed consent |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |
| Age [years]; mean (±SD) | 32.0 (3.03) |
| Gestational age [week]; median (IQR) | 39.0 (39.0–40.0) |
| Mode of delivery; n (%) | |
| Vaginal | 30 (61) |
| Cesarean section | 19 (39) |
| Infant characteristics | |
| Age [months]; median (IQR) | 3.22 (1.67) |
| Sex; n (%) | |
| Female | 29 (59) |
| Male | 20 (41) |
| Birth weight [g]; median (IQR) | 3650 (3340–3830) |
| Birth length [cm]; median (IQR) | 55.0 (54.0–57.0) |
| Apgar score at 5 min [points]; n (%) | |
| 10 | 46 (96) |
| <10 | 2 (4) |
| Additional feeding with formula milk; n (%) | 19 (39) |
| Breastfeeding initiated <2 h postpartum; n (%) | 40 (82) |
| History of antibiotic therapy; n (%) | 21 (43) |
| Environmental conditions | |
| Siblings; n (%) | 37 (75.5) |
| Co-sleeping; n (%) | 25 (51.0) |
| Pets in the household; n (%) | 12 (24.5) |
| Number of household members; n (%) | |
| 3 | 11 (22.4) |
| 4 | 30 (61.2) |
| ≥5 | 8 (16.3) |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| CD45-CD105+CD34+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.44 (0.20–0.98) |
| CD45-CD105+73+44+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.70 (0.84–2.46) |
| CD45-CD105+326+73+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.11 (0.55–2.43) |
| CD45-CD105+326+73− [%], median (IQR) | 92.34 (88.51–95.69) |
| CD45+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.18 (3.39–8.29) |
| CD3+ [%], median (IQR) | 82.43 (70.57–88.81) |
| CD4+ [%], median (IQR) | 25.53 (14.53–39.45) |
| CD8+ [%], median (IQR) | 17.78 (11.06–29.52) |
| CD16/56+ [%], median (IQR) | 6.84 (3.81–11.34) |
| CD19+ [%], median (IQR) | 4.58 (2.49–7.02) |
| Variable | One Child (n = 12) | More Than One Child (n = 37) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD45-CD105+CD34+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.77 (0.26–1.17) | 0.35 (0.18–0.86) | pUMW = 0.197 |
| CD45-CD105+73+44+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.68 (0.84–2.36) | 1.73 (0.75–2.46) | pUMW = 0.891 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73+ [%], median (IQR) | 2.54 (1.14–4.04) | 0.73 (0.53–1.71) | pUMW = 0.028 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73− [%], median (IQR) | 89.29 (84.38–92.85) | 93.79 (89.96–96.23) | pUMW = 0.028 |
| CD45+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.34 (5.06–8.24) | 4.44 (3.00–8.90) | pUMW = 0.449 |
| CD3+ [%], median (IQR) | 75.57 (66.24–83.75) | 85.46 (71.04–90.60) | pUMW = 0.165 |
| CD4+ [%], mean (±SD) | 20.51 (12.53) | 29.97 (13.93) | pst = 0.047 |
| CD8+ [%], mean (±SD) | 14.26 (7.93) | 24.13 (13.98) | pSt = 0.031 |
| CD16/56+ [%], median (IQR) | 6.33 (2.06–13.04) | 6.85 (4.02–11.07) | pUMW = 0.911 |
| CD19+ [%], median (IQR) | 6.60 (3.15–17.40) | 4.28 (2.27–5.84) | pUMW = 0.173 |
| Variable | Co-Sleeping (+) (n = 25) | Co-Sleeping (−) (n = 24) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD45-CD105+CD34+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.55 (0.20–1.13) | 0.35 (0.20–0.82) | pUMW = 0.317 |
| CD45-CD105+73+44+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.85 (0.95–3.57) | 1.52 (0.50–1.99) | pUMW = 0.062 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.75 (0.54–2.98) | 1.12 (0.60–2.32) | pUMW = 0.904 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73− [%], median (IQR) | 90.13 (87.53–93.19) | 94.85 (91.32–96.26) | pUMW = 0.055 |
| CD45+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.18 (3.48–8.82) | 5.16 (3.14–6.96) | pUMW = 0.639 |
| CD3+ [%], median (IQR) | 75.25 (62.52–86.74) | 84.99 (79.41–91.85) | pUMW = 0.021 |
| CD4+ [%], mean (±SD) | 27.28 (14.04) | 28.17 (14.38) | pst = 0.833 |
| CD8+ [%], mean (±SD) | 19.46 (11.20) | 23.88 (15.04) | pSt = 0.264 |
| CD16/56+ [%], median (IQR) | 6.87 (4.43–13.47) | 6.25 (3.75–9.93) | pUMW = 0.482 |
| CD19+ [%], median (IQR) | 4.81 (2.30–7.00) | 4.51 (2.43–7.05) | pUMW = 0.932 |
| Variable | Pets (+) (n = 12) | Pets (−) (n = 37) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD45-CD105+CD34+ [%], median (IQR) | 0.20 (0.12–0.80) | 0.47 (0.29–1.02) | pUMW = 0.127 |
| CD45-CD105+73+44+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.64 (0.66–2.36) | 1.73 (0.81–2.46) | pUMW = 0.608 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73+ [%], median (IQR) | 1.07 (0.62–3.95) | 1.13 (0.53–2.11) | pUMW = 0.453 |
| CD45-CD105+326+73− [%], median (IQR) | 93.62 (86.61–97.01) | 92.23 (89.21–95.41) | pUMW = 0.881 |
| CD45+ [%], median (IQR) | 5.18 (2.39–8.98) | 5.15 (3.96–8.18) | pUMW = 0.931 |
| CD3+ [%], median (IQR) | 76.99 (61.84–84.08) | 84.55 (72.91–89.50) | pUMW = 0.378 |
| CD4+ [%], mean (±SD) | 1.98 (14.00) | 29.52 (13.81) | pst = 0.121 |
| CD8+ [%], median (IQR) | 14.39 (7.22–17.11) | 23.73 (12.50–30.70) | pUMW = 0.048 |
| CD16/56+ [%], median (IQR) | 9.22 (1.59–11.34) | 6.39 (4.71–11.10) | pUMW = 0.951 |
| CD19+ [%], median (IQR) | 4.58 (2.81–7.19) | 4.59 (2.23–6.97) | pUMW = 0.701 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomaszewska, A.; Porębska, K.; Jeleniewska, A.; Królikowska, K.; Lipińska-Opałka, A.; Gościńska, A.; Zdanowski, R.; Pogonowska, M.; Kalicki, B. The Home as a Modulator of Milk Immunity: Association Between Domestic Factors and Immune Cell Populations in Human Breast Milk. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152574
Tomaszewska A, Porębska K, Jeleniewska A, Królikowska K, Lipińska-Opałka A, Gościńska A, Zdanowski R, Pogonowska M, Kalicki B. The Home as a Modulator of Milk Immunity: Association Between Domestic Factors and Immune Cell Populations in Human Breast Milk. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152574
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomaszewska, Agata, Klaudia Porębska, Alicja Jeleniewska, Katarzyna Królikowska, Agnieszka Lipińska-Opałka, Agnieszka Gościńska, Robert Zdanowski, Milena Pogonowska, and Bolesław Kalicki. 2025. "The Home as a Modulator of Milk Immunity: Association Between Domestic Factors and Immune Cell Populations in Human Breast Milk" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152574
APA StyleTomaszewska, A., Porębska, K., Jeleniewska, A., Królikowska, K., Lipińska-Opałka, A., Gościńska, A., Zdanowski, R., Pogonowska, M., & Kalicki, B. (2025). The Home as a Modulator of Milk Immunity: Association Between Domestic Factors and Immune Cell Populations in Human Breast Milk. Nutrients, 17(15), 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152574








