Flavonoid Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Damage via Activating the MyD88-Mediated Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation and Component Analysis of SSF
2.3. Analysis of Blood-Entering Components
2.4. Network Pharmacology Analysis
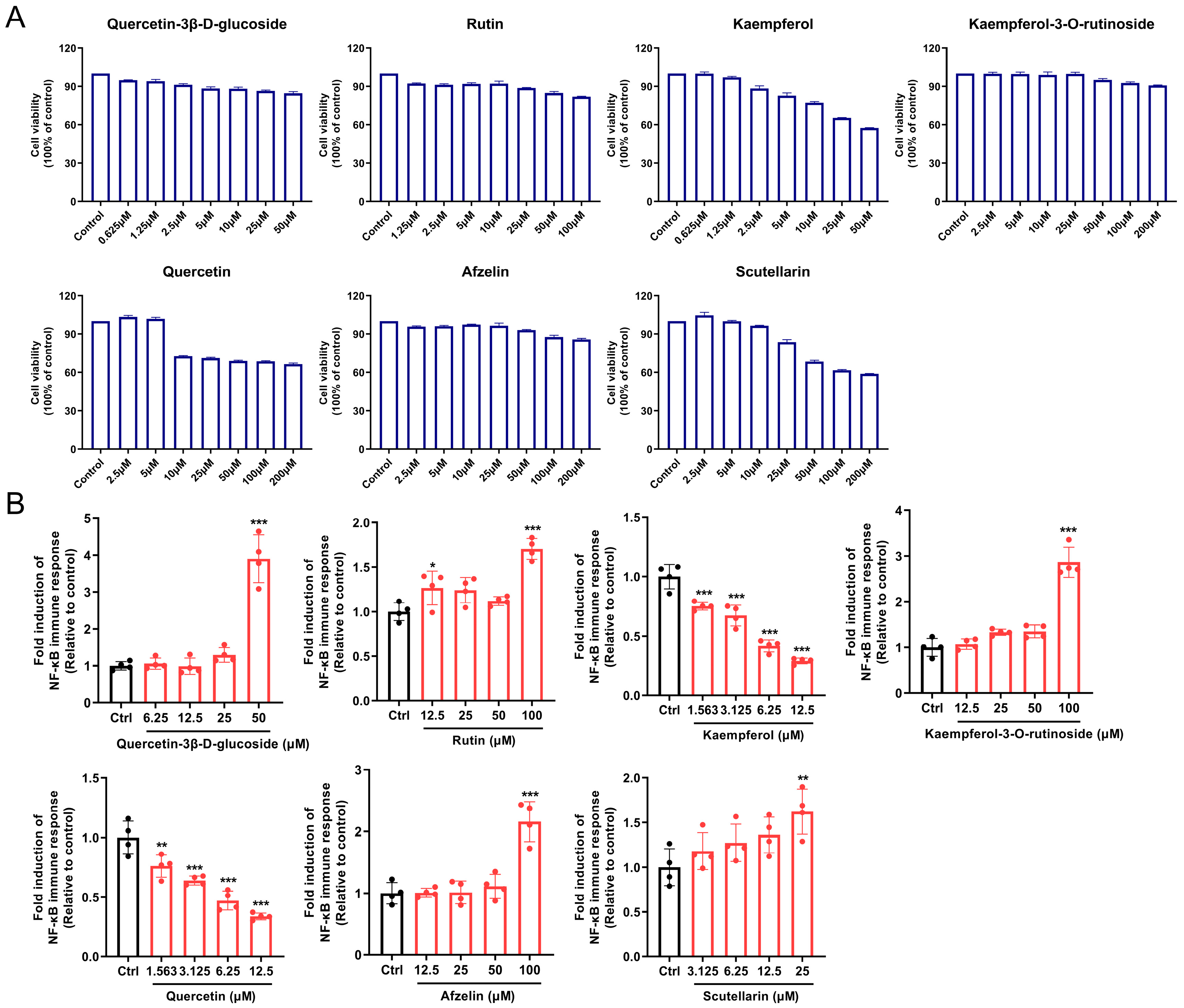
2.5. NF-κB Luciferase Activity Assay
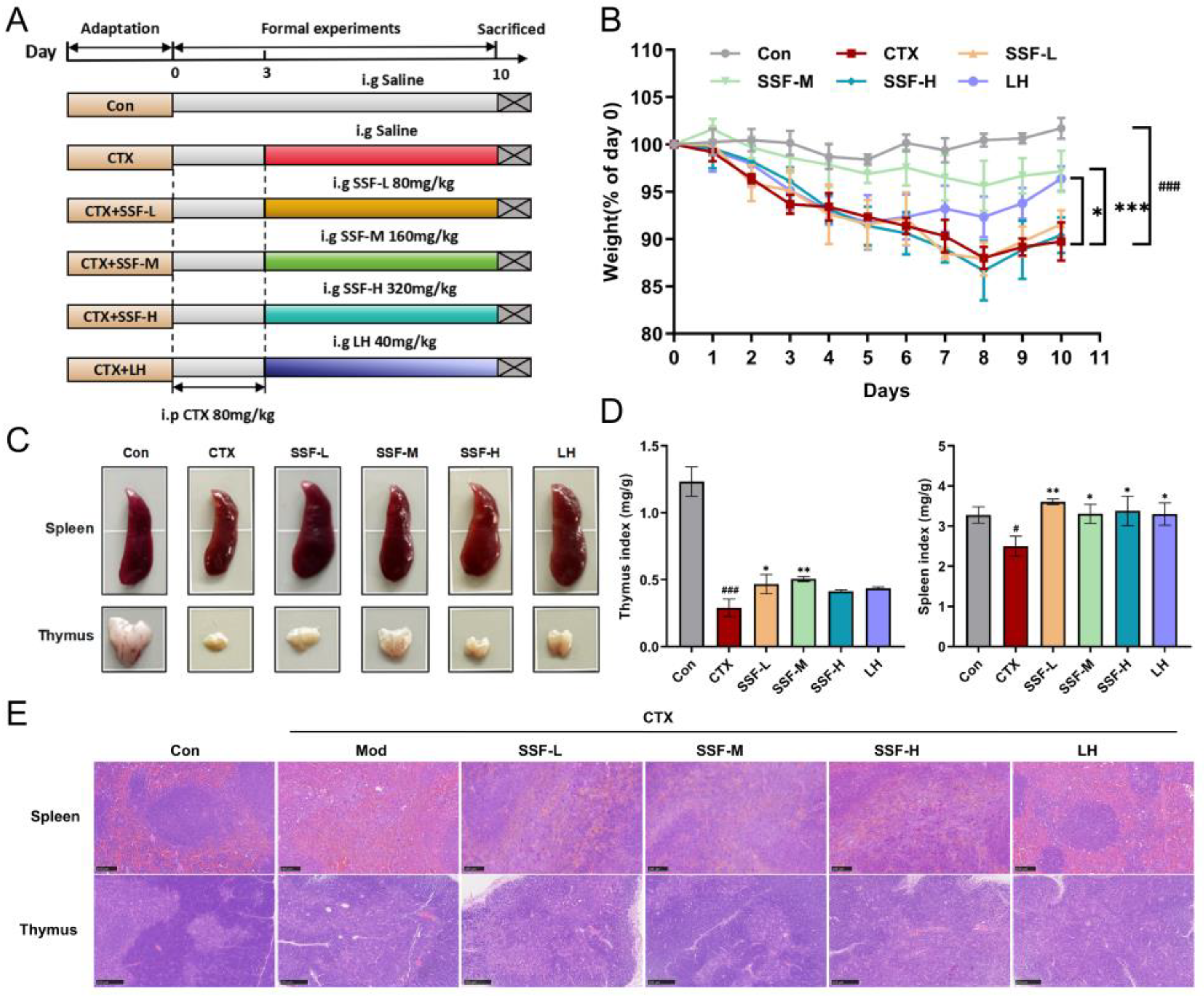
2.6. Experimental Design for Animal Studies
2.7. Body Weight and Immune Organ Indices
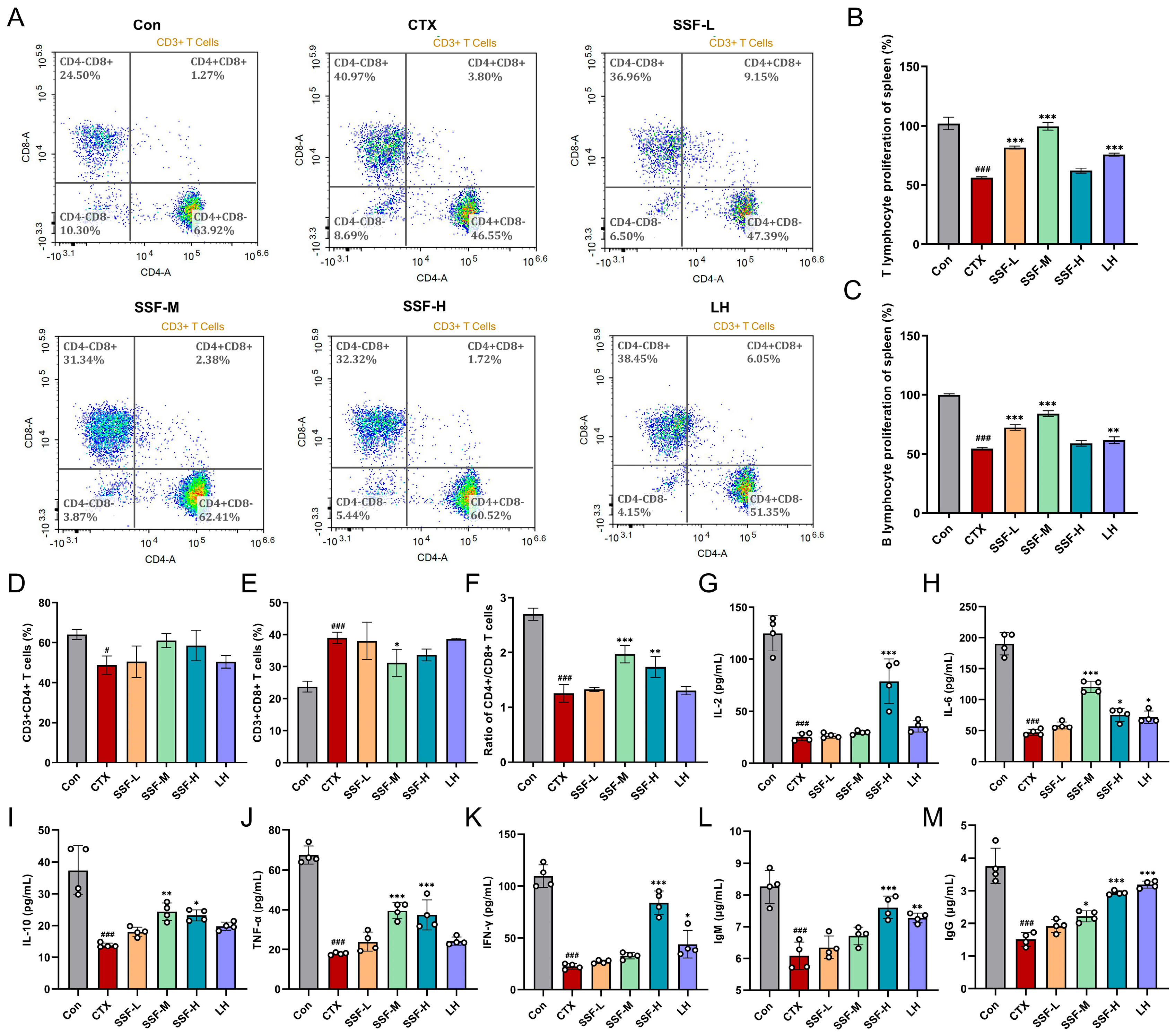
2.8. Splenic Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Detection of Serum Cytokines and Immunoglobulins
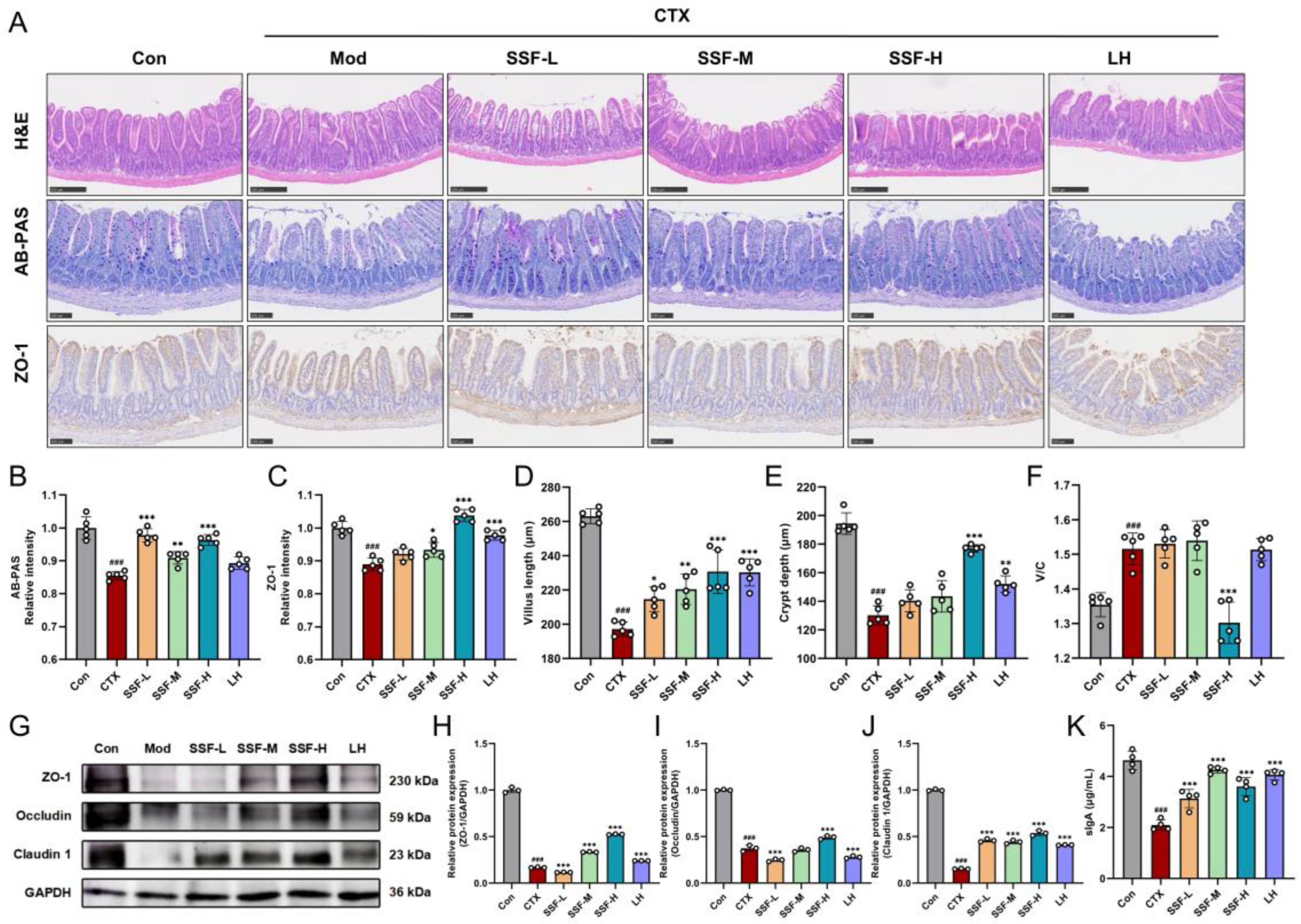
2.11. H&E and AB-PAS Staining
2.12. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis
2.13. Western Blot Analysis
2.14. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition Analysis of SSF In Vitro and In Vivo
3.2. SSF Attenuates CTX-Induced Weight Loss and Protects Immune Organ Damage in Mice
3.3. SSF Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immune Dysfunction
3.4. SSF Restores Intestinal Barrier Integrity in CTX-Treated Mice
3.5. SSF Reshapes the Composition of Gut Microbiota
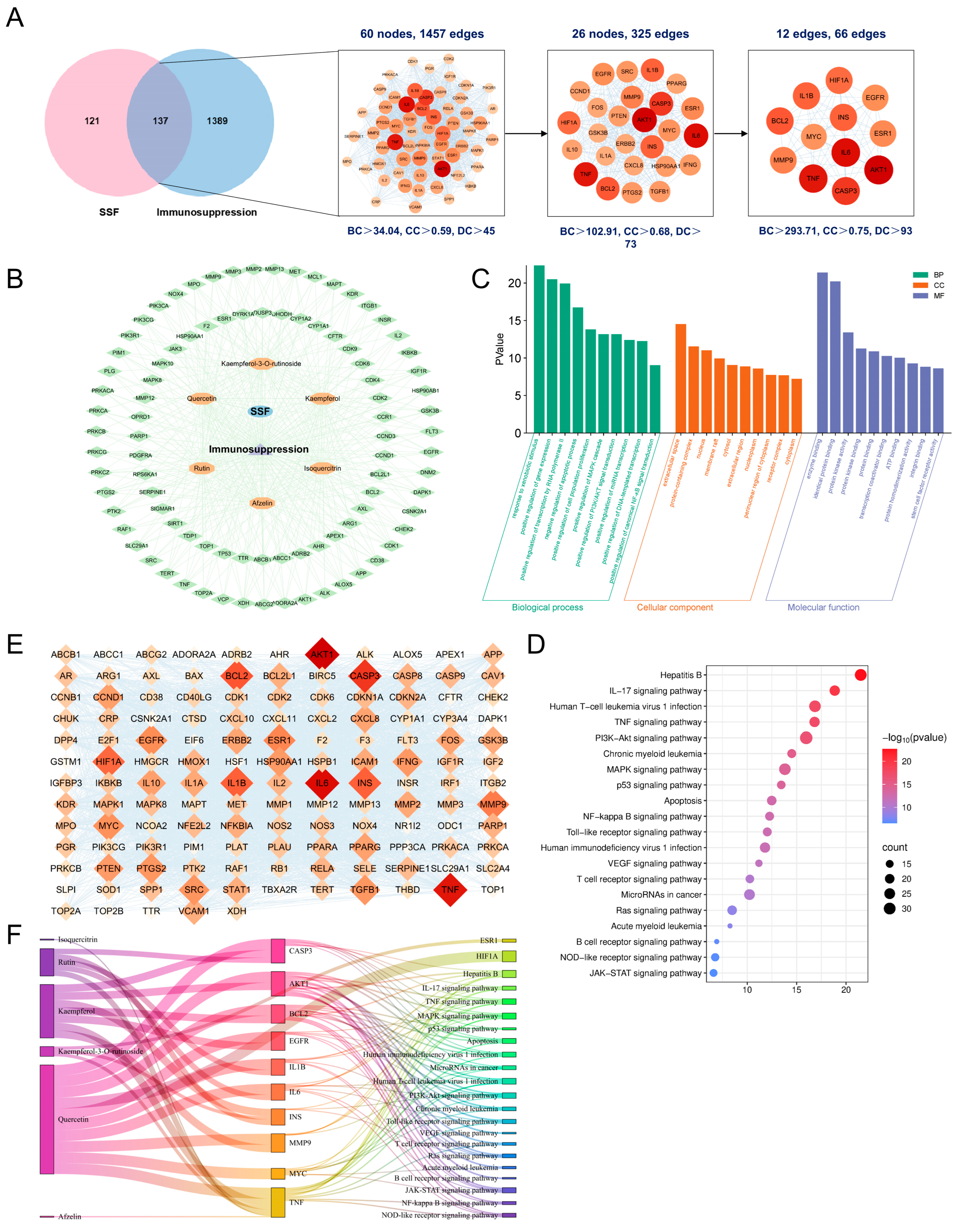
3.6. Network Pharmacology Analysis of SSF in Immunosuppression
3.7. SSF Enhances Immune Response by Activating the TLR/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
3.8. Screening and Evaluation of Potential Active Components in SSF
4. Discussion
4.1. SSF Alleviates CTX-Induced Systemic Immunosuppression
4.2. SSF Ameliorates CTX-Induced Intestinal Barrier Damage
4.3. SSF Restores Gut Microbiota Homeostasis and Mediates Immune Regulation
4.4. SSF Activates the TLR/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway: Molecular Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parkin, J.; Cohen, B. An Overview of the Immune System. Lancet 2001, 357, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.W.; Wheless, W.; Vrochides, D. Management of Long-Term Complications from Immunosuppression. Liver Transpl. 2024, 30, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinson, M.L.; Lapham, J. Prevalence of Immunosuppression among US Adults. JAMA 2024, 331, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delahousse, J.; Molina, L.; Paci, A. Cyclophosphamide and Analogues; a Matter of Dose and Schedule for Dual Anticancer Activities. Cancer Lett. 2024, 598, 217119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Duan, S.S.; Li, Y.P.; Pan, X.; Han, L.R. Polysaccharides in Natural Products That Repair the Damage to Intestinal Mucosa Caused by Cyclophosphamide and Their Mechanisms: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, M.Y.; Ji, J.J.; Gao, J.P.; Li, J.K. An Inulin-Type Fructan from Codonopsis pilosula Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Barrier Injury in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310 Pt 1, 143312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Tu, J.; Tang, M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Nabavi, N.; Sethi, G.; Zhao, P.Q.; Liu, S.J. Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy: Historical Perspectives, Current Developments, and Future Directions. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.N.; Deng, Y.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, P. Gut Microbiome and Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 447, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobels, A.; van Marcke, C.; Jordan, B.F.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. The Gut Microbiome and Cancer: From Tumorigenesis to Therapy. Nat. Metab. 2025, 7, 895–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigoli, S.; Boskabady, M.H. The Molecular Basis of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Huang, L.F.; Chen, S.L. Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham.: A Review on Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, H.; Jiang, X.; Ou, Q.; Gan, Z.; Han, F.; Cai, Y. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, Cell Communication, and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Potential Mechanism of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Inhibition. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Mai, K.; Xu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Su, N.; Ye, C. Effects of Dietary Senecio scandens Buch-Ham Extracts on Growth Performance, Plasma Biochemical, Histology and the Expression of Immune-Related Genes in Hybrid Grouper (Epinephelus Lanceolatus♂ × Epinephelus Fuscoguttatus♀). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Q.; Xie, S.S.; Zhou, M.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhou, F.M.; Ding, Z.S.; Ye, X.Q. Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Polysaccharides Exert Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects by Modulating Gut Microbiota and the Mapk/Nf-Κb Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1573135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, W.; Su, W. Extraction, Partial Characterization and Bioactivity of Polysaccharides from Senecio Scandens Buch.-Ham. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Neta, M.T.S.L.; Sathiyabama, R.G.; Quintans, J.D.S.; Silva, A.M.D.E.; Araujo, A.A.D.; Narain, N.; Quintans, L.J.J.; Gurgel, R.Q. Flavonoids as Th1/Th2 Cytokines Immunomodulators: A Systematic Review of Studies on Animal Models. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Z.N.; Zhu, G.X. Immunological Regulatory Effect of Flavonoid Baicalin on Innate Immune Toll-Like Receptors. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.Y. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunoregulatory Effects of Icariin and Icaritin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ni, X.; Wu, S.; Fang, Y.; Hao, Z. The Acute Oral Toxicity Test of Ethanol Extract of Salt-Processed Psoraleae Fructus and Its Acute Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity Risk Assessment. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, K.R.; Xu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, M.J.; Zhu, C.C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Integrating Serum Pharmacochemistry, Network Pharmacology, Metabolomics and 16s Rrna Sequencing to Explore the Mechanism of Total Flavonoids from Flemingia philippinensis in Treating Collagen Induced Arthritis Rats. Phytomedicine 2025, 139, 156531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Hou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Su, H.; Koci, M.D.; Yin, H.; Zhang, C. Nf-Κb Activation Enhances Sting Signaling by Altering Microtubule-Mediated Sting Trafficking. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Gui, F.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, H.; Bi, S.; Cao, L. Danggui Buxue Decoction Regulates the Immune Function and Intestinal Microbiota of Cyclophosphamide Induced Immunosuppressed Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1420411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Floyd, K.; Wu, S.; Fang, Z.; Tan, T.K.; Froggatt, H.M.; Powers, J.M.; Leist, S.R.; Gully, K.L.; Hubbard, M.L.; et al. Bcg Vaccination Stimulates Integrated Organ Immunity by Feedback of the Adaptive Immune Response to Imprint Prolonged Innate Antiviral Resistance. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jo, S.; Cho, M.J.; Cho, Y.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Byun, S. Immunomodulatory Functional Foods and Their Molecular Mechanisms. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, A.Z.; Fang, L.X.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Qi, M.; Kang, H.; Yang, L.; Tsim, K.W.K.; Wang, Z. An Application of Target Profiling Analyses in the Hepatotoxicity Assessment of Herbal Medicines: Comparative Characteristic Fingerprint and Bile Acid Profiling of Senecio vulgaris L. and Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7715–7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, R.S.; Liu, X.C.; Bolling, B. Flavonoids and Gut Health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, N.; Singh, M.; Sangwan, R.S. Flavonoids: Food Associations, Therapeutic Mechanisms, Metabolism and Nanoformulations. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, A.S.M.A.; Nasrin, S.; Hossen, A.; Rahman, A.; Jantan, I.; Haque, M.A.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Mechanistic Insight into Immunomodulatory Effects of Food-Functioned Plant Secondary Metabolites. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5546–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hao, N.; Zou, S.P.; Meng, T.T.; Tao, H.Q.; Ming, P.F.; Li, M.M.; Ding, H.Y.; Li, J.C.; Feng, S.B.; et al. Immune Regulation of Raw264.7 Cells In Vitro by Flavonoids from Astragalus complanatus Via Activating the Nf-Κb Signalling Pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7948068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.N.; Xie, H.Q.; Cui, S.Y.; Li, X.T.; Lang, M.Z.; Liu, M.M.; Shi, L.E. Immunomodulatory Effects of Sanghuangporus Flavonoids: Key Insights into Enhancing Immunity and Restoring Immune Function. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 153, 114474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. Protective Effect of Rutin on Humoral and Cell Mediated Immunity in Rat Model. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Shi, Z.Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, F.S. Kaempferol Remodels Liver Monocyte Populations and Treats Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Flora and Metabolic Reprogramming. Inflammation 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.Y.; Han, C.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.N.; Liu, H.N.; Yin, Y.L. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, G.; Badruddeen; Akhtar, J.; Singh, B.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.I. An Outlook on the Target-Based Molecular Mechanism of Phytoconstituents as Immunomodulators. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 5058–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, V.; Pittet, M.J. The Spleen in Local and Systemic Regulation of Immunity. Immunity 2013, 39, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Shi, X.F.; Lu, X.Q.; Zhao, X.P.; Yu, Y.M.; Fang, Y.S.; Wang, D.Y. Rehmannia glutinosa Polysaccharides Alleviate Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression by Enhancing Immunity and Restoring Intestinal Homeostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311 Pt 1, 143692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, D.D. Overview of the Immune Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S3–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundling, C.; Lau, A.W.Y.; Bourne, K.; Young, C.; Laurianto, C.; Hermes, J.R.; Menzies, R.J.; Butt, D.; Kräutler, N.J.; Zahra, D.; et al. Positive Selection of Igg+ over Igm+ B Cells in the Germinal Center Reaction. Immunity 2021, 54, 988–1001.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Fan, M.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liang, Z.G.; Zhang, L.C.; Gao, X.; He, X.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, D.Q.; et al. Prevention Effect of Total Ginsenosides and Ginseng Extract from Panax Ginseng on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression in Mice. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 3583–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Zheng, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.B.; Cao, L.; Gan, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.T. Immuno-Stimulatory Activity of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed Mice by Regulating Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242 Pt 2, 124789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Artis, D.; Becker, C. The Intestinal Barrier: A Pivotal Role in Health, Inflammation, and Cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 10, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Guo, J.; Qin, Y.; Huang, W.; You, Y.; Zhan, J. Dietary Regulation of the Siga-Gut Microbiota Interaction. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6379–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; Gan, Z.; Liu, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota Bridges Dietary Nutrients and Host Immunity. Sci. China-Life Sci. 2023, 66, 2466–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, M.; He, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Gut Microbiota Influence Immunotherapy Responses: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Li, Z.; Xue, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, T.; Liu, R.; Sui, W.; Zhang, M. Lactobacillus acidophilus La85 Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression by Modulating Notch and Tlr4/Nf-Κb Signal Pathways and Remodeling the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 8107–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.X.; Huang, D.C.; Qi, G.H.; Chen, G.T. Ginger Polysaccharides Enhance Intestinal Immunity by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppressed Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223 Pt A, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Liu, R.; Xu, T.; Cai, M.; Mao, R.; Huang, L.; Yang, K.; Zeng, X.; Peilong, S. Modulating Effects of Hericium erinaceus Polysaccharides on the Immune Response by Regulating Gut Microbiota in Cyclophosphamide-Treated Mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 3050–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Depommier, C.; Derrien, M.; Everard, A.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia Muciniphila: Paradigm for Next-Generation Beneficial Microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; Cassilly, C.D.; Liu, X.; Park, S.M.; Tusi, B.K.; Chen, X.; Kwon, J.; Filipcik, P.; Bolze, A.S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila Phospholipid Induces Homeostatic Immune Responses. Nature 2022, 608, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xiaojia, L.; Wei, Z.; Jian, Z.; Aiting, W.; Jing, W.; Lin, Y.; Bangwei, C.; Dan, Y. Baicalin Circumvents Anti-Pd-1 Resistance by Regulating the Gut Microbiota Metabolite Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; et al. Desulfovibrio vulgaris Interacts with Novel Gut Epithelial Immune Receptor Lrrc19 and Exacerbates Colitis. Microbiome 2024, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qin, H.; Liang, L.; Fang, J.; Hao, K.; Song, Y.; Sun, T.; Hui, G.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Y. Yam Protein Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Intestinal Immunosuppression by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279 Pt 4, 135415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, S. Network Pharmacology: Towards the Artificial Intelligence-Based Precision Traditional Chinese Medicine. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 25, bbad518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Nf-Κb in Immunobiology. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, K.A.; Vallez, C.N.; Meibers, H.E.; Pasare, C. Bidirectional Communication between the Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2025, 43, 489–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.Y.; Niu, H.Z.; Li, H.; Wu, W. Ginsenosides Modulate Immunity Via Tlr4/Myd88/Nf-Κb Pathway and Gut Microbiota. Phytomedicine 2025, 142, 156763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.W.; Liu, X.C.; Quan, C.X.; Tao, X.Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, X.F.; Peng, X.R.; Qiu, M.H. Novel Galactose-Rich Polysaccharide from Ganoderma Lucidum: Structural Characterization and Immunomodulatory Activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 362, 123695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentova, K.; Sima, P.; Rybkova, Z.; Krizan, J.; Malachova, K.; Kren, V. (Anti)Mutagenic and Immunomodulatory Properties of Quercetin Glycosides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 96, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
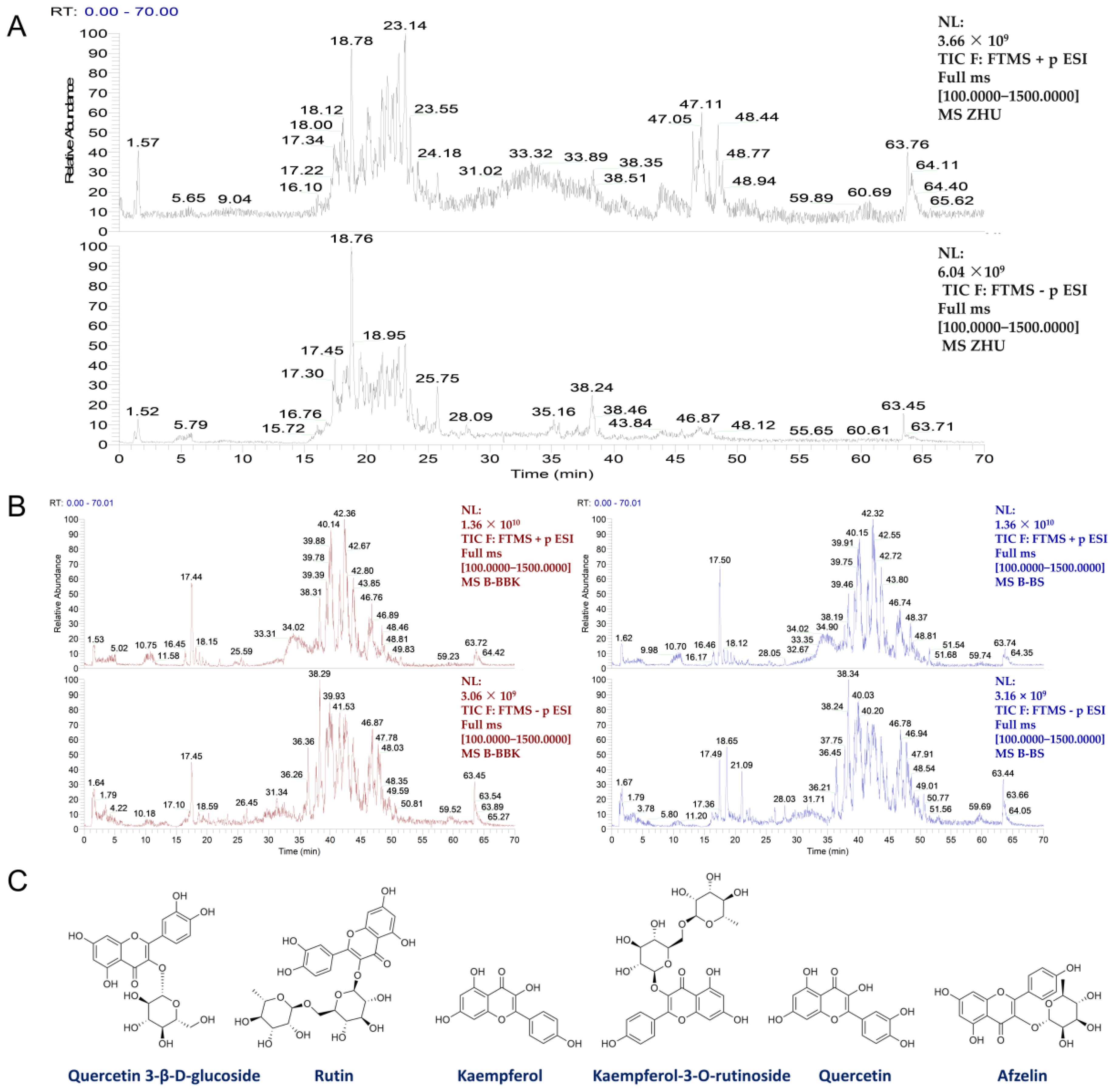


| Number | Name | Formula | Annot. Delta Mass [ppm] | Calc. MW | m/z | RT [min] | Reference Ion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quercetin | C15 H10 O7 | 0.19 | 302.04271 | 303.04999 | 21.644 | [M+H]+1 |
| 2 | Isoquercitrin | C21 H20 O12 | 0.4 | 464.09566 | 463.0882 | 21.645 | [M−H]-1 |
| 3 | Rutin | C27 H30 O16 | −0.02 | 610.15337 | 609.14587 | 21.298 | [M−H]-1 |
| 4 | Kaempferol | C15 H10 O6 | 0.66 | 286.04793 | 287.05521 | 23.558 | [M+H]+1 |
| 5 | Astragalin | C21 H20 O11 | 0.09 | 448.1006 | 447.09308 | 22.548 | [M−H]-1 |
| 6 | Afzelin | C21 H20 O10 | −0.15 | 432.10558 | 431.09818 | 23.559 | [M−H]-1 |
| 7 | Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside | C27 H30 O15 | 0.58 | 594.15882 | 593.15131 | 22.051 | [M−H]-1 |
| 8 | Kaempferitrin | C27 H30 O14 | −0.05 | 578.16353 | 577.15625 | 21.841 | [M−H]-1 |
| 9 | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one | C15 H10 O4 | 0.48 | 254.05803 | 255.06531 | 22.626 | [M+H]+1 |
| 10 | Quercetin-3-O-beta-glucopyranosyl-6′-acetate | C23 H22 O13 | 0.28 | 506.10618 | 505.09891 | 22.114 | [M−H]-1 |
| 11 | Apigenin 7-O-glucuronide | C21 H18 O11 | 1.31 | 446.0855 | 447.09293 | 22.816 | [M+H]+1 |
| 12 | Vicenin III | C26 H28 O14 | 0.77 | 564.14834 | 565.15588 | 20.303 | [M+H]+1 |
| 13 | Daidzein | C15 H10 O4 | 0.55 | 254.05805 | 255.06531 | 23.127 | [M+H]+1 |
| 14 | Engeletin | C21 H22 O10 | −0.37 | 434.12114 | 433.11386 | 22.862 | [M−H]-1 |
| 15 | Eriodictyol | C15 H12 O6 | 0.25 | 288.06346 | 287.05606 | 24.94 | [M−H]-1 |
| 16 | Luteolin | C15 H10 O6 | −0.41 | 286.04762 | 285.04034 | 25.48 | [M−H]-1 |
| 17 | Astilbin | C21 H22 O11 | 0.37 | 450.11638 | 449.1091 | 21.898 | [M−H]-1 |
| 18 | 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one | C15 H10 O5 | 0.06 | 270.05284 | 271.06018 | 27.284 | [M+H]+1 |
| 19 | Naringenin | C15 H12 O5 | −0.12 | 272.06844 | 271.0611 | 26.919 | [M−H]-1 |
| 20 | Didymin | C28 H34 O14 | 0.44 | 594.19512 | 595.20239 | 20.432 | [M+H]+1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ni, X.; Guo, J.; Fang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hao, Z. Flavonoid Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Damage via Activating the MyD88-Mediated Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152540
Zhu X, Zhang L, Ni X, Guo J, Fang Y, Xu J, Chen Z, Hao Z. Flavonoid Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Damage via Activating the MyD88-Mediated Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152540
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaolin, Lulu Zhang, Xuan Ni, Jian Guo, Yizhuo Fang, Jianghan Xu, Zhuo Chen, and Zhihui Hao. 2025. "Flavonoid Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Damage via Activating the MyD88-Mediated Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152540
APA StyleZhu, X., Zhang, L., Ni, X., Guo, J., Fang, Y., Xu, J., Chen, Z., & Hao, Z. (2025). Flavonoid Extract of Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham. Ameliorates CTX-Induced Immunosuppression and Intestinal Damage via Activating the MyD88-Mediated Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway. Nutrients, 17(15), 2540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152540






