Molecular Mechanisms of the Melatonin Receptor Pathway Linking Circadian Rhythm to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Melatonin and Its Receptors
3. Melatonin Signaling Pathways in T2DM
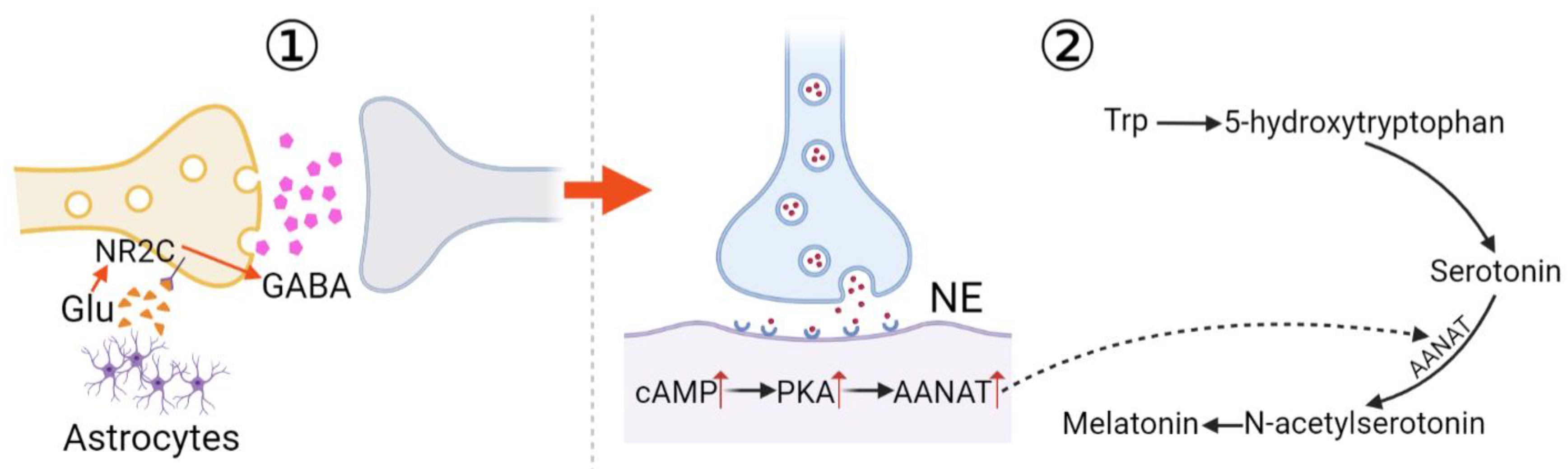
3.1. cAMP Pathway
3.2. cGMP Pathway
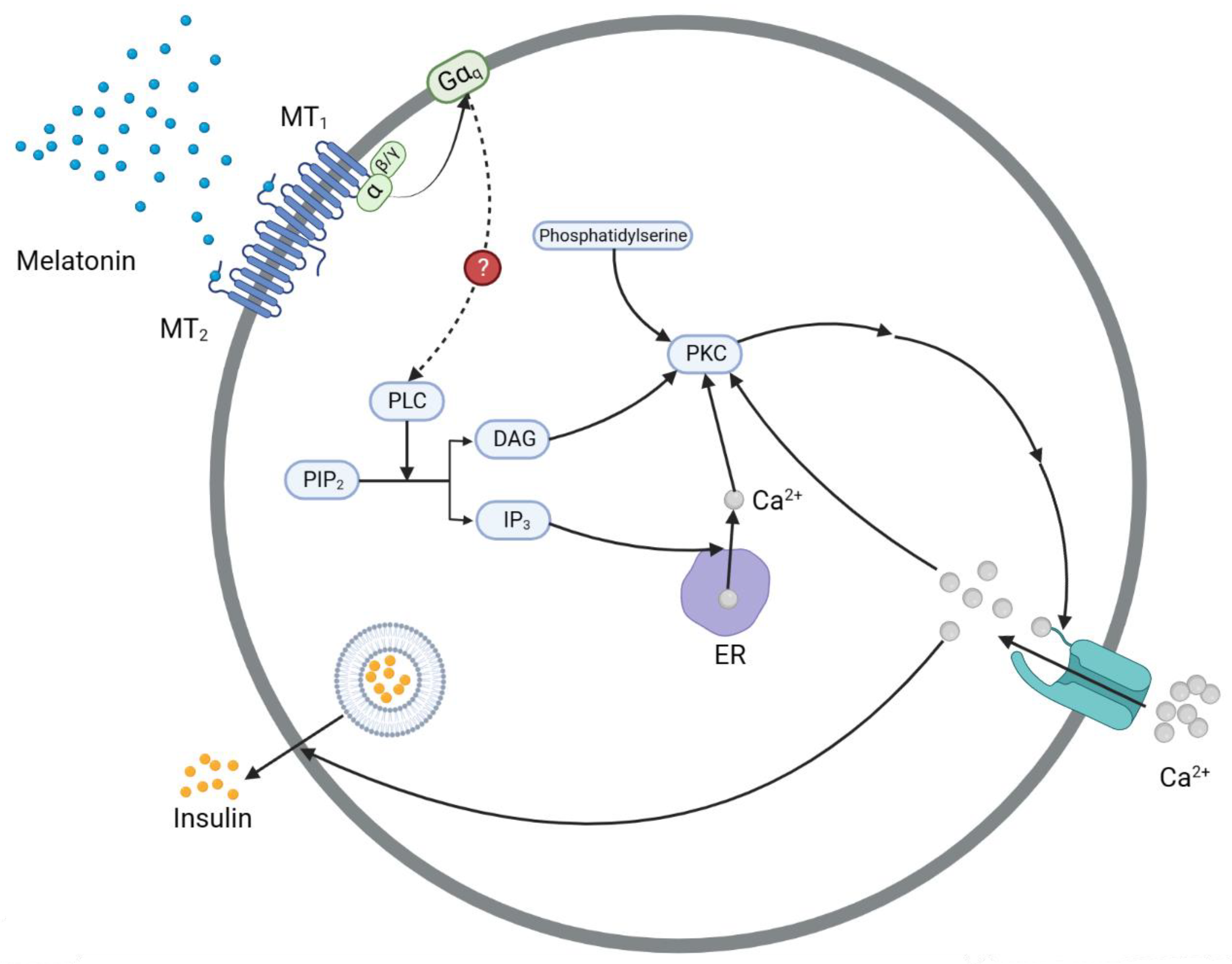
3.3. The IP3 Pathway
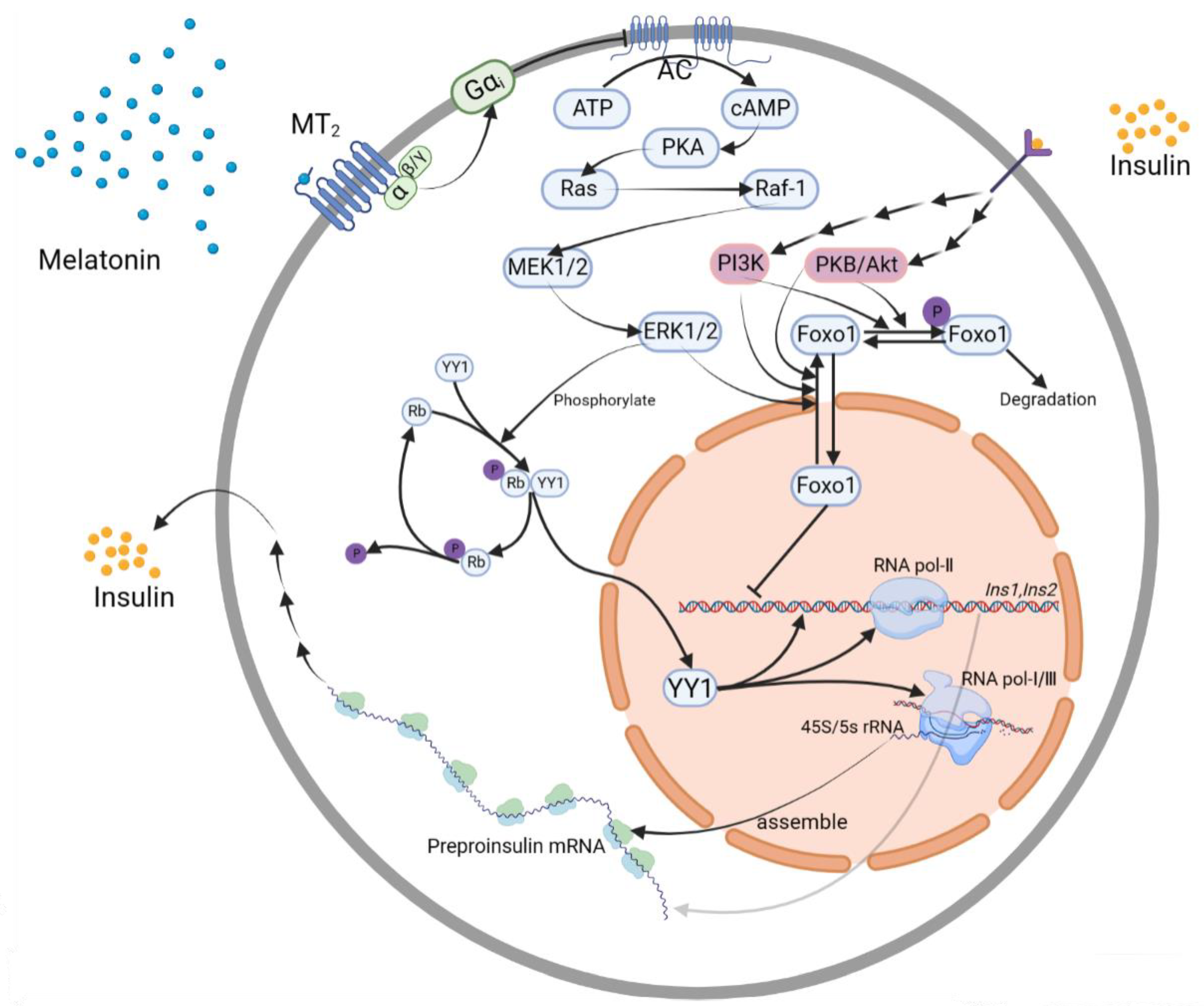
3.4. Transcription Factor Controlling Pathways
3.4.1. YY1
YY1→Ins1, Ins2 Gene
ERK1/2→YY1
3.4.2. Foxo1
ERK1/2→Foxo1→Ins2 Gene
Insulin Receptor→PI3K or PKB/Akt→Foxo1→Ins2 Gene
4. Regulation of MTNR1B Expression
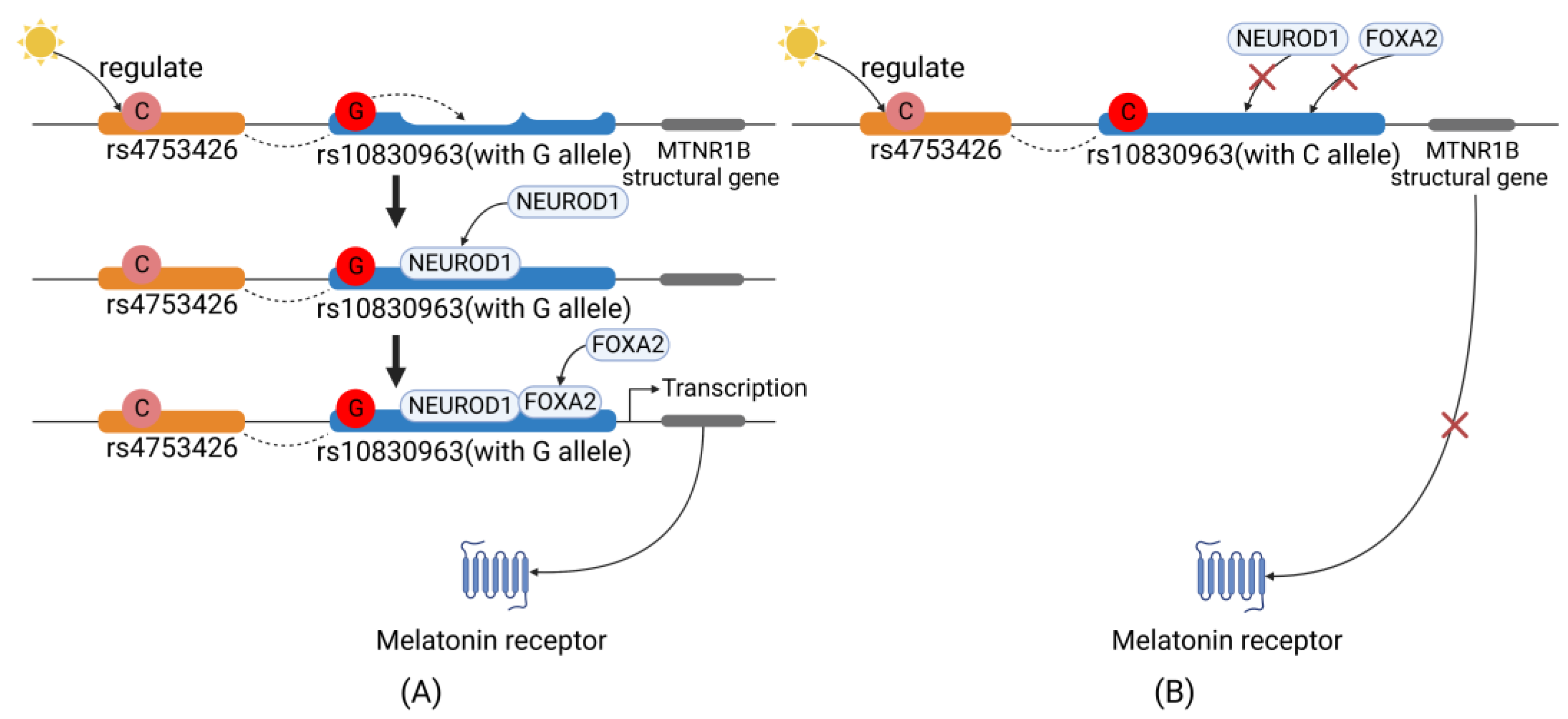
4.1. Sunshine→MTNR1B Gene Polymorphisms
4.2. MTNR1B Gene→MT2 Expression
5. Evolutionary Mechanisms
6. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patke, A.; Young, M.W.; Axelrod, S. Molecular mechanisms and physiological importance of circadian rhythms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, R.M.; Escobar, C.; Swaab, D.F. The circadian system and the balance of the autonomic nervous system. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 117, 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Rizza, S.; Longo, S.; Piciucchi, G.; Romanello, D.; Mavilio, M.; Montagna, M.; Coppeta, L.; Martelli, E.; Magrini, A.; Federici, M. Carotid intimal medial thickness in rotating night shift is related to IL1β/IL6 axis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizza, S.; Luzi, A.; Mavilio, M.; Ballanti, M.; Massimi, A.; Porzio, O.; Magrini, A.; Hannemann, J.; Menghini, R.; Lehrke, M.; et al. Alterations in Rev-ERBα/BMAL1 ratio and glycated hemoglobin in rotating shift workers: The EuRhythDia study. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizza, S.; Luzi, A.; Mavilio, M.; Ballanti, M.; Massimi, A.; Porzio, O.; Magrini, A.; Hannemann, J.; Menghini, R.; Cridland, J.; et al. Impact of light therapy on rotating night shift workers: The EuRhythDia study. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.A.; Huecker, M.R. Sleep Deprivation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, P.-D.; Chen, Q.; Gao, X.; Chung, V.C.H.; Shen, D.; Zhang, X.-R.; Zhong, W.-F.; Huang, Q.-M.; Liu, D.; et al. Association of sleep and circadian patterns and genetic risk with incident type 2 diabetes: A large prospective population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 185, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapra, A.; Bhandari, P. Diabetes Mellitus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Costa, A.; Rotenberg, L.; Toivanen, S.; Nobre, A.A.; Barreto, S.M.; Schmidt, M.I.; Fonseca, M.D.J.M.D.; Griep, R.H. Lifetime night work exposure and the risk of type 2 diabetes: Results from the longitudinal study of adult health (ELSA-Brasil). Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sang, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Di Li, D.; et al. Shift patterns, physical exercise, and Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): A prospective cohort study in China. Transl. Behav. Med. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvers, D.J.; Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Schrauwen, P.; la Fleur, S.E.; Kalsbeek, A. Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 15, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitri, A.; Jockers, R. Melatonin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 15, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.-D.; Xu, J.; Wu, D.-D.; Xie, S.-D.; Tang, N.L.S.; Zhang, Y.-P. Association of disease-predisposition polymorphisms of the melatonin receptors and sunshine duration in the global human populations. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 48, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- e Silva, A.C.P.; dos Santos, M.J.; Koike, B.; Moreira, M.S.A.; Gitai, D.L.G.; Coelho, J.A.P.D.M.; de Andrade, T.G. Melatonin receptor 1B −1193T>C polymorphism is associated with diurnal preference and sleep habits. Sleep Med. 2018, 53, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, Y.; Reinberg, A.; Touitou, D. Association between light at night, melatonin secretion, sleep deprivation, and the internal clock: Health impacts and mechanisms of circadian disruption. Life Sci. 2017, 173, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolla-Neto, J.; Amaral, F.G.D. Melatonin as a Hormone: New Physiological and Clinical Insights. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 990–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, D.; Honma, K.-I.; Yanagawa, Y.; Yamanaka, A.; Honma, S. Role of GABA in the regulation of the central circadian clock of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-J.; Yang, B.-B.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.-M.; Dai, Y.-T.; Song, N.-H.; Wang, Z.-J.; Xia, J.-D. Inhibitory Role of Gamma-Aminobutyric Receptors in Paraventricular Nucleus on Ejaculatory Responses in Rats. J. Sex. Med. 2020, 17, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Tamura, H.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin as a naturally occurring co-substrate of quinone reductase-2, the putative MT3melatonin membrane receptor: Hypothesis and significance. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Clough, S.J.; Hutchinson, A.J.; Adamah-Biassi, E.B.; Popovska-Gorevski, M.; Dubocovich, M.L. MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors: A Therapeutic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posa, L.; DE Gregorio, D.; Gobbi, G.; Comai, S. Targeting Melatonin MT2 Receptors: A Novel Pharmacological Avenue for Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3866–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, T.; Nagorny, C.L.F.; Singh, P.; Bennet, H.; Yu, Q.; Alenkvist, I.; Isomaa, B.; Östman, B.; Söderström, J.; Pesonen, A.-K.; et al. Increased Melatonin Signaling Is a Risk Factor for Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeto, M.; Cha, C.Y.; Rorsman, P.; Kaku, K. A role of PLC/PKC-dependent pathway in GLP-1-stimulated insulin secretion. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, S.; Shibasaki, T.; Brown, J.D.; McAnally, D.; Ayala, J.E.; Burmeister, M.A.; Morfa, C.; Smith, L.; Ayala, J.E.; Robichaux, W.G.; et al. PKA-Dependent and PKA-Independent Pathways for cAMP-Regulated Exocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1303–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneshamoorthy, A.; Seniveratne-Epa, D.; Calder, G.; Sawyer, M.; Kay, T.W.H.; Farrell, S.; Loudovaris, T.; Mariana, L.; McCarthy, D.; Lyu, R.; et al. Case Report: Hypoglycemia Due to a Novel Activating Glucokinase Variant in an Adult—A Molecular Approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 842937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-J.; Park, K.-H.; Yim, C.-Y.; Takasawa, S.; Okamoto, H.; Im, M.-J.; Kim, U.-H. Generation of Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate and Cyclic ADP-Ribose by Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Evokes Ca2+ Signal That Is Essential for Insulin Secretion in Mouse Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes 2008, 57, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.U.; Park, D.-R.; Joe, Y.; Jang, K.Y.; Chung, H.T.; Kim, U.-H. Critical Roles of Carbon Monoxide and Nitric Oxide in Ca2+Signaling for Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, K.J.; Sezen, S.F.; Lagoda, G.F.; Musicki, B.; Rameau, G.A.; Snyder, S.H.; Burnett, A.L. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase mediates penile erection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16624–16629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameau, G.A.; Chiu, L.-Y.; Ziff, E.B. Bidirectional Regulation of Neuronal Nitric-oxide Synthase Phosphorylation at Serine 847 by the N-Methyl-d-aspartate Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 14307–14314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.-R.; Shawl, A.I.; Ha, T.-G.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, U.-H. Arginine Thiazolidine Carboxylate Stimulates Insulin Secretion through Production of Ca2+-Mobilizing Second Messengers NAADP and cADPR in Pancreatic Islets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschke, E. Melatonin, endocrine pancreas and diabetes. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 44, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemková, H.; Vaněček, J. Inhibitory Effect of Melatonin on Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone-Induced Ca2+ Oscillations in Pituitary Cells of Newborn Rats. Neuroendocrinology 1997, 65, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemková, H.; VaněčEK, J. Differences in Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone-Induced Calcium Signaling between Melatonin-Sensitive and Melatonin-Insensitive Neonatal Rat Gonadotrophs. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, A.G.; Wolgast, S.; Muhlbauer, E.; Peschke, E. Melatonin stimulates inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate and Ca2+ release from INS1 insulinoma cells. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagdi, A.; Malan, D.; Sathyanarayanan, U.; Beauchamp, J.S.; Vogt, M.; Zipf, D.; Beiert, T.; Mansuroglu, B.; Dusend, V.; Meininghaus, M.; et al. Selective optogenetic control of Gq signaling using human Neuropsin. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Sastre, P.; Scheer, F.A.; Gómez-Abellán, P.; Madrid, J.A.; Garaulet, M. Acute Melatonin Administration in Humans Impairs Glucose Tolerance in Both the Morning and Evening. Sleep 2014, 37, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschke, E.; Fauteck, J.-D.; Mußhoff, U.; Schmidt, F.; Beckmann, A.; Peschke, D. Evidence for a melatonin receptor within pancreatic islets of neonate rats: Functional, autoradiographic, and molecular investigations. J. Pineal Res. 2000, 28, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschke, E.; Mühlbauer, E.; Mußhoff, U.; Csernus, V.J.; Chankiewitz, E.; Peschke, D. Receptor (MT1) mediated influence of melatonin on cAMP concentration and insulin secretion of rat insulinoma cells INS-1. J. Pineal Res. 2002, 33, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorsman, P.; Braun, M. Regulation of Insulin Secretion in Human Pancreatic Islets. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschke, E.; Peschke, D.; Hammer, T.; Csernus, V. Influence of melatonin and serotonin on glucose-stimulated insulin release from perifused rat pancreatic islets in vitro. J. Pineal Res. 1997, 23, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.M.; Ubeda, M.; Habener, J.F. Identification and functional characterization of melatonin Mel 1a receptors in pancreatic β cells: Potential role in incretin-mediated cell function by sensitization of cAMP signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 191, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.M. Evolution of the Insulin Gene: Changes in Gene Number, Sequence, and Processing. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 649255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, M.; Durel, B.; Languille, L.; Lamotte, L.; Tourrel-Cuzin, C.; Leroux, L.; Abou Sleymane, G.; Saint-Just, S.; Bucchini, D.; Ktorza, A.; et al. Transgenic expression of human INS gene in Ins1/Ins2 double knockout mice leads to insulin underproduction and diabetes in some male mice. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, N.; Cao, X.; Yang, Z.; Lu, B.; Hu, R.; Wang, X.; Wen, J. Melatonin exerts an inhibitory effect on insulin gene transcription via MTNR1B and the downstream Raf-1/ERK signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meur, G.; Qian, Q.; da Silva Xavier, G.; Pullen, T.J.; Tsuboi, T.; McKinnon, C.; Fletcher, L.; Tavaré, J.M.; Hughes, S.; Johnson, P.; et al. Nucleo-cytosolic Shuttling of FoxO1 Directly Regulates Mouse Ins2 but Not Ins1 Gene Expression in Pancreatic Beta Cells (MIN6). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13647–13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, N.; Wood, H.; Rabbitts, P. The many generations of sequencing technology. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezza, T.; Shirakawa, J.; Martinez, R.; Hu, J.; Giaccari, A.; Kulkarni, R.N. Nuclear Export of FoxO1 Is Associated with ERK Signaling in β-Cells Lacking Insulin Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21485–21495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, K.Y.; Chan, V.W.; Ye, W.; Chong, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, K.K.; Lui, K.O. YY1 Regulates Glucose Homeostasis Through Controlling Insulin Transcription in Pancreatic β-Cells. Diabetes 2022, 71, 961–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeckius, M.; Erat, A.; Fujikawa, T.; Hiromura, M.; Koulova, A.; Otterbein, L.; Bianchi, C.; Tobiasch, E.; Dagon, Y.; Sellke, F.W.; et al. Essential Roles of Raf/Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase/Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Pathway, YY1, and Ca2+ Influx in Growth Arrest of Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Bilirubin. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15418–15426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M.; Esguerra, J.L.; Asai, A.; Ofori, J.K.; Edlund, A.; Wendt, A.; Sugihara, H.; Wollheim, C.B.; Oikawa, S.; Eliasson, L. Potential Protection Against Type 2 Diabetes in Obesity Through Lower CD36 Expression and Improved Exocytosis in β-Cells. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibiger, I.B.; Leibiger, B.; Berggren, P.-O. Insulin feedback action on pancreatic β-cell function. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, F.; Mezza, T.; Li, P.; Shirakawa, J.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Goldfine, A.B. Insulin regulates arginine-stimulated insulin secretion in humans. Metabolism 2022, 128, 155117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remadevi, V.; Muraleedharan, P.; Sreeja, S. FOXO1: A pivotal pioneer factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 4700–4710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beesley, S.; Lee, J.; Olcese, J. Circadian clock regulation of melatonin MTNR1B receptor expression in human myometrial smooth muscle cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 21, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, K.; Chao, H.; Chen, A.; Chao, T.; Guo, C.; Hsieh, H.; Shih, H.; Sytwu, H.; Wu, C. The MTNR1A mRNA is stabilized by the cytoplasmic hnRNPL in renal tubular cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 236, 2023–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, L. The roles of ADIPOQ rs266729 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Gene 2019, 730, 144302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haljas, K.; Hakaste, L.; Lahti, J.; Isomaa, B.; Groop, L.; Tuomi, T.; Räikkönen, K. The associations of daylight and melatonin receptor 1B gene rs10830963 variant with glycemic traits: The prospective PPP-Botnia study. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, Y.-K.; Qin, L.-Y.; Wei, Q.; Liu, N.; Jiang, M.; Yu, H.-P.; Yu, X.-Y. A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, R.; Einarsdottir, E.; Riutta, A.; Hagman, S.; Raunio, M.; Mononen, N.; Lehtimäki, T.; Elovaara, I. Melatonin pathway genes are associated with progressive subtypes and disability status in multiple sclerosis among Finnish patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 250, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, B.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Association Between a Melatonin Receptor IB Genetic Polymorphism and Its Protein Expression in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 26, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaulet, M.; Gómez-Abellán, P.; Rubio-Sastre, P.; Madrid, J.A.; Saxena, R.; Scheer, F.A. Common type 2 diabetes risk variant in MTNR1B worsens the deleterious effect of melatonin on glucose tolerance in humans. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosta, K.; Al-Aissa, Z.; Hadarits, O.; Harreiter, J.; Nádasdi, A.; Kelemen, F.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Komlósi, Z.; Németh, L.; Rigó, J.; et al. Association Study with 77 SNPs Confirms the Robust Role for the rs10830963/G of MTNR1B Variant and Identifies Two Novel Associations in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychronakos, C.; Alriyami, M. Diabetes in the post-GWAS era. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1373–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, K.J.; Ferreira, T.; Lee, Y.; Raimondo, A.; Mägi, R.; Reschen, M.E.; Mahajan, A.; Locke, A.; Rayner, N.W.; Robertson, N.; et al. Genetic fine mapping and genomic annotation defines causal mechanisms at type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparsø, T.; Bonnefond, A.; Andersson, E.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Holmkvist, J.; Wegner, L.; Grarup, N.; Gjesing, A.P.; Banasik, K.; Cavalcanti-Proença, C.; et al. G-allele of Intronic rs10830963 in MTNR1B Confers Increased Risk of Impaired Fasting Glycemia and Type 2 Diabetes Through an Impaired Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Release: Studies involving 19,605 Europeans. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neel, J.V. Diabetes mellitus: A “thrifty” genotype rendered detrimental by “progress”? Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1962, 14, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Stocker, C.J.; Arch, J.R.S.; Cawthorne, M.A. Fetal origins of insulin resistance and obesity. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, I. Out of Africa: Modern human origins special feature: Human origins: Out of Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16018–16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, L.; Schiffels, S.; Gurdasani, D.; Danecek, P.; Scally, A.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Haber, M.; Ekong, R.; Oljira, T.; et al. Tracing the Route of Modern Humans out of Africa by Using 225 Human Genome Sequences from Ethiopians and Egyptians. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 96, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerri, E.M.L.; Chikhi, L.; Thomas, M.G. Beyond multiregional and simple out-of-Africa models of human evolution. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshkowitz, M.; Whiton, K.; Albert, S.M.; Alessi, C.; Bruni, O.; DonCarlos, L.; Hazen, N.; Herman, J.; Katz, E.S.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; et al. National sleep foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: Methodology and results summary. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münch, M.; Knoblauch, V.; Blatter, K.; Schröder, C.; Schnitzler, C.; Kräuchi, K.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Cajochen, C. Age-related attenuation of the evening circadian arousal signal in humans. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajochen, C.; Münch, M.; Knoblauch, V.; Blatter, K.; Wirz-Justice, A. Age-related Changes in the Circadian and Homeostatic Regulation of Human Sleep. Chronobiol. Int. 2006, 23, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, I.M.; Norman, T.R.; Burrows, G.D.; Armstrong, S.M. Human melatonin response to light at different times of the night. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1989, 14, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Yang, Q.; Tian, F.; Lyu, Y.; He, H.; Xin, X.; Zheng, X. A Meta-Analysis of a Cohort Study on the Association between Sleep Duration and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 8861038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritzen, E.S.; Kampmann, U.; Smedegaard, S.B.; Støy, J. Effects of daily administration of melatonin before bedtime on fasting insulin, glucose and insulin sensitivity in healthy adults and patients with metabolic diseases. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021, 95, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Chi, X.; Sun, Y.; Han, C.; Wan, F.; Hu, J.; Yin, S.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; et al. The circadian clock protein Rev-erbα provides neuroprotection and attenuates neuroinflammation against Parkinson’s disease via the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Xu, F.; Xu, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Du, M. Circadian gene Rev-erbα influenced by sleep conduces to pregnancy by promoting endometrial decidualization via IL-6-PR-C/EBPβ axis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehirli, A.; Chukwunyere, U.; Aksoy, U.; Sayiner, S.; Abacioglu, N. The circadian clock gene Bmal1: Role in COVID-19 and periodontitis. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, C.A.; Lee, J.; Cai, Y.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.; Musiek, E.S. Astrocytes deficient in circadian clock gene Bmal1 show enhanced activation responses to amyloid-beta pathology without changing plaque burden. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.A.; Kivimaki, M.; Hamer, M. Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellou, V.; Belbasis, L.; Tzoulaki, I.; Evangelou, E. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus: An exposure-wide umbrella review of meta-analyses. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, A.-Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wang, P.-H.; Ji, L.-D.; Xu, J. Molecular Mechanisms of the Melatonin Receptor Pathway Linking Circadian Rhythm to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061406
Xia A-Y, Zhu H, Zhao Z-J, Liu H-Y, Wang P-H, Ji L-D, Xu J. Molecular Mechanisms of the Melatonin Receptor Pathway Linking Circadian Rhythm to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061406
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, An-Yu, Hui Zhu, Zhi-Jia Zhao, Hong-Yi Liu, Peng-Hao Wang, Lin-Dan Ji, and Jin Xu. 2023. "Molecular Mechanisms of the Melatonin Receptor Pathway Linking Circadian Rhythm to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061406
APA StyleXia, A.-Y., Zhu, H., Zhao, Z.-J., Liu, H.-Y., Wang, P.-H., Ji, L.-D., & Xu, J. (2023). Molecular Mechanisms of the Melatonin Receptor Pathway Linking Circadian Rhythm to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients, 15(6), 1406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061406




