Sarcopenic Obesity in Community-Dwelling Spanish Adults Older than 65 Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
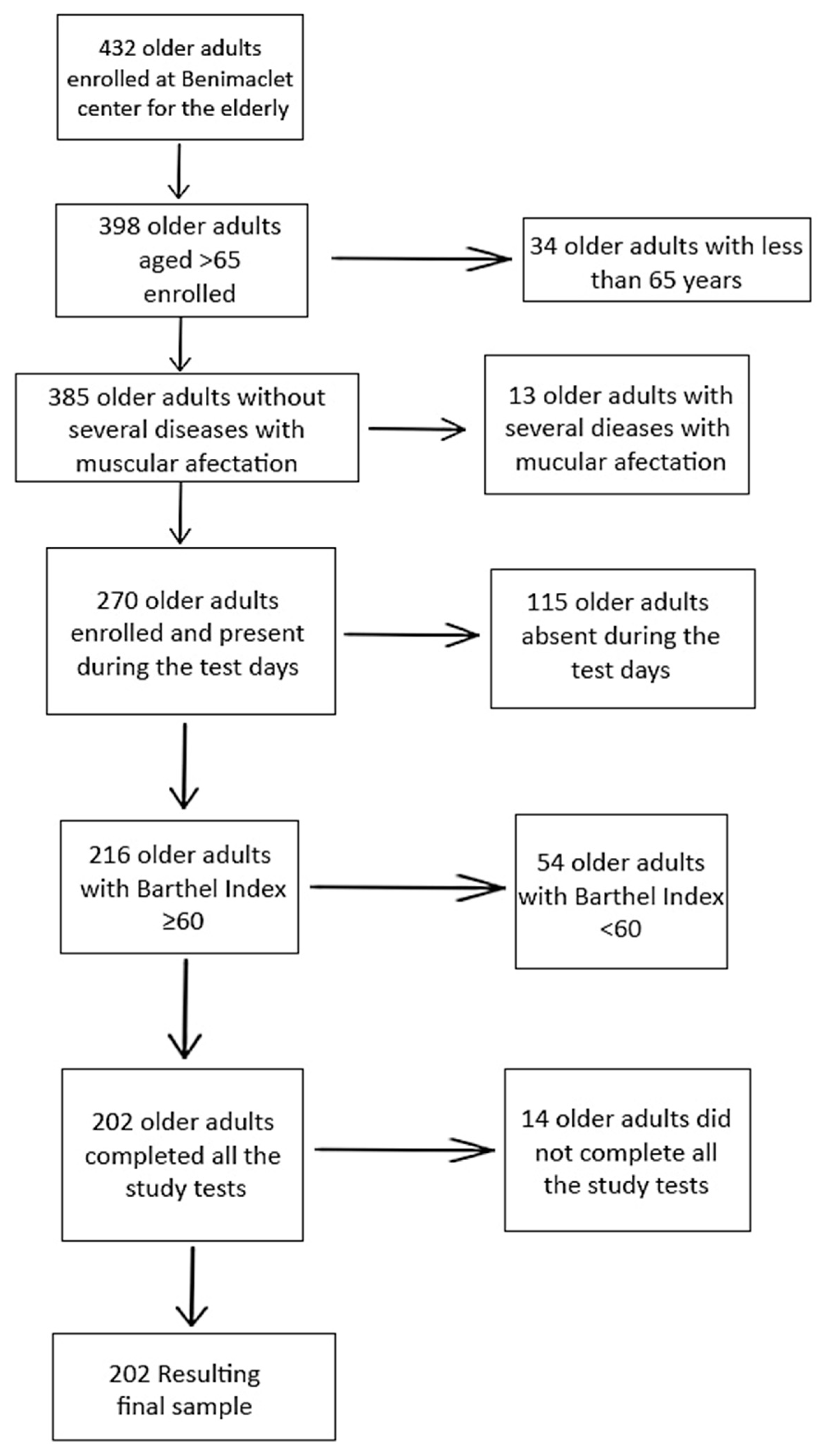
2.1. Participants (Study Population)
2.2. Sample Size Estimation
2.3. Exam Protocol and Measurements
2.3.1. General Information
2.3.2. Degree of Dependency
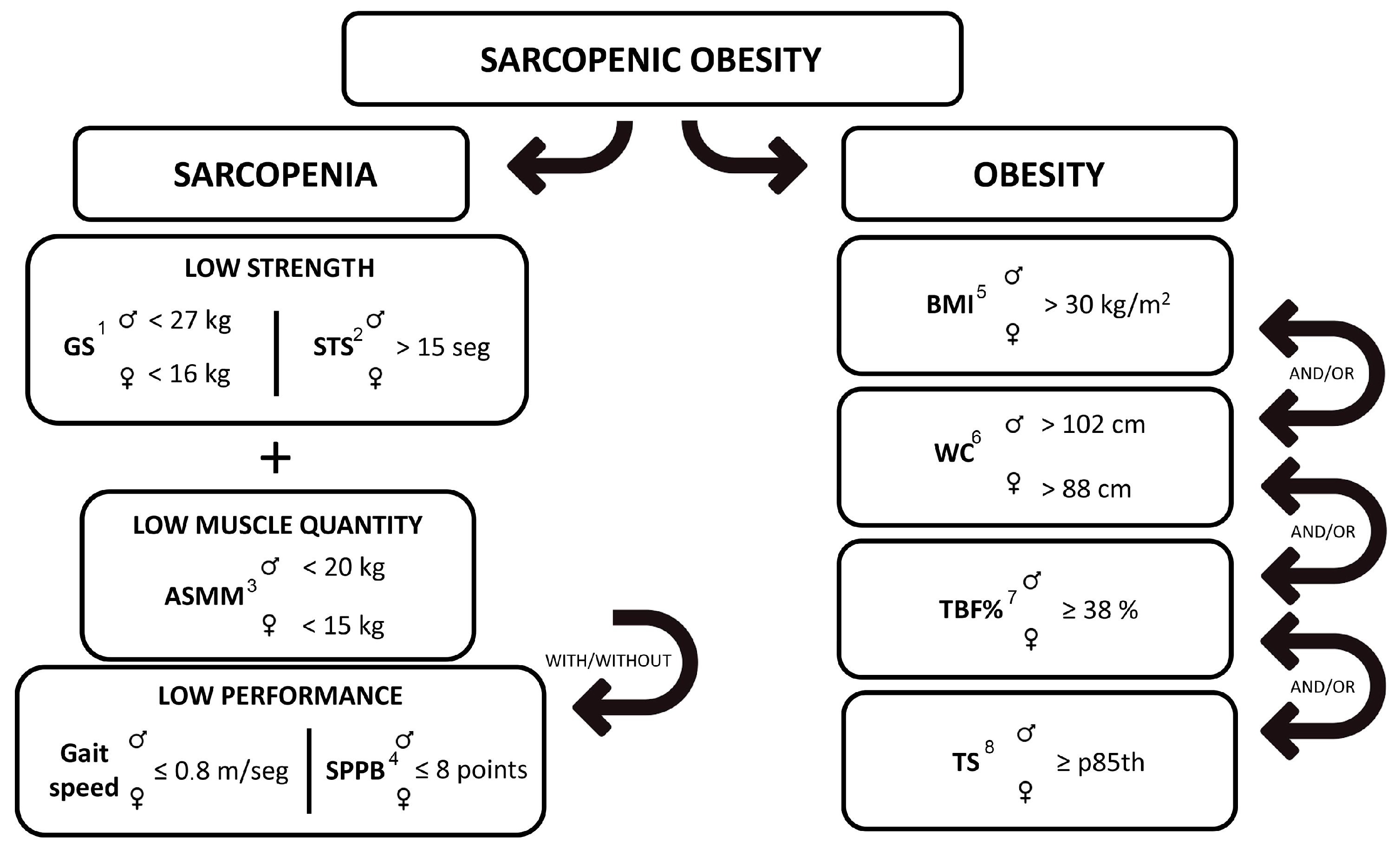
2.3.3. Sarcopenia Screening
2.3.4. Diagnosis of Sarcopenic Pathology
2.3.5. Grip Strength (Upper Body)
2.3.6. Lower Body Strength
2.3.7. Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass (ASMM)
2.3.8. Physical Performance
2.3.9. Diagnosis of Obesity
2.3.10. Body Mass Index (BMI)
2.3.11. Waist Circumference (WC)
2.3.12. Total Body Fat Percentage (TBF%)
2.3.13. Tricipital Skinfold (TS)
2.3.14. Diagnosis of Sarcopenic Obesity (SO)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamo, M.L.; Farrar, R.P. Resistance training, and IGF involvement in the maintenance of muscle mass during the aging process. Ageing Res. Rev. 2006, 5, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubenoff, R.; Hughes, V.A. Sarcopenia: Current concepts. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2000, 55, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.; Ruts, E.; Visser, M.; Heshka, S.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Heymsfield, S.B. Weight stability masks sarcopenia in elderly men and women. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 279, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Cabello, A.; Pedrero-Chamizo, R.; Olivares, P.R.; Luzardo, L.; Juez-Bengoechea, A.; Mata, E.; Albers, U.; Aznar, S.; Villa, G.; Espino, L.; et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in non-institutionalized people aged 65 or over from Spain: The elderly EXERNET multi-centre study. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenholm, S.; Harris, T.B.; Rantanen, T.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Ferrucci, L. Sarcopenic obesity: Definition, cause and consequences. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Cabello, A.; Vicente Rodríguez, G.; Vila-Maldonado, S.; Casajús, J.A.; Ara, I. Aging and body composition: The sarcopenic obesity in Spain. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heber, D.; Ingles, S.; Ashley, J.M.; Maxwell, M.H.; Lyons, R.F.; Elashoff, R.M. Clinical detection of sarcopenic obesity by bioelectrical impedance analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64 (Suppl. S3), 472S–477S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Wayne, S.J.; Waters, D.L.; Janssen, I.; Gallagher, D.; Morley, J.E. Sarcopenic obesity predicts instrumental activities of daily living disability in the elderly. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Ross, R. Estimation of skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.N.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Lim, K.I.; Kang, H.J.; Song, W.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Baik, S.H.; et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in Korean adults: The Korean sarcopenic obesity study. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N. Body composition in healthy aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 904, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoico, E.; Di Francesco, V.; Guralnik, J.M.; Mazzali, G.; Bortolani, A.; Guariento, S.; Sergi, G.; Bosello, O.; Zamboni, M. Physical disability and muscular strength in relation to obesity and different body composition indexes in a sample of healthy elderly women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, K.K.; Ford, E.S.; Cogswell, M.E.; Dietz, W.H. Percentage of body fat and body mass index are associated with mobility limitations in people aged 70 and older from NHANES III. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, K.K.; Birch, L.L. Childhood overweight: A contextual model and recommendations for future research. Obes. Rev. 2001, 2, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Koehler, K.M.; Gallagher, D.; Romero, L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R.R.; Garry, P.J.; Lindeman, R.D. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaola-Sagardui, I. Validation of the Barthel Index in the Spanish population. Enferm. Clin. 2018, 28, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafañe, J.H.; Pirali, C.; Dughi, S.; Testa, A.; Manno, S.; Bishop, M.D.; Negrini, S. Association between malnutrition and Barthel Index in a cohort of hospitalized older adults article information. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mii, S.; Guntani, A.; Kawakubo, E.; Shimazoe, H. Barthel Index and Outcome of Open Bypass for Critical Limb Ischemia. Circ. J. 2017, 82, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, A.P.; Ibarz, E.; Gracia, L.; Mateo, J.; Herrera, A. The use of Barthel index for the assessment of the functional recovery after osteoporotic hip fracture: One year follow-up. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A Simple Questionnaire to Rapidly Diagnose Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.B.; Kupelian, V.; Visser, M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Rubin, S.M.; Harris, T.B. Strength, but not muscle mass, is associated with mortality in the health, aging and body composition study cohort. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan van Kan, G. Epidemiology and consequences of sarcopenia. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Pahor, M.; Lauretani, F.; Zamboni, V.; Bandinelli, S.; Bernabei, R.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Skeletal Muscle and Mortality Results from the InCHIANTI Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2009, 64, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, B.; Kifley, A.; Liew, G.; Mitchell, P. Handgrip strength and its association with functional independence, depressive symptoms and quality of life in older adults. Maturitas 2017, 106, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.; Kim, Y.; Chung, H. Sex-Associated Differences in the Handgrip Strength of Elderly Individuals. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2019, 42, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.C.; Denison, H.J.; Martin, H.J.; Patel, H.P.; Syddall, H.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. A review of the measurement of grip strength in clinical and epidemiological studies: Towards a standardised approach. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.M.; de Roriz, A.K.C.; Barreto-Medeiros, J.M.; Ferreira, A.J.F.; Ramos, L. Sarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling older women, determined by different diagnostic methods. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.; Fielding, R.; Visser, M.V.; Van Loon, L.J.; Rolland, Y.; Orwoll, E.; Reid, K.; Boonen, S.; Dere, W.; Epstein, S.; et al. Tools in the assessment of sarcopenia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 93, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Genton, L.; Hans, D.; Pichard, C. Validation of a bioelectrical impedance analysis equation to predict appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASMM). Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenski, S.; Perera, S.; Patel, K.; Rosano, C.; Faulkner, K.; Inzitari, M.; Brach, J.; Chandler, J.; Cawthon, P.; Connor, E.B.; et al. Gait Speed and Survival in Older Adults. JAMA 2011, 305, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretani, F.; Ticinesi, A.; Gionti, L.; Prati, B.; Nouvenne, A.; Tana, C.; Meschi, T.; Maggio, M. Short-Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) score is associated with falls in older outpatients. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavasini, R.; Guralnik, J.; Brown, J.C.; di Bari, M.; Cesari, M.; Landi, F.; Vaes, B.; Legrand, D.; Verghese, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Short Physical Performance Battery and all-cause mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, W.; Teschler, M.; Weißenfels, A.; Sieber, C.; Freiberger, E.; von Stengel, S. Prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in older German men using recognized definitions: High accordance but low overlap! Osteoporos. Int. 2017, 28, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2000, 894, i-253.
- Kuczmarski, M.F.; Kuczmarski, R.J.; Najjar, M. Descriptive anthropometric reference data for older Americans. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2000, 100, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchonville, M.F.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity: How do we treat it? Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.M.; Siervo, M.; Mire, E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Stephan, B.C.; Broyles, S.; Smith, S.R.; Wells, J.C.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. A population-based approach to define body-composition phenotypes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S.; Wu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Li, H.; Hong, W.; et al. Sex differences in the prevalence and adverse outcomes of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in community dwelling elderly in East China using the AWGS criteria. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Shook, R.P.; Drenowatz, C.; Blair, S.N. Physical activity and sarcopenic obesity: Definition, assessment, prevalence and mechanism. Future Sci. OA 2016, 2, FSO127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.M.; Dias, J.M.D.; Samora, G.A.R.; Perracini, M.R.; Guerra, R.O.; Dias, R.C. Prevalence of obesity, sarcopenic obesity and associated factors: A FIBRA Network study. Fisioter. Em Mov. 2017, 30 (Suppl. S1), 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.K.; Chen, L.Y.; Yeh, K.P.; Lin, M.H.; Hwang, A.C.; Peng, L.N.; Chen, L.K. Sarcopenia, but not sarcopenic obesity, predicts mortality for older old men: A 3-year prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2014, 5, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Peroni, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Bartolo, A.; Naso, M.; Miccono, A.; Rondanelli, M. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in comparison: Prevalence, metabolic profile, and key differences. A cross-sectional study in Italian hospitalized elderly. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goisser, S.; Kemmler, W.; Porzel, S.; Volkert, D.; Sieber, C.C.; Bollheimer, L.C.; Freiberger, E. Sarcopenic obesity and complex interventions with nutrition and exercise in community-dwelling older persons—A narrative review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 1267–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Batsis, J.A.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Barre, L.K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Bartels, S.J. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and mortality in older adults: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Barre, L.K.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Pratt, S.I.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Bartels, S.J. Variation in the prevalence of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in older adults associated with different research definitions: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Women | Men | Total N = 202 n (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65–75 y N = 101 n (%) | 75–85 y N = 63 n (%) | Total N = 164 n (%) | 65–75 y N = 27 n (%) | 75–85 y N = 11 n (%) | Total N = 38 n (%) | ||
| Sarcopenia | |||||||
| Without sarcopenia 1 | 80 (79.2) | 42 (67) | 122 (74.4) | 21 (78) | 6 (55) | 27 (71) | 149 (73.8) |
| Sarcopenia probable 2 | 18 (17.8) | 12 (19) | 30 (18.3) | 5 (19) | 3 (27) | 8 (21) | 38 (18.8) |
| Sarcopenia confirmed 3 | 2 (2) | 4 (6) | 6 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (3) |
| Sarcopenia severe 4 | 1 (1) | 5 (8) | 6 (3.7) | 1 (4) | 2 (18) | 3 (8) | 9 (4.5) |
| Total sarcopenia 5 | 21 (20.8) | 21 (33) | 42 (25.6) | 7 (26) | 5 (45) | 11 (29) | 53 (26.2) |
| Obesity | |||||||
| Without obesity | 38 (37.6) | 27 (43) | 65 (39.6) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 66 (32.7) |
| Obesity per body mass index | 45 (44.6) | 19 (30) | 64 (39) | 14 (52) | 5 (46) | 19 (12) | 83 (41.1) |
| Obesity per central obesity | 55 (54.5) | 33 (52) | 88 (53.7) | 26 (96) | 11 (100) | 37 (97) | 125 (61.9) |
| Obesity per total body fat | 39 (38.6) | 26 (41) | 65 (39.6) | 14 (52) | 7 (64) | 21 (55) | 86 (42.6) |
| Obesity per triceps skinfold | 6 (5.9) | 3 (5) | 9 (5.5) | 4 (15) | 2 (18) | 6 (16) | 15 (39.5) |
| Total obesity | 63 (62.4) | 36 (57) | 99 (60.4) | 26 (96) | 11 (100) | 37 (97) | 136 (67.3) |
| Sarcopenic Obesity | |||||||
| Without sarcopenic obesity 6 | 86 (85.1) | 51 (81) | 137 (83.5) | 21 (78) | 6 (55) | 27 (71) | 164 (81.2) |
| Sarcopenic obesity per body mass index 7 | 13 (12.9) | 7 (11) | 20 (12.2) | 4 (15) | 1 (9) | 5 (13) | 25 (12.4) |
| Sarcopenic obesity per central obesity 8 | 15 (14.9) | 10 (16) | 25 (15.2) | 6 (22) | 5 (46) | 11 (29) | 36 (17.8) |
| Sarcopenic obesity per total body fat 9 | 13 (12.9) | 11 (18) | 24 (14.6) | 4 (15) | 3 (37) | 7 (18) | 31 (15.4) |
| Sarcopenic obesity per triceps skinfold 10 | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 2 (1.2) | 3 (11) | 1 (9) | 4 (11) | 6 (3) |
| Total sarcopenic obesity 11 | 15 (14.9) | 12 (19) | 27 (16.5) | 6 (22) | 5 (45) | 11 (29) | 38 (18.8) |
| 65–75 Years | 75–85 Years | WSO (Full Age Range) | SO Total (Full Age Range) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WSO | SO × BMI | SO × WC | SO × TBF% | SO × TS | SO Total | WSO | SO × BMI | SO × WC | SO × TBF% | SO × TS | SO Total | |||
| Men | N = 21 | N = 4 | N = 6 | N = 4 | N = 3 | N = 6 | N = 6 | N = 1 | N = 5 | N = 3 | N = 1 | N = 5 | N = 27 | N = 11 |
| Grip strength (kg) | 36.5 ± 7.5 | 30.5 ± 6.5 | 31.5 ± 5.5 | 30.5 ± 6.5 | 31 ± 5.6 | 31.5 ± 5.5 | 32.7 ± 4.5 | 22 ± 0 | 28.4 ± 4.4 | 28.3 ± 6 | 22 ± 0 | 28.4 ± 4.4 | 34.6 ± 6 | 29.9 ± 2.2 |
| Chair stand test (s) | 10.2 ± 2.4 | 17.5 ± 5.8 | 17 ± 4.6 | 17.5 ± 5.8 | 17.7 ± 2.8 | 17 ± 4.6 | 12.6 ± 2.7 | 20.2 ± 0 | 17.9 ± 1.6 | 18.6 ± 1.9 | 20.2 ± 0 | 17.9 ± 1.6 | 11.4 ± 2.6 | 17.4 ± 0.6 |
| ASMM total (kg) | 23.2 ± 3.1 | 23.3 ± 4.5 | 23.7 ± 3.5 | 23.3 ± 4.5 | 22.8 ± 5.4 | 23.7 ± 3.5 | 23 ± 2.5 | 26.1 ± 0 | 22.5 ± 3.2 | 23.9 ± 3.5 | 26.1 ± 0 | 22.5 ± 3.2 | 23.1 ± 2.8 | 23.1 ± 0.9 |
| Gait speed (m/s) | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0 |
| SPPB (score) | 10.3 ± 1 | 8 ± 3 | 8.3 ± 2 | 8 ± 3 | 8.7 ± 3 | 8.3 ± 2 | 9.3 ± 2 | 4 ± 0 | 5.8 ± 1 | 5.7 ± 2 | 4 ± 0 | 5.8 ± 1 | 9.8 ± 1.5 | 7.1 ± 1.8 |
| SARC F test (score) | 1.2 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 2.8 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | 2.3 ± 2 | 2.8 ± 1 | 3.2 ± 2 | 7 ± 0 | 3.4 ± 3 | 4.7 ± 3 | 7 ± 0 | 3.4 ± 3 | 2.2 ± 1.5 | 3.1 ± 0.4 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 28.1 ± 4.6 | 33.6 ± 2.3 | 30.6 ± 5 | 33.6 ± 2.3 | 31.8 ± 5.9 | 30.6 ± 5 | 28.6 ± 4.1 | 33.3 ± 0 | 26.4 ± 4 | 28.3 ± 4.3 | 33.3 ± 0 | 26.4 ± 4 | 28.4 ± 4.4 | 28.5 ± 3 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 101.4 ± 9.6 | 109.8 ± 3.8 | 104.8 ± 8.7 | 109.8 ± 3.8 | 105.7 ± 5.6 | 104.8 ± 8.7 | 104.4 ± 8.2 | 109.3 ± 0 | 104.2 ± 3.8 | 104 ± 4.7 | 109.3 ± 0 | 104.2 ± 3.8 | 102.9 ± 8.9 | 104.5 ± 0.4 |
| Total body fat (%) | 26.3 ± 6.1 | 32.7 ± 3.7 | 29.2 ± 6.3 | 32.7 ± 3.7 | 31.3 ± 6.7 | 29.2 ± 6.3 | 28.9 ± 4.1 | 37.4 ± 0 | 28.8 ± 5.6 | 32 ± 4.8 | 37.4 ± 0 | 28.8 ± 5.6 | 27.6 ± 5.1 | 29 ± 0.3 |
| Triceps skinfold (mm) | 12 ± 5.1 | 19 ± 9.5 | 18.5 ± 8.2 | 19 ± 9.5 | 25.7 ± 3.1 | 18.5 ± 8.2 | 15 ± 4.1 | 27 ± 0 | 14.2 ± 7.9 | 16.7 ± 10 | 27 ± 0 | 14.2 ± 7.9 | 13.5 ± 4.6 | 16.4 ± 3 |
| Women | N = 86 | N = 13 | N = 15 | N = 13 | N = 2 | N = 15 | N = 51 | N = 7 | N = 10 | N = 11 | N = 0 | N = 12 | N = 137 | N = 27 |
| Grip strength (kg) | 21.5 ± 4.1 | 16.2 ± 6.7 | 16 ± 6.2 | 16.6 ± 6.3 | 13 ± 1.4 | 16 ± 6.2 | 19 ± 4.3 | 14.3 ± 1.5 | 14.7 ± 2.3 | 14.8 ± 2.2 | - | 14.9 ± 2.1 | 20.3 ± 4.2 | 15.5 ± 0.8 |
| Chair stand test (s) | 10.6 ± 2.4 | 14.1 ± 4.6 | 14.2 ± 4.6 | 14.6 ± 4.8 | 12.8 ± 6.7 | 14.2 ± 4.6 | 11.8 ± 2.9 | 15.1 ± 5.8 | 16.2 ± 5.3 | 16.3 ± 5.3 | - | 16.2 ± 5.1 | 11.2 ± 2.7 | 15.2 ± 1.4 |
| ASMM total (kg) | 16.8 ± 2.4 | 18.2 ± 1.7 | 17.6 ± 2.3 | 18 ± 2 | 16.5 ± 1.9 | 17.6 ± 2.3 | 15.7 ± 2.4 | 17.8 ± 3.3 | 17 ± 3 | 17.1 ± 2.8 | - | 16.8 ± 2.8 | 16.3 ± 2.4 | 17.2 ± 0.6 |
| Gait speed (m/s) | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | - | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| SPPB (score) | 10.3 ± 2 | 8.7 ± 2 | 8.5 ± 2 | 8.5 ± 2 | 8.5 ± 2 | 8.5 ± 2 | 9.6 ± 2 | 8.4 ± 2 | 8.5 ± 2 | 8.2 ± 2 | - | 8.3 ± 2 | 9.9 ± 2 | 8.4 ± 0.1 |
| SARC F test (score) | 1.7 ± 1 | 3.3 ± 2 | 3.3 ± 1 | 3.1 ± 1 | 4 ± 0 | 3.3 ± 1 | 2.7 ± 1 | 3.9 ± 0 | 4.1 ± 1 | 4.1 ± 1 | - | 4 ± 1 | 2.2 ± 1 | 3.7 ± 0.5 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27.4 ± 4.4 | 30.7 ± 2 | 30.1 ± 2.6 | 30.5 ± 2.3 | 31.4 ± 3 | 30.1 ± 2.6 | 25.9 ± 3.7 | 32 ± 2.9 | 30 ± 4 | 30 ± 3.7 | - | 29.6 ± 3.7 | 26.7 ± 4.1 | 29.9 ± 0.4 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 89.1 ± 9.5 | 97.8 ± 5.1 | 97.7 ± 4.7 | 97.8 ± 5.1 | 97.8 ± 7.4 | 97.7 ± 4.7 | 87.6 ± 8.2 | 100.4 ± 10.8 | 98.9 ± 8.5 | 97.3 ± 9.6 | - | 96.6 ± 9.5 | 88.4 ± 8.9 | 97.2 ± 0.8 |
| Total body fat (%) | 35.9 ± 5.2 | 41.4 ± 2.9 | 40.9 ± 3.1 | 41.7 ± 2.6 | 41 ± 1.8 | 40.9 ± 3.1 | 35.9 ± 5.3 | 43.5 ± 3.7 | 42.2 ± 4 | 42.5 ± 3.4 | - | 41.9 ± 3.7 | 25.9 ± 5.3 | 41.4 ± 0.7 |
| Triceps skinfold (mm) | 20.9 ± 5.5 | 22.5 ± 6.3 | 22.5 ± 5.9 | 23 ± 6.2 | 28 ± 11.3 | 22.5 ± 5.9 | 20.3 ± 5.4 | 19.1 ± 3.6 | 19.4 ± 4.1 | 19.3 ± 4 | - | 19.3 ± 3.8 | 20.6 ± 5.5 | 20.9 ± 2.3 |
| Obesity Diagnosis Variables | Sarcopenia Diagnosis Variables | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI 1 | WC 2 | TS 3 | TBF% 4 | CST Test 5 | Grip Strength | ASSM 6 | Gait Speed | SPPB Test 7 | ||
| Obesity diagnosis variables | BMI 1 | 1 | 0.718 ** | 0.396 ** | 0.825 ** | 0.135 | 0.052 | 0.676 ** | −0.131 | −0.153 * |
| WC 2 | 0.718 ** | 1 | 0.037 | 0.573 ** | 0.241 ** | 0.314 ** | 0.719 ** | −0.143 * | −0.222 ** | |
| TS 3 | 0.396 ** | 0.037 | 1 | 0.652 ** | 0.068 | −0.255 ** | 0.005 | −0.129 | −0.042 | |
| TBF% 4 | 0.825 ** | 0.573 ** | 0.652 ** | 1 | 0.146 * | 0.054 | 0.451 ** | −0.072 | −0.085 | |
| Sarcopenia diagnosis variables | CS test 5 | 0.135 | 0.241 ** | 0.068 | 0.146 * | 1 | −0.104 | 0.134 | −0.491 ** | −0.709 ** |
| Grip strength | 0.052 | 0.314 ** | −0.255 ** | 0.054 | −0.104 | 1 | 0.353 ** | 0.225 ** | 0.161 * | |
| ASSM 6 | 0.676 ** | 0.719 ** | 0.005 | 0.451 ** | 0.134 | 0.353 ** | 1 | −0.104 | −0.183 ** | |
| Gait Speed | −0.131 | −0.143 * | −0.129 | −0.072 | −0.491 ** | 0.225 ** | −0.104 | 1 | 0.503 ** | |
| SPPB test 7 | −0.153 * | −0.222 ** | −0.042 | −0.085 | −0.071 ** | 0.161 * | −0.183 ** | 0.503 ** | 1 | |
| SO × BMI | SO × WC | SO × TBF% | SO × TS | SO Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Body mass index | 1.50 (1.20 to 1.87) | <0.001 | 1.20 (1.01 to 1.42) | 0.037 | ||||||
| Waist circumference | 10.41 (1.01 to 107.6) | 0.049 | 12.9 (3.0 to 55.5) | <0.001 | 11.4 (1.73 to 75.0) | 0.01 | 10.2 (2.34 to 44.6) | 0.002 | ||
| Triceps skinfold | 0.87 (0.77 to 0.98) | 0.025 | 1.25 (1.06 to 1.48) | 0.007 | ||||||
| Total body fat | 1.06 (0.95 to 1.19) | 0.27 | 0.88 (0.77 to 0.99) | 0.04 | ||||||
| ASMM total | 1.84 (1.04 to 3.25) | 0.048 | 2.42 (1.25 to 4.68) | 0.009 | ||||||
| Grip strength | 0.829 (0.74 to 1.15) | <0.001 | 0.89 (0.82 to 0.96) | 0.001 | 0.86 (0.77 to 0.94) | 0.002 | 0.87 (0.79 to 0.95) | 0.001 | ||
| Chair stand test | 1.35 (1.15 to 1.59) | <0.001 | 1.51 (1.29 to 1.77) | <0.001 | 1.54 (1.29 to 1.83) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.11 to 1.74) | 0.004 | 1.57 (1.33 to 1.85) | <0.001 |
| Gait speed | ||||||||||
| SPPB | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diago-Galmés, A.; Guillamon-Escudero, C.; Tenías-Burillo, J.M.; Soriano, J.M.; Fernández-Garrido, J. Sarcopenic Obesity in Community-Dwelling Spanish Adults Older than 65 Years. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4932. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234932
Diago-Galmés A, Guillamon-Escudero C, Tenías-Burillo JM, Soriano JM, Fernández-Garrido J. Sarcopenic Obesity in Community-Dwelling Spanish Adults Older than 65 Years. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4932. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234932
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiago-Galmés, Angela, Carlos Guillamon-Escudero, Jose M. Tenías-Burillo, Jose M. Soriano, and Julio Fernández-Garrido. 2023. "Sarcopenic Obesity in Community-Dwelling Spanish Adults Older than 65 Years" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4932. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234932
APA StyleDiago-Galmés, A., Guillamon-Escudero, C., Tenías-Burillo, J. M., Soriano, J. M., & Fernández-Garrido, J. (2023). Sarcopenic Obesity in Community-Dwelling Spanish Adults Older than 65 Years. Nutrients, 15(23), 4932. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234932








