Associations of Combined Lifestyle Factors with MAFLD and the Specific Subtypes in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Definition of Lifestyle Factors and Scores
2.3. Ascertainment of Baseline and Incident MAFLD
2.4. Statistical Analysis
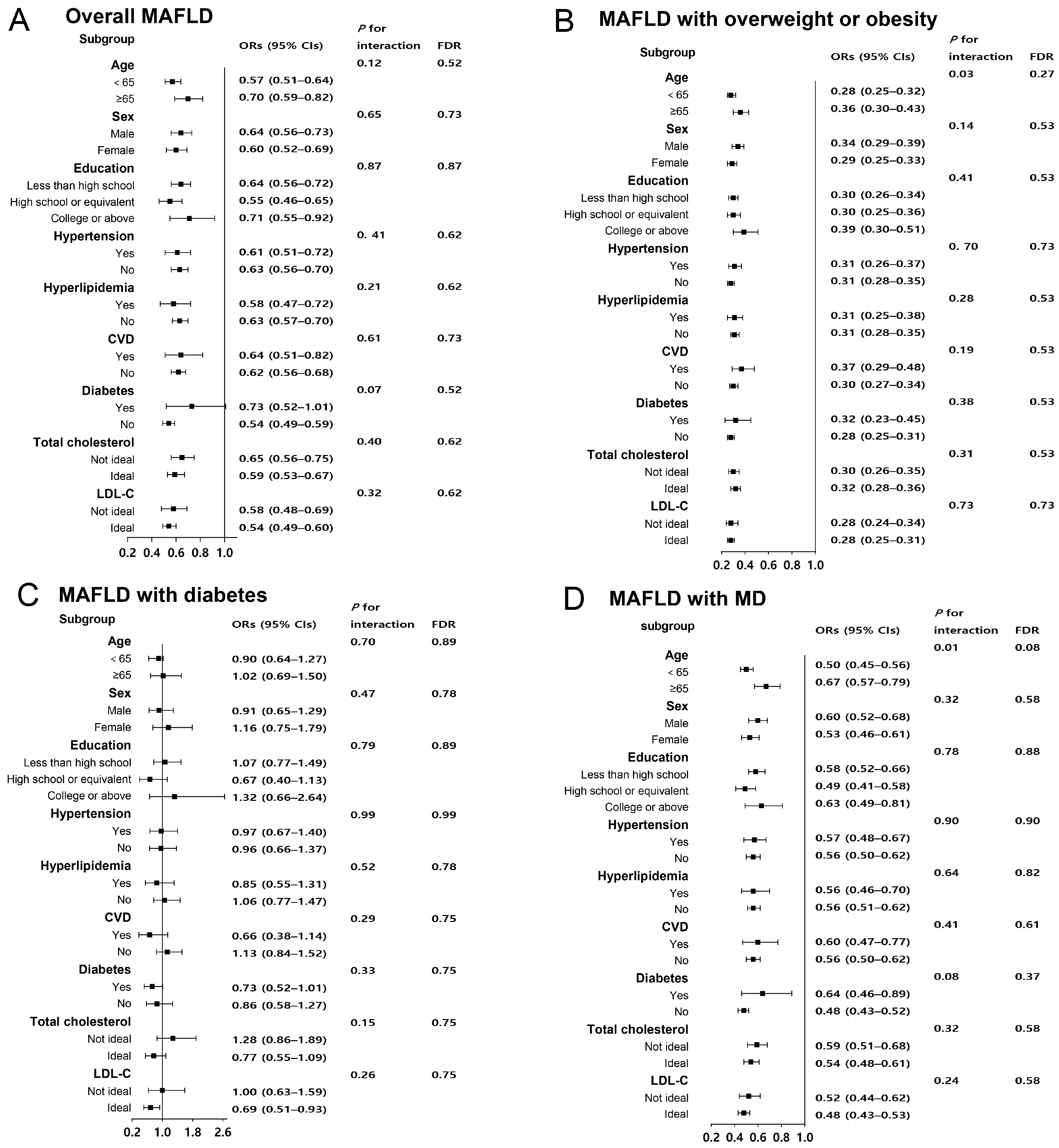
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wong, V.W.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, M.; Zheng, S.; Xia, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D.; Yin, C.; Cheng, N.; Bai, Y. Comparing the Diagnostic Criteria of MAFLD and NAFLD in the Chinese Population: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, H.C. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2138–2147.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J.; Cheung, R. Trends in the Prevalence of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in the United States, 2011–2018. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e610–e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, S.; Eslam, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Yoshinaga, S.; Takahashi, H.; Anzai, K.; George, J.; Torimura, T. MAFLD identifies patients with significant hepatic fibrosis better than NAFLD. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 3018–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Honda, Y.; Imajo, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Nogami, A.; Higurashi, T.; Kato, S.; et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with fatty liver disease as defined from the metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease point of view: A retrospective nationwide claims database study in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, N.F.; Radu, P.; Dufour, J.F. Prevention of NAFLD-associated HCC: Role of lifestyle and chemoprevention. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.; Naimimohasses, S.; Monaghan, A.; Kennedy, M.; Melo, A.M.; Ni Fhloinn, D.; Doherty, D.G.; Beddy, P.; Finn, S.P.; Moore, J.B.; et al. Improvement in histological endpoints of MAFLD following a 12-week aerobic exercise intervention. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Nakamura, N.; Fukumoto, S.; Kimura, T.; Nakano, A.; Nadatani, Y.; Tauchi, Y.; Nishii, Y.; Takashima, S.; Kamada, Y.; et al. Lifestyle changes during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic impact metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, E.; Bostick, R.M.; Hatami, B.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Moslem, A.; Mousavi Jarrahi, A.; Zali, M.R. Dietary and Lifestyle Inflammation Scores Are Inversely Associated with Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease among Iranian Adults: A Nested Case-Control Study. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldrup, D.; Wei, C.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Kristensen, K.; Rittig, S.; Lange, A.; Horlyck, A.; Solvig, J.; Gronbaek, H.; Birkebaek, N.H.; et al. Effects of lifestyle intervention on IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and insulin resistance in children with obesity with or without metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, S.; Li, R.; Ju, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Sun, M.; Fan, J.; Xia, M.; Zhu, W.; et al. Sleep Factors in Relation to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Middle-Aged and Elderly Chinese. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2874–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, J.; Yao, P.; Li, X.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, L.; Min, X.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Dongfeng-Tongji cohort study of retired workers. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Long, T.; Yuan, J.; Yao, P.; Wei, S.; et al. Genetic Risk, a Healthy Lifestyle, and Type 2 Diabetes: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e596–e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, F.C.; Department of Disease Control Ministry of Health, PR China. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Eslam, M.; Sarin, S.K.; Wong, V.W.; Fan, J.G.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ahn, S.H.; Zheng, M.H.; Shiha, G.; Yilmaz, Y.; Gani, R.; et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 889–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, T.; Yang, K.; Guo, K.; Min, X.; He, M.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Association of Lifestyle Factors and Antihypertensive Medication Use with Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality Among Adults with Hypertension in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2146118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.N.; Zhou, B.Q.; Ning, N.; Pan, T.; Xu, F.; He, S.H.; Chen, N.N.; Sun, M. Effects of lifestyle intervention on adults with metabolic associated fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1081096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogabe, M.; Okahisa, T.; Kurihara, T.; Kagawa, M.; Ueda, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Fukuya, A.; Kagemoto, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kida, Y.; et al. Comparison of the role of alcohol consumption and qualitative abdominal fat on NAFLD and MAFLD in males and females. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odegaard, A.O.; Jacobs, D.R.; Van Wagner, L.B.; Pereira, M.A. Levels of abdominal adipose tissue and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in middle age according to average fast-food intake over the preceding 25 years: The CARDIA Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, J.; Xie, W.; Ni, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, M.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, Y. Dietary Quality and Relationships with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) among United States Adults, Results from NHANES 2017-2018. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Kumar, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of MAFLD and NAFLD diagnostic criteria in real world. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Corey, K.E.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Lifestyle Modification Using Diet and Exercise to Achieve Weight Loss in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeb, E. Excess Body Weight and Metabolic (Dysfunction)-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD). Visc. Med. 2021, 37, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Uto, H.; Mawatari, S.; Ido, A. Clinical features of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A review of human studies. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.D.W.; George, J.; Qiao, L. From MAFLD to hepatocellular carcinoma and everything in between. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2022, 135, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Wei, L.; Bao, Y.; Yang, C.; Zong, G.; Wu, J.; Jia, W. Association of MAFLD With Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Cardiovascular Disease: A 4.6-Year Cohort Study in China. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Pan, X.F.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Geng, T.T.; Zhou, Y.F.; Liao, L.M.; Tu, Z.Z.; Chen, J.X.; Xia, P.F.; et al. Associations of combined healthy lifestyles with cancer morbidity and mortality among individuals with diabetes: Results from five cohort studies in the USA, the UK and China. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2044–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Xie, J.; Xu, C. Dietary Patterns and Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with NAFLD: A Prospective Analysis of 128,695 UK Biobank Participants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.M.; Mir, S.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Younossi, Y.; Ong, J.P.; Younossi, Z.M. Dietary Risks for Liver Mortality in NAFLD: Global Burden of Disease Data. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjua, M.; Knuiman, M.; Divitini, M.; McQuillan, B.; Olynyk, J.K.; Jeffrey, G.P.; Adams, L.A. Alcohol Consumption and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, M.G.; Fullman, N.; Hawley, C.; Arian, N.; Zimsen, S.R.; Tymeson, H.D.; Venkateswaran, V.; Tapp, A.D.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Salama, J.S.; et al. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 392, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Pan, L.; Ran, S.; Wang, M.; Huang, S.; Zhao, M.; Cao, Z.; Yao, Z.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; et al. Prediction of MAFLD and NAFLD using different screening indexes: A cross-sectional study in U.S. adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1083032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Allen, N.B.; Anderson, C.A.; Black, T.; Brewer, L.C.; Foraker, R.E.; Grandner, M.A.; Lavretsky, H.; Perak, A.M.; Sharma, G.; et al. Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct of Cardiovascular Health: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 146, e18–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Lei, W.; Liu, K.; Xu, M.; Diao, T.; Gao, H.; et al. Associations of Baseline and Changes in Leukocyte Counts with Incident Cardiovascular Events: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2022, 29, 1040–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Lifestyle Score | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poor (0–2) | Intermediate (3–4) | Ideal (5–6) | ||
| No. of cases | 4035 | 13,236 | 6137 | |
| Age, y | 62.0 (7.2) | 61.8 (7.9) | 61.4 (8.3) | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.2 (3.0) | 23.5 (2.9) | 22.4 (2.2) | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 83.5 (8.5) | 80.8 (8.4) | 77.9 (7.5) | <0.001 |
| Male | 2748 (68.1) | 6005 (45.4) | 1655 (27.0) | <0.001 |
| Education attainment, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Less than high school | 2356 (58.9) | 7679 (58.4) | 3380 (55.5) | |
| High school or equivalent | 1110 (27.7) | 3890 (29.6) | 1948 (32.0) | |
| College or above | 537 (13.4) | 1586 (12.1) | 757 (12.4) | |
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Never | 442 (22.0) | 7062 (62.4) | 9096 (90.4) | |
| Current | 1505 (74.9) | 3576 (31.6) | 463 (4.6) | |
| Former | 63 (3.1) | 672 (5.9) | 500 (5.0) | |
| Smoking status, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Never | 697 (34.7) | 7100 (63.0) | 8751 (87.4) | |
| Current | 1073 (54.3) | 2791 (24.8) | 398 (4.0) | |
| Former | 241 (12.0) | 1377 (12.2) | 861 (8.6) | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 1382 (34.4) | 4177 (31.8) | 1609 (26.4) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 928 (23.2) | 2404 (18.3) | 920 (15.1) | <0.001 |
| Gallstones, n (%) | 458 (11.4) | 1504 (11.5) | 679 (11.2) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 323 (8.1) | 1198 (9.1) | 434 (7.1) | <0.001 |
| CVD, n (%) | 686 (17.1) | 2057 (15.7) | 740 (12.2) | <0.001 |
| Vegetables and fruits (both more than daily), n (%) | 1248 (30.9) | 6254 (47.2) | 4689 (76.4) | <0.001 |
| Meat (less than daily), n (%) | 2320 (57.5) | 8593 (64.9) | 5112 (83.3) | <0.001 |
| Systolic pressure, mm Hg | 131.1 (20.0) | 129.5 (19.7) | 128.1 (19.3) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic pressure, mm Hg | 79.1 (11.8) | 77.7 (11.3) | 76.6 (10.7) | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose, mean (SD), mmol/L | 5.8 (1.5) | 5.8 (1.4) | 5.7 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.9 (1.0) | 5.0 (1.0) | 5.1 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.4 (1.0) | 1.3 (0.9) | 1.3 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.5 (0.4) | 1.5 (0.4) | 1.5 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.8 (0.8) | 2.9 (0.8) | 2.9 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| Alkaline phosphatase, mmol/L | 87.4 (26.0) | 89.0 (30.0) | 90.7 (34.1) | <0.001 |
| γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, mmol/L | 29.3 (35.2) | 24.1 (28.1) | 20.9 (19.0) | <0.001 |
| AST, mmol/L | 24.6 (14.2) | 24.5 (14.4) | 24.1 (10.7) | 0.085 |
| ALT, mmol/L | 22.2 (16.6) | 21.9 (19.8) | 21.1 (14.3) | 0.005 |
| Physical activity (h/wk) | 7.0 (6.4) | 8.7 (7.8) | 10.2 (7.5) | <0.001 |
| Sleep duration (h/d) | 8.5 (1.2) | 8.2 (1.1) | 7.9 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Lifestyle Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Poor (0–2) | Intermediate (3–4) | Ideal (5–6) | |
| Overall | |||
| No. of cases | 2248 | 6617 | 2627 |
| Univariate model | 1 [Reference] | 0.80 (0.74–0.85) | 0.60 (0.55–0.65) |
| Model a | 1 [Reference] | 0.83 (0.77–0.89) | 0.65 (0.60–0.70) |
| Model b | 1 [Reference] | 0.84 (0.78–0.90) | 0.68 (0.62–0.74) |
| Model c | 1 [Reference] | 0.79 (0.73–0.86) | 0.62 (0.57–0.68) |
| MAFLD with excess weight or obesity | |||
| No. of cases | 1869 | 4614 | 1228 |
| Univariate model | 1 [Reference] | 0.62 (0.58–0.67) | 0.29 (0.26–0.31) |
| Model a | 1 [Reference] | 0.64 (0.60–0.69) | 0.31 (0.28–0.34) |
| Model b | 1 [Reference] | 0.66 (0.61–0.71) | 0.33 (0.30–0.36) |
| Model c | 1 [Reference] | 0.63 (0.58–0.68) | 0.31 (0.28–0.34) |
| MAFLD with diabetes | |||
| No. of cases | 212 | 759 | 269 |
| Univariate model | 1 [Reference] | 1.10 (0.94–1.28) | 0.83 (0.69–0.99) |
| Model a | 1 [Reference] | 1.10 (0.94–1.28) | 0.83 (0.69–1.00) |
| Model b | 1 [Reference] | 1.09 (0.89–1.34) | 1.04 (0.82–1.33) |
| Model c | 1 [Reference] | 1.05 (0.85–1.31) | 0.97 (0.75–1.26) |
| MAFLD with MD | |||
| No. of cases | 2148 | 6209 | 2344 |
| Univariate model | 1 [Reference] | 0.75 (0.70–0.80) | 0.52 (0.48–0.57) |
| Model a | 1 [Reference] | 0.79 (0.74–0.85) | 0.54 (0.58–0.63) |
| Model b | 1 [Reference] | 0.80 (0.75–0.87) | 0.61 (0.56–0.67) |
| Model c | 1 [Reference] | 0.76 (0.70–0.82) | 0.56 (0.51–0.62) |
| Measures | Change in Lifestyle Score, ORs (95% CIs) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consistently Low | High to Low | Low to High | Consistently High | |
| No. of cases | 666 | 594 | 133 | 34 |
| MAFLD | 1 [Reference] | 0.88 (0.74–1.04) | 0.76 (0.68–0.86) | 0.71 (0.61–0.82) |
| MAFLD with excess weight or obesity | 1 [Reference] | 0.85 (0.71–1.00) | 0.72 (0.63–0.81) | 0.64 (0.56–0.74) |
| MAFLD with diabetes | 1 [Reference] | 0.76 (0.47–1.25) | 0.74 (0.54–1.02) | 0.87 (0.59–1.28) |
| MAFLD with MD | 1 [Reference] | 0.79 (0.66–0.94) | 0.49 (0.43–0.55) | 0.41 (0.35–0.48) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Li, J.; King, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Associations of Combined Lifestyle Factors with MAFLD and the Specific Subtypes in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214588
Li H, Cao Z, Li J, King L, Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Zhang S, Song Y, Zhang Q, Chen L, et al. Associations of Combined Lifestyle Factors with MAFLD and the Specific Subtypes in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214588
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongxia, Zhiqiang Cao, Jingxi Li, Lei King, Zhuangyu Zhang, Ying Zhao, Siyi Zhang, Yajing Song, Qian Zhang, Liangkai Chen, and et al. 2023. "Associations of Combined Lifestyle Factors with MAFLD and the Specific Subtypes in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study" Nutrients 15, no. 21: 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214588
APA StyleLi, H., Cao, Z., Li, J., King, L., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhang, S., Song, Y., Zhang, Q., Chen, L., Tang, Y., Dai, L., & Yao, P. (2023). Associations of Combined Lifestyle Factors with MAFLD and the Specific Subtypes in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults: The Dongfeng-Tongji Cohort Study. Nutrients, 15(21), 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214588







