NXP081, DNA Aptamer–Vitamin C Complex Ameliorates DNFB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Balb/c Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. NXP081 Preparation
2.3. DNFB-Induced AD
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. IFN-γ Production and IL-4 Production Measurements
2.7. Serum IgE Measurements
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. NXP081 Decreases DNFB-Induced AD-like Skin Inflammation
3.2. NXP081 Reduces Infiltration of Mast Cells in Skin Lesions
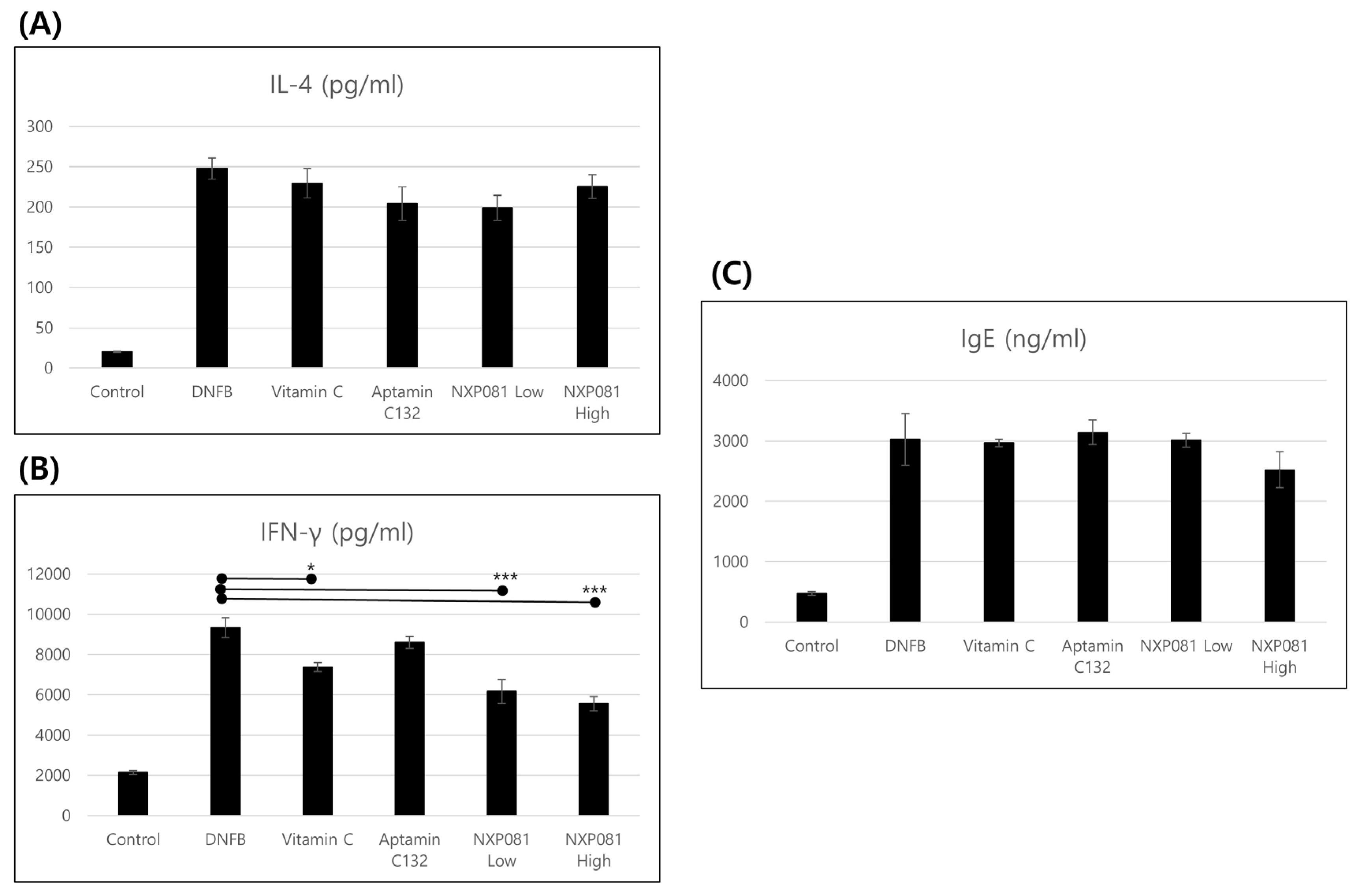
3.3. NXP081 Reduces the Levels of IFN-γ in Activated CD4+ T Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, D. Atopic dermatitis: New insights andopportunities for therapeutic intervention. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Li, X.K. Oxidative Stress in Atopic Dermatitis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2721469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, E.; Cicconi, R.; Rossi, P.; Casati, A.; Brunetti, E.; Mancino, G. Atopic dermatitis: Molecular mechanisms, clinical aspects and new therapeutical approaches. Curr. Mol. Med. 2003, 3, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Oh, S.G.; Seo, S.W.; Ahn, H.J.; Geum, D.; Cho, J.J.; Park, C.S. Oral administration of Astragalus membranaceus inhibits the development of DNFB-induced dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1468–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Long, H.; Yin, H.; Wang, L.; Gershwin, M.E.; Lu, Q. The critical role of epigenetics in systemic lupus erythematous. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.F.; Wang, G. Environmental agents, oxidative stress and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojiljković, D.; Pavlović, D.; Arsić, I. Oxidative stress, skin aging and antioxidant therapy/oksidacioni stres, starenje kože i antioksidaciona terapija. Acta Fac. Medicae Naissensis 2014, 31, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Han, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, W.; Yoon, M.Y.; Kim, G.; Kim, Y.S. Advances in dermatology using DNA aptamer “Aptamin C” innovation: Oxidative stress prevention and effect maximization of Vitamin C through antioxidation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 19, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.P.; Shin, K.O.; Park, K.; Yun, H.J.; Mann, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Cho, Y. Vitamin C Stimulates Epidermal Ceramide Production by Regulating Its Metabolic Enzymes. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, O.; Kim, N.I.; Cho, Y. Associations among plasma Vitamin C, epidermal ceramide and clinical severity of atopic dermatitis. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Qiang, M.; Dong, T.; Li, H. Role of Vitamin C in Skin Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Kwon, S.O.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Kwon, J.W.; Kim, B.J.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, W.K.; Jang, G.C.; et al. Association of Antioxidants with Allergic Rhinitis in Children from Seoul. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2013, 5, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevinho, B.N.; Carlan, I.; Blaga, A.; Rocha, F. Soluble Vitamins (Vitamin B12 and Vitamin C) microencapsulated with different biopolymers by a spray drying process. Powder Techol. 2016, 289, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carita, A.C.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Shultz, J.D.; Michniak-Kohn, B.; Chorilli, M.; Leonardi, G.R. Vitamin C: One compound, several uses. Advances for delivery, efficiency and stability. Nanomed. NBM 2020, 24, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhizkar, E.; Rashedinia, M.; Karimi, M.; Alipour, S. Design and development of Vitamin C-encapsulated proliposome with improved in-vitro and ex-vivo antioxidant efficacy. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, A.S.; Sankarapani, V.; Drabek, R.; Jackson, G.W.; Batchelor, R.H.; Kim, Y.-S. Inhibition of Vitamin C oxidation by DNA aptamers. Aptamers 2018, 2, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, T.; Xiao, W.; Gao, P.; Namiranian, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Tomimori, Y.; Hong, H.; Yamashita, H.; Kimura, M.; Kashiwakura, J.-I.; et al. Critical role for mast cell stat5 activity in skin inflammation. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2010, 22, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; He, R.; Oyoshi, M.; Geha, R. Animal models of atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-J. Neuroprotective effect of NXP031 in the MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 740, 135425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Jo, H.; Go, C.; Jeong, Y.; Jang, Y.; Kang, D.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kang, J.S. The Anti-inflammatory Effect of Aptamin C in House Dust Mite Extract-induced Inflammation in Keratinocytes via Regulation of IL-22 and GDNF Production. Amtioxidants 2021, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemila, H. Vitamin C and common cold-induced asthma: A systemic review and statistical analysis. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, T.-Y. Effects of VitabridC12 on skin inflammation. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.; Lim, H.; Moon, S.-K.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, D.; Hwang, Y.I. Mega-dose Vitamin C modulates T cell functions in Balb/c mice only when administered during T cell activation. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 98, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Ahn, K.; Paik, H.Y.; Chung, S.-J. Serum immunoglobulin E levels and dietary intake of Korean infants and young children with atopic dermatitis. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2012, 6, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, B.V.; Morton, J.I. Vitamin C and the immune response. Experientia 1977, 33, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, W.; Bloch, J.; Gilich, G.; Mitchell, G. A systemic study of the effect of Vitamin C supplementation on the humoral immune response in ascorbate-dependent mammals. I. The antibody response to sheep red blood cells (a T-dependent antigen) in guinea pigs. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1980, 50, 294–357. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Ahn, H.-J.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Cho, J.-J.; Park, C.-S. NXP081, DNA Aptamer–Vitamin C Complex Ameliorates DNFB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Balb/c Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194172
Lee S, Ahn H-J, Park YS, Kim J-H, Kim Y-S, Cho J-J, Park C-S. NXP081, DNA Aptamer–Vitamin C Complex Ameliorates DNFB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Balb/c Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194172
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sanggon, Hyun-Jong Ahn, Yong Seek Park, Ji-Hyun Kim, Yoon-Seong Kim, Jeong-Je Cho, and Cheung-Seog Park. 2023. "NXP081, DNA Aptamer–Vitamin C Complex Ameliorates DNFB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Balb/c Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194172
APA StyleLee, S., Ahn, H.-J., Park, Y. S., Kim, J.-H., Kim, Y.-S., Cho, J.-J., & Park, C.-S. (2023). NXP081, DNA Aptamer–Vitamin C Complex Ameliorates DNFB-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Balb/c Mice. Nutrients, 15(19), 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194172





