Effect of Lactobacillaceae Probiotics on Colonic Microbiota and Metabolite Production in Cystic Fibrosis: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Probiotic Strains
2.2. In Vitro Colonic Fermentation Using the SHIME®®
2.3. Microbiota Composition by 16S rRNA Amplicon Gene Sequencing
2.4. Metabolic Activity: Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs), Ammonia and Lactate
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
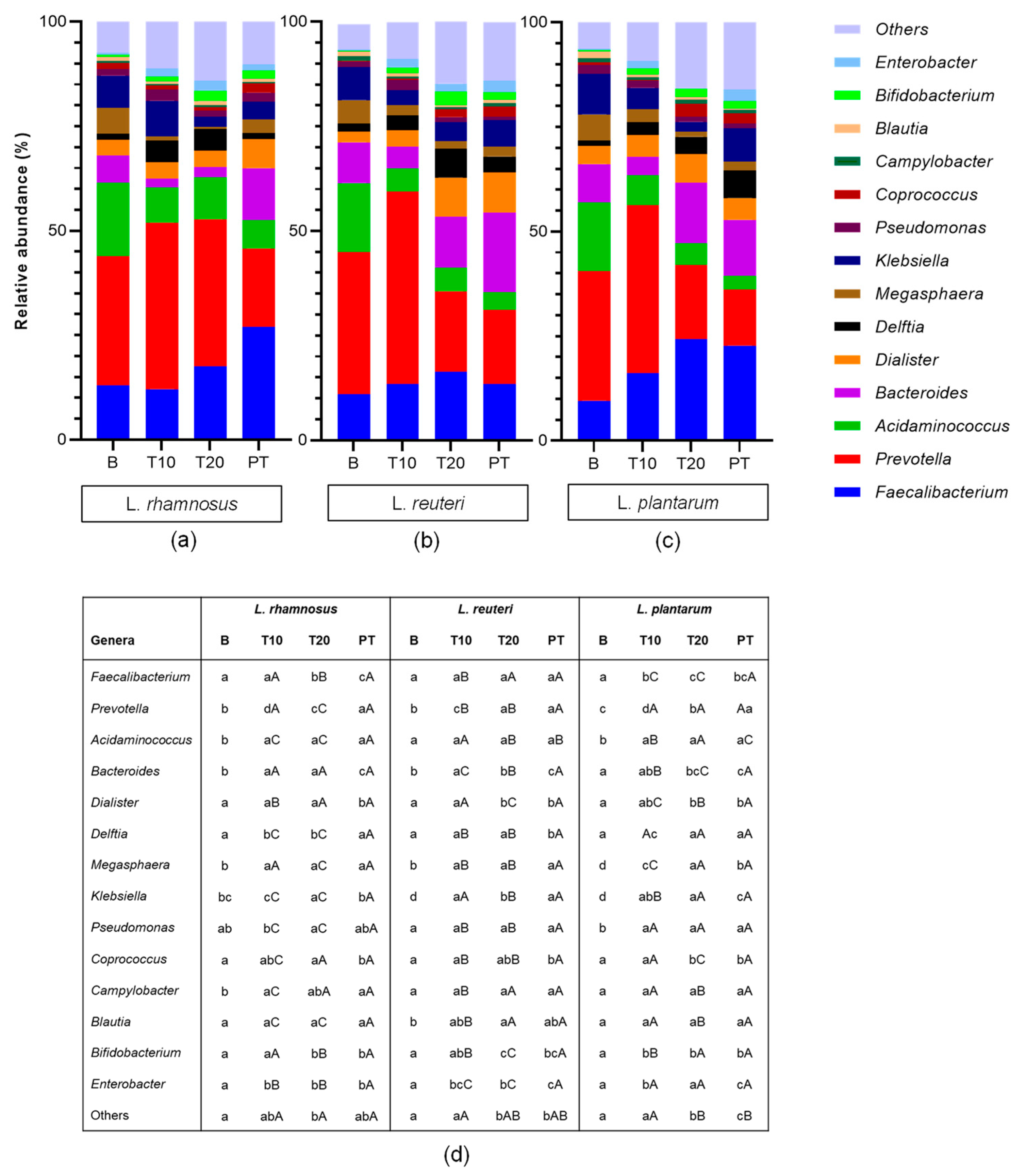
3.1. Effect of Probiotic Administration on Colonic Microbiota Populations
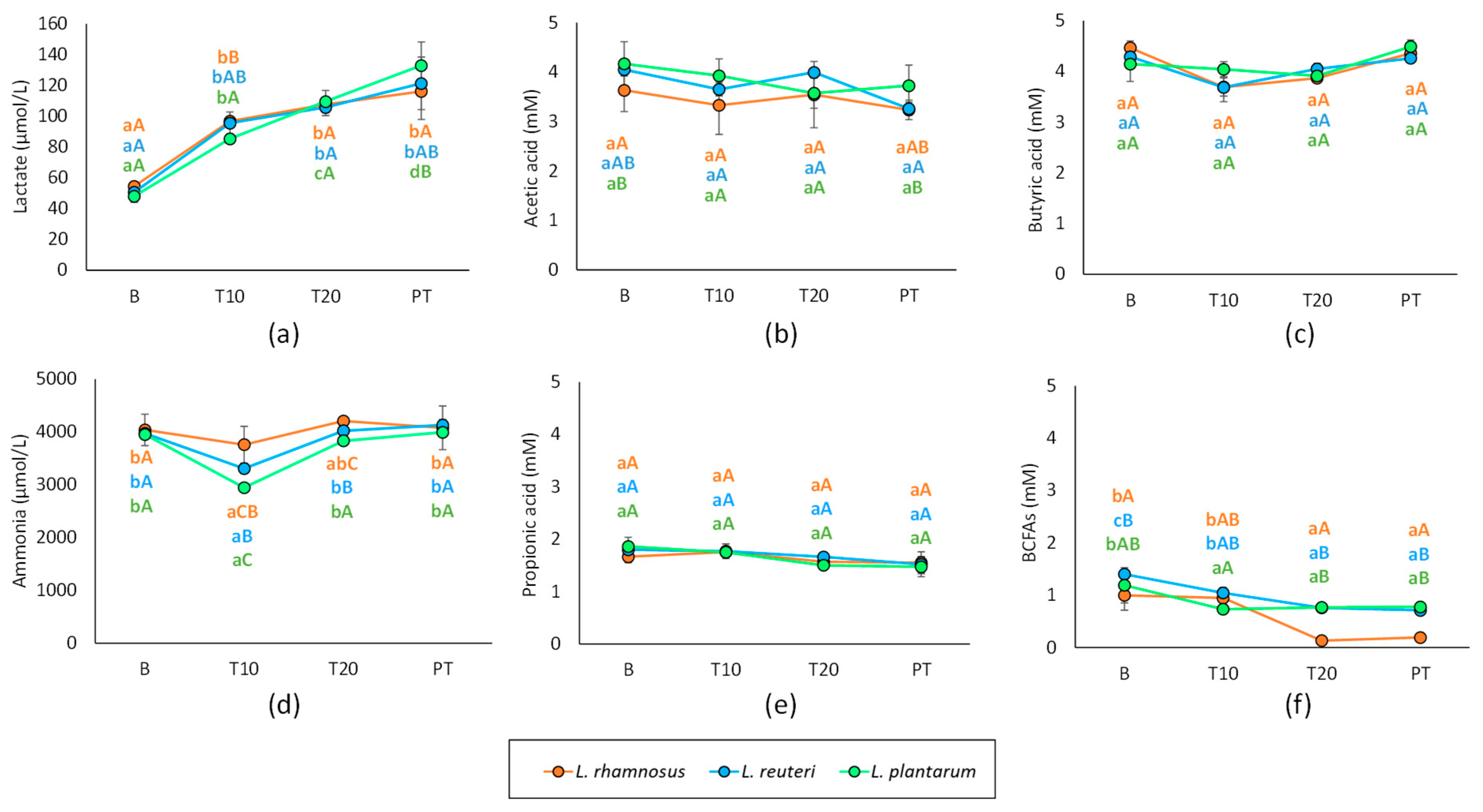
3.2. Effect of Probiotic Administration on Metabolic Activity
3.3. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lusman, S.; Sulliva, J. Nutrition and Growth in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2016, 63, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Leach, S.T.; Katz, T.; Day, A.S.; Ja, A.; Ooi, C.Y. Update of faecal markers of inflammation in children with cystic fibrosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 948367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Lerma, J.; Boon, M.; Hulst, J.; Colombo, C.; Asseiceira, I.; Garriga, M.; Masip, E.; Claes, I.; Bulfamante, A.; Janssens, H.M.; et al. Change in nutrient and dietary intake in European children with cystic fibrosis after a 6-month intervention with a self-management mHealth tool. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duytschaever, G.; Huys, G.; Bekaert, M.; Boulanger, L.; De Boeck, K.; Vandamme, P. Dysbiosis of Bifidobacteria and Clostridium cluster XIVa in the cystic fibrosis fecal microbiota. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antosca, K.M.; Chernikova, D.A.; Price, C.E.; Ruoff, K.L.; Li, K.; Guill, M.F.; Sontag, N.R.; Morrison, H.G.; Hao, S.; Drumm, M.L.; et al. Altered Stool Microbiota of Infants with Cystic Fibrosis Shows a Reduction in Genera Associat-ed with Immune. Programming from Birth. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, e00274-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, M.B.; Moreira, E.A.M.; Tomio, C.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Daltoé, F.; Barbosa, E.; Neto, N.L.; Buccigrossi, V.; Guarino, A. Altered intestinal microbiota composition, antibiotic therapy and intestinal inflammation in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, S.; Iebba, V.; Santangelo, F.; Gagliardi, A.; De Biase, R.V.; Stamato, A.; Bertasi, S.; Lucarelli, M.; Conte, M.P.; Quattrucci, S. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) allelic variants relate to shifts in faecal microbiota of cystic fibrosis patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albedewi, H.; Bindayel, I.; Albarrag, A.; Banjar, H. Correlation of Gut Microbiota, Vitamin D Status, and Pulmonary Function Tests in Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 884104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.G.; Fouhy, F.; Harrison, M.J.; Rea, M.C.; Cotter, P.D.; O’sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C.; Shanahan, F.; Plant, B.J.; et al. The altered gut microbiota in adults with cystic fibrosis. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Coffey, M.J.; Nielsen, S.; Wemheuer, B.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Garg, M.; Needham, B.; Pickford, R.; Jaffe, A.; Thomas, T.; Ooi, C.Y. Gut microbiota in children with cystic fibrosis: A taxonomic and functional dysbiosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Levy, R.; Pope, C.E.; Hayden, H.S.; Brittnacher, M.J.; Carr, R.; Radey, M.C.; Hager, K.R.; Heltshe, S.L.; Ramsey, B.W.; et al. Metagenomic evidence for taxonomic dysbiosis and functional imbalance in the gastrointestinal tracts of children with cystic fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Pope, C.E.; Hayden, H.S.; Heltshe, S.; Levy, R.; McNamara, S.; Jacobs, M.A.; Rohmer, L.; Radey, M.; Ramsey, B.W.; et al. Escherichia coli dysbiosis correlates with gastrointestinal dysfunction in children with cystic fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caley, L.R.; White, H.; de Goffau, M.C.; Floto, R.A.; Parkhill, J.; Marsland, B.; Peckham, D.G. Cystic Fibrosis-Related Gut Dysbiosis: A Systematic Review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 1797–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, M.; Prevaes, S.; Kalkman, G.; Tramper-Stranders, G.A.; Hasrat, R.; Groot, K.M.W.; Janssens, H.M.; Tiddens, H.A.; van Westreenen, M.; Sanders, E.A.M.; et al. Development of the gut microbiota in early life: The impact of cystic fbrosis and antibiotic treatment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miragoli, F.; Federici, S.; Ferrari, S.; Minuti, A.; Rebecchi, A.; Bruzzese, E.; Buccigrossi, V.; Guarino, A.; Callegari, M.L. Impact of cystic fbrosis disease on archaea and bacteria composition of gut microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhere, M.; He, J.; Chassaing, B.; Ziegler, T.R.; Alvarez, J.A.; Ivie, E.A.; Hao, L.; Hanfelt, J.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Tangpricha, V. Bolus weekly vitamin D3 supplementation impacts gut and airway microbiota in adults with cystic fibrosis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dorst, J.M.; Tam, R.Y.; Ooi, C.Y. What Do We Know about the Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis? Is There a Role for Probiotics and Prebiotics? Nutrients 2022, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Testa, I.; Zani, E.M.; Cunico, D.; Torelli, L.; Grandinetti, R.; Fainardi, V.; Pisi, G.; Principi, N. Probiotics Administration in Cystic Fibrosis: What Is the Evidence? Nutrients 2022, 14, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veintimilla-Gozalbo, E.; Asensio-Grau, A.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. In vitro simulation of human colonic fermentation: A practical approach towards models’ design and analytical tools. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, L. Thirty Years of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: A Review. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53 (Suppl. 1), S1–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; He, B.; Hoang, T.K.; Taylor, C.M.; Blanchard, E.; Freeborn, J.; Park, S.; Luo, M.; Couturier, J.; et al. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 feeding of healthy newborn mice regulates immune responses while modulating gut microbiota and boosting beneficial metabolites. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G824–G838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.N.; Marcelino-Guimarães, F.C.; Vilas-Bôas, G.T.; Matsuo, T.; Miglioranza, L.H. Potential fate of ingested Lactobacillus plantarum and its occurrence in human feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adorno, M.A.T.; Hirasawa, J.S.; Varesche, M.B.A. Development and validation of two methods to quantify volatile acids (C2-C6) by GC/FID: Headspace (automatic and manual) and liquid-liquid extraction (LLE). Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E. Prevotella in the gut: Choose carefully. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, A.; Pasolli, E.; Masetti, G.; Ercolini, D.; Segata, N. Prevotella diversity, niches and interactions with the human host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfond, D.; Ma, C.; Semler, J.; Borowitz, D. Intestinal pH and gastrointestinal transit profiles in cystic fibrosis patients measured by wireless motility capsule. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, N.W.; De Zoete, M.R.; Cullen, T.W.; Barry, N.A.; Stefanowski, J.; Hao, L.; Degnan, P.H.; Hu, J.; Peter, I.; Zhang, W.; et al. Immunoglobulin A coating identifies colitogenic bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2014, 158, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljazovic, A.; Amend, L.; Galvez, E.J.; de Oliveira, R.; Strowig, T. Modulation of inflammatory responses by gastrointestinal Prevotella spp.–from associations to functional studies. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 311, 151472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, Z.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus rhamnosus FJSYC4-1 and Lactobacillus reuteri FGSZY33L6 alleviate metabolic syndrome via gut microbiota regulation. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3919–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Needham, B.; Leach, S.T.; Day, A.S.; Jaffe, A.; Thomas, T.; Ooi, C.Y. Disrupted progression of the intestinal microbiota with age in children with cystic fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.; Gavillet, H.; Hanson, L.; Ng, C.; Mitchell-Whyte, M.; Major, G.; Smyth, A.R.; Rivett, D.; van der Gast, C. Intestinal function and transit associate with gut microbiota dysbiosis in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, S.H.; Greysson-Wong, J.; Somayaji, R.; Storey, D.G.; Rabin, H.R.; Surette, M.G.; Parkins, M. Incidence, impact and natural history of Klebsiella species infections in cystic fibrosis: A longitudinal single center study. Can. J. Respir. Crit. 2019, 3, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins, M.L.; Roy, D.; Toupin, C.; Goulet, J. Uncoupling of growth and acids production in Bifidobacterium ssp. J. Dairy. Sci. 1990, 73, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.H.; Hold, G.L.; Harmsen, H.J.; Stewart, C.S.; Flint, H.J. Growth requirements and fermentation products of Fusobacterium prausnitzii, and a proposal to reclassify it as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, S.; Nirmalkar, K.; Hoyo-Vadillo, C.; García-Espitia, M.; Ramírez-Sánchez, D.; García-Mena, J. Gut microbiome production of short-chain fatty acids and obesity in children. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zanten, G.C.; Krych, L.; Röytiö, H.; Forssten, S.; Lahtinen, S.J.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sørensen, S.; Svensson, B.; Jespersen, L.; Jakobsen, M. Synbiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and cellobiose does not affect human gut bacterial diversity but increases abundance of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and branched-chain fatty acids: A randomized, double-blinded cross-over trial. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.; De Souza, R.; Kendall, C.W.; Emam, A.; Jenkins, D.J. Colonic health: Fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windey, K.; De Preter, V.; Verbeke, K. Relevance of protein fermentation to gut health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.J. Production of branched-chain volatile fatty acids by certain anaerobic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzese, E.; Raia, V.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Volpicelli, M.; De Marco, G.; Maiuri, L.; Guarino, A. Effect of Lactobacillus GG supplementation on pulmonary exacerbations in patients with cystic fibrosis: A pilot study. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.J.; Santee, C.; McCauley, K.; Panzer, A.R.; Lynch, S.V. Gut Bifidobacteria enrichment following oral Lactobacillus-supplementation is associated with clinical improvements in children with cystic fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Campo, R.; Garriga, M.; Pérez-Aragón, A.; Guallarte, P.; Lamas, A.; Máiz, L.; Bayón, C.; Roy, G.; Cantón, R.; Zamora, J.; et al. Improvement of digestive health and reduction in proteobacterial populations in the gut microbiota of cystic fibrosis patients using a Lactobacillus reuteri probiotic preparation: A double blind prospective study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzese, E.; Raia, V.; Ruberto, E.; Scotto, R.; Giannattasio, A.; Bruzzese, D.; Cavicchi, M.C.; Francalanci, M.; Colombo, C.; Faelli, N.; et al. Lack of efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in reducing pulmonary exacerbations and hospital admissions in children with cystic fibrosis: A randomised placebo controlled trial. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikniaz, Z.; Nikniaz, L.; Bilan, N.; Somi, M.H.; Faramarzi, E. Does probiotic supplementation affect pulmonary exacerbation and intestinal inflammation in cystic fibrosis: A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. World J. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzorati, M.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Bubeck, S.; Bayne, T.; Krishnan, K.; Young, A. Treatment with a spore-based probiotic containing five strains of Bacillus induced changes in the metabolic activity and community composition of the gut microbiota in a SHIME® model of the human gastrointestinal system. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque, A.L.R.F.; Demarqui, F.M.; Santoni, M.M.; Zanelli, C.F.; Adorno, M.A.T.; Milenkovic, D.; Mesa, V.; Sivieri, K. Effect of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic on the gut microbiota of autistic children using an in vitro gut microbiome model. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Abbeele, P.; Venema, K.; Van de Wiele, T.; Verstraete, W.; Possemiers, S. Different human gut models reveal the distinct fermentation patterns of arabinoxylan versus inulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9819–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asensio-Grau, A.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Ferriz-Jordán, M.; García-Hernández, J.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. Effect of Lactobacillaceae Probiotics on Colonic Microbiota and Metabolite Production in Cystic Fibrosis: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173846
Asensio-Grau A, Calvo-Lerma J, Ferriz-Jordán M, García-Hernández J, Heredia A, Andrés A. Effect of Lactobacillaceae Probiotics on Colonic Microbiota and Metabolite Production in Cystic Fibrosis: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(17):3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173846
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsensio-Grau, Andrea, Joaquim Calvo-Lerma, Miguel Ferriz-Jordán, Jorge García-Hernández, Ana Heredia, and Ana Andrés. 2023. "Effect of Lactobacillaceae Probiotics on Colonic Microbiota and Metabolite Production in Cystic Fibrosis: A Comparative In Vitro Study" Nutrients 15, no. 17: 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173846
APA StyleAsensio-Grau, A., Calvo-Lerma, J., Ferriz-Jordán, M., García-Hernández, J., Heredia, A., & Andrés, A. (2023). Effect of Lactobacillaceae Probiotics on Colonic Microbiota and Metabolite Production in Cystic Fibrosis: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Nutrients, 15(17), 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15173846





