High Frequency of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Patients Diagnosed with Celiac Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
2.2. Helicobacter pylori Status
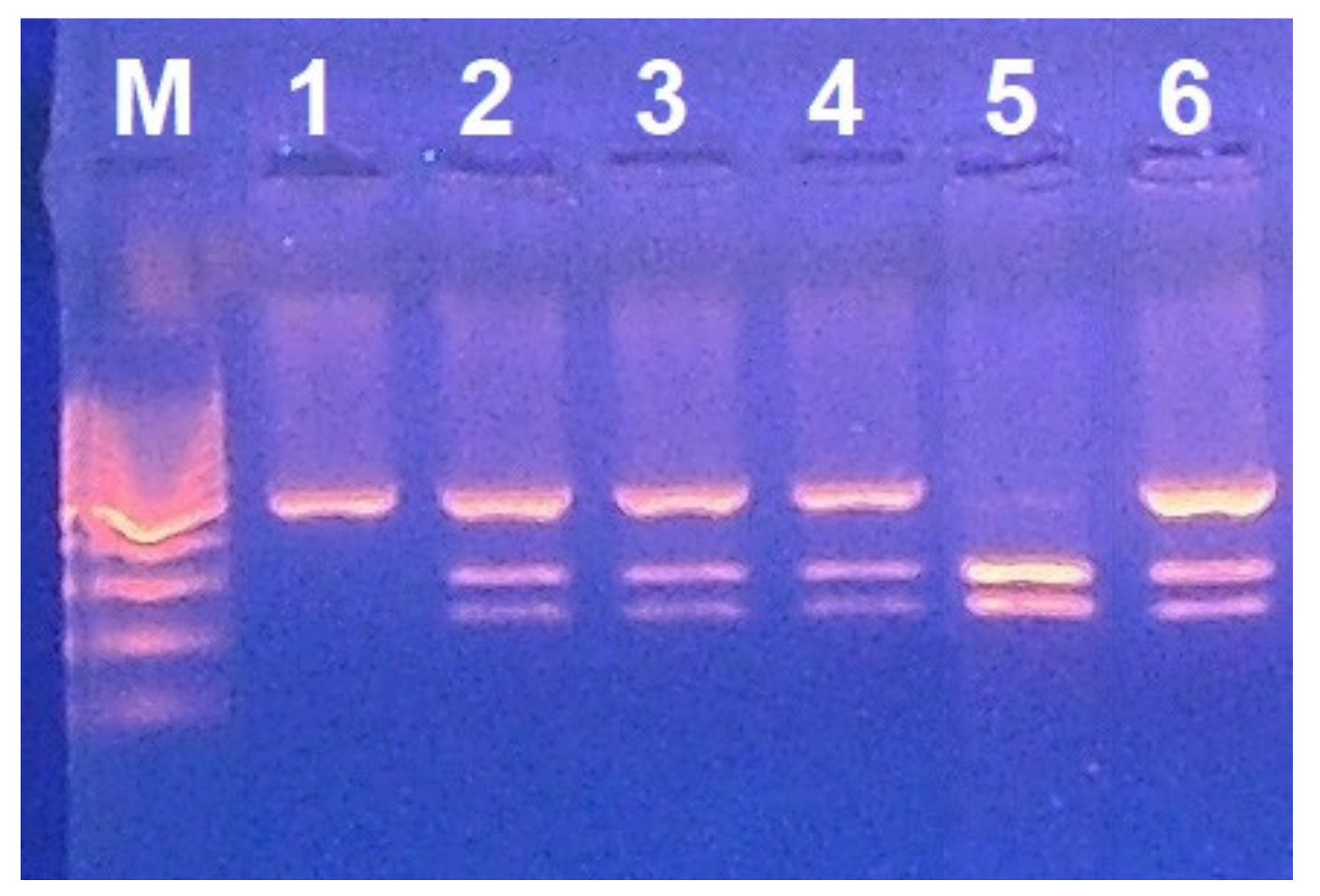
2.3. G6PD Deficiency Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; van Dyke, C.T.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Lahr, B.D.; Murray, J.A. Increasing incidence of celiac disease in a North American population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catassi, C.; Gatti, S.; Fasano, A. The new epidemiology of celiac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59 (Suppl. S1), S7–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, C.; Rostom, A.; Sy, R.; Cranney, A.; Saloojee, N.; Garritty, C.; Sampson, M.; Zhang, L.; Yazdi, F.; Mamaladze, V.; et al. The prevalence of celiac disease in average-risk and at-risk Western European populations: A systematic review. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, S57–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, M.P.; Cuccu, M.; Pes, G.M.; Mameli, L.; Manca, A.; Vidili, G.; Togniotti, E. Clinical pattern of celiac disease in a population residing in North Sardinia (Italy). Recenti Prog. Med. 2012, 103, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakireva, A.V.; Zamyatnin, A.A. Properties of Gluten Intolerance: Gluten Structure, Evolution, Pathogenicity and Detoxification Capabilities. Nutrients 2016, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, K.M.; Lu, R.; Brownley, J.; Lu, B.; Gerard, C.; Thomas, K.; Rallabhandi, P.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Tamiz, A.; Alkan, S.; et al. Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to the chemokine receptor CXCR3. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 194–204.e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitnes, A.C.; Raki, M.; Brottveit, M.; Lundin, K.E.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Sollid, L.M. Rapid accumulation of CD14+CD11c+ dendritic cells in gut mucosa of celiac disease after in vivo gluten challenge. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, D.; Kovaleva, E.; Schatz, P.J. A minimal peptide substrate in biotin holoenzyme synthetase-catalyzed biotinylation. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, S.; Molina, I.J.; Romero, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Pena, J.; Sanchez, F.; Reynoso, F.R.; Perez-Navero, J.L.; Estevez, O.; Ortega, C.; et al. Characterization of gliadin-specific Th17 cells from the mucosa of celiac disease patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, I.; Sarra, M.; Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Franze, E.; Fina, D.; Fabrizi, A.; MacDonald, T.T.; Pallone, F.; Monteleone, G. Characterization of IL-17A-producing cells in celiac disease mucosa. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamut, G.; El Machhour, R.; Montcuquet, N.; Martin-Lanneree, S.; Dusanter-Fourt, I.; Verkarre, V.; Mention, J.J.; Rahmi, G.; Kiyono, H.; Butz, E.A.; et al. IL-15 triggers an antiapoptotic pathway in human intraepithelial lymphocytes that is a potential new target in celiac disease-associated inflammation and lymphomagenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2131–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl, B.; Blaser, M.J.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Green, P.H.; Rundle, A.; Sonnenberg, A.; Genta, R.M. Decreased risk of celiac disease in patients with Helicobacter pylori colonization. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Salis, R.; Loria, M.F.; Villanacci, V.; Bassotti, G.; Pes, G.M. Helicobacter pylori infection and occurrence of celiac disease in subjects HLA-DQ2/DQ8 positive: A prospective study. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, Y.L.; Bondar, C.; Guzman, L.; Cueto Rua, E.; Chopita, N.; Fuertes, M.; Zwirner, N.W.; Chirdo, F.G. Broad MICA/B expression in the small bowel mucosa: A link between cellular stress and celiac disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odetti, P.; Valentini, S.; Aragno, I.; Garibaldi, S.; Pronzato, M.A.; Rolandi, E.; Barreca, T. Oxidative stress in subjects affected by celiac disease. Free Radic. Res. 1998, 29, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivabene, R.; Mancini, E.; De Vincenzi, M. In vitro cytotoxic effect of wheat gliadin-derived peptides on the Caco-2 intestinal cell line is associated with intracellular oxidative imbalance: Implications for coeliac disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1453, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojiljkovic, V.; Todorovic, A.; Radlovic, N.; Pejic, S.; Mladenovic, M.; Kasapovic, J.; Pajovic, S.B. Antioxidant enzymes, glutathione and lipid peroxidation in peripheral blood of children affected by coeliac disease. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 44, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaflarska-Poplawska, A.; Siomek, A.; Czerwionka-Szaflarska, M.; Gackowski, D.; Rozalski, R.; Guz, J.; Szpila, A.; Zarakowska, E.; Olinski, R. Oxidatively damaged DNA/oxidative stress in children with celiac disease. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2010, 19, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Roncoroni, L.; Vezzoli, A.; Dellanoce, C.; Monguzzi, E.; Branchi, F.; Ferretti, F.; Lombardo, V.; Doneda, L.; et al. Oxidative stress as a biomarker for monitoring treated celiac disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, T.Y. Intestinal glutathione: Determinant of mucosal peroxide transport, metabolism, and oxidative susceptibility. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegers, C.P.; Riemann, D.; Thies, E.; Younes, M. Glutathione and GSH-dependent enzymes in the gastrointestinal mucosa of the rat. Cancer Lett. 1988, 40, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmanski, J.; Siddiqi, M.; Deitch, E.A.; Spolarics, Z. Augmented IL-10 production and redox-dependent signaling pathways in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient mouse peritoneal macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorelli, G.; Meloni, T.; Palomba, V.; Manoussakis, C.; Villa, S.; Cappellini, M.D. Gene frequency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) polymorphic variants in Sardinia. Gene Geogr. 1990, 4, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement. Celiac Disease 2004. Available online: http://consensus.nih.gov/ (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Hill, I.D.; Kelly, C.P.; Calderwood, A.H.; Murray, J.A.; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guidelines: Diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husby, S.; Murray, J.A.; Katzka, D.A. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Diagnosis and Monitoring of Celiac Disease-Changing Utility of Serology and Histologic Measures: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K.E.A. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberhuber, G.; Granditsch, G.; Vogelsang, H. The histopathology of coeliac disease: Time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1999, 11, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, M.P.; Cipolli, A.; Ruggiu, M.W.; Manca, A.; Bassotti, G.; Pes, G.M. Helicobacter pylori eradication may influence timing of endoscopic surveillance for gastric cancer in patients with gastric precancerous lesions: A retrospective study. Medicine 2018, 97, e9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Pes, G.M. What Is New in Helicobacter pylori Diagnosis. An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, A.; Paleari, R.; Rosti, E.; Luzzana, M.; Barella, S.; Sollaino, C.; Galanello, R. Simultaneous automated determination of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase activities in whole blood. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1996, 34, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Vita, G.; Alcalay, M.; Sampietro, M.; Cappellini, M.D.; Fiorelli, G.; Toniolo, D. Two point mutations are responsible for G6PD polymorphism in Sardinia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1989, 44, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.C. An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2011, 46, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, C.; Cirillo, M.; Sollazzo, R.; Savino, G.; Sabbatini, F.; Mazzacca, G. Gender and clinical presentation in adult celiac disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 30, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, A.; Maino, C.; Niveloni, S.; Pedreira, S.; Vazquez, H.; Smecuol, E.; Fiorini, A.; Cabanne, A.; Bartellini, M.A.; Kogan, Z.; et al. Characterization of gastric mucosal lesions in patients with celiac disease: A prospective controlled study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, C.; Squillante, A.; Rendina, D.; Limauro, S.; Bencivenga, C.; Labanca, F.; Romano, R.; Mazzacca, G. Helicobacter pylori infection and peptic disease in coeliac disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 12, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betke, K.; Beutler, E.; Brewer, G.H. Standardization of Procedures for the Study of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase; Report of a WHO Scientific Group; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Pes, G.M.; Errigo, A.; Bitti, A.; Dore, M.P. Effect of age, period and birth-cohort on the frequency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in Sardinian adults. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comba, A.; Gureser, A.S.; Karasartova, D.; Senat, A.; Erel, O.; Taylan Ozkan, A. Thiol-disulfide homeostasis in children with celiac disease. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf, S.W.; Wilhelm Filho, D.; Parisotto, E.B.; Medeiros, G.D.S.; Pereira, C.H.J.; Maraslis, F.T.; Dornelles Schoeller, C.C.; Rosa, J.S.D.; Frode, T.S. DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation in children with celiac disease. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2020, 43, e20180390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosnut, F.O.; Canan, O.; Ozcay, F.; Ozbek, N. Awareness of glucose-6 phosphate-dehydrogenase deficiency in celiac disease. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISTAT. Available online: https://www.tuttitalia.it/sardegna/statistiche/popolazione-andamento-demografico/ (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- AIC. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_3025_allegato.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Sollid, L.M.; Thorsby, E. HLA susceptibility genes in celiac disease: Genetic mapping and role in pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninfali, P.; Malatesta, M.; Biagiotti, E.; Aluigi, G.; Gazzanelli, G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in small intestine of rabbit: Biochemical properties and subcellular localization. Acta Histochem. 2001, 103, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Gu, H.; Zhang, H.; Fan, R. G6PD downregulation triggered growth inhibition and induced apoptosis by regulating STAT3 signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piomelli, S.; Corash, L.M.; Davenport, D.D.; Miraglia, J.; Amorosi, E.L. In vivo lability of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in GdA- and GdMediterranean deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 1968, 47, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moras, M.; Lefevre, S.D.; Ostuni, M.A. From Erythroblasts to Mature Red Blood Cells: Organelle Clearance in Mammals. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. G6PD deficiency shifts polarization of monocytes/macrophages towards a proinflammatory and profibrotic phenotype. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, G.; Songini, M.; Doria, A.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Lorenzi, M. Increased prevalence of proliferative retinopathy in patients with type 1 diabetes who are deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saha, N.; Tay, J.S.; Das, M.K.; Das, K.; Roy, M.; Dey, B.; Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, B.N. The distribution of some serum protein and red cell enzyme polymorphisms in the Koch ethnic group of West Bengal, India. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi 1990, 35, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K.E.; Murray, J.A.; David, C.S. HLA-DQ determines the response to exogenous wheat proteins: A model of gluten sensitivity in transgenic knockout mice. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5595–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, T.; Ulfgren, A.K.; Lindroos, E.; Dann, A.A.; Dahlbom, I.; Klareskog, L. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and tissue transglutaminase expression in the small intestine in children with coeliac disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2002, 56, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, F.; Bonatesta, R.R.; Frongia, B.; Uda, S.; Banni, S.; Melis, M.P.; Collu, M.; Madeddu, C.; Serpe, R.; Puddu, S.; et al. Production of inflammatory molecules in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from severely glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient subjects. J. Vasc. Res. 2007, 44, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, G.; Daveson, A.J.M.; Hooi, C.E.; Tye-Din, J.A.; Wang, S.; Szymczak, E.; Williams, L.J.; Dzuris, J.L.; Neff, K.M.; Truitt, K.E.; et al. Serum cytokines elevated during gluten-mediated cytokine release in coeliac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benahmed, M.; Meresse, B.; Arnulf, B.; Barbe, U.; Mention, J.J.; Verkarre, V.; Allez, M.; Cellier, C.; Hermine, O.; Cerf-Bensussan, N. Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling by IL-15: A new role for IL-15 in the loss of immune homeostasis in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney-Francis, N.L.; Wahl, S.M. Transforming growth factor beta: A matter of life and death. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 55, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurien, M.; Trott, N.; Sanders, D.S. Long-term care for patients with coeliac disease in the UK: A review of the literature and future directions. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | No Celiac Disease (n = 7711) | Celiac Disease (n = 627) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 2826 (36.6) | 125 (19.9) |
| Female | 4885 (63.4) | 502 (80.1) ** |
| Age, n (%) | ||
| <30 | 856 (11.1) | 177 (28.2) |
| 30–39 | 1096 (14.2) | 126 (20.1) |
| 40–49 | 1280 (16.6) | 138 (22.0) |
| 50–59 | 1456 (18.9) | 87 (13.9) |
| 60–69 | 1593 (20.7) | 61 (9.7) |
| 70–79 | 1122 (14.6) | 33 (5.3) |
| ≥80 | 308 (4.0) | 5 (0.8) |
| Residence, n (%) | ||
| Urban | 3790 (49.2) | 410 (65.4) |
| Rural | 3921 (50.8) | 217 (34.6) * |
| Smoke, n (%) | ||
| Never | 4066 (52.7) | 380 (60.6) |
| Current or former | 3645 (47.3) | 247 (39.4) ** |
| H. pylori infection, n (%) | ||
| No | 3361 (43.6) | 421 (67.1) |
| Yes | 4350 (56.4) | 206 (32.9) ** |
| G6PD 1 deficiency, n (%) | ||
| No | 6782 (88.0) | 529 (84.4) |
| Yes | 929 (12.0) | 98 (15.6) ** |
| Variable | G6PD 1 Normal (n = 2054) | G6PD 1-Deficient (n = 1027) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 530 (25.8) | 265 (25.8) |
| Female | 1524 (64.2) | 762 (64.2) |
| Age, n (%) | ||
| <50 | 872 (42.5) | 440 (42.9) |
| ≥50 | 1182 (57.5) | 587 (57.1) |
| Residence, n (%) | ||
| Urban | 1059 (51.5) | 528 (51.4) |
| Rural | 995 (48.5) | 499 (48.6) |
| Smoke, n (%) | ||
| Never | 1092 (53.2) | 560 (54.5) |
| Current or former | 962 (46.8) | 467 (45.5) |
| H. pylori infection, n (%) | ||
| No | 903 (44.0) | 448 (43.6) |
| Yes | 1151 (56.0) | 579 (56.4) |
| Celiac disease, n (%) | ||
| No | 1917 (93.3) | 929 (90.5) |
| Yes | 137 (6.7) | 98 (9.5) ** |
| Variable | Males | Females | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD 1 | G6PD 1 | G6PD 1 | G6PD 1 | |
| normal | deficient | normal | -deficient | |
| No. patients | 530 | 265 | 1524 | 762 |
| CD (%) | 2.6 | 7.5 | 9.1 | 11.9 |
| Parameters | ||||
| Estimate 2 | 0.049 | 0.023 | ||
| SE 3 | 0.015 | 0.013 | ||
| t value | 3.256 | 1.770 | ||
| p | 0.001 | 0.076 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dore, M.P.; Errigo, A.; Bibbò, S.; Manca, A.; Pes, G.M. High Frequency of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Patients Diagnosed with Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091815
Dore MP, Errigo A, Bibbò S, Manca A, Pes GM. High Frequency of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Patients Diagnosed with Celiac Disease. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091815
Chicago/Turabian StyleDore, Maria Pina, Alessandra Errigo, Stefano Bibbò, Alessandra Manca, and Giovanni Mario Pes. 2022. "High Frequency of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Patients Diagnosed with Celiac Disease" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091815
APA StyleDore, M. P., Errigo, A., Bibbò, S., Manca, A., & Pes, G. M. (2022). High Frequency of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Patients Diagnosed with Celiac Disease. Nutrients, 14(9), 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091815









