Associations of Human Milk Oligosaccharides with Infant Brain Tissue Organization and Regional Blood Flow at 1 Month of Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
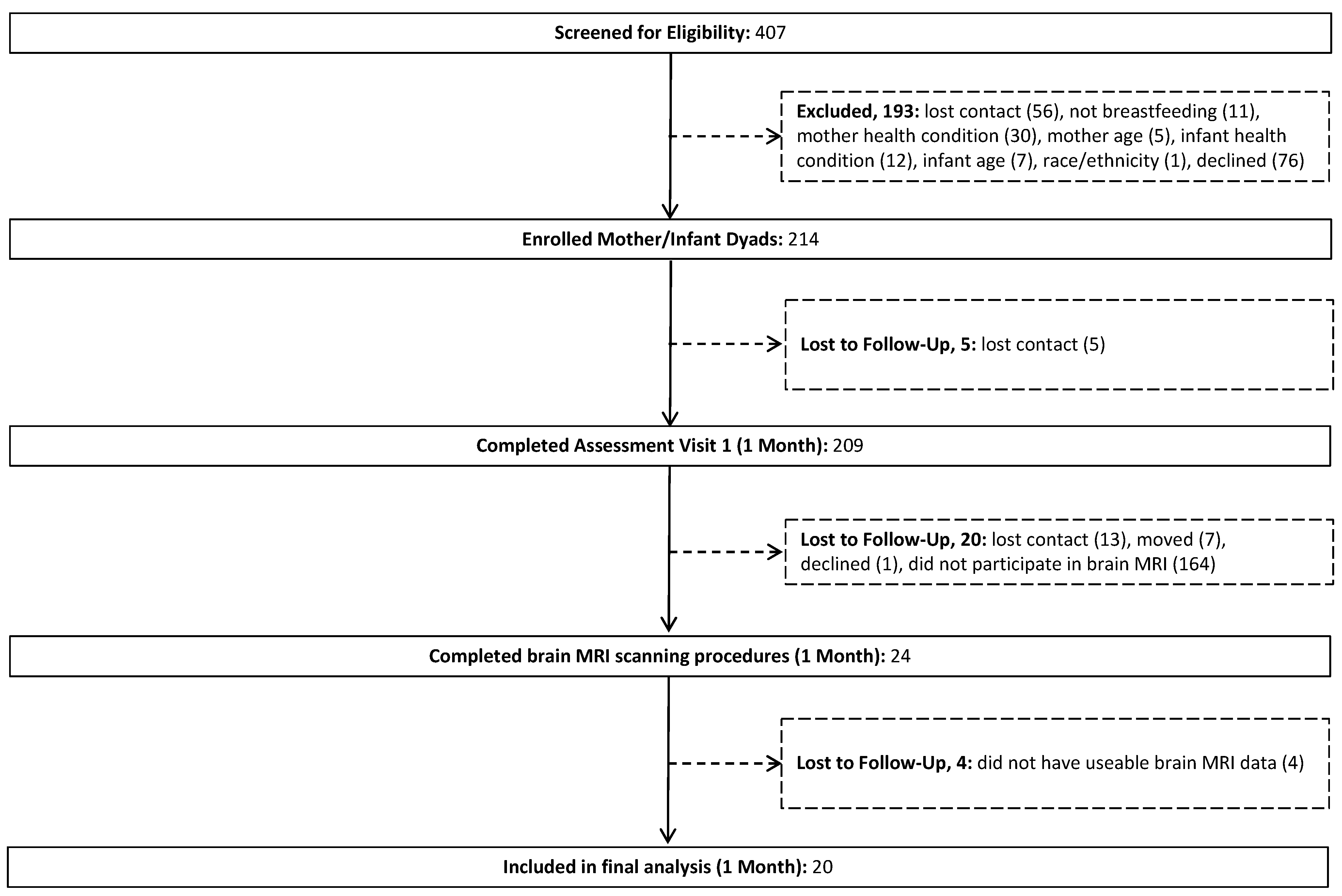
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Human Milk Collection and Analysis
2.4. MRI Scanning Procedures
2.5. Image Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HMO 2′FL Exposure at 1 Month of Age and Newborn MRI Measures
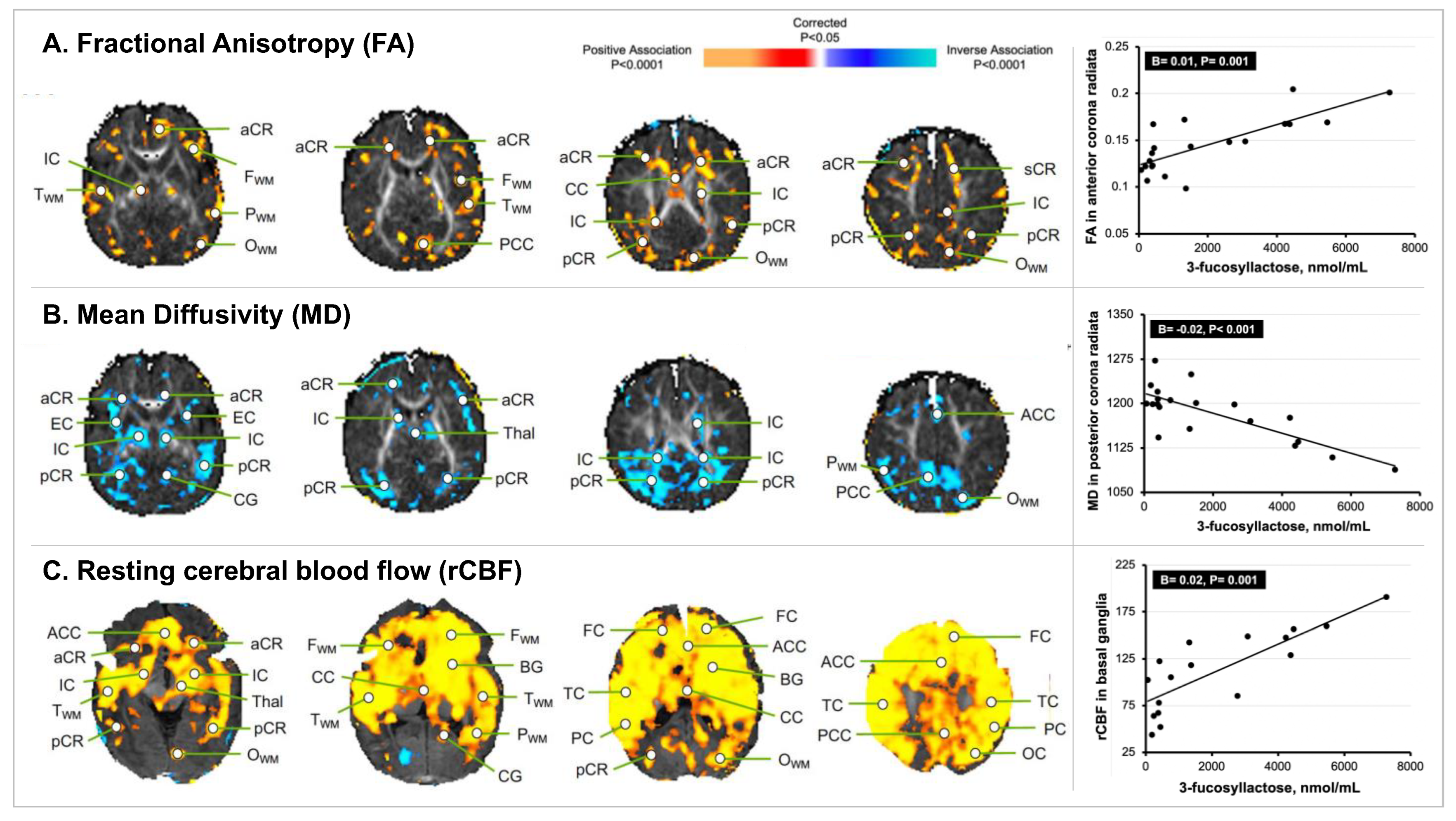
3.2. HMO 3FL Exposure at 1 Month of Age and Newborn MRI Measures
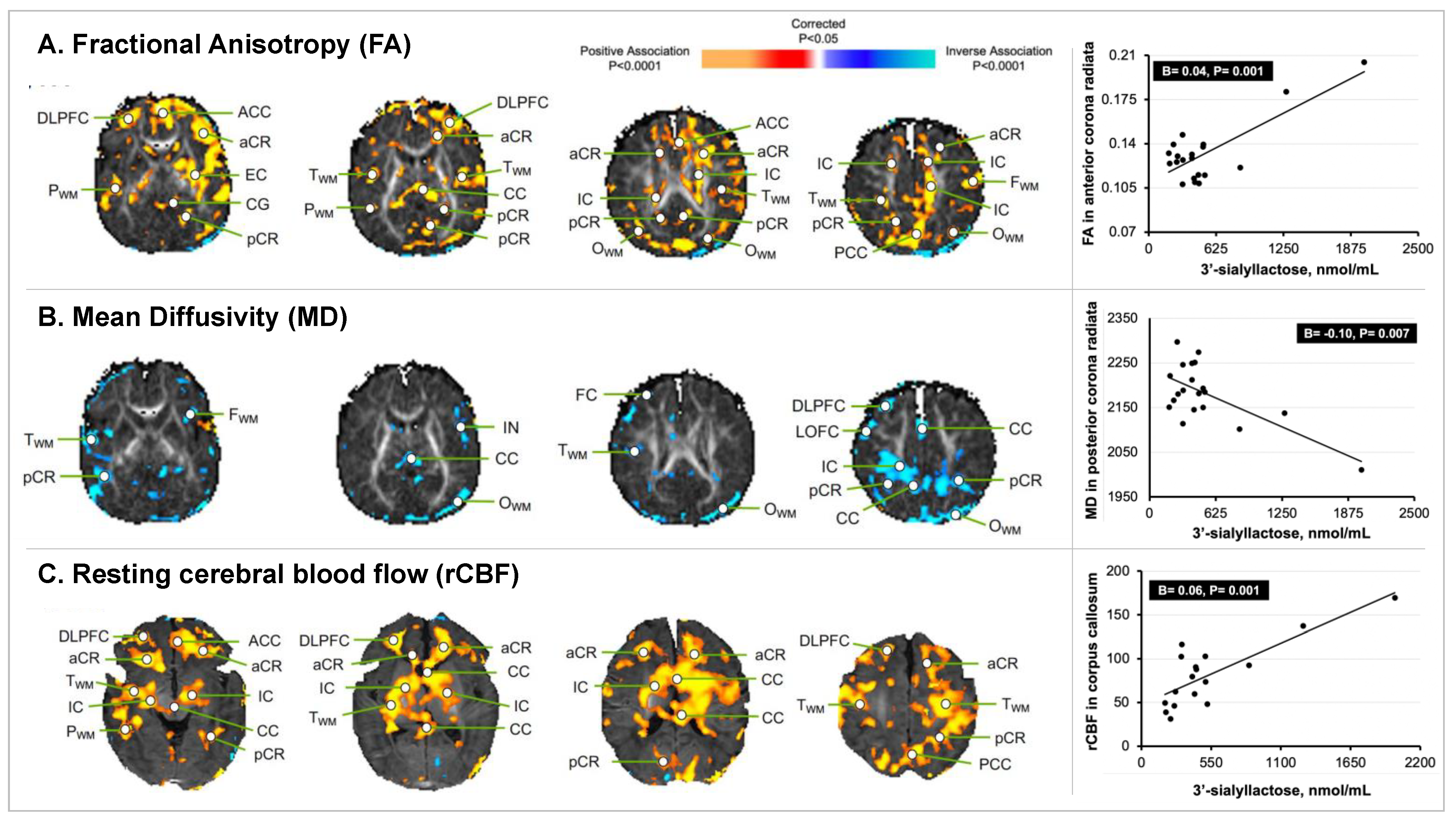
3.3. HMO 3′SL Exposure at 1 Month of Age and Newborn MRI Measures
3.4. Sia Exposure at 1 Month of Age and Newborn MRI Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gillman, M.W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Berkey, C.S.; Frazier, A.L.; Rockett, H.R.; Field, A.E.; Colditz, G.A. Risk of overweight among adolescents who were breastfed as infants. JAMA 2001, 285, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfort, M.B.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Kleinman, K.P.; Guthrie, L.B.; Bellinger, D.C.; Taveras, E.M.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Infant feeding and childhood cognition at ages 3 and 7 years: Effects of breastfeeding duration and exclusivity. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, T.; Bergmann, R.; Kallischnigg, G.; Plagemann, A. Duration of breastfeeding and risk of overweight: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L.; Raman, A.S.; Murch, S.H.; Rollins, N.C.; Gordon, J.I. Understanding the mother-breastmilk-infant “triad”. Science 2020, 367, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niekerk, E.; Autran, C.A.; Nel, D.G.; Kirsten, G.F.; Blaauw, R.; Bode, L. Human milk oligosaccharides differ between HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected mothers and are related to necrotizing enterocolitis incidence in their preterm very-low-birth-weight infants. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, P.K.; Plows, J.F.; Jones, R.B.; Alderete, T.L.; Yonemitsu, C.; Poulsen, M.; Ryoo, J.H.; Peterson, B.S.; Bode, L.; Goran, M.I. Human milk oligosaccharide 2′-fucosyllactose links feedings at 1 month to cognitive development at 24 months in infants of normal and overweight mothers. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L.; Jantscher-Krenn, E. Structure-function relationships of human milk oligosaccharides. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 383S–391S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, B.; Karim, M.; Hu, H.; Sun, Y.; McGreevy, P.; Petocz, P.; Held, S.; Brand-Miller, J. Dietary sialic acid supplementation improves learning and memory in piglets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, S.K.; Yatsunenko, T.; Li, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Yu, R.K.; Berg, B.M.; Chichlowski, M.; Odle, J. Dietary Isomers of Sialyllactose Increase Ganglioside Sialic Acid Concentrations in the Corpus Callosum and Cerebellum and Modulate the Colonic Microbiota of Formula-Fed Piglets. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.T.; Chen, C.; Newburg, D.S. Utilization of major fucosylated and sialylated human milk oligosaccharides by isolated human gut microbes. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, A.J.; Galley, J.D.; Fisher, S.E.; Chichlowski, M.; Berg, B.M.; Bailey, M.T. The prebiotics 3′Sialyllactose and 6′Sialyllactose diminish stressor-induced anxiety-like behavior and colonic microbiota alterations: Evidence for effects on the gut-brain axis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 50, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, C.; Georgieff, M.K.; Xu, D.; Hao, X.; Bansal, R.; Gustafsson, H.; Spicer, J.; Peterson, B.S. Maternal prenatal iron status and tissue organization in the neonatal brain. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, P.K.; Monk, C.; Bansal, R.; Sawardekar, S.; Goran, M.I.; Peterson, B.S. Association of Prenatal Sugar Consumption with Newborn Brain Tissue Organization. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.S.; Zargarian, A.; Peterson, J.B.; Goh, S.; Sawardekar, S.; Williams, S.C.R.; Lythgoe, D.J.; Zelaya, F.O.; Bansal, R. Hyperperfusion of Frontal White and Subcortical Gray Matter in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, P.K.; Plows, J.F.; Jones, R.B.; Alderete, T.L.; Yonemitsu, C.; Ryoo, J.H.; Bode, L.; Goran, M.I. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Hispanic Infant Weight Gain in the First 6 Months. Obesity 2020, 28, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, M.C.; Keller, R.P.; Seacat, J.; Casey, C.E.; Allen, J.C.; Archer, P. Studies on human lactation. I. Within-feed and between-breast variation in selected components of human milk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalpando, S.; del Prado, M. Interrelation among dietary energy and fat intakes, maternal body fatness, and milk total lipid in humans. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 1999, 4, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferovic, M.D.; Mohammad, M.; Pace, R.M.; Engevik, M.; Versalovic, J.; Bode, L.; Haymond, M.; Aagaard, K.M. Maternal diet alters human milk oligosaccharide composition with implications for the milk metagenome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, E.; Vazquez, E.; Barranco, A.; Ramirez, M.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Buck, R.; Rueda, R.; Martin, M.J. Sialic Acid and Sialylated Oligosaccharide Supplementation during Lactation Improves Learning and Memory in Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, E.; Ramirez, M.; Vazquez, E.; Barranco, A.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Buck, R.; Rueda, R.; Martin, M.J. Oral supplementation of 2′-fucosyllactose during lactation improves memory and learning in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 31, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Sialic acid is an essential nutrient for brain development and cognition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 177–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Robertson, B.; Atakora, F.; Becker, A.B.; Subbarao, P.; Moraes, T.J.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Lefebvre, D.L.; Sears, M.R.; et al. Human Milk Oligosaccharide Concentrations Are Associated with Multiple Fixed and Modifiable Maternal Characteristics, Environmental Factors, and Feeding Practices. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessen, K.J.; Bansal, R.; Zhu, H.; Whiteman, R.; Amat, J.; Quackenbush, G.A.; Martin, L.; Durkin, K.; Blair, C.; Royal, J.; et al. Hippocampus and amygdala morphology in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006, 63, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amat, J.A.; Bansal, R.; Whiteman, R.; Haggerty, R.; Royal, J.; Peterson, B.S. Correlates of intellectual ability with morphology of the hippocampus and amygdala in healthy adults. Brain Cogn 2008, 66, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, R.; Staib, L.; Xu, D.; Zhu, H.; Peterson, B. Statistical analyses of brain surfaces using Gaussian random fields on 2-D manifolds. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2007, 26, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, G.; Joshi, S.; Miller, M. Volumetric transformation of brain anatomy. IEEE. Trans. Med. Imaging 1997, 16, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.C.; Detre, J.A.; Golay, X.; Gunther, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Lu, H.Z.; MacIntosh, B.J.; Parkes, L.M.; Smits, M.; et al. Recommended Implementation of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI for Clinical Applications: A Consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the European Consortium for ASL in Dementia. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; Steketee, R.M.E.; Heijtel, D.F.R.; Kuijer, J.P.A.; van Osch, M.J.P.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; Smits, M.; Nederveen, A.J. Inter-Vendor Reproducibility of Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labeling at 3 Tesla. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herscovitch, P.; Raichle, M.E. What Is the Correct Value for the Brain Blood Partition-Coefficient for Water. J. Cerebr. Blood F Met. 1985, 5, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijtel, D.F.R.; Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; Bakker, E.; Schober, P.; Stevens, M.F.; Petersen, E.T.; van Berckel, B.N.M.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; Booij, J.; van Osch, M.J.P.; et al. Accuracy and precision of pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion during baseline and hypercapnia: A head-to-head comparison with O-15 H2O positron emission tomography. NeuroImage 2014, 92, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalela, J.A.; Alsop, D.C.; Gonzalez-Atavales, J.B.; Maldjian, J.A.; Kasner, S.E.; Detre, J.A. Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke using continuous arterial spin labeling. Stroke 2000, 31, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotardi, S.; Gollub, R.L.; Bates, S.V.; Weiss, R.; Murphy, S.N.; Grant, P.E.; Ou, Y. Voxelwise and Regional Brain Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Changes on MRI from Birth to 6 Years of Age. Radiology 2021, 298, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. False Discovery Rate: Adjusted Multiple Confidence Intervals for Selected Parameters. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2005, 100, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, H.; Oishi, K.; Mishra, V.; Song, L.; Peng, Q.; Ouyang, M.; Wang, J.; Slinger, M.; Jeon, T.; et al. Age-specific gray and white matter DTI atlas for human brain at 33, 36 and 39 postmenstrual weeks. Neuroimage 2019, 185, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, W.A. Age terminology during the perinatal period. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L. Human milk oligosaccharides: Every baby needs a sugar mama. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knickmeyer, R.C.; Gouttard, S.; Kang, C.; Evans, D.; Wilber, K.; Smith, J.K.; Hamer, R.M.; Lin, W.; Gerig, G.; Gilmore, J.H. A structural MRI study of human brain development from birth to 2 years. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12176–12182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Jeon, T.; Sotiras, A.; Peng, Q.; Mishra, V.; Halovanic, C.; Chen, M.; Chalak, L.; Rollins, N.; Roberts, T.P.L.; et al. Differential cortical microstructural maturation in the preterm human brain with diffusion kurtosis and tensor imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4681–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, S.N.; Leigland, L.A.; Cornea, A.; Kroenke, C.D. Determination of axonal and dendritic orientation distributions within the developing cerebral cortex by diffusion tensor imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppi, P.S.; Maier, S.E.; Peled, S.; Zientara, G.P.; Barnes, P.D.; Jolesz, F.A.; Volpe, J.J. Microstructural development of human newborn cerebral white matter assessed in vivo by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 44, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, G.; Rioux, P.; Petit-Taboue, M.C.; Sette, G.; Travere, J.M.; Le Poec, C.; Courtheoux, P.; Derlon, J.M.; Baron, J.C. Regional cerebral oxygen consumption, blood flow, and blood volume in healthy human aging. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzi, G.L.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Jones, T.; Heather, J.D.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Rhodes, C.G.; Pozzilli, C. CMRO2 and CBF by the oxygen-15 inhalation technique. Results in normal volunteers and cerebrovascular patients. Eur. Neurol. 1981, 20, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantano, P.; Baron, J.C.; Lebrun-Grandie, P.; Duquesnoy, N.; Bousser, M.G.; Comar, D. Regional cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in human aging. Stroke 1984, 15, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallermann, S.; de Kock, C.P.; Stuart, G.J.; Kole, M.H. State and location dependence of action potential metabolic cost in cortical pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, B.; Stemmler, M.; Laughlin, S.B.; Niven, J.E. Action potential energy efficiency varies among neuron types in vertebrates and invertebrates. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, P.; Fraenz, C.; Schluter, C.; Ocklenburg, S.; Madler, B.; Gunturkun, O.; Genc, E. The Relationship Between Axon Density, Myelination, and Fractional Anisotropy in the Human Corpus Callosum. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 2042–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmithorst, V.J.; Wilke, M.; Dardzinski, B.J.; Holland, S.K. Cognitive functions correlate with white matter architecture in a normal pediatric population: A diffusion tensor MRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 26, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giezendanner, S.; Fisler, M.S.; Soravia, L.M.; Andreotti, J.; Walther, S.; Wiest, R.; Dierks, T.; Federspiel, A. Microstructure and Cerebral Blood Flow within White Matter of the Human Brain: A TBSS Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, T.; Rothstein, J.D. Oligodendroglia: Metabolic supporters of neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Xu, D.; Bansal, R.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kangarlu, A.; Liu, F.; Duan, Y.; Shova, S.; et al. Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging: The coordinated use of multiple, mutually informative probes to understand brain structure and function. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horga, G.; Kaur, T.; Peterson, B.S. Annual research review: Current limitations and future directions in MRI studies of child- and adult-onset developmental psychopathologies. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 659–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.S.; Liu, J.; Dantec, L.; Newman, C.; Sawardekar, S.; Goh, S.; Bansal, R. Using tissue microstructure and multimodal MRI to parse the phenotypic heterogeneity and cellular basis of autism spectrum disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2021, 63, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, B.S.; Bansal, R.; Sawardekar, S.; Nati, C.; Elgabalawy, E.R.; Hoepner, L.A.; Garcia, W.; Hao, X.; Margolis, A.; Perera, F.; et al. Prenatal exposure to air pollution is associated with altered brain structure, function, and metabolism in childhood. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plows, J.F.; Berger, P.K.; Jones, R.B.; Alderete, T.L.; Yonemitsu, C.; Najera, J.A.; Khwajazada, S.; Bode, L.; Goran, M.I. Longitudinal Changes in Human Milk Oligosaccharides (HMOs) Over the Course of 24 Months of Lactation. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, A.L.; Xia, K.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Goldman, B.D.; Ahn, M.; Styner, M.A.; Thompson, A.L.; Geng, X.; Gilmore, J.H.; Knickmeyer, R.C. Infant Gut Microbiome Associated With Cognitive Development. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, P.A.; Raiha, N.; Rahiala, E.L.; Kekomaki, M. Oxidation of glucose and D-B-OH-butyrate by the early human fetal brain. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1975, 64, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCastro, M.; Nankova, B.B.; Shah, P.; Patel, P.; Mally, P.V.; Mishra, R.; La Gamma, E.F. Short chain fatty acids regulate tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression through a cAMP-dependent signaling pathway. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 142, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Nankova, B.B.; Parab, S.; La Gamma, E.F. Short chain fatty acids induce TH gene expression via ERK-dependent phosphorylation of CREB protein. Brain Res. 2006, 1107, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Molecular mechanism underlying sialic acid as an essential nutrient for brain development and cognition. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 465S–472S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bashir, N.; Mellado, W.; Filbin, M.T. Sialic Acid Is Required for Neuronal Inhibition by Soluble MAG but not for Membrane Bound MAG. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quin, C.; Estaki, M.; Vollman, D.M.; Barnett, J.A.; Gill, S.K.; Gibson, D.L. Probiotic supplementation and associated infant gut microbiome and health: A cautionary retrospective clinical comparison. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Yang, L.; Liu, K.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y. Effects of Antibiotic Treatment and Probiotics on the Gut Microbiome of 40 Infants Delivered Before Term by Cesarean Section Analysed by Using 16S rRNA Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Sequencing. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e928467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huda, M.N.; Ahmad, S.M.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Taft, D.H.; Alam, M.J.; Khanam, A.; Raqib, R.; Underwood, M.A.; Mills, D.A.; Stephensen, C.B. Neonatal Vitamin A Supplementation and Vitamin A Status Are Associated with Gut Microbiome Composition in Bangladeshi Infants in Early Infancy and at 2 Years of Age. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Mean | SD | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mothers | ||||
| Age at delivery (years) | 28.5 | 6.74 | 18 | 40 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 27.8 | 6.25 | 18.7 | 42.5 |
| Secretor status (%) | 85.0 | |||
| Education level (%) | ||||
| Less than high school | 20.8 | |||
| Completed high school | 58.4 | |||
| Completed college | 20.8 | |||
| Infants | ||||
| Female (%) | 62.5 | |||
| Birthweight (g) | 3360 | 498 | 2300 | 4510 |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks) | 39.5 | 1.03 | 37.0 | 41.1 |
| Postmenstrual age at MRI scanning (days) 2 | 323 | 10.5 | 300 | 351 |
| Breast feedings per day, 1-month (number) | 7.08 | 1.64 | 1 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berger, P.K.; Bansal, R.; Sawardekar, S.; Yonemitsu, C.; Furst, A.; Hampson, H.E.; Schmidt, K.A.; Alderete, T.L.; Bode, L.; Goran, M.I.; et al. Associations of Human Milk Oligosaccharides with Infant Brain Tissue Organization and Regional Blood Flow at 1 Month of Age. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183820
Berger PK, Bansal R, Sawardekar S, Yonemitsu C, Furst A, Hampson HE, Schmidt KA, Alderete TL, Bode L, Goran MI, et al. Associations of Human Milk Oligosaccharides with Infant Brain Tissue Organization and Regional Blood Flow at 1 Month of Age. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183820
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerger, Paige K., Ravi Bansal, Siddhant Sawardekar, Chloe Yonemitsu, Annalee Furst, Hailey E. Hampson, Kelsey A. Schmidt, Tanya L. Alderete, Lars Bode, Michael I. Goran, and et al. 2022. "Associations of Human Milk Oligosaccharides with Infant Brain Tissue Organization and Regional Blood Flow at 1 Month of Age" Nutrients 14, no. 18: 3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183820
APA StyleBerger, P. K., Bansal, R., Sawardekar, S., Yonemitsu, C., Furst, A., Hampson, H. E., Schmidt, K. A., Alderete, T. L., Bode, L., Goran, M. I., & Peterson, B. S. (2022). Associations of Human Milk Oligosaccharides with Infant Brain Tissue Organization and Regional Blood Flow at 1 Month of Age. Nutrients, 14(18), 3820. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14183820






