Tight Junction Protein Expression-Inducing Probiotics Alleviate TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment with Colitis in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Culture of Gut Bacteria
2.3. Culture of Caco-2 Cells
2.4. Animals
2.5. Preparation of Mice with Colitis
2.6. Assessment of Cognitive Behavior Tasks
2.7. Measurement of LPS Concentration
2.8. ELISA Assay and Immunblotting
2.9. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
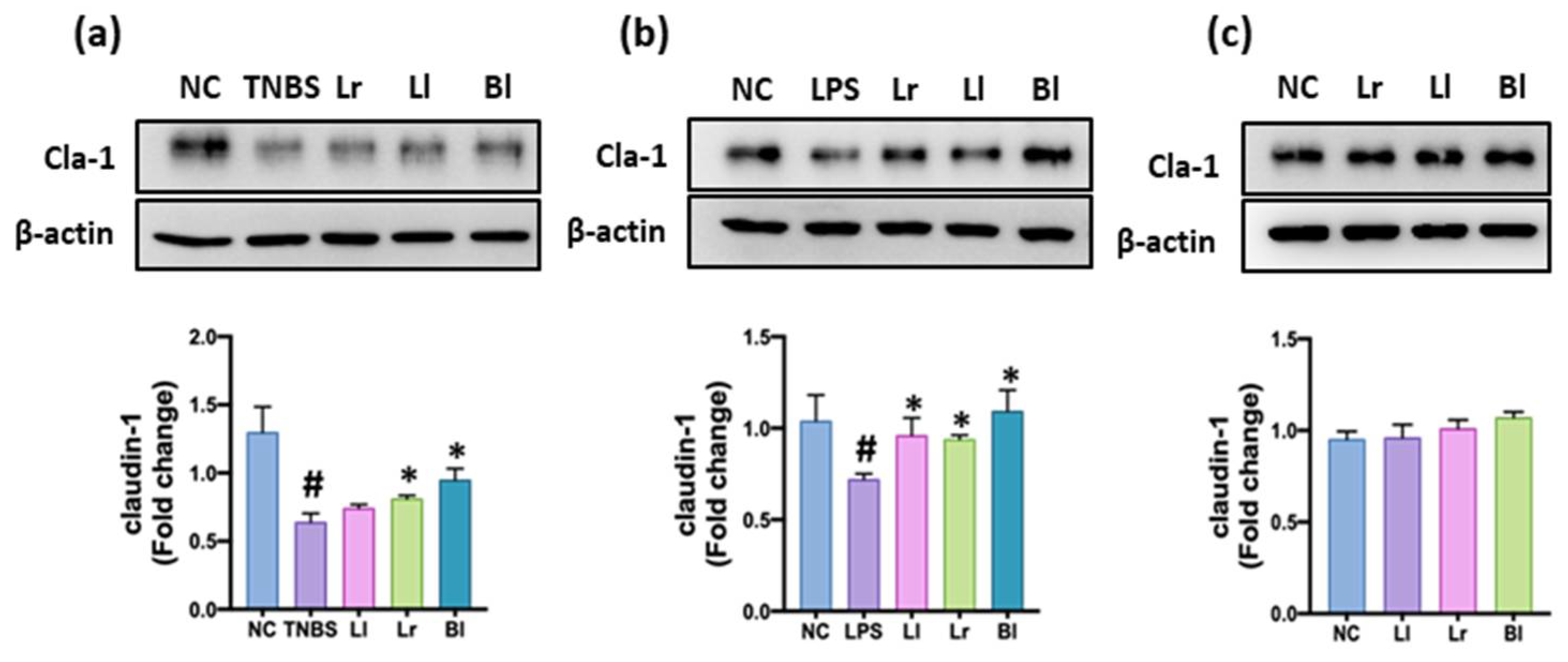
3.1. NK209, NK210, and NK219 Increased Claudin-1 Expression in TNBS-Stimulated Caco-2 Cells
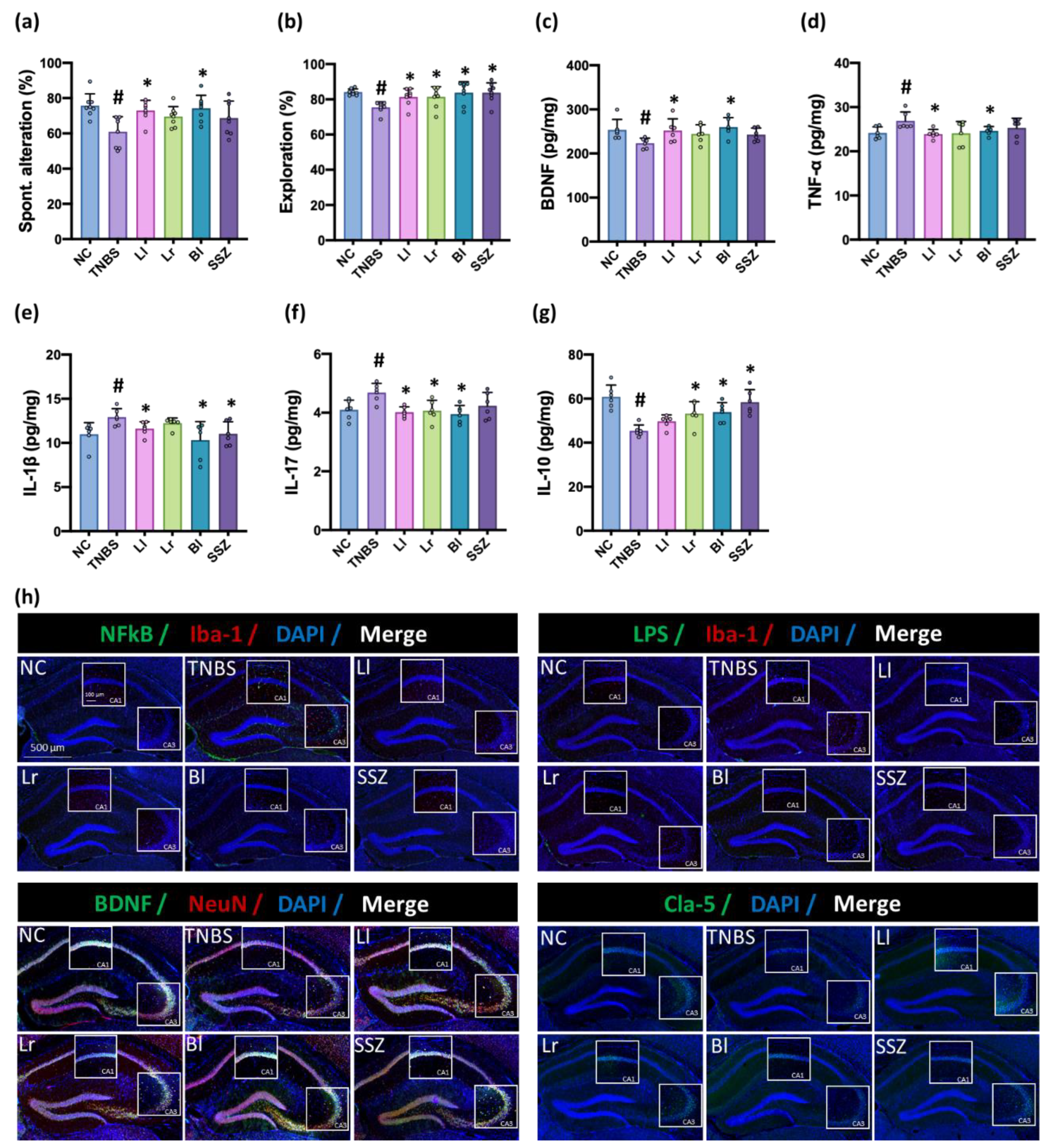
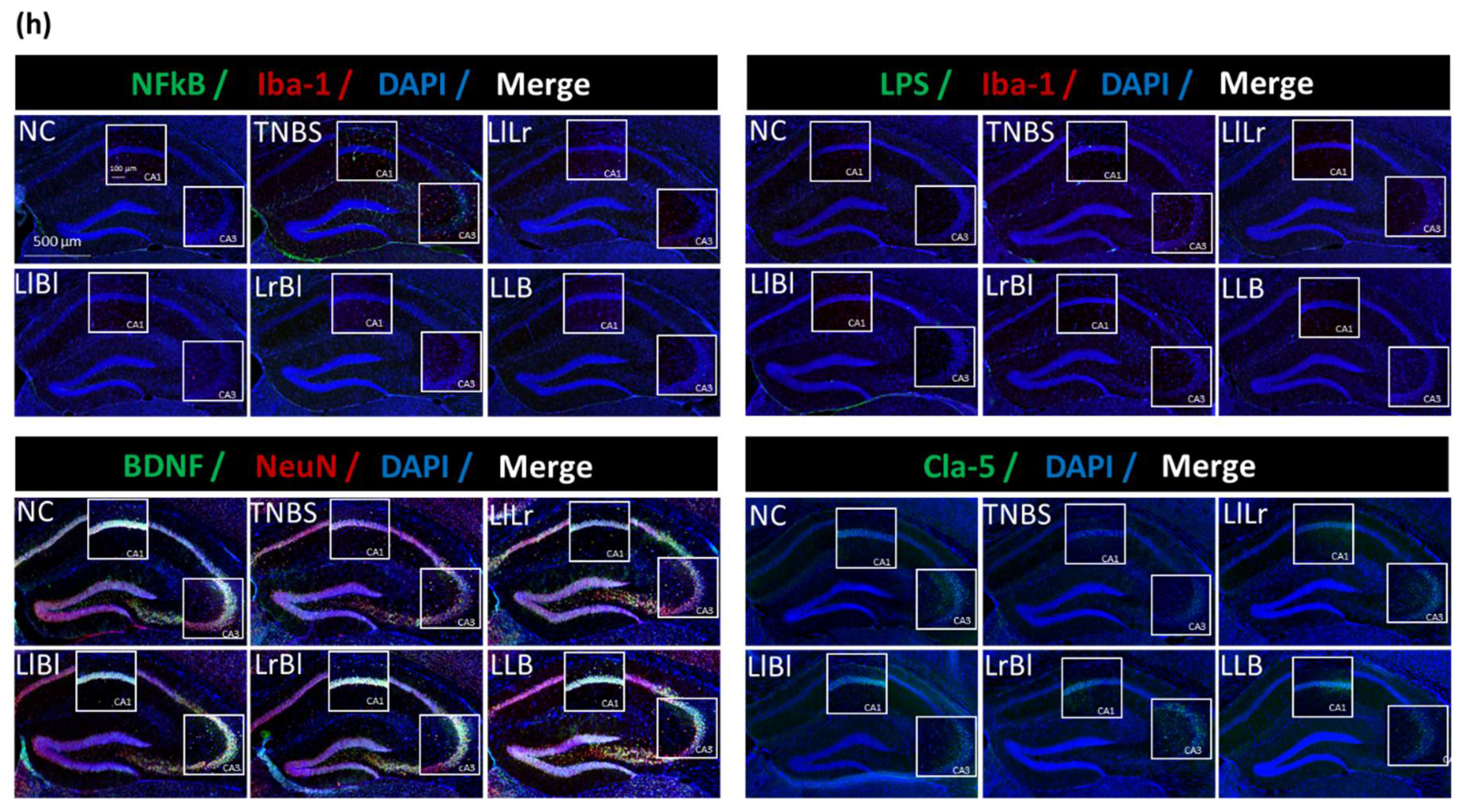
3.2. NK209, NK210, and NK219 Mitigated TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation in Mice
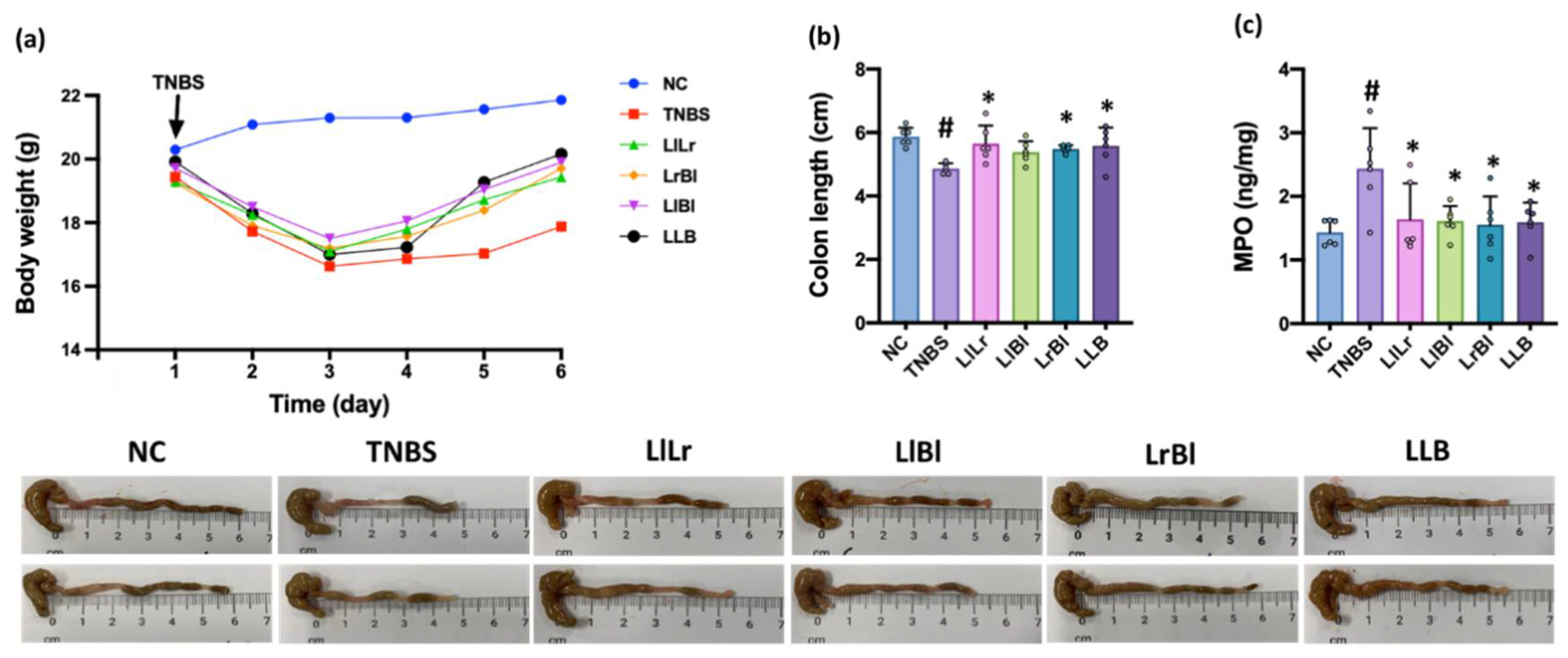
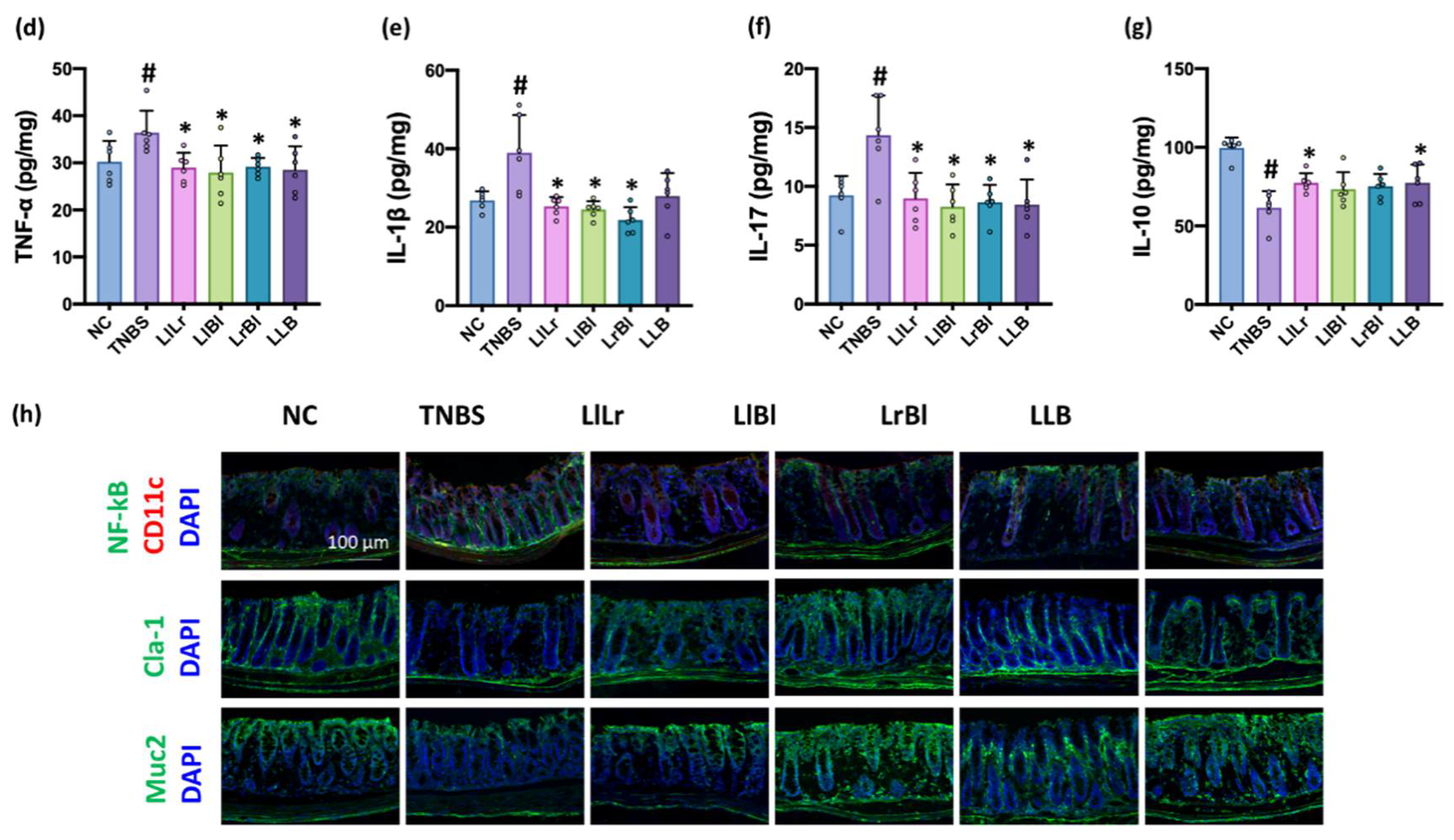
3.3. NK209, NK210, and NK219 Mitigated TNBS-Induced Gut Inflammation in Mice
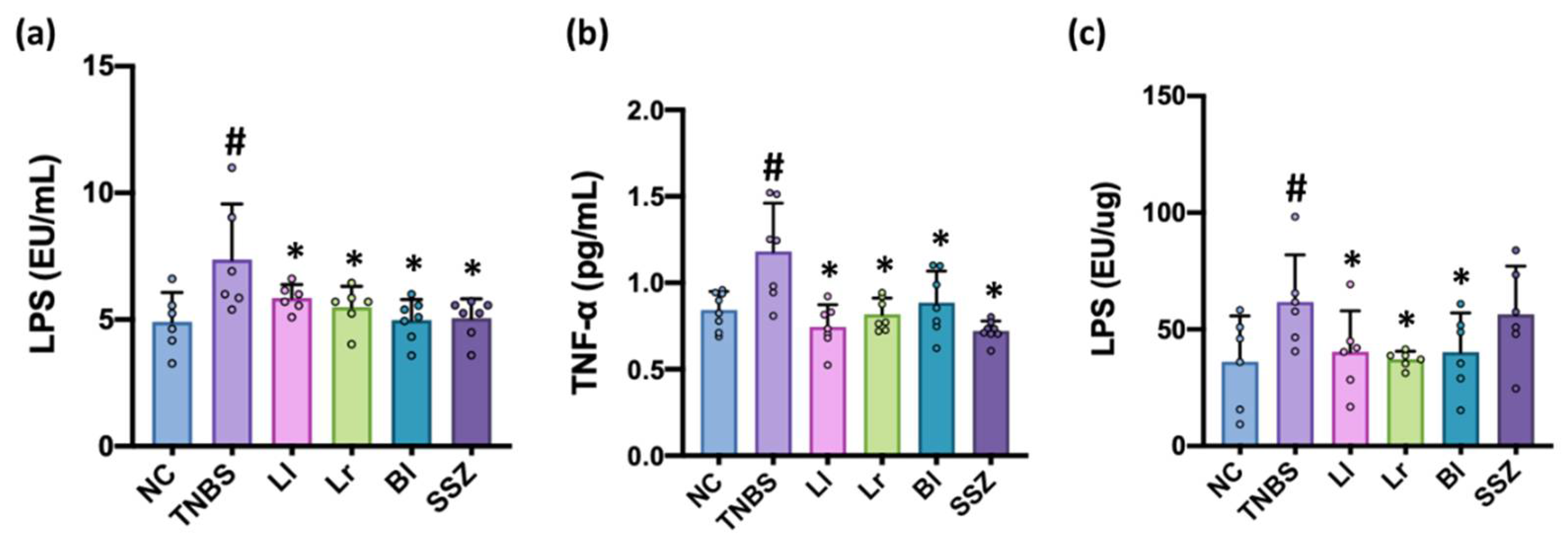
3.4. NK209, NK210, and NK219 Suppressed TNBS-Induced LPS Levels in the Blood and Feces
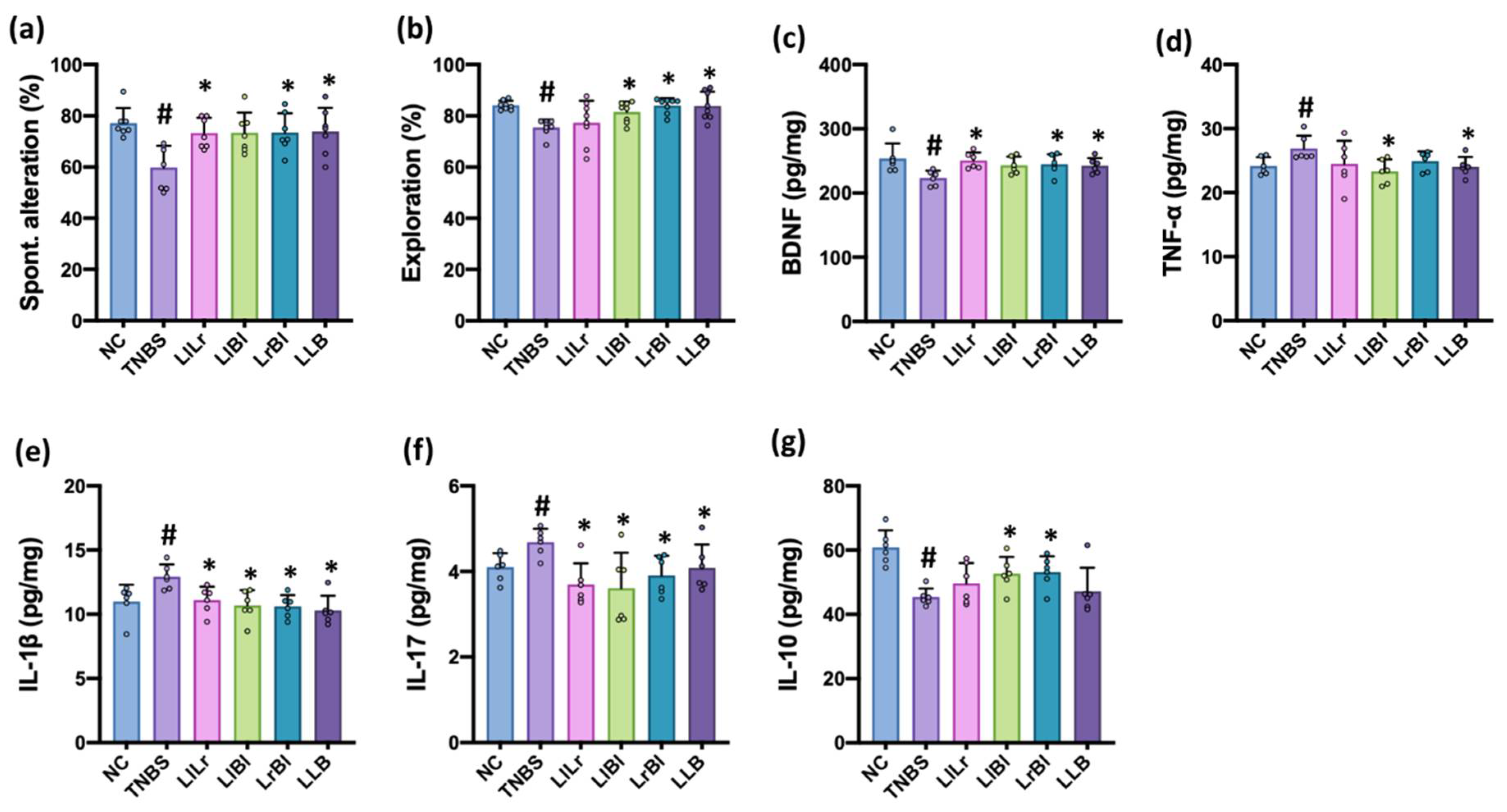
3.5. The Combined Effects of NK209, NK210, and NK219 on TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Gut Inflammation in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Sorrell, M.F.; Batra, S.K.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. Gut permeability and mucosal inflammation: Bad, good or context dependent. Mucosal. Immunol. 2017, 10, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Kamolvit, W.; Hertting, O.; Brauner, A. Vitamin D strengthens the bladder epithelial barrier by inducing tight junction proteins during E. coli urinary tract infection. Cell Tissue Res. 2020, 380, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licini, C.; Tossetta, G.; Avellini, C.; Ciarmela, P.; Lorenzi, T.; Toti, P.; Gesuita, R.; Voltolini, C.; Petraglia, F.; Castellucci, M.; et al. Analysis of cell-cell junctions in human amnion and chorionic plate affected by chorioamnionitis. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossetta, G.; Paolinelli, F.; Avellini, C.; Salvolini, E.; Ciarmela, P.; Lorenzi, T.; Emanuelli, M.; Toti, P.; Giuliante, R.; Gesuita, R.; et al. IL-1β and TGF-β weaken the placental barrier through destruction of tight junctions: An in vivo and in vitro study. Placenta 2014, 35, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, M.; Richardson, J.C.; Gentleman, S.M.; Brooks, D.J. Inflammatory risk factors and pathologies associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2011, 8, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trollor, J.N.; Smith, E.; Baune, B.T.; Kochan, N.A.; Campbell, L.; Samaras, K.; Crawford, J.; Brodaty, H.; Sachdev, P. Systemic inflammation is associated with MCI and its subtypes: The Sydney Memory and Aging Study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2010, 30, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marizzoni, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Mirabelli, P.; Festari, C.; Lopizzo, N.; Nicolosi, V.; Mombelli, E.; Mazzelli, M.; Luongo, D.; Naviglio, D.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Lipopolysaccharide as Mediators Between Gut Dysbiosis and Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 78, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.E.; Lim, S.M.; Jeong, J.J.; Jang, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Gastrointestinal inflammation by gut microbiota disturbance induces memory impairment in mice. Mucosal. Immunol. 2018, 11, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.; Fuss, I.; Strober, W. TNBS-colitis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 19, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.T. Probiotics. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.P.; Quigley, E.M.M. Probiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.T.; Selmi, C.; Meyers, F.J.; Keen, C.L.; Gershwin, M.E. Probiotics and immunity. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Brietzke, E.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Musial, N.; Zuckerman, H.; Ragguett, R.M.; Pan, Z.; Rong, C.; Fus, D.; McIntyre, R.S. Probiotics for the treatment of depressive symptoms: An anti-inflammatory mechanism? Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Kahouli, I.; Dia, S.Y.; Singh, S.P.; Prakash, S. Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: Deciphering the gut brain axis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3769–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Hwang, Y.H.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus plantarum C29-Fermented Soybean (DW2009) Alleviates Memory Impairment in 5XFAD Transgenic Mice by Regulating Microglia Activation and Gut Microbiota Composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Park, S.; Paik, J.W.; Chae, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, D.G.; Ha, E.; Kim, M.; Hong, G.; Park, S.H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Lactobacillus plantarum C29-Fermented Soybean (DW2009) in Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A 12-Week, Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Yun, S.W.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.H. Suppression of gut dysbiosis by Bifidobacterium longum alleviates cognitive decline in 5XFAD transgenic and aged mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, D.H. The Preventive and Curative Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri NK33 and Bifidobacterium adolescentis NK98 on Immobilization Stress-Induced Anxiety/Depression and Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, J.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Jang, S.W.; Han, S.W.; Yoon, I.Y. Effects of Probiotic NVP-1704 on Mental Health and Sleep in Healthy Adults: An 8-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Shin, Y.J.; Jang, H.M.; Joo, M.K.; Yoo, J.W.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium longum alleviate colitis and cognitive impairment in mice by regulating IFN-γ to IL-10 and TNF-α to IL-10 expression ratios. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Kim, H.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Jang, S.E.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus plantarum LC27 and Bifidobacterium longum LC67 simultaneously alleviate high-fat diet-induced colitis, endotoxemia, liver steatosis, and obesity in mice. Nutr. Res. 2019, 67, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, S.E.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Evidence for interplay among antibacterial-induced gut microbiota disturbance, neuro-inflammation, and anxiety in mice. Mucosal. Immunol. 2018, 11, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E.; Kim, J.K.; Han, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Yim, S.V.; Kim, D.H. The extracellular vesicle of gut microbial Paenalcaligenes hominis is a risk factor for vagus nerve-mediated cognitive impairment. Microbiome 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Grenham, S.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Brain-gut-microbe communication in health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, L. The gut microbiome and the brain. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodiya, H.B.; Forsyth, C.B.; Voigt, R.M.; Engen, P.A.; Patel, J.; Shaikh, M.; Green, S.J.; Naqib, A.; Roy, A.; Kordower, J.H.; et al. Chronic stress-induced gut dysfunction exacerbates Parkinson’s disease phenotype and pathology in a rotenone-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 135, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiippala, K.; Jouhten, H.; Ronkainen, A.; Hartikainen, A.; Kainulainen, V.; Jalanka, J.; Satokari, R. The Potential of Gut Commensals in Reinforcing Intestinal Barrier Function and Alleviating Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. The Relationship Between Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Diseases: The Role of Macrophages. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Baptista, L.C.; Roberts, L.M.; Jumbo-Lucioni, P.; McMahon, L.L.; Buford, T.W.; Carter, C.S. The Gut Microbiome as a Therapeutic Target for Cognitive Impairment. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Li, G.; Huang, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B. The Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobionda, S.; Sittipo, P.; Kwon, H.Y.; Lee, Y.K. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Intestinal Inflammation with Respect to Diet and Extrinsic Stressors. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Kim, D.H. Bifidobacterium adolescentis IM38 ameliorates high-fat diet-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-κB activation and lipopolysaccharide production by gut microbiota. Nutr. Res. 2017, 41, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.H. Immobilization stress-induced Escherichia coli causes anxiety by inducing NF-κB activation through gut microbiota disturbance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, H.M.; Joo, M.K.; Kim, D.H. Alleviation of cognitive impairment by gut microbiota lipopolysaccharide production-suppressing Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10750–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus johnsonii CJLJ103 Attenuates Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice by Increasing BDNF Expression and Inhibiting NF-κB Activation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, D.; Xue, L.; Li, H.; Du, J. Probiotics modulate the microbiota-gut-brain axis and improve memory deficits in aged SAMP8 mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.-Y.; Son, Y.-H.; Yoo, J.-W.; Joo, M.-K.; Kim, D.-H. Tight Junction Protein Expression-Inducing Probiotics Alleviate TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment with Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142975
Ma X-Y, Son Y-H, Yoo J-W, Joo M-K, Kim D-H. Tight Junction Protein Expression-Inducing Probiotics Alleviate TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment with Colitis in Mice. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142975
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiao-Yang, Young-Hoo Son, Jong-Wook Yoo, Min-Kyung Joo, and Dong-Hyun Kim. 2022. "Tight Junction Protein Expression-Inducing Probiotics Alleviate TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment with Colitis in Mice" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142975
APA StyleMa, X.-Y., Son, Y.-H., Yoo, J.-W., Joo, M.-K., & Kim, D.-H. (2022). Tight Junction Protein Expression-Inducing Probiotics Alleviate TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment with Colitis in Mice. Nutrients, 14(14), 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142975




