(-)-Oleocanthal Nutraceuticals for Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Pathology: Novel Oral Formulations, Therapeutic, and Molecular Insights in 5xFAD Transgenic Mice Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Antibodies
2.2. Oleocanthal Isolation from Extra-Virgin Olive Oil
2.3. Preparation of OC Powder Mixture and Solid Dispersion Formulations
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (ScEM)
2.7. In-Vitro Dissolution Study
2.8. Animals
2.9. OC Formulations Orally Administered in 5xFAD Mice
2.10. Behavioral Studies
2.10.1. Morris Water Maze
2.10.2. Open-Field Activity
2.10.3. Elevated Plus Maze
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Immunostaining
2.13. Congo-Red Staining
2.14. Hematoxylin and Eosin Y (H&E) Staining
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
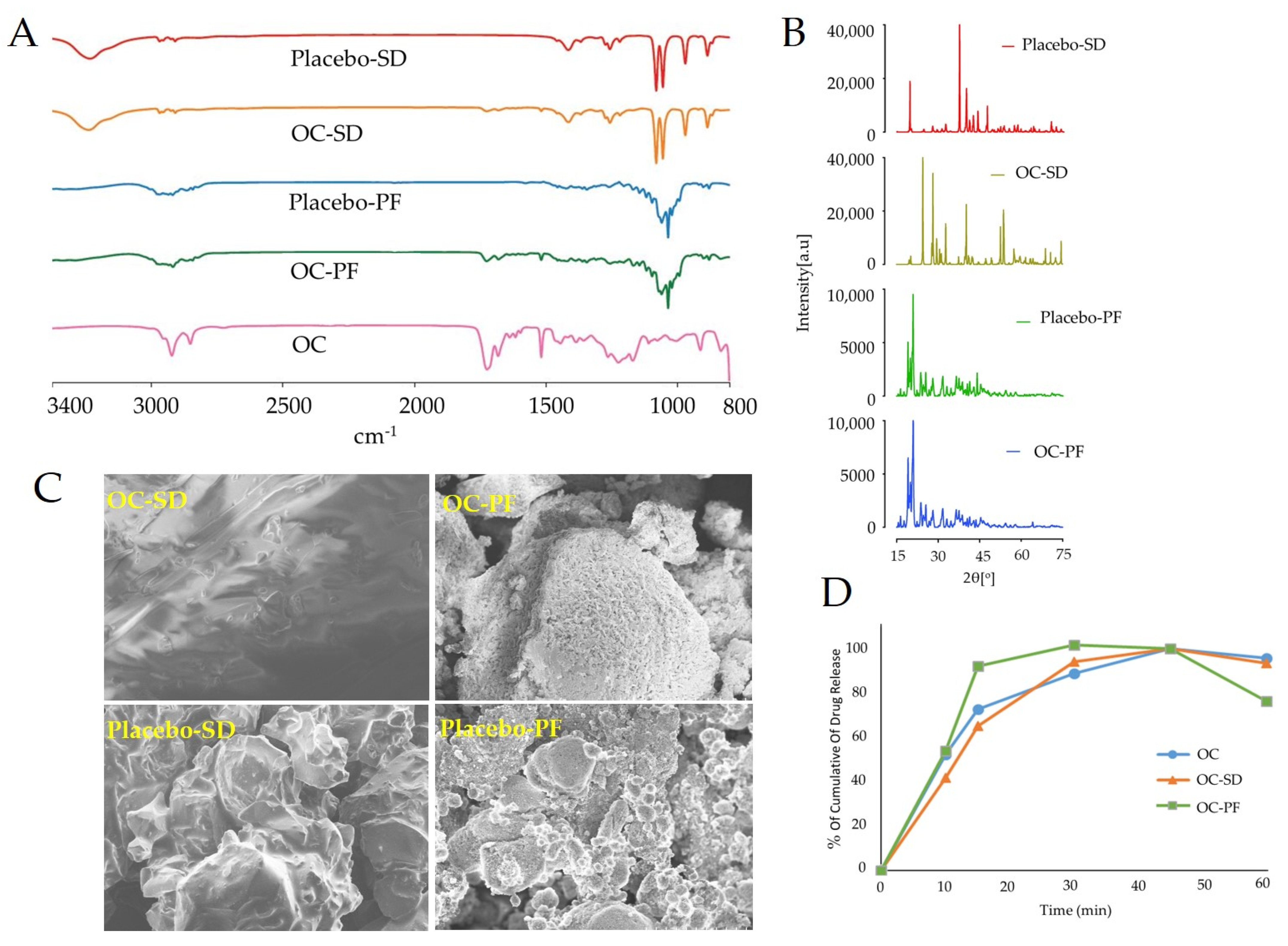
3.1. Characterization of OC-PF and OC-SD
3.2. In Vitro Dissolution Study
3.3. OC Formulation Treatments Effects on Mice Body Weight and Food Intake
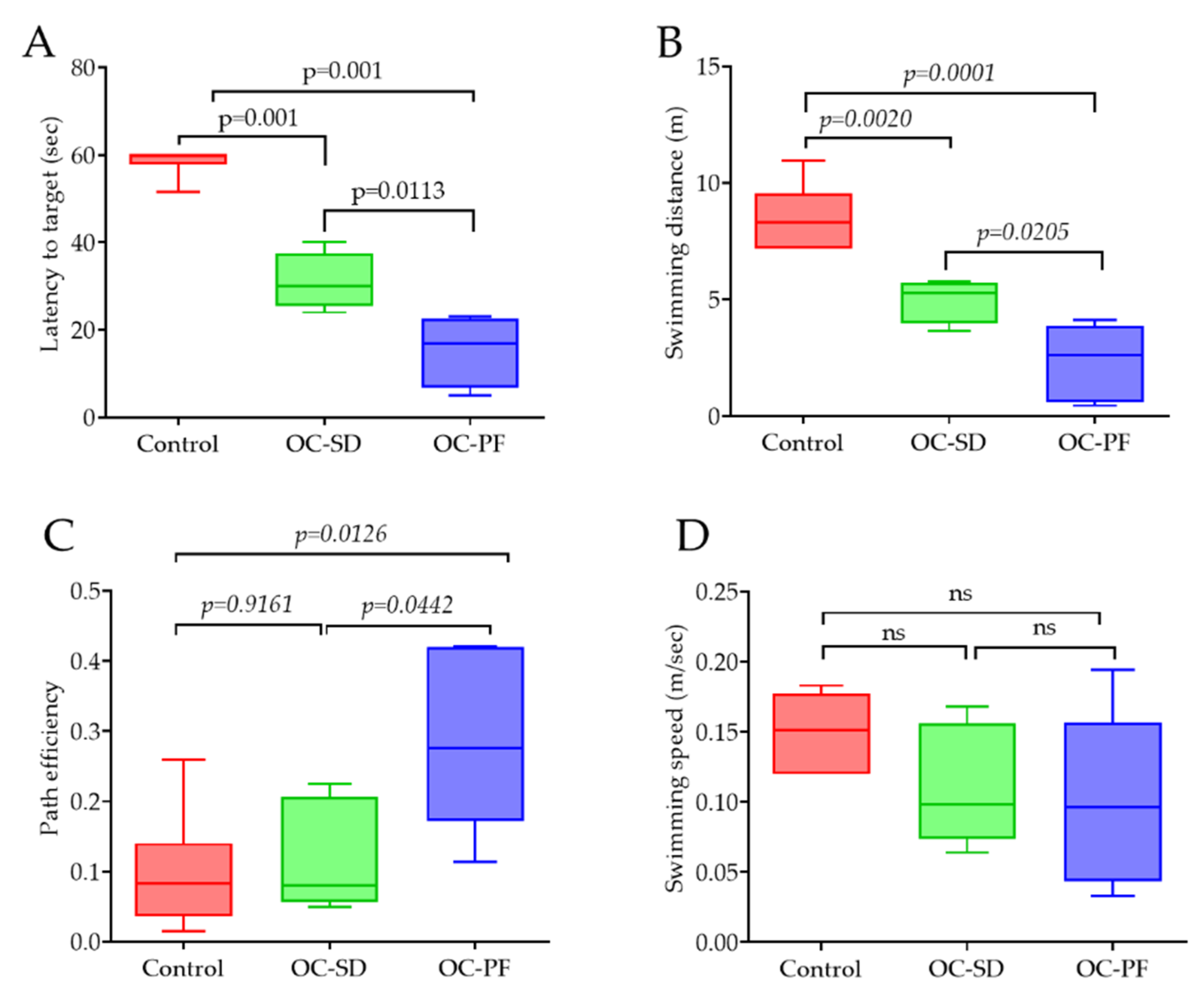
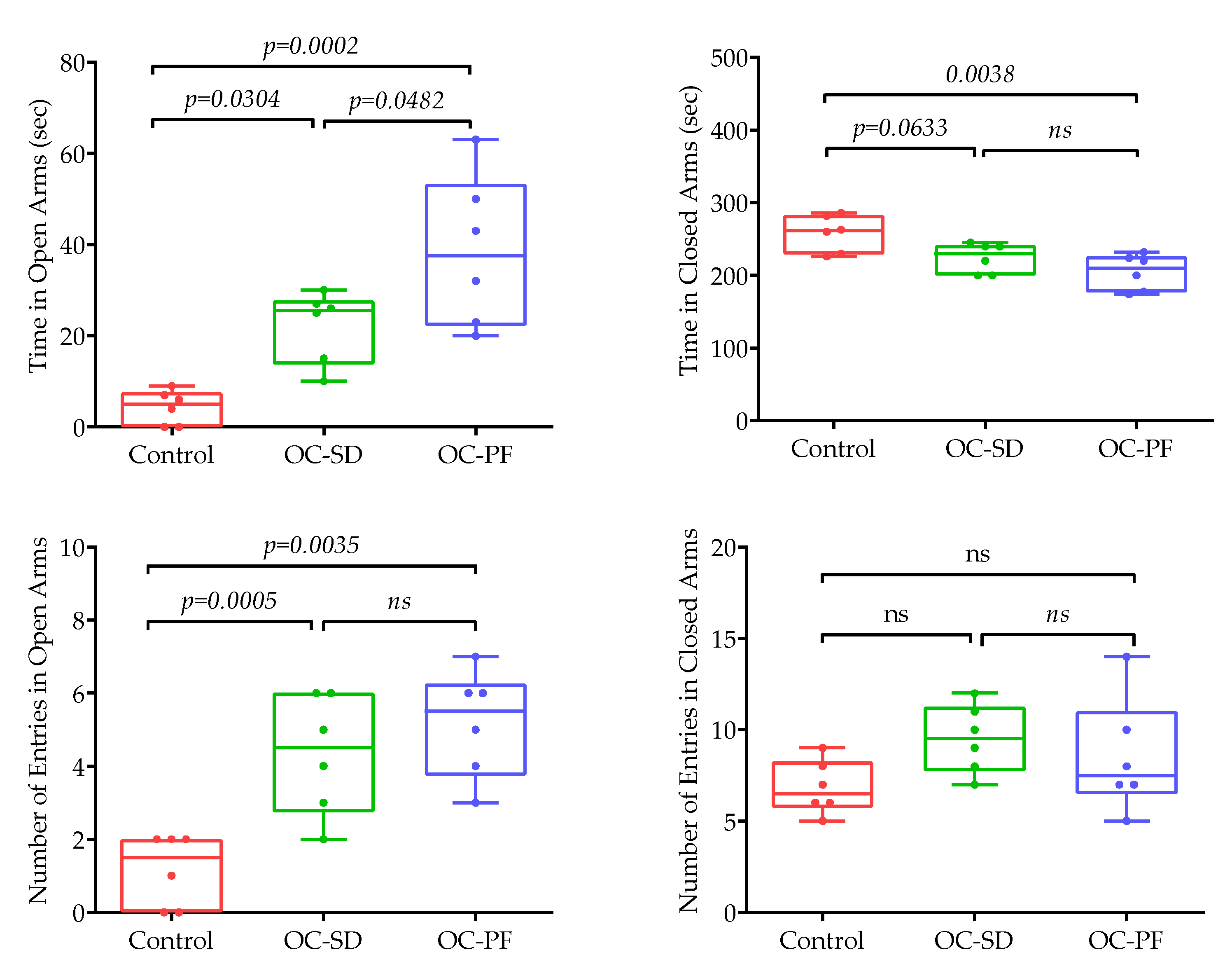
3.4. OC Formulation Treatments Improved 5xFAD Mice Spatial Learning and Memory Ability
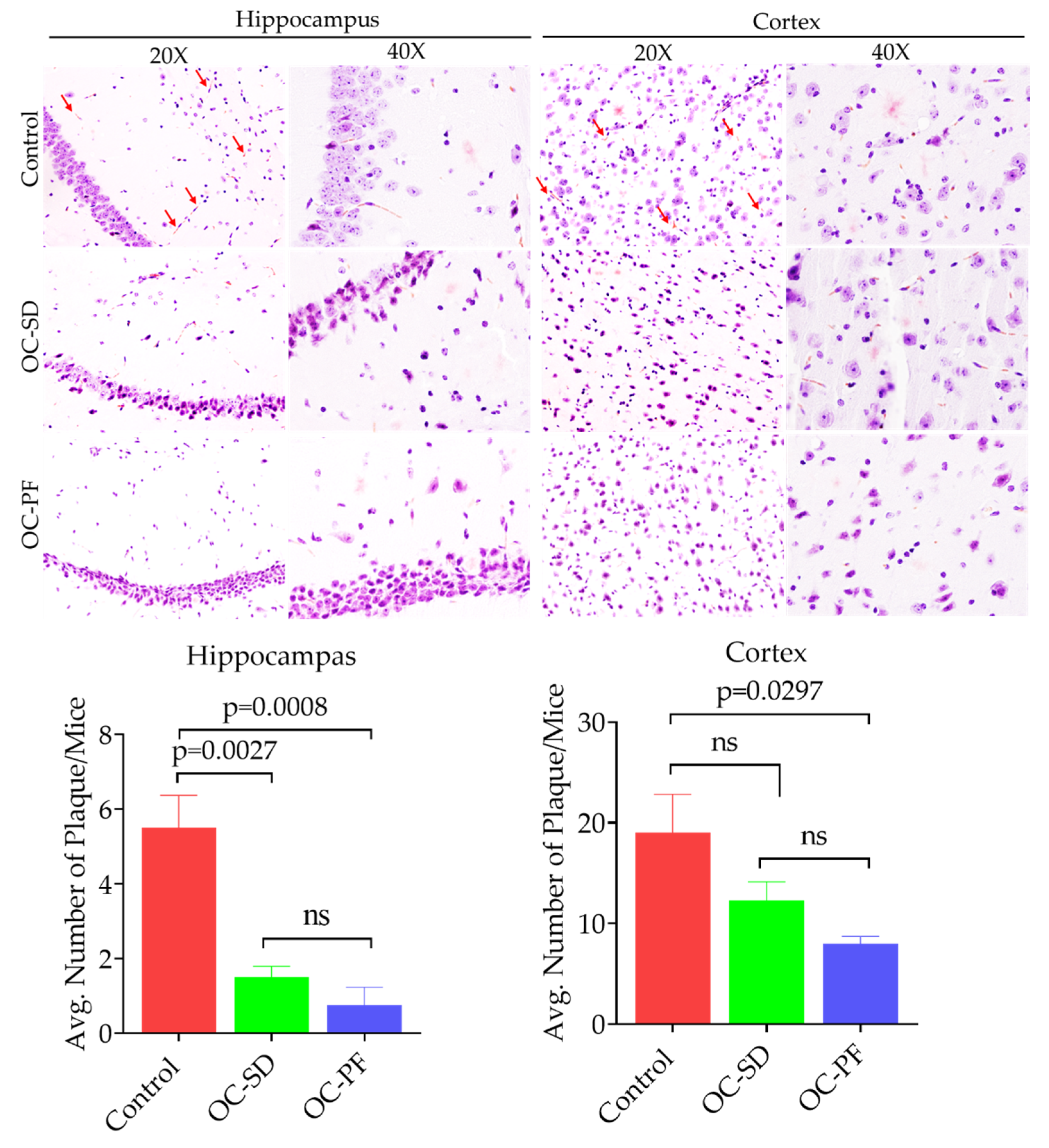
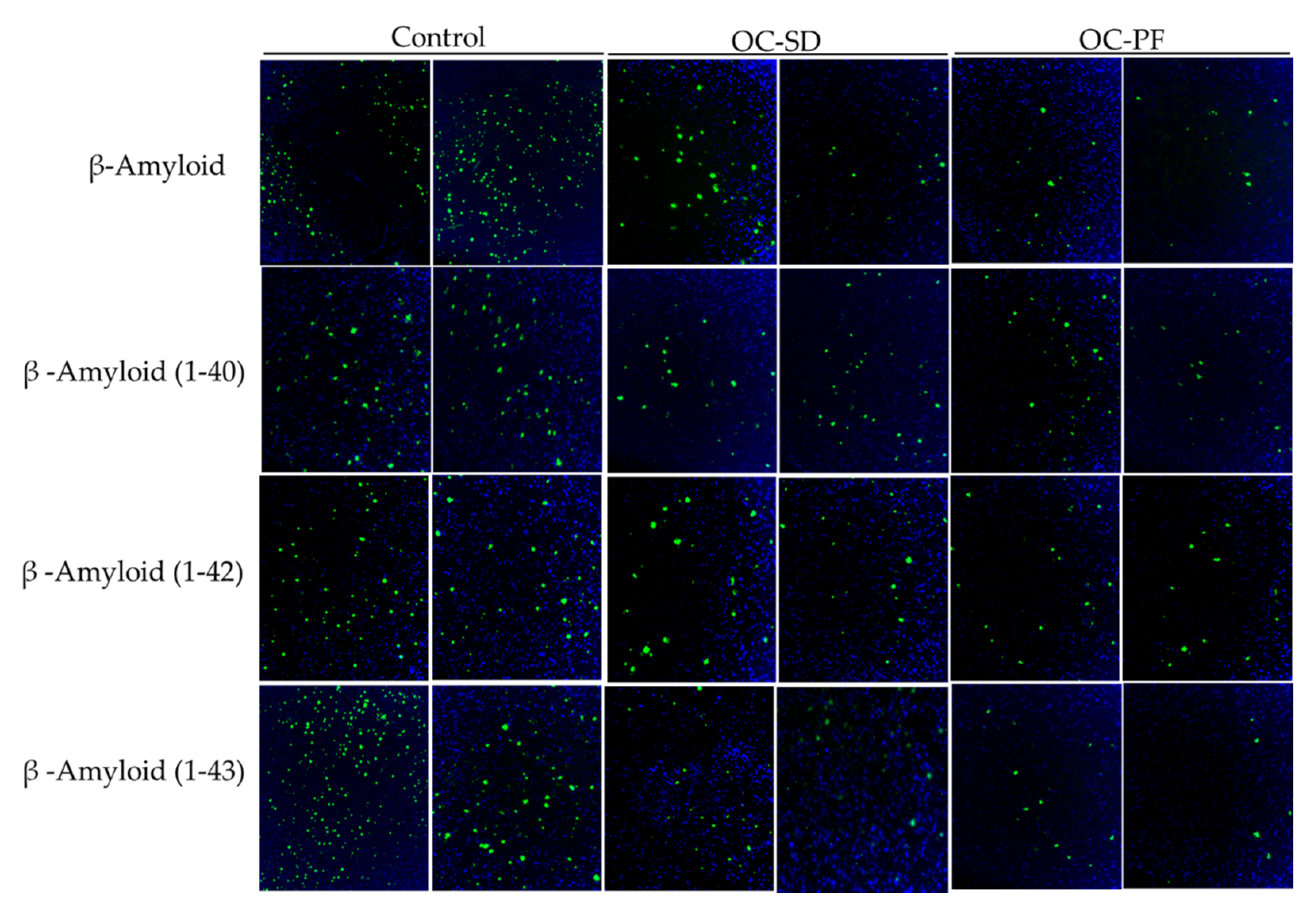
3.5. OC Formulations Attenuated Aβ Plaque Accumulation in 5xFAD Mice
3.6. OC Formulations Effect on Tau Pathology in 5xFAD Mice
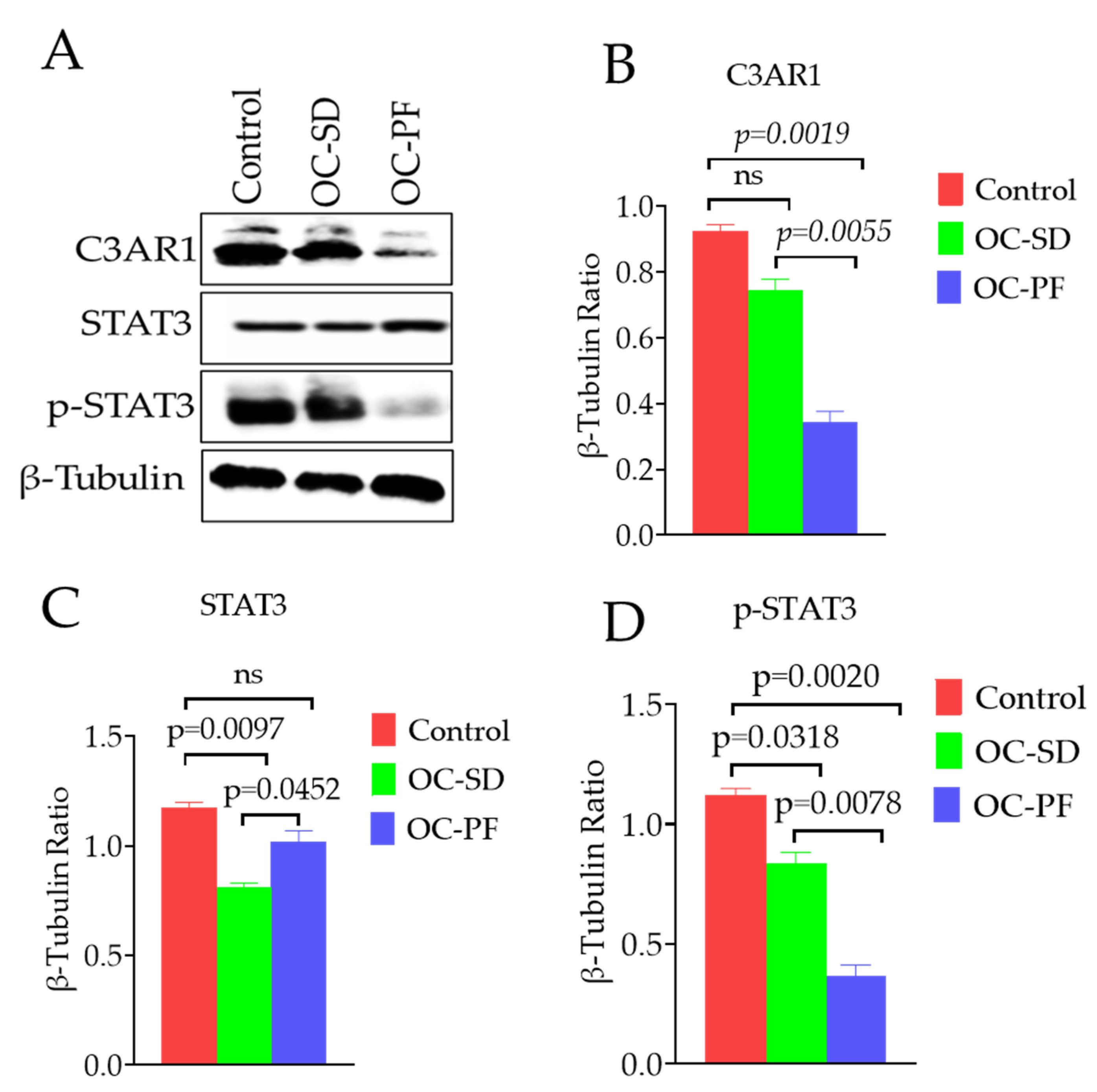
3.7. Effects of OC Formulation Treatments on C3AR1 and STAT3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| Aβ | Aβ-amyloid |
| ADDLs | Aβ-Derived Diffusible Ligands |
| C3AR1 | Complement component 3a receptor 1 |
| EVOO | Extra-virgin olive oil |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| MWM | Morris Water Maze |
| NFT | Neurofibrillary tangles |
| NS | Non-significant |
| OC-PF | Oleocanthal Powder Formulation |
| OC-SD | Oleocanthal Solid Dispersion |
| PXRD | Powder X-ray Diffraction |
| ScEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| STAT3 TRPA1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 Transient receptor potential cation channel subtype A1 receptor |
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2020 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Available online: https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Rahman, R.; Tajmim, A.; Ali, M.; Sharif, M. Overview and Current Status of Alzheimer’s Disease in Bangladesh. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Rep. 2017, 1, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, 391–460. [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, R.; Mousseau, N. Mitigating Alzheimer’s disease with natural polyphenols: A review. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.U.; Levey, A.I. Alzheimer’s disease: A clinical perspective and future nonhuman primate research opportunities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26224–26229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerhuis, R.; Nielsen, H.M.; Tenner, A.J. Complement in the brain. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, A.H.; Barres, B.A.; Stevens, B. The complement system: An unexpected role in synaptic pruning during development and disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Litvinchuk, A.; Chiang, A.C.-A.; Aithmitti, N.; Jankowsky, J.L.; Zheng, H. Astrocyte-microglia cross talk through complement activation modulates amyloid pathology in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Yang, L.; Cole, A.; Sun, L.; Chiang, A.C.-A.; Fowler, S.W.; Shim, D.J.; Rodriguez-Rivera, J.; Taglialatela, G.; Jankowsky, J.L.; et al. NFκB-Activated aastroglial release of complement C3 compromises neuronal morphology and function associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2015, 85, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Chowdhury, S.; Ma, R.; Le, K.X.; Hong, S.; Caldarone, B.J.; Stevens, B.; Lemere, C.A. Complement C3 deficiency protects against neurodegeneration in aged plaque-rich APP/PS1 mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaf6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasek, M.J.; Garber, C.; Dorsey, D.; Durrant, D.M.; Bollman, B.; Soung, A.; Yu, J.; Perez-Torres, C.; Frouin, A.; Wilton, D.K.; et al. A complement–microglial axis drives synapse loss during virus-induced memory impairment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 534, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czirr, E.; Castello, N.A.; Mosher, K.I.; Castellano, J.M.; Hinkson, I.V.; Lucin, K.M.; Baeza-Raja, B.; Ryu, J.K.; Li, L.; Farina, S.N.; et al. Microglial complement receptor 3 regulates brain Aβ levels through secreted proteolytic activity. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannedouche, S.; Beck, V.; Leighton-Davies, J.; Beibel, M.; Roma, G.; Oakeley, E.J.; Lannoy, V.; Bernard, J.; Hamon, J.; Barbieri, S.; et al. Identification of the C3a receptor (C3AR1) as the target of the VGF-derived peptide TLQP-21 in rodent cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27434–27443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvinchuk, A.; Wan, Y.-W.; Swartzlander, D.B.; Chen, F.; Cole, A.; Propson, N.E.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, H. Complement C3aR inactivation attenuates Tau pathology and reverses an immune network deregulated in tauopathy models and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2018, 100, 1337–1353.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.-L.; Chin, K.-Y. The biological activities of oleocanthal from a molecular perspective. Nutrients 2018, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, L.; Keast, R. Oleocanthal, a phenolic derived from virgin olive oil: A review of the beneficial effects on inflammatory disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12323–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerale, S.; Lucas, L.; Keast, R. Biological activities of phenolic compounds present in virgin olive oil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Carretero, A.; Curiel, J.A. Current disease-targets for oleocanthal as promising natural therapeutic agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, G.K.; Keast, R.S.; Morel, D.; Lin, J.; Pika, J.; Han, Q.; Lee, C.H.; Smith, A.B.; Breslin, P.A. Phytochemistry: Ibu-profen-like activity in extra-virgin olive oil. Nature 2005, 437, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, N.M.; Siddique, A.B.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; El Sayed, K.A. The olive oil phenolic (-)-oleocanthal modulates estrogen receptor expression in luminal breast cancer in vitro and in vivo and synergizes with tamoxifen treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 810, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Ayoub, N.M.; Tajmim, A.; Meyer, S.A.; Hill, R.A.; El Sayed, K.A. (−)-Oleocanthal prevents breast cancer lo-coregional recurrence after primary tumor surgical excision and neoadjuvant targeted therapy in orthotopic nude mouse Models. Cancers 2019, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Akl, M.R.; Ayoub, N.M.; Goda, A.A.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Nagumalli, S.K.; Hananeh, W.M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Meyer, S.A.; et al. (−)-Oleocanthal combined with lapatinib treatment synergized against HER-2 positive breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Nutrients 2019, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.B.; Kilgore, P.C.; Tajmim, A.; Singh, S.S.; Meyer, S.A.; Jois, S.D.; Cvek, U.; Trutschl, M.; El Sayed, K.A. (−)-Oleocanthal as a dual c-MET-COX2 inhibitor for the control of lung cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.; Roth, W.; Lacor, P.; Smith, A.B.; Blankenship, M.; Velasco, P.; De Felice, F.; Breslin, P.; Klein, W.L. Alzheimer’s-associated Aβ oligomers show altered structure, immunoreactivity and synaptotoxicity with low doses of oleocanthal. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 240, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sperry, J.B.; Crowe, A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Iii, A.B.S.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Inhibition of tau fibrillization by oleocanthal via reaction with the amino groups of tau. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, M.C.; Margarucci, L.; Riccio, R.; Casapullo, A. Modulation of Tau protein fibrillization by oleocanthal. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuznait, A.H.; Qosa, H.; Busnena, B.A.; El Sayed, K.A.; Kaddoumi, A. Olive-oil-derived oleocanthal enhances β-amyloid clearance as a potential neuroprotective mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease: In vitro and in vivo studies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qosa, H.; Batarseh, Y.S.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; El Sayed, K.A.; Keller, J.N.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal enhances amyloid-β clearance from the brains of TgSwDI mice and in vitro across a human blood-brain barrier model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, Y.S.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal-rich extra-virgin olive oil enhances donepezil effect by reducing amyloid-β load and related toxicity in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 55, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, Y.S.; Mohamed, L.A.; Al Rihani, S.B.; Mousa, Y.M.; Siddique, A.B.; El Sayed, K.A.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal ameliorates amyloid-β oligomers’ toxicity on astrocytes and neuronal cells: In vitro studies. Neuroscience 2017, 352, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qusa, M.H.; Siddique, A.B.; Nazzal, S.; El Sayed, K.A. Novel olive oil phenolic (−)-oleocanthal (+)-xylitol-based solid dispersion formulations with potent oral anti-breast cancer activities. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmim, A.; Siddique, A.B.; El Sayed, K.; Sayed, E. Optimization of taste-masked (–)-oleocanthal effervescent formulation with potent breast cancer progression and recurrence suppressive activities. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, K.K. Gastrointestinal disturbances associated with the consumption of sugar alcohols with special consideration of xylitol: Scientific review and instructions for dentists and other health-care professionals. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Gil, A. Effects of sweeteners on the gut microbiota: A review of experimental studies and clinical trials. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S31–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohi, H.; Sultana, Y.; Khar, R.K. Taste masking technologies in oral pharmaceuticals: Recent developments and approaches. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.B.; Ebrahim, H.E.; Qusa, M.; Btarsah, Y.; Fayaad, A.; Tajmim, A.; Nazzal, S.; Kaddoumi, A.; El Sayed, K.A. Novel liquid-liquid extraction and self-emulsion methods for simplified isolation of extra-virgin olive oil phenolics with emphasis on (-)-oleocanthal and its oral anti-breast cancer activity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Lautrup, S.; Cordonnier, S.; Wang, Y.; Croteau, D.L.; Zavala, E.; Zhang, Y.; Moritoh, K.; O’Connell, J.F.; Baptiste, B.A.; et al. NAD+ supplementation normalizes key Alzheimer’s features and DNA damage responses in a new AD mouse model with introduced DNA repair deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1876–E1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaey, C.; Schreurs, A.; Stroobants, S.; Balschun, D. Early cognitive and behavioral deficits in mouse models for tauopathy and Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rihani, S.B.; Darakjian, L.I.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal-rich extra-virgin olive oil restores the blood–brain barrier function through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition simultaneously with autophagy induction in TgSwDI mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3543–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcock, N.M.; Gordon, M.N.; Morgan, D. Quantification of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and parenchymal amyloid plaques with Congo red histochemical stain. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1591–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, F.; Blaton, N.; Naesens, L.; Balzarini, J.; Kinget, R.; Augustijns, P.; Van den Mooter, G. Physicochemical characteri-zation of solid dispersions of the antiviral agent UC-781 with polyethylene glycol 6000 and Gelucire 44/14. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 10, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, F.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Micieli, D.; Ottimo, S.; Pitarresi, G.; Tripodo, G.; Carlisi, B.; Giammona, G. Differential scan-ning calorimetry study on drug release from an inulin-based hydrogel and its interaction with a biomembrane model: pH and loading effect. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 35, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Lee, G.; Ritter, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2020. Alzheimer’s Dementia: Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2020, 6, e12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielden, M.R.; Werner, J.; Jamison, J.A.; Coppi, A.; Hickman, D.; Dunn, R.T.; Trueblood, E.; Zhou, L.; Afshari, C.A.; Lightfoot-Dunn, R. Retinal toxicity induced by a novel β-secretase inhibitor in the Sprague-Dawley rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 43, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salloway, S.; Sperling, R.; Keren, R.; Porsteinsson, A.P.; Van Dyck, C.H.; Tariot, P.N.; Gilman, S.; Arnold, D.; Abushakra, S.; Hernandez, C.; et al. A phase 2 randomized trial of ELND005, scyllo-inositol, in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2011, 77, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.B.; King, J.A.; Meyer, S.A.; Abdelwahed, K.; Busnena, B.; El Sayed, K.A. Safety evaluations of single dose of the olive secoiridoid S-(−)-oleocanthal in Swiss albino mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotece, M.; Gómez, R.; Conde, J.; Lopez, V.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Lago, F.; Smith, A.B.; Gualillo, O. Further evidence for the anti-inflammatory activity of oleocanthal: Inhibition of MIP-1α and IL-6 in J774 macrophages and in ATDC5 chondrocytes. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gachons, C.P.D.; Uchida, K.; Bryant, B.; Shima, A.; Sperry, J.B.; Dankulich-Nagrudny, L.; Tominaga, M.; Smith, A.B.; Beauchamp, G.K.; Breslin, P.A.S. Unusual pungency from extra-virgin olive oil is attributable to restricted spatial expression of the receptor of oleocanthal. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerale, S.; Breslin, P.A.; Beauchamp, G.K.; Keast, R.S. Sensory characterization of the irritant properties of oleocanthal, a natural anti-Inflammatory agent in extra virgin olive oils. Chem. Senses 2009, 34, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J. CSF phosphorylated tau in the diagnosis and prognosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of 51 studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Wang, X. Abnormal mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 33, S253–S262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brier, M.R.; Thomas, J.B.; Ances, B.M. Network dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: Refining the disconnection hypothesis. Brain Connect. 2014, 4, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.C.; Benitez, B.A.; Karch, C.M.; Cooper, B.; Skorupa, T.; Carrell, D.; Norton, J.B.; Hsu, S.; Harari, O.; Cai, Y.; et al. Coding variants in TREM2 increase risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 5838–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almdahl, I.S.; Lauridsen, C.; Selnes, P.; Kalheim, L.F.; Coello, C.; Gajdzik, B.; Møller, I.; Wettergreen, M.; Grambaite, R.; Bjørnerud, A.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of amyloid beta 1–43 mirror 1–42 in relation to imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, K.-I.; Ando, K.; Takeda, S.; Satoh, Y.; Seki, T.; Itohara, S.; Greengard, P.; Kirino, Y.; Nairn, A.C.; Suzuki, T. Neuron-specific phosphorylation of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein by cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J. Neurochem. 2002, 75, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welander, H.; Frånberg, J.; Graff, C.; Sundström, E.; Winblad, B.; Tjernberg, L.O. Aβ43 is more frequent than Aβ40 in amyloid plaque cores from Alzheimer disease brains. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.; Welander, H.; Chiang, H.-H.; Tjernberg, L.O.; Nennesmo, I.; Wallin, A.K.; Graff, C. The PSEN1 I143T mutation in a Swedish family with Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical report and quantification of Aβ in different brain regions. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanger, D.P.; Betts, J.C.; Loviny, T.L.; Blackstock, W.P.; Anderton, B.H. New phosphorylation sites identified in hyperphosphorylated tau (paired helical filament-tau) from Alzheimer’s disease brain using nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.P. Complement in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Dejanovic, B.; Gandham, V.D.; Gogineni, A.; Edmonds, R.; Schauer, S.; Srinivasan, K.; Huntley, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.-M.; et al. Complement C3 is activated in human AD brain and is required for neurodegeneration in mouse models of amyloidosis and tauopathy. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2111–2123.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral-Rios, D.; Patiño-López, G.; Gómez-Lira, G.; Gutiérrez, R.; Becerril-Pérez, F.; Rosales-Córdova, A.; León-Contreras, J.C.; Hernández-Pando, R.; León-Rivera, I.; Soto-Cruz, I.; et al. Activation of STAT3 regulates reactive astrogliosis and neuronal death induced by AβO neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbach, N.; Delekate, A.; Plescher, M.; Schmitt, F.; Krauss, S.; Blank, N.; Halle, A.; Petzold, G.C. Inhibition of Stat3-mediated astrogliosis ameliorates pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease model. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, 9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Kim, H.; Yang, E.-J.; Kim, H.-S. Inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation attenuates impairments in learning and memory in 5xFAD mice, an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 143, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| % Tau Downregulation | ||
|---|---|---|
| OC-SD | OC-PF | |
| Total Tau | 23.4 | 55.1 |
| p-Tau(Ser404) | 27.8 | 44.9 |
| p-Tau(Thr181) | 0.1 | 4.7 |
| p-Tau(Ser199) | 8.8 | 39.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tajmim, A.; Cuevas-Ocampo, A.K.; Siddique, A.B.; Qusa, M.H.; King, J.A.; Abdelwahed, K.S.; Sonju, J.J.; El Sayed, K.A. (-)-Oleocanthal Nutraceuticals for Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Pathology: Novel Oral Formulations, Therapeutic, and Molecular Insights in 5xFAD Transgenic Mice Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051702
Tajmim A, Cuevas-Ocampo AK, Siddique AB, Qusa MH, King JA, Abdelwahed KS, Sonju JJ, El Sayed KA. (-)-Oleocanthal Nutraceuticals for Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Pathology: Novel Oral Formulations, Therapeutic, and Molecular Insights in 5xFAD Transgenic Mice Model. Nutrients. 2021; 13(5):1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051702
Chicago/Turabian StyleTajmim, Afsana, Areli K. Cuevas-Ocampo, Abu Bakar Siddique, Mohammed H. Qusa, Judy Ann King, Khaldoun S. Abdelwahed, Jafrin Jobayer Sonju, and Khalid A. El Sayed. 2021. "(-)-Oleocanthal Nutraceuticals for Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Pathology: Novel Oral Formulations, Therapeutic, and Molecular Insights in 5xFAD Transgenic Mice Model" Nutrients 13, no. 5: 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051702
APA StyleTajmim, A., Cuevas-Ocampo, A. K., Siddique, A. B., Qusa, M. H., King, J. A., Abdelwahed, K. S., Sonju, J. J., & El Sayed, K. A. (2021). (-)-Oleocanthal Nutraceuticals for Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Pathology: Novel Oral Formulations, Therapeutic, and Molecular Insights in 5xFAD Transgenic Mice Model. Nutrients, 13(5), 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051702








