NPC1L1 Facilitates Sphingomyelin Absorption and Regulates Diet-Induced Production of VLDL/LDL-associated S1P
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Lipoprotein Fractionation
2.3. Proteomics Analysis
2.4. Quantification of S1P
2.5. Emulsion Preparation
2.6. In Vivo Acute Absorption Study
2.7. Cells
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Preparation of SM-Containing Medium for In Vitro Uptake Assay
2.10. In Vitro Uptake Assay
2.11. Ethic Committee Approval
3. Results
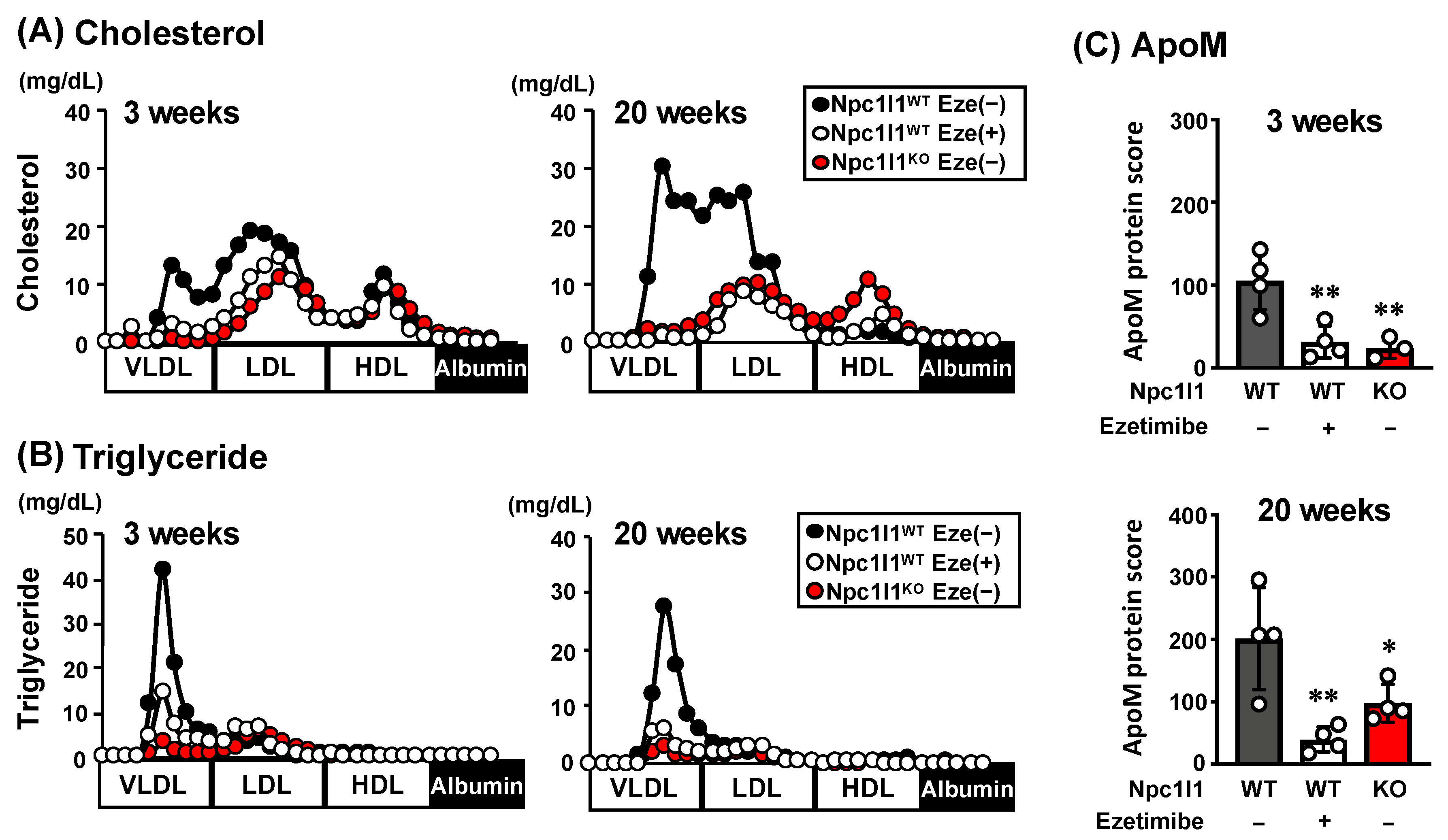
3.1. Characterization of NPC1L1-Dependent VLDL/LDL in Mice Fed WD
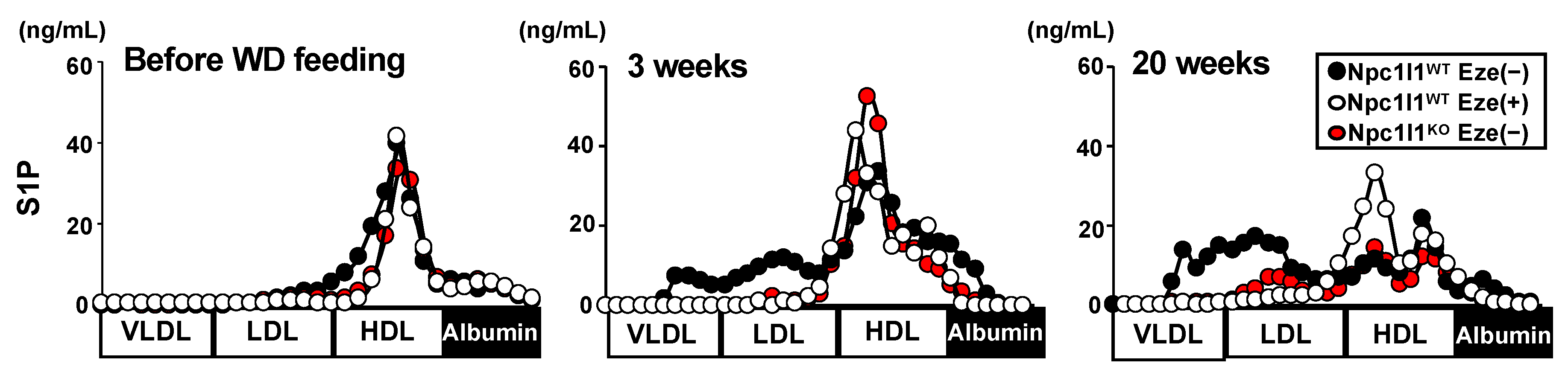
3.2. S1P Levels in NPC1L1-Dependent VLDL/LDL in Mice Fed a WD
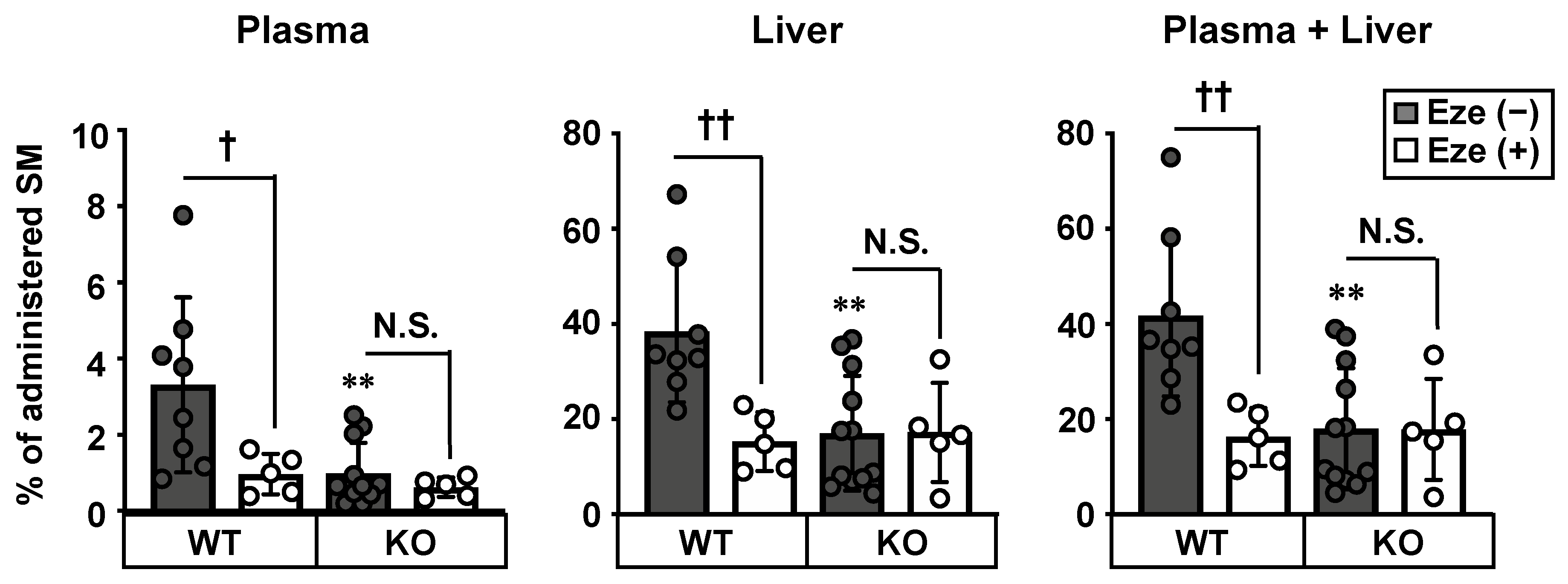
3.3. Involvement of NPC1L1 in Intestinal Absorption of SM
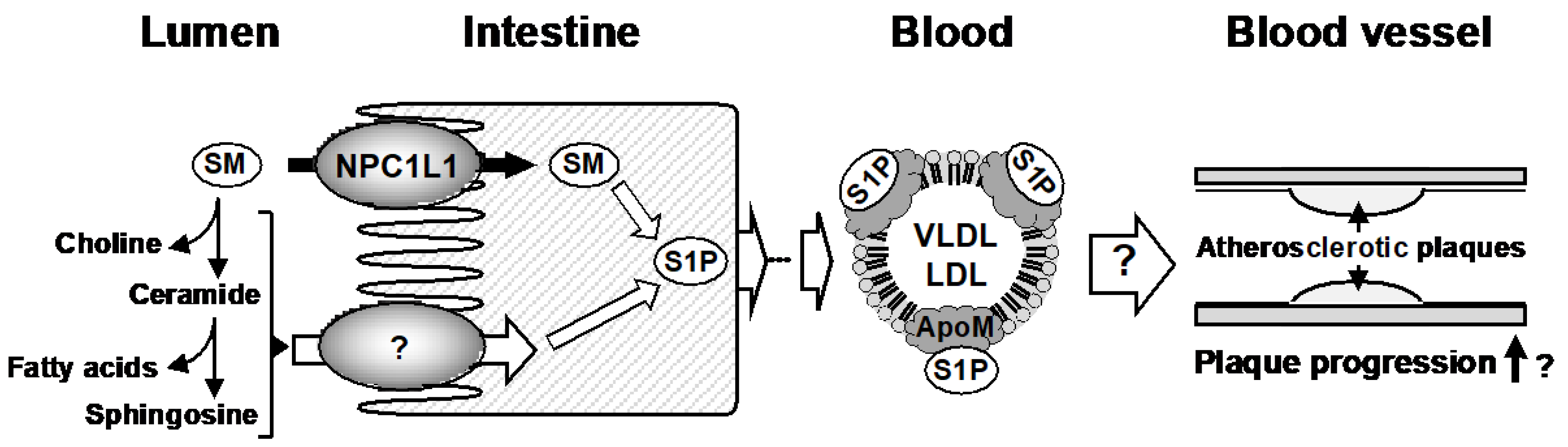
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| apoM | apolipoprotein M |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| NPC1L1 | Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| S1P | sphingosine-1-phosphate |
| VLDL | very low-density lipoprotein |
| WD | Western diet |
References
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, G.H.; Blesso, C.N. Dietary sphingolipids: Potential for management of dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dei Cas, M.; Ghidoni, R. Cancer Prevention and Therapy with Polyphenols: Sphingolipid-Mediated Mechanisms. Nutrients 2018, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, S.W.; Davis, H.R., Jr.; Zhu, L.J.; Yao, X.; Hoos, L.M.; Tetzloff, G.; Iyer, S.P.; Maguire, M.; Golovko, A.; Zeng, M.; et al. Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science 2004, 303, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Suzuki, H. Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 overexpression facilitates ezetimibe-sensitive cholesterol and beta-sitosterol uptake in CaCo-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Calvo, M.; Lisnock, J.; Bull, H.G.; Hawes, B.E.; Burnett, D.A.; Braun, M.P.; Crona, J.H.; Davis, H.R., Jr.; Dean, D.C.; Detmers, P.A.; et al. The target of ezetimibe is Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8132–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narushima, K.; Takada, T.; Yamanashi, Y.; Suzuki, H. Niemann-pick C1-like 1 mediates alpha-tocopherol transport. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Suzuki, H. Molecular mechanisms of membrane transport of vitamin E. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Yamanashi, Y.; Konishi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Toyoda, Y.; Masuo, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Suzuki, H. NPC1L1 is a key regulator of intestinal vitamin K absorption and a modulator of warfarin therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 275ra223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Mu, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Komine, T.; Suzuki, H. Hepatic Expression of Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1, a Cholesterol Reabsorber from Bile, Exacerbates Western Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in LDL Receptor Mutant Mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 96, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Takada, T.; Yamanashi, Y.; Ogura, M.; Masuo, Y.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Suzuki, H. VLDL/LDL acts as a drug carrier and regulates the transport and metabolism of drugs in the body. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; He, Q.; Han, W.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Evaluation and optimization of removal of an acid-insoluble surfactant for shotgun analysis of membrane proteome. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikebuchi, Y.; Aoki, S.; Honma, M.; Hayashi, M.; Sugamori, Y.; Khan, M.; Kariya, Y.; Kato, G.; Tabata, Y.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse signalling. Nature 2018, 561, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Suzuki, H. In-vitro characterization of the six clustered variants of NPC1L1 observed in cholesterol low absorbers. Pharm. Genom. 2009, 19, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.M.; Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Suzuki, H. Clinical Importance of Drug-Drug Interaction Between Warfarin and Prednisolone and Its Potential Mechanism in Relation to the Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1-Mediated Pathway. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, C.; Obinata, H.; Kumaraswamy, S.B.; Galvani, S.; Ahnstrom, J.; Sevvana, M.; Egerer-Sieber, C.; Muller, Y.A.; Hla, T.; Nielsen, L.B.; et al. Endothelium-protective sphingosine-1-phosphate provided by HDL-associated apolipoprotein M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9613–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, C.; Pedersen, T.X.; Gordts, P.L.; Roebroek, A.J.; Dahlback, B.; Nielsen, L.B. Opposing effects of apolipoprotein m on catabolism of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurano, M.; Hara, M.; Ikeda, H.; Tsukamoto, K.; Yatomi, Y. Involvement of CETP (Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein) in the Shift of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Among Lipoproteins and in the Modulation of its Functions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvani, S.; Sanson, M.; Blaho, V.A.; Swendeman, S.L.; Obinata, H.; Conger, H.; Dahlback, B.; Kono, M.; Proia, R.L.; Smith, J.D.; et al. HDL-bound sphingosine 1-phosphate acts as a biased agonist for the endothelial cell receptor S1P1 to limit vascular inflammation. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Barrett, T.J.; Fisher, E.A. HDL and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.P.; Scott, C.; Oishi, K.; Liapis, A.; Ioannou, Y.A. Inactivation of NPC1L1 causes multiple lipid transport defects and protects against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12710–12720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, G.H.; Milard, M.; Michalski, M.C.; Blesso, C.N. Protective properties of milk sphingomyelin against dysfunctional lipid metabolism, gut dysbiosis, and inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 73, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, A.; Duan, R.D. Absorption and lipoprotein transport of sphingomyelin. J. Lipid. Res. 2006, 47, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Ge, L.; Qi, W.; Zhang, L.; Miao, H.H.; Li, B.L.; Yang, M.; Song, B.L. The N-terminal domain of NPC1L1 protein binds cholesterol and plays essential roles in cholesterol uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25088–25097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.S.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Xu, C.Q.; Ma, Y.T.; Li, B.L.; Song, B.L. The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.S.; Yu, X.; Fordstrom, P.; Choi, K.; Chung, B.C.; Roh, S.H.; Chiu, W.; Zhou, M.; Min, X.; Wang, Z. Cryo-EM structures of NPC1L1 reveal mechanisms of cholesterol transport and ezetimibe inhibition. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotte, J.P. Sphingomyelin-cholesterol interactions in biological and model membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1999, 102, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.K.; Koo, S.I. Egg sphingomyelin lowers the lymphatic absorption of cholesterol and alpha-tocopherol in rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3571–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, L.; Duan, R.D.; Nilsson, A. A mutual inhibitory effect on absorption of sphingomyelin and cholesterol. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000, 11, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, A.; Nishi, T.; Hisano, Y.; Fukui, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Mochizuki, N. The sphingolipid transporter spns2 functions in migration of zebrafish myocardial precursors. Science 2009, 323, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.M.; Ishizu, A.N.; Foo, J.C.; Toh, X.R.; Zhang, F.; Whee, D.M.; Torta, F.; Cazenave-Gassiot, A.; Matsumura, T.; Kim, S.; et al. Mfsd2b is essential for the sphingosine-1-phosphate export in erythrocytes and platelets. Nature 2017, 550, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Suzuki, H. NPC1L1 Facilitates Sphingomyelin Absorption and Regulates Diet-Induced Production of VLDL/LDL-associated S1P. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092641
Yamanashi Y, Takada T, Yamamoto H, Suzuki H. NPC1L1 Facilitates Sphingomyelin Absorption and Regulates Diet-Induced Production of VLDL/LDL-associated S1P. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092641
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamanashi, Yoshihide, Tappei Takada, Hideaki Yamamoto, and Hiroshi Suzuki. 2020. "NPC1L1 Facilitates Sphingomyelin Absorption and Regulates Diet-Induced Production of VLDL/LDL-associated S1P" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092641
APA StyleYamanashi, Y., Takada, T., Yamamoto, H., & Suzuki, H. (2020). NPC1L1 Facilitates Sphingomyelin Absorption and Regulates Diet-Induced Production of VLDL/LDL-associated S1P. Nutrients, 12(9), 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092641




