Establishment of Adequate Nutrient Intake Criteria to Achieve Target Weight Loss in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. General Characteristics and Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Dietary Intake Analysis
2.4. Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics and Weight Loss
3.2. Changes in Nutrient Intake over Time
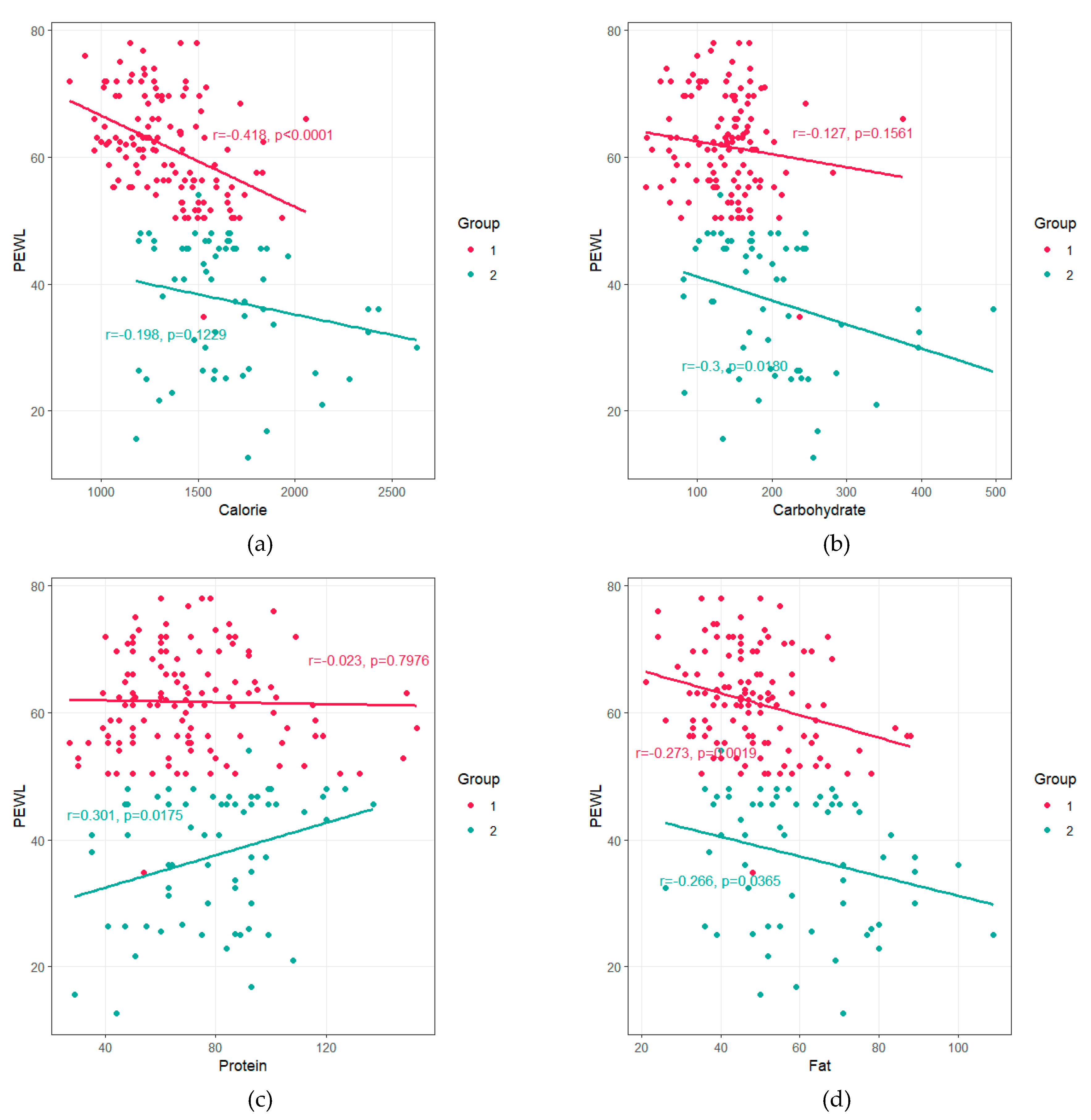
3.3. Correlation between %EWL and Nutrient Intake
3.4. Factors Affecting the %EWL in Subjects
3.5. Optimal Nutrient Intakes for Determining Success after Bariatric Surgery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, E.; Ko, E.; Luong, V.; Wang, H.J.; Romanova, M.; Li, Z. Long-term changes in weight loss and obesity-related comorbidities after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A primary care experience. Am. J. Surg. 2008, 195, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handzlik-Orlik, G.; Holecki, M.; Orlik, B.; Wyleżoł, M.; Duława, J. Nutrition management of the post-bariatric surgery patient. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2015, 30, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupoli, R.; Lembo, E.; Saldalamacchia, G.; Avola, C.K.; Angrisani, L.; Capaldo, B. Bariatric surgery and long-term nutritional issues. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherf Dagan, S.; Goldenshluger, A.; Globus, I.; Schweiger, C.; Kessler, Y.; Kowen Sandbank, G.; Ben-Porat, T.; Sinai, T. Nutritional recommendations for adult bariatric surgery patients: Clinical practice. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, D.O.; Geloneze, B.; Delfini, R.; Pareja, B.C.; Callejas, F.; Pareja, J.C. Long-term weight regain after gastric bypass: A 5-year prospective study. Obes. Surg. 2008, 18, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Kahan, S. Maintenance of lost weight and long-term management of obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lozano, T.; Vidal, J.; de Hollanda, A.; Scheer, F.; Garaulet, M.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M. Timing of food intake is associated with weight loss evolution in severe obese patients after bariatric surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanerva, N.; Larsson, I.; Peltonen, M.; Lindroos, A.K.; Carlsson, L.M. Changes in total energy intake and macronutrient composition after bariatric surgery predict long-term weight outcome: Findings from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aills, L.; Blankenship, J.; Buffington, C.; Furtado, M.; Parrott, J. ASMBS Allied Health Nutritional Guidelines for the Surgical Weight Loss Patient. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2008, 4, S73–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanick, J.I.; Apovian, C.; Brethauer, S.; Garvey, W.T.; Joffe, A.M.; Kim, J.; Kushner, R.F.; Lindquist, R.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Seger, J.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the perioperative nutrition, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of patients undergoing bariatric procedures—2019 update: Cosponsored by American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, The Obesity Society, American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery, Obesity Medicine Association, and American Society of Anesthesiologists. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2020, 16, 175–247. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. 2018 Korean society for metabolic and bariatric surgery guidelines. J. Metab. Bariatr. Surg. 2018, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kasama, K.; Mui, W.; Lee, W.J.; Lakdawala, M.; Naitoh, T.; Seki, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Wakabayashi, G.; Sasaki, I.; Kawamura, I.; et al. IFSO-APC consensus statements 2011. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snehalatha, C.; Viswanathan, V.; Ramachandran, A. Cutoff values for normal anthropometric variables in asian Indian adults. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simel, D.L.; Samsa, G.P.; Matchar, D.B. Likelihood ratios with confidence: Sample size estimation for diagnostic test studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1991, 44, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conason, A.; Teixeira, J.; Hsu, C.H.; Puma, L.; Knafo, D.; Geliebter, A. Substance use following bariatric weight loss surgery. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J. Bariatric surgery-which procedure is the optimal choice? Lancet 2019, 393, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, D. Bariatric surgeries: Beyond restriction and malabsorption. Int. J. Obes. Lond. 2011, 35, S45–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.M.; Sarr, M.G.; Clark, M.M.; Gall, M.M.; Knoetgen, J., 3rd; Service, F.J.; Laskowski, E.R.; Hurley, D.L. Clinical management after bariatric surgery: Value of a multidisciplinary approach. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, S34–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Pilone, V.; Rossetti, G.; Iannelli, A. The role of the nutritionist in a multidisciplinary bariatric surgery team. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, M.P.; Santo, M.A.; Gadducci, A.V.; Scabim, V.M.; Cecconello, I.; de Cleva, R. Very low-calorie diet in candidates for bariatric surgery: Change in body composition during rapid weight loss. Clin. Sao Paulo 2019, 74, e560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.L.; Faria, O.P.; de Almeida Cardeal, M.; Ito, M.K. Effects of a very low calorie diet in the preoperative stage of bariatric surgery: A randomized trial. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajoux, I.; Lorenzo, P.M.; Gomez-Arbelaez, D.; Zulet, M.A.; Abete, I.; Castro, A.I.; Baltar, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Tinahones, F.J.; Martinez, J.A.; et al. Effect of a very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on circulating myokine levels compared with the effect of bariatric surgery or a low-calorie diet in patients with obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edholm, D.; Kullberg, J.; Karlsson, F.A.; Haenni, A.; Ahlström, H.; Sundbom, M. Changes in liver volume and body composition during 4 weeks of low calorie diet before laparoscopic gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, J.; Chong, L.; Ward, S.; Sutherland, T.R.; Read, M.; Hii, M.W. Body composition changes following a very-low-calorie pre-operative diet in patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder-Marlow, G.; Taylor, D.; Lenhard, M.J. Nutrition care for patients undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for weight loss. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Gilhooly, C.H.; Golden, J.K.; Pittas, A.G.; Fuss, P.J.; Cheatham, R.A.; Tyler, S.; Tsay, M.; McCrory, M.A.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; et al. Long-term effects of 2 energy-restricted diets differing in glycemic load on dietary adherence, body composition, and metabolism in CALERIE: A 1-y randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joslowski, G.; Halim, J.; Goletzke, J.; Gow, M.; Ho, M.; Louie, J.C.; Buyken, A.E.; Cowell, C.T.; Garnett, S.P. Dietary glycemic load, insulin load, and weight loss in obese, insulin resistant adolescents: RESIST study. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, C.F.; Cortes-Oliveira, C.; Pinhel, M.A.S.; Nonino, C.B. Bariatric surgery and precision nutrition. Nutrients 2017, 9, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea Health Statistics 2018: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES ⅦI-3). Available online: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/sub04/sub04_03.do (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Swenson, B.R.; Saalwachter Schulman, A.; Edwards, M.J.; Gross, M.P.; Hedrick, T.L.; Weltman, A.L.; Northrup, C.J.; Schirmer, B.D.; Sawyer, R.G. The effect of a low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet on post laparoscopic gastric bypass weight loss: A prospective randomized trial. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 142, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Total (n = 189) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.6 ± 10.7 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 54 (28.6%) |
| Female | 135 (71.4%) |
| Operative method | |
| LRYGB | 146 (77.2%) |
| SG | 43 (22.8%) |
| Comorbidity | |
| Yes | 43 (22.8%) |
| Diabetes | 18 (9.5%) |
| Hypertension | 10 (5.3%) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 11 (5.8%) |
| Joint problem | 6 (3.2%) |
| Depression | 4 (2.1%) |
| Apnea | 7 (3.7%) |
| Number of comorbidities | |
| One | 26 (60.4%) |
| Two | 11 (25.6%) |
| Three or more | 6 (14.0%) |
| Lifestyle habit | |
| Alcohol drinking | 66 (34.9%) |
| Smoking | 36 (19.0%) |
| Exercise | 28 (14.8%) |
| Experience of diet control | 86 (46.0%) |
| Weight (kg) | 108.0 ± 19.8 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 38.9 ± 5.9 |
| Excess weight (kg) | 44.2 ± 16.6 |
| Fat Mass (kg) | 55.7 ± 11.3 |
| Fat Free Mass (kg) | 51.6 ± 13.9 |
| Variable | Total (n = 189) | Achievement of Weight Loss | Operative Method | Comorbidity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success (n = 127) | Failure (n = 62) | p-Value | LRYGB (n = 146) | SG (n = 43) | p-Value | Yes (n = 43) | No (n = 146) | p-Value | ||
| Postop 1 month | 24.69 ± 9.23 | 25.85 ± 10.00 | 22.50 ± 6.52 | 0.005 | 24.52 ± 9.66 | 25.24 ± 7.64 | 0.615 | 24.59 ± 7.82 | 25.25 ± 13.39 | 0.695 |
| Postop 3 months | 41.66 ± 11.57 | 45.38 ± 10.87 | 34.03 ± 8.96 | <0.001 | 42.18 ± 12.91 | 41.50 ± 11.19 | 0.736 | 45.35 ± 16.06 | 48.71 ± 17.57 | 0.258 |
| Postop 6 months | 46.42 ± 17.27 | 52.76 ± 17.12 | 33.48 ± 7.78 | <0.001 | 50.05 ± 18.66 | 46.67 ± 16.75 | 0.289 | 41.98 ± 10.87 | 42.24 ± 13.58 | 0.900 |
| Postop 12 months | 53.05 ± 15.90 | 61.71 ± 7.90 | 37.46 ± 10.21 | <0.001 | 54.40 ± 16.38 | 53.57 ± 13.75 | 0.762 | 53.15 ± 14.80 | 54.81 ± 13.81 | 0.511 |
| Variable | Calorie (kcal) | Carbohydrate (g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success (n = 127) | Failure (n = 62) | p-Value | Success (n = 127) | Failure (n = 62) | p-Value | Success (n = 127) | Failure (n = 62) | p-Value | Success (n = 127) | Failure (n = 62) | p-Value | |
| Preop | 2282.97 ± 626.93 | 2234.31 ± 609.10 | 0.610 | 293.31 ± 90.00 (53.5%) | 311.18 ± 113.16 (56.4%) | 0.280 | 92.06 ± 32.42 (16.8%) | 84.02 ± 28.75 (15.1%) | 0.086 | 74.24 ± 32.67 (29.9%) | 70.77 ± 31.61 (28.5%) | 0.485 |
| Postop 1 month | 769.33 ± 217.88 | 765.73 ± 178.30 | 0.904 | 70.48 ± 34.82 (36.7%) | 70.56 ± 35.47 (39.6%) a | 0.987 | 58.02 ± 21.95 (30.1%) | 50.55 ± 23.74 (28.9%) | 0.040 | 30.04 ± 14.53 (33.2%) | 27.59 ± 14.25 (31.5%) | 0.272 |
| Postop 6 months | 999.82 ± 259.30 | 1120.81 ± 272.43 | 0.004 | 97.58 ± 44.1 (40.6%) | 133.98 ± 54.96 (46.4%) | <0.001 | 57.87 ± 20.91 (25.4%) | 53.79 ± 18.06 (20.2%) b | 0.169 | 34.71 ± 11.53 (34.0%) | 38.98 ± 12.10 (33.4%) | 0.022 |
| Postop 12 months | 1336.75 ± 229.03 | 1646.21 ± 315.55 | <0.001 | 139.13 ± 49.04 (48.4%) | 198.60 ± 81.10 (53.1%) A | <0.001 | 79.19 ± 24.09 (28.0%) | 70.43 ± 25.04 (20.4%) B | 0.023 | 47.87 ± 12.32 (23.6%) | 59.42 ± 17.53 (26.5%) C | <0.001 |
| Variable | Univariable | Multiple 1 | Multiple 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (year) | 0.96 (0.93–0.99) | 0.009 | 0.97 (0.94–0.99) | 0.046 | 0.96 (0.93–0.99) | 0.027 |
| Female | 1.83 (0.94–3.52) | 0.072 | ||||
| LRYGB | 0.74 (0.34–1.54) | 0.437 | ||||
| No. of comorbidities | 0.85 (0.65–1.13) | 0.249 | ||||
| Calorie (100 kcal) | ||||||
| at 1 month | 1.05 (0.91–1.22) | 0.515 | ||||
| at 6 months | 0.78 (0.68–0.88) | <0.001 | ||||
| at 12 months | 0.37 (0.27–0.48) | <0.001 | ||||
| Carbohydrates (10 g) | ||||||
| at 1 month | 0.98 (0.9–1.07) | 0.607 | ||||
| at 6 months | 0.85 (0.78–0.91) | <0.001 | ||||
| at 12 months | 0.63 (0.54–0.72) | <0.001 | ||||
| Protein (10 g) | ||||||
| at 1 month | 1.17 (1.01–1.36) | 0.038 | ||||
| at 6 months | 0.99 (0.85–1.15) | 0.853 | ||||
| at 12 months | 0.85 (0.74–0.96) | 0.008 | ||||
| Fat (10 g) | ||||||
| at 1 month | 1.11 (0.9–1.39) | 0.323 | ||||
| at 6 months | 0.55 (0.41–0.72) | <0.001 | ||||
| at 12 months | 0.46 (0.35–0.6) | <0.001 | ||||
| Proportion of calories at 12 months | ||||||
| Carbohydrate (%) | 0.98 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 | 0.98 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 |
| Protein (%) | 0.99 (0.97–1.00) | 0.026 | 0.99 (0.97–1.00) | 0.171 | ||
| Fat (%) | 0.95 (0.93–0.97) | <0.001 | 0.96 (0.93–0.99) | 0.002 | 0.96 (0.93–0.98) | <0.001 |
| Variable | AUC (95% CI) | Optimal Cutoff * | Estimates (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | LR (+) | LR (−) | |||
| Calories (kcal) | |||||||
| at 1 month | 0.529 (0.442–0.615) | <835.0 | 0.57 (0.48–0.65) | 0.32 (0.21–0.45) | 0.49 (0.41–0.56) | 0.84 (0.67–1.05) | 1.34 (0.89–2.03) |
| at 6 months | 0.673 (0.593–0.754) | <1132.5 | 0.75 (0.66–0.82) | 0.55 (0.42–0.68) | 0.68 (0.61–0.75) | 1.66 (1.24–2.22) | 0.46 (0.32–0.67) |
| at 12 months | 0.912 (0.872–0.953) | <1523.0 | 0.87 (0.79–0.92) | 0.82 (0.7–0.91) | 0.85 (0.79–0.90) | 4.88 (2.84–8.38) | 0.16 (0.10–0.26) |
| Carbohydrate (g) | |||||||
| at 1 month | 0.513 (0.424–0.602) | <115.5 | 0.91 (0.85–0.96) | 0.15 (0.07–0.26) | 0.66 (0.59–0.73) | 1.07 (0.95–1.20) | 0.60 (0.26–1.36) |
| at 6 months | 0.703 (0.624–0.781) | <103.0 | 0.58 (0.49–0.67) | 0.79 (0.67–0.88) | 0.65 (0.58–0.72) | 2.78 (1.68–4.61) | 0.53 (0.41–0.67) |
| at 12 months | 0.878 (0.819–0.937) | <172.5 | 0.93 (0.87–0.97) | 0.76 (0.63–0.86) | 0.87 (0.82–0.92) | 3.84 (2.47–5.98) | 0.09 (0.05–0.18) |
| Protein (g) | |||||||
| at 1 month | 0.617 (0.529–0.705) | >44.5 | 0.76 (0.67–0.83) | 0.52 (0.39–0.65) | 0.68 (0.61–0.74) | 1.56 (1.19–2.06) | 0.47 (0.32–0.70) |
| at 6 months | 0.524 (0.440–0.609) | >41.5 | 0.86 (0.79–0.91) | 0.02 (0.00–0.09) | 0.58 (0.51–0.65) | 0.87 (0.81–0.94) | 8.79 (1.02–64.33) |
| at 12 months | 0.618 (0.531–0.705) | >86.5 | 0.21 (0.15–0.29) | 0.55 (0.42–0.68) | 0.32 (0.26–0.39) | 0.47 (0.31–0.73) | 1.44 (1.13–1.83) |
| Fat (g) | |||||||
| at 1 month | 0.564 (0.475–0.652) | <21.5 | 0.49 (0.38–0.61) | 0.58 (0.48–0.67) | 0.54 (0.47–0.62) | 0.58 (0.4–0.83) | 1.45 (1.09–1.92) |
| at 6 months | 0.682 (0.599–0.766) | <46.5 | 0.85 (0.78–0.91) | 0.48 (0.35–0.61) | 0.73 (0.66–0.79) | 1.65 (1.28–2.12) | 0.31 (0.19–0.50) |
| at 12 months | 0.781 (0.709–0.853) | <52.5 | 0.78 (0.70–0.85) | 0.69 (0.56–0.8) | 0.75 (0.68–0.81) | 2.54 (1.73–3.74) | 0.32 (0.22–0.46) |
| Proportion of calorie at 12 months | |||||||
| Carbohydrate (%) | 0.714 (0.637–0.792) | <49.0 | 0.85 (0.78–0.91) | 0.60 (0.46–0.72) | 0.77 (0.7–0.83) | 2.11 (1.54–2.88) | 0.25 (0.16–0.40) |
| Protein (%) | 0.609 (0.523–0.695) | >24.5 | 0.52 (0.40–0.64) | 0.74 (0.65–0.81) | 0.65 (0.58–0.72) | 1.98 (1.36–2.88) | 0.65 (0.50–0.84) |
| Fat (%) | 0.855 (0.792–0.917) | <28.0 | 0.73 (0.65–0.81) | 0.60 (0.46–0.72) | 0.69 (0.62–0.75) | 1.82 (1.32–2.50) | 0.45 (0.32–0.64) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, H.-S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Yoon, S.-J.; Lee, B. Establishment of Adequate Nutrient Intake Criteria to Achieve Target Weight Loss in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061774
Lim H-S, Kim YJ, Lee J, Yoon S-J, Lee B. Establishment of Adequate Nutrient Intake Criteria to Achieve Target Weight Loss in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients. 2020; 12(6):1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061774
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Hee-Sook, Yong Jin Kim, Jihyun Lee, Su-Jin Yoon, and Bora Lee. 2020. "Establishment of Adequate Nutrient Intake Criteria to Achieve Target Weight Loss in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery" Nutrients 12, no. 6: 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061774
APA StyleLim, H.-S., Kim, Y. J., Lee, J., Yoon, S.-J., & Lee, B. (2020). Establishment of Adequate Nutrient Intake Criteria to Achieve Target Weight Loss in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients, 12(6), 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061774





