High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
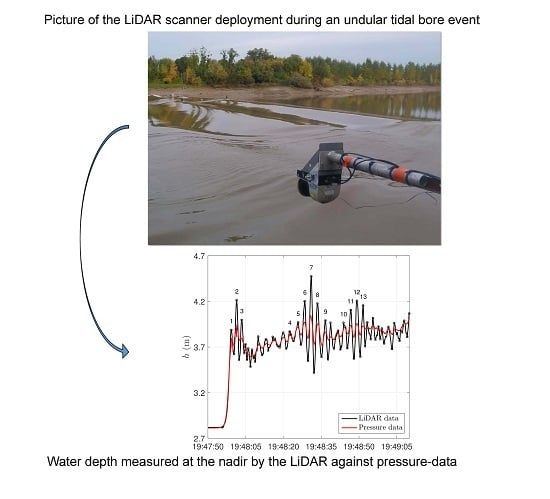
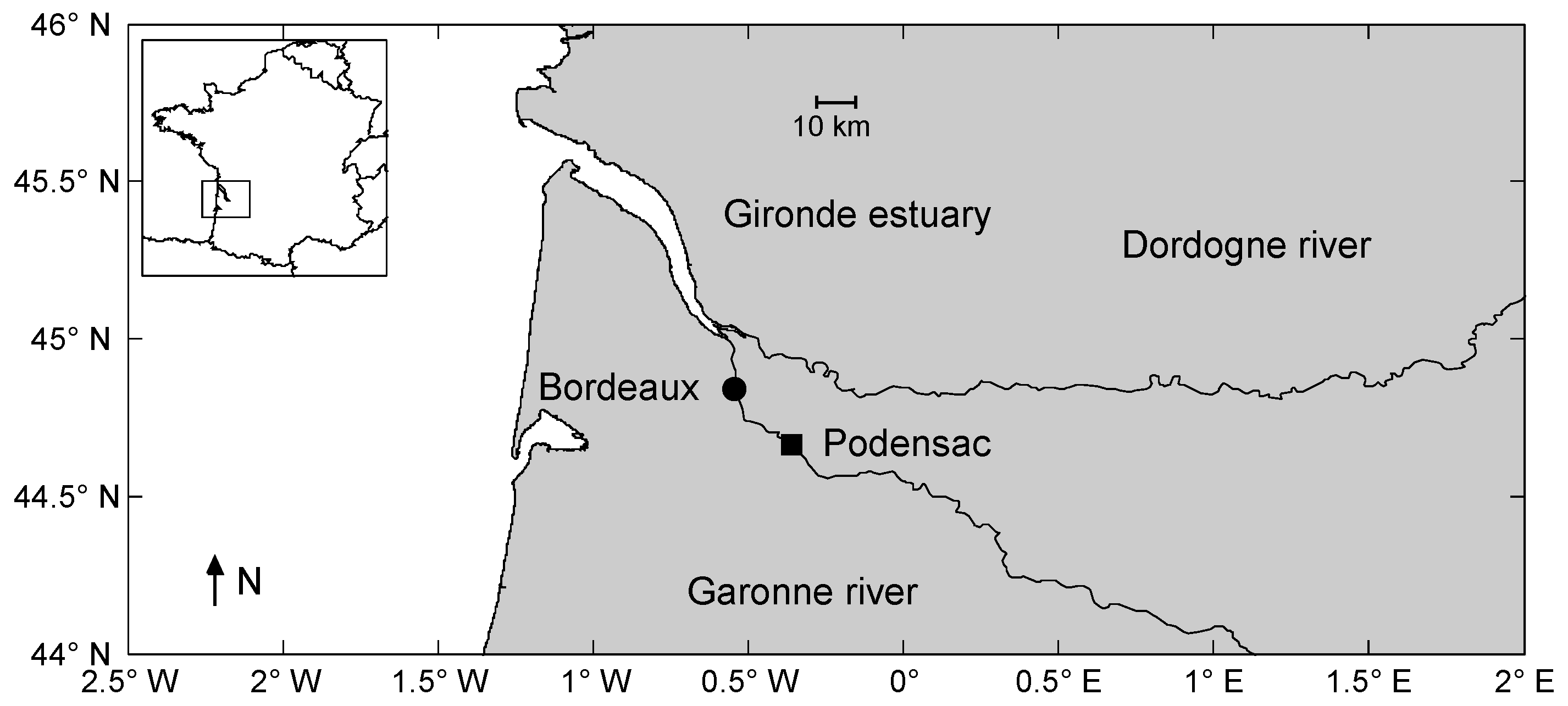
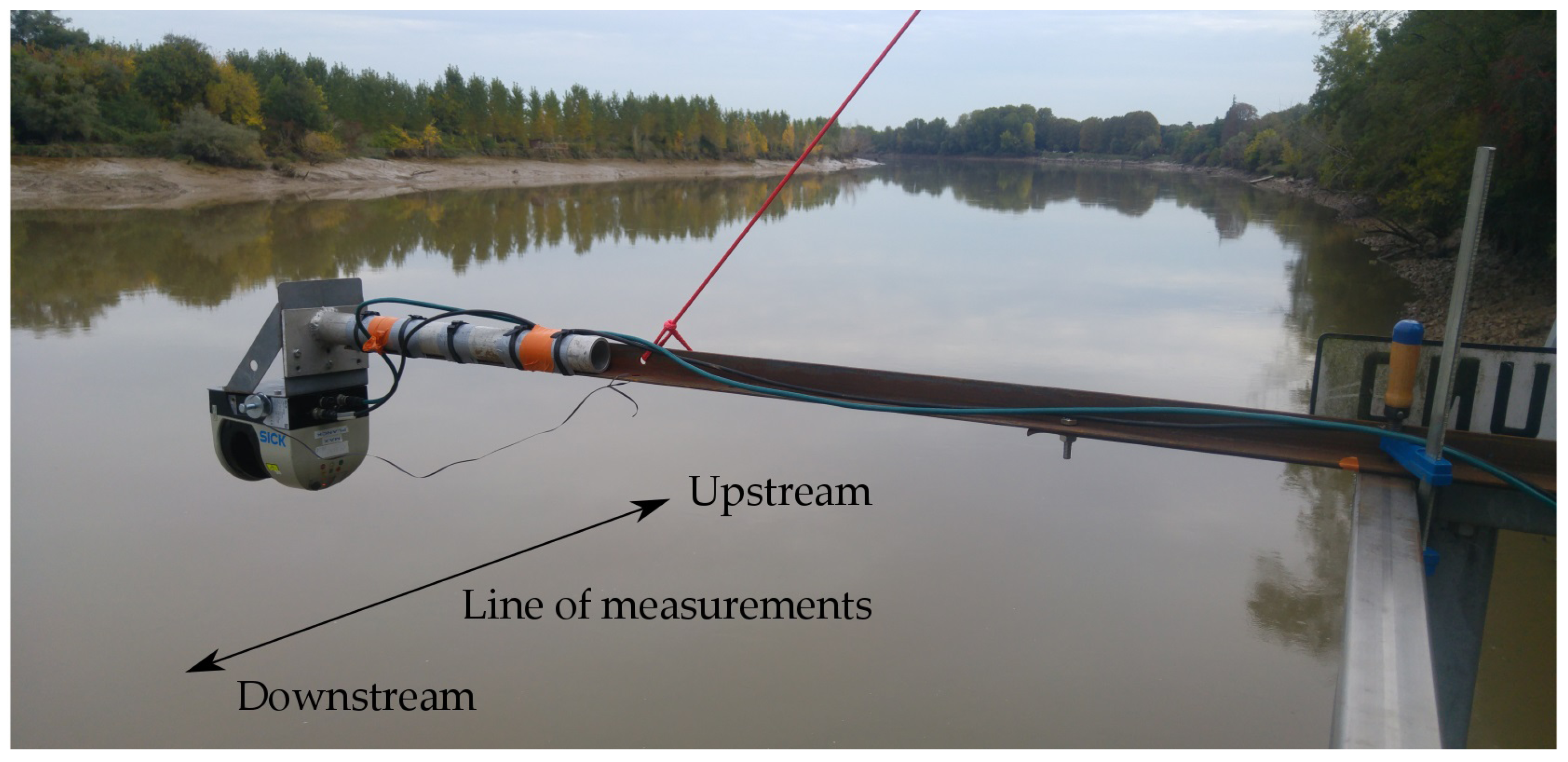
2.1. Field Experiments Description
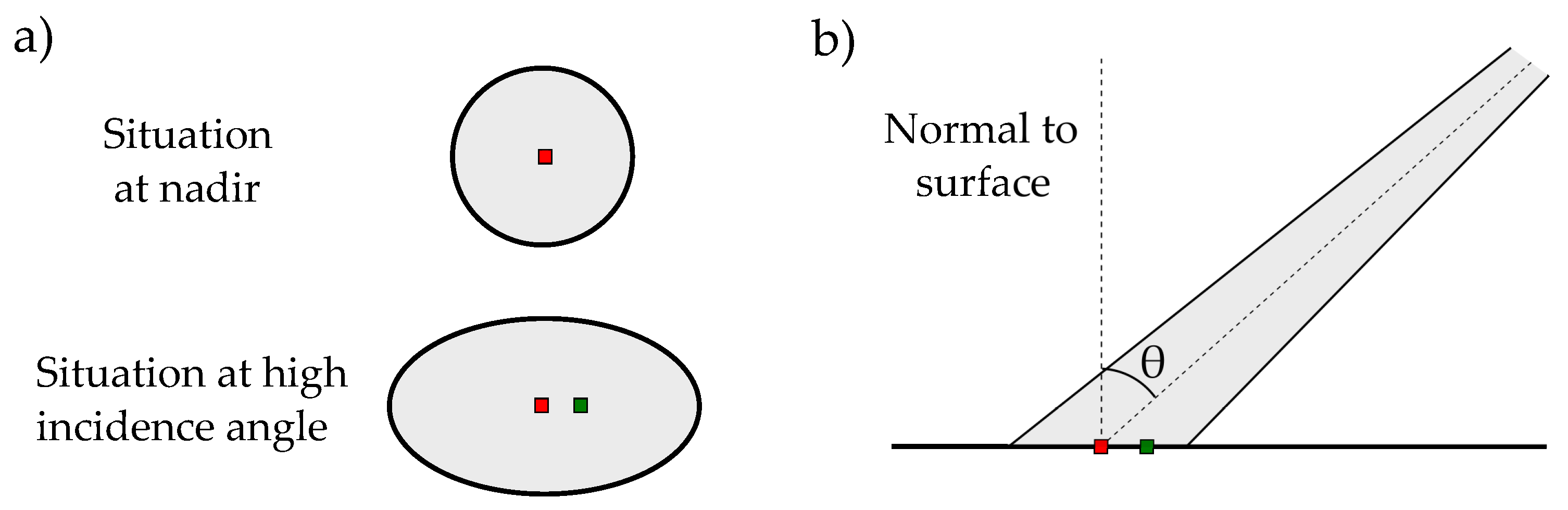
2.2. Processing of the LiDAR Data
3. Results
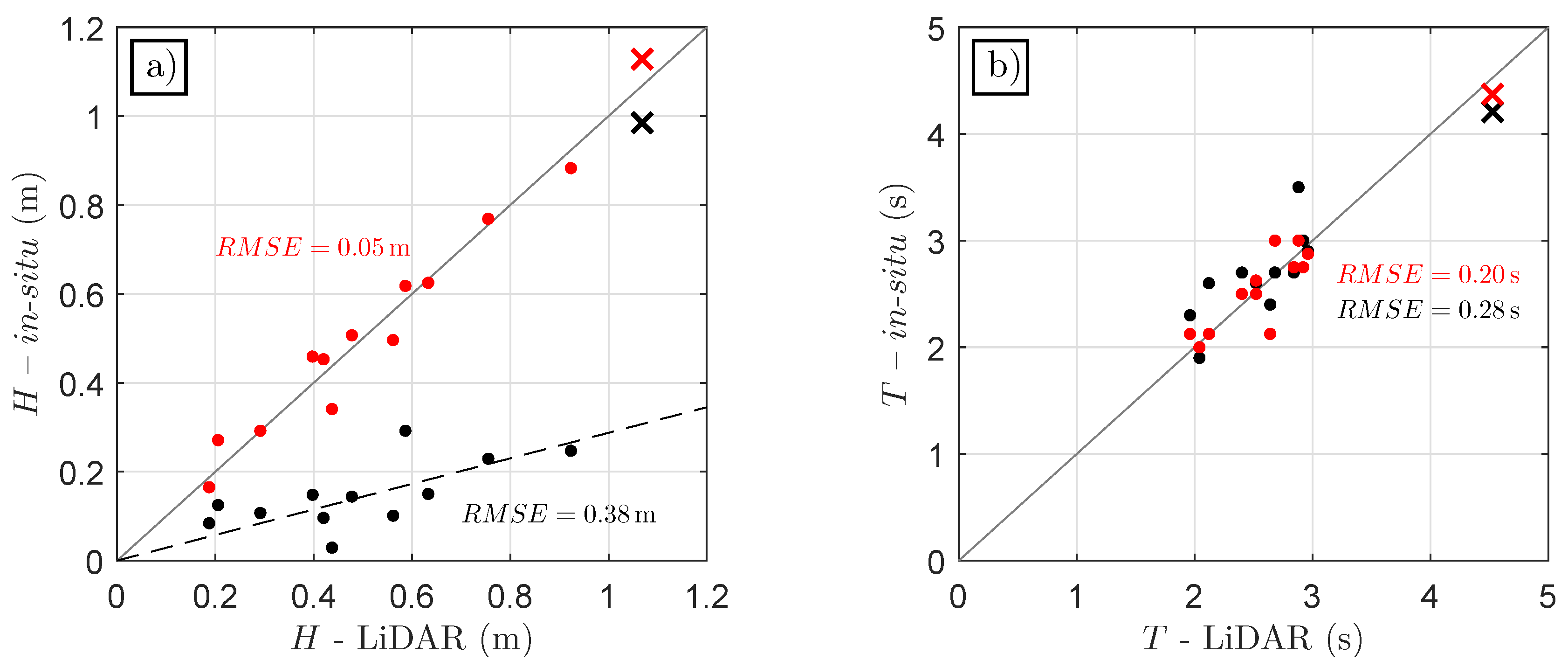
3.1. Comparison with In Situ Sensors
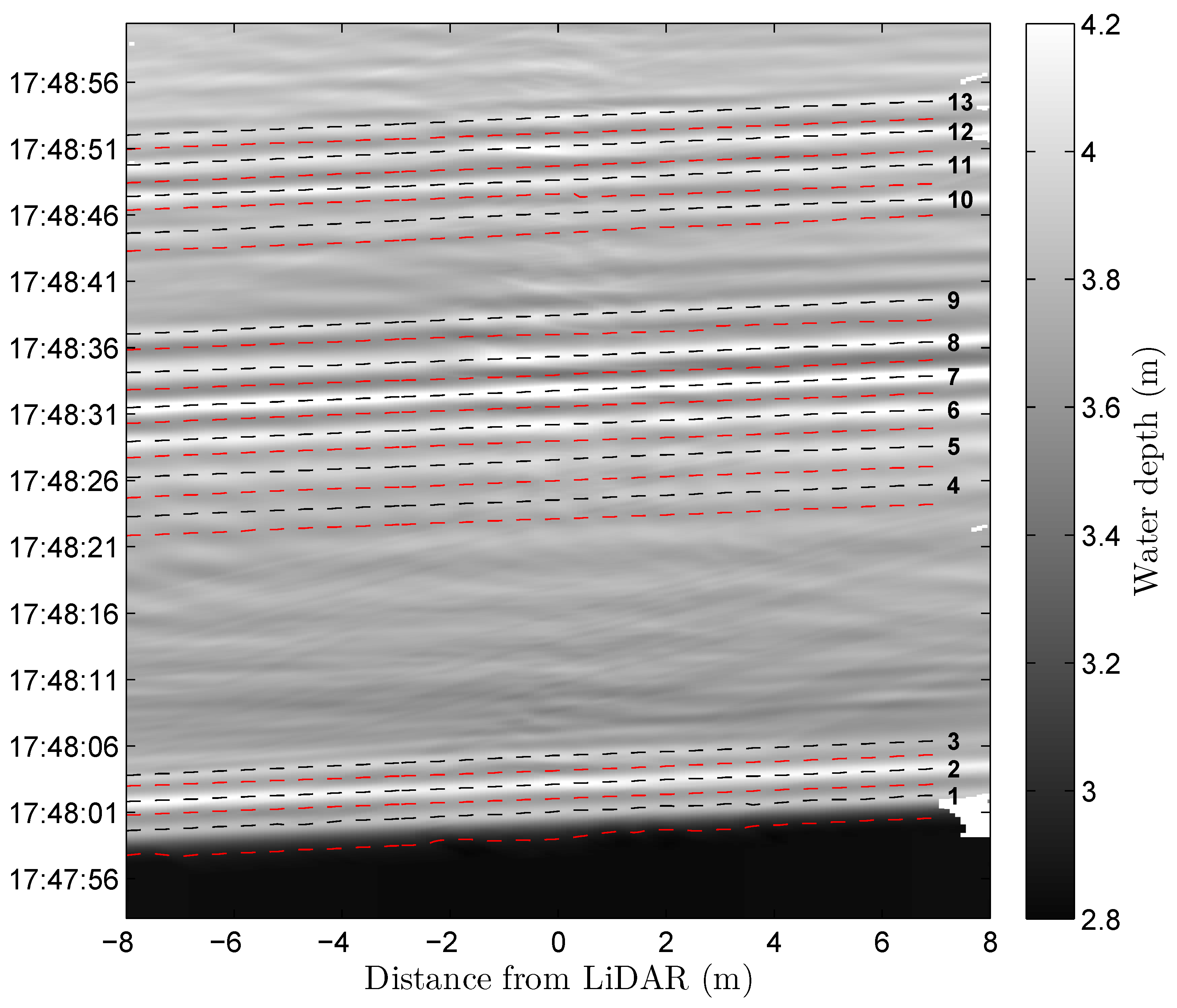
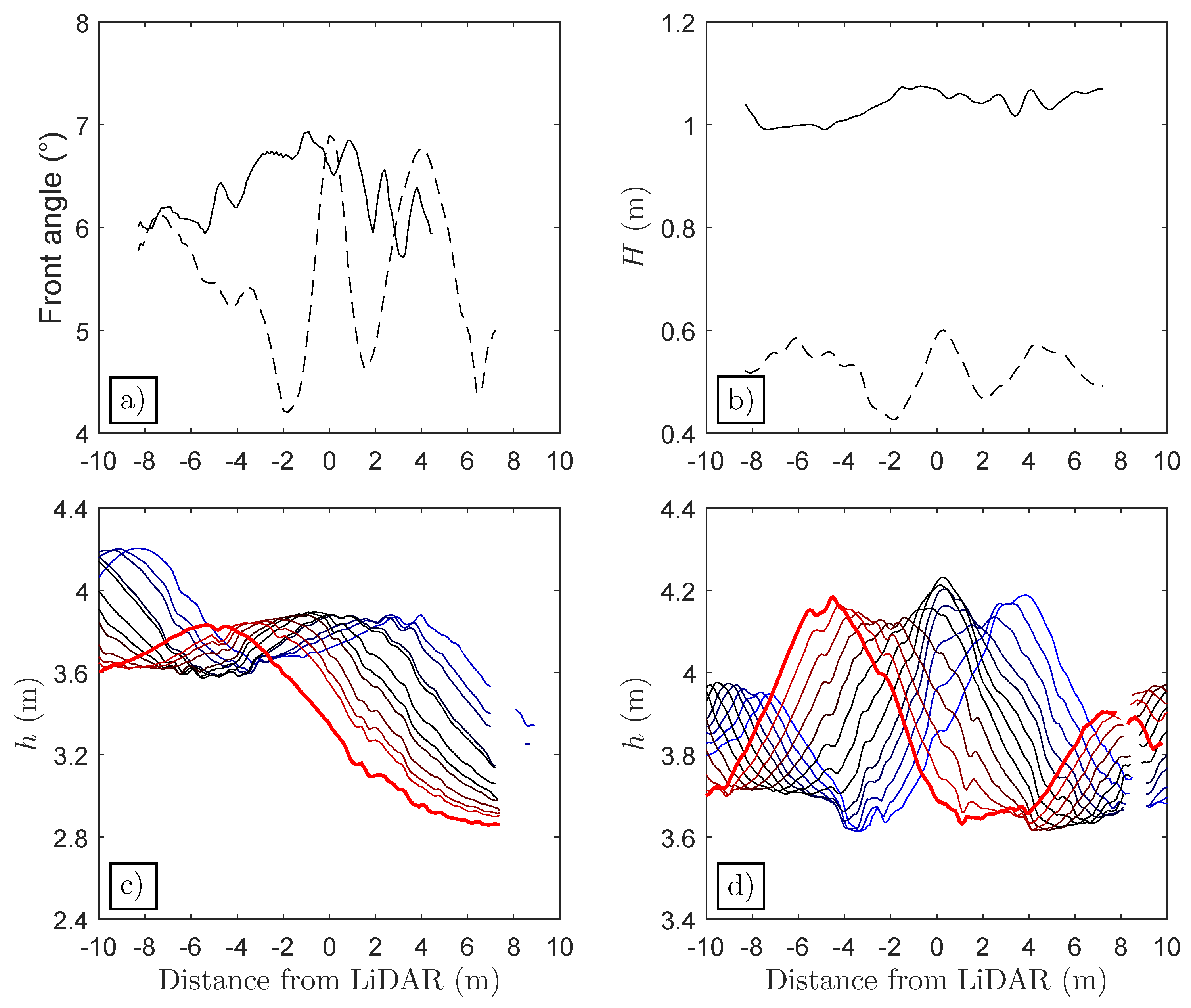
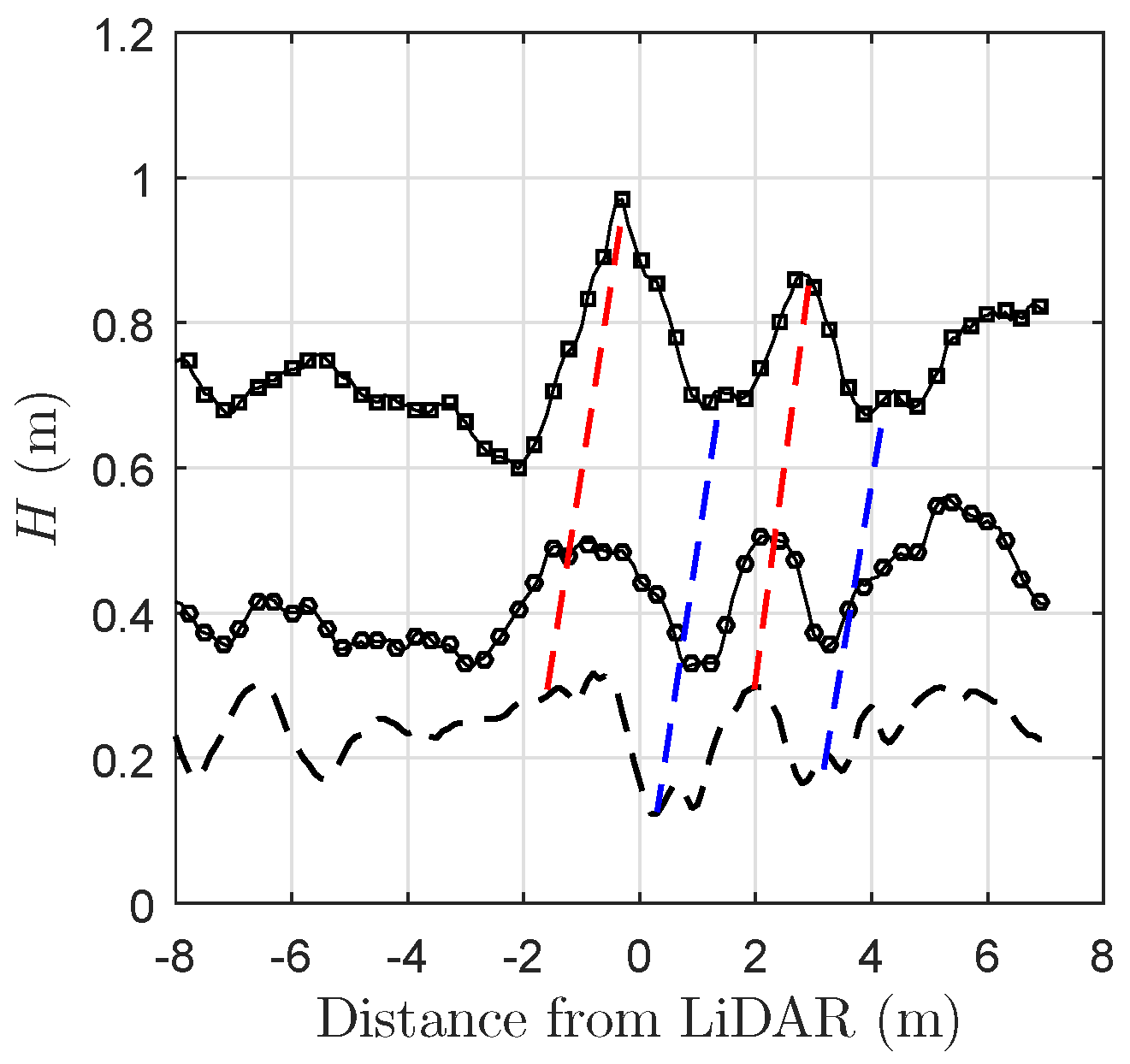
3.2. Spatial Structure of the Tidal Bore
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
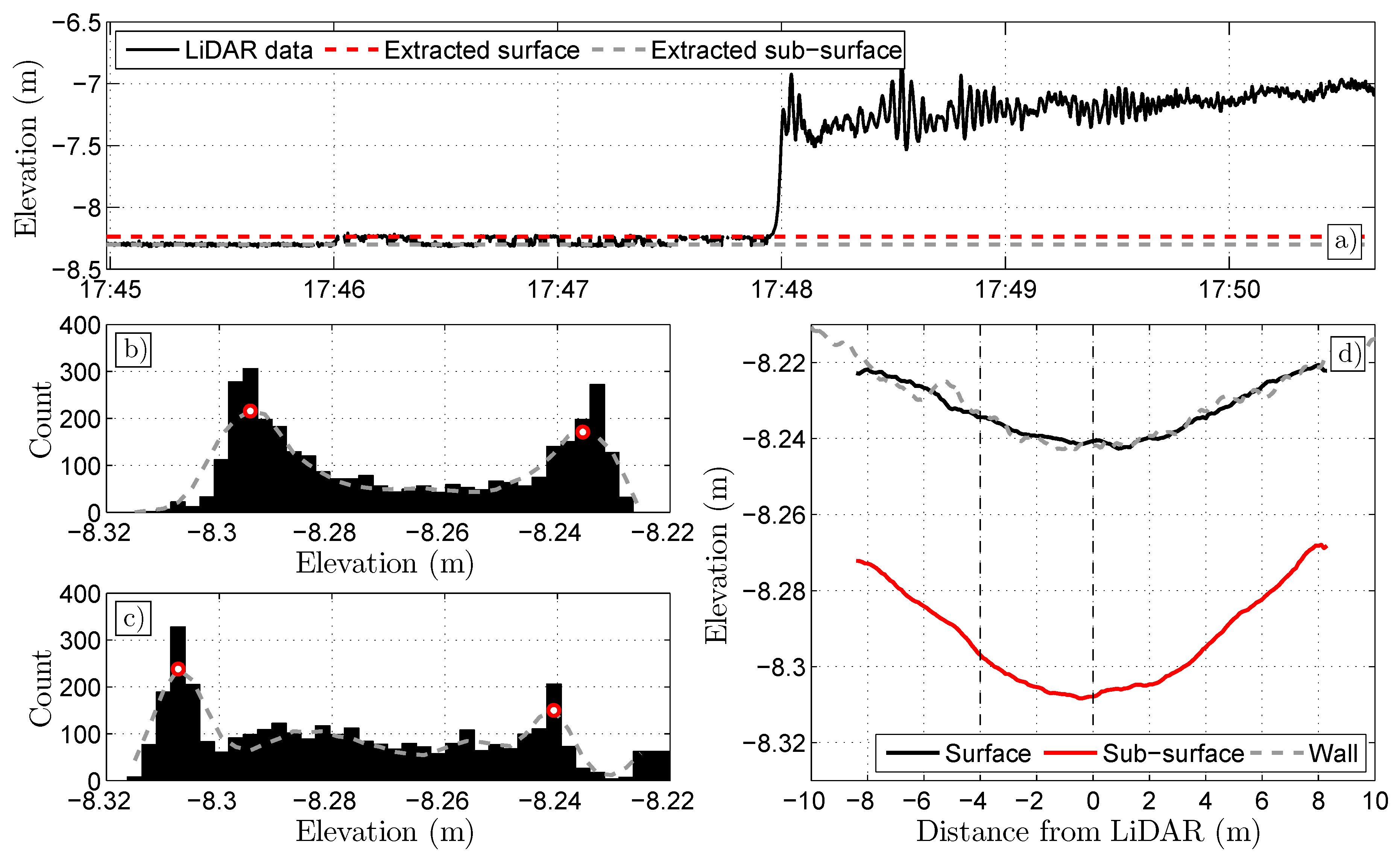
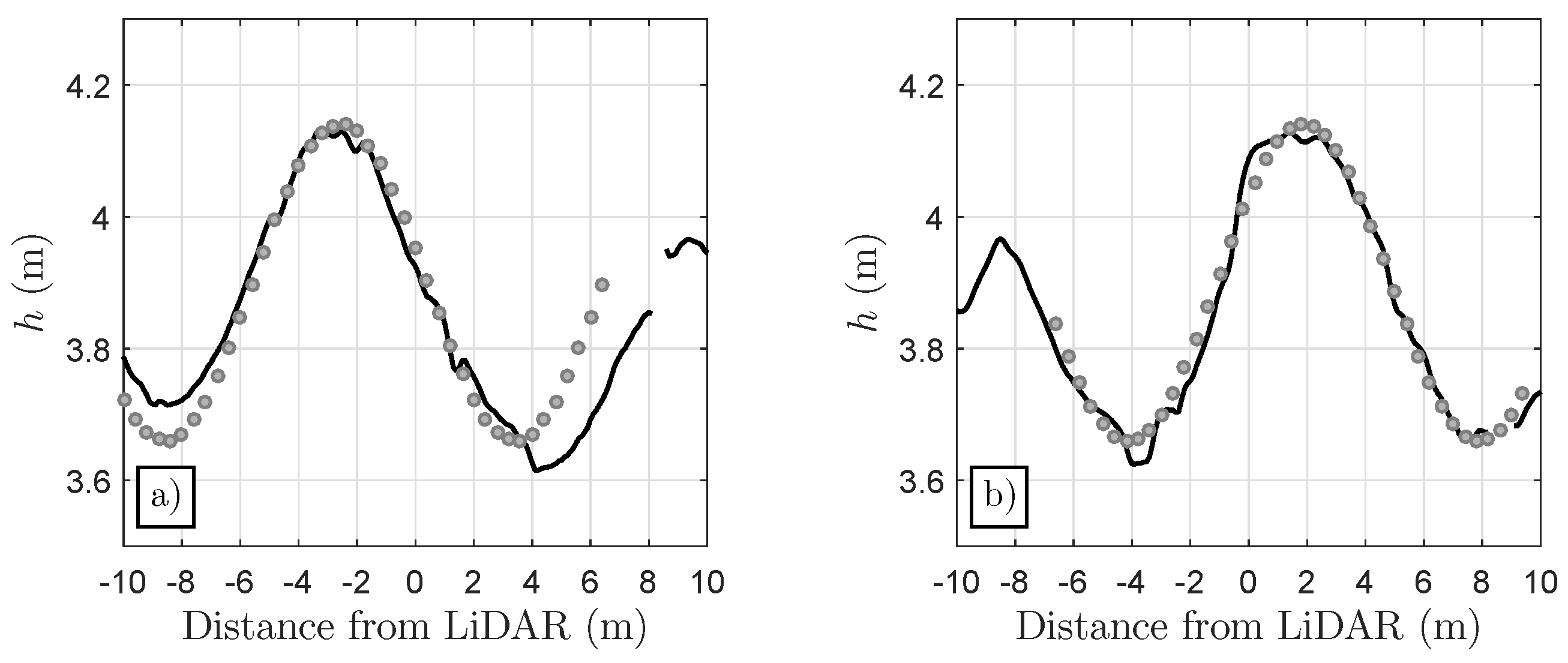
Appendix A. Accurate Detection of Steady Water Surface with a 2D LiDAR Scanner
References
- Bonneton, P.; Filippini, A.G.; Arpaia, L.; Bonneton, N.; Ricchiuto, M. Conditions for tidal bore formation in convergent alluvial estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 172, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, P.A.; Fuhrman, D.R.; Schäffer, H.A. On the solitary wave paradigm for tsunamis. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissier, M.; Bonneton, P.; Marche, F.; Chazel, F.; Lannes, D. Nearshore dynamics of tsunami-like undular bores using a fully nonlinear Boussinesq model. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 603. [Google Scholar]
- Vignoli, G.; Toffolon, M.; Tubino, M. Non-linear frictional residual effects on tide propagation. In Proceedings of the XXX IAHR Congress, Thessaloniki, Greece, 1–31 August 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bonneton, P.; Bonneton, N.; Parisot, J.-P.; Castelle, B. Tidal bore dynamics in funnel-shaped estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Roussel, N.; Darrozes, J.; Bonneton, P.; Bonneton, N.; Detandt, G.; Perosanz, F.; Loyer, S. High rate GNSS measurements for detecting non-hydrostatic surface wave. Application to tidal bore in the Garonne River. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Mole, M.A.; Turner, I.L.; Peirson, W.L. Measurements of the time-varying free-surface profile across the swash zone obtained using an industrial (LIDAR). Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, K.L.; Raubenheimer, B.; Elgar, S.; Slocum, R.K.; McNinch, J.E. Lidar and Pressure Measurements of Inner-Surfzone Waves and Setup. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 32, 1945–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.; Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Zang, J. Monitoring Individual Wave Characteristics in the Inner Surf with a 2-Dimensional Laser Scanner (LiDAR). J. Sens. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamari, S.; Guerrero-Meza, V. Flash Flood Monitoring with an Inclined Lidar Installed at a River Bank: Proof of Concept. Remote Sens. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamari, S.; Guerrero-Meza, V.; Rifad, Y.; Bravo-Inclán, L.; Sánchez-Chávez, J.J. Stage Monitoring in Turbid Reservoirs with an Inclined Terrestrial Near-Infrared Lidar. Remote Sens. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.; Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Almar, R.; Zang, J. The influence of swash-based reflection on surf zone hydrodynamics: A wave-by-wave approach. Coast. Eng. 2017, 122, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, M.; Hofland, B.; Lindenbergh, R.C. Laser Ranging For Monitoring Water Waves in the New Deltares Delta Flume. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 2, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, B.; Furgerot, L.; Mouazé, D. Sedimentary signatures of tidal bores: A brief synthesis. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneton, P.; Parisot, J.-P.; Bonneton, N.; Sottolichio, A.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; Pochon, N.; van de Loock, J. Large Amplitude Undular Tidal Bore Propagation in the Garonne River, France. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First (2011) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 19–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Damiani, L.; Valentini, N. Terrestrial Laser Scanner as a measurement instrument for laboratory water waves. In SCORE@ POLIBA 2014; Cangemi Editore SPA: Roma, Italy, 2014; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.T.; Donelan, M.A. Measuring waves with pressure transducers. Coast. Eng. 1987, 11, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H. Undular Tidal Bores: Basic Theory and Free-Surface Characteristics. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 136, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kerkering, H.; Weisberg, R.H. Coastal Ocean Observing Systems; Elsevier (Academic Press): London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soudarissanane, S.; Lindenbergh, R.; Menenti, M.; Teunissen, P. Incidence angle influence on the quality of terrestrial laser scanning points. In Laser Scanning 2009; Bretar, F., Pierrot-Deseilligny, M., Vosselman, G., Eds.; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Paris, France, 2009; Volume XXXVIII, pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar]



| Properties | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m/s) | 5.62 | 6.07 | 5.84 | 6.27 | 6.22 | 6.17 | 6.18 | 6.37 | 5.76 | 5.75 | 6.11 | 5.76 | 5.74 |
| (m/s) | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.82 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.19 |
| (m) | 1.04 | 0.52 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.74 | 0.62 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 0.36 |
| (m) | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| (s) | 2.90 | 2.15 | 2.51 | 2.86 | 2.96 | 2.61 | 2.43 | 3.06 | 2.39 | 2.80 | 2.25 | 2.47 | 2.08 |
| (s) | 0.24 | 0.03 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| (°) | 6.37 | 5.54 | 2.85 | 1.21 | 1.51 | 3.39 | 7.57 | 5.80 | 3.83 | 2.01 | 4.01 | 3.73 | 3.66 |
| (°) | 0.35 | 0.75 | 1.41 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.92 | 1.37 | 1.93 | 1.37 | 1.93 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 1.01 |
| (m) | - | 12.3 | 17.9 | 16.6 | 16.8 | 15.3 | 14.2 | 17.4 | 13.1 | 15.4 | 16.5 | 12.8 | 10.8 |
| (m) | - | 0.78 | 0.83 | 1.20 | 0.88 | 1.27 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 1.68 | 0.04 | 1.53 | 0.38 | 0.58 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, K.; Bonneton, P.; Frappart, F.; Detandt, G.; Bonneton, N.; Blenkinsopp, C.E. High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050462
Martins K, Bonneton P, Frappart F, Detandt G, Bonneton N, Blenkinsopp CE. High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(5):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050462
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Kévin, Philippe Bonneton, Frédéric Frappart, Guillaume Detandt, Natalie Bonneton, and Chris E. Blenkinsopp. 2017. "High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner" Remote Sensing 9, no. 5: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050462
APA StyleMartins, K., Bonneton, P., Frappart, F., Detandt, G., Bonneton, N., & Blenkinsopp, C. E. (2017). High Frequency Field Measurements of an Undular Bore Using a 2D LiDAR Scanner. Remote Sensing, 9(5), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050462