Desertification Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression Analysis in the Djelfa Area, Algeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Methodology
3.1. Methods
3.2. Causal Factors and Desertification
3.2.1. Soil Factors
3.2.2. Geomorphological Factors
3.2.3. Environmental Factors
3.2.4. Socioeconomic Factors
3.2.5. The Desertification Inventory Response Factor
3.3. Input Database for Logistic Regression Analysis
3.4. Variables Selection and Model Development
3.5. Model Prediction and Uncertainties
4. Results
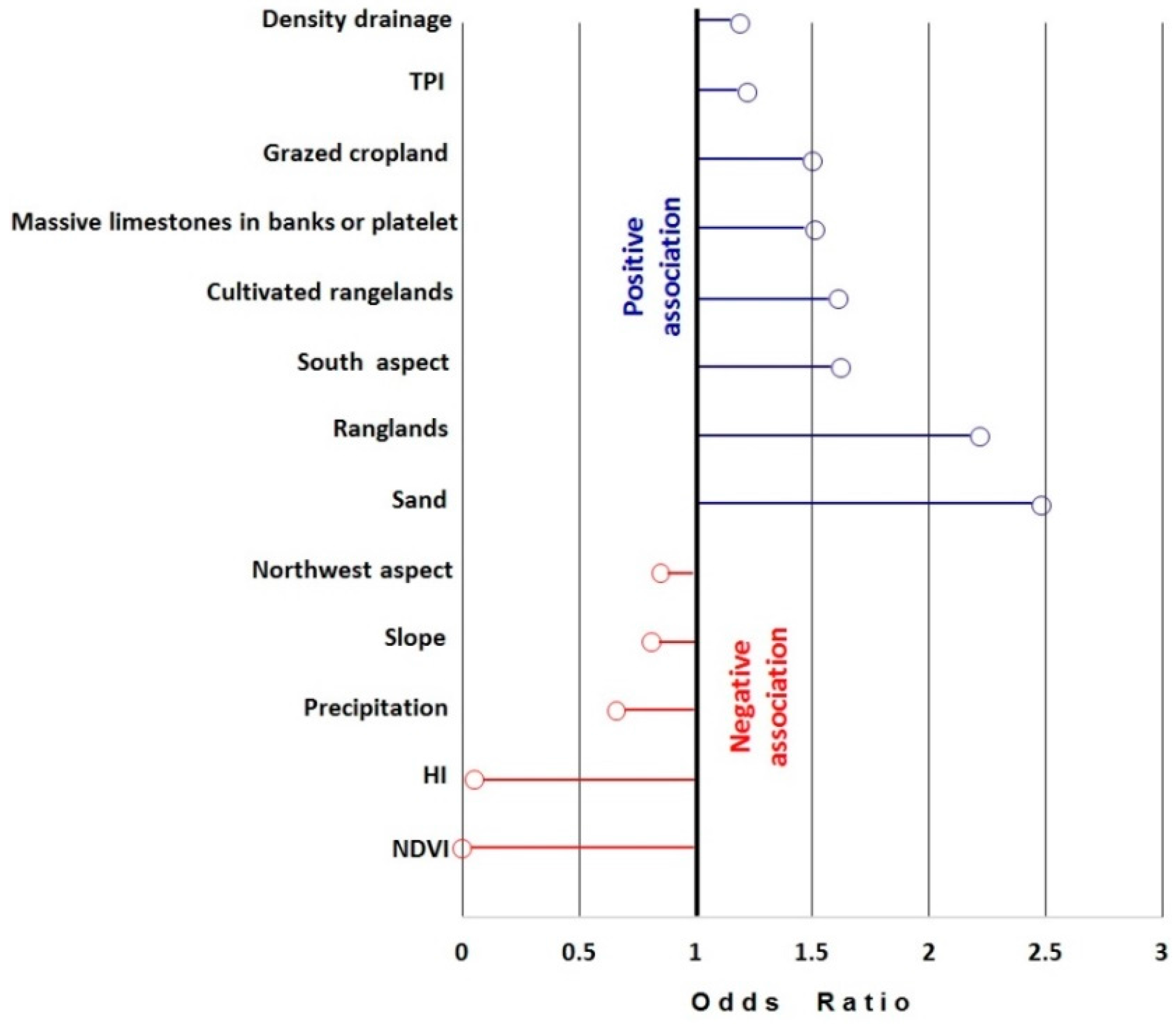
4.1. Evaluation of Predictive Factors
4.2. Selected Variables and Desertification Probability
5. Discussion
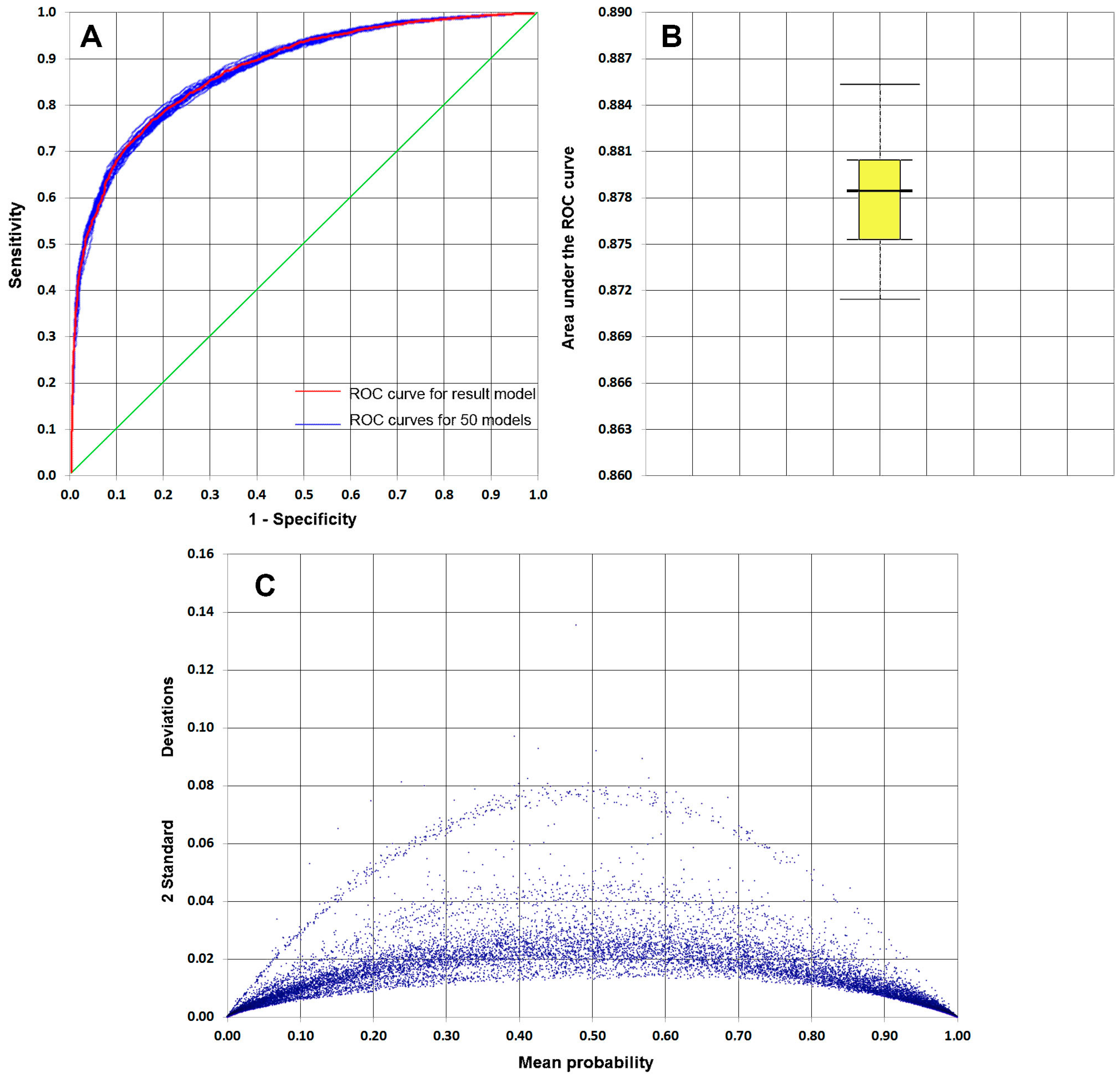
5.1. Model Validation
5.2. Key Factors and Desertification Occurrence
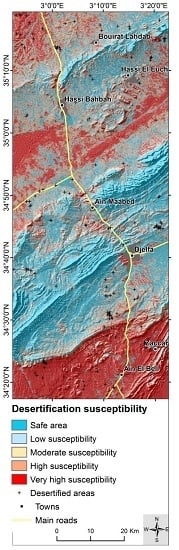
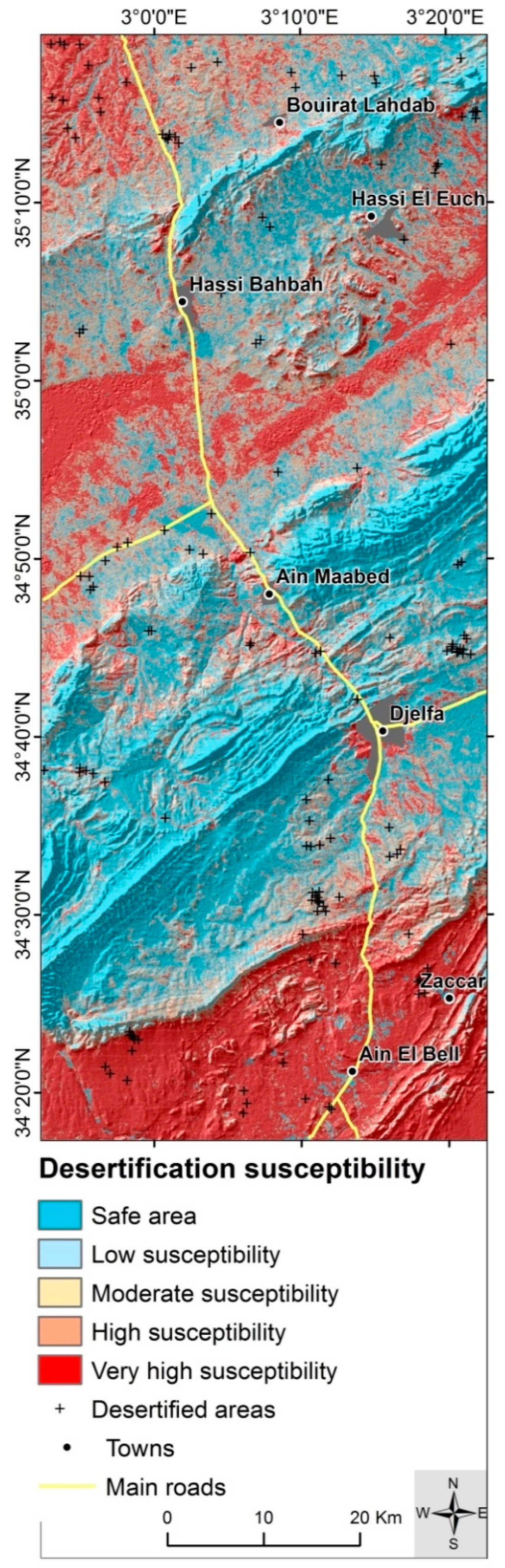
5.3. Desertification Susceptibility Map
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albalawi, E.K.; Kumar, L. Using remote sensing technology to detect, model and map desertification: A review. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2013, 11, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. World Development Report 2003: Sustainable Development in a Dynamic World Transforming Institutions, Growth and Quality of Life; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hadeel, A.S.; Jabbar, M.T.; Chen, X. Application of remote sensing and GIS in the study of environmental sensitivity to desertification: A case study in Basrah Province, southern part of Iraq. Appl. Geomat. 2010, 2, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscarelli, R.; Minervino, I.; Sorriso-Valvo, M. Methods for the characterization of areas sensitive to desertification: An application to the Calabrian territory (Italy). In Geomorphological Processes and Human Impacts in River Basins; Batalla, R.J., García, C., Eds.; IAHS Publication: Catalonia, Spain, 2005; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- De Pina Tavares, J.; Baptista, I.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Amiotte-Suchet, P.; Coelho, C.; Gomes, S.; Amoros, R.; Dos Reis, E.A.; Mendes, A.F.; Costa, L.; et al. Assessment and mapping the sensitive areas to desertification in an insular Sahelian mountain region Case study of the Ribeira Seca Watershed, Santiago Island, Cabo Verde. Catena 2015, 128, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadeid, M. Approche anthropique du phénomène de désertification dans un espace steppique: Le cas des hautes plaines occidentales algériennes. VertigO 2008, 8. Available online: https://vertigo.revues.org/5368 (accessed on 1 May 2016). [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z. Determination and Analysis of Desertification Process with Satellite Data Alsat-1 and Landsat in the Algerian Steppe. Eng. Geol. Soc. Territ. 2015, 2, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Benabderrahmane, M.C.; Chenchouni, H. Assessing environmental sensitivity areas to desertification in Eastern Algeria using Mediterranean desertification and land use “MEDALUS” model. Int. J. Sustain. Water Environ. Syst. 2010, 1, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, M.; Mederbal, K.; Chouieb, M. Suivi de la dégradation de la végetation steppique a l’aide de la Télédétection: Cas des parcours steppiques région de Djelfa (Algérie). Courrier du Savoir 2014, 18, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Dalila, N.; Slimane, B. La désertification dans les steppes algériennes: Causes, impacts et actions de lutte. VertigO 2008, 8. Available online: http://vertigo.revues.org/5375 (accessed on 1 May 2016). [CrossRef]
- Oussedik, A.; Iftene, T.; Zegrar, A. Réalisation par télédétection de la carte d ‘Algérie de sensibilité à la désertification. Sécheresse 2003, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Benslimane, M.; Hamimed, A.; El Zerey, W.; Khaldi, A.; Mederbal, K. Analyse et suivi du phénomène de la désertification en Algérie du nord. VertigO 2008, 8. Available online: https://vertigo.revues.org/6782 (accessed on 1 May 2016). [CrossRef]
- Salamani, M.; Kadi Hanafi, H.; Hirche, A.; Nedjraoui, D. Évaluation de la sensibililé à la désertification en Algérie. Revue d Ecologie 2013, 68, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- BNEDER. Identification et Cartographie des Zones Potentielles à l’Agriculture en Steppe (Rapport Provisoire); Bureau National d’Etude pour le Développement Rural: Alger, Algérie, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Centre des Techniques Spatiales (CTS). Finalisation de la carte nationale de sensibilité à la désertification par l’outil spatial. Spat. Data Infrastruct. Afr. Newsl. 2010, 9, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Collado, A.D.; Chuvieco, E.; Camarasa, A. Satellite remote sensing analysis to monitor desertification processes in the crop-rangeland boundary of Argentina. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 52, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiry, M.A. Spectral Mixture Analysis for Monitoring and Mapping Desertification Processes in Semi-arid Areas in North Kordofan State, Sudan. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Dawson, R.; Li, H.; Li, B. Modeling desertification change in Minqin County, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 108, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannenbecker, A. Identification of desertification indicators using bi-temporal change detection. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop of the EARSeL SIG on Remote Sensing of Land Use & Land Cover “Application and Development”, Bonn, Germany, 28–30 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Bai, Z.; Wei, S.; Yanfen, H.; Zongming, W.; Kaishan, S.; Dianwei, L.; Zhiming, L. Sandy desertification change and its driving forces in western Jilin Province, North China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harbi, K.M. Monitoring of agricultural area trend in Tabuk region—Saudi Arabia using Landsat TM and SPOT data. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2010, 13, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Tateishi, R. Remote sensing and GIS for mapping and monitoring land cover and land-use changes in the Northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Dutta, D. Monitoring desertification risk through climate change and human interference using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2010, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yanli, Y.; Jabbar, M.T.; Zhou, J. Study of Environmental Change Detection Using Remote Sensing and GIS Application: A Case Study of Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 783–790. [Google Scholar]
- Shafie, H.; Hosseini, S.M.; Amiri, I. RS-based assessment of vegetation cover changes in Sistan Plain. Int. J. For. Soil Eros. 2012, 2, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Jianya, G.; Haigang, S.; Guorui, M.; Qiming, Z. A Review of Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data Change Detection. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmas, C.; Kirkby, M.J.; Geeson, N. Medalus Project: Mediterranean Desertification and Land Use: Manual on Key Indicators of Desertification and Mapping Environmentally Sensitive Areas; EUR 18882; European Commission, Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development: Brussels, Belgium, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kairis, O.; Kosmas, C.; Karavitis, C.; Ritsema, C.; Salvati, L.; Acikalin, S.; Alcalá, M.; Alfama, P.; Atlhopheng, J.; Barrera, J.; et al. Evaluation and Selection of Indicators for Land Degradation and Desertification Monitoring: Types of Degradation, Causes, and Implications for Management. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, S. Logistic Regression: From Introductory to Advanced Concepts and Applications, 1st ed.; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, R.H.; Abuelgasim, A.; Latifovic, R. A method for detecting large-scale forest cover change using coarse spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, S.; Boudewyn, P.; Alfaro, R. Spatial prediction of the onset of spruce budworm defoliation. For. Chron. 2004, 80, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenoff, D.J.; Sickley, T.A.; Wydeven, A.P. Predicting gray wolf landscape recolonization: Logistic regression models vs. new field data. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.; Ferrier, S. Evaluating the predictive performance of habitat models developed using logistic regression. Ecol. Model. 2000, 133, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessler, P.E.; Moore, I.D.; McKenzie, N.J.; Ryan, P.J. Soil-landscape modelling and spatial prediction of soil attributes. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pino, J.S.N.; Ruiz-Gallardo, J.-R. Modelling post-fire soil erosion hazard using ordinal logistic regression: A case study in South-eastern Spain. Geomorphology 2015, 232, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Khezri, S.; Ahmad, B.B.; Hashim, M. Landslide susceptibility mapping at central Zab basin, Iran: A comparison between analytical hierarchy process, frequency ratio and logistic regression models. Catena 2014, 115, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B. Remote sensing and GIS-based landslide hazard analysis and cross-validation using multivariate logistic regression model on three test areas in Malaysia. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 45, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.B.; Wang, J.; Lü, G.-N.; Zhou, P.-G.; Hou, S.-S.; Xu, S.-N. GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping of the Zhongxian segment in the Three Gorges area, China. Geomorphology 2010, 115, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Sambath, T. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Damrei Romel area, Cambodia using frequency ratio and logistic regression models. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, N.R.; Giardino, J.R.; McDonald, E.V.; Vitek, J.D. A comparison of logistic regression-based models of susceptibility to landslides in western Colorado, USA. Landslides 2014, 11, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brague-Bouragba, N.; Brague, A.; Dellouli, S.; Lieutier, F. Comparaison des peuplements de Coléoptères et d’Araignées en zone reboisée et en zone steppique dans une région présaharienne d’Algérie. C. R. Biol. 2007, 330, 923–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Office National de la Météorologie (ONM). Données Mensuelles de Relevés des Paramètres Climatologiques (1975–2009), Station Djelfa; ONM: Djelfa, Algeria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Merzouk, N.K. Carte des Vents de l’Algérie (Résultats Préliminaires). Revue des Energies Renouvelables 1999, 2, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Direction de Planification et de l’Aménagement du Territoire (DPAT). Monographie de la Wilaya de Djelfa; Wilaya de Djelfa: Djelfa, Algerie, 2008.
- Mathew, J.; Jha, V.K.; Rawat, G.S. Landslide susceptibility zonation mapping and its validation in part of Garhwal Lesser Himalaya, India, using binary logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic curve method. Landslides 2009, 6, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- El Sanharawi, M.; Naudet, F. Comprendre la régression logistique. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2013, 36, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, M.M.; Brink, A.B.; Scholes, R.J.; Beniston, M.; Stafford Smith, M. Climate change and desertification: Where do we stand, where should we go? Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F. Landslide characteristics and slope instability modeling using GIS, Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Geomorphology 2002, 42, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agency for Regional Planning-Algeria. Lithological Map of Djelfa Province at 1:250,000; Ministry of Regional Planning and the Environment: Algiers, Algeria, 2001.
- Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, Z. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from Landsat 8 TIRS—Comparison between Radiative Transfer Equation-Based Method, Split Window Algorithm and Single Channel Method. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9829–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghith, A. Les indicateurs radiométriques pour l ‘étude de la dynamique des écosystèmes arides (région de Zougrata, Sud-Est tunisien). Sécheresse 2003, 14, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Aixia, L.; Changyao, W.; Jing, W.; Xiaomei, S. Method for remote sensing monitoring of desertification based on MODIS and NOAA/AVHRR data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 23, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature-vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook. Available online: http://landsat.usgs.gov/documents/Landsat8DataUsersHandbook.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2015).
- Das, A. Estimation of land surface temperature and its relation to land cover land use: A case study on Bankura district, West Bengal, India. Res. Dir. 2015, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat-TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paola, F.; Ducci, D.; Giugni, M. Desertification and erosion sensitivity. A case study in southern Italy: The Tusciano River catchment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, A.; Hassanli, A.M.; Ekhtesasi, M.R.; Jamali, J.B. Quantitative Assessment of Desertification in South of Iran Using Medalus Method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.S. Spatial assessment of desertification in north Sinai using modified MEDLAUS model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4647–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Sadrafshari, S.; Fayzolahpour, M. Desertification hazard zoning in Sistan Region, Iran. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmoures, M.; Jafari, M.; Ahmadi, H.; Naghiloo, M. An Integrated Methodology for Assessment and Mapping of Land Degradation Risk in Markazi Province, Iran. Desert 2013, 18, 27–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Hasi, E.; Li, J. Desertification in China: An assessment. Earth Sci. Rev. 2008, 88, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J. Characteristics of desertification and its rehabilitation in China. J. Arid Environ. 1997, 37, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Encyclopedia of Geomorphology; Routledge Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Collection, User Guide. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/sites/default/files/public/measures/docs/NASA_SRTM_V3.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2016).
- Weiss, A.D. Topographic position and landforms analysis. In Proceedings of the Annual Esri International User Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.A.; Gloaguen, R.; Andreani, L.; Rahnama, M. Landslide susceptibility mapping in Mawat area, Kurdistan Region, NE Iraq: A comparison of different statistical models. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 3, 1789–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reu, J.; Bourgeois, J.; Bats, M.; Zwertvaegher, A.; Gelorini, V.; De Smedt, P.; Chu, W.; Antrop, M.; De Maeyer, P.; Finke, P.; et al. Application of the topographic position index to heterogeneous landscapes. Geomorphology 2013, 186, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.; Sarangi, A.; Sharma, M.C. Hypsometric Integral Estimation Methods and its Relevance on Erosion Status of North-Western Lesser Himalayan Watersheds. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 1545–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, V.; Biju, C.; Deshmukh, B. Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru River Basin of Harur Taluk, Dharmapuri Districts, Tamilnadu, India using Geomatics Technology. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2011, 2, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenau, M.R. Tectonics of the Southern Andean Intra-arc Zone (38°–42°S). Ph.D. Thesis, Freie Universität, Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Strahler, A.N. Hypsometric (Area-Altitude) Analysis of Erosional Topography. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1952, 63, 1117–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, L.; Stanek, K.; Gloaguen, R.; Krentz, O.; Domínguez-González, L. DEM-Based Analysis of Interactions between Tectonics and Landscapes in the Ore Mountains and Eger Rift (East Germany and NW Czech Republic). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7971–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Bryan, R.B. The relationship of soil loss by interrill erosion to slope gradient. Catena 2000, 38, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, M.; Giourga, C. Land abandonment and slope gradient as key factors of soil erosion in Mediterranean terraced lands. Catena 2007, 69, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeson, N.A.; Brandt, C.J.; Thornes, J.B. Mediterranean Desertification: A Mosaic of Processes and Responses; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Loveland, P.J. Soil Responses to Climate Change; NATO ASI Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gallant, J.C. Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pennock, D.J.; De Jong, E. The influence of slope curvature on soil erosion and deposition in hummock terrain. Soil Sci. 1987, 144, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijitkosum, S. The impact of land use and spatial changes on desertification risk in degraded areas in Thailand. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agency of Water Resources-Algeria. Rainfall Map of Djelfa Province at 1:250,000; Ministry of Water Resources: Algiers, Algeria, 2002.
- Cai, X.; Zou, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, B. Evaluation of TRMM precipitation data over the Inland River Basins of Northwest China. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Geomatics for Integrated Water Resource Management, Lanzhou, China, 19–21 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. First results from Version 7 TRMM 3B43 precipitation product in combination with a new downscaling-calibration procedure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamchin, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, W.-K.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, M.; Lim, C.-H.; Choi, H.-A.; Kim, S.-R. Assessment of land cover change and desertification using remote sensing technology in a local region of Mongolia. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 57, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Commissariat for Steppe Development. Land Cover Map of the Steppe Area at 1:250,000; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development: Djelfa, Algeria, 2009.
- Goyal, R.K. Sensitivity of evapotranspiration to global warming: A case study of arid zone of Rajasthan (India). Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 69, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ardekani, H.; Kousari, M.R.; Esfandiari, M. Assessment and mapping of desertification sensitivity in central part of Iran. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2014, 2, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Balling, R.C. Interactions of desertification and climate in Africa. In Climate Change and Africa; Low, P.S., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- National Agency of Water Resources-Algeria. Potential Evapotranspiration Map of Djelfa Province at 1:250,000; Ministry of Water Resources: Algiers, Algeria, 2002.
- Helldén, U. A coupled human-environment model for desertification simulation and impact studies. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Schaldach, R.; Köchy, M. Modeling the impacts of grazing land management on land-use change for the Jordan River region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olehowski, C.; Naumann, S.; Fischer, D.; Siegmund, A. Geo-ecological spatial pattern analysis of the island of Fogo (Cape Verde). Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbow, C.; Mertz, O.; Diouf, A.; Rasmussen, K.; Reenberg, A. The history of environmental change and adaptation in eastern Saloum–Senegal—Driving forces and perceptions. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Bajocco, S. Land Sensitivity to Desertification Across Italy: Past, Present, and Future. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Population Division. Manuals on Methods of Estimating Population. Manual 1. Methods of Estimating Total Population for Current Dates; United Nation Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Djeddaoui, F.; Gloaguen, R.; Chadli, M. Environmental change detection in the central part of Algerian steppe. 2017; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-J.; Guo, M.; Sawada, K.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J. Landslide susceptibility mapping in Mizunami City, Japan: A comparison between logistic regression, bivariate statistical analysis and multivariate adaptive regression spline models. Catena 2015, 135, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Lü, G.; Wang, J.; Zhou, P.; Ding, L. GIS-based rare events logistic regression for landslide-susceptibility mapping of Lianyungang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.Rproject.org/ (accessed on 12 May 2016).
- Falissard, B. Analysis of Questionnaire Data with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins, J. L’analyse de régression logistique. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2005, 1, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 4th ed.; Allyn and Bacon: Needham Heights, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyer, J.; Hémon, D.; Cordier, S.; Derriennic, F.; Strücker, I.; Stengel, B.; Clavel, J. Epidémiologie: Principes et Méthodes Quantitatives; INSERM: Paris, France, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bewick, V.; Cheek, L.; Ball, J. Statistics review 14: Logistic regression. Crit. Care 2005, 9, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, W.; Hosking, P. Statistical Methods for Geographers; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Eeckhaut, M.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; Verstraeten, G.; Vandekerckhove, L. Prediction of landslide susceptibility using rare events logistic regression: A case-study in the Flemish Ardennes (Belgium). Geomorphology 2006, 76, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, K.C.; Regmi, A.D.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Yoshida, K.; Pradhan, B.; Ryu, I.C.; Dhital, M.R.; Althuwaynee, O.F. Landslide susceptibility mapping using certainty factor, index of entropy and logistic regression models in GIS and their comparison at Mugling–Narayanghat road section in Nepal Himalaya. Nat. Hazards 2013, 65, 135–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatorre, L.C.; Sánchez-Andrés, R.; Cirujano, S.; Beguería, S.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S. Identification of mangrove areas by remote sensing: The ROC curve technique applied to the northwestern Mexico coastal zone using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1568–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, A.; Haywood, A.; Stone, C.; Jones, S. The performance of random forests in an operational setting for large area sclerophyll forest classification. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2838–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Armenteras, D.; Panagos, P.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B. The implications of fire management in the andean paramo: A preliminary assessment using satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11061–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, B.; Groos, A.; Schulz, M.; Li, C.F.; Chang, S.C.; Bendix, J. Frequency of low clouds in taiwan retrieved from MODIS data and its relation to cloud forest occurrence. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12986–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begueria, S.; Lorente, A. Landslide Hazard Mapping by Multivariate Statistics: Comparison of Methods and Case Study in the Spanish Pyrenees; Technical Report; Instituto Pirenaico de Ecologia: Zaragoza, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, C.A.; Pickle, L. Evaluation of methods for classifying epidemiological data on choropleth maps in series. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2002, 92, 662–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Lv, J. Research on geographical environment unit division based on the method of natural breaks (Jenks). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-4/W3, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Ardizzone, F.; Cardinali, M.; Galli, M. Estimating the quality of landslide susceptibility models. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Mondini, A.C.; Peruccacci, S. Geomorphology Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouial, A. Etude de la dynamique de la végétation sur les dunes fixées dans la zone d’El-Mesrane (cordon-dunaire, Djelfa). Journal Algérien des Régions Arides 2003, 2, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, F.G. Engineering Geology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Motroni, A.; Canu, S.; Bianco, G.; Loj, G. Monitoring Sensitive Areas To Desertification in Sardinia: The Contribute of the Regional Agrometeorological Service. In Desertification and Risk Analysis Using High and Medium Resolution Satellite Data; Marini, A., Talbi, M., Eds.; Springer & Nato Public Diplomacy Division: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmas, C.S.; Danalatos, N.G. Climate change, desertification and the Mediterranean region. In Soil Responses to Climate Change; Rounsevell, M.D.A., Loveland, P.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1994; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- BNEDER. Étude d’Inventaire Forestier National, Wilaya de Djelfa; Bureau National d’Etude pour le Développement Rural: Alger, Algérie, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Hassen, M.; Deffontaines, B.; Turki, M.M. Recent tectonic activity of the Gafsa fault through morphometric analysis: Southern Atlas of Tunisia. Quat. Int. 2014, 338, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, K.P. Statisttics for Geoscientists Techniques and Applications, 1st ed.; Concept Publishing Company: New Delhi, India, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wen, M.; Li, T.; Lian, J.; Qin, S. Geo-hazard initiation and assessment in the Three Gorges reservoir. In Landslide Disaster Mitigation in Three Gorges Reservoir, China; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–40. [Google Scholar]
- Benderradji, M.E.; Alatou, D.; Arfa, A.M.T.; Benachour, K. Problemes de degradation de l’environnement par la desertification et la deforestation Impact du phenomene en Algerie. New Medit 2006, 5, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. liang Validation of the land-surface temperature products retrieved from terra moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidoum, A.; Nemouchi, A.; Hamlat, A. Modeling and mapping of water erosion in northeastern Algeria using a seasonal multicriteria approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 3925–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallentine, J.F. Grazing Management, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, P.; Raff, D.; Lauenroth, W. The effect of grazing on the spatial heterogeneity of vegetation. Oecologia 2001, 128, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

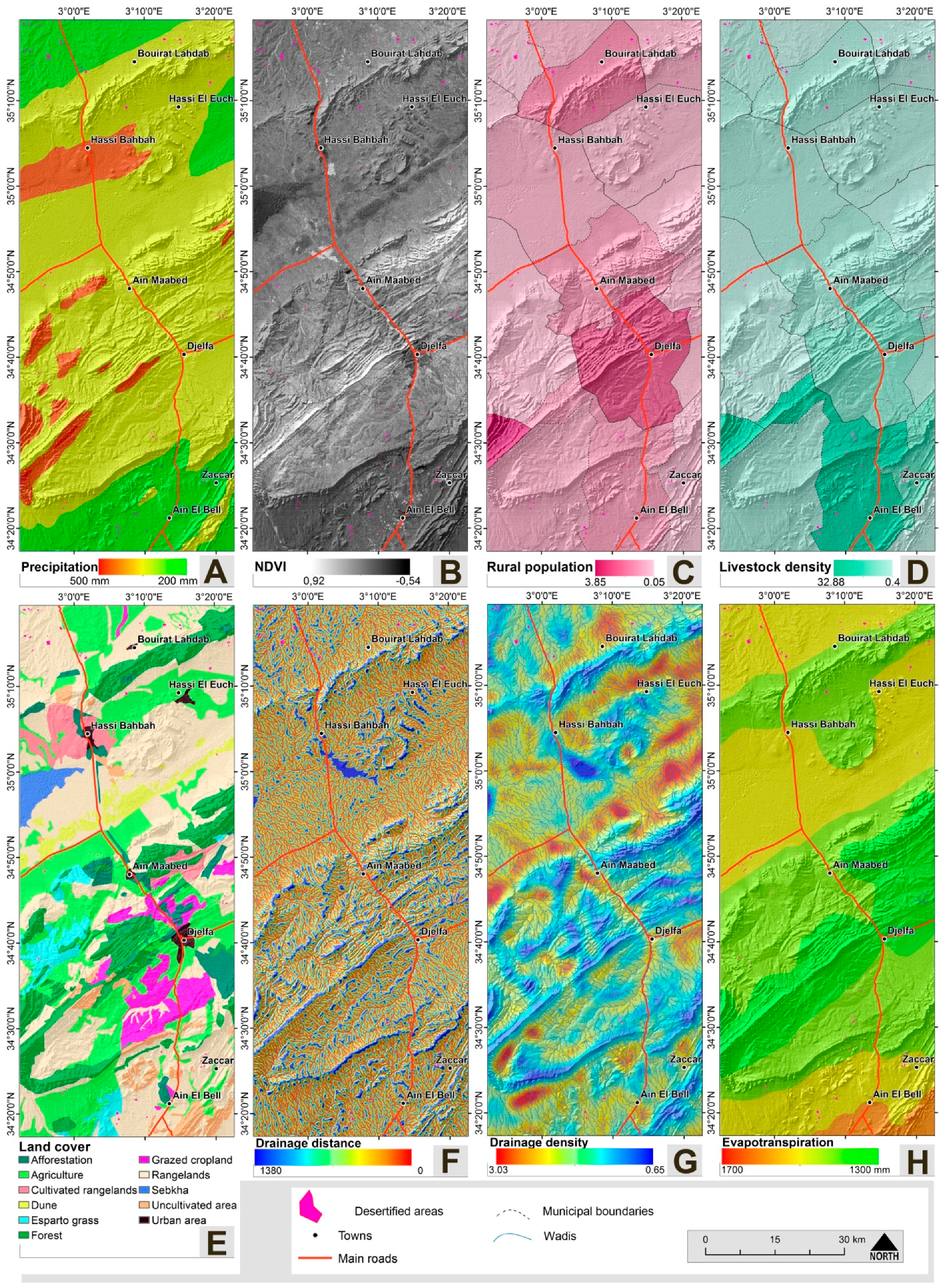
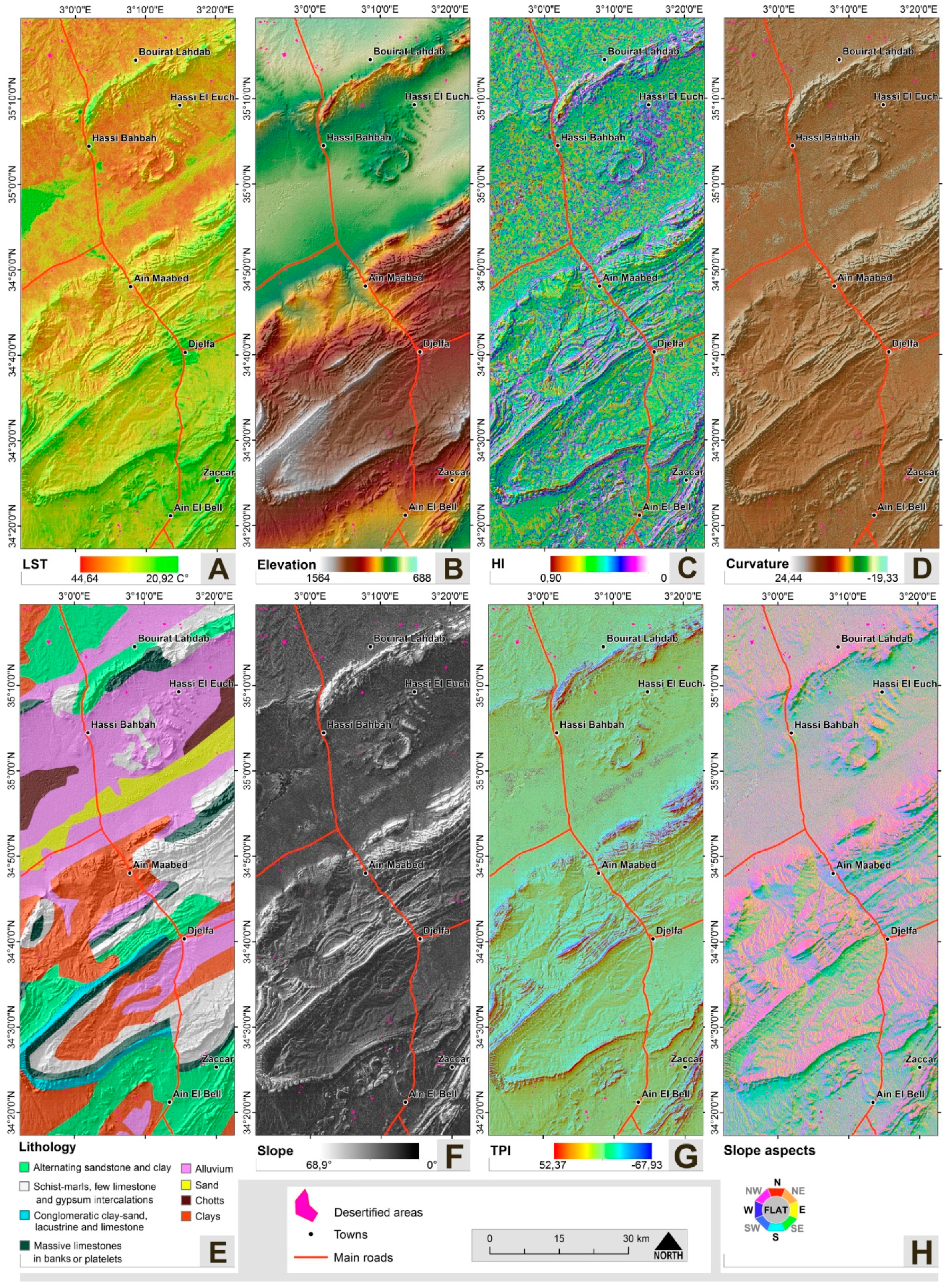
| Factor | Class | Desertified (%) | Factor | Class | Desertified (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPI | (−9.56)–0 | 46.33 | Land cover | Agriculture | 19.32 |
| 0–8.78 | 53.67 | Grazed cropland | 7.81 | ||
| HI | <0.35 | 0.00 | Cultivated rangelands | 0.59 | |
| 0.35–0.6 | 93.89 | Rangelands | 64.27 | ||
| >0.6 | 6.11 | Forest | 1.04 | ||
| Slope (◦) | <5 | 84.62 | Afforestation | 0.45 | |
| 5–10 | 14.28 | Esparto grass | 5.76 | ||
| >10 | 1.10 | Dune | 0.25 | ||
| Curvature (1/m) | <0 | 41.31 | Sebkha | 0 | |
| 0 | 13.31 | Uncultivated area | 0.14 | ||
| >0 | 45.38 | Urban area | 0.38 | ||
| Aspect (degree) | Flat | 2.90 | Distance to drainage (m) | <100 | 17.51 |
| N—(337.5–22.5) | 12.19 | 100–200 | 26.36 | ||
| S—(22.5–67.5) | 14.07 | 200–300 | 28.75 | ||
| W—(67.5–112.5) | 10.30 | 300–400 | 17.15 | ||
| E—(112.5–157.5) | 12.09 | 400–500 | 8.16 | ||
| NW—(157.5–202.5) | 12.18 | 500–600 | 1.91 | ||
| NE—(202.5–247.5) | 11.98 | >600 | 0.15 | ||
| SW—(247.5–292.5) | 10.17 | LST (°C) | <38 | 36.43 | |
| SE—(292.5–337.5) | 14.73 | >38 | 63.57 | ||
| Lithology | Alluvium | 27.46 | Rural population | <0.49 | 65.00 |
| Conglomeratic clay–sand formations, lacustrine and limestone | 2.13 | >0.49 | 35.00 | ||
| Livestock density | 0.48–2.88 | 20.56 | |||
| Clay | 31.40 | 2.89–9.94 | 60.34 | ||
| Schist-marls, few limestone and gypsum intercalations | 12.66 | 9.95–17 | 4.99 | ||
| >17 | 14.11 | ||||
| Massive limestones in banks or platelets | 2.75 | Evapotranspiration | 1300–1400 | 7.19 | |
| 1400–1500 | 25.76 | ||||
| Alternating sandstone and clay | 20.49 | 1500–1600 | 65.58 | ||
| Chotts | 0.00 | 1600–1700 | 1.47 | ||
| Sand | 3.12 | <300 | 43.92 | ||
| Elevation | 700–800 | 19.33 | Precipitation (mm) | 300–400 | 54.54 |
| 800–900 | 33.11 | 400–500 | 1.54 | ||
| 900–1000 | 7.51 | >500 | 0.00 | ||
| 1000–1100 | 11.22 | Drainage density (m km−2) | 1–2 | 55.31 | |
| 1100–1200 | 10.68 | 2–4 | 44.69 | ||
| 1200–1300 | 17.06 | NDVI | <0.22 | 96.21 | |
| >1300 | 1.09 | >0.22 | 3.79 |
| Category | Factor | VIF |
|---|---|---|
| Land Cover | Rangelands | 1.22 |
| Cultivated rangelands | 1.03 | |
| Grazed cropland | 1.23 | |
| Slope Aspect | South aspect | 1.04 |
| Northwest aspect | 1.07 | |
| Lithology | Sand | 1.09 |
| Massive limestones in banks or platelets | 1.04 | |
| Slope | 1.30 | |
| NDVI | 1.38 | |
| HI | 1.04 | |
| Precipitation | 1.35 | |
| Density drainage | 1.15 | |
| TPI | 1.19 | |
| Pseudo R2 Test | Value |
|---|---|
| Cox and Snell R2 | 0.40 |
| Nagelkerke R2 | 0.53 |
| Category | Factor | βi | Standard Error of Estimate | Wald χ2 Values | Significance (p Value) | Exp (βi) (Odds Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land cover | Rangelands | 0.800 | 0.054 | 14.805 | 0.000 | 2.22 |
| Cultivated rangelands | 0.473 | 0.238 | 1.986 | 0.047 | 1.61 | |
| Grazed cropland | 0.405 | 0.088 | 4.628 | 0.000 | 1.50 | |
| Slope aspect | South aspect | 0.481 | 0.084 | 5.663 | 0.000 | 1.62 |
| Northwest aspect | −0.166 | 0.068 | −2.462 | 0.014 | 0.85 | |
| Lithology | Sand | 0.909 | 0.138 | 6.583 | 0.000 | 2.48 |
| Massive limestones in banks or platelets | 0.412 | 0.168 | 2.448 | 0.014 | 1.51 | |
| Slope | −0.209 | 0.009 | −22.617 | 0.000 | 0.81 | |
| NDVI | −52.391 | 1.270 | −41.242 | 0.000 | ~0 | |
| HI | −2.982 | 0.373 | −8.006 | 0.000 | 0.05 | |
| Precipitation | −0.420 | 0.054 | −7.763 | 0.000 | 0.66 | |
| Density drainage | 0.176 | 0.073 | 2.416 | 0.016 | 1.19 | |
| TPI | 0.198 | 0.016 | 12.263 | 0.000 | 1.22 | |
| Susceptibility Class | Range | Number of Pixels | Area Covered (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Safe area | 0–0.14 | 1,325,603 | 23.99 |
| Low susceptibility | 0.15–0.36 | 930,010 | 16.83 |
| Moderate susceptibility | 0.37–0.60 | 807,834 | 14.62 |
| High susceptibility | 0.61–0.83 | 848,277 | 15.35 |
| Very-high susceptibility | 0.84–1 | 1,614,946 | 29.22 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Djeddaoui, F.; Chadli, M.; Gloaguen, R. Desertification Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression Analysis in the Djelfa Area, Algeria. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101031
Djeddaoui F, Chadli M, Gloaguen R. Desertification Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression Analysis in the Djelfa Area, Algeria. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(10):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101031
Chicago/Turabian StyleDjeddaoui, Farid, Mohammed Chadli, and Richard Gloaguen. 2017. "Desertification Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression Analysis in the Djelfa Area, Algeria" Remote Sensing 9, no. 10: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101031
APA StyleDjeddaoui, F., Chadli, M., & Gloaguen, R. (2017). Desertification Susceptibility Mapping Using Logistic Regression Analysis in the Djelfa Area, Algeria. Remote Sensing, 9(10), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9101031