New Automated Method to Develop Geometrically Corrected Time Series of Brightness Temperatures from Historical AVHRR LAC Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data and Software
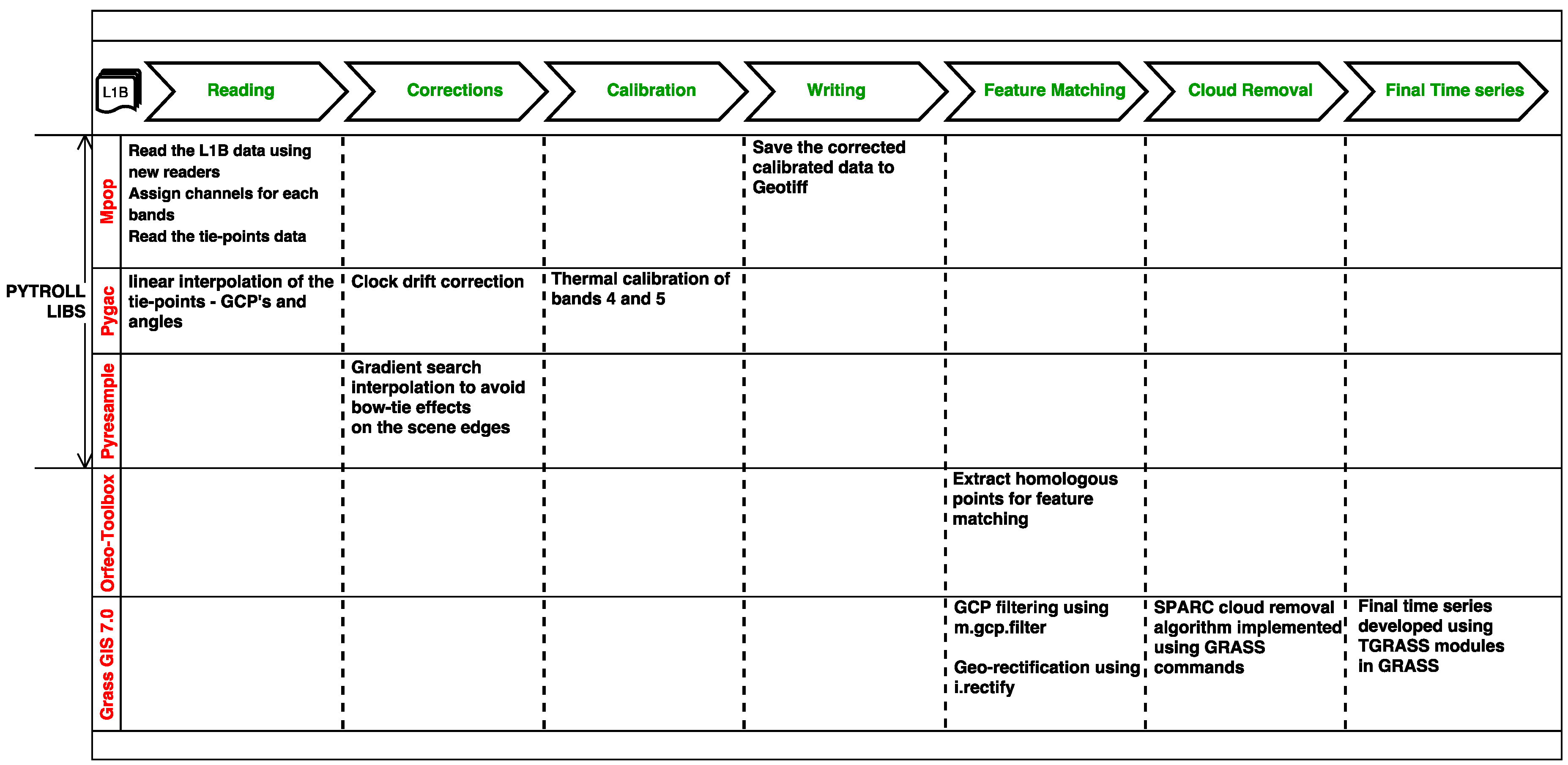
2.2. Pre-Processing
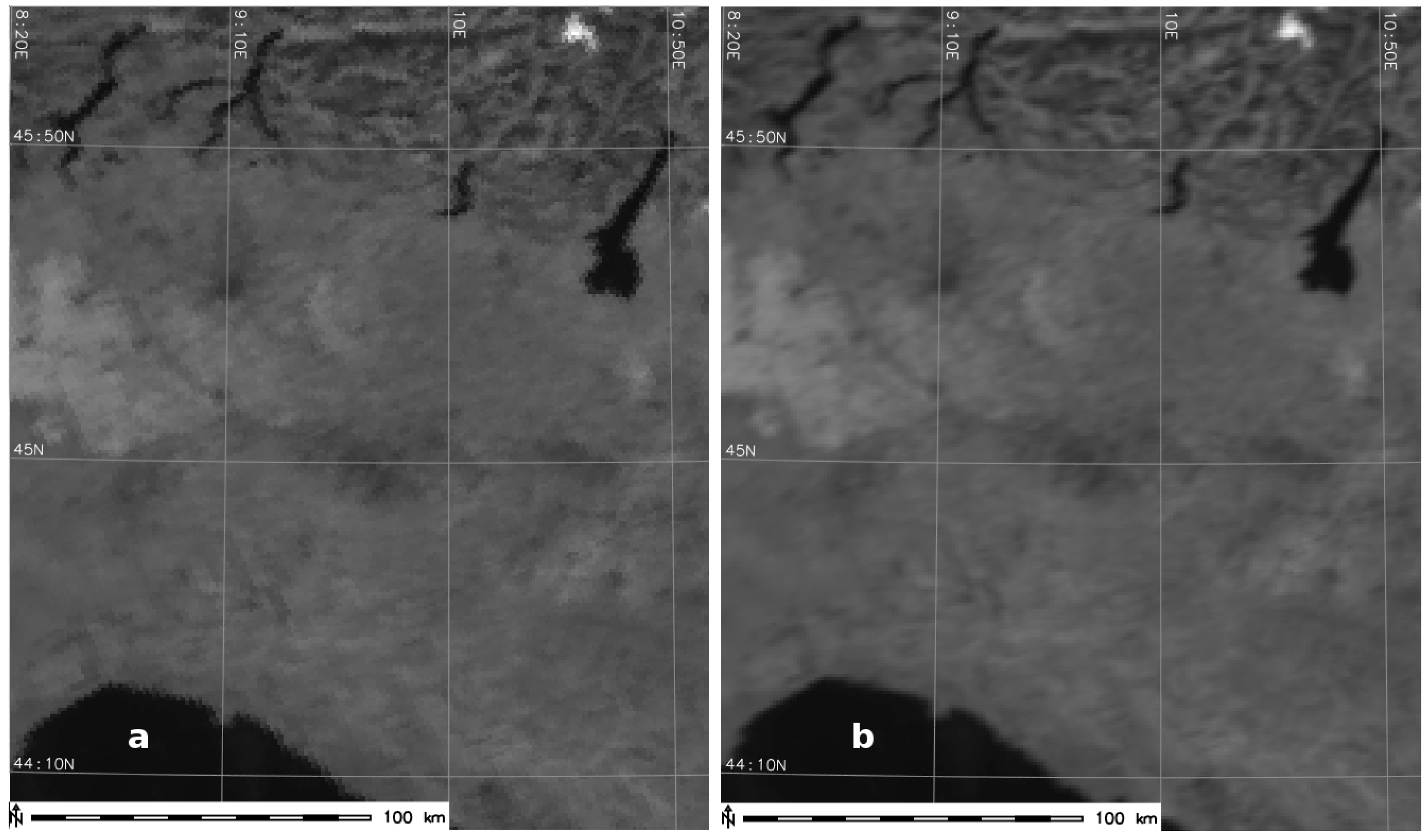
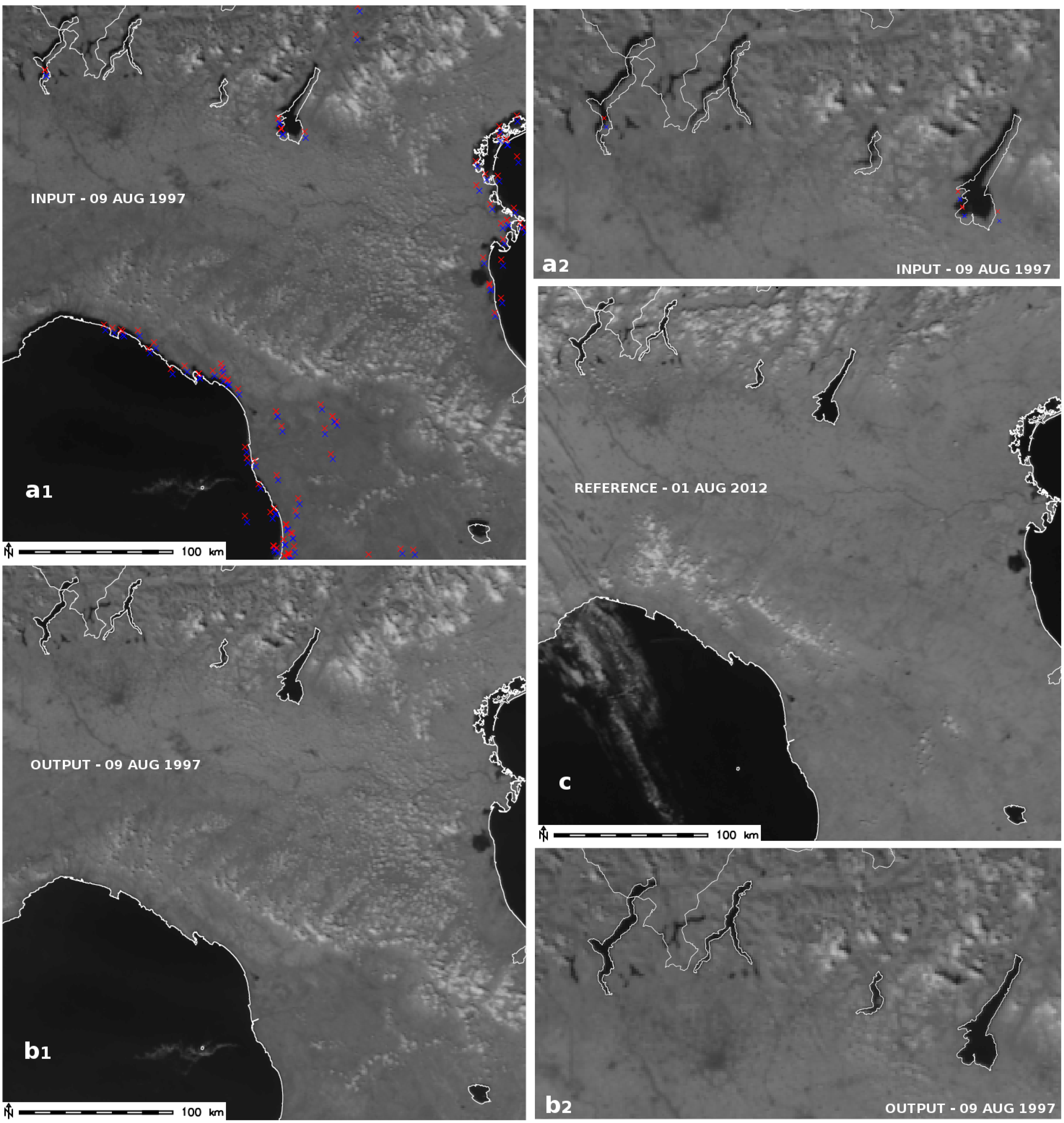
2.3. Precise Geo-Rectification Using SIFT
2.4. Validation of Thermal Calibration by Estimating LSWT
3. Results
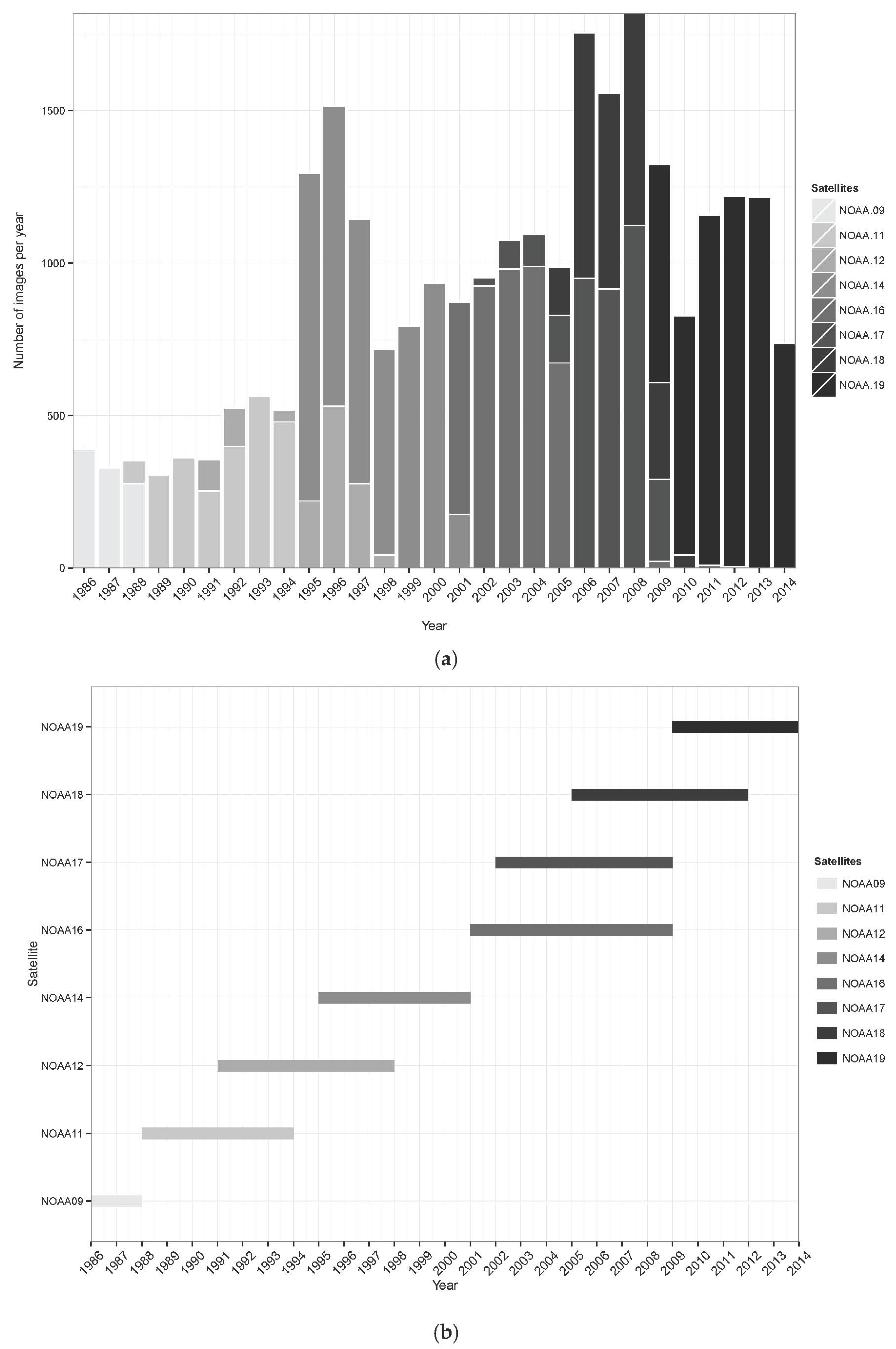
3.1. Time Series of Calibrated AVHRR LAC Data
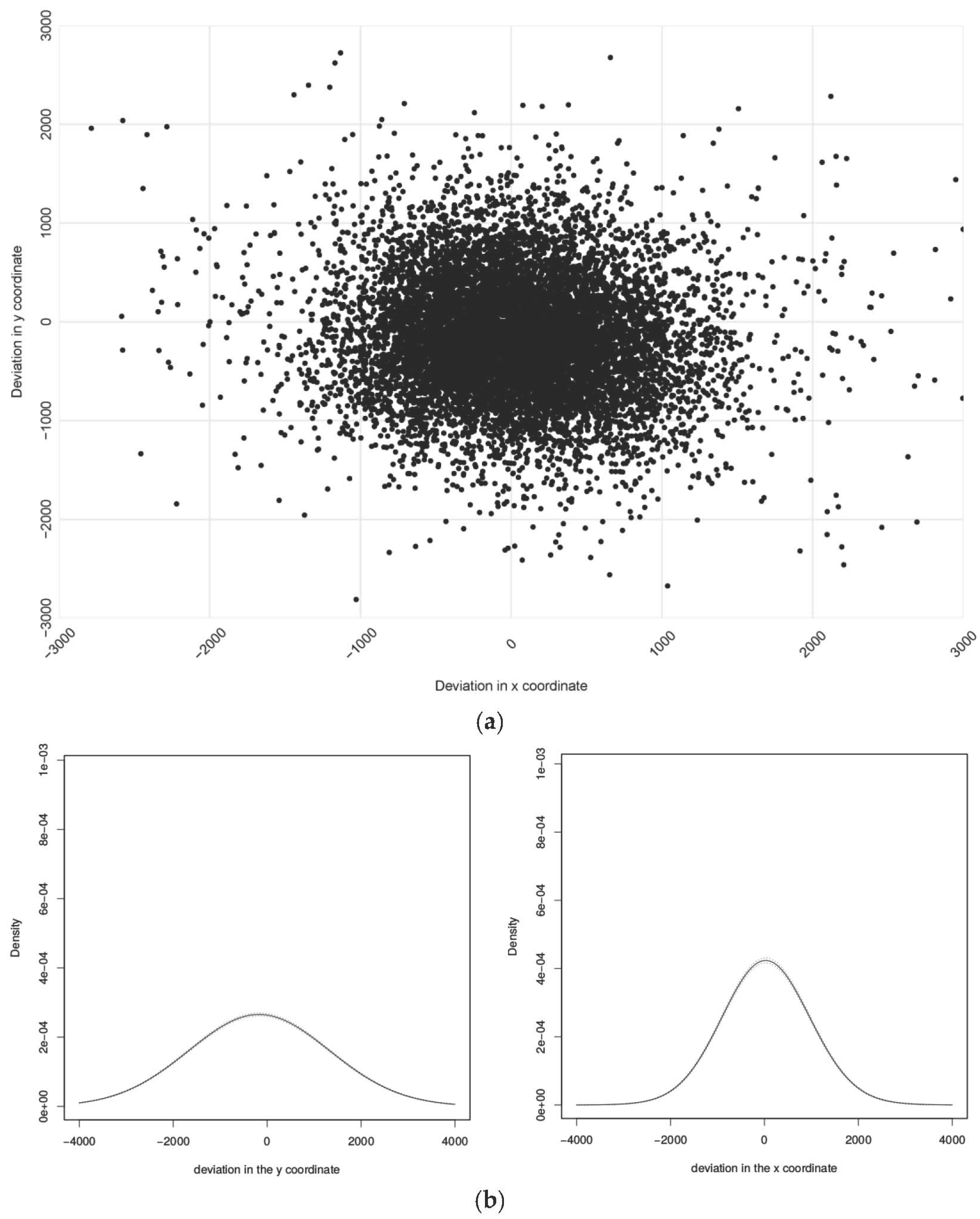
3.2. Geo-Rectification of Calibrated AVHRR LAC Data Using SIFT
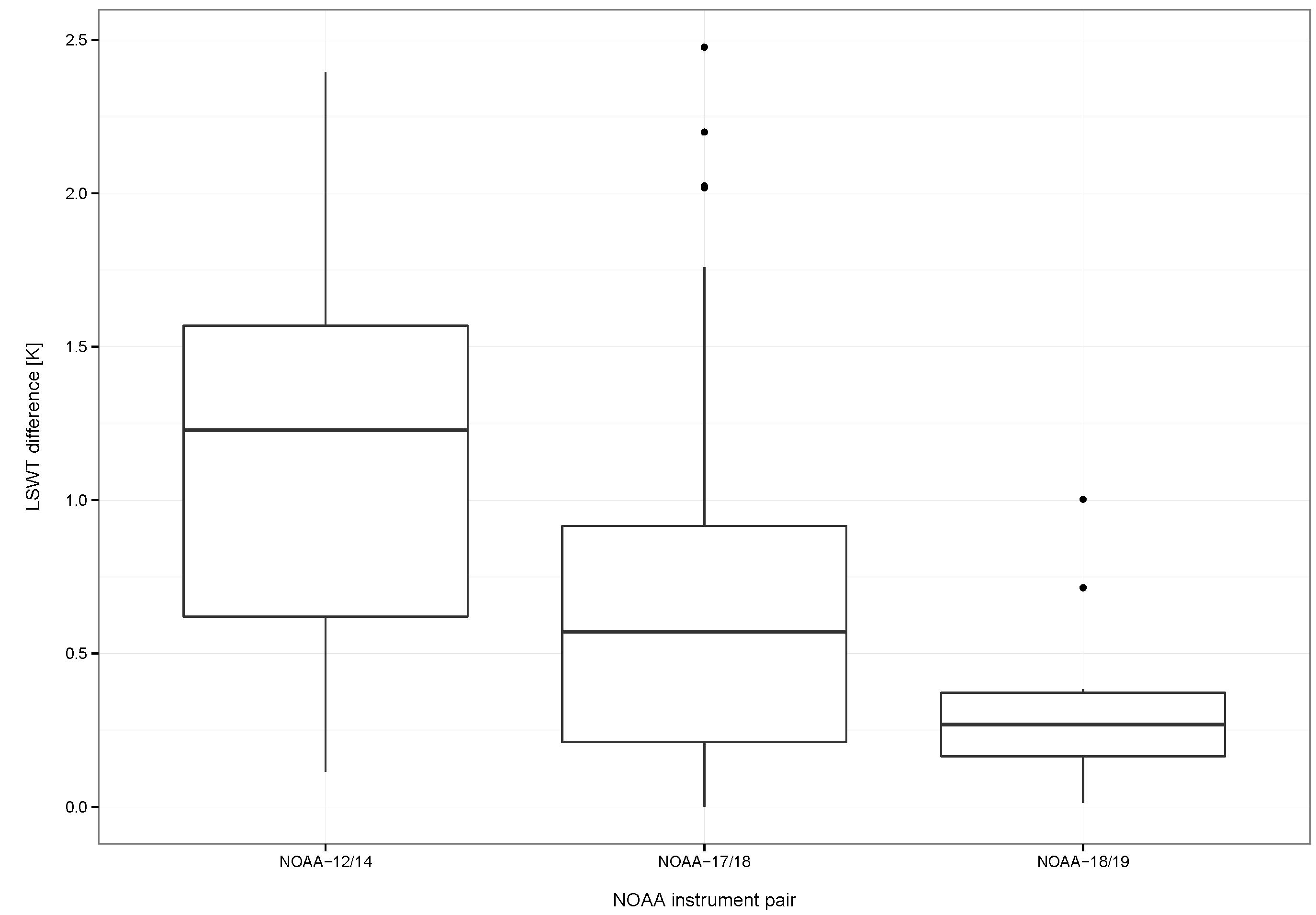
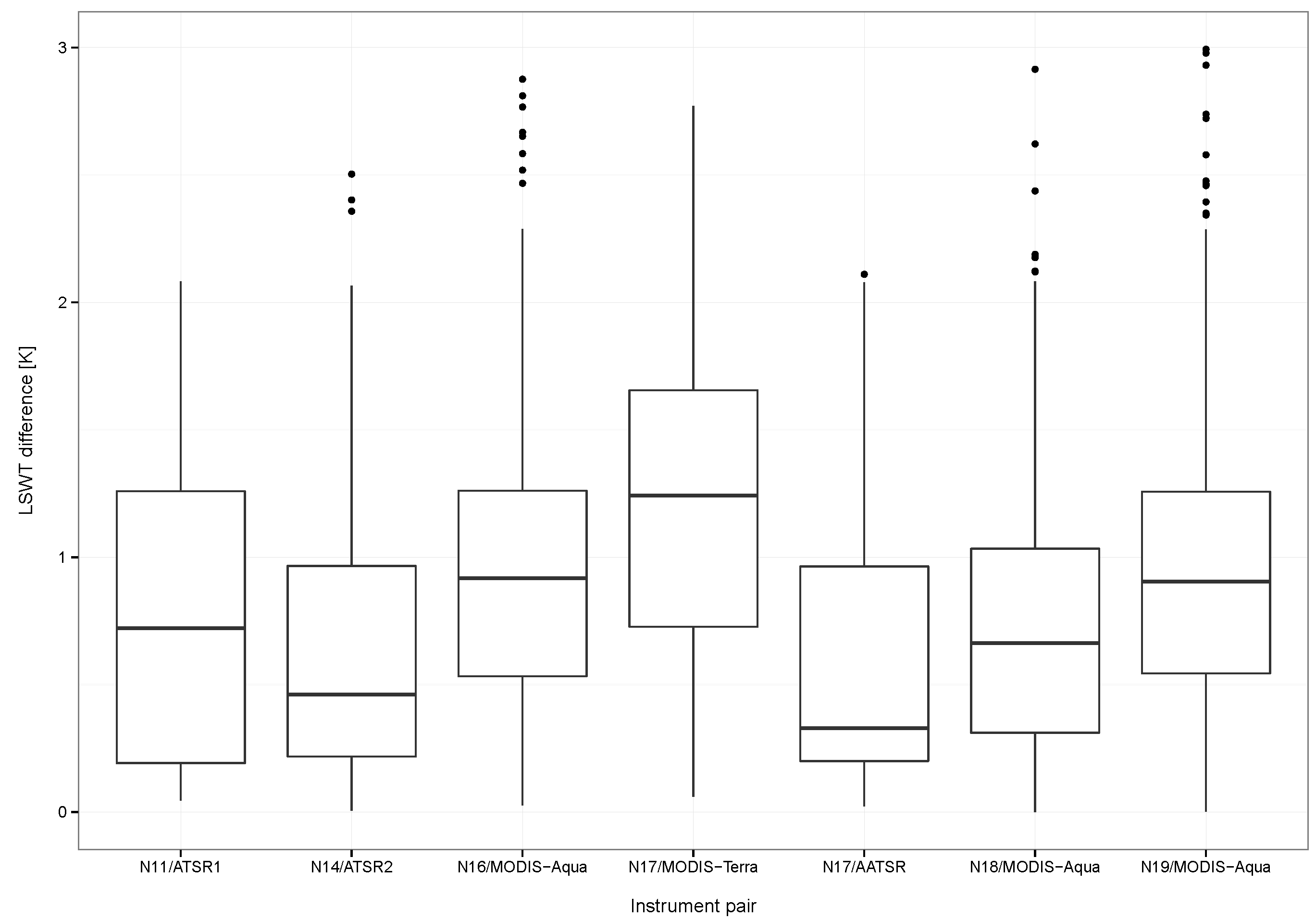
3.3. Quality Assessment of the Time Series Using Estimated LSWT
3.4. Software Code for Deploying the Method Elsewhere
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix
A. Python Script to Read and Calibrate Level 1B AVHRR LAC Data Using Pytroll Libraries
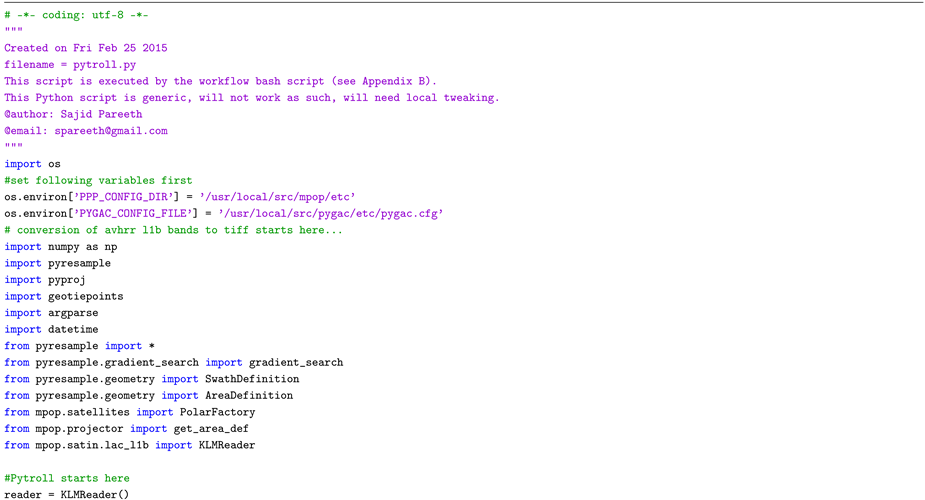

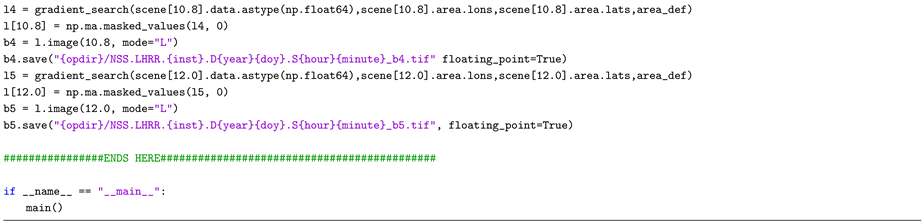
B. Bash Script to Process the Level 1B AVHRR LAC Data—Entire Workflow


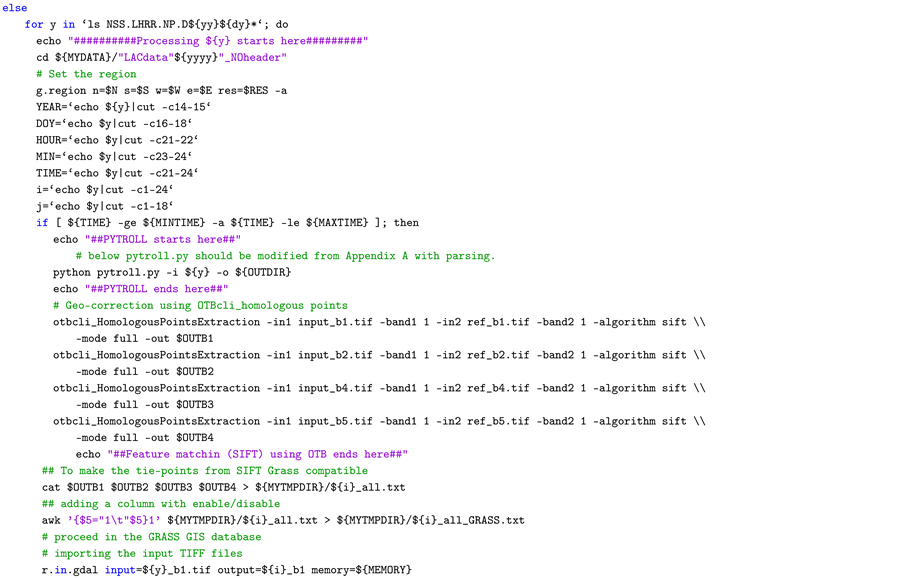
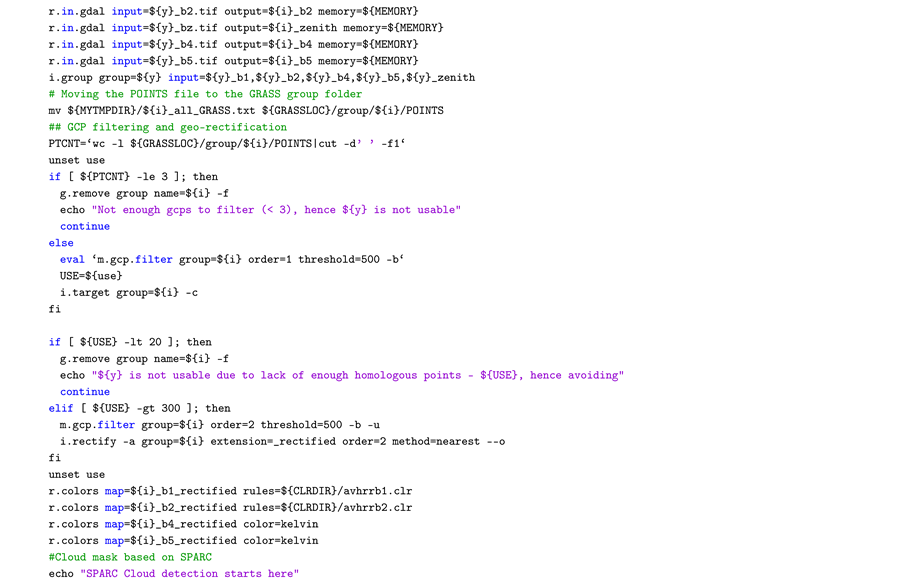


References
- Brunel, P.; Marsouin, A. Operational AVHRR navigation results. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privette, J.; Fowler, C.; Wick, G.; Baldwin, D.; Emery, W. Effects of orbital drift on advanced very high resolution radiometer products: Normalized difference vegetation index and sea surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 53, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.; Emery, W.J. Spacecraft attitude variations of NOAA-11 inferred from AVHRR imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.M.; Breaker, L.C. The problem of AVHRR image navigation revisited. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 979–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, W.J.; Brown, J.; Nowak, Z.P. AVHRR image navigation - Summary and review. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1989, 4, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Comprehensive Large Array-Data Stewardship System NOAA Data. Available online: http://www.class.ncdc.noaa.gov/ ( accessed on 29 July 2015).
- Cracknell, A.P. Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer AVHRR, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Bristol, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA KLM LAC Data Set Header Records. Available online: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/pod-guide/ncdc/docs/klm/html/c8/sec83132-2.htm#t8313221 (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Trishchenko, A.P.; Fedosejevs, G.; Li, Z.; Cihlar, J. Trends and uncertainties in thermal calibration of AVHRR radiometers onboard NOAA-9 to NOAA-16. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA POD LAC Data Set Header Records. Available online: http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/pod-guide/ncdc/docs/podug/html/c2/sec2-0.htm (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Price, J.C. Timing of NOAA afternoon passes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, R.; Zhou, L.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Shabanov, V.; Myneni, R.; Tucker, C. Effect of orbital drift and sensor changes on the time series of AVHRR vegetation index data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2584–2597. [Google Scholar]
- Historical TLE Records. Available online: http://celestrak.com/ (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Rosborough, G.; Baldwin, D.; Emery, W. Precise AVHRR image navigation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, P.; Brunel, P.; Marsouin, A. Automatic Adjustment of AVHRR Navigation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, F.M.; Coops, N.C.; Khlopenkov, K.V.; Trishchenko, A.P.; Riffler, M.; Wulder, M.A. Generation of a novel 1km NDVI data set over Canada, the northern United States, and Greenland based on historical AVHRR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; Melia, J. A method for accurate geometric correction of NOAA AVHRR HRPT data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifovic, R.; Trishchenko, A.P.; Chen, J.; Park, W.B.; Khlopenkov, K.V.; Fernandes, R.; Pouliot, D.; Ungureanu, C.; Luo, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Generating historical AVHRR 1 km baseline satellite data records over Canada suitable for climate change studies. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 31, 324–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopenkov, K.; Trishchenko, A.; Luo, Y. Achieving Subpixel Georeferencing Accuracy in the Canadian AVHRR Processing System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2150–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsler, F.; Fontana, F.; Neuhaus, C.; Riffler, M.; Musial, J.; Wunderle, S. AVHRR archive and processing Facility at the university of Bern: A comprehensive 1-km satellite data set for climate change studies. EARSeL eProc. 2011, 10, 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Riffler, M.; Lieberherr, G.; Wunderle, S. Lake surface water temperatures of European Alpine lakes (1989–2013) based on the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) 1 km data set. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2015, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovelli, M.A.; Mitasova, H.; Neteler, M.; Raghavan, V. Free and open source desktop and Web GIS solutions. Appl. Geomat. 2012, 4, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M.; Bowman, M.H.; Landa, M.; Metz, M. GRASS GIS: A multi-purpose open source GIS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytroll Home Page. Available online: http://www.pytroll.org/ (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Inglada, J.; Christophe, E. The Orfeo Toolbox Remote Sensing Image Processing Software. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; pp. 733–736.
- GRASS Development Team. Geographic Resources Analysis Support System (GRASS GIS) Software; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: USA, 2015. Available online: http://grass.osgeo.org (accessed on 16 February 2016).
- Neteler, M.; Mitasova, H. Open Source GIS: A GRASS GIS Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- m.gcp.filter man. Available online: https://grass.osgeo.org/grass70/manuals/addons/m.gcp.filter.html (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Pygac Git Repository. Available online: https://github.com/adybbroe/pygac (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Mpop Git Repository. Available online: https://github.com/pytroll/mpop (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Heidinger, A.K.; Straka, W.C.; Molling, C.C.; Sullivan, J.T.; Wu, X. Deriving an inter-sensor consistent calibration for the AVHRR solar reflectance data record. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 6493–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Weinreb, M.; Sullivan, J. Solar contamination effects on the infrared channels of the advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR). J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 33463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trishchenko, A.P. Removing unwanted fluctuations in the AVHRR thermal calibration data using robust techniques. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1939–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopenkov, K.; Trishchenko, A. Implementation and evaluation of concurrent gradient search method for reprojection of MODIS level 1B imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopenkov, K.V.; Trishchenko, A.P. SPARC: New cloud, snow, and cloud shadow detection scheme for historical 1-km AVHHR data over Canada. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; pp. 1150–1157.
- Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Holden, E.J. A fast and fully automatic registration approach based on point features for multi-source remote-sensing images. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Huo, C.; Pan, C.; Kong, Q. Registration of Optical and SAR Satellite Images by Exploring the Spatial Relationship of the Improved SIFT. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, D.; Di Rita, A. Relief effects on aerial photos geometric correction. Appl. Geogr. 2005, 25, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J. Split-Window Coefficients for Land Surface Temperature Retrieval From Low-Resolution Thermal Infrared Sensors. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.C.; Hook, S.J.; Schneider, P. Optimized split-window coefficients for deriving surface temperatures from inland water bodies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3758–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchini, D.; Neteler, M. Let the four freedoms paradigm apply to ecology. Trends Ecol. Evolut. 2012, 27, 310–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichman, O.J.; Jones, M.B.; Schildhauer, M.P. Challenges and Opportunities of Open Data in Ecology. Science 2011, 331, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; Hook, S.J. Space observations of inland water bodies show rapid surface warming since 1985. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L22405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Hook, S.J.; Schneider, P.; Schladow, S.G. Skin and bulk temperature difference at Lake Tahoe: A case study on lake skin effect. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10332–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, S.J.; Prata, F.J.; Alley, R.E.; Abtahi, A.; Richards, R.C.; Schladow, S.G.; Pálmarsson, S. Retrieval of Lake Bulk and Skin Temperatures Using Along-Track Scanning Radiometer (ATSR-2) Data: A Case Study Using Lake Tahoe, California. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.G.; Johansson, E. Multi-Sensor Calibration Studies of AVHRR-Heritage Channel Radiances Using the Simultaneous Nadir Observation Approach. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1845–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Menenti, M.; Verhoef, W. Reconstructing cloudfree NDVI composites using Fourier analysis of time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.; Rocchini, D.; Neteler, M. Surface temperatures at the continental scale: Tracking changes with remote sensing at unprecedented detail. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3822–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Channels | AVHRR/1 | AVHRR/2 | AVHRR/3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.58–0.68 | 0.58–0.68 | 0.58–0.68 |
| 2 | 0.725–1.10 | 0.725–1.10 | 0.725–1.10 |
| 3a | N.A | N.A | 1.58–1.68 |
| 3b | 3.55–3.93 | 3.55–3.93 | 3.55–3.93 |
| 4 | 10.50–11.50 | 10.3–11.3 | 10.3–11.3 |
| 5 | Ch.4 repeated | 11.5–12.5 | 11.5–12.5 |
| Software | Source | Version | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pytroll/mpop | https://github.com/pytroll/mpop | - | GNU GPL v3 |
| Pytroll/pygac | https://github.com/adybbroe/pygac | - | GNU GPL v3 |
| Pytroll/pyresample | https://github.com/pytroll/pyresample/ | - | GNU GPL v3 |
| Orfeo Toolbox | https://www.orfeo-toolbox.org/ | 4.4.0 | CeCILL v2 |
| GRASS GIS | http://grass.osgeo.org/ | 7.0.0 | GNU GPL v3 |
| Sensor pair | N12/N14 | N17/N18 | N18/N19 | N11/ATS1 | N14/ATS2 | N17/AATSR | N17/MODT | N16/MODA | N18/MODA | N19/MODA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 1.18 | 0.67 | 0.35 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.99 | 0.75 | 0.95 |
| RMSE | 1.36 | 0.88 | 0.44 | 1.0 | 0.98 | 0.85 | 1.35 | 1.16 | 0.92 | 1.12 |
| N | 26 | 75 | 10 | 38 | 98 | 28 | 75 | 149 | 262 | 385 |
| Satellites | Slope | R2 | RMSE | MAE | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOAA-11 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.81 | 0.65 | 12 |
| NOAA-14 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 1.38 | 1.05 | 22 |
| NOAA-16 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 10 |
| NOAA-17 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.56 | 0.46 | 7 |
| NOAA-18 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.04 | 0.77 | 12 |
| NOAA-19 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 1.40 | 1.08 | 21 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pareeth, S.; Delucchi, L.; Metz, M.; Rocchini, D.; Devasthale, A.; Raspaud, M.; Adrian, R.; Salmaso, N.; Neteler, M. New Automated Method to Develop Geometrically Corrected Time Series of Brightness Temperatures from Historical AVHRR LAC Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030169
Pareeth S, Delucchi L, Metz M, Rocchini D, Devasthale A, Raspaud M, Adrian R, Salmaso N, Neteler M. New Automated Method to Develop Geometrically Corrected Time Series of Brightness Temperatures from Historical AVHRR LAC Data. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(3):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030169
Chicago/Turabian StylePareeth, Sajid, Luca Delucchi, Markus Metz, Duccio Rocchini, Abhay Devasthale, Martin Raspaud, Rita Adrian, Nico Salmaso, and Markus Neteler. 2016. "New Automated Method to Develop Geometrically Corrected Time Series of Brightness Temperatures from Historical AVHRR LAC Data" Remote Sensing 8, no. 3: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030169
APA StylePareeth, S., Delucchi, L., Metz, M., Rocchini, D., Devasthale, A., Raspaud, M., Adrian, R., Salmaso, N., & Neteler, M. (2016). New Automated Method to Develop Geometrically Corrected Time Series of Brightness Temperatures from Historical AVHRR LAC Data. Remote Sensing, 8(3), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030169







