Temporal Monitoring of the Soil Freeze-Thaw Cycles over a Snow-Covered Surface by Using Air-Launched Ground-Penetrating Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
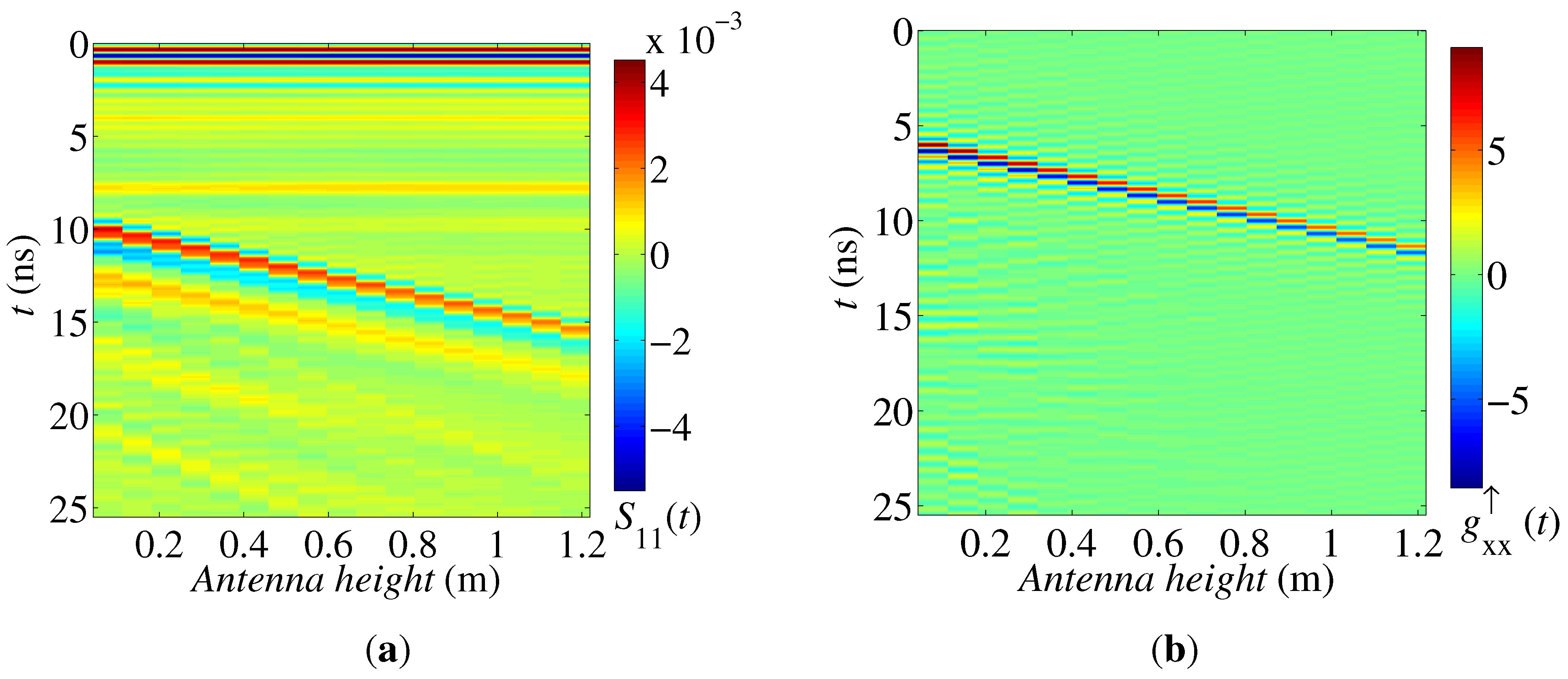
2.1. GPR System
2.2. GPR Forward Modeling
2.3. Time Domain Inversion Method

3. Test Site and Experimental Setup

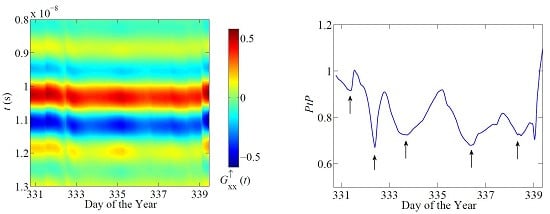
4. Results and Discussion
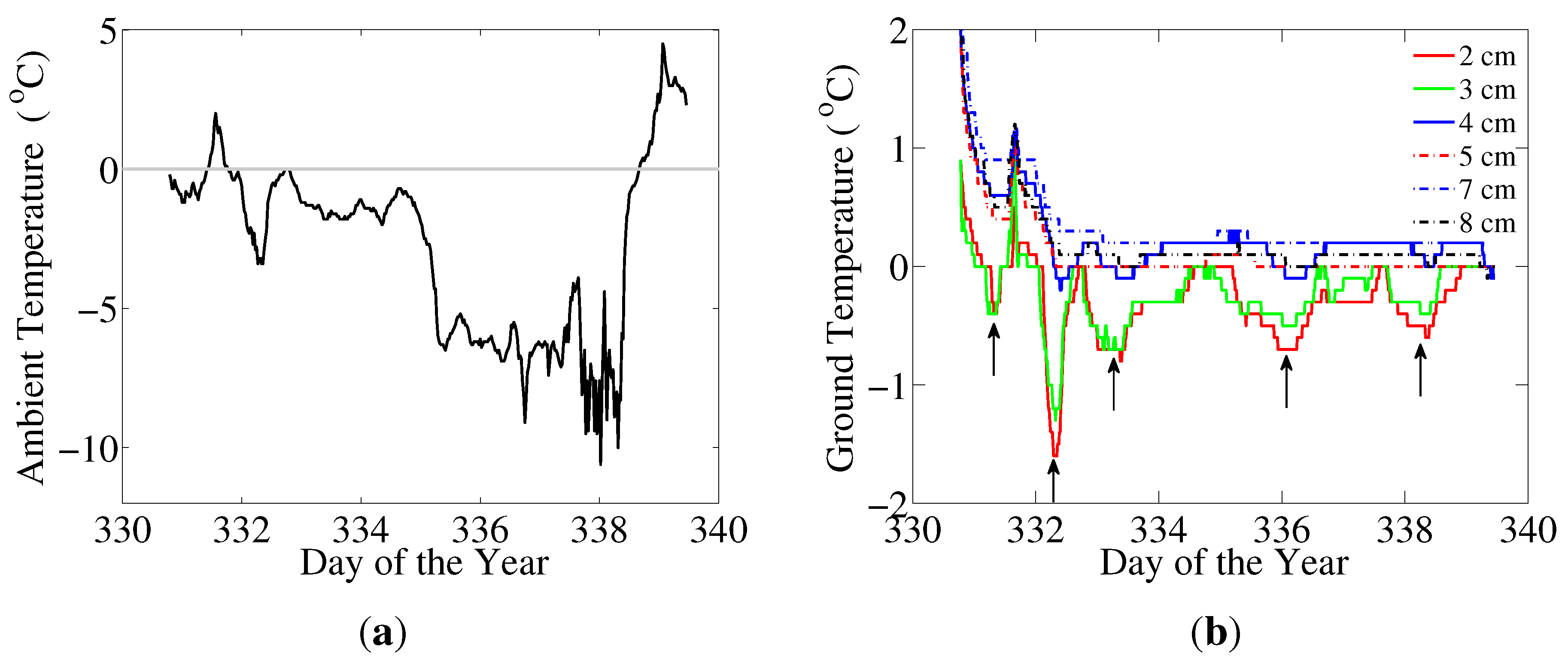

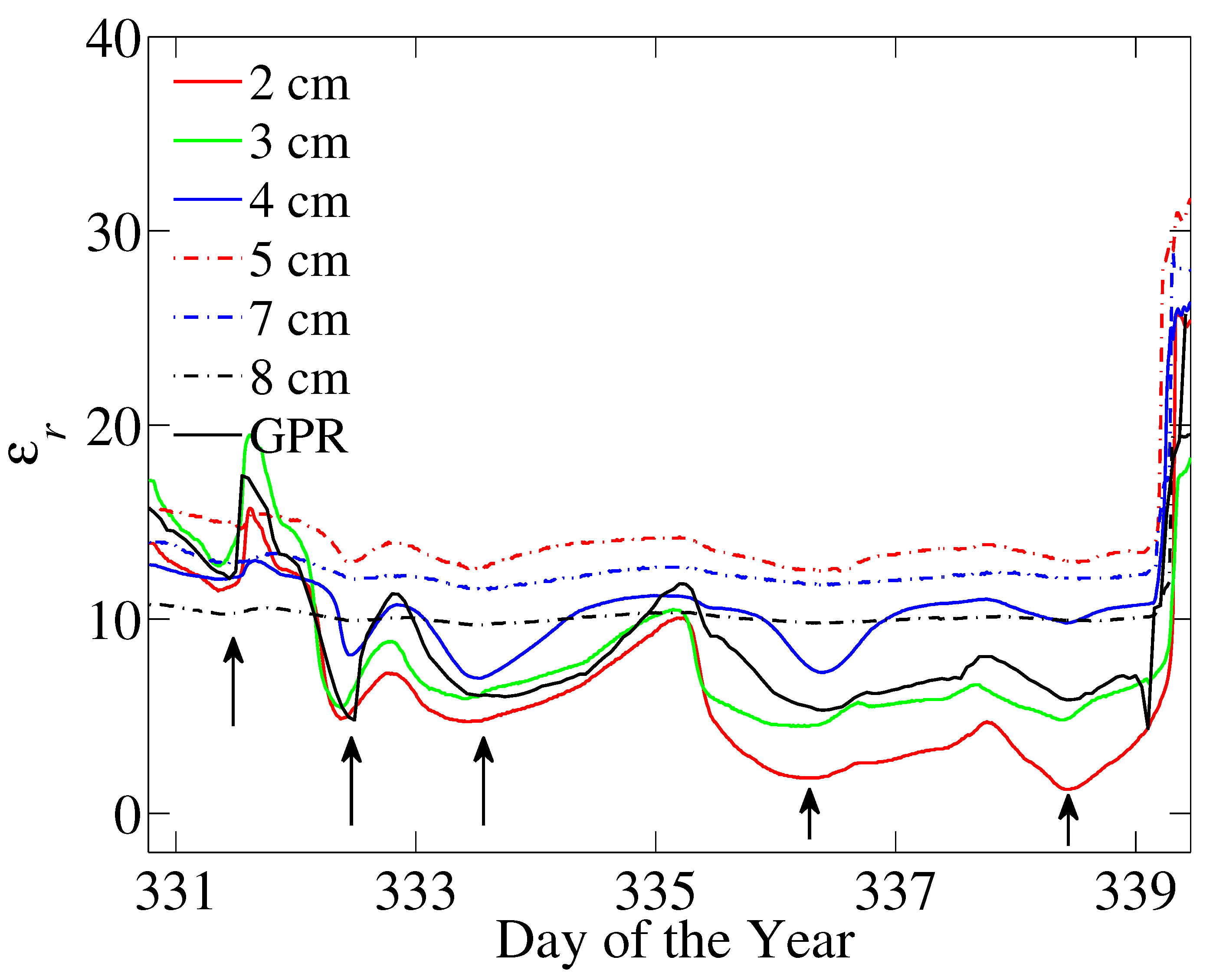
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Armstrong, R.L. Soil freeze/thaw cycles over snow-free land detected by passive microwave remote sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkauer, K.A.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Simulation of spatial variability in snow and frozen soil. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2003, 108, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, J.B.; Chalmers, A. The effect of frozen soil on snowmelt runoff at Sleepers River, Vermont. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1843–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, K.J.; Westra, S.; Evans, J.P.; McCabe, M.F. Spatial and temporal variability in seasonal snow density. J. Hydrol. 2013, 484, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.J. Influence of the seasonal snow cover on the ground thermal regime: An overview. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43, RG4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Riddle, C.; Rapai, J.; Warland, J.; Furon, A. Nitrous oxide fluxes related to soil freeze and thaw periods identified using heat pulse probes. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 90, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaesche, P.; Veit, H.; Huwe, B. Snow cover and soil moisture controls on solifluction in an area of seasonal frost, eastern Alps. Permaf. Periglac. Process. 2003, 14, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayard, D.; StÃd’hli, M.; Parriaux, A.; FlÃijhler, H. The influence of seasonally frozen soil on the snowmelt runoff at two Alpine sites in southern Switzerland. J. Hydrol. 2005, 309, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Barry, R.G.; Armstrong, R.L. Application of satellite remote sensing techniques to frozen ground studies. Polar Geogr. 2004, 28, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; van Dijk, A.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Canadell, J.G.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; Wang, G.J. Recent reversal in loss of global terrestrial biomass. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rignot, E.; Way, J.B.; McDonald, K.; Viereck, L.; Williams, C.; Adams, P.; Payne, C.; Wood, W.; Shi, J.C. Monitoring of environmental-conditions in taiga forests using ERS-1 SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwank, M.; Stahli, M.; Wydler, H.; Leuenberger, J.; Matzler, C.; Fluhler, H. Microwave L-band emission of freezing soil. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, T.; Crosby, B. Comparing two methods of surface change detection on an evolving thermokarst using high-temporal-frequency terrestrial laser scanning, Selawik River, Alaska. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2813–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Lyon, S.; Destouni, G. Temporal behavior of lake size-distribution in a thawing permafrost landscape in northwestern Siberia. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 621–636. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, M.; Vanderborght, J.; Kostov, K.G.; Jadoon, K.Z.; Weihermüller, L.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Pachepsky, Y.; Schwank, M.; Vereecken, H. Soil hydraulic parameters and surface soil moisture of a tilled bare soil plot inversely derived from L-band brightness temperatures. Vadose Zone J. 2014, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieback, S.; Paulik, C.; Wagner, W. Frozen soil detection based on advanced scatterometer observations and air temperature data as part of soil moisture retrieval. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3206–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.F.; Chylek, P.; Dubey, M.K. Detecting ice-sheet melt area over western Greenland using MODIS and AMSR-E data for the summer periods of 2002–2006. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 2, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kimball, J.S.; McDonald, K.C.; Glassy, J. Developing a global data record of daily landscape freeze/thaw status using satellite passive microwave remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.A.; Kimball, J.S.; McDonald, K.C.; Chan, S.T.K.; Njoku, E.G.; Oechel, W.C. Satellite microwave remote sensing of boreal and arctic soil temperatures from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2004–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, M.; Pulliainen, J.; Praks, J.; Arslan, A. Progress and challenges in radar remote sensing of snow. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Retrieval of Bio- and Geophysical Parameters from Sar Data for Land Applications, Sheffield, UK, 11–14 September 2001; Wilson, A., Ed.; ESA Special Publications: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Rautiainen, K.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Schwank, M.; Kontu, A.; Menard, C.B.; Matzler, C.; Drusch, M.; Wiesmann, A.; Ikonen, J.; Pulliainen, J. Detection of soil freezing from L-band passive microwave observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seungbum, K.; Van Zyl, J.; McDonald, K.; Njoku, E. Monitoring surface soil moisture and freeze-thaw state with the high-resolution radar of the Soil Moisture Active/Passive (SMAP) mission. In Proceedings of IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 May 2010; pp. 735–739.
- Munroe, J.S.; Doolittle, J.A.; Kanevskiy, M.Z.; Hinkel, K.M.; Nelson, F.E.; Jones, B.M.; Shur, Y.; Kimble, J.M. Application of ground-penetrating radar imagery for three-dimensional visualisation of near-surface structures in ice-rich permafrost, Barrow, Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2007, 18, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.W.; Moorman, B.J.; Solomon, S.M.; Hugenholtz, C.H. Mapping subsurface conditions within the near-shore zone of an Arctic delta using ground penetrating radar. Cold Reg. Sci. Techno. 2009, 56, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steelman, C.M.; Endres, A.L.; van der Kruk, J. Field observations of shallow freeze and thaw processes using high-frequency ground-penetrating radar. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2022–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, J.; Burke, M.J. Applications of ground-penetrating radar to glacial and frozen materials. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2007, 12, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneisel, C.; Hauck, C.; Fortier, R.; Moorman, B. Advances in geophysical methods for permafrost investigations. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2008, 19, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, K.; Liu, L.; Parsekian, A.; Jafarov, E.; Chen, A.; Zhang, T.; Gusmeroli, A.; Panda, S.; Zebker, H.; Schaefer, T. Remotely sensed active layer thickness (ReSALT) at Barrow, Alaska using interferometric synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3735–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, B.J.; Robinson, S.D.; Burgess, M.M. Imaging periglacial conditions with ground-penetrating radar. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2003, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfricht, K.; Kuhn, M.; Keuschnig, M.; Heilig, A. Lidar snow cover studies on glaciers in the Otztal Alps (Austria): comparison with snow depths calculated from GPR measurements. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkel, K.M.; Doolittle, J.A.; Bockheim, J.G.; Nelson, F.E.; Paetzold, R.; Kimble, J.M.; Travis, R. Detection of subsurface permafrost features with ground-penetrating radar, Barrow, Alaska. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2001, 12, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Dossi, M.; Colucci, R.R.; Pipan, M. A new fast methodology to estimate the density of frozen materials by means of common offset GPR data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 99, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steelman, C.M.; Endres, A.L. Evolution of high-frequency ground-penetrating radar direct ground wave propagation during thin frozen soil layer development. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2009, 57, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnor, J.R.; Campbell, J.L.; Shanley, J.B.; Zarnoch, S.J. Measuring soil frost depth in forest ecosystems with ground penetrating radar. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 192, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Slob, E.C.; van den Bosch, I.; Stockbroeckx, B.; Vanclooster, M. Modeling of ground-penetrating radar for accurate characterization of subsurface electric properties. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Slob, E.C.; Vanclooster, M.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Uniqueness and stability analysis of hydrogeophysical inversion for time-lapse ground-penetrating radar estimates of shallow soil hydraulic properties. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W09421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadas, D.; Jadoon, K.Z.; Vanderborght, J.; Lambot, S.; Vereecken, H. Effects of near surface soil moisture profiles during evaporation on far-field ground-penetrating radar data: A numerical study. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, F.; Weihermüller, L.; Schwank, M.; Jadoon, K.Z.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Estimation of hydraulic properties of a sandy soil using ground-based active and passive microwave remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3095–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slob, E.C.; Fokkema, J. Coupling effects of two electric dipoles on an interface. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Slob, E.; Vereecken, H. Fast evaluation of zero-offset Green’s function for layered media with application to ground-penetrating radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L21405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Weihermüller, L.; Huisman, J.A.; Vereecken, H.; Vanclooster, M.; Slob, E.C. Analysis of air-launched ground-penetrating radar techniques to measure the soil surface water content. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W11403. [Google Scholar]
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Lambot, S.; Weihermüller, L.; Moghadas, D.; Dimitrov, M.; Vereecken, H. Temporal monitoring of the soil freeze-thaw cycles over snow-cover land by using off-ground GPR. In Proceedings of 7th International Workshop on Advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (IWAGPR), Nantes, France, 2–5 July 2013; pp. 1–4.
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Lambot, S.; Slob, E.C.; Vereecken, H. Analysis of horn antenna transfer functions and phase-center position for modeling off-ground GPR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1649–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Montzka, C.; Stadler, A.; Menz, G.; Thonfeld, F.; Vereecken, H. Estimation and validation of RapidEye-based time-series of leaf area index for winter wheat in the Rur catchment (Germany). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2808–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Lambot, S.; Scharnagl, B.; van der Kruk, J.; Slob, E.; Vereecken, H. Quantifying field-scale surface soil water content from proximal GPR signal inversion in the time domain. Near Surf. Geophys. 2010, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Weihermüller, L.; Scharnagl, B.; Kowalsky, M.B.; Bechtold, M.; Hubbard, S.S.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Estimation of soil hydraulic parameters in the field by integrated hydrogeophysical inversion of time-lapse ground-penetrating radar data. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, F.; Weihermüller, L.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Accounting for soil surface roughness in the inversion of ultrawideband off-ground GPR signal for soil moisture retrieval. Geophysics 2012, 77, H1–H7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Andre, F. Full-wave modeling of near-field radar data for planar layered media reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jadoon, K.Z.; Weihermüller, L.; McCabe, M.F.; Moghadas, D.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Temporal Monitoring of the Soil Freeze-Thaw Cycles over a Snow-Covered Surface by Using Air-Launched Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12041-12056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70912041
Jadoon KZ, Weihermüller L, McCabe MF, Moghadas D, Vereecken H, Lambot S. Temporal Monitoring of the Soil Freeze-Thaw Cycles over a Snow-Covered Surface by Using Air-Launched Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(9):12041-12056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70912041
Chicago/Turabian StyleJadoon, Khan Zaib, Lutz Weihermüller, Matthew F. McCabe, Davood Moghadas, Harry Vereecken, and Sebastíen Lambot. 2015. "Temporal Monitoring of the Soil Freeze-Thaw Cycles over a Snow-Covered Surface by Using Air-Launched Ground-Penetrating Radar" Remote Sensing 7, no. 9: 12041-12056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70912041
APA StyleJadoon, K. Z., Weihermüller, L., McCabe, M. F., Moghadas, D., Vereecken, H., & Lambot, S. (2015). Temporal Monitoring of the Soil Freeze-Thaw Cycles over a Snow-Covered Surface by Using Air-Launched Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sensing, 7(9), 12041-12056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70912041