Index of Soil Moisture Using Raw Landsat Image Digital Count Data in Texas High Plains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Theory
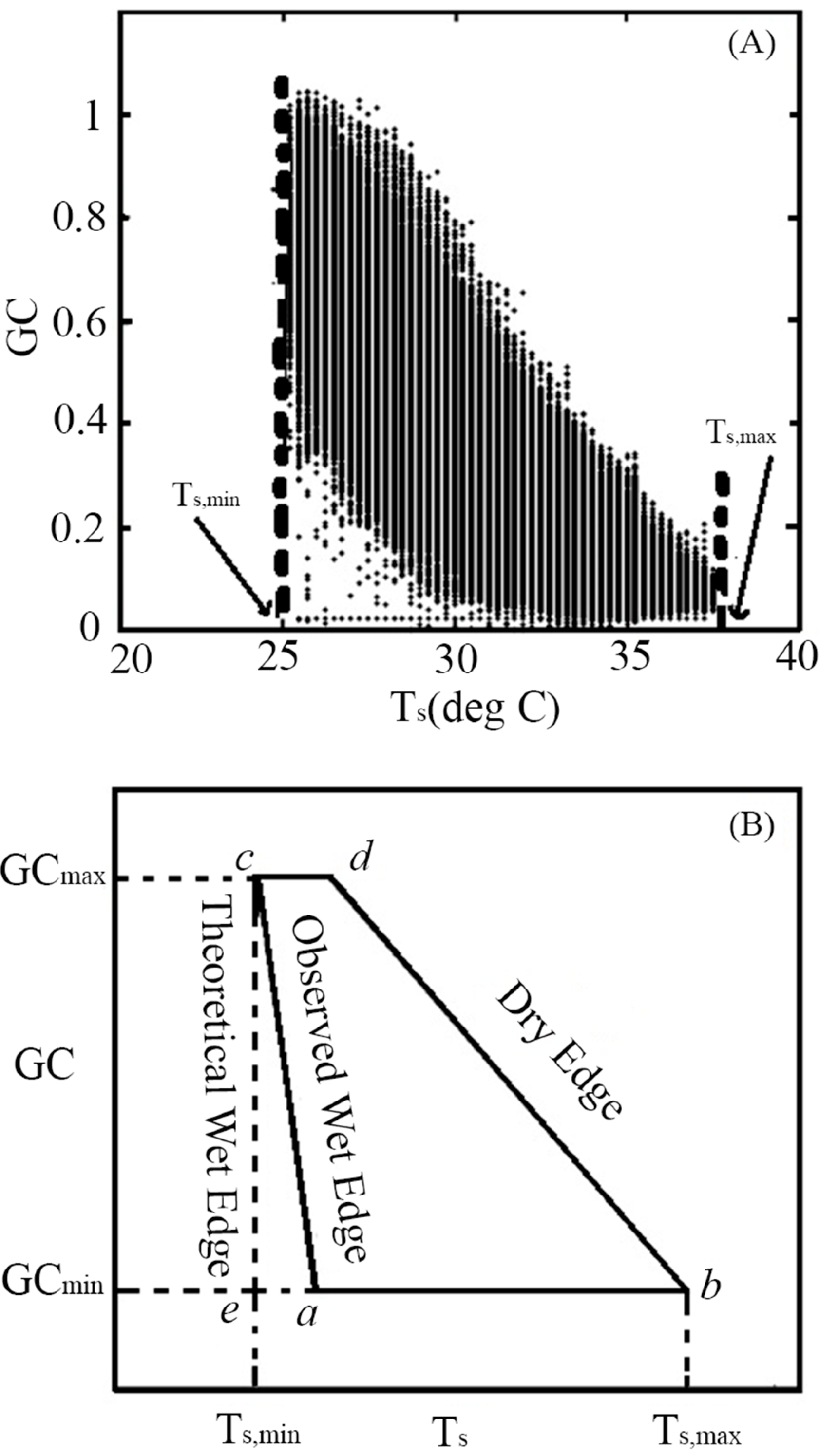
2.1.1. Normalizing TIR-GC Space
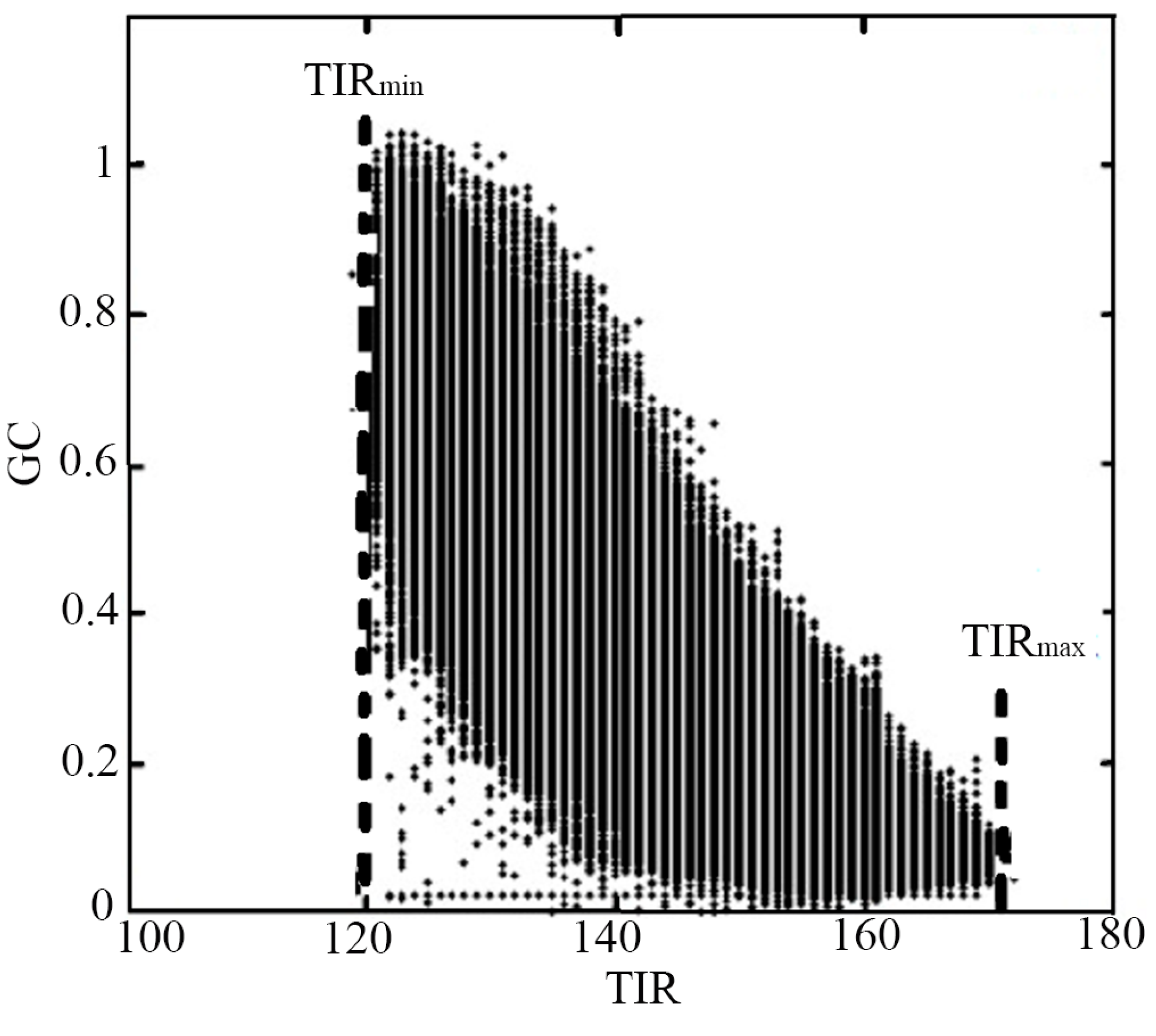
2.1.2. Perpendicular Soil Moisture Index
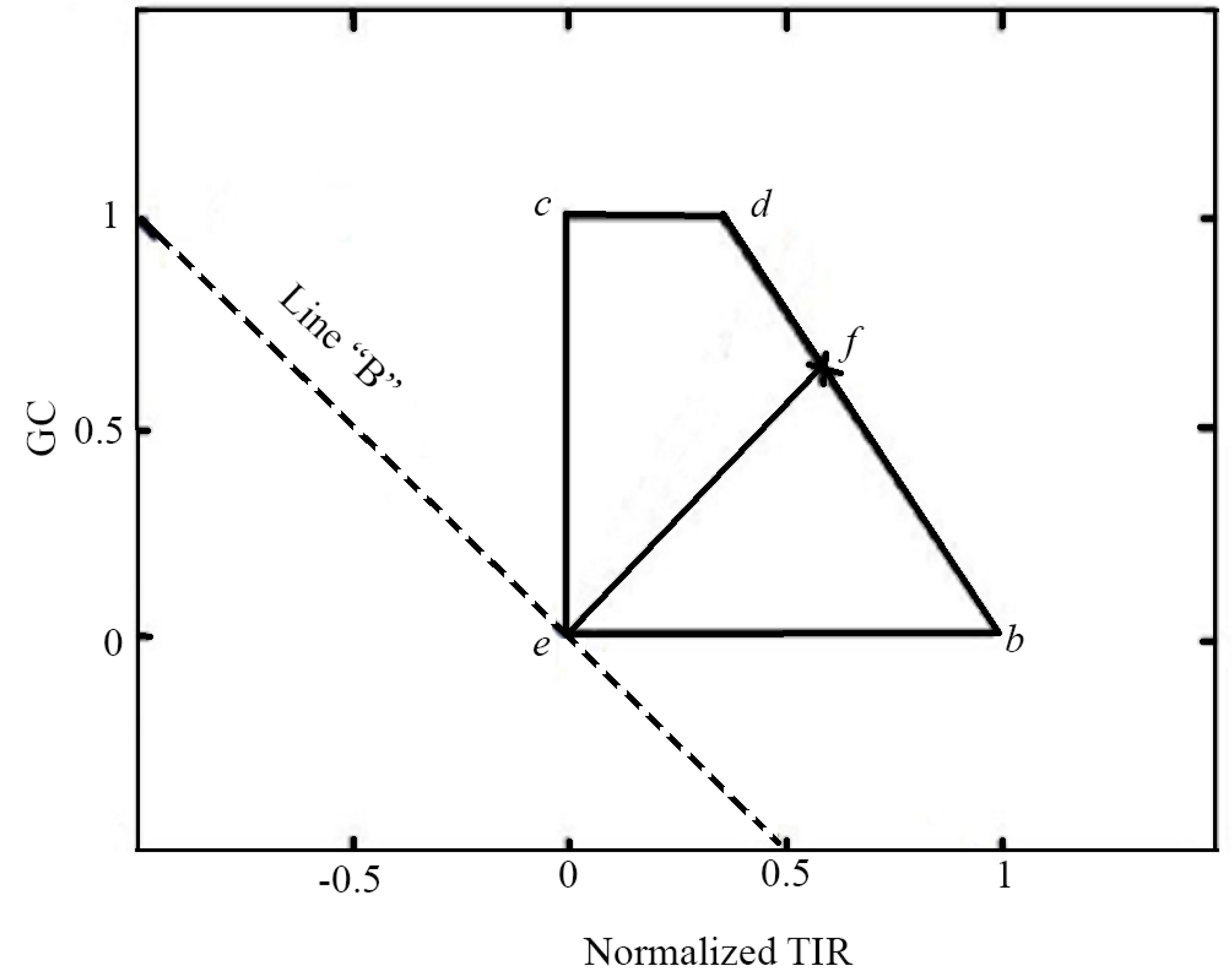
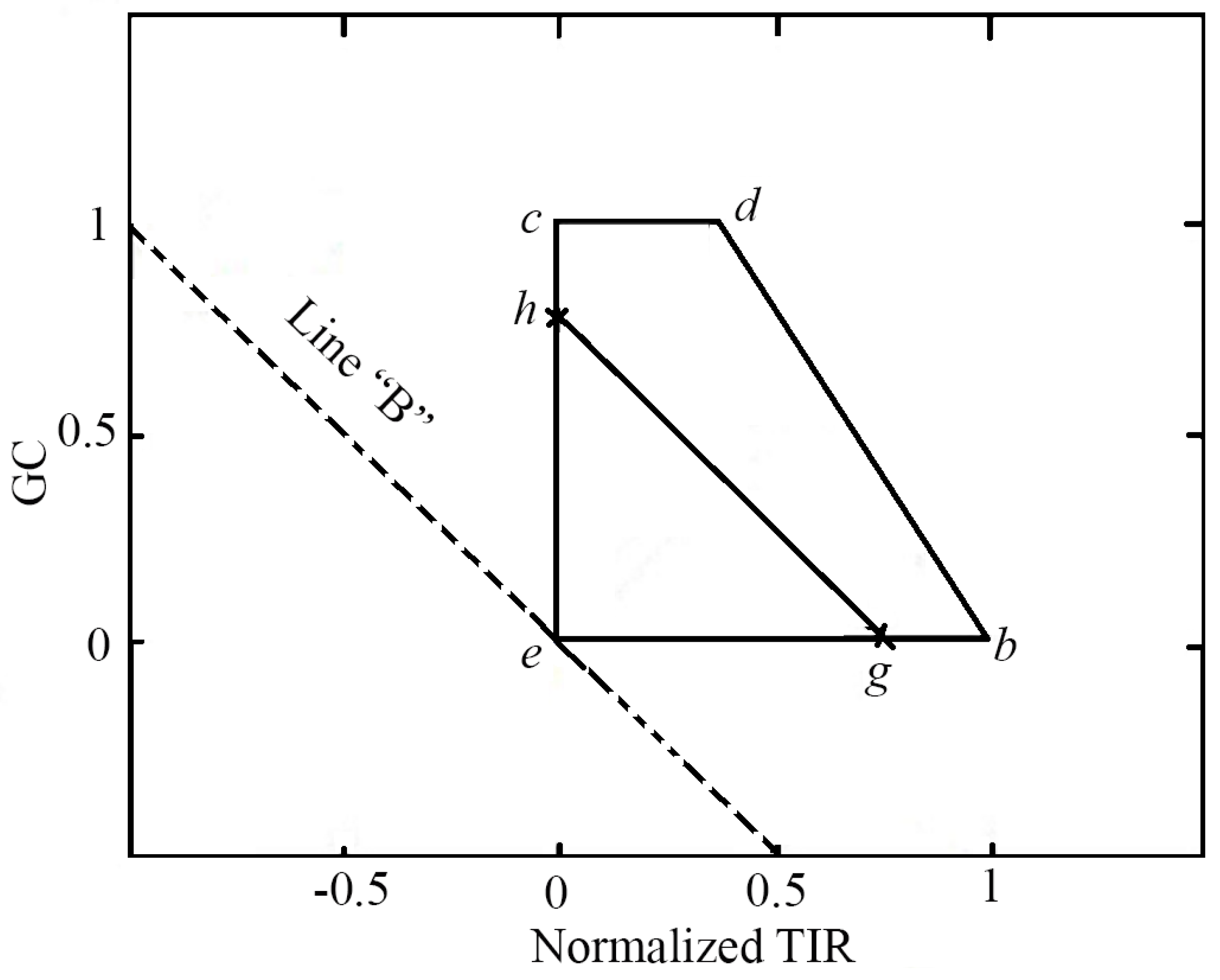
2.1.3. Assumptions and Sources of Error
2.2. Field Study
2.3. Satellite Image Data
| Year | Acquisition Date | |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat-7 | Landsat-8 | |
| 2012 | 22 June | |
| 9 August | ||
| 25 August | ||
| 10 September | ||
| 26 September | ||
| 2013 | 29 September | 4 August |
| 5 September | ||
| 21 September | ||
| 7 October | ||
2.4. Soil Moisture Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. TIR–GC Space vs. Ts-GC Space
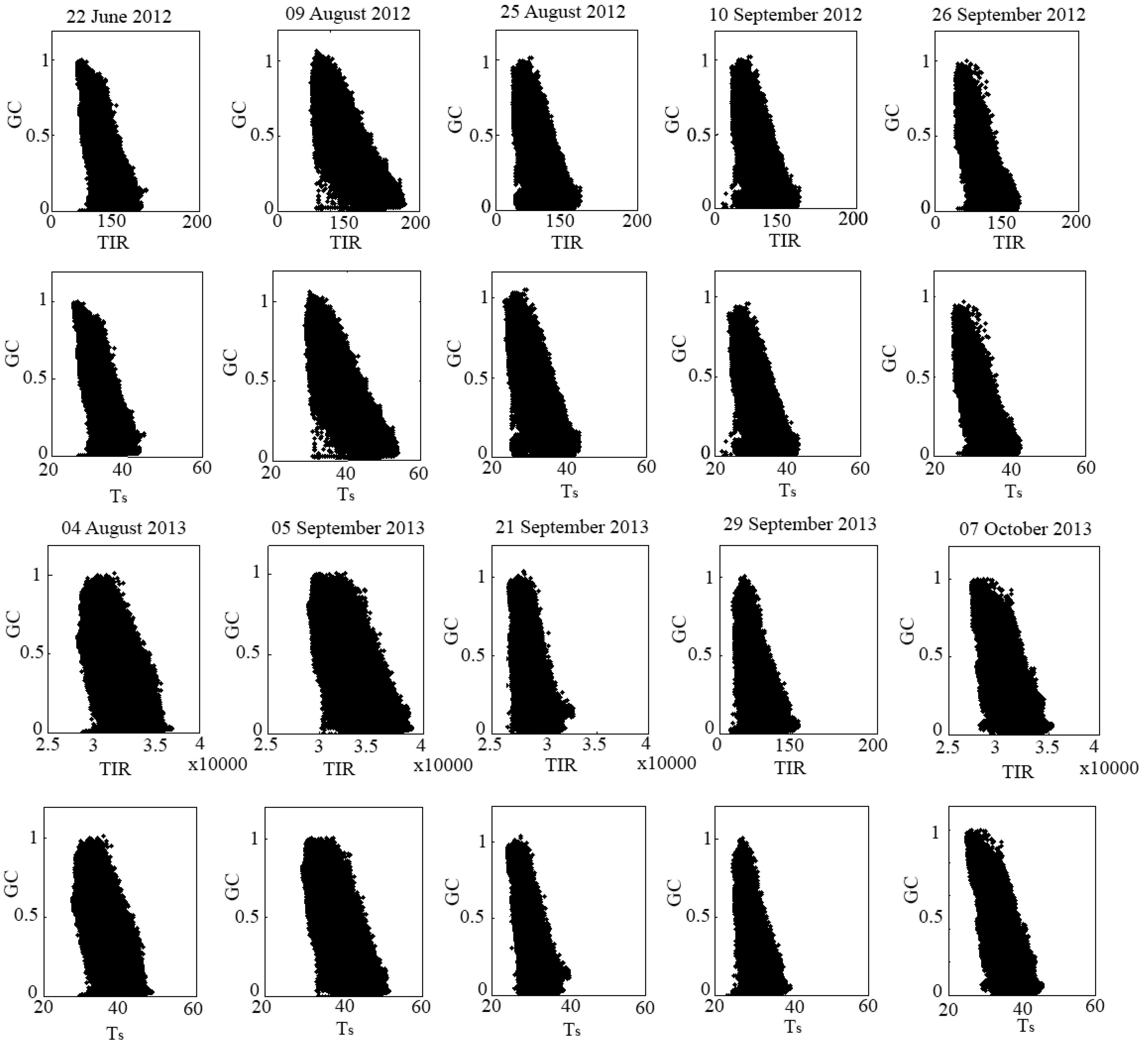
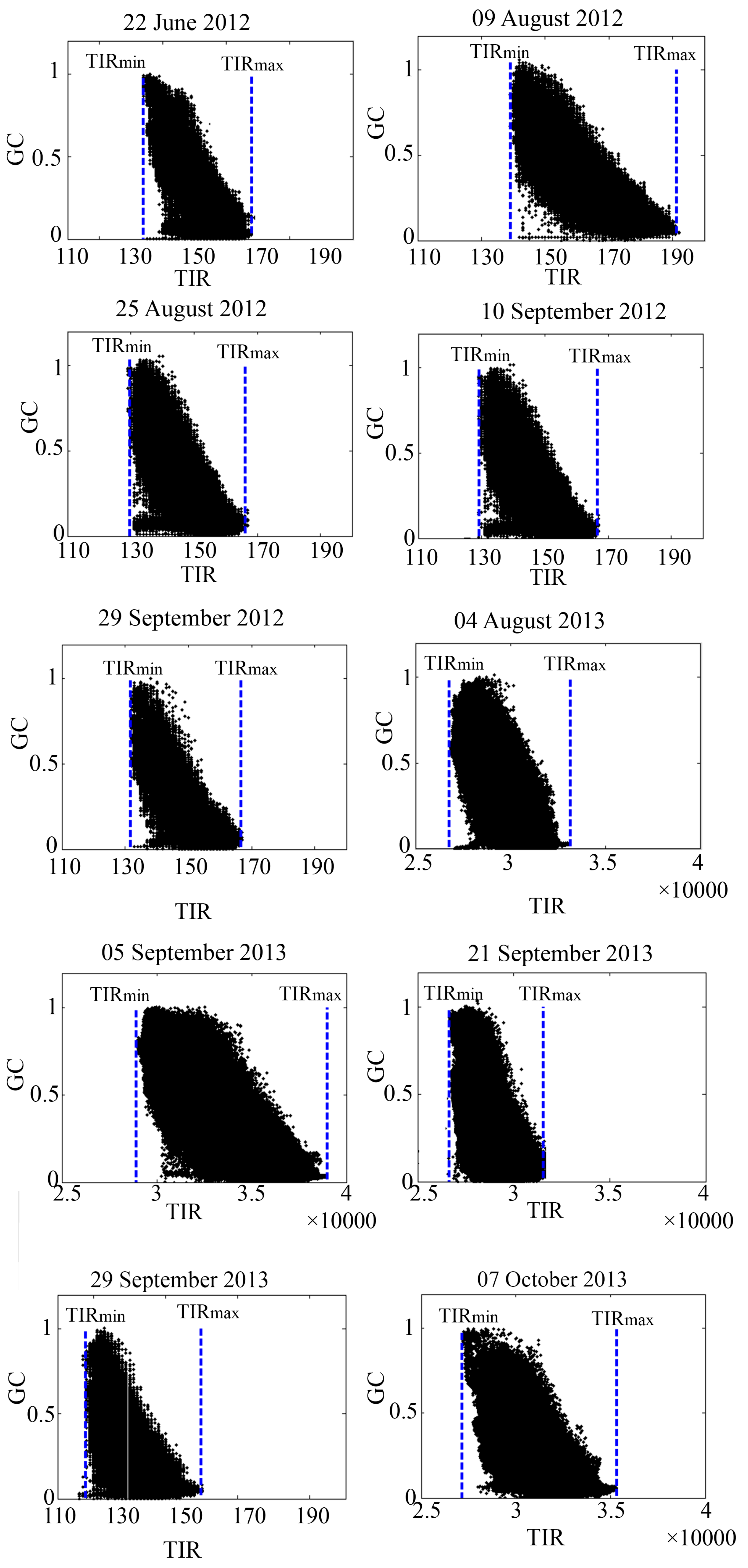
3.2. TIRnorm vs. Ts,norm
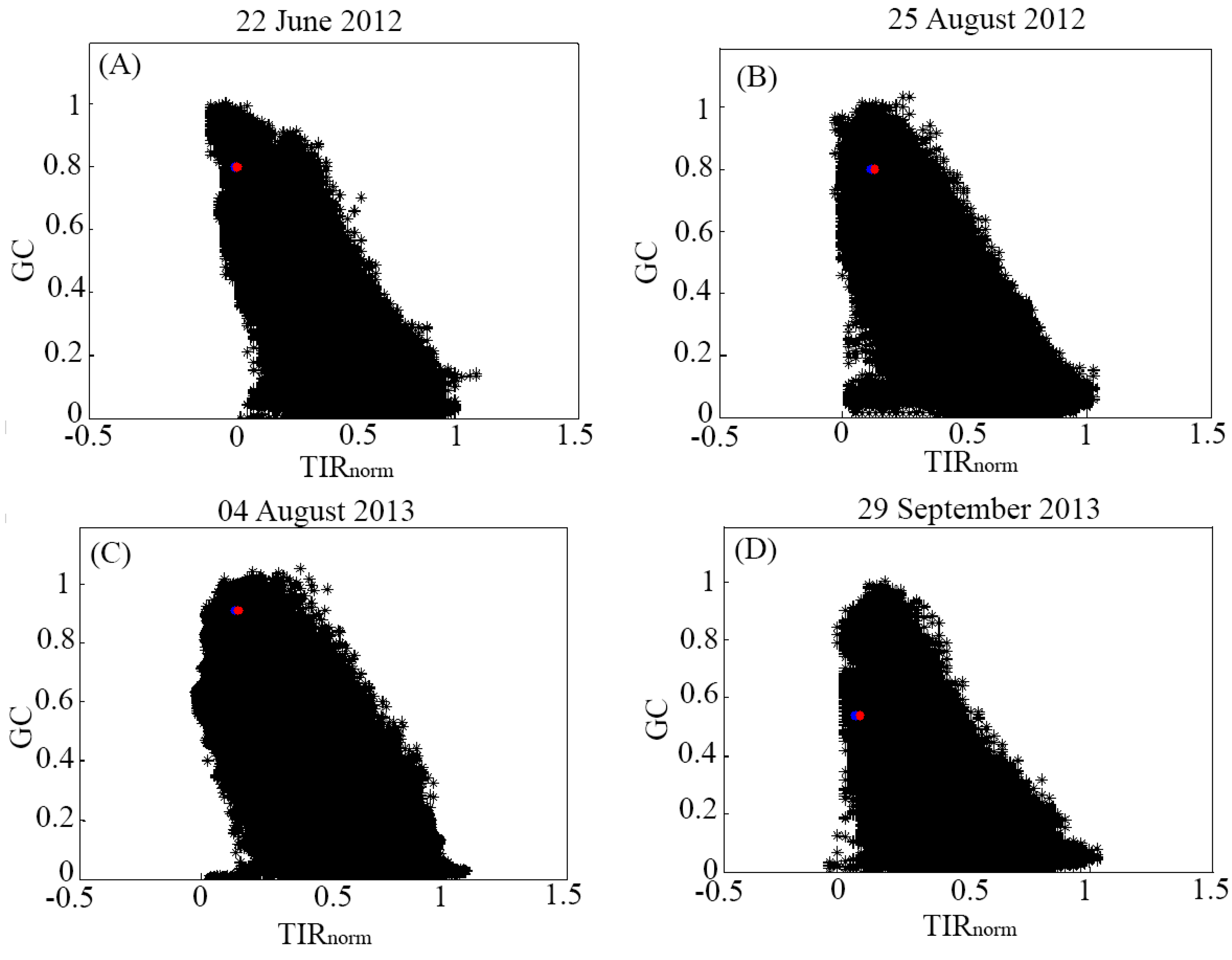
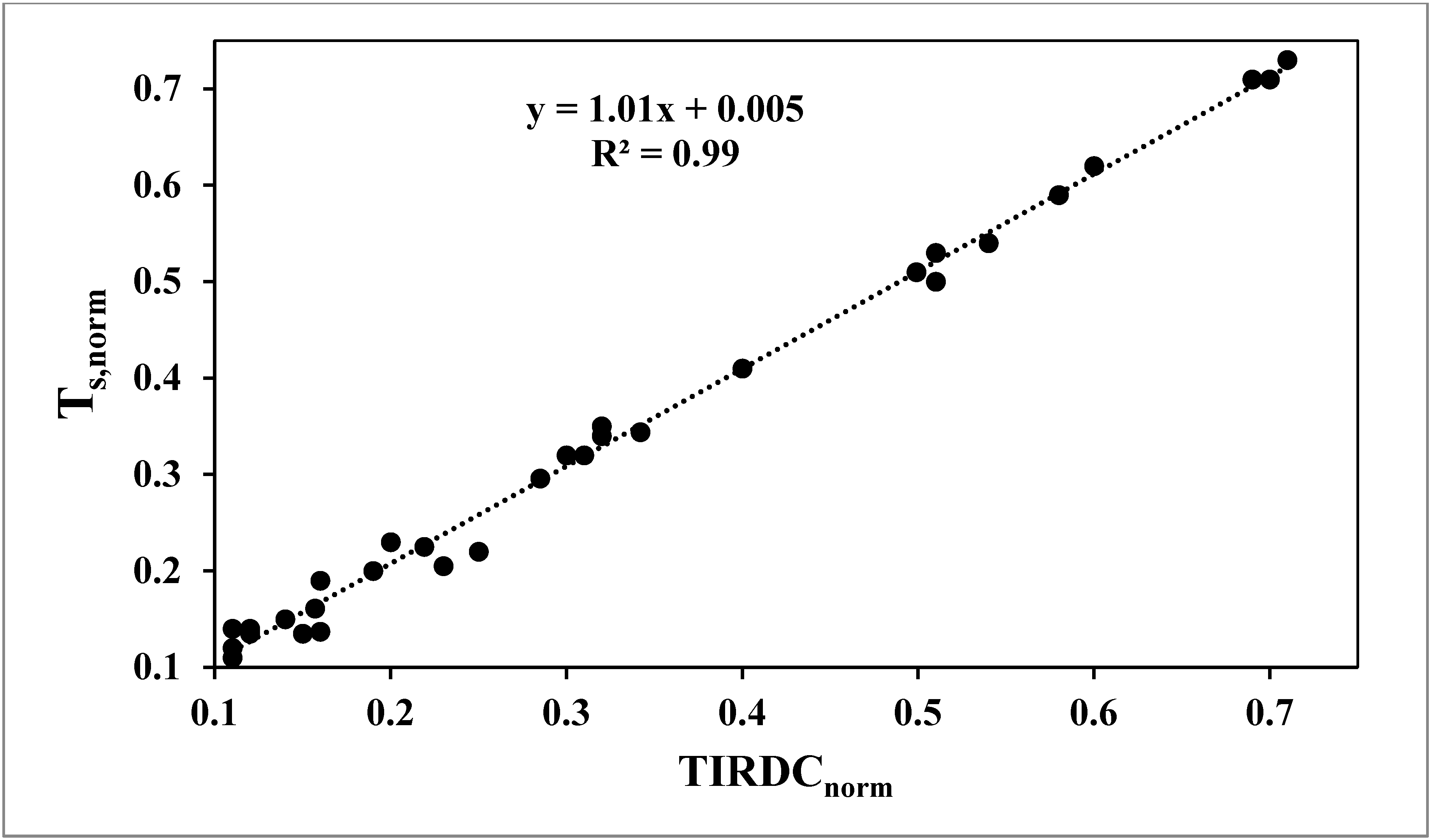
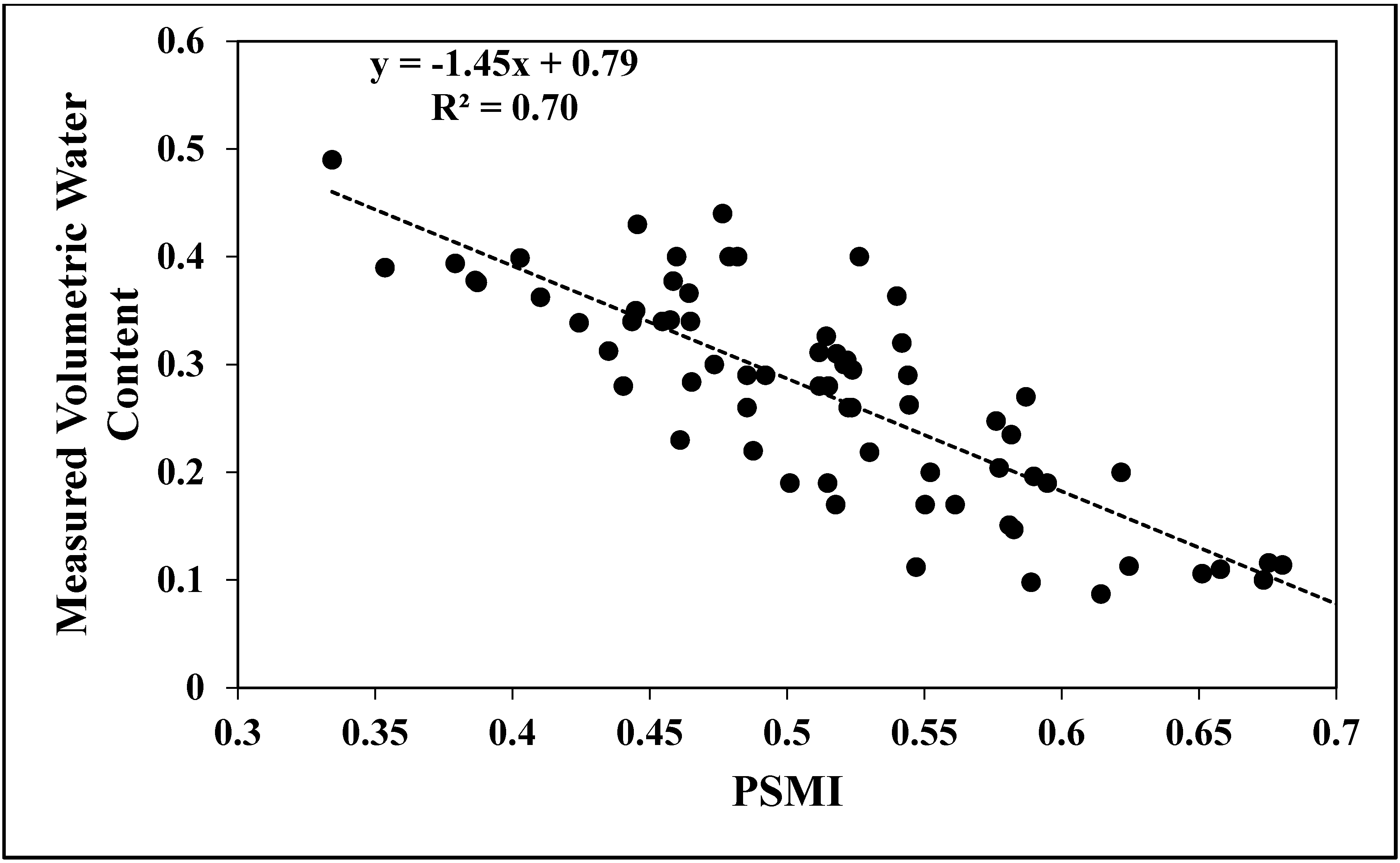
3.3. Comparison to Measured Soil Moisture

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajan, N.; Maas, S.J.; Kathilankal, J.C. Estimating crop water use of cotton in the Southern High Plains. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payero, J.O.; Tarkalson, D.D.; Irmak, S.; Davison, D.; Petersen, J.L. Effect of irrigation amounts applied with subsurface drip irrigation on corn evapotranspiration, yield, water use efficiency, and dry matter production in a semiarid climate. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Piccinni, G. Corn yield responses under crop evapotranspiration-based irrigation management. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Gourdji, S.M. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Boote, K.J.; Kimball, B.A.; Ziska, L.H.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Ort, D.; Thomson, A.M.; Wolfe, D. Climate impacts on agriculture: Implications for crop production. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemakumara, M.H. Aggregation and Disaggregation of Soil Moisture Measurements. Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Newcastle, Newcastle, NSW, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Goward, S.N.; Waring, R.H.; Dye, D.G.; Yang, J. Ecological remote sensing at Otter: Macro scale satellite observations. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Rüdiger, C.; Bitar, A.A.; Richaume, P.; Walker, J.P.; Kerr, Y.H. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture in Southeastern Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, W.W.; Veroustraete, F.; van der Sande, C.J.; Grootaers, I.; Feyen, J. Soil moisture retrieval using thermal inertia, determined with visible and thermal space borne data, validated for European forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Naeimi, V.; Scipal, K.; Jeu, R.D.; Fernandez, J.M. Soil moisture from operational meteorological satellite. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courault, D.; Seguin, B.; Olioso, A. Review on estimation of evapotranspiration from remote sensing data: From empirical to numerical modelling approaches. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Clarke, T.R.; Inoue, Y.; Vidal, A. Estimating crop water deficit using the relation between surface-air temperature and spectral vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.N.; Xue, Y.; Czajkowski, K.P. Evaluating land surface moisture conditions from the remotely sensed temperature/vegetation index measurements: An exploration with the simplified simple biosphere model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Anapashsha, R.; Kumar, S.; Saha, S.K.; Dadhwal, V.K. Assessing potential of MODIS derived temperature/vegetation condition index (TVDI) to infer soil moisture status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, B.P.; Berg, A.A.; Champagne, C.; Omasa, K. Estimation of soil moisture using optical/thermal infrared remote sensing in the Canadian Prairies. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N. An overview of the “triangle method” for estimating surface evapotranspiration and soil moisture from satellite imagery. Sensors 2007, 7, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Dodd, J.K.; Benjamin, S.G.; Cooper, J.N. Satellite estimation of surface energy balance, moisture availability and thermal inertia. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.; Heck, R.J.; Brenning, A.; Brown, R.; Miller, S. Remote sensing of soil moisture in vineyards using airborn and ground-based thermal inertia data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3729–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hain, C.R.; Mecikalski, J.R. Retrieval of an available water-based soil moisture proxy from thermal infrared remote sensing. Part I: methodology and validation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 665–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. The potential of remotely sensed data to infer surface soil moisture and evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V. Soil moisture at watershed scale: Remote sensing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasischke, E.S.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Johnstone, J.F. Assessing spatial and temporal variations in surface soil moisture in fire-disturbed black spruce forests in Interior Alaska using space borne synthetic aperture radar imagery—Implications for post-fire tree recruitment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupigny-Giroux, L.L. Using air MISR data to explore moisture-driven land use–land covers variations at the Howland Forest, Maine-A case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Valdez, M.C.; Chang, N.B.; Chang, L.Y.; Yuan, P.Y. Monitoring spatiotemporal surface soil moisture variations during dry seasons in central America with multisensor cascade data fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1939–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Liao, J.; Yang, S. Retrieving China’s surface soil moisture and land surface temperature using AMSR-E brightness temperatures. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 7, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.; Carlson, T.N.; Wooster, M.J.; Islam, S. A review of Ts/VI remote sensing based methods for the retrieval of land surface energy fluxes and soil surface moisture. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M. Estimation of evaporative fraction from a combination of day and night land surface temperatures and NDVI: A new method to determine the Priestley-Taylor parameter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, X. Using MODIS land surface temperature and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index products for monitoring drought in the Southern Great Plains, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.D.; Idso, D.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Pinter, P.J. Canopy temperature as a crop water stress indicator. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, G.; Bonnefond, J.M.; Chen, J.; Davis, K.; Desai, A.R.; Goldstein, A.H.; Gianelle, D.; Rossi, F.; et al. Global estimates of evapotranspiration and gross primary production based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1416–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, S.N.; Hope, A.S. Evapotranspiration from combined reflected solar and emitted terrestrial radiation: Preliminary FIFE results from AVHRR data. Adv. Space Res. 1989, 9, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, J.J.; Shi, P.J.; Yan, F. Modified triangle method to estimate soil moisture with Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) products. Int. Arc. Photogramm. 2008, 37, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, T.N. Triangle models and misconceptions. Int. J. Remote Sens. Appl. 2013, 3, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Tang, R.; Zhao, W.; Tang, B.; Wu, H.; Shao, K.; Li, Z.L. Surface soil water content estimation from thermal remote sensing based on the temporal variation of land surface temperature. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3170–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I.; Norgaard, A.; Fensholt, R.; Jensen, K.H. Combining the triangle method with thermal inertia to estimate regional evapotranspiration—Applied to MSG SEVIRI data in the Senegal River basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.L.; Li, Z.-L.; Chen, K.S. Validating MODIS-derived land surface evapotranspiration with in situ measurements at two AmeriFlux sites in a semiarid region. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.L.; Li, Z.-L.; Chen, K.S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W. Verification of land surface evapotranspiration estimation from remote sensing spatial contextual information. Hydrol. Process 2012, 26, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhong, S.; Qi, S. Soil moisture retrieval from MODIS data in Northern China Plain using thermal inertia model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3567–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Arthur, S.T. The impact of land use—Land cover changes due to urbanization on surface microclimate and hydrology: A satellite perspective. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2000, 25, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, D.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, Y.R.; Zhou, F. Estimate soil moisture using trapezoidal relationship between remotely sensed land surface temperature and vegetation index. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7, 8703–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.A.; Guo, W.; Jutla, A.S.; Senarath, S.U.S.; Ramsay, B.H.; Eltahir, E. A satellite-based daily actual evapotranspiration estimation algorithm over South Florida. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Scott, R.L.; Shang, S. Modeling evapotranspiration and its partitioning over a semiarid shrub ecosystem from satellite imagery: A multiple validation. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 073495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Singh, V.P. A two-source trapezoid model for evapotranspiration (TTME) from satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shang, S. A hybrid dual-source scheme and trapezoid framework–based evapotranspiration model (HTEM) using satellite images: Algorithm and model test. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2013, 118, 2284–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.A. Methodology for estimation of surface evapotranspiration over large areas using remote sensing observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2773–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.A. Estimation of surface evaporation map over Southern Great Plains using remote sensing data. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A simple interpretation of the surface temperature/vegetation index space for assessment of soil moisture status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.A. An intercomparison of regional heat flux estimation using remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, K.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Patel, N.K. Estimating volumetric surface moisture content for cropped soils using a soil wetness index based on surface temperature and NDVI. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, T.; Brown, J.; Hayes, M. A new approach for predicting drought-related vegetation stress: Integrating satellite, climate, and biophysical data over the U.S. central plains. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2005, 59, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.J.; Rajan, N. Estimating ground cover of field crops using medium-resolution multispectral satellite imagery. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S. Crop Stress. In Encyclopedia Earth Sciences Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Shafian, S.; Maas, S.J. Improvement of the Trapezoid method using raw Landsat image digital count data for soil moisture estimation in the Texas (USA) High Plains. Sensors 2015, 15, 1925–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafian, S. Estimation of soil moisture status in the Texas high plains using remote sensing. Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A.J.; Wiegand, C.L. Distinguishing vegetation from soil background. Photogram. Eng. Remote Sens. 1977, 43, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar]
- USGS science for a changing world. Available online: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 18 August 2014).
- Chander, G.; Markham, B. Revised Landsat-5 TM radiometric calibration procedures and post calibration dynamic ranges. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2674–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, A.R.; Holtslag, A.M. A remote sensing Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shafian, S.; Maas, S.J. Index of Soil Moisture Using Raw Landsat Image Digital Count Data in Texas High Plains. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2352-2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70302352
Shafian S, Maas SJ. Index of Soil Moisture Using Raw Landsat Image Digital Count Data in Texas High Plains. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(3):2352-2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70302352
Chicago/Turabian StyleShafian, Sanaz, and Stephan J. Maas. 2015. "Index of Soil Moisture Using Raw Landsat Image Digital Count Data in Texas High Plains" Remote Sensing 7, no. 3: 2352-2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70302352
APA StyleShafian, S., & Maas, S. J. (2015). Index of Soil Moisture Using Raw Landsat Image Digital Count Data in Texas High Plains. Remote Sensing, 7(3), 2352-2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70302352





