Abstract
Current spectrometer design and the increasingly affordable price of field hyperspectral sensors are making feasible their use for water quality monitoring. In this study, we parameterized a semi-analytical algorithm to derive constituent concentrations from field spectroradiometer measurements in ten freshwater reservoirs over two years. In contrast to algorithms parameterized for single airborne or satellite sensor deployments, we optimized the algorithm for robust performance across all reservoirs and for multi-temporal application. Our algorithm produced chlorophyll-a concentration estimates with a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 7.7 mg∙m−3 over a range of 4–135 mg∙m−3. The model also produced estimates of total suspended solids (TSS) concentration with an RMSE of 4.0 g∙m−3 over a range of 0–25 g∙m−3. Choosing a non-linear objective function during inversion reduced variance of residuals in chlorophyll-a and TSS estimates by 20 and 18 percentage points, respectively. Application of our algorithm to two years of data and over ten study sites allowed us to specify sources of suboptimal parameterization and measure the non-stationarity of algorithm performance, analyses difficult for short or single deployments. Suboptimal parameterization, especially of backscatter properties between reservoirs, was the greatest source of error in our algorithm, accounting for 17%–20% of all error. In only one reservoir was time-dependent error apparent. In this reservoir, decreases in TSS over time resulted in less TSS estimate error due to imperfect model parameterization. For future applications, especially with ground-based sensors, model performance can easily be improved by using non-linear inversion procedures and replicating spectral measurements.
1. Introduction
Despite the advantages of airborne and satellite hyperspectral sensors, in situ or handheld sensors still have an important role to play in water quality monitoring efforts. The large geographical coverage of airborne and satellite imaging spectrometers has made them useful for measuring global and regional water quality, especially in the determination of concentrations of water constituents such as phytoplankton, suspended sediment, and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) [1,2,3]. However, in tropical regions, frequent cloud cover and unpredictable weather constrain the use of airborne and satellite optical sensors [4]. Additionally, hyperspectral satellite sensors used for water quality retrieval often have coarse spatial resolution that can be unsuitable for small or narrow water bodies [5], and use of airborne sensors to monitor these regions can be prohibitively expensive. Conversely, while in situ hyperspectral sensors lack synoptic coverage, they also lack these associated disadvantages and their use is becoming increasingly popular due to their decreasing cost, their high spectral resolution, and flexibility in their method of deployment and measurement setup [6].
Compared with airborne and satellite sensors, field hyperspectral sensors can more cheaply and rapidly perform repeated measurements over an extended time period, and thus have utility for exploring the temporal dynamics of water constituents [6,7] and spatio-temporal variability in bio-geochemical properties [8]. Deploying them for this purpose, however, requires that any algorithm used to process their data be robust to changes in measurement conditions and viewing geometry [9,10] and optical variability of water constituents over the entire deployment area and time period [7,8]. Compared with more conventional algorithms optimized for relatively short airborne or satellite sensor deployments (e.g., [2,3]), for long term deployments of field sensors, changes in measurement conditions, such as solar zenith angle, cloud cover and water waves, can be major sources of error in measurements of remote sensing reflectance [10,11]. Additionally, developing algorithms to produce results whose accuracy is invariant to water constituent variability is especially important for eutrophic lakes, where, for example, chlorophyll-a concentrations in near-surface waters can vary by an order of magnitude within one day [7].
In this paper, we introduce a semi-analytical (SA) algorithm to retrieve concentrations of chlorophyll-a (chl-a) and total suspended solids (TSS) from optically-deep water. In contrast to previous algorithms parameterized for single airborne sensor flights over a study area with constrained variability, we optimized our algorithm for rapid deployment and long term monitoring of water quality in ten of Singapore’s freshwater reservoirs. We identified potential improvements of algorithm performance through two procedures: (1) comparison of four error functions used during inversion of remote sensing reflectance for their ability to return accurate concentrations of water constituents and overcome common sources of error; and (2) perform a full accounting of sources of error in the parameterized algorithm to identify weaknesses and determine if algorithm accuracy deteriorated with time. By applying our algorithm for two years of data and over ten study sites, we were able to examine model performance as a function of time and identify specific algorithm parameters as causes of error, analyses that are more difficult or impossible for studies with narrow spatio-temporal focus.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Deriving Reflectance and Accounting for the Air–Water Interface
Remote sensing reflectance, Rrs, measured over a water body can be defined as in Simis and Olsson [10]:
where λ represents wavelength dependence, θv is the viewing zenith angle, ϕv is the azimuth angle between the viewing direction and the azimuth angle of the sun, Lu is upwelling radiance above the water surface, Lsky is sky radiance incident on the water surface, ρ is a surface reflectance term determining how much sky radiance is reflected off the water surface and into the radiometer, and Ed is downwelling irradiance incident on the water surface. Lu is measured directly by the radiometer, and in the case of satellite or airborne sensors, Lsky and Ed are often generated using radiative transfer software. In our case, and in the case of in situ radiometers, Lsky and Ed can be measured directly. As made explicit in Equation (1), radiance and ρ values are dependent on the specific viewing geometry from which they are measured. It is assumed in Equation (1) and throughout this paper that ρ and Lu are estimated or measured with the same θv and ϕv, and Lsky is measured with the same geometry, but with θv mirrored in the horizontal plane. From this point on we treat these terms as implicit to improve readability.
In this paper, we adopt the terminology of Lee et al. [12,13], where Rrs refers to the ratio of upwelling radiance to downwelling irradiance measured just above the water surface, and subsurface remote sensing reflectance, rrs, refers to the same ratio translated through the air–water interface.
Surface reflectance, ρ, is strongly affected by waves (and thus wind speed), viewing/solar geometry, and sky conditions [10,14]. In this study, we employ two methods for estimating ρ. The first uses a Fresnel reflectance model, as detailed in de Haan and Kokke [15], and the second uses simulations of reflectance as carried out by Mobley [14]. Mobley [14] calculated that a surface reflectance term of 0.028 was optimal for an off-nadir viewing angle of 40° and azimuth angle of 135° from the sun, while Fresnel reflectance is often considered accurate enough for nadir-viewing sensors. However, the 0.028 value was calculated for a simulated clear sky with wind speeds less than or equal to 5 ms−1 or a uniformly overcast sky under a range of wind speeds. If these assumptions are violated, for example by the presence of variable cloud cover, the true value of ρ could deviate by a factor of two or more [14]. Recent research has developed more advanced methods to accurately estimate ρ, but these methods are restricted by assumed water type [16], or have had limited success and require further validation [10]. For simplicity, in this paper the Mobley correction and Fresnel reflectance correction are used for 40° and 0° viewing angles, respectively.
After removing the sky radiance contribution, Rrs can be converted to rrs using a Fresnel reflection-based physical model as detailed in de Haan and Kokke [15] and Mobley [17], taking into account transmittance through the air–water interface in both directions, the spherical albedo of water from below the surface, the level of diffusion of the above-water light field, and solar and viewing geometry. The parameters for this physical model can either be calculated for the specific measurement setup and environmental conditions [18,19] or estimated from a large number of radiative transfer simulations [3,12]. The requisite geometry and environmental conditions of our field measurements were well known, so the former method was used. This method assumes that the water surface can reasonably be modeled as flat. This assumption is often inaccurate for oceanic applications and at higher spatial resolution of sensors, but on small inland lakes the likelihood of extensive error is reduced due to the smaller size of waves.
Using this Fresnel reflection-based correction for the air–water interface requires knowledge or estimation of the ratio of upwelling irradiance to upwelling radiance below the water surface, Q. The term Q has been found to have some wavelength dependence [20], but most approximations assume it is constant over visible wavelengths. Often, the value of Q is taken from the literature and assumed constant, but it can also be approximated as in Gons [11]:
where is the average cosine of the downwelling light field above the water, θs is the solar zenith angle, and F is the ratio of diffuse to total irradiance incident on the water surface between 400 and 700 nm. Gons [11] modeled the downwelling cosine assuming the light field was isotropic when the sky was clear or had variable cloud cover and cardioidal when the sky was overcast. Here we assume that the sky always has variable cloud cover, as this is more often the case in Singapore than complete overcast skies. We compare this approximation with a literature value of 3.5 taken from Morel et al. [20].
2.2. Relating Remote Sensing Reflectance to Inherent Optical Properties
Sub-surface remote sensing reflectance, an apparent optical property (AOP) of water is related to the inherent optical properties (IOPs), or absorption, backscattering, and attenuation, of the water column using a formulation introduced by Gordon et al. [21]:
where rrs is remote sensing reflectance just below the surface, bb(λ) is the backscatter coefficient of water molecules and particles in the water column, a(λ) is the absorption coefficient of all water constituents, and li are free parameters. The li coefficients have been determined from extensive radiative transfer or Monte Carlo simulations [12,21,22] and are assumed accurate enough for many different applications [23,24,25,26]. There are other models used to relate reflectance to IOPs (e.g., see [9,27]), but we examine only this common version using values for li (l1 = 0.084, l2 = 0.170) taken from Lee et al. [13].
Note that most of the above simplifications and summary of single-scattering theory are valid for optically deep water alone. See Lee et al. [12] for the full optically-shallow water equations.
2.3. Modeling Inherent Optical Properties
Absorption and backscattering in semi-analytical algorithms are considered well-defined by the sum of the individual absorption and backscatter properties of the water constituents, each scaled by the concentration of that constituent. The four constituents assumed to contribute to absorption in the water column are water molecules, phytoplankton, total suspended solids (TSS) such as suspended sediment or biotic debris, and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM). CDOM is assumed to contribute negligibly to backscatter, so its effect on backscatter is ignored. The absorption and backscattering caused by water molecules are assumed known and constant. The IOPs are defined by:
where aw is the absorption coefficient of pure water, bbw is the backscatter coefficient of pure water, Ci is the wavelength-independent concentration of constituent i, and ai* and bbi* are the absorption and backscattering coefficients of constituent i per unit of concentration. The pure water properties aw and bbw are taken from Smith and Baker [28] and Pope and Fry [29], respectively, with the latter replaced by values from Buiteveld et al. [30] for wavelengths greater than 700 nm.
The concentration-normalized absorption and backscattering coefficients, or specific inherent optical properties (SIOPs), are idealized for phytoplankton, TSS, and CDOM. Phytoplankton and TSS specific backscatter coefficients are modeled as a function of wavelength according to a common power law exponent model [19,31,32,33]:
where bb*TSS is the specific backscattering coefficient of TSS, bb*PHY is the specific backscattering coefficient of phytoplankton, λ0 is a reference wavelength, here set to 542 nm for both constituents, and YTSS and YPHY are slope parameters for TSS and phytoplankton, respectively. Due to a lack of the specialized equipment required to measure backscatter, in this algorithm, bbPHY*(542) was taken from Brando et al. [19], while bbTSS*(542) was optimized as in Section 3.5.
The absorption coefficients for CDOM and TSS are modeled according to an exponential model first introduced by Jerlov [34]:
where a*CDOM is the specific absorption coefficient of CDOM, a*TSS is the specific absorption coefficient of TSS, λ0 is a reference wavelength, set to 440 nm for both CDOM and TSS and SCDOM and STSS are slope parameters for the exponential equation. Specific absorption at the reference wavelengths and the slope parameter for both constituents are measured as in Section 3.4. In this study, a*CDOM(440) is set to one and thus the optimization produces CDOM absorption at 440 nm, not concentration.
The entire visible spectrum of the phytoplankton specific absorption coefficient, a*PHY(λ), is directly measured in the lab from samples collected in the field, as in Section 3.4. In this study phytoplankton absorption is normalized by chl-a concentration so that rrs inversion retrieves chl-a concentration.
2.4. Inversion of Reflectance
To employ the bio-optical algorithm described in Equations (3)–(7), rrs needs to be inverted to retrieve water constituent concentrations. Some early bio-optical algorithms employed linear matrix inversion, treating the inversion problem as a linear least-squares optimization [18,35]. More recent efforts have concentrated on a variety of non-linear optimization algorithms (for a review see [26]). Despite this switch to more advanced optimization methods, many authors still use simple error, or objective functions based on the sum of squared error (SSE) or mean squared error (MSE) to measure the disparity between measured and modeled rrs during optimization [2,3,25,26,36,37]:
where s and n are the starting and ending wavelength bands of the spectra, respectively, rmeas is measured rrs, and rmodel is modeled rrs. However, these statistics only measure the amplitude differences between the two curves. Through Equations (1)–(3), respectively, relating Lu to IOPs requires values of ρ, Q, and two li coefficients. These parameters can contain a significant amount of uncertainty for unfavorable field conditions or multi-temporal applications. Any error in ρ, Q, or li will cause amplitude differences between the modeled and measured rrs(λ). If these differences are small or the algorithm is applied only over a short period of time, error introduced by these parameters can be assumed to be uniform across the reflectance data collected. If sufficient data regarding wind speed, sky conditions, and the ambient light field are available they can be used to adjust ρ or Q to produce more accurate results, as discussed in Mobley [14] and Gons [11], respectively.
However, if the algorithm is to be used over a significant time period, or without accurate data regarding ambient weather and sky conditions, ρ and Q will change with changing light field and the error introduced into the optimization will be unquantifiable, i.e., one would be unable to estimate the correct parameters and how far they deviate from those used in the algorithm. Additionally, as discussed in Brando et al. [19], as the magnitude of modeled rrs increases so does SSE for the same percentage change as at a lower magnitude. If a wide range of rrs magnitudes is expected, such as for multi-temporal applications or in waters with highly variable constituent concentrations, using SSE or MSE as an objective function could be a major source of error. To reduce this chance of error, Brando et al. [19] introduced to their objective function a measure of the relative fit between modeled and measured rrs based on the shape of their curves. They used the spectral angle mapper (SAM) [38], which measures the angle between the two spectra when treated as vectors in n-dimensional space, where n is the number of bands considered. Here we consider a similar method, the spectral multiple correlation mapper (SCM) [39], based on the Pearson’s correlation coefficient, that has the slight advantage over SAM of being able to distinguish negative from positive correlation between two spectral shapes. SCM ranges in values from −1, indicating perfect negative correlation, to 1, indicating perfect positive correlation.
where is rrs averaged over all wavelengths being considered. We evaluate four objective functions incorporating SSE and SCM to determine their relative applicability for multi-temporal reflectance inversion: SSE, (1 − SCM), SSE + (1 − SCM), and SSE × (1 − SCM).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
This study collected water and spectral samples from 10 of Singapore’s 17 freshwater reservoirs. All of Singapore’s reservoirs have anthropogenic origins, having been created either through the damming of natural river or wetland habitats or through the excavation of artificial lakes. The oldest was created in the 1860s by British colonial administrators, while construction of the two newest reservoirs was only completed in 2011. Most of the reservoirs are relatively shallow with a maximum depth across all reservoirs of 22 m and a minimum of 2 m [40]. With surface areas 59–750 ha, the reservoirs drain small, mainly urban catchments 360–5400 ha large [41]. Three of the reservoirs visited for this study are located within lowland forest in Singapore’s Central Nature Reserve. Many of the reservoirs support recreational activities, with golf courses adjacent to five of the reservoirs studied and most circumscribed with running/walking trails and public gardens. Singapore’s Public Utility Board (PUB) actively manages the reservoirs, primarily for drinking water, often shunting water between reservoirs or to the ocean as needed to maintain water levels and avoid flooding. PUB also maintains artificial mixing systems in many of the reservoirs to maintain dissolved oxygen levels above 3 g∙m−3 [40]. Phosphate and nitrate levels vary widely, between <0.01 and 1.5 g∙m−3 [40]. The sampling was undertaken over two years, from June 2011 to August 2013. Not every reservoir was sampled every month as access was predicated on work being done by an associated lab.
The reservoirs exhibited a wide range of apparent optical properties, but could be classified mainly as Case 2 waters, as defined by Morel and Prieur [42]. Even in the Case 2 waters, however, phytoplankton concentrations were often high and strongly affected the apparent optical properties. It was hoped that by including water bodies with such different optical properties in our analysis, the algorithm results would be more generalizable, as Case 2 waters are considered more difficult to model than Case 1 and often restrict the usefulness of a given algorithm to a particular locality or water type [11,22,43,44].
For security reasons, each reservoir has been assigned a random number between one and ten. Individual reservoirs will be referred to using this number for all further analysis.
3.2. Remote Sensing Reflectance Measurements
Radiance measurements were recorded using a handheld spectroradiometer, model HH2 (Analytical Spectral Devices (ASD), Inc., Boulder, CO, USA), with 10-degree field of view. Radiometric calibration of the sensor was performed by ASD using NIST-traceable standards before deployment. Irradiance and reflectance uncertainty ranged from 2.3% to 3.6% over the measured wavelength spectrum. The spectroradiometer records radiance in bands spaced every nanometer for wavelengths 325–1075 nm, with a bandwidth of less than 3 nm. Rrs was obtained by normalizing upwelling radiance with downwelling irradiance estimated using a standard Spectralon panel with known reflectance. All Rrs measurements were made using two viewing geometries, one at-nadir and one with a 40° zenith view angle and azimuth angle of 135° from the direction of the sun, as suggested by Mobley [14]. Three replicate measurements were made at each viewing angle for each sample point and averaged to minimize measurement error. All Lu(λ) radiance measurements were made from a boom extending 1.5 meters from the side of the boat and roughly 0.3 meters above the surface of the water to avoid shading effects from the boat or equipment. Measurements of diffuse downwelling irradiance were made using a Spectralon reflectance panel while blocking direct solar irradiance. Sky radiance was also directly recorded for each measurement at corresponding view angles. The sky radiance and air–water interface corrections were applied as detailed in Section 2.1 to retrieve rrs (Figure 1).
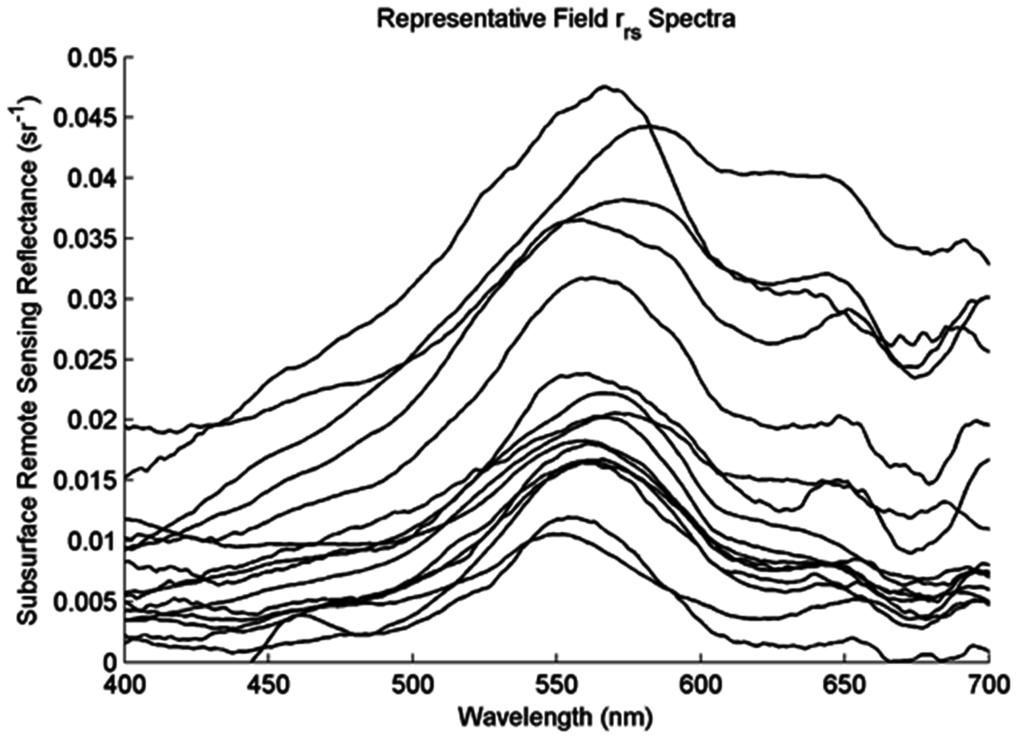
Figure 1.
Representative rrs spectra in Singapore’s reservoirs. Spectra were drawn randomly from all collected spectra measured with an at-nadir view angle.
Figure 1.
Representative rrs spectra in Singapore’s reservoirs. Spectra were drawn randomly from all collected spectra measured with an at-nadir view angle.
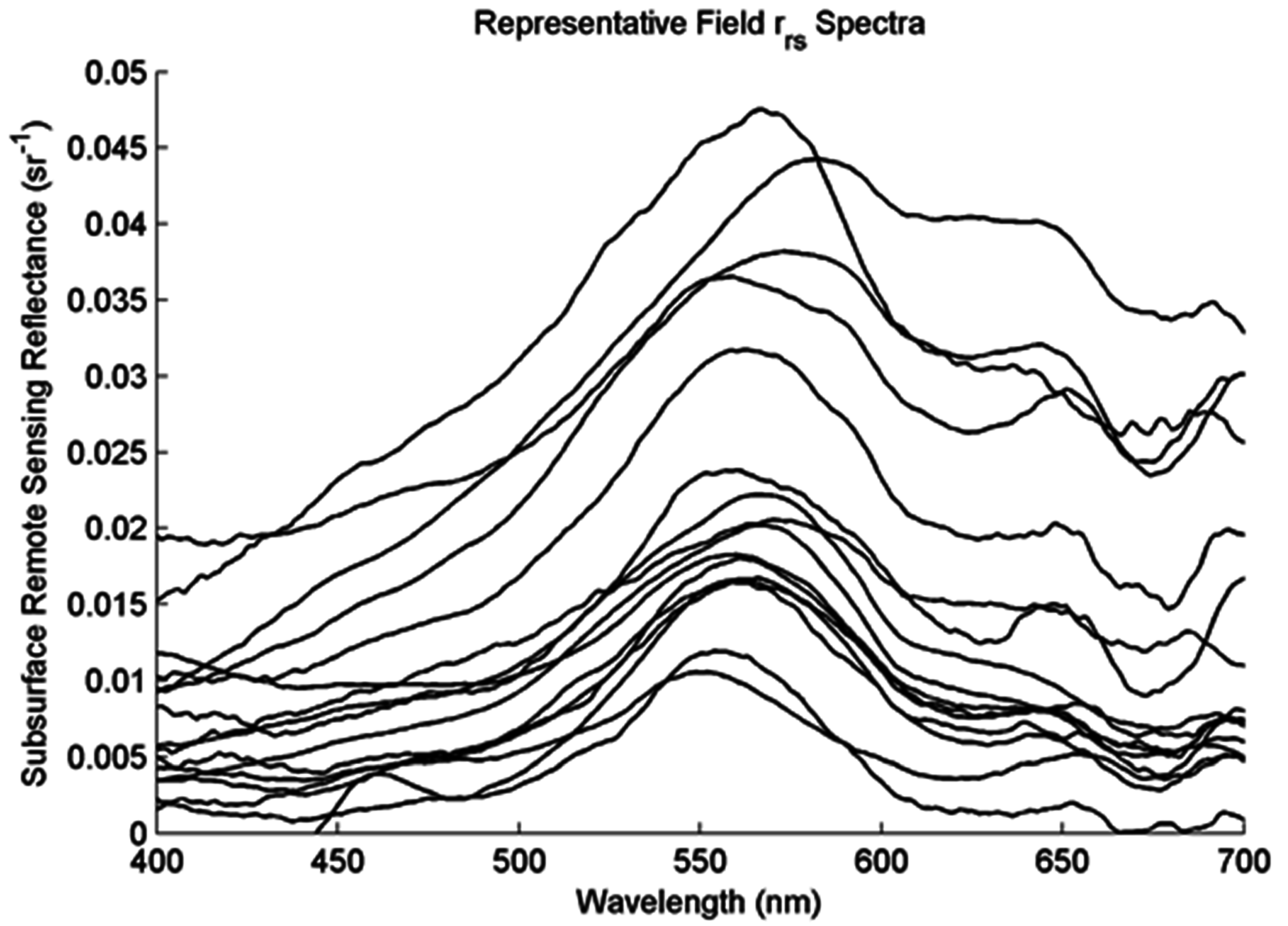
Many measurements had high frequency noise because of variable cloud cover and the sensor’s low signal-to-noise ratio when measuring highly absorbing water. This noise and its effect on algorithm outputs are analyzed in Section 4.6.2.
3.3. Constituent Concentrations
Water samples were collected immediately after every reflectance measurement (Figure 2). Two liters of water were collected 0.3 m below the water’s surface using a PVC horizontal bottle sampler and were immediately put on ice and stored out of light until they could be filtered through Whatmann GF/F fiber-glass filters using a low-vacuum filtration system. Filter papers were then stored frozen until chl-a concentration could be determined spectrophotometrically using United States EPA method 446.0 [45]. All water samples were filtered within 8 h of collection and chl-a concentration measured in duplicate 500 mL samples within one week of filtration.
Total suspended solids (TSS) concentration of water samples was measured gravimetrically according to APHA [46]. For each of two duplicates, at least 500 mL of each water sample was filtered through pre-ashed and pre-weighed fiber glass filters. These filters were then dried in an oven at 103 °C for one hour, weighed, and the process repeated until concurrent measurements agreed within 0.2 mg to obtain the mass of total suspended solids.
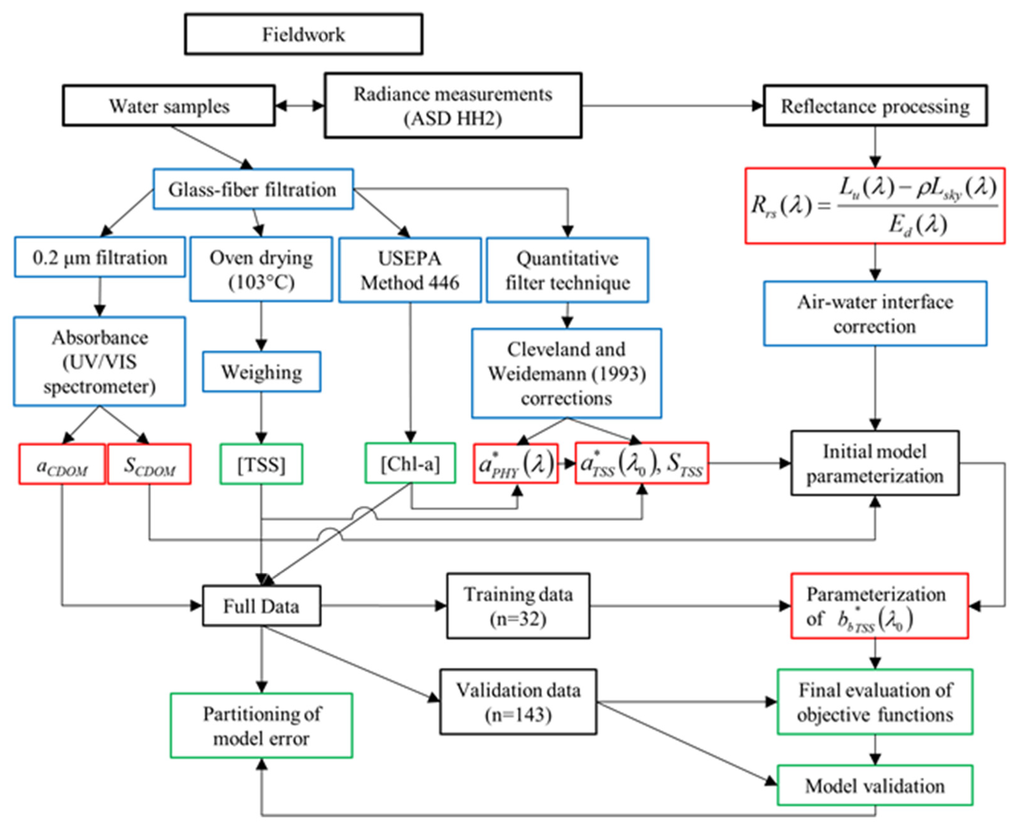
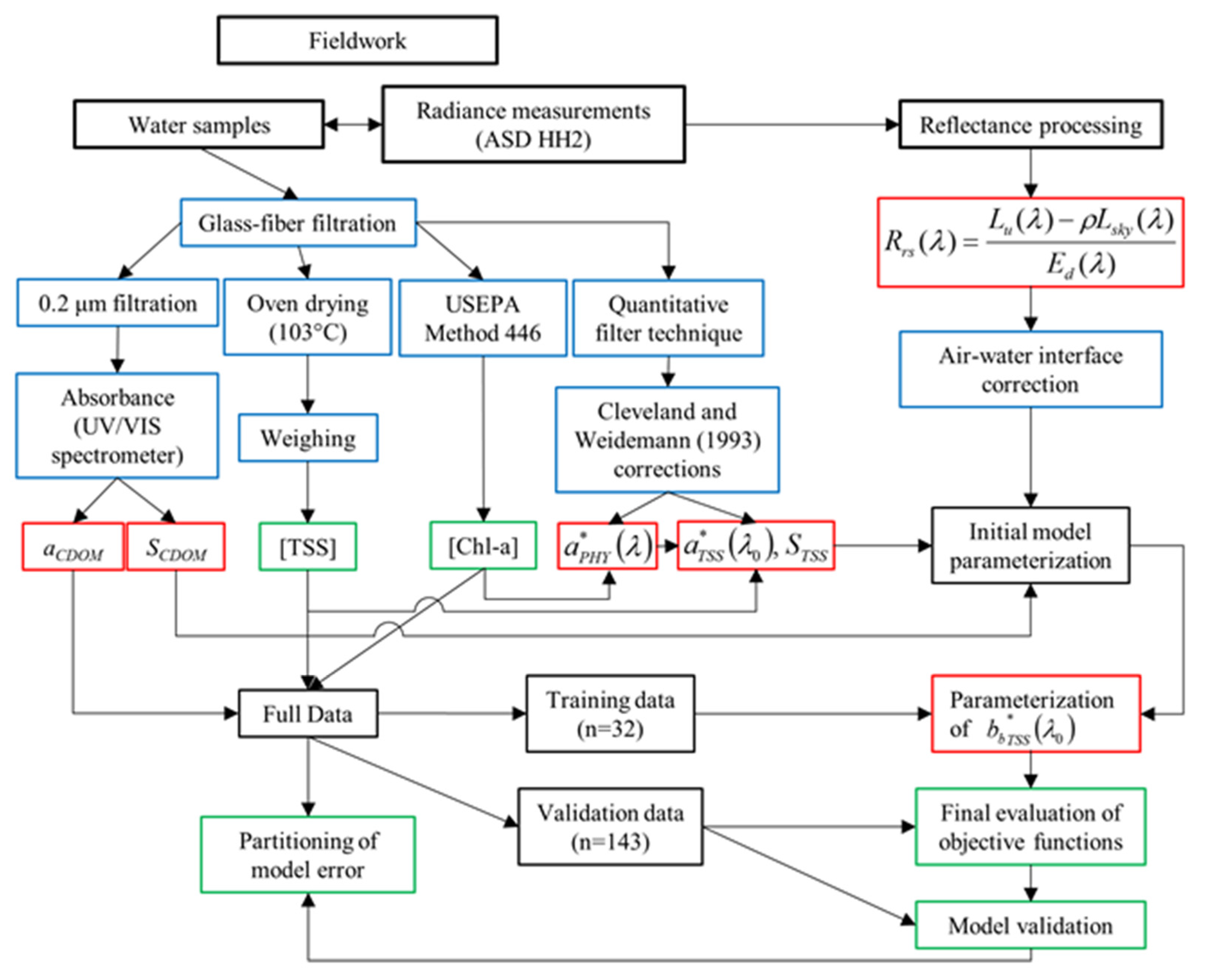
Figure 2.
Full workflow used to collect and process field data, optimize and validate the semi-analytical algorithm, and perform statistical analyses. Green outlines refer to final products, red outlines to optical parameters, and blue outlines to intermediate processing steps. [TSS] and [Chl-a] refer to the concentrations of total suspended solids and chlorophyll-a, respectively.
Figure 2.
Full workflow used to collect and process field data, optimize and validate the semi-analytical algorithm, and perform statistical analyses. Green outlines refer to final products, red outlines to optical parameters, and blue outlines to intermediate processing steps. [TSS] and [Chl-a] refer to the concentrations of total suspended solids and chlorophyll-a, respectively.
3.4. Water Constituent SIOPs
In June–August 2013, an additional liter of water was collected at each sample point in the field and specific absorption coefficients for TSS and phytoplankton were measured using the quantitative filter technique [47], applying the multiple-scattering correction equations of Cleveland and Weidemann [48]. For each of two duplicate measurements, 500 mL of water sample were filtered onto GF/F filters using a low-vacuum filtration system. The optical density of the filtered samples was measured using an integrating sphere attached to the ASD handheld spectroradiometer, using a xenon lamp as the light source. Filters were pressed against the sample port of the integrating sphere and light from the xenon lamp projected through the filters with a custom flange blocking all ambient light from entering the system. Blank reference filters from the same batch as the sample filters were wetted with post-filtration water samples and measured the same way. After phytoplankton absorption was determined, pigments were extracted by soaking the filters for an hour in 90% methanol as in Kishino et al. [49] and the filters again measured in the same manner for TSS absorption. The TSS absorption parameters a*TSS(λ0) and STSS in Equation (7) were then determined by fitting an exponential curve to the data and averaged for all training samples in each reservoir. Phytoplankton absorption determined through QFT was normalized by chlorophyll-a concentration to produce a*PHY(λ).
CDOM absorption was determined by measuring the absorbance of water samples filtered through 0.2 µm nylon filters and converting to absorption coefficients as in Clementson et al. [50] and Oubelkheir et al. [8]:
where A is absorbance as a function of wavelength, in nanometers, with A(750) subtracted in the numerator to adjust for backscatter, and lpath = 0.01 m is the path-length of the quartz cell used in the Shimadzu UV/VIS spectrophotometer. To obtain SCDOM, aCDOM(λ) was then normalized by aCDOM(440), as in Brando et al. [19], and fitted with an exponential curve of the form Equation (6). However, we found that after filtering through 0.2 µm filters, CDOM absorption barely registered above our spectrophotometer’s detection limits. This, coupled with the facts that TSS absorption and CDOM absorption are often indistinguishable during remote sensing [1], and that the absorption due to material between 0.7 µm and 0.2 µm in diameter is unaccounted for with these methods, led us to ignore CDOM absorption in our constituent retrievals. We allow this parameter in the algorithm to account for absorption not accounted for by the other constituents during inversion, but do not evaluate its estimates for accuracy.
The correct specialized equipment were not available to directly measure specific backscattering of phytoplankton and TSS, so bb*TSS(542) was determined separately through algorithm optimization, as detailed in Section 3.5.
3.5. Bio-Optical Algorithm Parameterization
The SA algorithm was initially parameterized as in Table 1 [12,19] and backscattering properties were initially set to values taken from Brando et al. [19]. A recent study has shown that choice of non-linear solver does not have a large impact on results for a given objective function [26]. Here we use the Sequential Quadratic Programming solver in the MATLAB Optimization Toolbox [51], a constrained optimization procedure that requires maximum and minimum values for each output variable. The maximum bounds for all constituents were set to at least 10% more than the maximum measured over the two year study period. Minimum bounds were all set to zero, and initial estimates of each constituent were set to the midpoint of their modeled range. To optimize the algorithm for multi-temporal use, we followed the procedure outlined in Figure 3. Essentially, we optimized the algorithm using chl-a and TSS concentrations collected in June–August 2013, and then tested the fully parameterized algorithm on the previous two years’ data.

Table 1.
Initial Parameters used in the full semi-analytical algorithm.
| Initial Parameterization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Value | Source | Constituent | Range |
| YTSS | 0.681 | [19] | Chl-a | 0–150 mg∙m−3 |
| SCDOM | 0.014 | This study | ||
| STSS | 0.007 | This study | TSS | 0–30 g∙m−3 |
| aCDOM(λ0) | 440 nm | [12] | ||
| aTSS(λ0) | 440 nm | [12] | CDOM | 0–5 m−1 |
| bbTSS λ0 | 542 nm | [19] | ||
| a*PHY(λ) | Variable | This study | ||
| a*TSS(λ0) | 0.06–0.15 m2∙g−1 | This study | ||
| a*CDOM(λ0) | 1 | N/A | ||
| bb*TSS(λ0) | 0.054 m2∙g−1 | [19] | ||
| Start wavelength | 400 nm | N/A | ||
| End wavelength | 725 nm | N/A | ||
| End wavelength | 725 nm | N/A | ||
After initial parameterization, we simultaneously determined the best-performing objective function, expression for Q, and a*PHY(λ). To perform this determination, we ran the algorithm on the 2013 training set data for every combination of two viewing angles, two expressions for Q (Table 2 [11,20]), four objective functions, and 15 a*PHY(λ) spectra measured in the lab, for a total of 240 modeling runs. For each run we calculated the coefficient of determination, R2, between modeled and actual concentrations of both chl-a and TSS. We wanted the final algorithm to be applicable for both viewing angles and concentrations of both chl-a and TSS, so we averaged the R2 values across viewing angles and both constituents. The best set of objective function, Q expression, and a*PHY(λ) spectrum was chosen as the set that produced the minimum averaged R2 across out of all modeling runs. To best adapt the algorithm for multi-temporal use, we wanted to minimize the effect variables dependent on the time of day or sun angle could have on optimization. We also hypothesized that the objective function used to evaluate rmodel relative to rmeas would have a large impact in minimizing these effects.
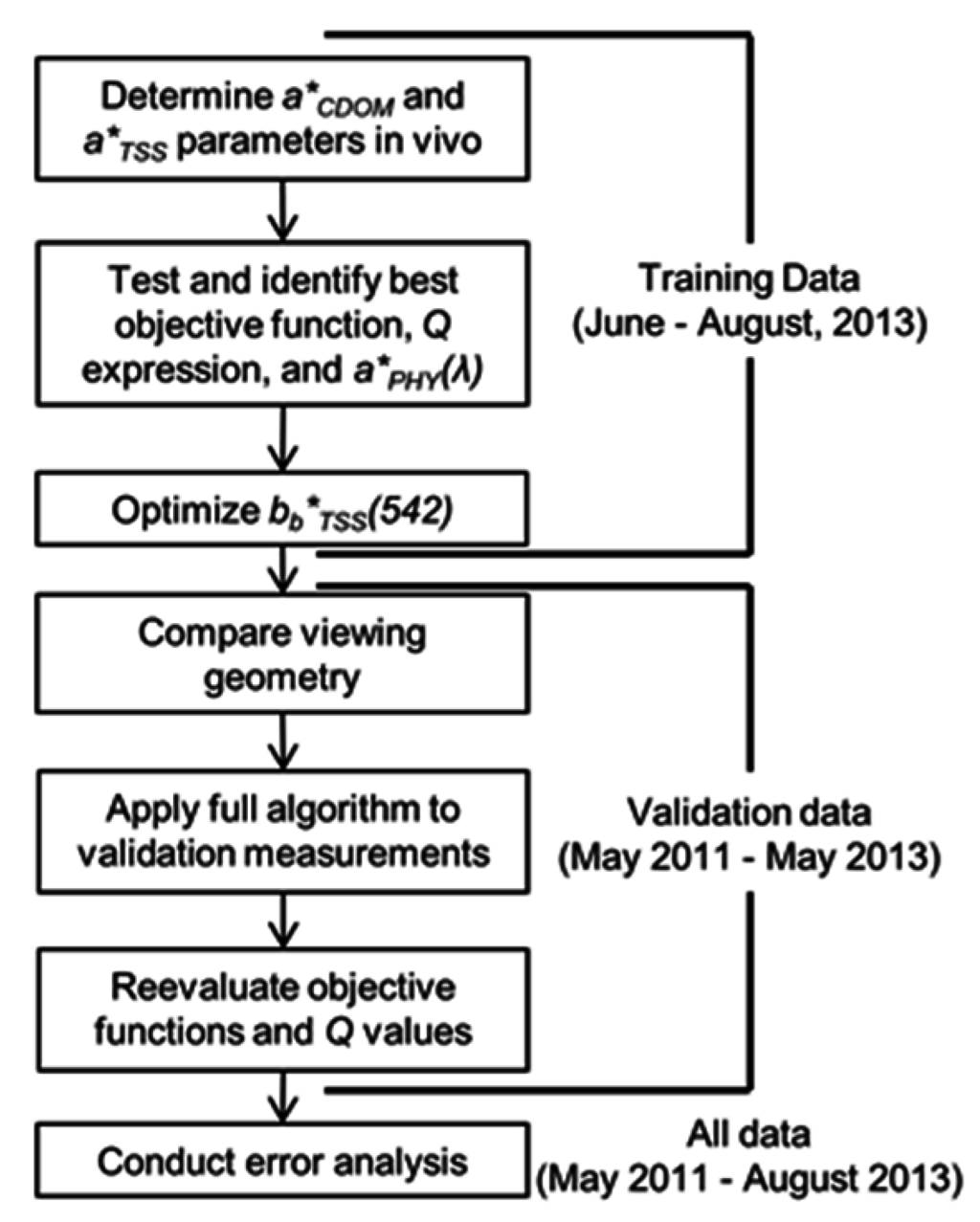
Figure 3.
Separation of data for algorithm parameterization, validation, and partitioning of error.
Figure 3.
Separation of data for algorithm parameterization, validation, and partitioning of error.
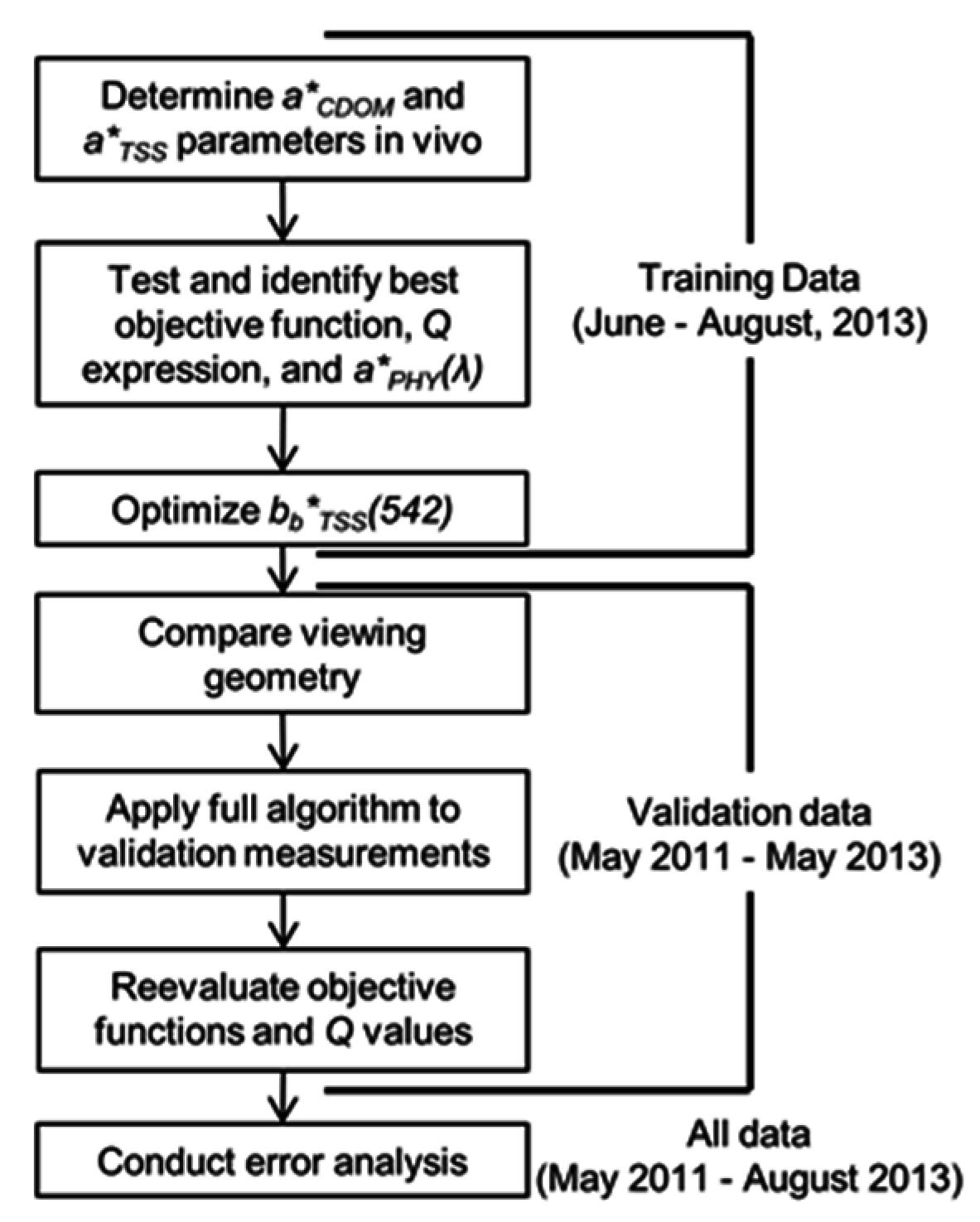

Table 2.
Abbreviations used for evaluation of best-performing Q.
| Abbreviation | Expression for Q |
|---|---|
| SET_Q | Q = 3.5 [20] |
| VAR_Q | [11] |
After choosing the objective function, Q expression, and a*PHY(λ), bb*TSS(542) was estimated through optimization. To perform the optimization of bb*TSS(542) the full SA optimization algorithm was altered to estimate only aCDOM(440) and bb*TSS(542) with chl-a and TSS concentrations set to values measured in the field for each rrs spectrum in the training set. Thus a separate, optimal, bb*TSS(542) value was produced for each spectrum. The optimized bb*TSS(542) values were then averaged over all reservoirs and that single average used for all further modeling. The relative accuracies of the two viewing geometries were then compared with the fully parameterized algorithm. Finally, the objective functions and Q expressions were reevaluated with the full algorithm and for all training and test data.
Unless otherwise stated, all calculations, modeling, algorithm runs, and optimization described in Section 3.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4 and Section 3.5 were performed in MATLAB v7.13 (The MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA, 2011).
3.6. Statistical Analysis
To conduct a thorough sensitivity analysis of the algorithm, we built a series of linear models to elucidate sources of error. Unless otherwise noted, for all statistical analyses in Section 4 we report the results of F tests on Type III sums of squares [52]. This test accounts for the effects of each independent variable relative to all others and is therefore conservative in attributing significance to individual relationships between dependent and independent variables. All effects reported as significant are done so with 95% confidence (p < 0.05). Where necessary, we used square root or natural log transformations to normalize the distributions of variables and fulfill assumptions of normality. The coefficient of determination (R2) is interpreted as the proportion of variance in the dependent variable explained by all of the independent variables, while comparisons of R2 and adjusted R2 statistics can be used as a heuristic to determine and remove the influence of degrees of freedom or over-fitting [53].
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Characterization of Reservoirs
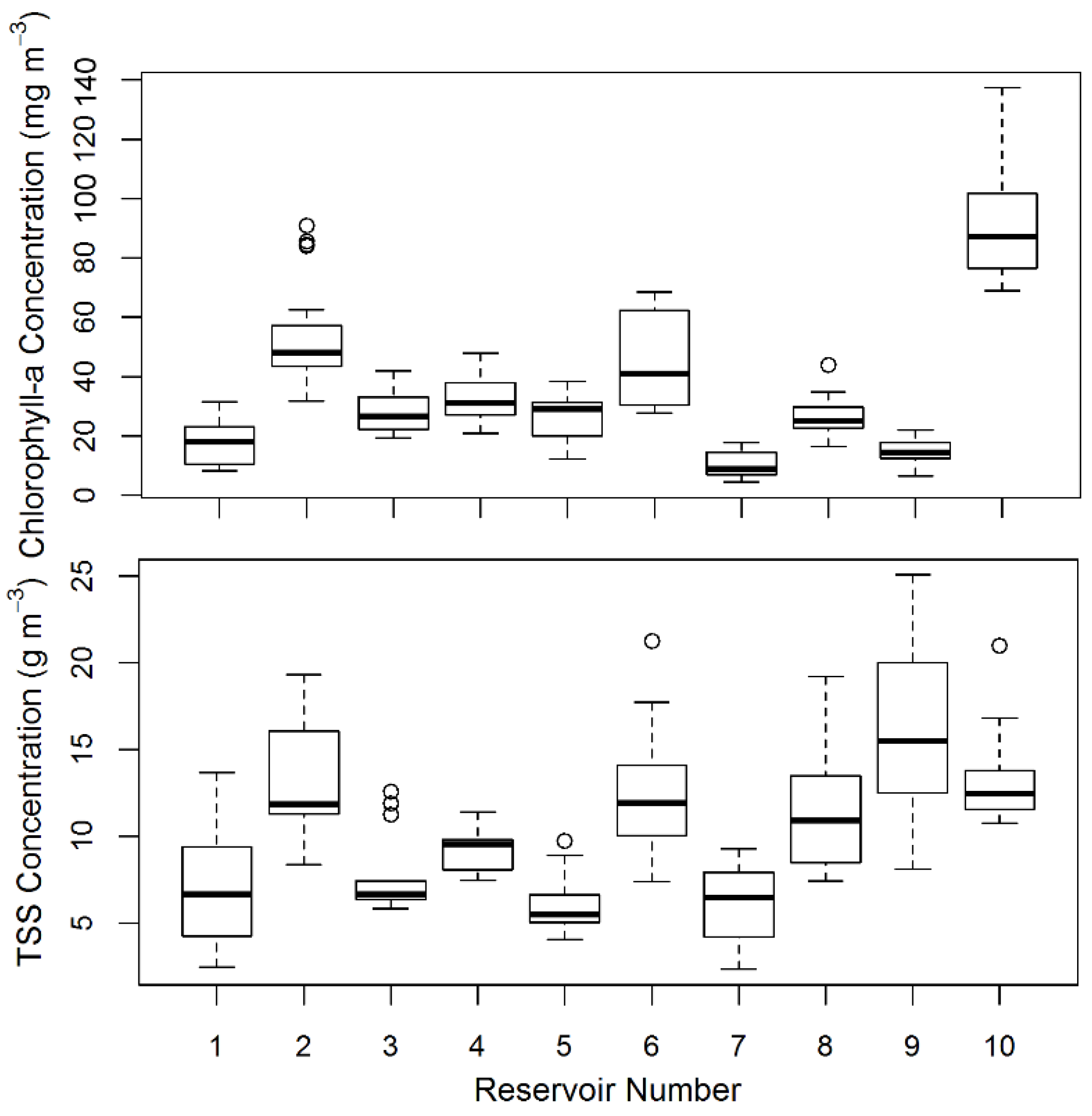
Chl-a and TSS concentrations varied widely between reservoirs (Figure 4). Chl-a ranged from 4.4 mg∙m−3 to 137.3 mg∙m−3 while TSS concentrations ranged from 0.89 g∙m−3 to 25.06 g∙m−3. Within each reservoir chl-a concentration did not vary much, except in Reservoirs 6 and 10, which also had the largest absolute chl-a values. In contrast, TSS concentration had wide variability in most reservoirs, with Reservoir 9 containing by far the highest concentration and range of TSS. We performed a rough analysis of trends in the reservoirs over time, using linear models of constituent concentrations as a function of month since the start of sampling as a proxy for time. There were no trends across all reservoirs for either constituent. However, within individual reservoirs there were some significant shifts. Within Reservoirs 2 and 3, chl-a increased significantly from May 2011 to August 2013, each by 100% to roughly 40 and 80 mg∙m−3, respectively (p < 0.001). Within Reservoirs 4 and 7, chl-a concentrations decreased significantly, roughly 50% to 25 mg∙m−3 (p = 0.01) and 7 mg∙m−3 (p < 0.001), respectively. A fully factorial linear model between chl-a concentration and reservoir crossed with month explained 90% of total variance in all reservoir chl-a data (p < 0.001; adj. R2 = 0.89). As for TSS, in Reservoir 7 concentrations dropped by about 50% to 3.5 g∙m−3 (p < 0.001). The linear model between TSS and reservoir crossed with month only explained 62% of the variance in TSS data (p < 0.005; adj. R2 = 0.58). Overall, the variability and time-dependent shifts in constituent concentrations in our dataset make it very useful in determining components of error and trying to correct for algorithm deterioration over time.
Figure 4.
Concentrations of TSS and chl-a in all reservoirs collected throughout the study period. The boxplots represent first quartile, median, and third quartile. Whiskers represent 95% confidence interval of data, and open circles represent outliers.
Figure 4.
Concentrations of TSS and chl-a in all reservoirs collected throughout the study period. The boxplots represent first quartile, median, and third quartile. Whiskers represent 95% confidence interval of data, and open circles represent outliers.
4.2. Parameterizing Objective Function, Q, a*PHY(λ), and bb*TSS(542)
The results from the initial analysis of objective functions and Q expression are displayed in Figure 5, but only for the best performing a*PHY(λ), which was obtained from Reservoir 2 water samples (Figure 6). The literature-derived Q with the objective function (1 − SCM) + SSE had the best performance. Representative lab-measured a*PHY(λ) spectra, including the one finally chosen, are shown in Figure 6. The specific absorption spectrum that produced the best results has four prominent peaks at 440, 490, 625, and 680 nm, which reflect concentrations of chl-a, chlorophyll-c, and carotenoids. Most of the specific absorption spectra measured shared these peaks, although some appeared to have additional accessory pigments and pigments in different relative quantities (Figure 6).
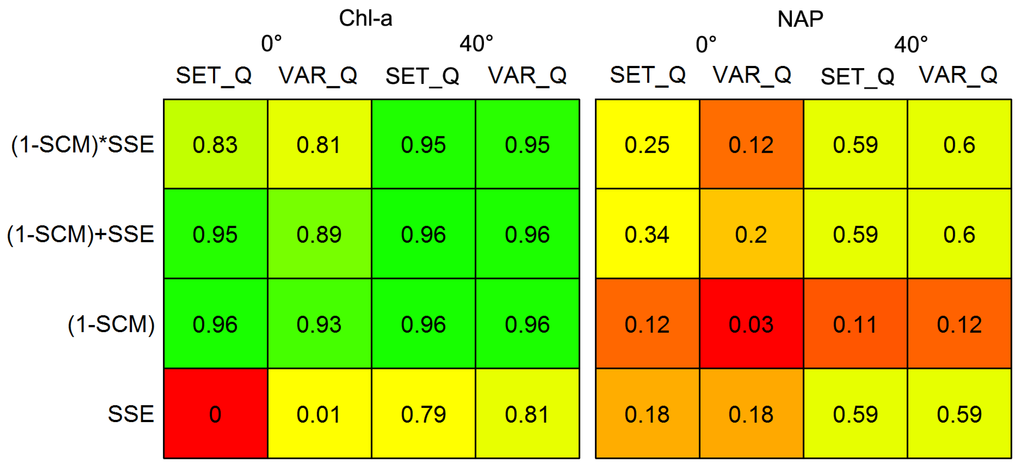
Figure 5.
R2 values between modeled and measured constituent concentrations produced by every combination of Q from Table 2, objective function, and viewing angle.
Figure 5.
R2 values between modeled and measured constituent concentrations produced by every combination of Q from Table 2, objective function, and viewing angle.
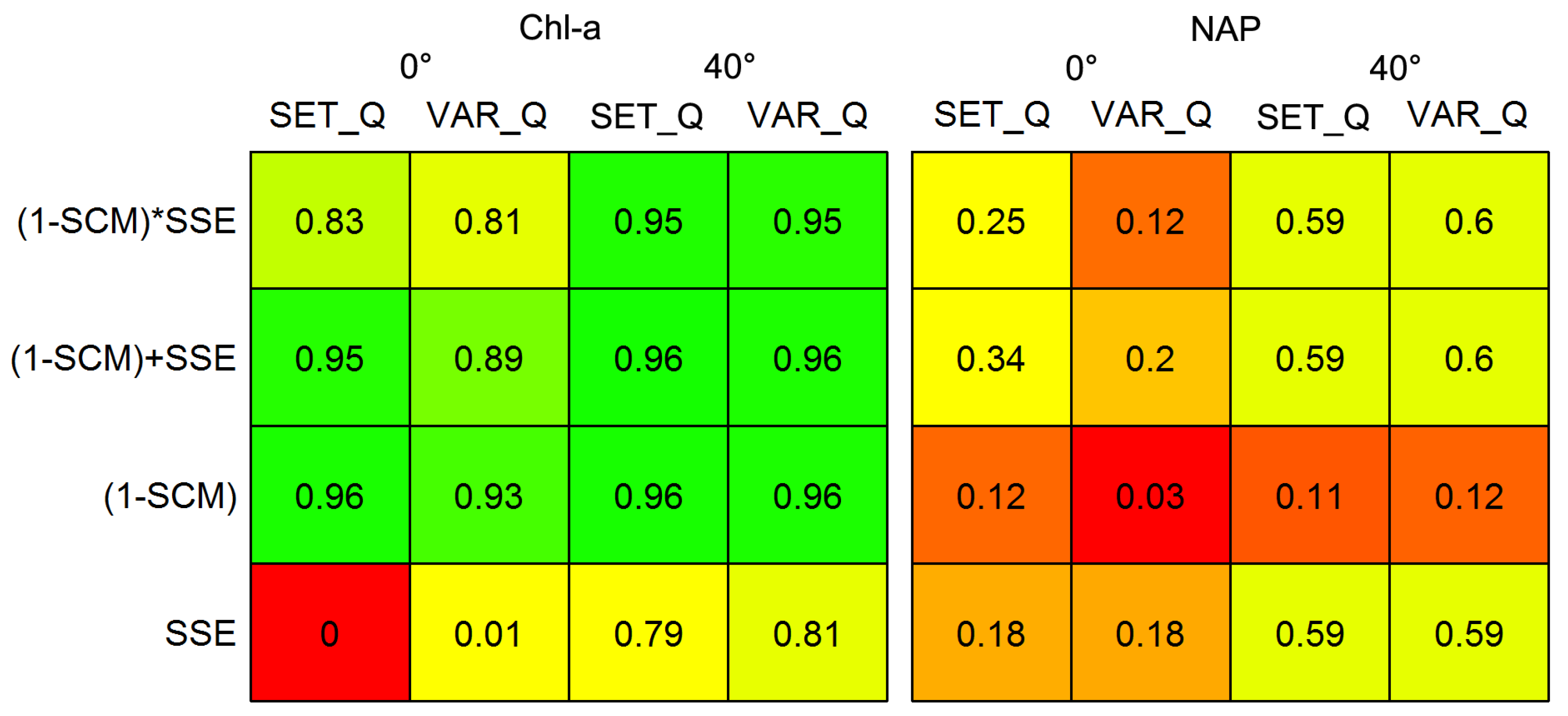
Figure 6.
Representative specific absorption coefficient spectra of phytoplankton assemblages in Singapore’s reservoirs. The specific absorption coefficient measured in Reservoir 2 was chosen for our algorithm.
Figure 6.
Representative specific absorption coefficient spectra of phytoplankton assemblages in Singapore’s reservoirs. The specific absorption coefficient measured in Reservoir 2 was chosen for our algorithm.
Using the chosen objective function, Q expression, and a*PHY(λ), we optimized bb*TSS(542) to produce the most accurate TSS concentrations possible. The median bb*TSS(542) estimated this way for all reservoirs equaled 0.0144 m2 g−1 (±0.008 m2 g−1).
4.3. Comparison of View Angles
After parameterization, we compared the algorithm results when applied to spectra collected with an at-nadir viewing angle to results from spectra collected at a 40° zenith angle. We found that the 40° viewing angle produced more accurate TSS estimates, with a TSS concentration retrieval R2 of 0.68 compared to an R2 of 0.40 for the at-nadir viewing angle. Both view angles produced the same R2 for chl-a retrievals. The algorithm was then applied to 40° viewing angle data for the rest of our statistical error and objective function comparative analyses. Our finalized parameterization of the full SA algorithm is outlined in Table 3 [12,19] and the results from this algorithm applied to the training data set can be seen in Figure 7. We calculated the root mean squared error (RMSE) for both constituents. Our algorithm achieved an RMSE of 7.7 mg∙m−3 for chl-a concentration and an RMSE of 3.0 g∙m−3 for TSS concentration.

Table 3.
Final parameterization of full semi-analytical model.
| Final Parameterization | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | Value | Source |
| YTSS | 0.681 | [19] |
| SCDOM | 0.014 | This study |
| STSS | 0.007 | This study |
| aCDOM λ0 | 440 nm | [12] |
| aTSS λ0 | 440 nm | [12] |
| bbTSS λ0 | 542 nm | [19] |
| a*PHY | Spectrum (Figure 6) | This study |
| a*TSS | 0.06–0.3 m2∙g−1 | This study |
| a*CDOM | 1 | N/A |
| bb*TSS | 0.0147 m2∙g−1 | This study |
| Start wavelength | 400 nm | N/A |
| End wavelength | 725 nm | N/A |
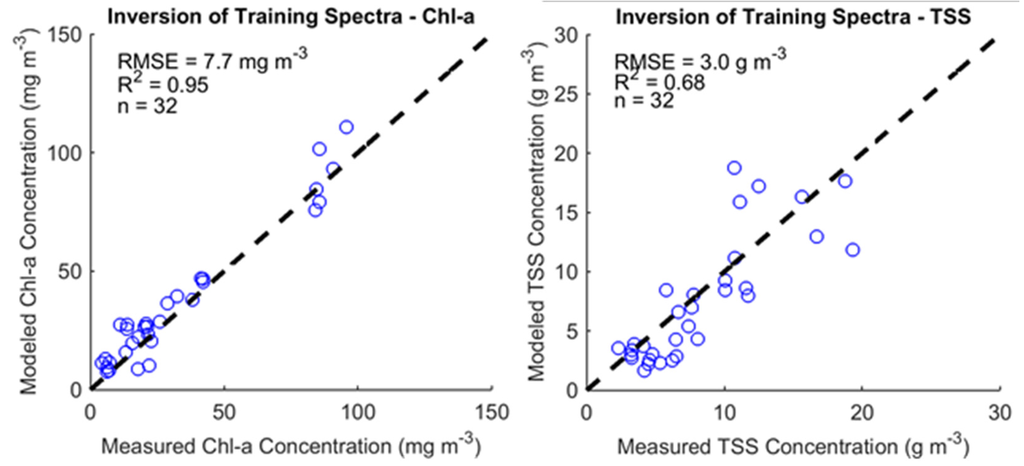
Figure 7.
Results from the inversion of training spectra to obtain chl-a and TSS concentrations. The dotted black line indicates 1:1 correspondence. n is the number of samples displayed. R2 is the coefficient of determination calculated for each sub-plot data.
Figure 7.
Results from the inversion of training spectra to obtain chl-a and TSS concentrations. The dotted black line indicates 1:1 correspondence. n is the number of samples displayed. R2 is the coefficient of determination calculated for each sub-plot data.
4.4. Applying SA Algorithm to All Available Data
After we parameterized our algorithm, we applied it to all data for the study period that was not used for training (Figure 8). Compared to the results in Figure 7, there was a decrease in accuracy. RMSE of the chl-a estimates remained at 7.7 mg∙m−3 and the RMSE of the TSS estimates increased to 4.0 g∙m−3. RMSE was also calculated separately for all available data, for both at-nadir and 40° viewing angles (Table 4).
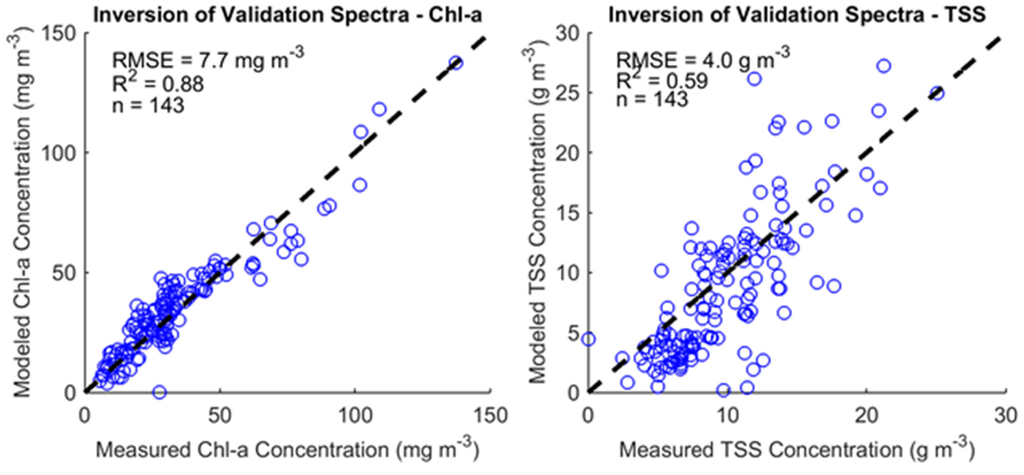
Figure 8.
Results from the inversion of validation field spectrometer spectra. The dotted black line indicates 1:1 correspondence. n is the number of samples displayed. R2 is the coefficient of determination calculated for each sub-plot data.
Figure 8.
Results from the inversion of validation field spectrometer spectra. The dotted black line indicates 1:1 correspondence. n is the number of samples displayed. R2 is the coefficient of determination calculated for each sub-plot data.

Table 4.
RMSE of constituent estimates for all runs.
| Chl-a RMSE (mg∙m−3) | |||
| Viewing Angle | Optimized Algorithm—Training Data | Optimized Algorithm—Validation Data | Optimized Algorithm—All Data |
| 0° | 9.2 | 10.5 | 10.3 |
| 40° | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.7 |
| TSS RMSE (g∙m−3) | |||
| Viewing Angle | Optimized Algorithm—Training data | Optimized Algorithm—Validation data | Optimized Algorithm—All data |
| 0° | 6.3 | 5.2 | 5.4 |
| 40° | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.9 |
4.5. Comparison of Objective Functions and Q Expressions
The objective function and Q combinations were reevaluated using the full algorithm after parameterization and application to all available data (Figure 9). The objective function, (1 − SCM) + SSE, and simplification, SET_Q, initially chosen remained the best performing options. Most R2 values decreased, consistent with the increase in RMSE when applying the algorithm to all data, which is again indicative of wider variability in parameters and constituents in the total dataset relative to the training dataset. However, after optimizing bb*TSS(542), estimates of chl-a produced with SSE improved significantly for the at-nadir viewing angle. With the initial optimization, this combination of viewing angle and objective function produced TSS estimates equal to their maximum bound and chl-a estimates unchanged from their initial value in the constrained optimization. This indicates that there are large magnitude errors with the at-nadir viewing angle that the algorithm was unable to account for with the relatively small bb*TSS(542) used in the initial parameterization. Thus whenever chl-a estimates were changed during optimization, any reduction in error was small and the objective function essentially became stuck in a local minimum with TSS concentration at its maximum.
Objective functions incorporating (1 − SCM) estimated chl-a equally well for both view angles, but TSS estimates were worse with an at-nadir view angle. The objective function (1 − SCM) produced the worst TSS estimates for both viewing angles. This is unsurprising, as TSS concentrations strongly control backscatter, which is relatively flat across the visible spectrum, and without a mechanism to evaluate magnitude error of rmodel, (1 − SCM) is unable to account for differences in backscatter. Adopting a hybrid objective function that accounts for both spectral magnitude and shape reduced residual variance in chl-a estimates by 2–26 percentage points compared with common linear objective functions. These hybrid functions also reduced residual variance in simultaneously derived TSS estimates by 6–18 percentage points. Some of the variance accounted for by choosing the best-performing objective function is likely error from the other sources discussed in Section 4.6. Choice of objective function has a large impact on overall algorithm accuracy.
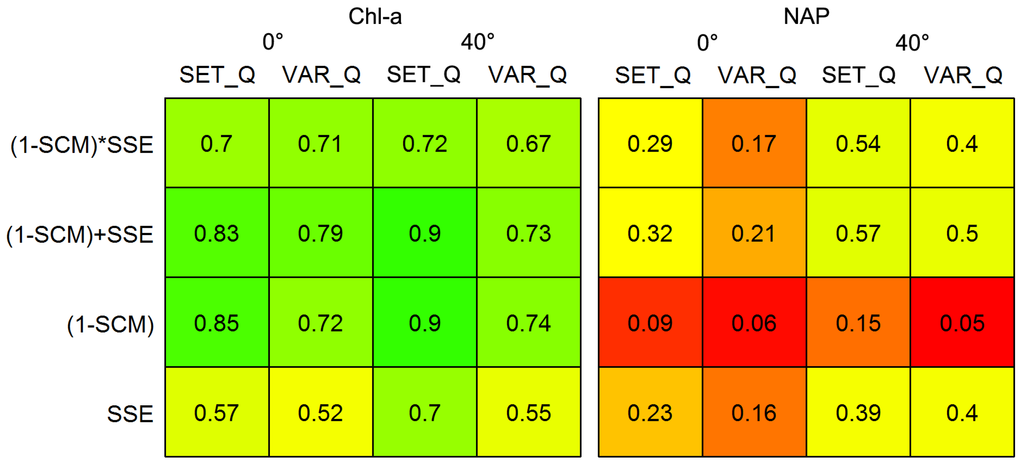
Figure 9.
Objective functions and Q evaluated for both viewing angles after full model parameterization. The values reported in the boxes R2 calculated between modelled and measured constituent concentrations.
Figure 9.
Objective functions and Q evaluated for both viewing angles after full model parameterization. The values reported in the boxes R2 calculated between modelled and measured constituent concentrations.
Of the two hybrid objective functions, (1 − SCM) + SSE consistently outperformed (1 − SCM) × SSE. At first glance this appears counterintuitive, as each function incorporates the same two statistics. Not only did (1 − SCM) + SSE produce more accurate constituent estimates, but optimization with this objective function required fewer iterations, with a median and standard deviation of 239 ± 31.4 runs, compared to 305 ± 72.1 runs for the optimization incorporating (1 − SCM) × SSE. In both objective functions, (1 − SCM) values were larger than SSE values 98% of the time and often by an order of magnitude. By the end of optimization, the median (1 − SCM) values were still an order of magnitude greater than the median SSE values for both hybrid objective functions. Between the two objective functions the final statistic values were nearly identical. However, closer inspection of the progression of both objective functions revealed that (1 − SCM) + SSE performed better than (1 − SCM) × SSE because it allowed for large increases in SSE during optimization.
For (1 − SCM) × SSE, a percentage increase in either (1 − SCM) or SSE will cause the same percentage increase in the total objective function value, assuming all else held equal. However, for (1 − SCM) + SSE, a percentage increase in either statistic will cause a smaller percentage increase in the total objective function. In fact, a percentage increase in SSE will often cause a much smaller percentage increase in the total objective function, because SSE is often an order of magnitude smaller than (1 − SCM). This means that the first derivative of SSE was positive 10% more often in (1 − SCM) + SSE optimizations than in (1 − SCM) × SSE, and the first derivative of total (1 − SCM) + SSE was positive 20% more often than total (1 − SCM) × SSE (Figure 10). A positive first derivative indicates that the objective function or statistic is increasing between iterations of the optimization algorithm. Generally, these increases are penalized by the optimization function, with the penalty scaled to the relative magnitude of the increase (Mathworks, 2011), meaning the smaller relative increases in (1 − SCM) + SSE are probably penalized less than the larger relative increases in (1 − SCM) × SSE. We hypothesize that this greater flexibility allows the optimization function using (1 − SCM) + SSE to avoid local objective function minima, i.e., regions of the solution space where further minimization requires temporary increases in the objective function. This flexibility translates into greater ability for the algorithm to change constituent concentrations rapidly, as displayed in Figure 10, although in this instance both objective functions produced similar constituent concentration estimates.
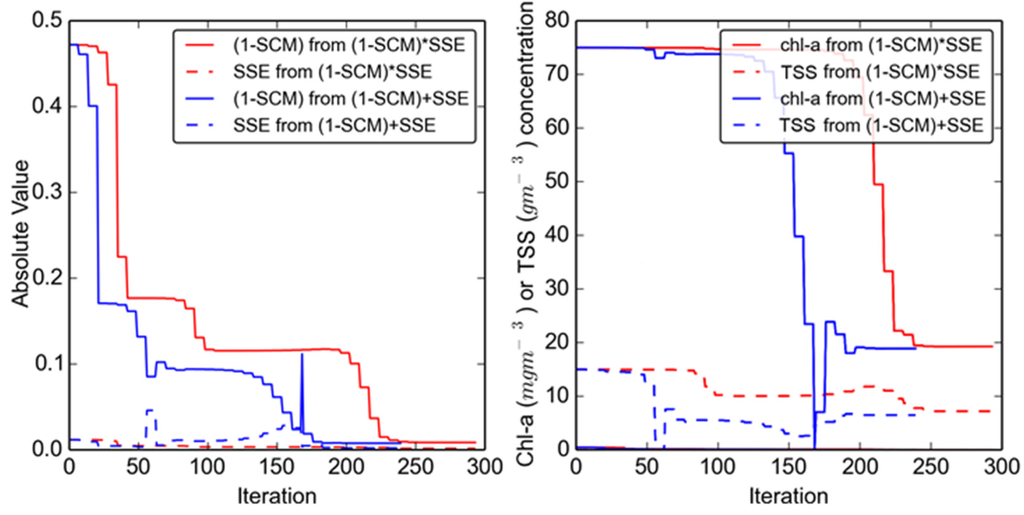
Figure 10.
Representative values of the two hybrid objective functions and constituent concentrations during model optimization.
Figure 10.
Representative values of the two hybrid objective functions and constituent concentrations during model optimization.
When translating Rrs through the air–water interface, the expression used for Q had a small but significant effect on the performance of the SA algorithm for the at-nadir viewing angle. When using the Gons [11] expression for Q in Equation (2), the SA algorithm produced worse results for all objective functions and both constituents with an at-nadir viewing angle. Q estimated from Equation (2) was incredibly variable, almost to the point of random noise, with a median of 1.2 and standard deviation of 12. We hypothesize that the variability from this Q expression is greater than the variability in actual Q values and that this increase in variability, compounded with Rrs measurement variability described in Section 4.6.2 caused the poor results.
One concern when using non-linear optimization schemes is decreased computational efficiency. For example, without especially optimizing the MATLAB code for efficiency, using the SSE + (1 – SCM) objective function required on average 80 ms to invert each field spectrum, while the same code using linear matrix inversion instead of non-linear optimization required only 7 ms per spectrum, an order of magnitude faster. For large satellite images or hyperspectral datasets, this gap in computational efficiency could be problematic. However, using the more computationally efficient linear inversion resulted in an immense decrease in accuracy. Using basic linear matrix inversion (QR decomposition) for all of the spectra in this study, the semi-analytical algorithm produced chl-a values with an RMSE of 37 mg∙m−3 and TSS values with an RMSE of 5.7 g∙m−3. Additionally, without constraints on estimate values, some of the chl-a concentrations returned by the basic linear inversion were negative. Using a linear least squares solver with constraints to keep estimates positive decreased chl-a RMSE to 31 mg∙m−3 and TSS RMSE to 5.1 mg∙m−3, but increased the time spent per spectrum to 29 ms. For a hypothetical hyperspectral satellite with global coverage, the computational efficiency of linear matrix inversion might be necessary or desirable enough to accept such a large reduction in accuracy. However, for field spectrometer deployments the non-linear, hybrid objective function approach is efficient enough to invert spectra between measurements, which generally require integration times of O (500 ms) or greater for deep water targets.
4.6. Analysis of Error
Ignoring error resulting from the imperfect model representation inherent in any model of complex physical processes, there are four major sources of error probable in our modeling effort: insufficiency of algorithm parameterization; variability in Rrs measurements; measurement uncertainty in constituent quantification and lab measurements; and variability in water constituents, especially over time.
4.6.1. Error from Algorithm Parameterization
Due to the simultaneous application of the algorithm to ten different water bodies, insufficient algorithm parameterization was possibly the most significant source of error. We expected between-reservoir variability in the specific absorption and scattering properties of water constituents and attempted to account for some of this variability with TSS absorption coefficients individually measured for each reservoir. Despite this precaution, inter-reservoir differences accounted for 25% of the variance in chl-a absolute error (Table 5, Model 1) and 15% of the variance in TSS absolute error (Table 5, Model 2). The parameters bb*TSS(542), STSS, and a*PHY(λ) are naturally variable between reservoirs due to differences in phytoplankton community and sources of sediment. The same values of these parameters were used for all reservoirs, however, and so the inter-reservoir differences in error are likely due to insufficient parameterization of the semi-analytical algorithm.

Table 5.
Linear statistical models used to partition sources of algorithm error.
| Model Number | Dependent Variable | Independent Variables 1 | R2 | Adj. R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chl-a error | Reservoir | 0.25 | 0.21 |
| 2 | TSS error | Reservoir | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| 3 | Chl-a error | Reservoir + [Chl-a] + Reservoir × [Chl-a] | 0.34 | 0.26 |
| 4 | TSS error | Reservoir + [TSS] + Reservoir × [TSS] | 0.39 | 0.31 |
| 5 | Chl-a error | Reservoir + Month 2 + Reservoir × Month 2 | 0.32 | 0.23 |
| 6 | TSS error | Reservoir + Month 2 + Reservoir × Month 2 | 0.24 | 0.14 |
| 7 | TSS error | Month 2, 3 | 0.6 | 0.58 |
| 8 | Chl-a errorreplicate4 | Reservoir + σspectral + Reservoir × σspectral | 0.46 | 0.39 |
| 9 | Chl-a errorreplicate4 | Reservoir | 0.3 | 0.27 |
| 10 | Chl-a error | Reservoir + σspectral + Reservoir × σspectral | 0.3 | 0.21 |
| 11 | TSS errorreplicate4 | Reservoir + σspectral + Reservoir × σspectral | 0.22 | 0.12 |
1 Square brackets, [], refer to concentrations. σ refers to variance. Variables in bold are statistically significant at p < 0.05. Chl-a refers to chlorophyll-a; 2 Month refers to months from start of data collection, not month of year; 3 This model was applied to only Reservoir 7; 4 These are results from algorithm application to non-replicate-averaged spectral measurements.
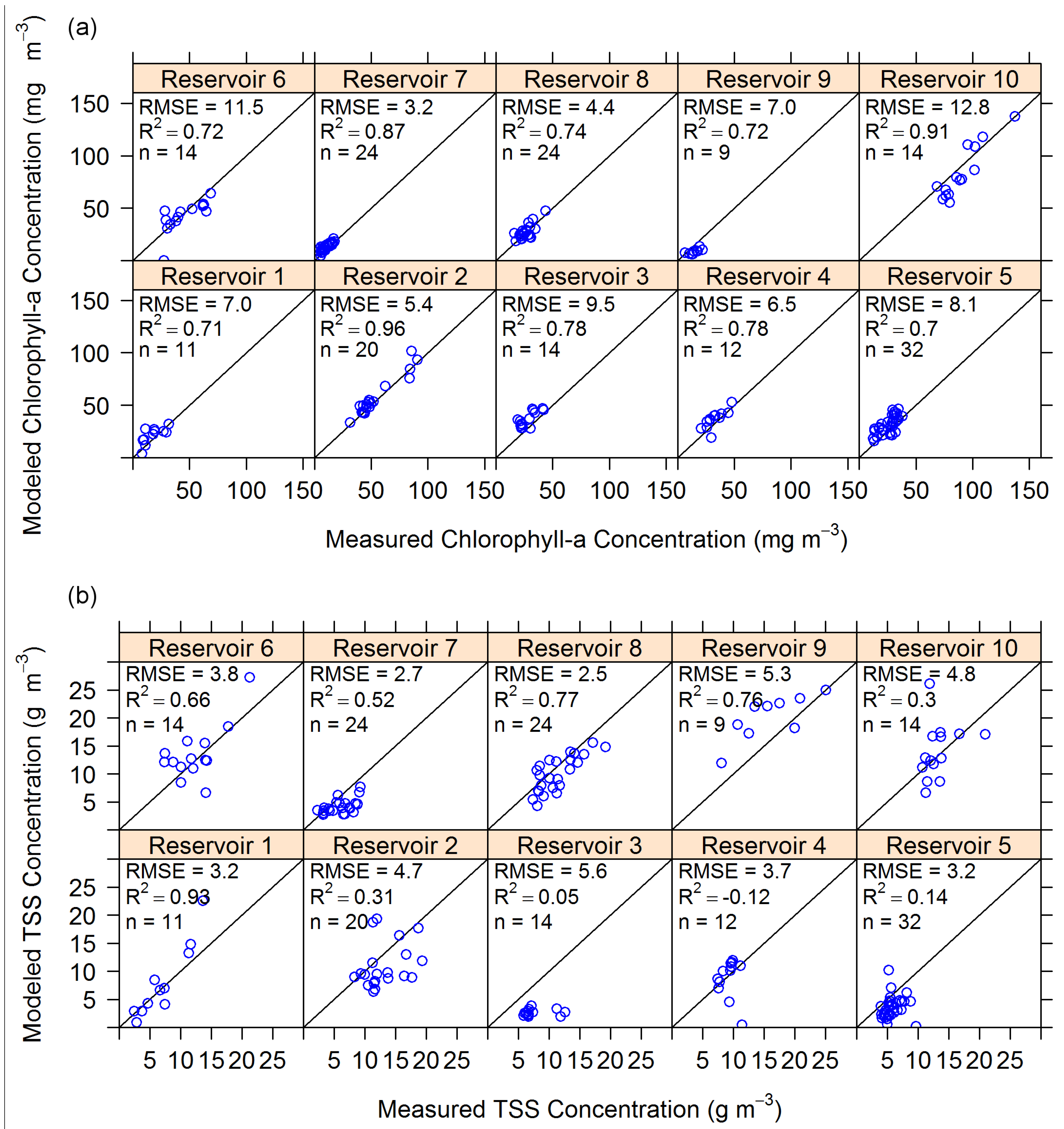
When looking at algorithm results broken down by reservoir, chl-a estimates appear to fall along the 1-to-1 line of perfect correspondence with measured values (Figure 11a), but three reservoirs have measured-modeled TSS slopes different from perfect correspondence (Figure 11b). If parameterization error results from an incorrect specific absorption or specific backscatter coefficient, there would be constant bias, such as that in chl-a estimates in Reservoirs 3 and 5 (Figure 11a). Error in the slope of the backscatter power law model results in significantly different slopes from 1-to-1 correspondence, as expressed in TSS estimates in Reservoirs 3, 7, and 9 (Figure 11b). These errors are quantified by regressing TSS concentration with TSS error (Table 5, Model 4), which shows that Reservoirs 1, 3, 7, and 9 have systematically changing error with increasing concentration. For Reservoirs 3, 7, and 9, this is due to parameterization error. In Reservoir 1, this relationship is caused by an outlier, upon whose removal the relationship disappears. There is no corresponding relationship between chl-a concentration and chl-a error in any of the reservoirs. Hence, although there is probably error in both absorption and backscatter parameters, the error has a more pronounced effect on TSS estimates.
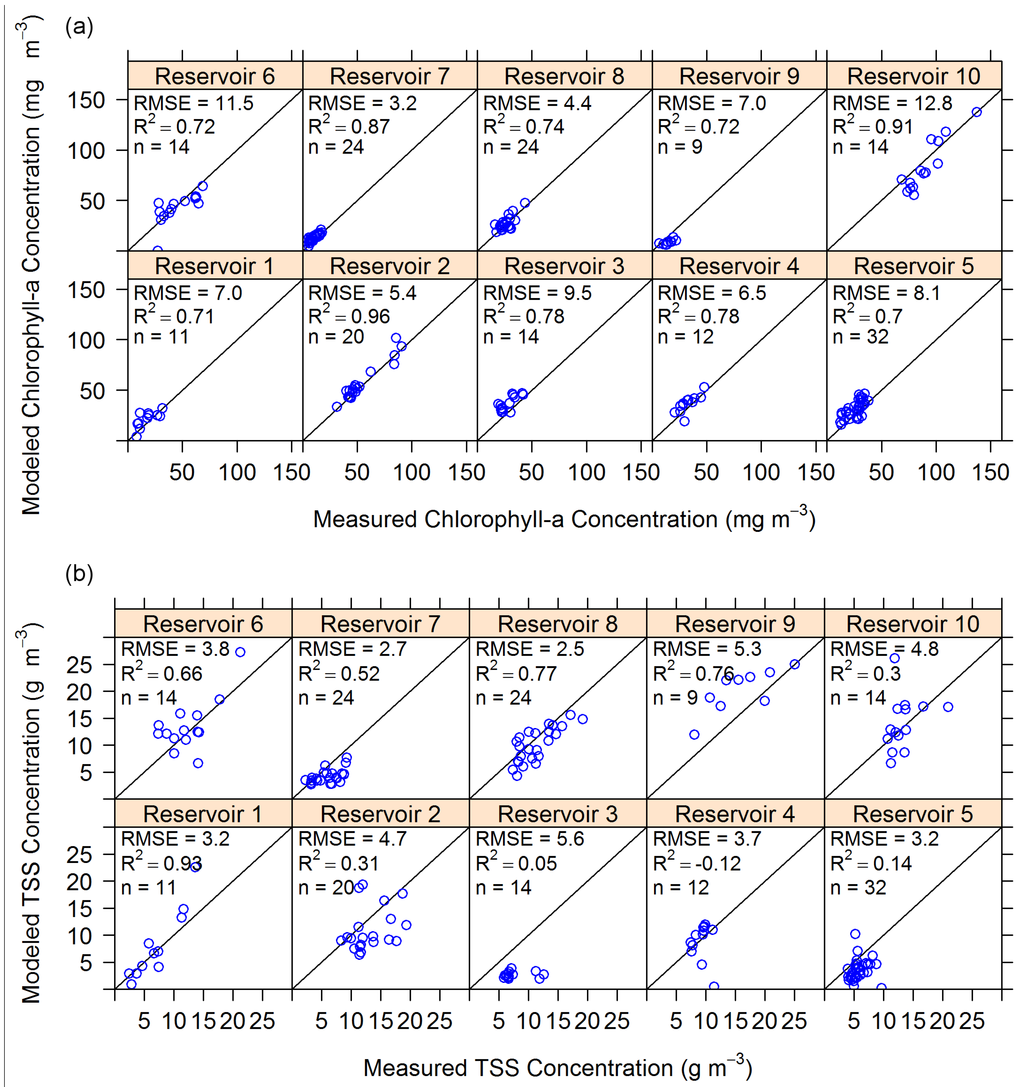
Figure 11.
Algorithm results separated by reservoir, including estimates of (a) chl-a concentration and (b) TSS concentration. The thin black lines indicate 1:1 correspondence. RMSE is in mg∙m−3 for chl-a concentration and g∙m−3 for TSS concentration. n is the number of samples displayed in each sub-graph. R2 is the coefficient of determination between modeled and measured values in each sub-graph.
Figure 11.
Algorithm results separated by reservoir, including estimates of (a) chl-a concentration and (b) TSS concentration. The thin black lines indicate 1:1 correspondence. RMSE is in mg∙m−3 for chl-a concentration and g∙m−3 for TSS concentration. n is the number of samples displayed in each sub-graph. R2 is the coefficient of determination between modeled and measured values in each sub-graph.
4.6.2. Error from Optical Parameter Variability
The most problematic source of error specific to multi-temporal applications is variability in water constituent optical properties. In our algorithm, we assumed stationarity of TSS SIOPs with time and phytoplankton SIOPs with both time and between study areas. However, changes in phytoplankton community composition could change a*PHY(λ) over time. Additionally, TSS optical properties are likely a function of distance from TSS source material and could change over time due to land use change or periodic events like storms. We attempted to quantify the error from this assumption of temporal stationarity by statistically analyzing error as a function of time or constituent concentration.
By regressing absolute chl-a error with time (Table 5, Model 5), we found no relationship between time and chl-a error, either within individual reservoirs or over all reservoirs. When regressing absolute TSS error with time (Table 5, Model 6), we found no significant relationship with time over all reservoirs, nor within most reservoirs. However, in Reservoir 7, there was a significant negative correlation between time and absolute TSS error accounting for 60% of the variance in error (p < 0.001). As TSS concentration decreased in this reservoir, error in TSS estimates decreased by 0.02 g∙m−3 per month. However, this is unlikely to be due to non-stationarity. Reservoir 7 was already identified as a site with significant parameterization error for TSS. In fact, the plot of measured to modeled TSS is flat (Figure 11b), indicating that TSS optical properties were mis-parameterized in this reservoir over the entire study period. The lack of change in slope of the measured-modeled plot indicates that the optical parameters were stationary, even though incorrect. Thus, despite the large shifts in constituent concentrations in Reservoirs 2, 3, 4, and 7 (Section 4.1), our semi-analytical algorithm was robust to non-stationarity in model parameters over the duration of the study.
4.6.3. Error from Field Spectrometer Measurements
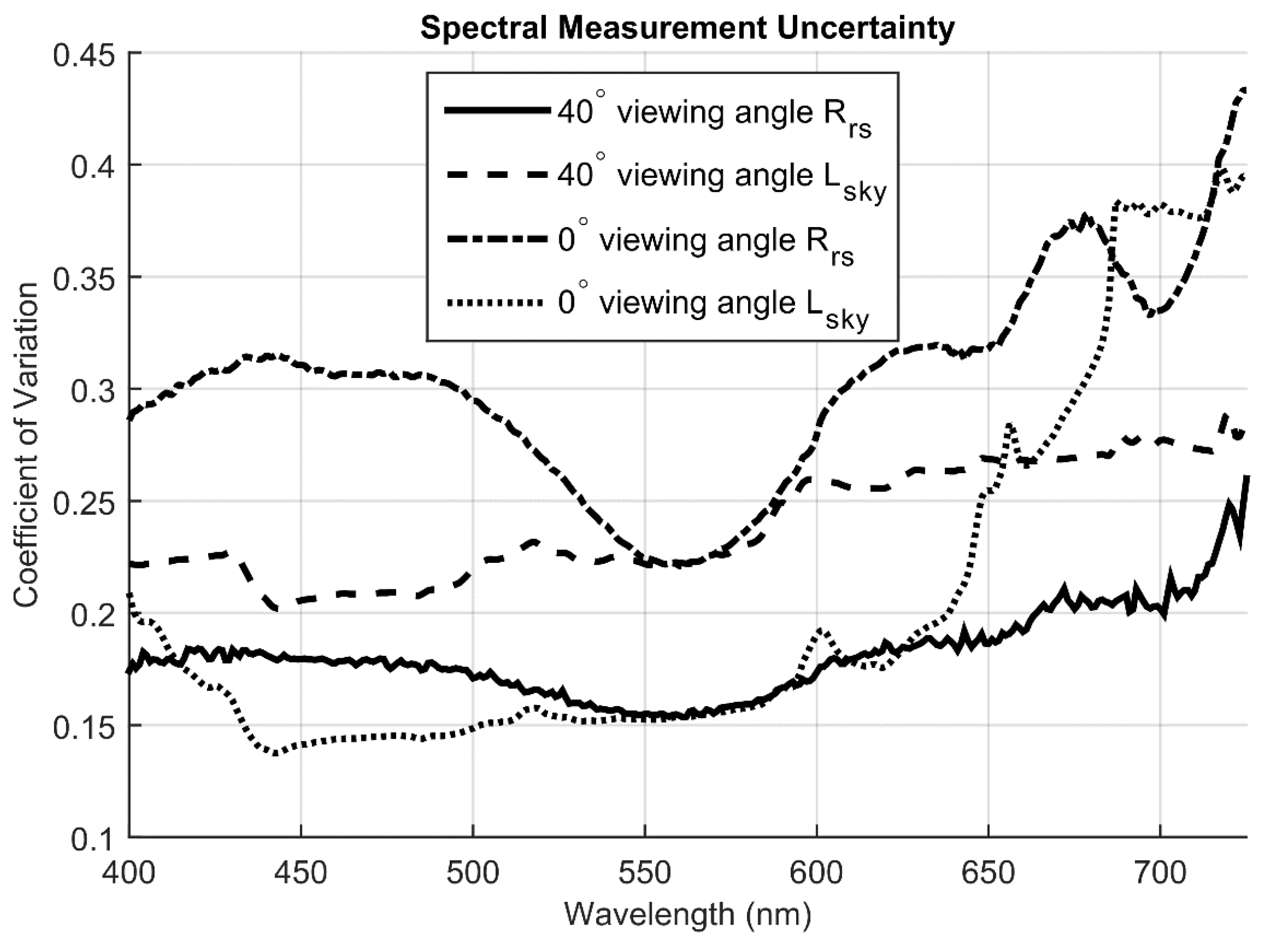
Variability in Rrs measurements using the field spectrometer accounts for the second largest but possibly most problematic source of error in this algorithm. This variability likely results from highly variable cloud cover, deviation from optimal viewing geometry, rapidly changing light fields, and waves on the water surface. We calculated the coefficient of variation between replicate spectrometer Rrs and Lsky measurements and found high uncertainty. The coefficient of variation for Rrs measurements made at a 40-degree viewing angle ranged between 0.155 and 0.26 and averaged 0.18 (Figure 12). The Rrs measurements taken at-nadir had much greater variance between replicates with a coefficient of variation that ranged between 0.23 and 0.43 and averaged 0.3 for this geometry (Figure 12). These wide dispersions are especially problematic because they are difficult to account for in the field and the error they cause is necessarily propagated through the inversion process.
The difference in Rrs measurement variability between viewing geometries suggests surface reflectance in Equation (1) and sub-optimal cloud cover as sources. Sky radiance reflected off the water surface can have similar magnitude as the upwelling radiance signal originating within the water column and thus can be the largest source of error in Rrs measurements [54]. Correction for this reflected sky radiance requires accurate estimates of an assumed spectrally independent reflection term, ρ(θv,ϕv), and accurate measurement of Lsky(λ,θv,ϕv) (Equation (1)). However, under variable cloud cover small variations in θv and ϕv between replicate measurements with a field spectrometer can cause large errors in Lsky(λ,θv,ϕv) and Rrs [5]. Small differences in viewing angle can also change the value of ρ and compound the error in Lsky. For this reason, Mobley [14] suggested using a θv of 40° and ϕv of 135°, as small perturbations in this viewing geometry have a relatively small effect on ρ and the azimuth angle avoids platform self-shading. Conversely, when attempting measurements from an at-nadir viewing angle, ρ changes significantly with small perturbations in θv and ϕv.
We hypothesize that the Rrs measurement variability with θv = 40° is due to variability in Lsky from complex and changing cloud cover. The much greater variance with θv = 0° would then be due to the same error, compounded by greater variability in ρ from small perturbations in view and azimuth angles. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that variability in Lsky is actually greater than in Rrs for θv = 40°, but lower than in Rrs for θv = 0° (Figure 12). Greater errors in ρ for θv = 0° could cause more of the variability in Lsky at this angle to affect Rrs calculations, while more stable ρ for θv = 40° could limit this effect. Lsky for θv = 40° was likely greater than for θv = 0°, as small perturbations in ϕv would have more effect on an oblique viewing angle than a vertical viewing angle. We are unsure of the cause of far greater variability in Lsky for θv = 0° at wavelengths greater than 650 nm, though this obviously had a significant impact on Rrs at these wavelengths. This variability at longer wavelengths, and greater Rrs variance in general, could explain the worse TSS estimates using θv = 0°, relative to θv = 40°, as TSS optical signals are more likely to dominate phytoplankton optical signals at these wavelengths.
To determine the effect of averaging replicates, we ran the SA algorithm inversion on all Rrs replicate measurements separately and collated the output from the replicate with the minimum objective function value from each set of replicates. Regressing chl-a error from this procedure with between-replicate coefficient of variation of spectral measurements at 450 nm, we found that this model accounted for 46% of the variance in absolute error, as opposed to 30% with reservoir alone (Table 5, Models 8–9). These results indicate that Rrs measurement variance could have a significant detrimental effect on chl-a estimates. TSS estimate error did not significantly correlate with Rrs measurement variability, which could be due to the poor parameterization of TSS backscatter described in Section 4.6.1. Averaging replicate field measurements removed chl-a error dependence on Rrs variability (Table 5, Model 10).
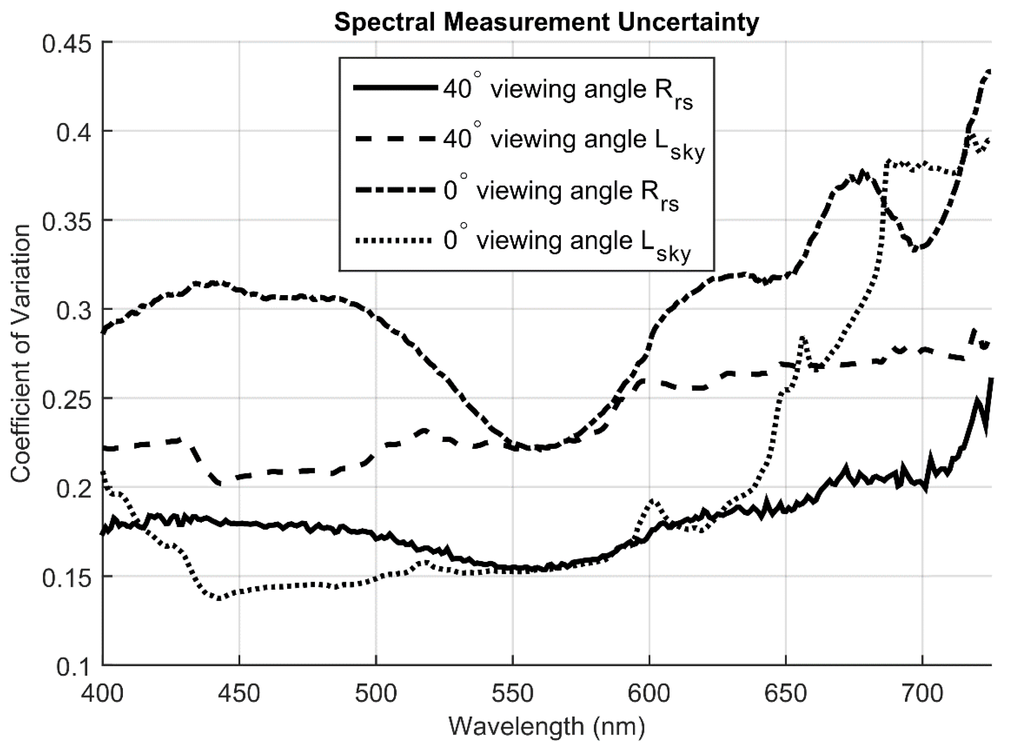
Figure 12.
Measurement uncertainty present in all field Rrs and Lsky measurements. The coefficient of variation was calculated among triplicate replicate measurements and averaged over all sample points.
Figure 12.
Measurement uncertainty present in all field Rrs and Lsky measurements. The coefficient of variation was calculated among triplicate replicate measurements and averaged over all sample points.
4.6.4. Error from constituent quantification and laboratory methods
A less prominent source of error is measurement uncertainty in field sampling and laboratory techniques used to determine constituent concentrations for training and validation. Duplicate measurements taken for the water samples allowed us to quantify combined measurement error due to lab and field sampling techniques. We calculated the coefficient of variation for each of our constituent determination techniques using pooled sample variance of the differences between duplicates [55]. The coefficients of variation for chl-a and TSS concentrations were 0.05 and 0.09, respectively, which are both much lower than the uncertainty in our Rrs measurements. The coefficient of variation for CDOM absorption was 0.36, which is large. This error is due to the fact that CDOM absorption was near the detection limits of our equipment, as explained in Section 3.4. Its removal from analysis and parameter optimization at that point was likely a good decision, as it prevented this error from propagating through the algorithm. It appears that measurement error from water sample analysis is unlikely to contribute greatly to overall algorithm error.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we optimized a semi-analytical algorithm to derive water quality information from field hyperspectral data over long-term deployments and across ten separate freshwater reservoirs. Our algorithm estimated chl-a concentration with an RMSE of 8.3 mg∙m−3 over a range of 4–135 mg∙m−3 and TSS concentration with an RMSE of 4.2 g∙m−3 over a range of 0–25 g∙m−3. These results were produced by optimizing our algorithm for three months of data and applying it to two years of data from ten freshwater reservoirs. This accuracy was obtained by designing the algorithm for multi-temporal applications involving a wide range of water constituent variability and by analyzing the utility of several different objective functions during inversion of rrs. Using a non-linear objective function during rrs inversion was the easiest way to improve performance of the semi-analytical algorithm as it had the greatest impact on error while requiring no extra field or lab work. Choice of objective function accounted for up to 42% of residual variance. By choosing a non-linear, hybrid objective function as we did in our algorithm, 17%–20% more residual variance was explained than when using a linear objective function. After fully parameterizing our algorithm, concentrations of TSS and chl-a were produced with error invariant over the two year study period.
Insufficient parameterization of optical parameters in our algorithm accounted for 15%–25% of all algorithm error, representing the largest source after implementation. Implementing an algorithm that performs accurately in ten separate reservoirs proved difficult, as all reservoirs had different constituent optical properties. The algorithm parameters with the greatest error were backscattering properties, which we were unable to directly measure. Runtime optimization and inversion of a training set to derive specific backscatter coefficients proved unable to solve this issue, serving as a warning for others attempting to implement semi-analytical algorithms over large spatio-temporal scales.
Without replicate measurements to aggregate, remote sensing reflectance measurement variability accounted for roughly 16% of chl-a estimation error. By examining the variance of replicate spectral measurements, we found wide dispersion in field spectra, which is most likely due to variable cloud cover and small changes in viewing geometry between replicate measurements. The detrimental effect of sub-optimal sky conditions and inaccurate estimates of water surface reflectance is still a significant issue for the application of in situ sensors for water quality monitoring [5,10]. This variability can be partially controlled for using a 40 degree viewing angle. By averaging replicate spectral measurements, the error statistically attributable to spectral variability was more than halved, to 5%. In algorithms with greater average error or without replicates, this uncertainty may become problematic, while application of these algorithms under clear sky conditions may remove a great portion the uncertainty.
When designing semi-analytical bio-optical algorithms for in situ sensors, future effort should focus on accounting for spatially dependent parameterization, using non-linear objective functions that take into account spectral shape, and controlling for remote sensing reflectance measurement variability as much as possible to minimize error.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Esther Clews and the freshwater team at Tropical Marine Science Institute, National University of Singapore for allowing us to accompany them in the field and for providing field logistics. This research was internally funded by the Tropical Marine Science Institute, internal grant number N-347-000-014-001.
Author Contributions
James Bramante and Tsai Min Sin conceived and designed the experiments; James Bramante performed the experiments; James Bramante analyzed the data; Tsai Min Sin contributed reagents, materials, equipment, and analysis tools; James Bramante wrote the paper; and Tsai Min Sin edited the paper and improved the analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IOCCG. Why Ocean Colour? The Societal Benefits of Ocean-Colour Technology; Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group, Platt, T., Hoepffner, N., Stuart, V., Brown, C., Eds.; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchinke, C.P.; Gordon, H.R.; Franz, B.A. Spectral optimization for constituent retrieval in Case 2 waters II: Validation study in the Chesapeake Bay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 610–621. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, F.; Alberotanza, L.; Cavalli, R.M.; Pignatti, S. A two-step optimization procedure for assessing water constituent concentrations by hyperspectral remote sensing techniques: An application of the highly turbid Venice lagoon waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Sheldon, S.; Biradar, C.; Duong, N.D.; Hazarika, M. A comparison of forest cover maps in Mainland Southeast Asia from multiple sources: PALSAR, MERIS, MODI and FRA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommersom, A.; Kratzer, S.; Laanen, M.; Ansko, I.; Ligi, M.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Beltran-Abaunza, J.M.; Moore, G.; Wernand, M.; et al. Intercomparison in the field between new WISP-3 and other radiometers (TriOS Ramses, ASD FieldSpec, and TACCS). J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 063615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, E.; Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A.; Millan-Nunez, E.; Piera, J. Cluster analysis of hyperspectral optical data for discriminating phytoplankton pigment assemblages in the open ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2578–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, M.; Rossini, M.; Morabito, G.; Matta, E.; Pinardi, M.; Cogliati, S.; Julitta, T.; Colombo, R.; Braga, F.; Giardino, C. Analysis of within- and between-day chlorophyll-a dynamics in Mantua Superior Lake, with a continuous spectroradiometric measurement. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 64, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubelkheir, K.; Clementson, L.A.; Webster, I.T.; Ford, P.W.; Dekker, A.G.; Radke, L.C.; Daniel, P. Using inherent optical properties to investigate biogeochemical dynamics in a tropical macrotidal coastal system. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C0702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Du, K.; Voss, K.J.; Zibordi, G.; Lubac, B.; Arnorne, R.; Weidemann, A. An inherent-optical-property-centered approach to correct the angular effects in water-leaving radiance. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 3155–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simis, S.G.H.; Olsson, J. Unattended processing of shipborne hyperspectral reflectance measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J. Optical teledetection of chlorophyll a in turbid inland waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: I. A semianalytical model. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 6329–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, J.F.; Kokke, J.M.M. Remote Sensing Algorithm Development Toolkit I: Operationalization of Atmospheric Correction Methods for Tidal and Inland Waters; Netherlands Remote Sensing Board: Delft, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddick, K.G.; de Cauwer, V.; Park, Y.J.; Moore, G. Seaborne measurements of near infrared water-leaving reflectance: The similarity spectrum for turbid waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Academic Press, Inc.: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hakvoort, H.; de Haan, J.; Jordans, R.; Vos, R.; Peters, S.; Rijkeboer, M. Towards operational airborne remote sensing of water quality in The Netherlands. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Brando, V.E.; Anstee, J.M.; Wettle, M.; Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C. A physics based retrieval and quality assessment of bathymetry from suboptimal hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Voss, K.J.; Gentili, B. Bidirectional reflectance of oceanic waters: A comparison of modeled and measured upward radiance fields. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 13143–13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, J.W.; Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S.; Clark, D.K. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnorne, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garver, S.A.; Siegel, D.A. Inherent optical property inversion of ocean color spectra and its biogeochemical interpretation 1: Time series from the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 18607–18625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semi-analytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardino, C.; Candiani, G.; Bresciani, M.; Lee, Z.P.; Gagliano, S.; Pepe, M. BOMBER: A tool for estimating water quality and bottom properties from remote sensing images. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 45, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Shang, S.; Shang, S. Impacts of computational methods and spectral models on the retrieval of optical properties via spectral optimization. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 6257–6273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cannizzaro, J.P.; Carder, K.L. Estimating chlorophyll a concentrations from remote-sensing reflectance in optically shallow waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S. Optical properties of the clearest natural waters (200–800 nm). Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, R.M.; Fry, E.S. Absorption spectrum (380–700 nm) of pure water. II. Integrating cavity measurements. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 8710–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buiteveld, H.; Hakvoort, J.H.M.; Donze, M. The optical properties of pure water. Proc. SPIE 1994, 2258, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.H.; Liu, C.C.; Wen, C.G. Integrating semianalytical and genetic algorithms to retrieve the constituents of water bodies from remote sensing of ocean color. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardino, C.; Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G.; Strombeck, N.; Candiani, G. Assessment of water quality in Lake Garda (Italy) using Hyperion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisan, T.A.H.; Moisan, J.R.; Linkswiler, M.A.; Steinhardt, R.A. Algorithm development for predicting biodiversity based on phytoplankton absorption. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 55, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlov, N.G. Optical Oceanography; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G. Satellite hyperspectral remote sensing for estuarine and coastal water quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Woerd, H.J.; Pasterkamp, R. HYDROPT: A fast and flexible method to retrieve chlorophyll-a from multispectral satellite observations of optically complex coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1795–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Roelfsema, C.; Phinn, S.R. Efficient radiative transfer model inversion for remote sensing applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Lefkoff, A.B.; Boardman, J.W.; Heidebrecht, K.B.; Shapiro, A.T.; Barloon, P.J.; Goetz, A.F.H. The spectral image processing system (SIPS)—Interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, O., Jr.; Guimaraes, R.; Gomes, R.; de Carvalho, A.; da Silva, N.; Martins, E. Spectral multiple correlation mapper. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Geosciences and Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006.
- Low, E.W.; Clews, E.; Todd, P.A.; Tai, Y.C.; Ng, P.K.L. Top-down control of phytoplankton by zooplankton in tropical reservoirs in Singapore? Raffles Bull. Zool. 2010, 58, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Clews, E.; Low, E.W.; Belle, C.C.; Todd, P.A.; Eikaas, H.S.; Ng, P.K.L. A pilot macroinvertebrate index of water quality of Singapore’s reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar]
- IOCCG. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal, and Other Optically-Complex, Waters; Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group, Sathyendranath, S., Eds.; IOCCG: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, M.W.; Bernard, S.; Winter, K. Remote sensing of cyanobacteria-dominant algal blooms and water quality parameters in Zeekoevlei, a small hypertrophic lake, using MERIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2070–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arar, E.J. In Vitro Determination of Chlorophylls a, b, c1 + c2 and Pheopigments in Marine and Freshwater Algae by Visible Spectrophotometry; EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- America Public Health Assocation (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bricaud, A.; Stramski, D. Spectral absorption coefficients of living phytoplankton and nonalgal biogenous matter: A comparison between the Peru upwelling area and the Sargasso Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 562–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, J.S.; Weidemann, A.D. Quantifying absorption by aquatic particles: A multiple scattering correction for glass-fiber filters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishino, M.; Takahashi, M.; Okami, N.; Ichimura, S. Estimation of the spectral Absorption coefficients of phytoplankton in the sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 634–642. [Google Scholar]
- Clementson, L.A.; Parslow, J.S.; Turnbull, A.R.; McKenzie, D.C.; Rathbone, C.E. Optical properties of waters in the Australasian sector of the Southern Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 31611–31625. [Google Scholar]
- Mathworks. Optimization Toolbox: User's Guide (r2011b); The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2011; Available online: http://www.mathworks.com/help/releases/R2014a/pdf_doc/optim/optim_tb.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2014).
- Fox, J. Applied Regression Analysis and Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied Regression Analysis, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Doxaran, D.; Cherukuru, R.C.N.; Lavender, S.J. Estimation of surface reflection effects on upwelling radiance field measurements in turbid waters. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2004, 6, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.H. Statistical concepts in metrology. In Precision Measurement and Calibration: Statistical Concepts and Procedures; Ku, H.H., Ed.; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1969; Volume 1, pp. 296–330. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
