Satellite Image Time Series Decomposition Based on EEMD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Framework
2.1. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition
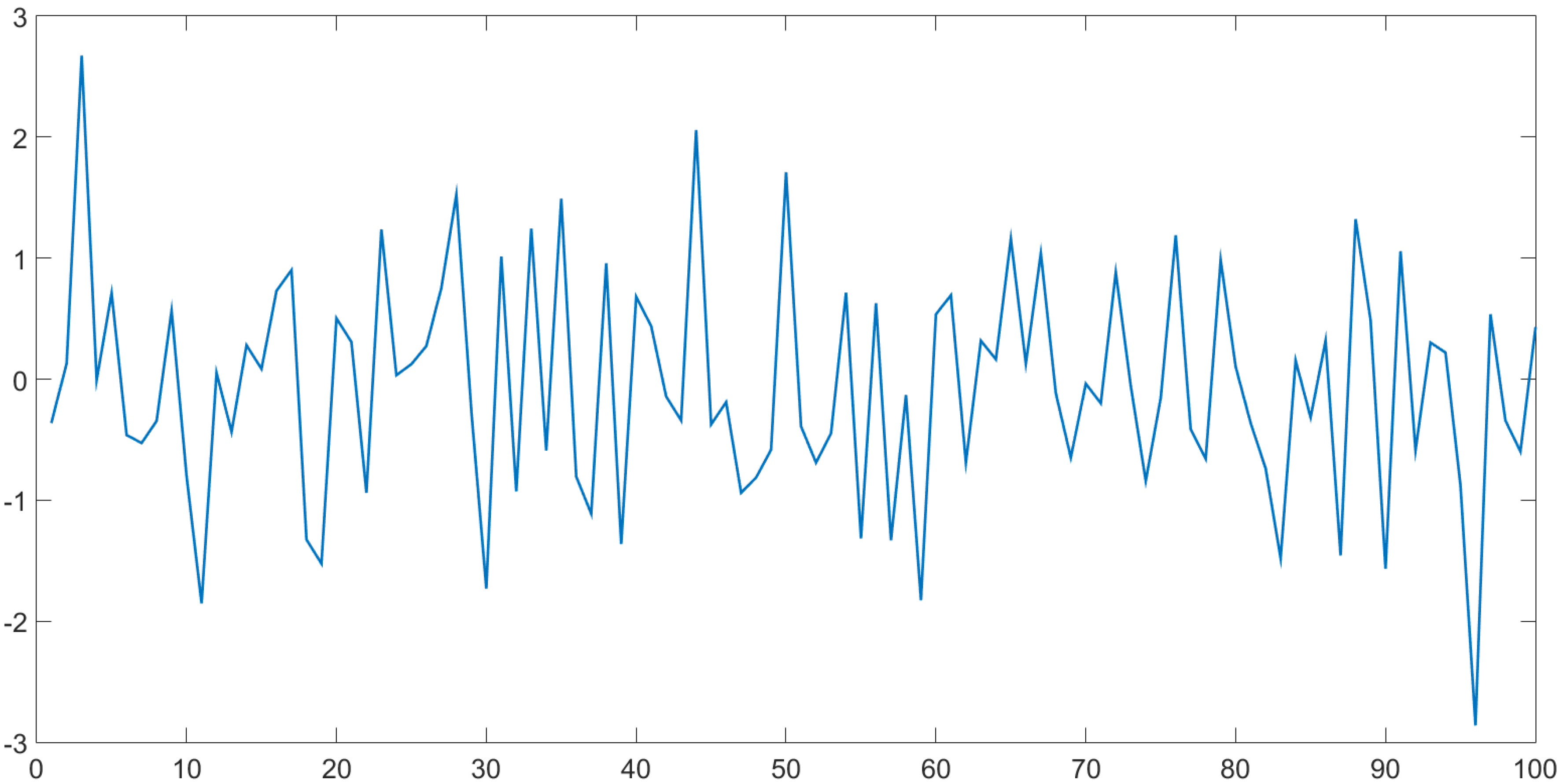

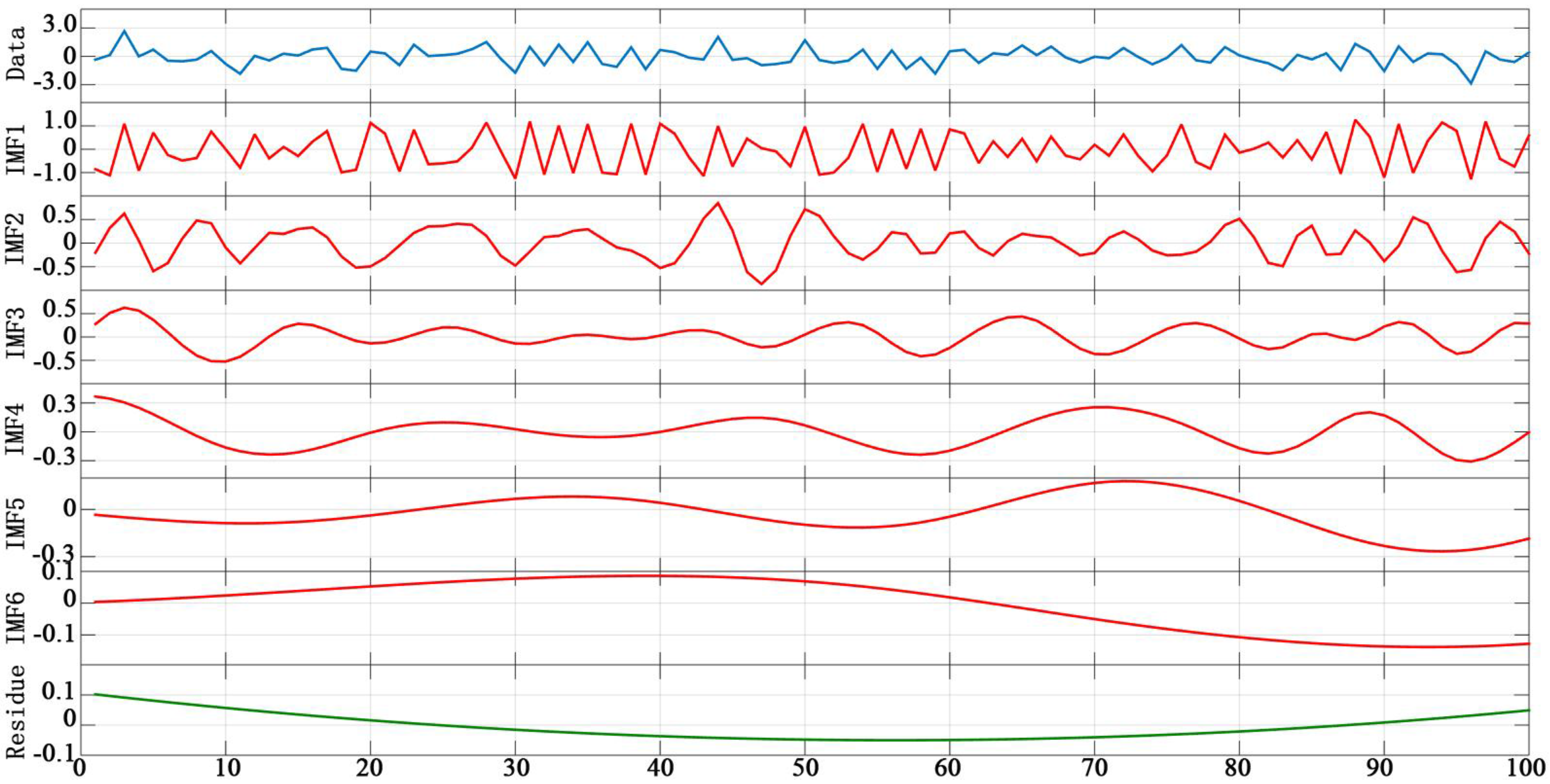
2.2. EEMD for SITS
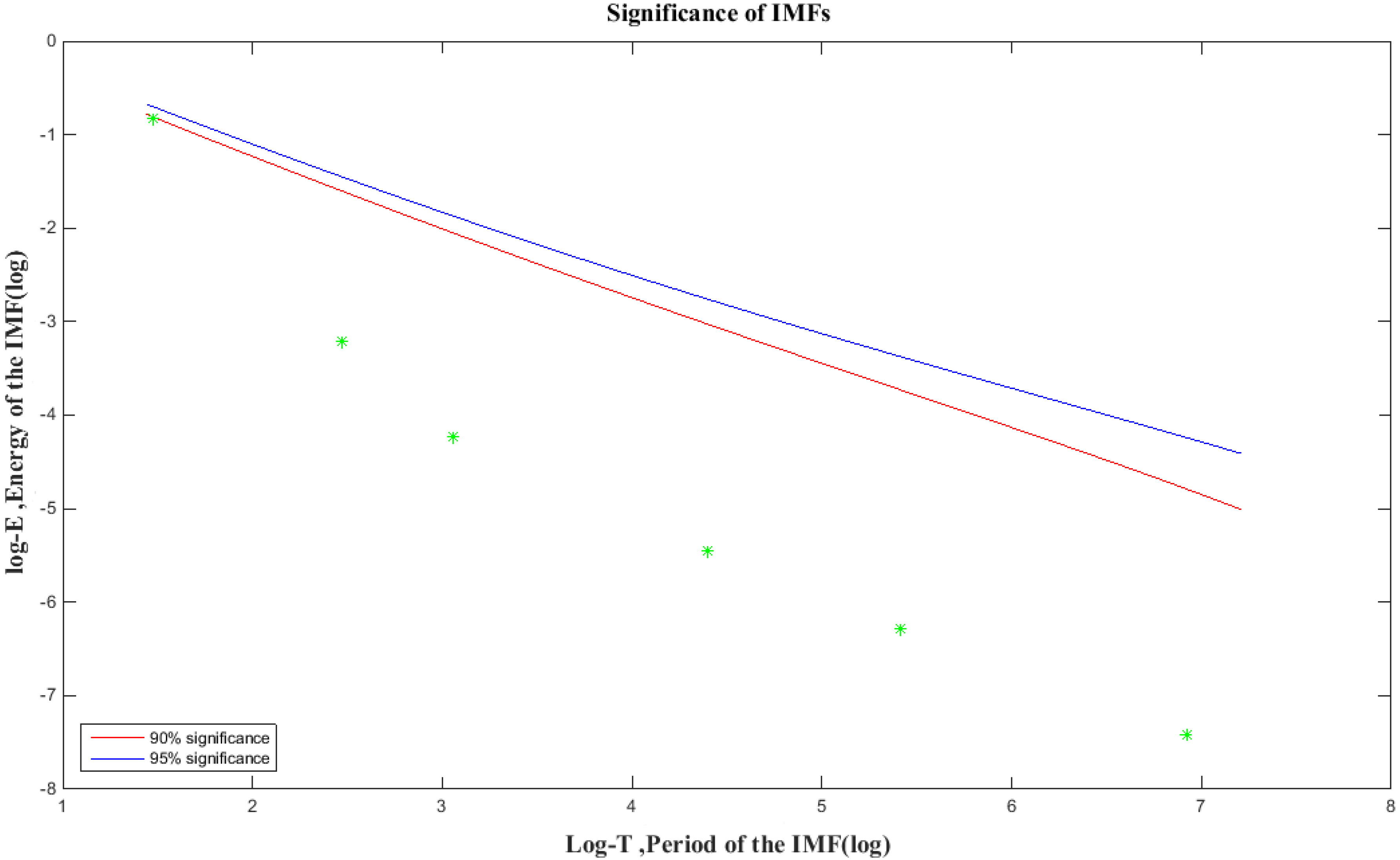
2.2.1. Seasonal Component Extraction
2.2.2. Trend Component Extraction
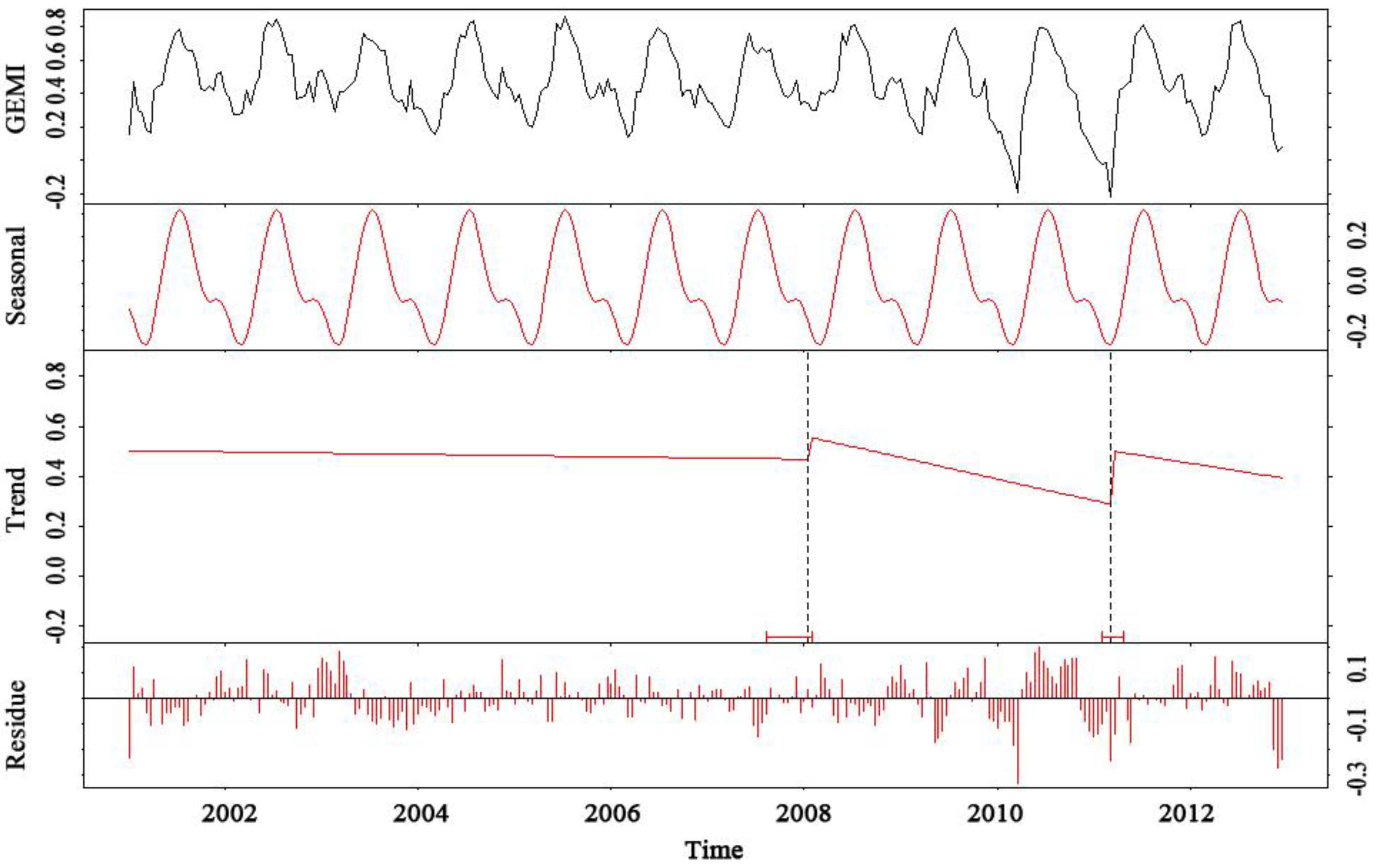
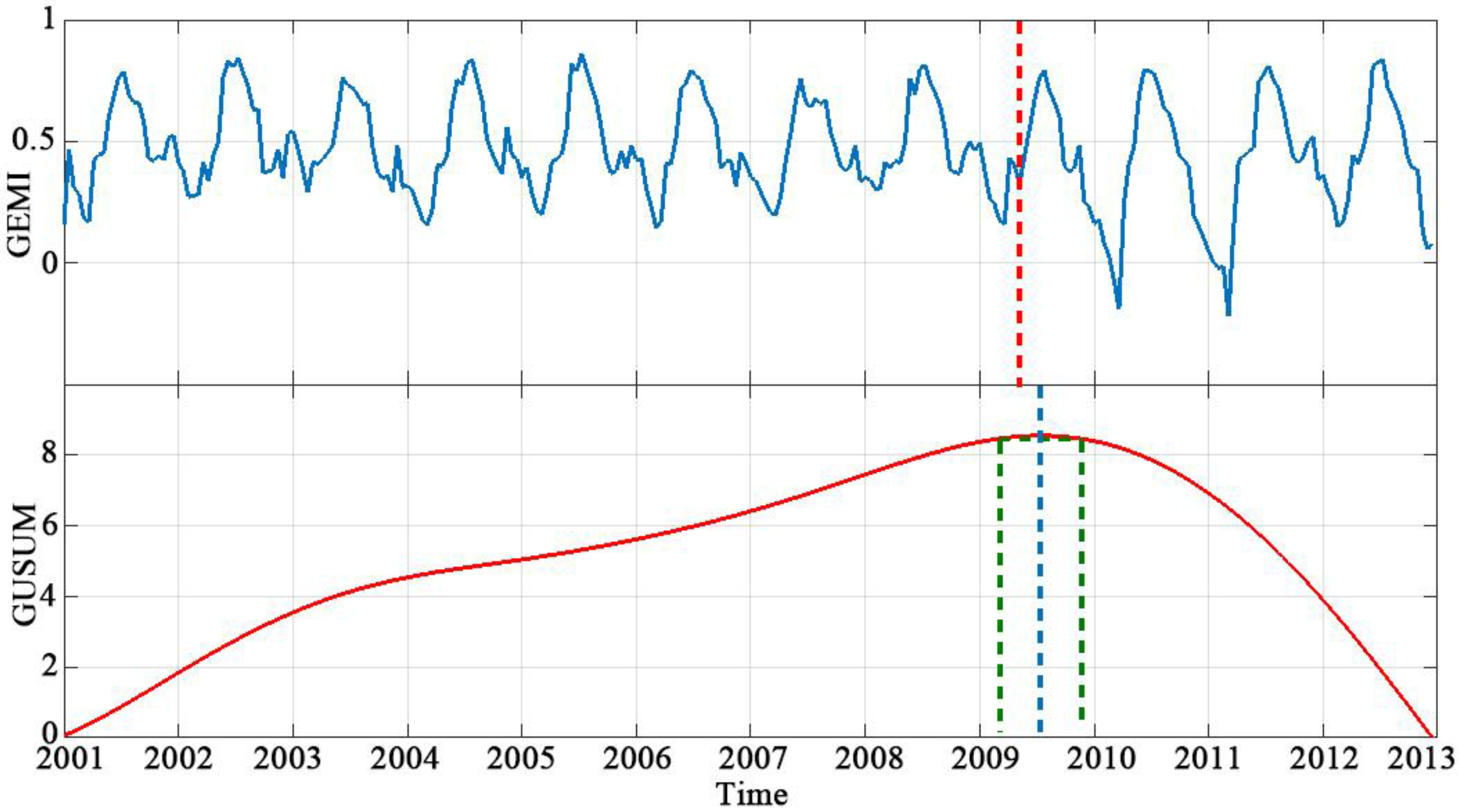
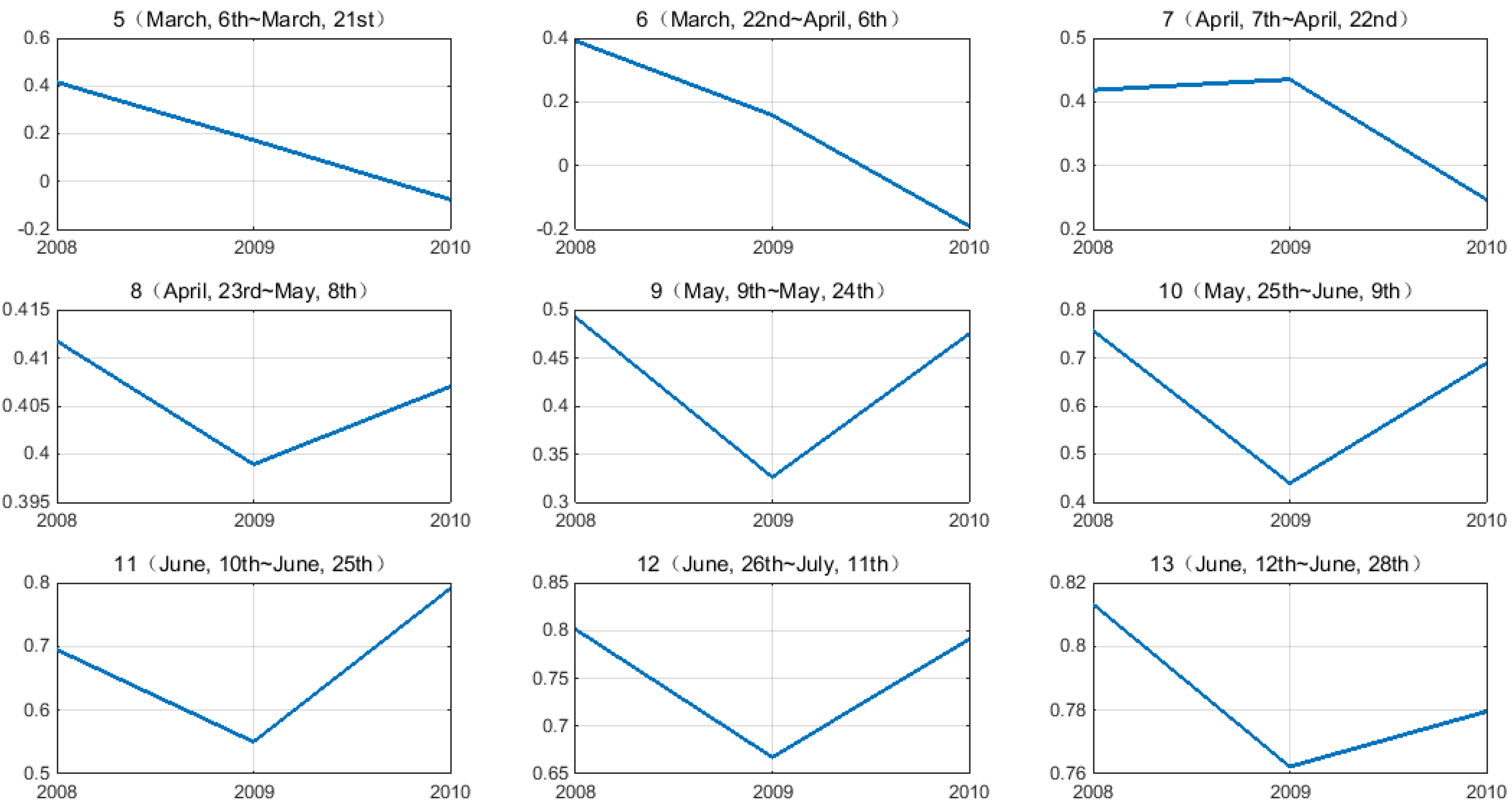
2.2.3. Trend Component for Change Detection
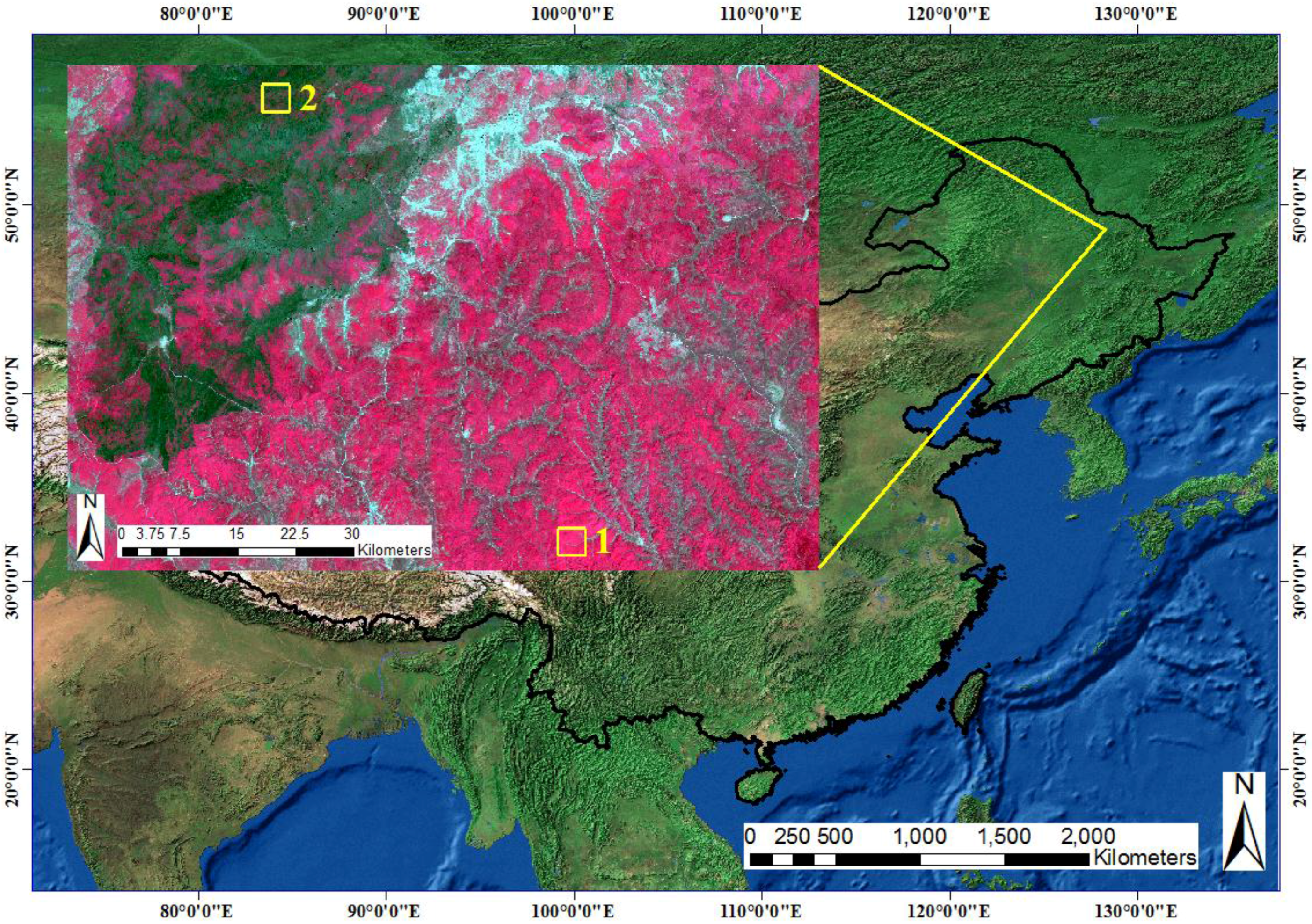
3. Experiment and Discussion
3.1. 16-Day Composite NDVI Time Series of Forest Type

3.1.1. Seasonal-Trend Decomposition
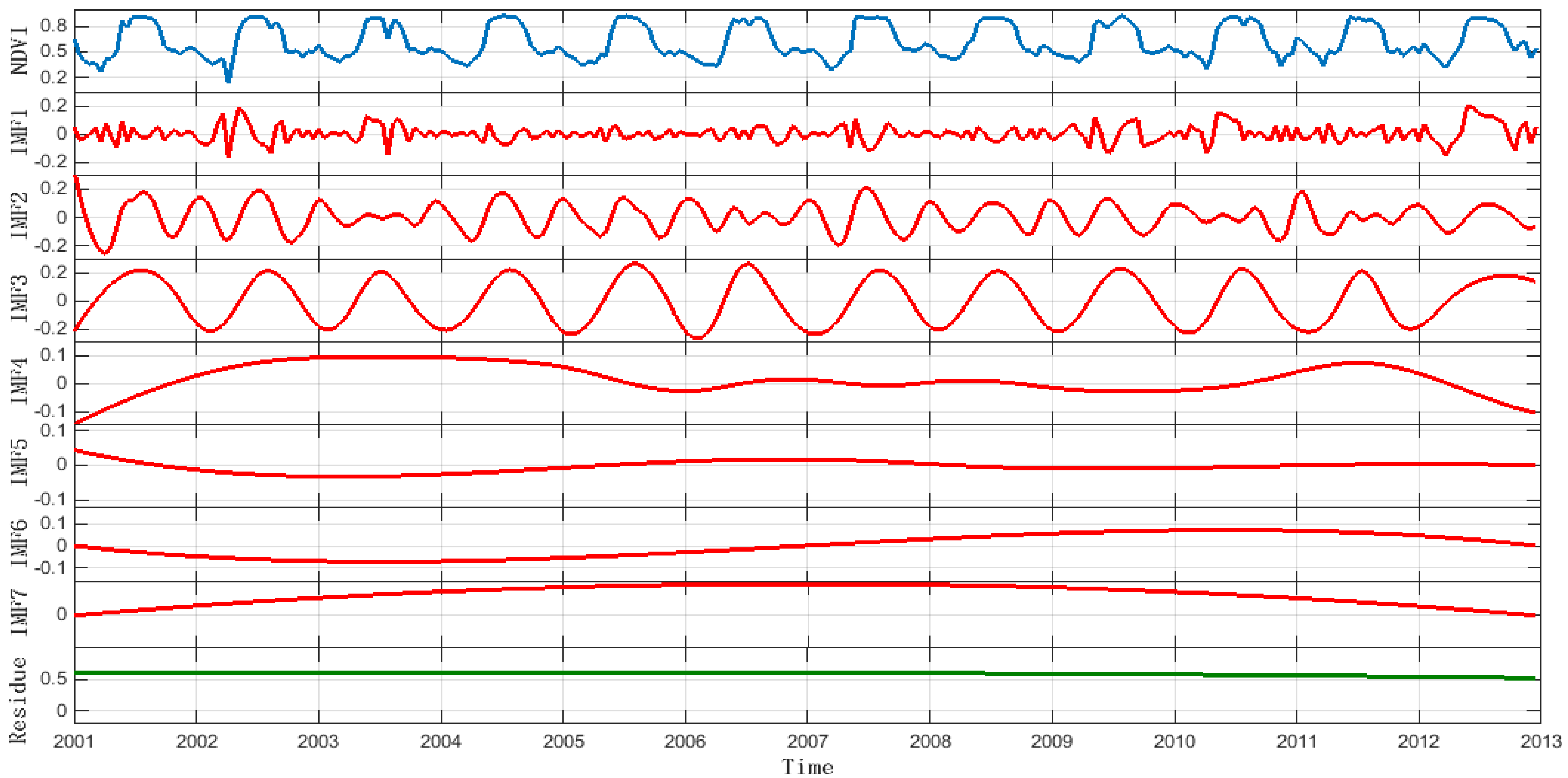
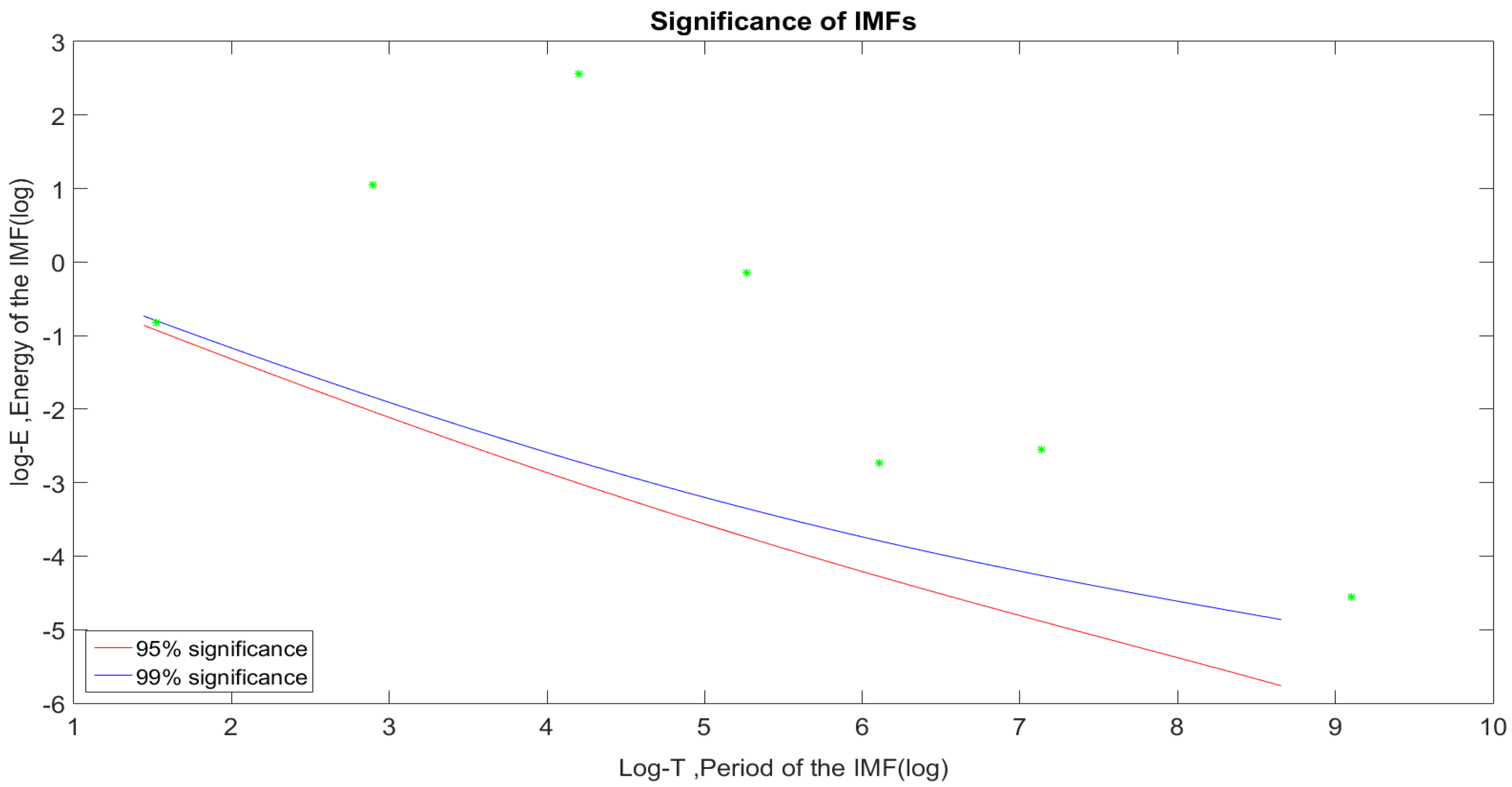

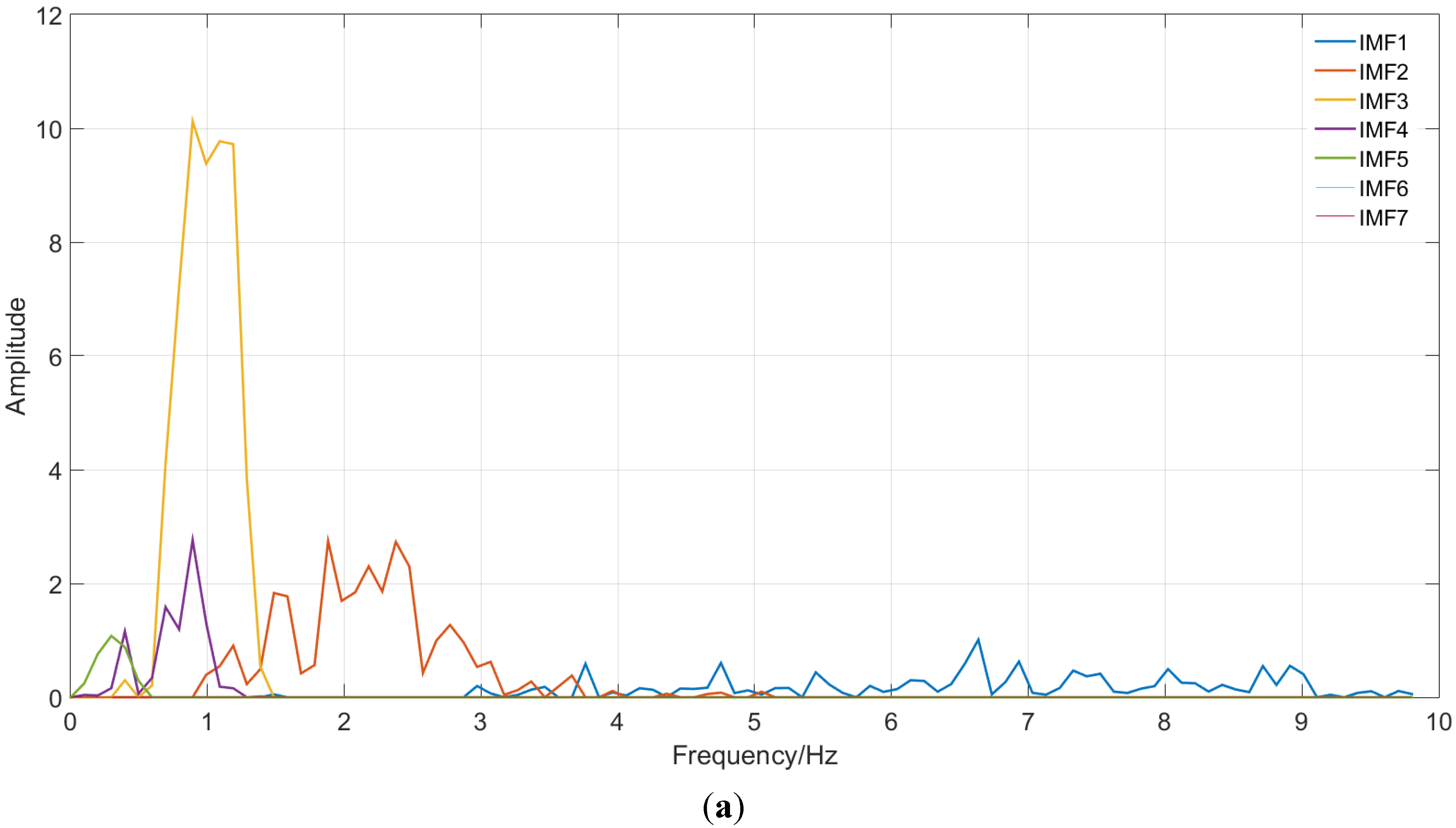
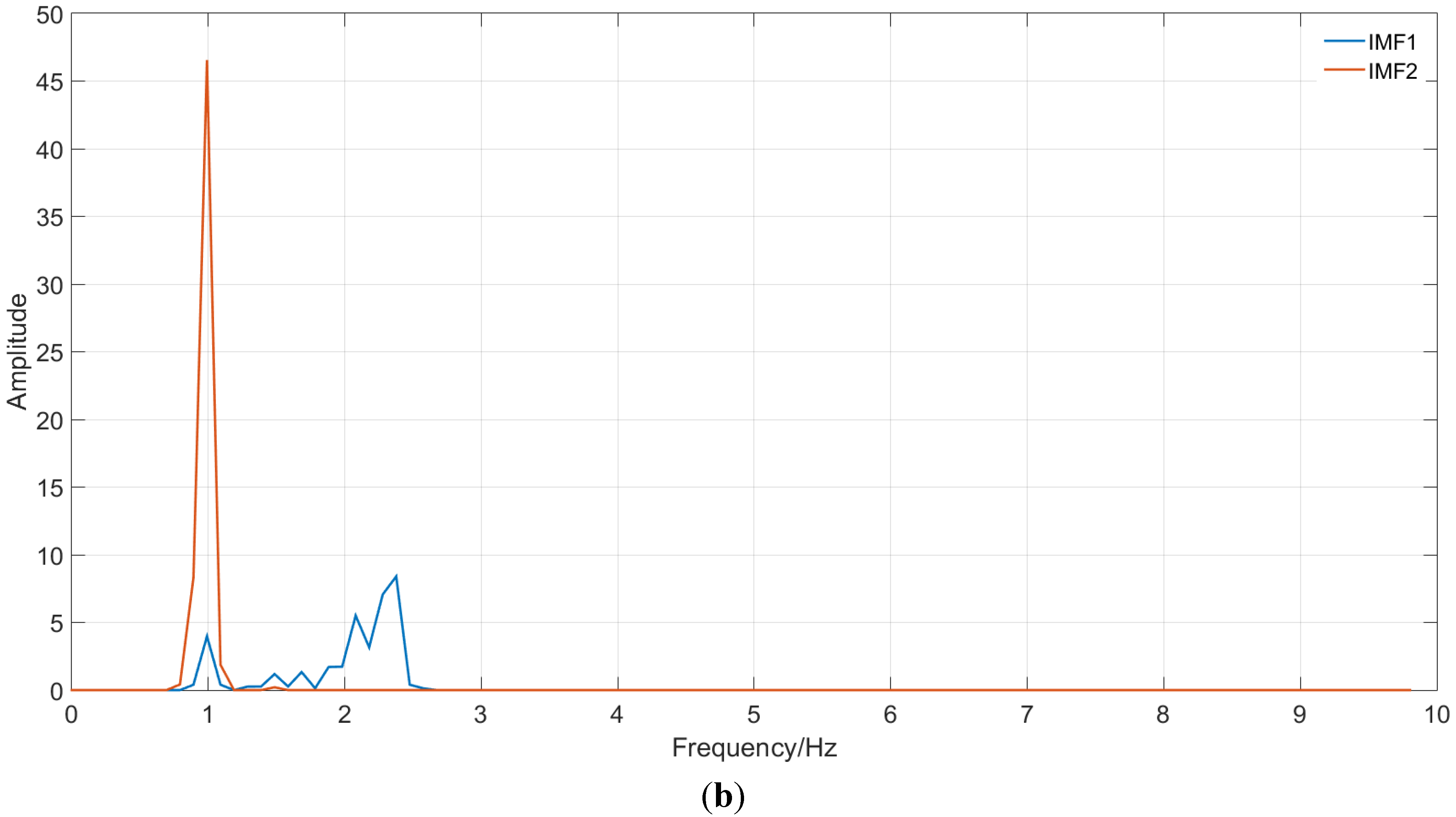
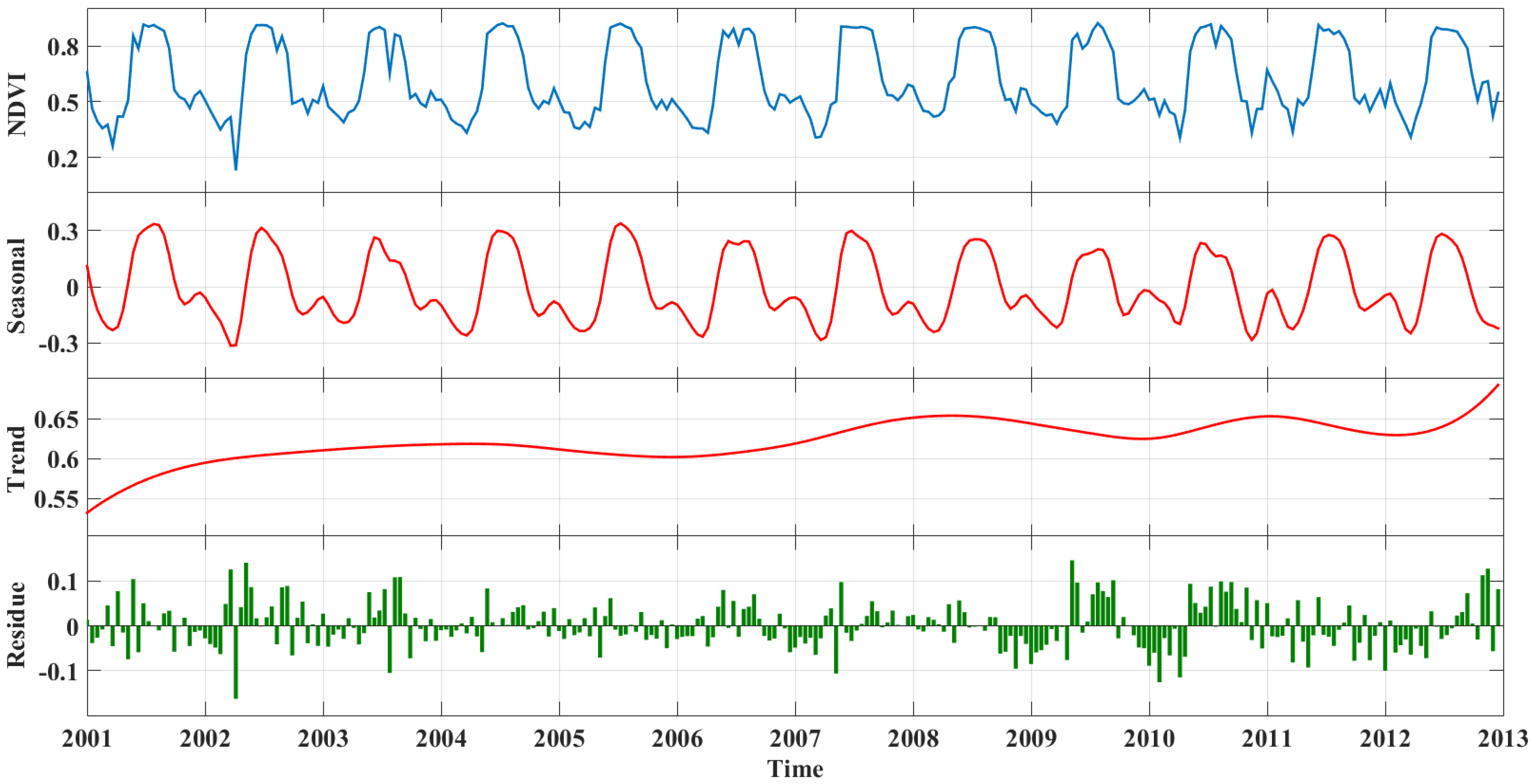
3.1.2. Validation of the Seasonal Component
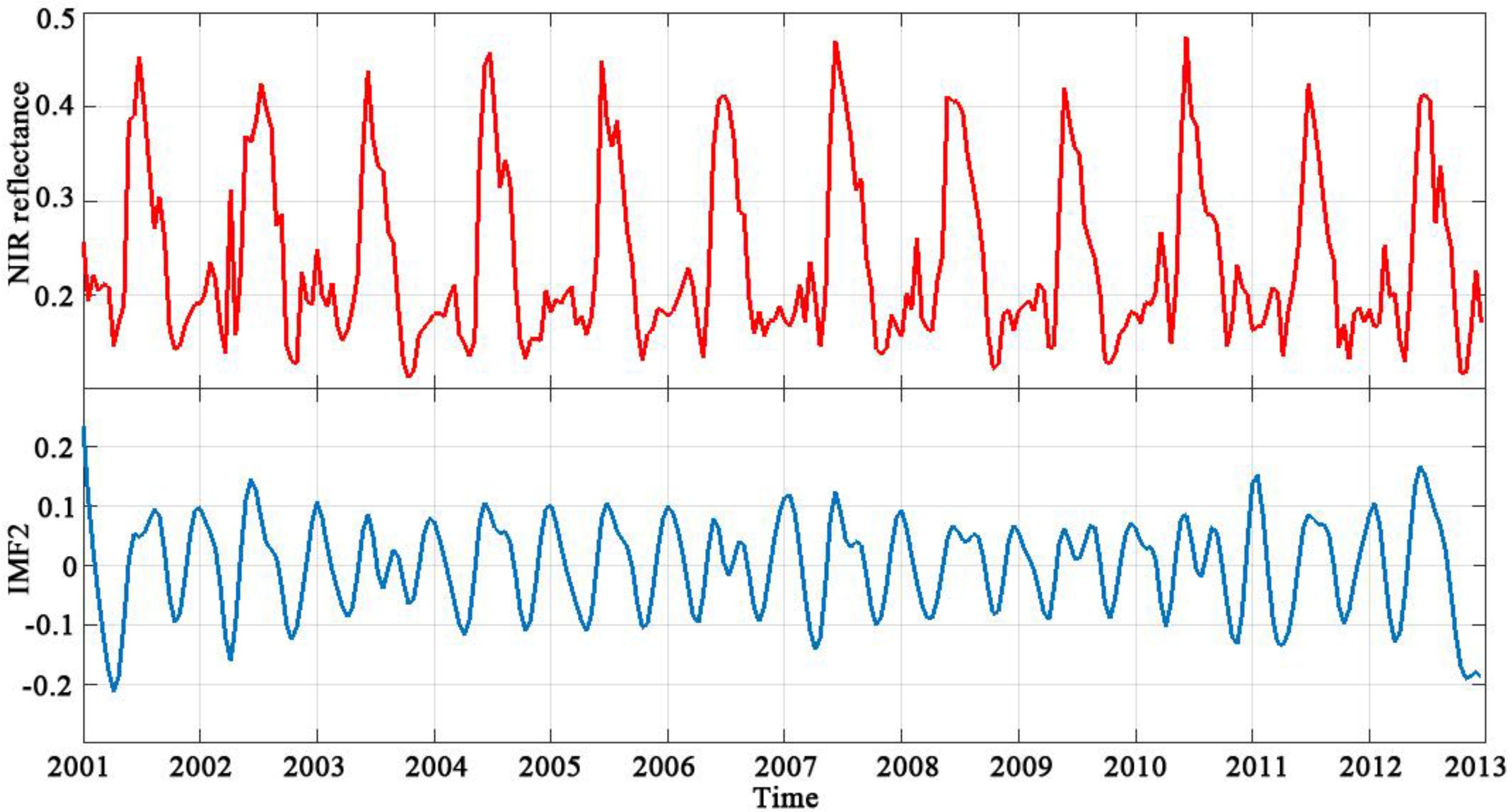
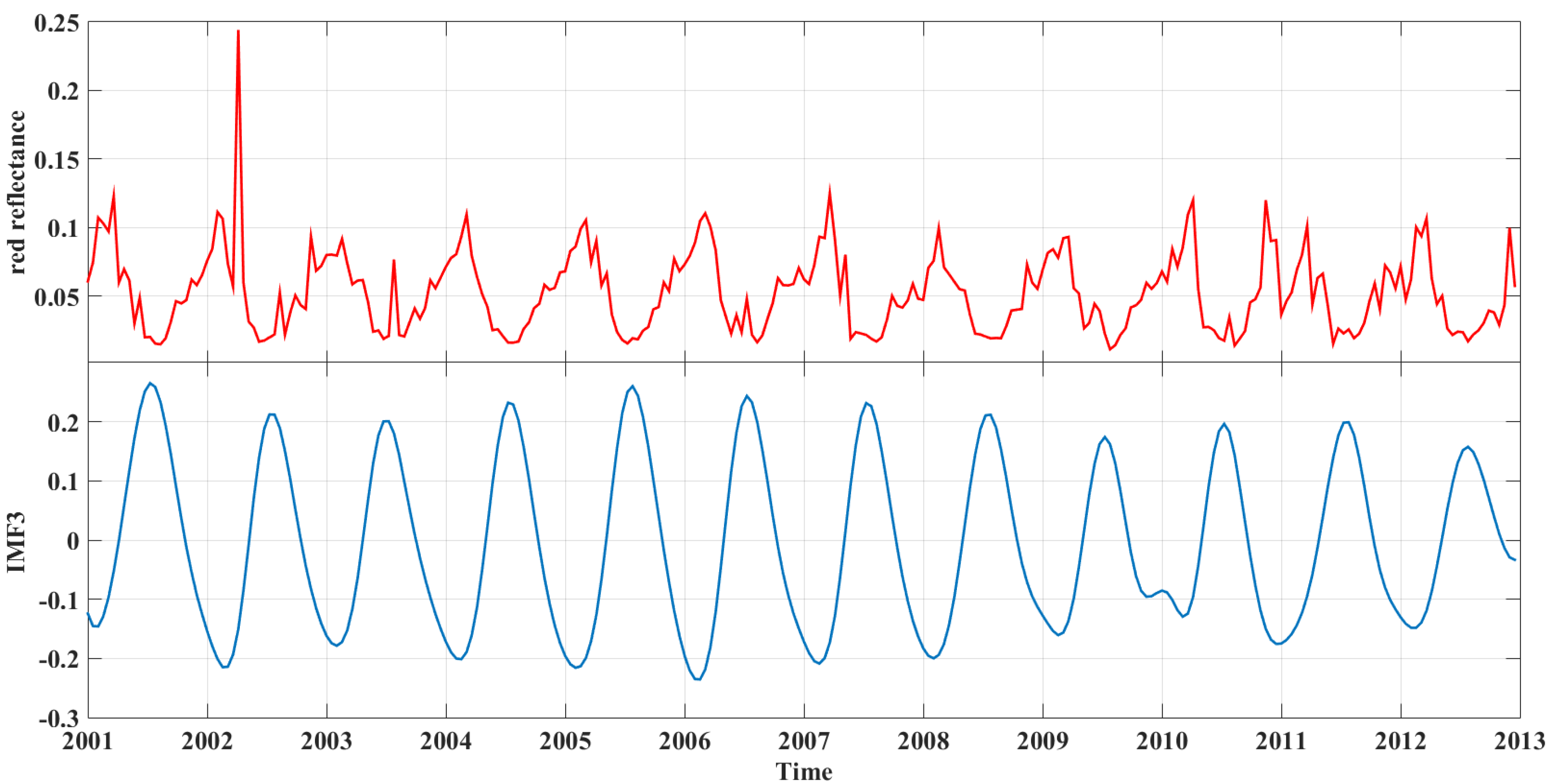
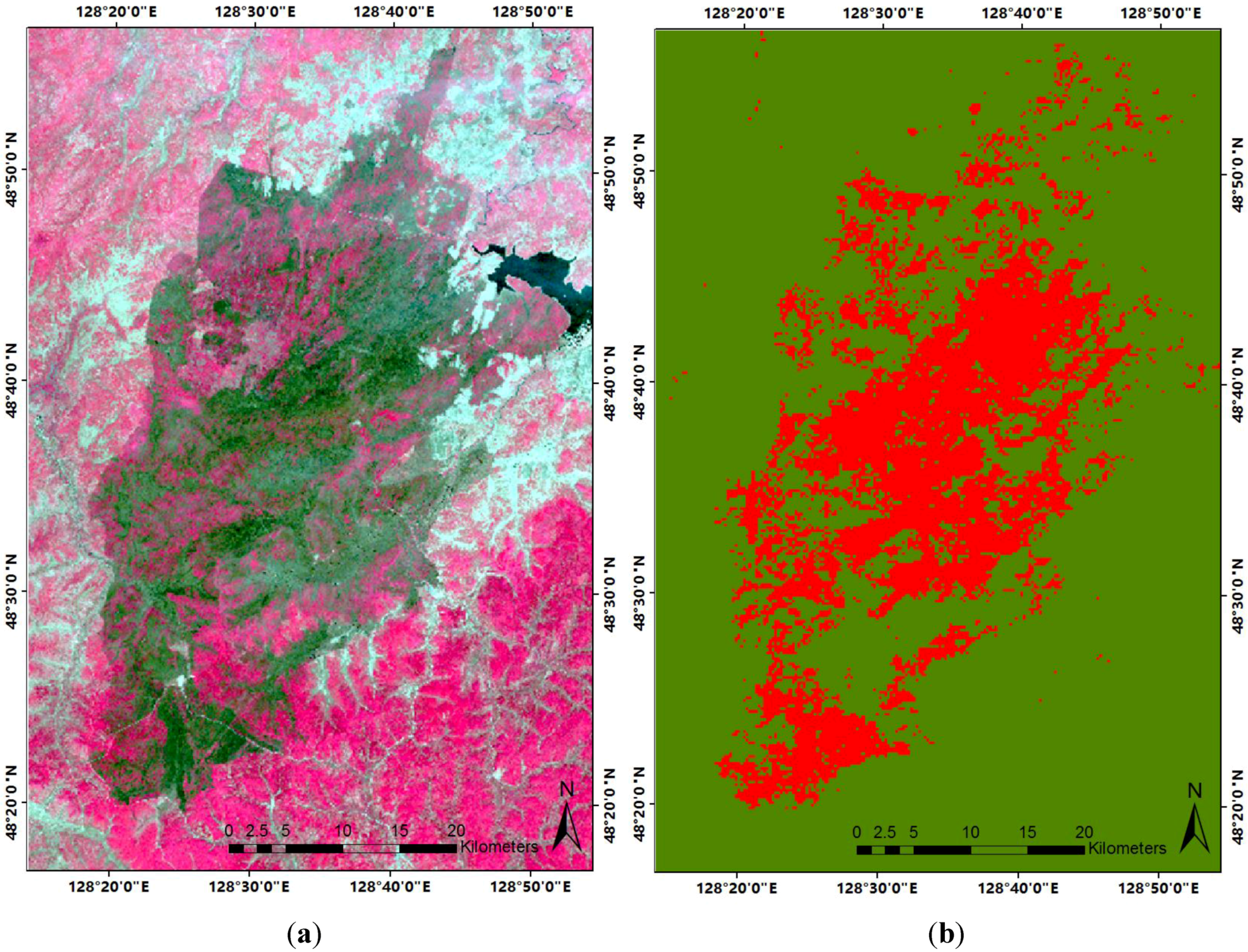
3.2. Sixteen-Day Composition GEMI Time Series with Disturbance


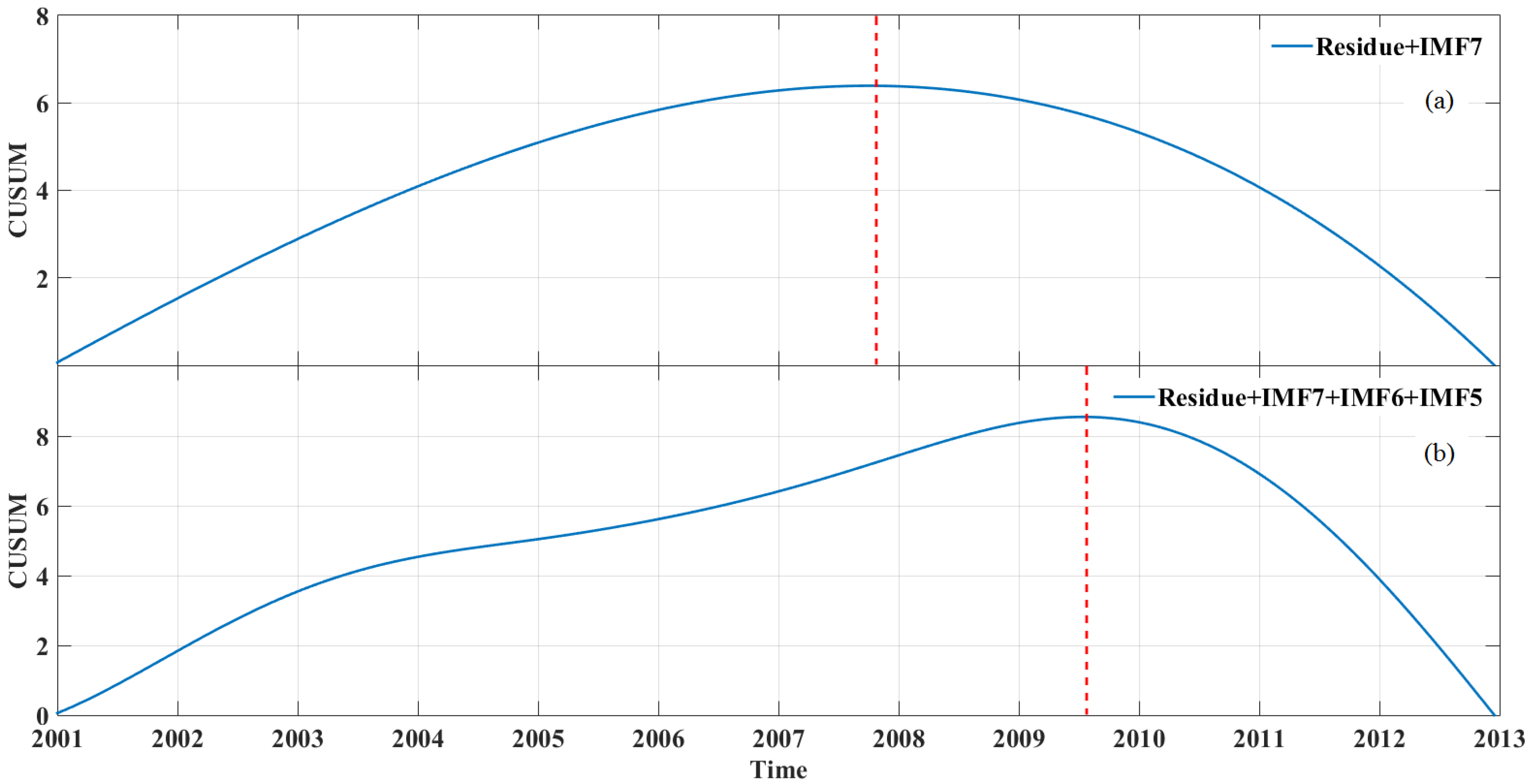
| IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | IMF6 | IMF7 | Residue | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 0.878 | 2.606 | 6.860 | 1.522 | 0.370 | 0.002 | 0.212 | 0.760 |
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Further algorithm improvement should consider the sensitivity of change point detection of the seasonal or trending component.
- (2)
- Further research is necessary to incrementally update an event database when new observations are available and to enhance the prediction algorithm to achieve real-time change detection (see Schnebele, et al. [35]).
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petitjean, F.; Inglada, J.; Gançarski, P. Satellite image time series analysis under time warping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, B.L.; O’Connell, R.T.; Koehler, A.B. Forecasting, Time Series, and Regression: An Applied Approach, 4th ed.; South-Western College Pub: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Du, Q.; Yang, H.; Ma, B. Optical flow and principal component analysis-based motion detection in outdoor videos. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Baret, F.; Verger, A.; Neveux, P.; Weiss, M. A comparison of methods for smoothing and gap filling time series of remote sensing observations—Application to MODIS LAI products. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4055–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Friedl, M.A.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Schneider, A. The footprint of urban climates on vegetation phenology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beurs, K.M.; Henebry, G.M. A statistical framework for the analysis of long image time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1551–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R.; Sangermano, F.; Ghimire, B.; Zhu, H.; Chen, H.; Neeti, N.; Cai, Y.; Machado, E.A.; Crema, S.C. Seasonal trend analysis of image time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2721–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, B.; Eastman, J.R. Land transitions from multivariate time series: Using seasonal trend analysis and segmentation to detect land-cover changes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 671–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.E.; Terpenning, I. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on LOESS. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Vautard, R.; Yiou, P.; Ghil, M. Singular-spectrum analysis: A toolkit for short, noisy chaotic signals. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1992, 58, 95–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahecha, M.D.; Fürst, L.M.; Gobron, N.; Lange, H. Identifying multiple spatiotemporal patterns: A refined view on terrestrial photosynthetic activity. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkel, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Verbesselt, J.; Mahecha, M.D.; Neigh, C.S.; Reichstein, M. Trend change detection in NDVI time series: Effects of inter-annual variability and methodology. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2113–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M. GEMI: A non-linear index to monitor global vegetation from satellites. Vegetatio 1992, 101, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloersen, P.; Huang, N. Comparison of interannual intrinsic modes in hemispheric sea ice covers and other geophysical parameters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, S.S. Hilbert-Huang Transform and Its Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, N.; Erer, I. An additive empirical mode decomposition based method for the fusion of remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), Istanbul, Turkey, 12–14 June 2013; pp. 165–169.
- Wang, T.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, H. Comparing the applications of emd and eemd on time-frequency analysis of seismic signal. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 83, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Shang, P.; Lin, A. Cross-correlation analysis of stock markets using EMD and EEMD. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 442, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; He, Z.; Zi, Y. Application of the EEMD method to rotor fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 23, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, G.; Hatzinakos, D. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition for time series prediction in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 February 2014; pp. 594–598.
- Ren, H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Huang, M.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L.; Kao, H.-M. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition parameters optimization for spectral distance measurement in hyperspectral remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2069–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, S.; Neyt, X.; Pattyn, N.; Migeotte, P.-F. Comparison between eemd, wavelet and fir denoising: Influence on event detection in impedance cardiography. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 806–809.
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E.; Long, S.R.; Peng, C.-K. On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14889–14894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. A study of the characteristics of white noise using the empirical mode decomposition method. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 2004, 460, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtaderi, A.; Flandrin, P.; Borgnat, P. Trend filtering via empirical mode decompositions. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2013, 58, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučera, J.; Barbosa, P.; Strobl, P. Cumulative sum charts-a novel technique for processing daily time series of MODIS data for burnt area mapping in Portugal. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Analysis of Multi-temporal Remote Sensing Images, Leuven, Belgium, 18–20 July 2007; pp. 1–6.
- Grobler, T.L.; Ackermann, E.R.; van Zyl, A.J.; Olivier, J.C.; Kleynhans, W.; Salmon, B.P. Using page’s cumulative sum test on MODIS time series to detect land-cover changes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Zeileis, A.; Culvenor, D. Phenological change detection while accounting for abrupt and gradual trends in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Zeileis, A.; Herold, M. Near real-time disturbance detection using satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnebele, E.; Cervone, G.; Kumar, S.; Waters, N. Real time estimation of the calgary floods using limited remote sensing data. Water 2014, 6, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Y.-l.; Meng, Y.; Li, W.; Yue, A.-z.; Yuan, Y. Satellite Image Time Series Decomposition Based on EEMD. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15583-15604. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71115583
Kong Y-l, Meng Y, Li W, Yue A-z, Yuan Y. Satellite Image Time Series Decomposition Based on EEMD. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(11):15583-15604. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71115583
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Yun-long, Yu Meng, Wei Li, An-zhi Yue, and Yuan Yuan. 2015. "Satellite Image Time Series Decomposition Based on EEMD" Remote Sensing 7, no. 11: 15583-15604. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71115583
APA StyleKong, Y.-l., Meng, Y., Li, W., Yue, A.-z., & Yuan, Y. (2015). Satellite Image Time Series Decomposition Based on EEMD. Remote Sensing, 7(11), 15583-15604. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71115583








