PSI Deformation Map Retrieval by Means of Temporal Sublook Coherence on Reduced Sets of SAR Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Test Site and Dataset
2.1. Test Site

2.2. Dataset


| RiskSAR-X | TerraSAR-X (Sliding Spotlight Mode) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Parameter | Magnitude | Sensor Parameter | Magnitude |
| Carrier Frequency | 9.65 GHz | Carrier Frequency | 9.65 GHz |
| Sampling Frequency | 81 MHz | Incidence Angle | 20–55◦; |
| Pulse Repetition Frequency | 20 KHz | Pulse Repetition Frequency | 8.2 KHz |
| Bandwidth | 120 MHz | Bandwidth | 150 MHz |
| Deramped Signal Bandwidth | 40 MHz | Slant Range Resolution | 1.2 m |
| Transmitted Power | 27 dBm | Azimuth Resolution | 1.1 m |
| 3dB Antenna Beamwidth | 27◦ | Range Scene Size | 10 km |
| Range Time-Average Factor | 128 | Azimuth Scene Size | 5 km |
| Synthetic Aperture Length | 2 m | Frequency Modulation Rate | ca. −5700 Hz/s |
| Scanning Time: Single-Pol / PolSAR | 1/2.5 min | Zero Doppler Scene Duration | 3.2 s |
| RiskSAR-X Dataset | TerraSAR-X Dataset | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campaign | Date | Start Time | Stop Time | No. of Scans | Polarization | Acquisition | Date | Polarization |
| 1 | 21 October 2010 | 09:57 | 12:08 | 15 | HH HV VH VV | 1 | 18 November 2010 | HH |
| 2 | 18 November 2010 | 17:04 | 19:13 | 24 | HH HV VH VV | 2 | 29 November 2010 | HH |
| 3 | 9 February 2011 | 17:00 | 19:48 | 33 | HH HV VH VV | 3 | 14 February 2011 | HH |
| 4 | 7 April 2011 | 18:17 | 23:30 | 60 | HH HV VH VV | 4 | 21 April 2011 | HH |
| 5 | 6 May 2011 | 10:02 | 11:47 | 22 | HH HV VH VV | 5 | 13 May 2011 | HH |
| 6 | 25 May 2011 | 16:09 | 20:08 | 50 | HH HV VH VV | 6 | 15 June 2011 | HH |
| 7 | 9 June 2011 | 13:20 | 16:32 | 51 | HH HV VH VV | 7 | 18 July 2011 | HH |
| 8 | 5 July 2011 | 08:25 | 12:24 | 52 | HH HV VH VV | 8 | 20 August 2011 | HH |
| 9 | 6 September 2011 | 11:49 | 04:05 | 88 | HH HV VH VV | 9 | 22 September 2011 | HH |
| 10 | 5 October 2011 | 11:57 | 16:42 | 66 | HH HV VH VV | 10 | 14 October 2011 | HH |

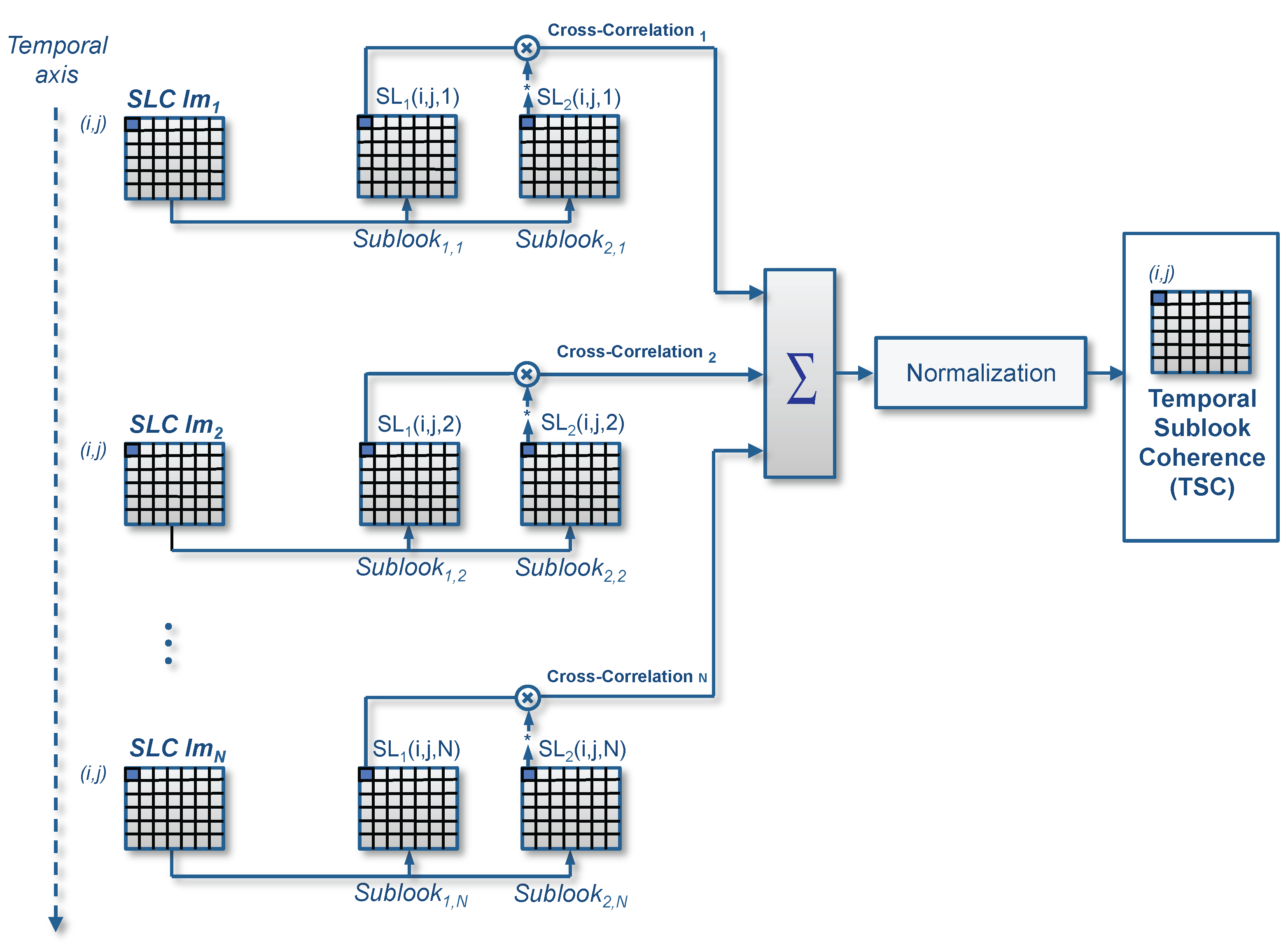
3. Sublook Generation and Temporal Sublook Coherence Evaluation
- First of all, the SLC spectrum must be unweighted. SAR images are typically filtered with linear windows in order to reduce the impact of side-lobes. Taking the sublooks directly from the taperedspectra may lead to unbalanced distributions of energy in the sublooks, which could have a negative impact during the later TSC evaluation.
- Once the image spectrum is unweighted, it is divided into two non-overlapping sublooks, which, at the same time, are base-banded to the same center frequency. This step is carried out in order to avoid linear phase terms during the TSC evaluation.
- Each sublook spectrum may be additionally weighted to reduce the side-lobes in the detection.
- An inverse Fourier transform is finally applied to each sublook in order to obtain them in the spatial domain.

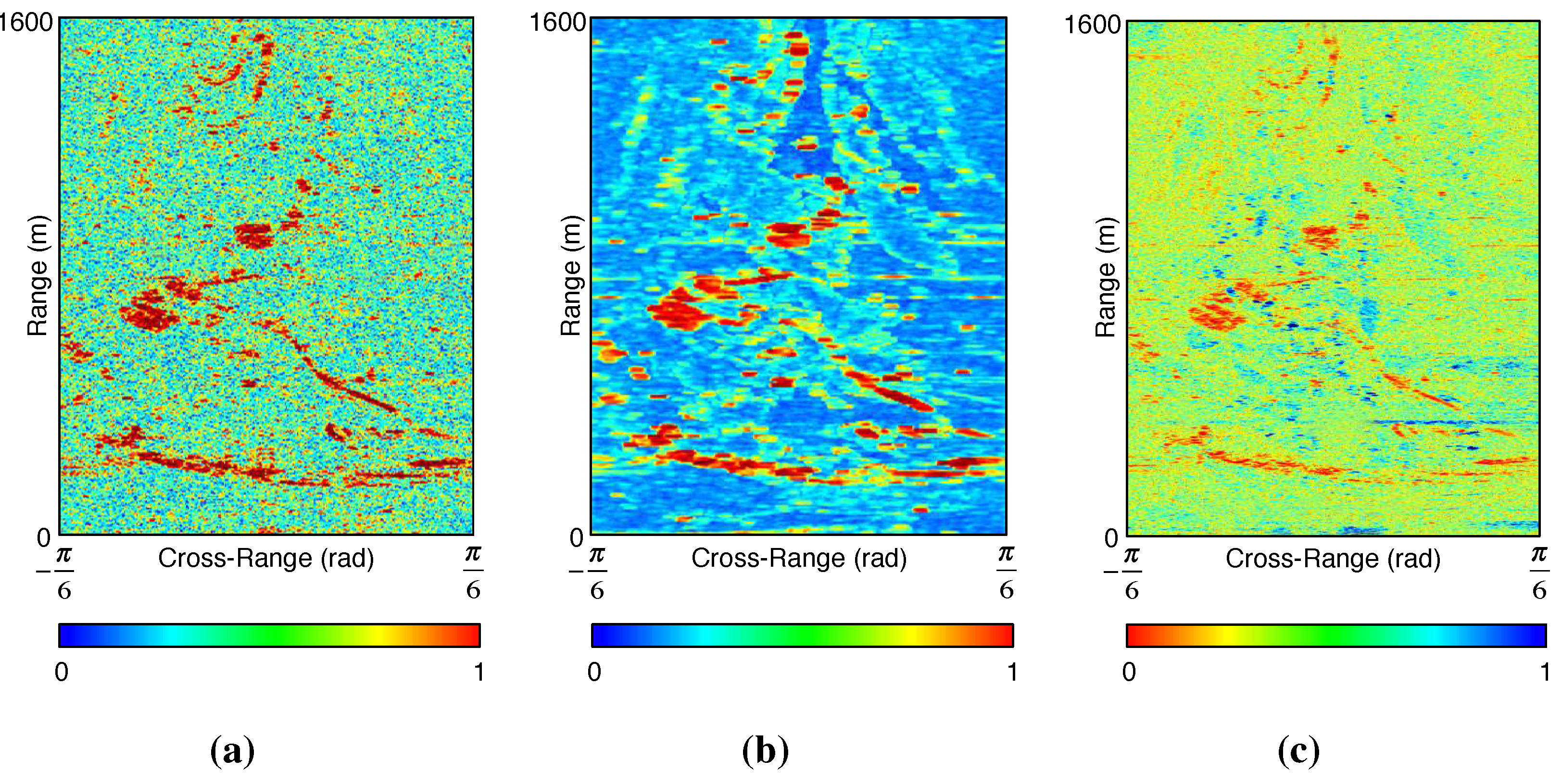
4. Phase Statistics and Pixel Selection Candidates
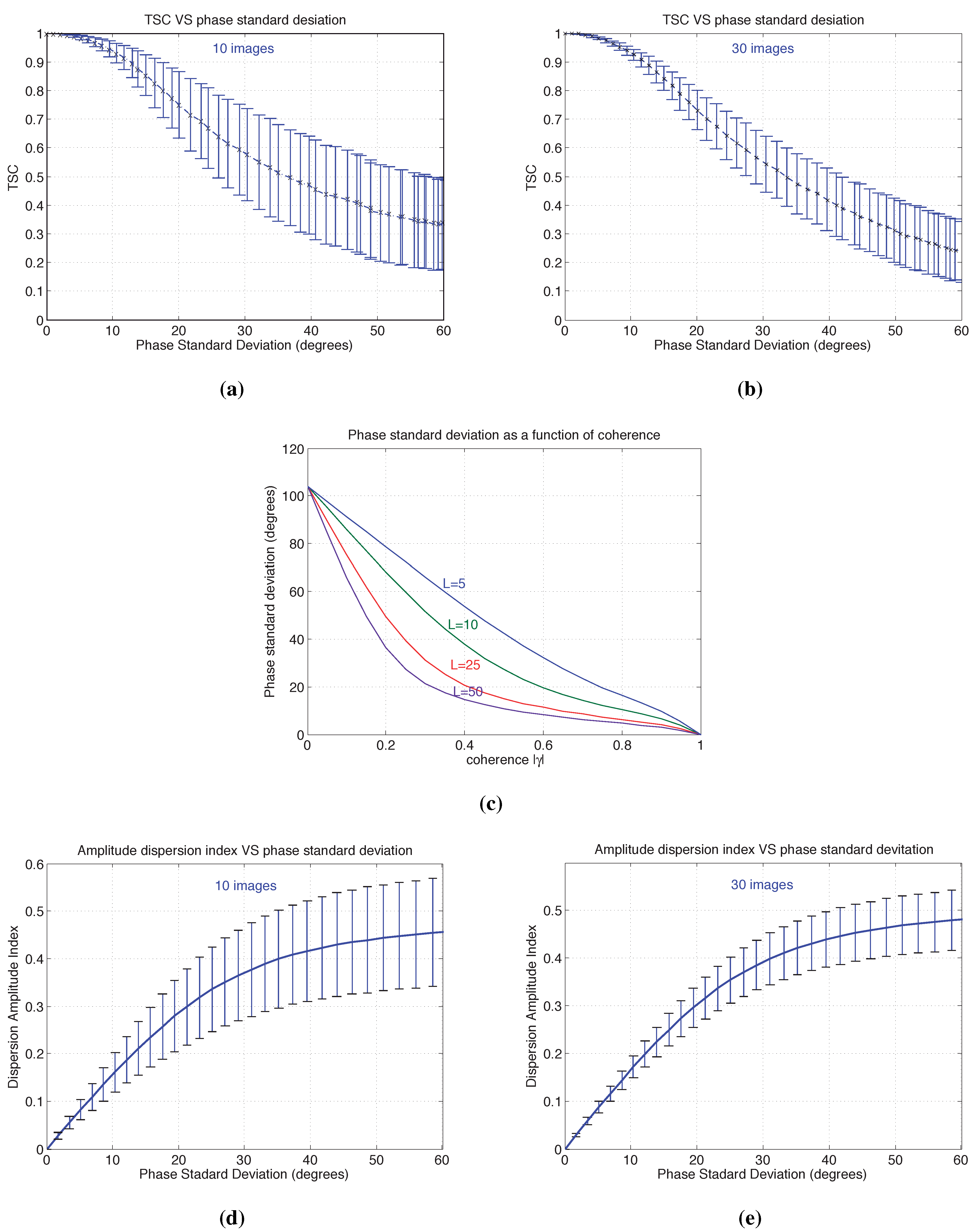
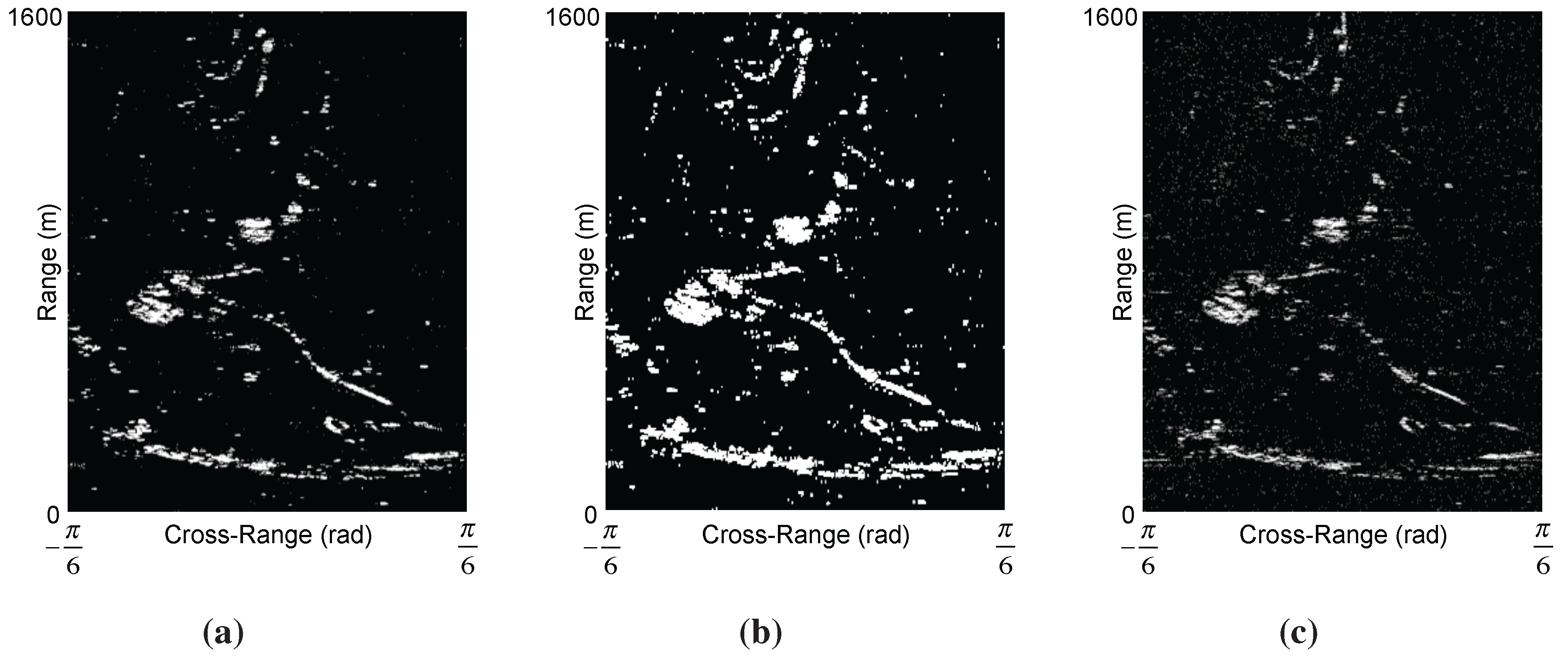
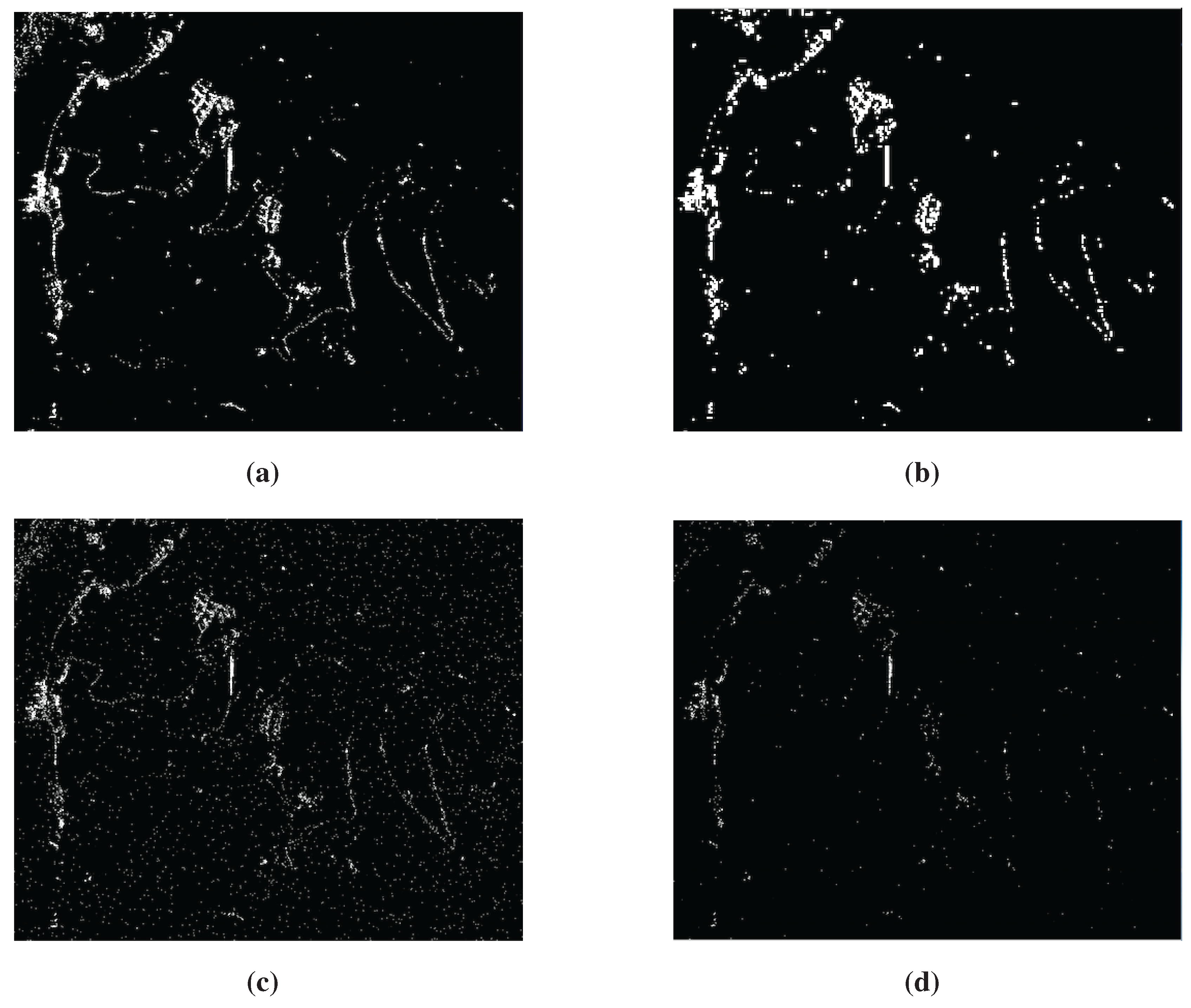

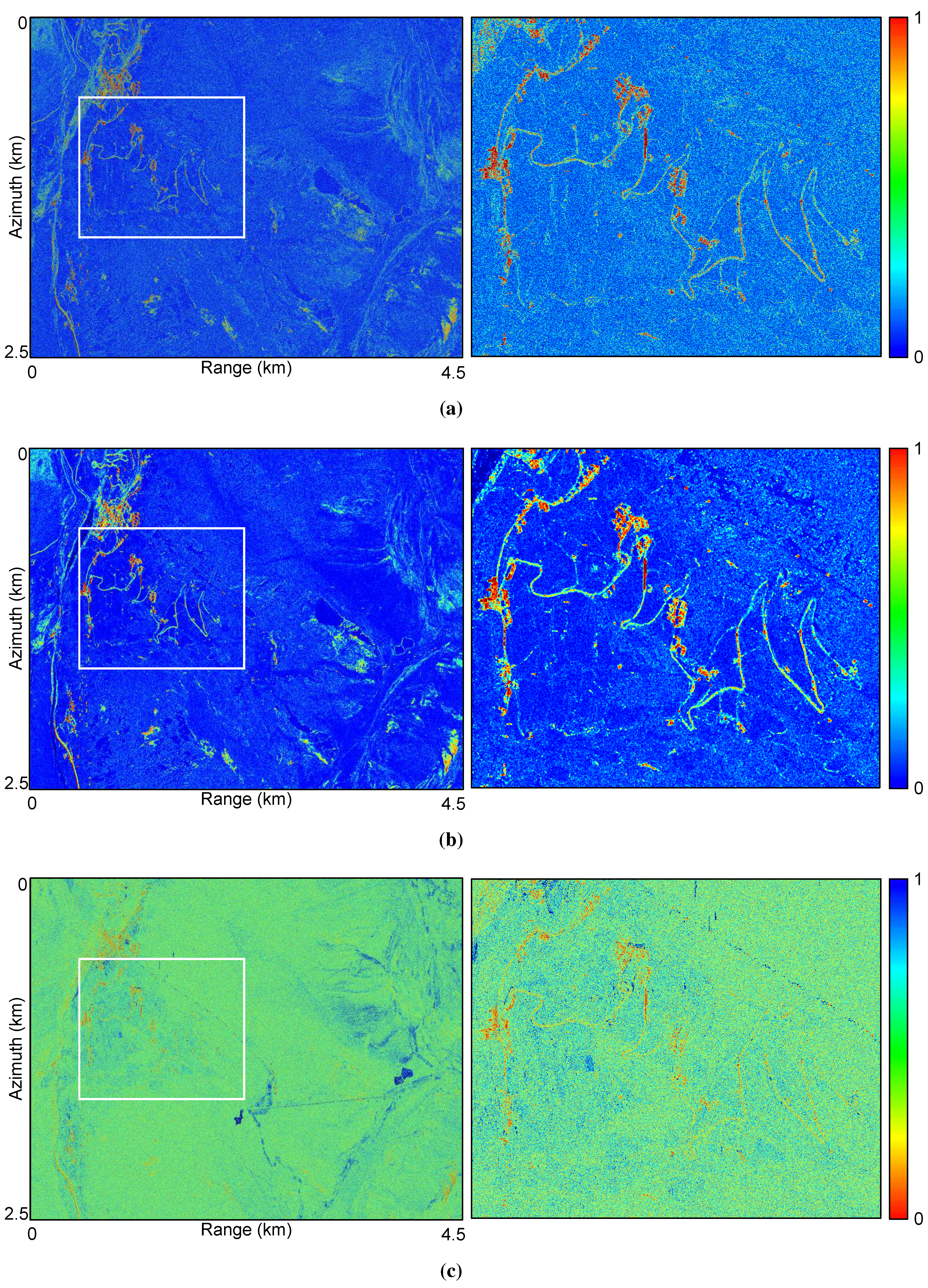
5. PSI by Means of TSC: Results and Discussion
5.1. Interferometric Processing Chain Considerations and CPT Overview
5.1.1. GB-SAR Interferometry
- The first block, referred to as short-term processing (STP) [33], basically consists of two steps.The first one is based on carrying out the focus of the raw data. On the one hand, since the RiskSAR-X sensor is based on a LFM-CW radar, the range compression can be carried out with a simple FFT of the time-domain deramped received signal [34,35]. On the other hand, since the cross-range resolution is not constant due to the limited length of the synthetic aperture of GB-SAR sensors, the back-projection technique proved to be the most suited for the azimuth focusing [34]. Once the images has been focused, a temporal averaging of each daily dataset, composed of Mi zero-baseline acquisitions corresponding to the same measurement day i, is carried out in order to improve the SNR of time-stationary targets, leading to a higher quality time-averaged SLC image from each daily dataset corresponding to each measurement campaign. For the dataset used in this paper, 10 time-averaged SLC images will be finally available after this step.
- The following step, referred to as long-term processing (LTP), consists of compensating for the APS present between the different time-averaged SLC images obtained in the previous STP block. From all of the methods available in the literature [33,36,37,38], the RiskSAR-X makes use of model-based solutions [33]. This kind of solution proved to be very effective, reaching very good performances with no use of extra meteorological data or stable ground control point (GCP) information. The APS estimation and compensation process is a key issue in GB-SAR processing in order to obtain a reliable set of APS-free interferograms suitable for the PSI processing. For the dataset used in this paper, 45 APS-free interferograms are finally available. Finally, to face temporal decorrelation phenomena and enhance the phase quality of interferograms, the processing can be benefited by the exploitation of polarimetric information, such as the one provided by the RiskSAR-X sensor. In classical PSI, only a single-polarimetric channel is considered for the processing. This means that all pixels involved in PSI algorithms belong to the same polarimetric channel. In this context, polarimetric optimization techniques may be employed in order to improve the phase quality of interferograms [39].
5.1.2. Spotlight SAR Interferometry
5.1.3. The Coherent Pixels Technique
5.2. PSI Displacement Results

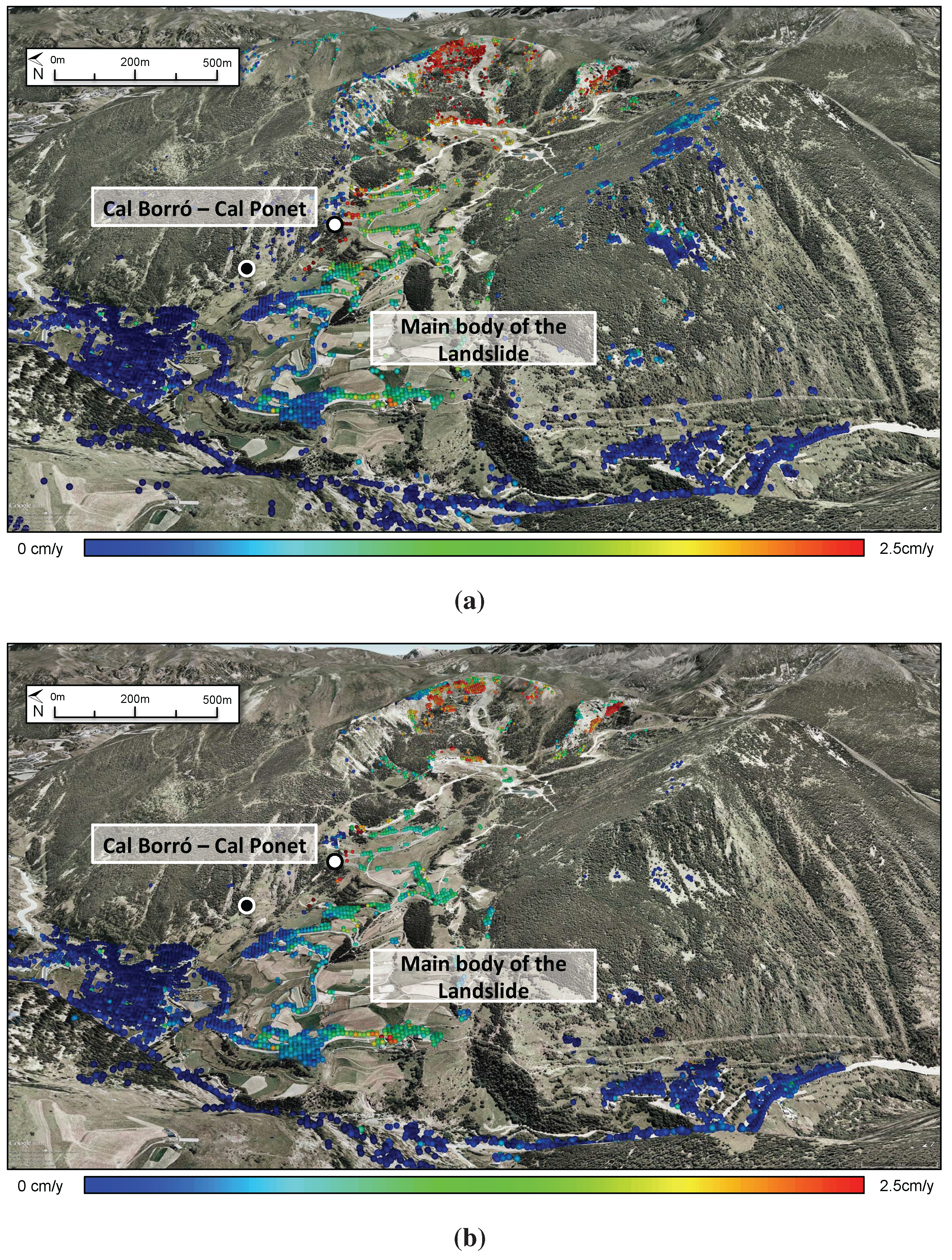
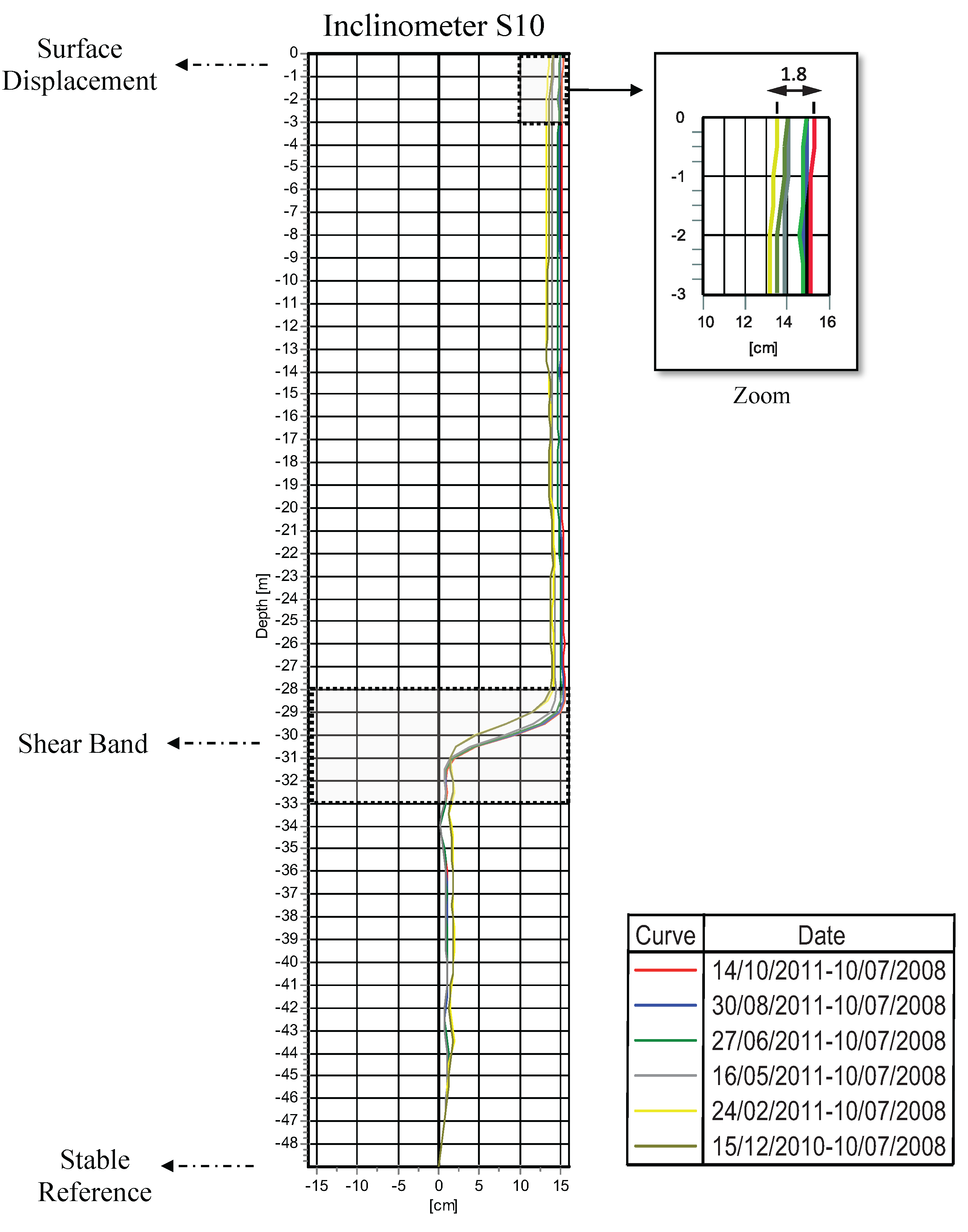

6. Conclusions
Abbreviations/Nomenclature
| APS | atmospheric phase screen |
| CPT | coherent pixel technique |
| CS | coherent scatterers |
| DA | amplitude dispersion |
| DDS | digital direct synthesizer |
| DEM | digital elevation model |
| DInSAR | differential SAR interferometry |
| FMCW | frequency modulated continuous wave |
| GB-SAR | ground-based SAR |
| GCP | ground control point |
| LFM-CW | linear frequency modulated continuous wave |
| LTP | long-term processing |
| LOS | line-of-sight |
| MAF | model adjustment function |
| ML | multi-look |
| PS | permanent scatterer |
| PSI | persistent scatterer interferometry |
| RSLab | remote sensing laboratory |
| SAR | synthetic aperture radar |
| SCS | stable coherent scatterers |
| SLC | single look complex |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| STP | short-term processing |
| SVA | spatial variant apodization |
| TSC | temporal sublook coherence |
| UPC | Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic Aperture Radar interferometry to measure Earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Duro, J. Generation of deformation maps at low resolution using differential interferometric SAR data. In Proceedings of 2002 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’02. Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002.
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping. In Proceedings of 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’03. Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003.
- Arnaud, A.; Adam, N.; Hanssen, R.; Inglada, J.; Duro, J.; Closa, J.; Eineder, M. ASAR ERS interferometric phase continuity. In Proceedings of 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’03. Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003.
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Reale, D.; Serafino, F. Four-dimensional SAR imaging for height estimation and monitoring of single and double scatterers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Briole, P.; Arnaud, A. Deflation of Mount Etna monitored by spaceborne radar interferometry. Nature 1995, 375, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, P.; Usai, S.; Sansosti, E.; Lanari, R.; Tesauro, M.; Fornaro, G.; Berardino, P. Modeling surface deformation observed with synthetic aperture radar interferometry at Campi Flegrei caldera. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 19355–19366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Mallorqui, J.; Broquetas, A. Linear and nonlinear terrain deformation maps from a reduced set of interferometric sar images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2243–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Fahnestock, M. Ice sheet motion and topography from radar interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; Bovenga, F.; Guerriero, L.; Wasowski, J. DInSAR applications to landslide studies. In Proceedings of IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’01. Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001.
- Kim, S.-W.; Won, J.-S. Measurements of soil compaction rate by using JERS-1 SAR and a prediction model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2683–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckreuss, S.; Balzer, W.; Muhlbauer, P.; Werninghaus, R.; Pitz, W. The terraSAR-X satellite project. In Proceedings of 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’03. Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003.
- Buckreuss, S.; Roth, A. Status Report on the TerraSAR-X Mission. In Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS 2008. Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008.
- Venturini, R.; Fois, F.; Sirocchi, G.; Bauleo, A.; Bazzoni, A.; Borgarelli, L.; Capece, P.; Cereoli, L.; Croci, R.; Farina, C.; et al. Experimental verification of COSMO-SkyMed SAR capabilities. In Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, RADAR ’08. Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2008.
- Iglesias, R.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Lopez-Dekker, P. DInSAR pixel selection based on sublook spectral correlation along time. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3788–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Papathanassiou, K.; Hajnsek, I.; Moreira, A. Polarimetric and interferometric characterization of coherent scatterers in urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacana, N. Estudi dels grans esllavissaments d’Andorra: Els casos del Forn i del vessant d’Encampadana. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Dynamic Geology, Geophysics and Paleontology, Faculty of Geology, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Torrebadella, J.; Villaró, I.; Altimir, J.; Amigó, J.; Vilaplana, J.M.; Corominas, J.; Planas, X. El Deslizamiento del Forn de Canilloen Andorra. Un Ejemplo de Gestión del Riesgo Geológico en Zonas Habitadas en Grandes Deslizamientos. In Proceedings of VII Simposio Nacional sobre Taludes y Laderas Inestables, Barcelona, Spain, 27–30 October 2009.
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Luzi, G.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N. Discontinuous GBSAR deformation monitoring. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eineder, M.; Adam, N.; Bamler, R.; Yague-Martinez, N.; Breit, H. Spaceborne spotlight SAR interferometry with TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Mallorqui, J.J. Side-Lobe Cancelation in DInSAR Pixel Selection With SVA. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bruniquel, J.; Vachon, P. Coherence estimation for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Fabregas, X.; Aguasca, A.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Gili, J.A.; Corominas, J. Atmospheric phase screen compensation in Ground-Based SAR with a multiple-regression model over mountainous regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2436–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumekh, M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing: With MATLAB Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cumming, I.; Wong, F. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Artech House: London, UK and Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pipia, L.; Fabregas, X.; Aguasca, A.; Lopez-Martinez, C. Atmospheric artifact compensation in ground-based DInSAR applications. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leva, D.; Nico, G.; Tarchi, D.; Fortuny-Guasch, J.; Sieber, A. Temporal analysis of a landslide by means of a ground-based SAR interferometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannini, L.; Guarnieri, A.M. Atmospheric phase screen in ground-based radar: Statistics and compensation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Monells, D.; Fabregas, X.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Aguasca, A.; Lopez-Martinez, C. Phase quality optimization in polarimetric differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Sánchez, P.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Duque, S.; Monells, D. The coherent pixels technique (CPT): An advanced DInSAR technique for nonlinear deformation monitoring. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2008, 165, 1167–1193. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iglesias, R.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Monells, D.; López-Martínez, C.; Fabregas, X.; Aguasca, A.; Gili, J.A.; Corominas, J. PSI Deformation Map Retrieval by Means of Temporal Sublook Coherence on Reduced Sets of SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 530-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100530
Iglesias R, Mallorqui JJ, Monells D, López-Martínez C, Fabregas X, Aguasca A, Gili JA, Corominas J. PSI Deformation Map Retrieval by Means of Temporal Sublook Coherence on Reduced Sets of SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(1):530-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100530
Chicago/Turabian StyleIglesias, Rubén, Jordi J. Mallorqui, Dani Monells, Carlos López-Martínez, Xavier Fabregas, Albert Aguasca, Josep A. Gili, and Jordi Corominas. 2015. "PSI Deformation Map Retrieval by Means of Temporal Sublook Coherence on Reduced Sets of SAR Images" Remote Sensing 7, no. 1: 530-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100530
APA StyleIglesias, R., Mallorqui, J. J., Monells, D., López-Martínez, C., Fabregas, X., Aguasca, A., Gili, J. A., & Corominas, J. (2015). PSI Deformation Map Retrieval by Means of Temporal Sublook Coherence on Reduced Sets of SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 7(1), 530-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100530





